Voltammetric Determination of Salbutamol, Sulfamethoxazole, and Trimethoprim as Anthropogenic Impact Indicators Using Commercial Screen-Printed Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Differential Pulse Voltammetric Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
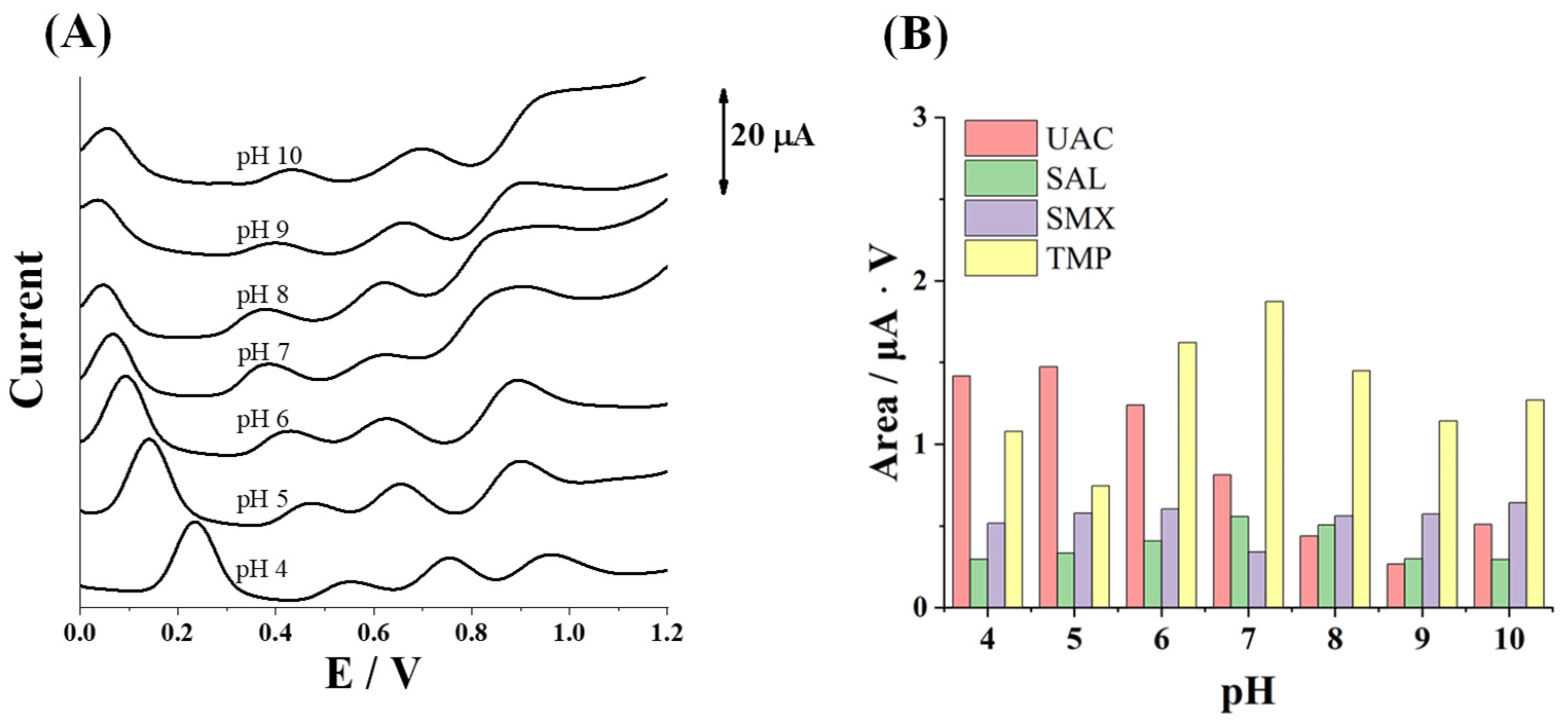
3.1. pH Optimization
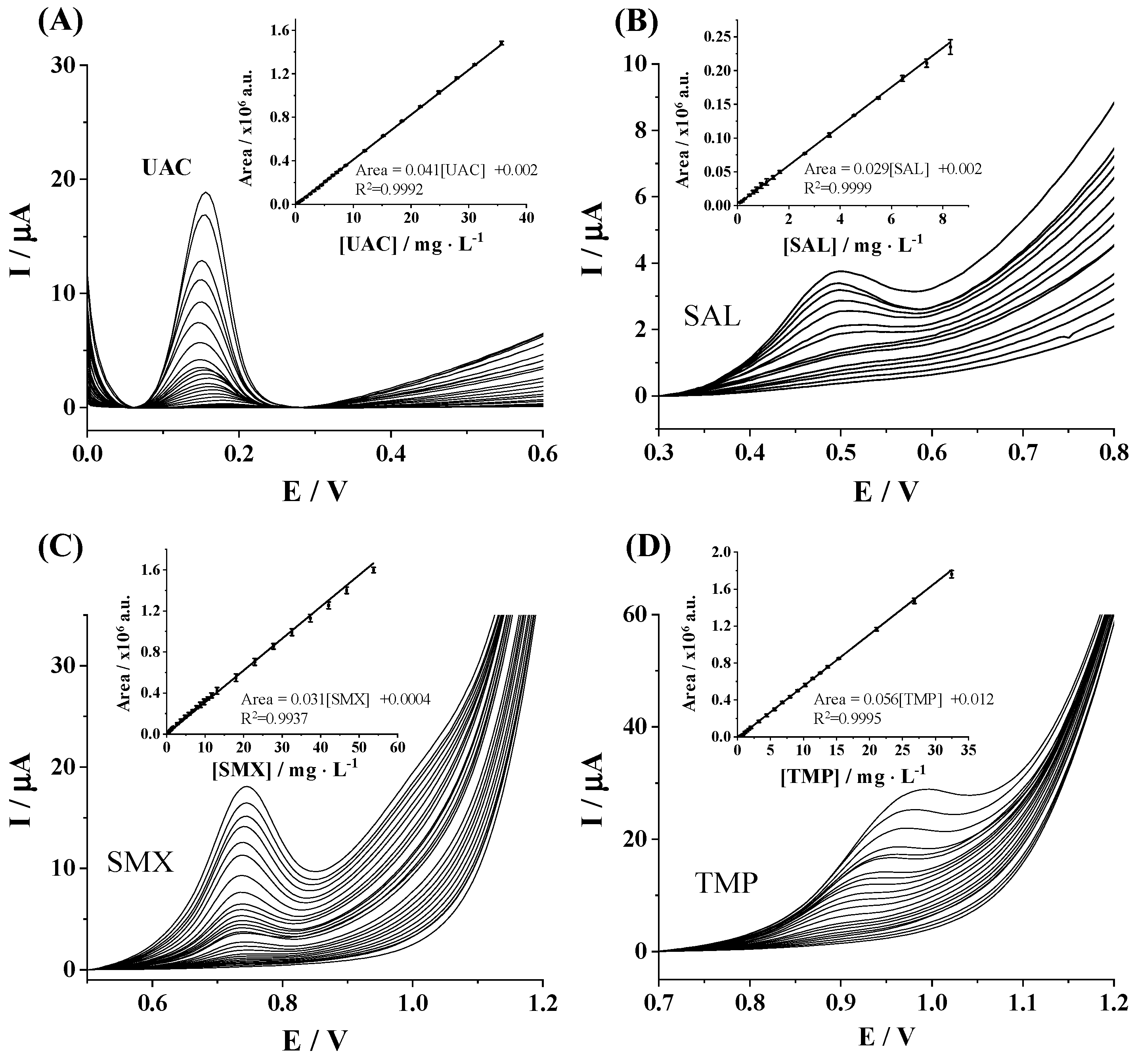
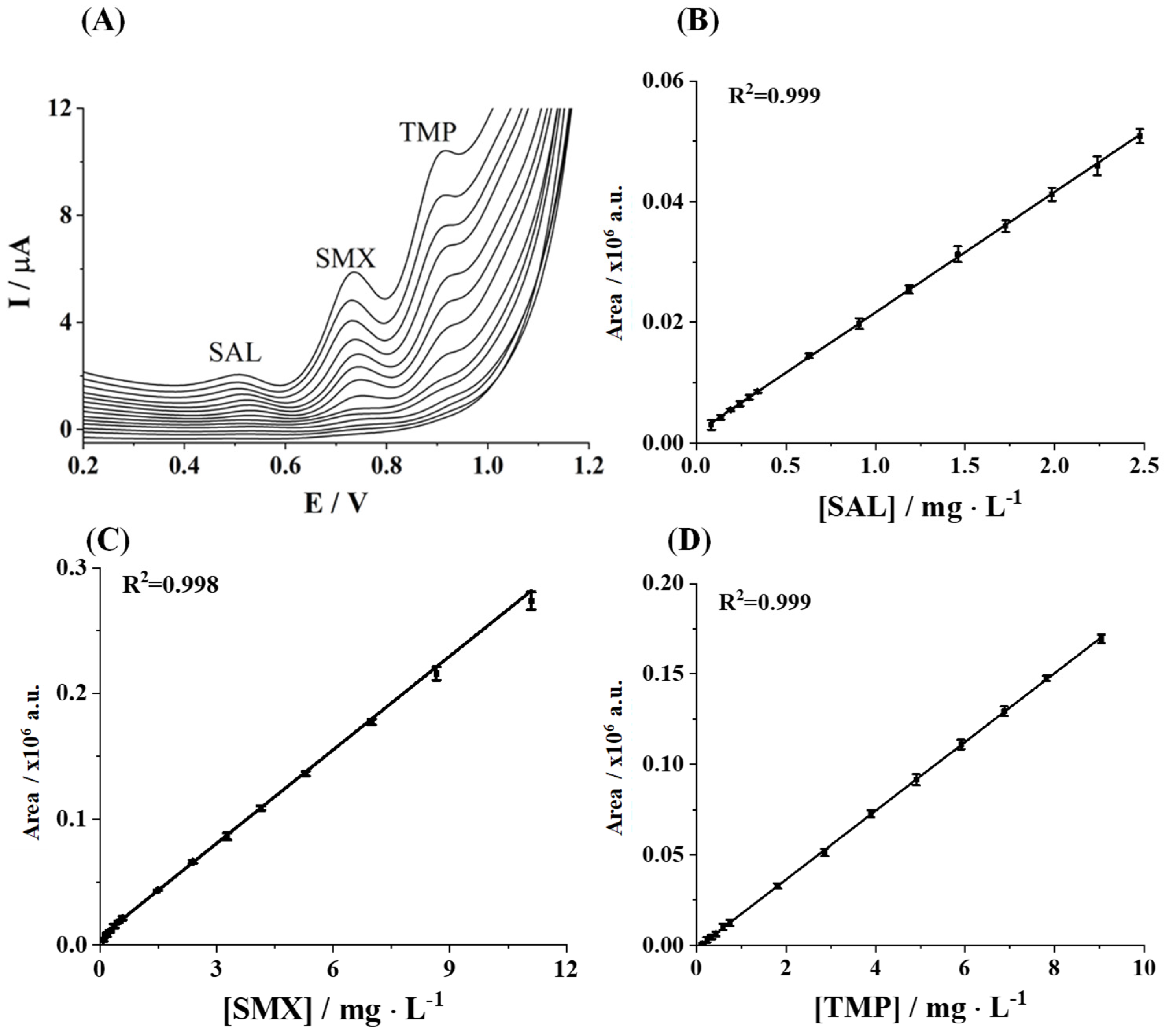
3.2. Analytical Performance Evaluation
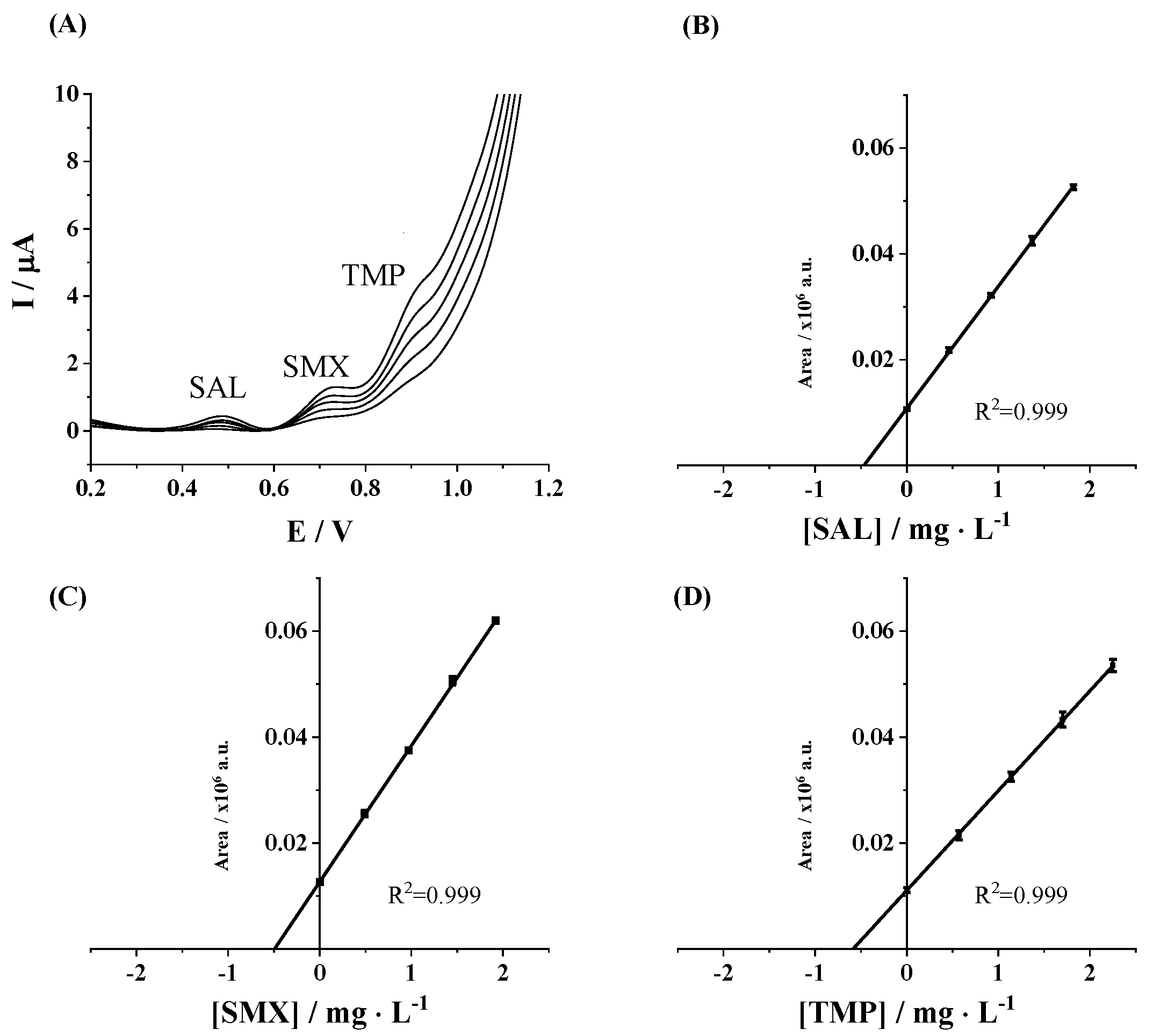
3.3. Application to a Real Sample
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Ara Jahan, S. A Review of the Consequences of Global Climate Change on Human Health. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2014, 32, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.; Hetta, H.F.; Mabrok, M.; Behzadi, P. Editorial: Emerging Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens “Superbugs”: A Rising Public Health Threat. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1135614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.M.; Bečanová, J.; Scheringer, M.; Sharma, A.; Bharat, G.K.; Whitehead, P.G.; Klánová, J.; Nizzetto, L. Health and Ecological Risk Assessment of Emerging Contaminants (Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care Products, and Artificial Sweeteners) in Surface and Groundwater (Drinking Water) in the Ganges River Basin, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Aguirre, K.; Hernández-Núñez, E.; González-Sánchez, A.; Méndez-Novelo, R.; Ponce-Caballero, C.; Giácoman-Vallejos, G. A Rapid and Green Method for the Determination of Veterinary Pharmaceuticals in Swine Wastewater by Fluorescence Spectrophotometry. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Lemus, N.; López-Serna, R.; Pérez-Elvira, S.I.; Barrado, E. Analysis of 60 Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Sewage Sludge by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Tandem Mass Spectroscopy. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaca, S.; Rosado, T.; Restolho, J.; Rodilla, J.M.; Rocha, P.M.M.; Silva, L.; Margalho, C.; Barroso, M.; Gallardo, E. Determination of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants in Urine Samples Using Microextraction by Packed Sorbent and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1120, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarakatsanou, C.; Karastogianni, S.; Girousi, S. Promising Electrode Surfaces, Modified with Nanoparticles, in the Sensitive and Selective Electroanalytical Determination of Antibiotics: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, C. Contemporary Voltammetric Techniques and Its Application to Pesticide Analysis: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadon, N.; Jain, R.; Sharma, S.; Singh, K. Recent Trends in Electrochemical Sensors for Multianalyte Detection—A Review. Talanta 2016, 161, 894–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Jain, R.; Radhapyari, K.; Jadon, N.; Agarwal, S. Voltammetric Techniques for the Assay of Pharmaceuticals—A Review. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 408, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.R.G.; Rodrigues, J.G.A.; Vasconcellos, M.d.L.S.; Ribeiro, E.S.; D’Elia, E.; Ferreira, R.d.Q. Portable and Simple Electroanalytical Procedure for Simultaneous Detection of Dipyrone and Norfloxacin with Disposable Commercial Electrodes in Water and Organic Fertilizers. Ionics 2022, 28, 4833–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkumar, V.; Sangili, A.; Chen, S.-M.; Abinaya, M. Additive-Free Synthesis of BiVO4 Microspheres as an Electrochemical Sensor for Determination of Antituberculosis Drug Rifampicin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 624, 126849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-M.; Huang, C.P.; Chen, S.-K.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Electrochemical Analysis of Naproxen in Water Using Poly(l-Serine)-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koventhan, C.; Pandiyan, R.; Chen, S.-M.; Lo, A.-Y. Nickel Molybdate/Cobalt Molybdate Nanoflakes by One-Pot Synthesis Approach for Electrochemical Detection of Antipsychotic Drug Chlorpromazine in Biological and Environmental Samples. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.-T.; Li, D.-W.; Long, Y.-T. Recent Developments and Applications of Screen-Printed Electrodes in Environmental Assays—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyszczuk-Rotko, K.; Kozak, J.; Czech, B. Screen-Printed Voltammetric Sensors—Tools for Environmental Water Monitoring of Painkillers. Sensors 2022, 22, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, N.; Castilla, Ò.; Ariño, C.; Diaz-Cruz, M.S.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Commercial Screen-Printed Electrodes Based on Carbon Nanomaterials for a Fast and Cost-Effective Voltammetric Determination of Paracetamol, Ibuprofen and Caffeine in Water Samples. Sensors 2019, 19, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clares, P.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Voltammetric Determination of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Using Screen-Printed Electrodes. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, J.; Serrano, N.; Ariño, C.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. A Chemometric Survey about the Ability of Voltammetry to Discriminate Pharmaceutical Products from the Evolution of Signals as a Function of PH. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.M.; Wong, A.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Simultaneous Determination of Salbutamol and Propranolol in Biological Fluid Samples Using an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Functionalized-Graphene, Ionic Liquid and Silver Nanoparticles. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 824, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgobbi, L.F.; Razzino, C.A.; Machado, S.A.S. A Disposable Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim Antibiotics in Urine Based on Multiwalled Nanotubes Decorated with Prussian Blue Nanocubes Modified Screen-Printed Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 191, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aafria, S.; Kumari, P.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, S.; Batra, B.; Rana, J.S.; Sharma, M. Electrochemical Biosensing of Uric Acid: A Review. Microchem. J. 2022, 182, 107945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, E.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Serrano, N.; Silvia Díaz-Cruz, M.; Manuel Díaz-Cruz, J. Voltammetric Determination of Sulfamethoxazole Using Commercial Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V. Methods for the Determination of Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation of the Analytical Methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, W.T.; Putra, B.R.; Heryanto, R.; Rohaeti, E.; Yanto, D.H.Y.; Fauzi, A. A Simple Approach to Fabricate a Screen-Printed Electrode and Its Application for Uric Acid Detection. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.C.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, X.J.; Xia, Z.Y.; Kang, W.Y.; Zhou, W.H. One Step Electrodeposition of Graphene-Au Nanocomposites for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Salbutamol. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrinha, Á.; Tavares, M.; Dibo, V.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S. Carbon Fiber Paper Sensor for Determination of Trimethoprim Antibiotic in Fish Samples. Sensors 2023, 23, 3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, W.B.V.; Lisboa, T.P.; da Silva, G.C.; Oliveira, R.S.; de Souza, C.C.; Matos, M.A.C.; de Oliveira, M.A.L.; Matos, R.C. Chemometric Tools Applied to Silver Nanoparticles Electrodeposition in 3D-Printed Disposable Device for the Determination of Sulfamethoxazole in Different Samples by Voltammetry. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursaeed, A.A.; Jahani, S.; Moradalizadeh, M.; Shahidi Zandi, M.; Foroughi, M.M. Ultra-Sensitive Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim Based on the Flower-like-Nanostructures-Modified Screen-Printed Electrode. Monatsh Chem. 2023, 154, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Ternes, T.A. Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 398–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipingana, L.N.N.; Shivaraju, H.P.; Yashas, S.R. Quantitative Assessment of Pharmaceutical Drugs in a Municipal Wastewater and Overview of Associated Risks. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-B.; Yang, B.; Xue, N.-D. Enhanced Adsorption of Benzene Vapor on Granular Activated Carbon under Humid Conditions Due to Shifts in Hydrophobicity and Total Micropore Volume. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, T.; Horikoshi, K.; Kumagai, S.; Saito, Y.; Yoshioka, T. Adsorption of Urea, Creatinine, and Uric Acid onto Spherical Activated Carbon. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedras, J.; Dominguez, R.B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Determination of Uric Acid in Artificial Saliva with Compact AMP3291 Reader and Au Nanoparticles Modified Electrode. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkkan, G.; Bas, S.Z.; Atacan, K.; Ozmen, M. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Co3O4-ERGO Nanocomposite Modified Screen-Printed Electrode for Detection of Uric Acid in Artificial Saliva. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizpour Moallem, Q.; Beitollahi, H. Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on a Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with Nanostructured Cu-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuwan, C.; Sriprachuabwong, C.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Phokharatkul, D.; Sritongkham, P.; Tuantranont, A. Inkjet-Printed Graphene-Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(Styrene- Sulfonate) Modified on Screen Printed Carbon Electrode for Electrochemical Sensing of Salbutamol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.M.; Toan Tran, T.T.; Doan, M.D.; Le, V.T.; Dinh, Q.K. Differential Pulse Voltammetry Determination of Salbutamol Using Disulfite Tungsten/Activated Carbon Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, M.M.; Shetti, N.P.; Kalanur, S.S.; Pollet, B.G.; Upadhyaya, K.P.; Ayachit, N.H.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Hf-Doped Tungsten Oxide Nanorods as Electrode Materials for Electrochemical Detection of Paracetamol and Salbutamol. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, L.C.; Wahl, A.; Ogourstov, V.; Seymour, I.; Barry, F.; Rohan, J.F.; Mac Loughlin, R. Electrochemical Discrimination of Salbutamol from Its Excipients in VentolinTM at Nanoporous Gold Microdisc Arrays. Sensors 2021, 21, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.N.; Oyama, M.; Singh, S.P. Fast Determination of Salbutamol, Abused by Athletes for Doping, in Pharmaceuticals and Human Biological Fluids by Square Wave Voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 611, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Voltammetric Determination of Salbutamol on a Glassy Carbon Electrode Coated with a Nanomaterial Thin Film. J. Anal. Chem. 2010, 65, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.S.; Abdullah, A.A.; Yardım, Y.; Şentürk, Z.; Talay Pınar, P. Electroanalytical Determination of Salbutamol in Pharmaceutical Formulations Using Cathodically Pretreated Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. J. Res. Pharm. 2018, 22, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, A.; Corvaglia, S.; Pompa, P.P.; Malitesta, C. An Innovative and Simple All Electrochemical Approach to Functionalize Electrodes with a Carbon Nanotubes/Polypyrrole Molecularly Imprinted Nanocomposite and Its Application for Sulfamethoxazole Analysis. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 599, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, A.; Shams, A. Silver-Filled MWCNT Nanocomposite as a Sensing Element for Voltammetric Determination of Sulfamethoxazole. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1039, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruncho-Pérez, S.; Bernárdez, N.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.Á.; González-Romero, E. Voltammetric Methodology for the Quality Control and Monitoring of Sulfamethoxazole Removal from Water. Talanta 2025, 284, 127255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Ansari, R.; Heydari, L. Electrocatalytic Oxidation and Differential Pulse Voltammetric Determination of Sulfamethoxazole Using Carbon Nanotube Paste Electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, S.; Girish Kumar, K. Voltammetric Determination of Sulfamethoxazole at a Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Modified Glassy Carbon Sensor and Its Application Studies. Drug Test. Anal. 2009, 1, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.D.; Braga, O.C.; Vieira, I.C.; Spinelli, A. Electroanalytical Determination of Sulfadiazine and Sulfamethoxazole in Pharmaceuticals Using a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 135, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Sreeja, B.S.; Krishna Kumar, K.; Padmalaya, G. Static and Dynamic Analysis of Sulfamethoxazole Using GO/ZnO Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode by Differential Pulse Voltammetry and Amperometry Techniques. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Settu, R.; Chen, S.-M.; Chen, T.-W. Voltammetric Sensing of Sulfamethoxazole Using a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with a Graphitic Carbon Nitride and Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari Javar, H.; Rajabizadeh, A.; Dehghannoudeh, G.; Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H. Electrochemical Determination of Sulfamethoxazole in Biological and Drug Samples Using Ce (III)-Doped CuO Modified Electrode. Measurement 2022, 203, 111936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Măgeruşan, L.; Pogăcean, F.; Leoştean, C.; Pruneanu, S. Selective Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensing Platform for Enhanced Sulfamethoxazole Assay. Microchem. J. 2024, 197, 109886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaraldo, T.T.; Goulart, L.A.; Moraes, F.C.; Lanza, M.R.V. Carbon Black Nanospheres Modified with Cu (II)-Phthalocyanine for Electrochemical Determination of Trimethoprim Antibiotic. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.S.; Rocha-Filho, R.C.; Cass, Q.B.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Simultaneous Differential Pulse Voltammetric Determination of Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim on a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.S.; Bott-Neto, J.L.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Machado, S.A.S. Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensors with Reduced Graphene Nanoribbons for Simultaneous Detection of Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim in Water Samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 882, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarino, I.; Cesarino, V.; Lanza, M.R.V. Carbon Nanotubes Modified with Antimony Nanoparticles in a Paraffin Composite Electrode: Simultaneous Determination of Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golinelli, D.L.C.; Machado, S.A.S.; Cesarino, I. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticle-Graphene Composites for Electroanalysis Applications Using Chemical and Electrochemical Methods. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, S. A New Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim Antibiotics Based on Graphene and ZnO Nanorods Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.F.; Abu-Nameh, E.S.M.; Saket, M.M.; Khateeb, L.T.A.; Al Ahmad, A.; Asaad, Z.; Salem, Z.; Alnuman, N. Detection of Hydrochlorothiazide, Sulfamethoxazole, and Trimethoprim at Metal Oxide Modified Glassy Carbon Electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 1771–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.L.; Maurya, A.K.; Priyadarshini, S.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Sahu, K. Measurement Uncertainty and Validation for Quantitation of Salbutamol in Human Urine by Gas Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2023, 61, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sravani Ratnam Arji; Sarma SRS Eranki; Anitha Kadimi; Prakash Nathaniel Kumar Sarella; Vinny Therissa Mangam Development and Validation of an HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Salbutamol, Theophylline and Ambroxol in Tablet Dosage Form. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2023, 10, 634–645. [CrossRef]
- El Sharkasy, M.E.; Aboshabana, R.; Tolba, M.M.; Walash, M.I.; Belal, F. A Factorial-Design/Assisted HPLC Method for Simultaneous Monitoring of Phenytoin, Trimethoprim, and Sulphamethoxazole in Plasma Samples to Optimize Therapy and Mitigate Toxicity Risks. Microchem. J. 2024, 206, 111462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatica, E.; Faber, J.; Gaffron, C.; Bjergum, M.; Langman, L.; Jannetto, P. Quantification of Serum Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim by Ultra-Fast Solid-Phase Extraction–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Ther. Drug Monit. 2020, 42, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshina, A.; Yelnikova, A.; Safronova, E.; Kolganova, T.; Kuleshova, V.; Bobreshova, O.; Yaroslavtsev, A. Multisensory Systems Based on Perfluorosulfonic Acid Membranes Modified with Functionalized CNTs for Determination of Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim in Pharmaceuticals. Membranes 2022, 12, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-W.; Tsai, I.-C.; Liu, Y.-F.; Chen, C. Upcycling Fruit Peel Waste into a Green Reductant to Reduce Graphene Oxide for Fabricating an Electrochemical Sensing Platform for Sulfamethoxazole Determination in Aquatic Environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraupner, N.; Ebmeyer, S.; Hutinel, M.; Fick, J.; Flach, C.-F.; Larsson, D.G.J. Selective Concentrations for Trimethoprim Resistance in Aquatic Environments. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patze, S.; Huebner, U.; Liebold, F.; Weber, K.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J. SERS as an Analytical Tool in Environmental Science: The Detection of Sulfamethoxazole in the Nanomolar Range by Applying a Microfluidic Cartridge Setup. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 949, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Z.; Kong, F. Development of a Highly Sensitive Time-Resolved Fluoroimmunoassay for the Determination of Trace Salbutamol in Environmental Samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| UAC | SAL | SMX | TMP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ind. | Sim. | Ind. | Sim. | Ind. | Sim. | Ind. | Sim. | |
| Sensitivity (nA V mg−1 L) | 1.17 (0.01) | - | 1.62 (0.08) | 1.14 (0.04) | 1.95 (0.04) | 1.59 (0.04) | 4.89 (0.07) | 1.16 (0.02) |
| Linear range (mg L−1) | 0.2–35.7 | - | 0.3–8.3 | 0.3–2.5 | 0.4–53.8 | 0.3–11.1 | 0.8–32.5 | 0.5–9.0 |
| R2 | 0.999 | - | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.994 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| LOD (μg L−1) | 67.0 | - | 95.3 | 83.8 | 108.9 | 88.7 | 235.1 | 139.2 |
| Electrode | Analyte | Technique | Linear Range (mg·L−1) | LOD (μg·L−1) | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNPs/SPE | UAC | Amperometry | 3.36–33.62 | 2002.19 | Artificial saliva | [34] |
| Co3O4-ERGO/SPE | UAC | DPV | 0.84–84.06 | 252.17 | Artificial saliva | [35] |
| Cu-BTC/CPE | UAC; DA | DPV | 0.08–100.87; 0.0095–94.82 | 33.62 5.69 | Dopamine injection and urine | [36] |
| GP-PEDOT: PSS/SPCE | SAL | CV | 1.20–131.62 | 299.14 | Syrup AdSV and tablets | [37] |
| WS2/AC/GCE | SAL | DPV | 0.24–50.26 | 124.44 | Human urine | [38] |
| Hf.WO3/CPE | PC; SAL | SWV | / | 28.72 138.80 | Pharmaceutical formulation, human urine | [39] |
| nanoporous gold microdisc arrays | SAL | LSV | 250–2000 | 2530 | Pharmaceutical formulation | [40] |
| nano gold particles modified indium tin oxide (NGITO) electrode | SAL | SWV | 0.05–2.0 | 0.075 | Pharmaceutical formulation and human biological fluids | [41] |
| MWCNT film coated GCE | SAL | SWV | 0.19–2.4 | 47.8 | Pharmaceutical formulation | [42] |
| BDD | SAL | AdSV | 4.15–83 | 1210 | Pharmaceutical formulation | [43] |
| oxMWCNTs/UPPy/GCE | SMX | DPV | 0.50–2.76 | 104.60 | Milk | [44] |
| Silver-filled MWCNT nanocomposite | SMX | DPV | 0.013–17.7 | 2.53 | Pharmaceutical formulation and human urine | [45] |
| SPCE | SMX | DPV | 1.67–24.4 | 501.4 | Water | [46] |
| CNT paste | SMX | DPV | 0.35–30 | 100 | Pharmaceutical formulation | [47] |
| MWCNT-Nafion modified GCE | SMX | DPV | 12.6–2530 | 2530 | Pharmaceutical formulation and human urine | [48] |
| BDD | SMX | SWV | 1.5–15.5 | 291 | Pharmaceutical formulation | [49] |
| Composite material modified with AgNP, immobilized on 3D ABS support | SMX | DPV | 2.5–12.7 | 253 | Tap water, synthetic urine, drug, cow milk, breast milk, goat milk, and honey | [28] |
| GO/ZnO nanocomposite modified electrode | SMX | DPV | 0.025–0.38 | 7.32 | Waste water | [50] |
| GCE modified with a nanocomposite prepared from graphitic carbon nitride and ZnO | SMX | DPV | 0.005–280 | 1.67 | Spiked human blood serum samples | [51] |
| SPCE modified with Ce(III)-doped CuO nanocomposite | SMX | DPV | 7.60–91,000 | 2.53 | Biological and drug samples | [52] |
| graphene-modified GCE | SMX | DPV | 0.0023–7.3 | 0.69 | Pharmaceutical formulation | [53] |
| SPCE | SMX | DPV | 0.05–0.6 | 15 | Water | [23] |
| carbon fiber paper electrode | TMP | SWV | 14.5–580 | 18.87 | Fish | [27] |
| CuPh/PC/GCE | TMP | SWAdASV | 0.12–0.33, 0.44–1.78 | 198.48 | River water | [54] |
| SPCE modified with MWCN decorated with Prussian blue nanocubes | SMX; TMP | DPV | 0.25–2.5 0.03–2.9 | 9.6 17.4 | Human urine | [21] |
| BDD | SMX; TMP | DPV | 1.0–10 0.2–2.0 | 0.0036 0.0039 | Pharmaceutical formulation | [55] |
| paper-based fully printed electrochemical sensor with reduced graphene nanoribbons | SMX; TMP | DPV | 0.25–2.5 0.29–2.9 | 22.8 11.6 | Water | [56] |
| Paraffin composite electrode based on MWCNT modified with SbNP | SMX; TMP | DPV | 0.1–0.7 0.1–0.7 | 6.1 9.0 | Water | [57] |
| rGO-AgNP/GCE | SMX; TMP | DPV | 0.25–2.53; 0.30–2.96 | 151.97 118.50 | Synthetic wastewater | [58] |
| GR-ZnO/GCE | SMX; TMP | DPV | 0.25–10.13, 10.13–43.06; 0.30–2.96, 2.96–50.36 | 101.31 88.87 | Tap water, lake water, urine, and human serum | [59] |
| MoO2/GCE | SMX; TMP | DPV | 2.53–25.33; 0.59–5.92 | 36.47 37.62 | / | [60] |
| SPCE | SAL; SMX; TMP | DPV | 0.27–2.47; 0.29–11.10; 0.47–9.04 | 83.76 88.65 139.23 | River water | This work |
| / | SAL | GC-MS/MS | 0.25–2 | 10 | Human urine | [61] |
| / | SAL | HPLC | 0.5–3.0 | 21 | Tablet | [62] |
| / | TMP, SMX | HPLC | 0.5–20.0, 1.0–25.0 | 410, 820 | Human plasma | [63] |
| / | SMX, TMP | SPE–tandem mass spectrometry | 12–400, 1.2–40 | 470, 60 | Human serum | [64] |
| SAL | SMX | TMP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repeatability (RSD, %) | 1.3 | 3.5 | 1.6 |
| Reproducibility (RSD, %) | 2.8 | 3.9 | 4.3 |
| Analyte | Cspiked (mg L−1) | Cdetermined (mg L−1) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAL | 0.96 | 0.94 (0.02) | 1.8 | 98.8 |
| SMX | 1.02 | 1.00 (0.03) | 3.3 | 98.8 |
| TMP | 1.19 | 1.16 (0.03) | 2.4 | 97.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Voltammetric Determination of Salbutamol, Sulfamethoxazole, and Trimethoprim as Anthropogenic Impact Indicators Using Commercial Screen-Printed Electrodes. Sensors 2025, 25, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102998
Huang J, Bastos-Arrieta J, Serrano N, Díaz-Cruz JM. Voltammetric Determination of Salbutamol, Sulfamethoxazole, and Trimethoprim as Anthropogenic Impact Indicators Using Commercial Screen-Printed Electrodes. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102998
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jing, Julio Bastos-Arrieta, Núria Serrano, and José Manuel Díaz-Cruz. 2025. "Voltammetric Determination of Salbutamol, Sulfamethoxazole, and Trimethoprim as Anthropogenic Impact Indicators Using Commercial Screen-Printed Electrodes" Sensors 25, no. 10: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102998
APA StyleHuang, J., Bastos-Arrieta, J., Serrano, N., & Díaz-Cruz, J. M. (2025). Voltammetric Determination of Salbutamol, Sulfamethoxazole, and Trimethoprim as Anthropogenic Impact Indicators Using Commercial Screen-Printed Electrodes. Sensors, 25(10), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102998










