Button-Type Beam Position Monitor Development for Fourth-Generation Synchrotron Light Sources: Numerical Modeling and Test Bench Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Theoretical Analysis
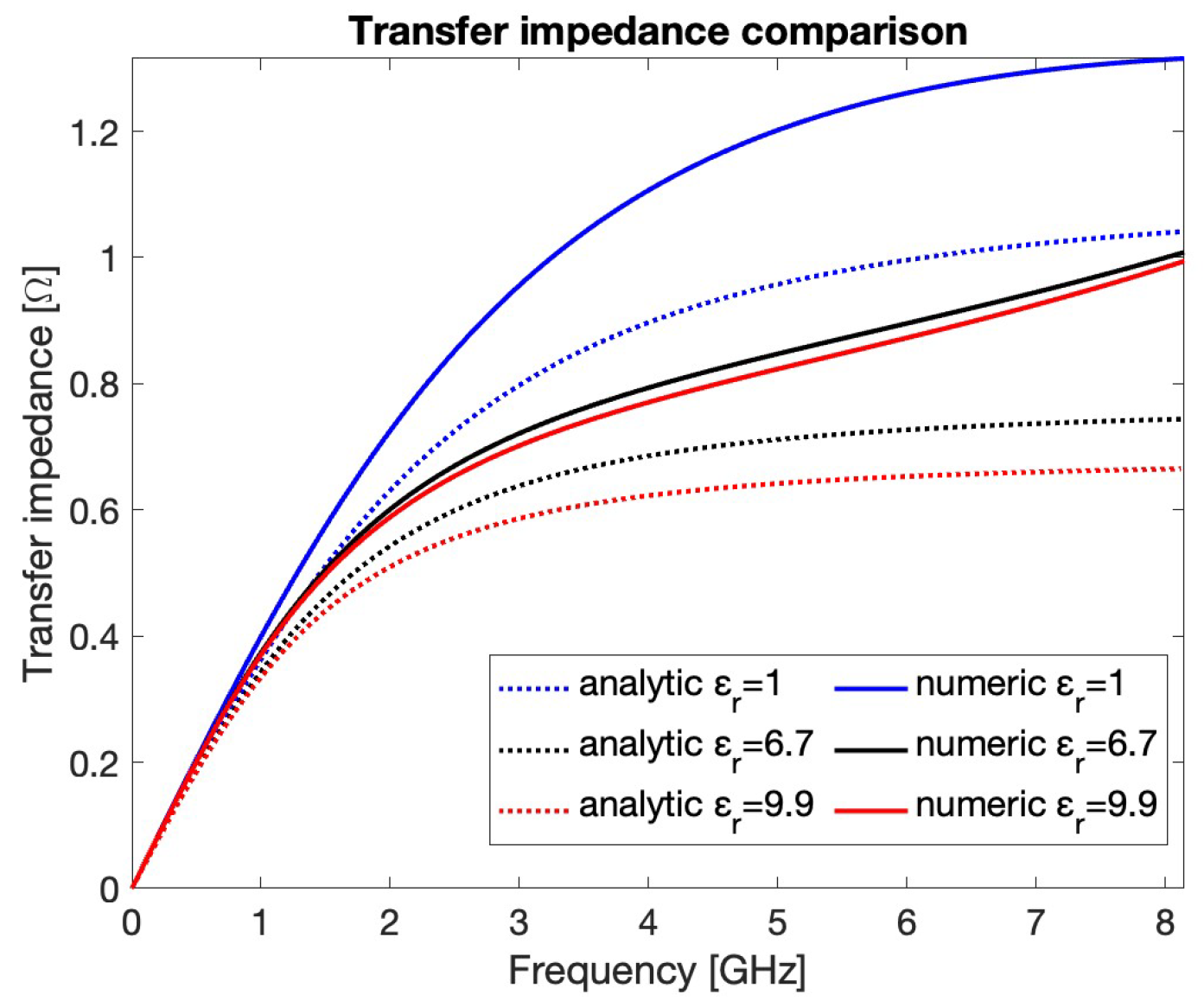
2.1. Transfer Impedance and Signal Extraction
2.2. Longitudinal Coupling Impedance and Wake Losses
3. Numerical Analysis
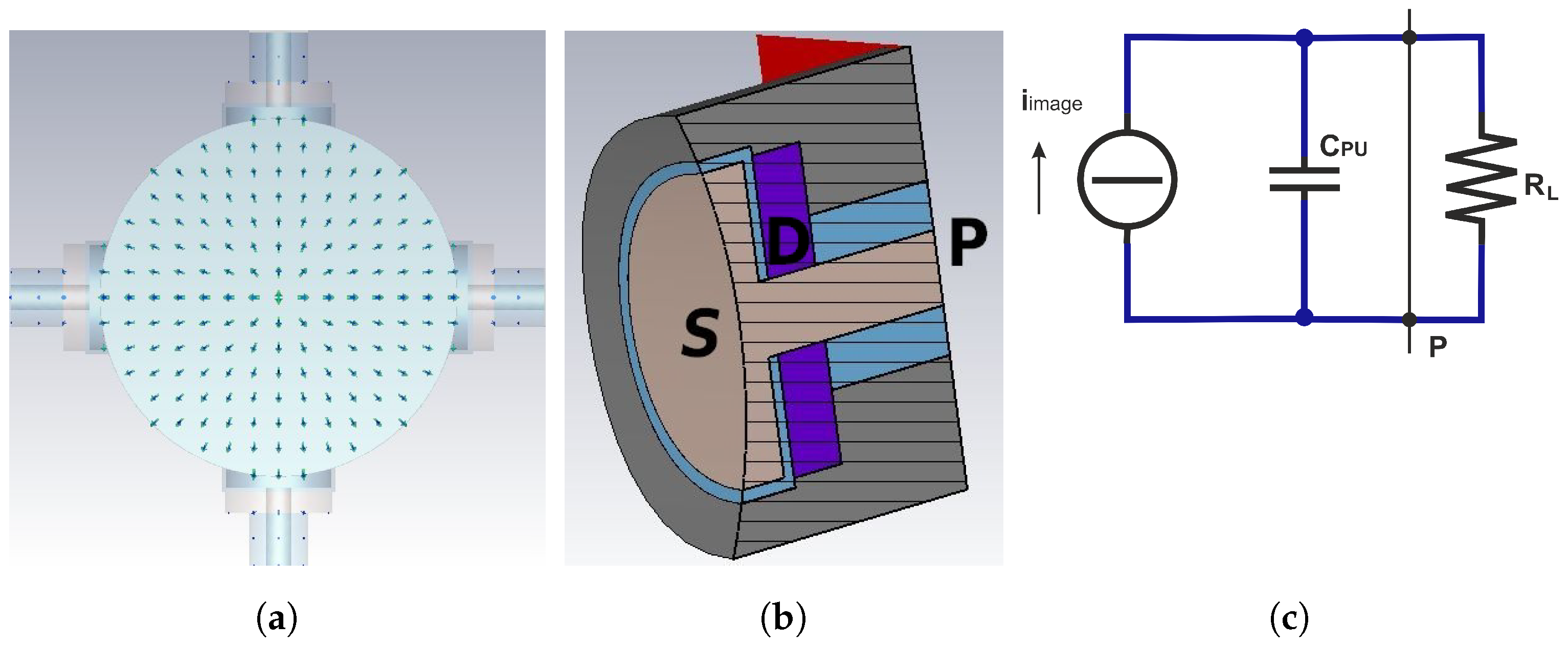
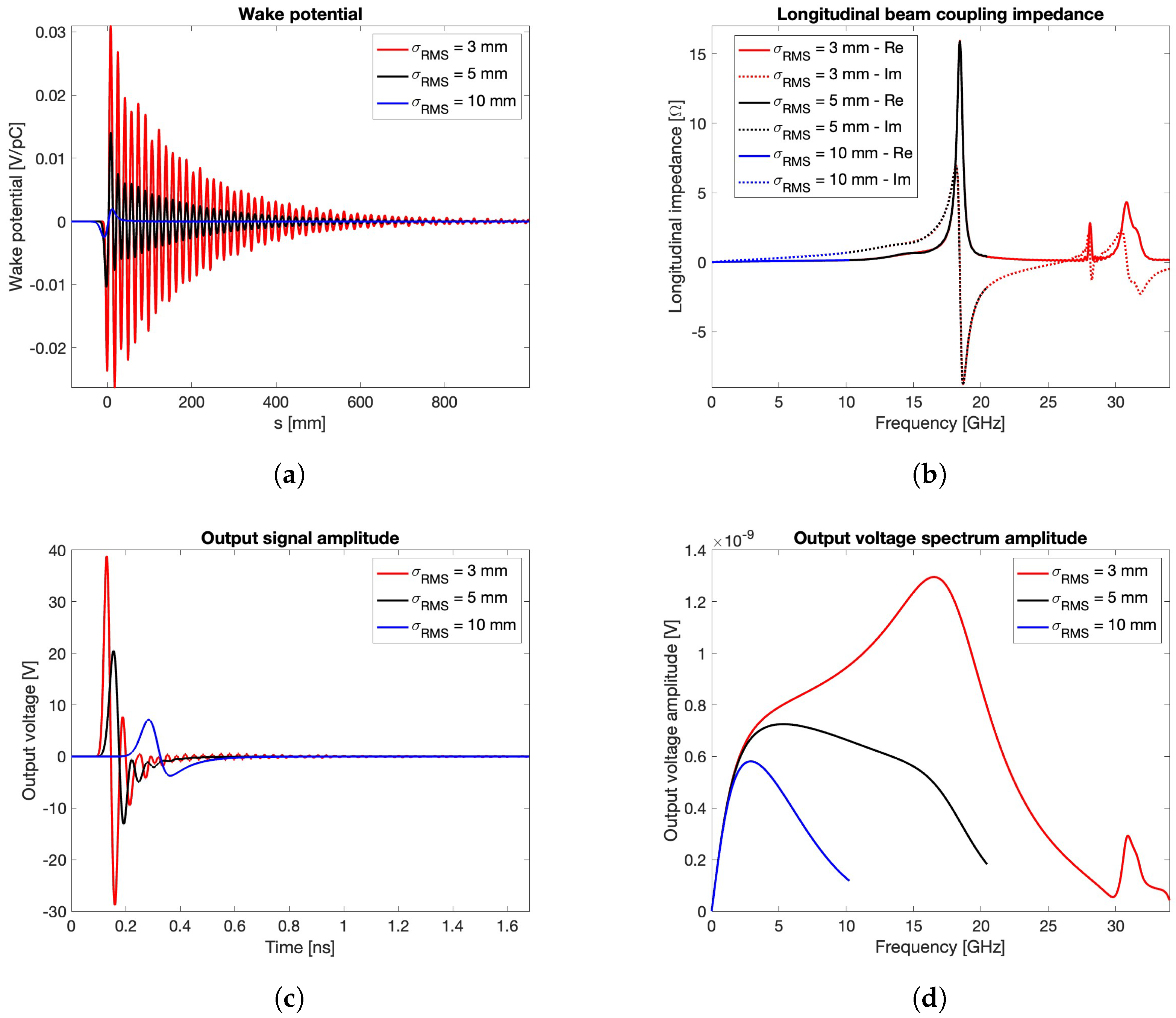
- The bunch shape is represented by a Gaussian distribution characterized by a standard deviation , expressed in length unit (mm), and by a total charge , identified by the area under the curve. In the presented simulations, this latter parameter is fixed to 1 nC, while different values ranging from 3 to 10 mm are considered. With reference to the shapes reported in Figure 3a, the vertical axis unit represents the linear charge density in C/m. Taking into account the propagation characteristics of the charged bunch at the speed of light, the horizontal axis can be rescaled in time unit (ns), and the vertical axis in electric current unit (C/s). The TD representation of the Gaussian distributions is shown in Figure 3b, while the corresponding spectra, obtained by the Fourier transformation, are reported in Figure 3c.
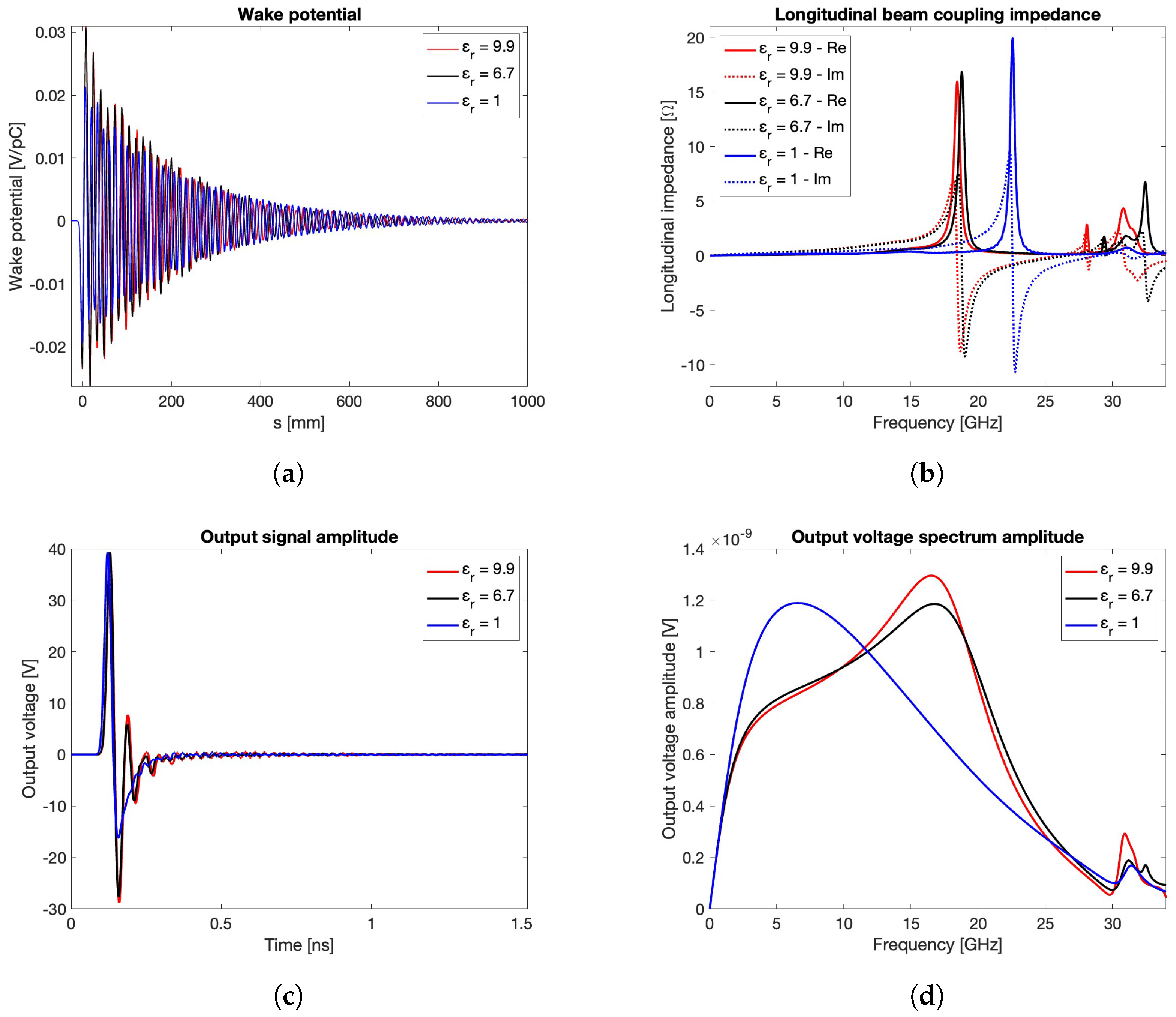
- Concerning the adopted materials, all of them are realistically characterized by a lossy behavior and a relative magnetic permeability . In particular, stainless steel AISI316L with electric conductivity MS/m is chosen for the BPM body, while molybdenum with electric conductivity MS/m is selected for the central pin and the PU button. The vacuum sealing D (Figure 2b) is modeled by a dielectric material with relative electric permittivity , whose value ranges from 1 to 10.
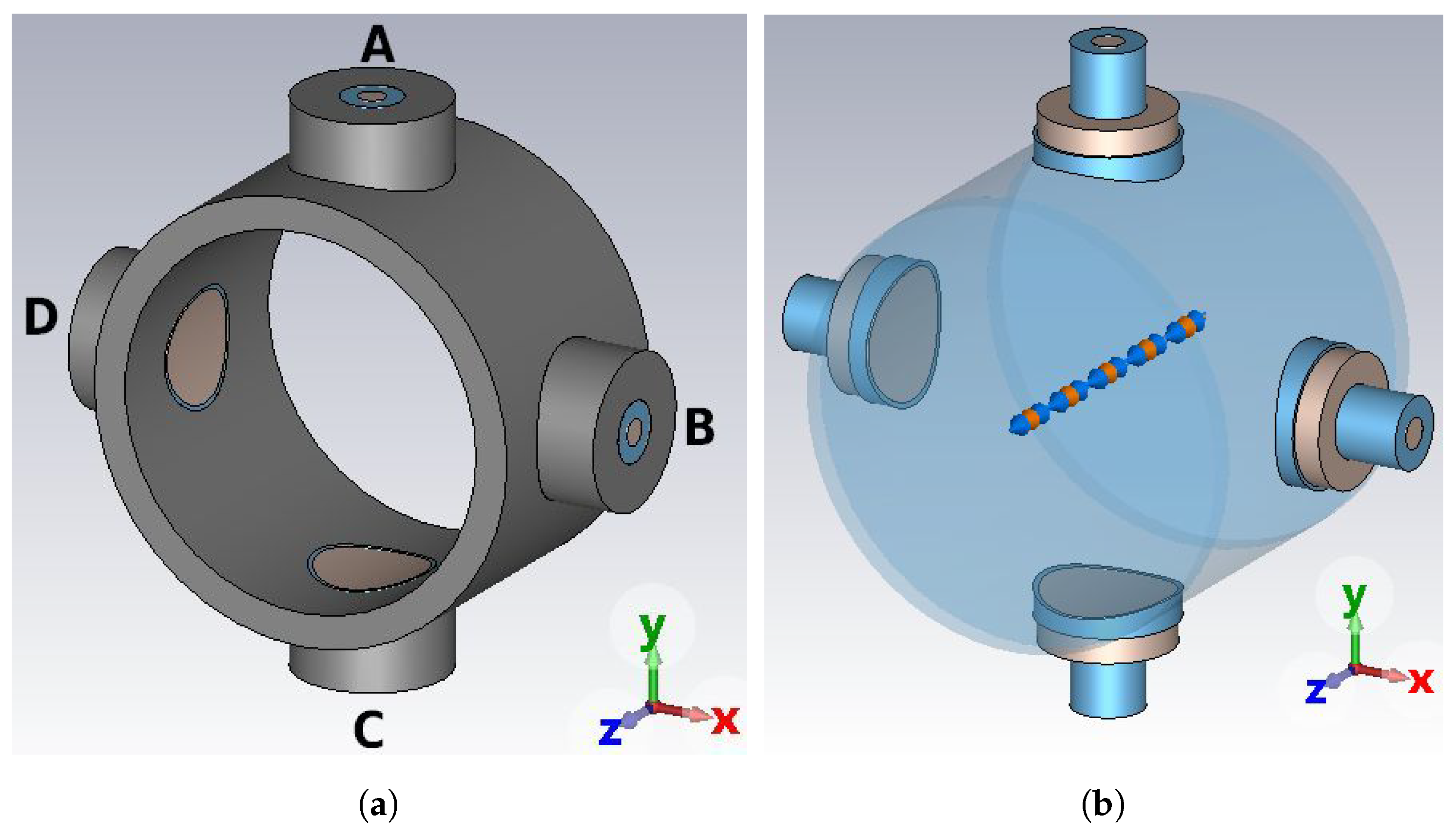
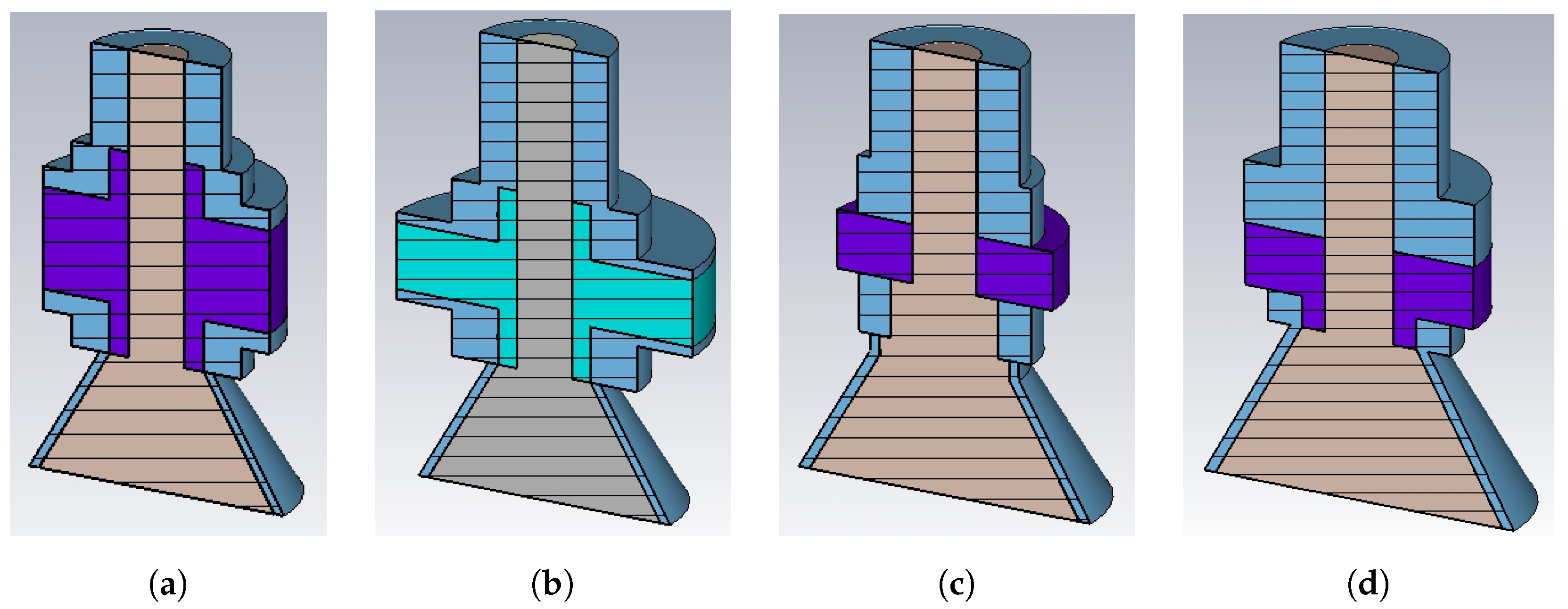
- Regarding the simulator configuration, the beam input and output cross-sections of the vacuum pipe are set as open boundaries to emulate an infinitely long vacuum pipe, in order to avoid perturbations of the incoming and outgoing quantities. The signal propagating along the coaxial feedthrough of the PU is terminated on a 50 matched waveguide port. Additionally, only one fourth of the BPM structure is required to be actually simulated by the CST wake solver, thanks to the on-axis beam excitation and the symmetry of the component. The mesh density is always set fine enough to properly cover the gap between the button and its housing.

3.1. Round Pipe with Cylindrical PUs
3.2. Square/Rhomboidal Pipes with Conical PUs
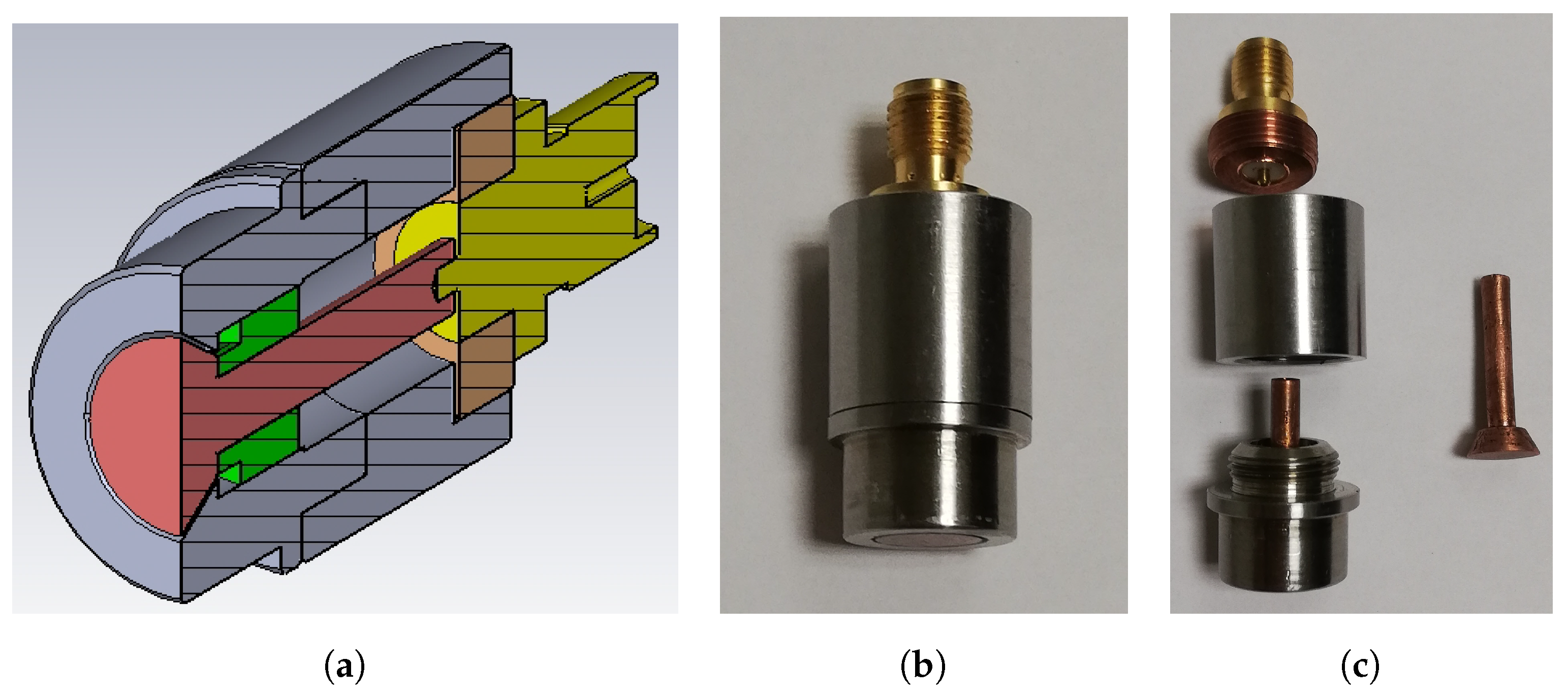
4. Experimental Results
4.1. TDR Measurements
4.2. VNA Measurements
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| BPM | Beam position monitor |
| DC | Direct current |
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| FD | Frequency domain |
| HOM | High-order modes |
| PU | Pick-up |
| RF | Radio frequency |
| SMA | SubMiniature version A |
| TD | Time domain |
| TDR | TD reflectometer |
| TEM | Trasverse EM |
| VNA | Vector network analyzer |
References
- Meirose, B.; Abelin, V.; Bertilsson, F.; Bolling, B.E.; Brandin, M.; Holz, M.; Høier, R.; Johansson, A.; Kalbfleisch, S.; Lilja, P.; et al. Real-time accelerator diagnostic tools for the MAX IV storage rings. Instruments 2020, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinker, A. Adaptive machine learning for robust diagnostics and control of time-varying particle accelerator components and beams. Information 2021, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sui, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Yue, J.; Cao, J. Beam position monitor characterization for the high energy photon source synchrotron. Symmetry 2023, 15, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlachter, A.S. Third-generation synchrotron light sources. In New Directions in Research with Third-Generation Soft X-ray Synchrotron Radiation Sources; Schlachter, A.S., Wuilleumier, F.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Nederlands, 1994; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Winick, H. Fourth generation light sources. In Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference (Cat. No.97CH36167), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16 May 1997; Volume 1, pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.L. History of synchrotron radiation. Synchrotron Radiat. News 2015, 28, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantzoulis, E.; Di Mitri, S.; Barbo, F.; Barletta, W.; Bassanese, S.; Bracco, R.; Brajnik, G.; Buonanno, A.; Caiazza, D.; Carniel, A.; et al. Design strategies and technology of Elettra 2.0 for a versatile offer to the user community. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Acceler. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2024, 1060, 169007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadji, A.; Nadolski, L.S. Upgrade project of the SOLEIL accelerator complex. Synchr. Radiat. News. 2023, 36, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.R. Beam position monitor engineering. AIP Beam Instrum. Work. BIW 1997, 390, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, R.E. Beam position monitoring. AIP Beam Instrum. Work. BIW 1990, 212, 26–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.A.; Lambertson, G.R. Dynamic devices. A primer on pickups and kickers. AIP Beam Instrum. Work. BIW 1992, 249, 537–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, W.C. Broad-band characteristics of circular button pickups. AIP Beam Instrum. Work. BIW 1992, 281, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, M. BPM systems: A brief introduction to beam position monitoring. arXiv 2018, arXiv:2005.1408. [Google Scholar]
- Forck, P.; Kowina, P.; Liakin, D. Beam position monitors. arXiv 2008, arXiv:2009.10411. [Google Scholar]
- Lipka, D.; Vilcins, S. BPMs from design to real measurement. Int. Part. Accel. Conf. IPAC 2014, 1, 2774–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.F.D. Technological review of beam position button design and manufacture. Int. Beam Instrum. Conf. IBIC 2019, 1, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, M.; Feghhi, S.A.H.; Rahighi, J. Numerical analysis of the beam position monitor pickup for the Iranian light source facility. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Acceler. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2017, 847, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sui, Y.-F.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.-H.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Yu, L.-D.; Liu, X.-Y.; Xu, T.-G.; et al. Design and fabrication of button-style beam position monitors for the HEPS synchrotron light facility. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2022, 33, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, V.G. Longitudinal Instability of a Coasting Beam above Transition, Due to the Action of Lumped Discontinuities; Technical Report CERN-ISR-RF-66-35; Intersecting Storage Rings Division, Radio Frequency and Beam Observation Group (ISR-RF): Geneva, Switzerland, 1966; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo, L.; Vaccaro, V.G.; Zobov, M. Wake fields and impedance. arXiv, 2003; arXiv:physics/0309023. [Google Scholar]
- Marcellini, F.; Serio, M.; Stella, A.; Zobov, M. DAΦNE broad-band button electrodes. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Acceler. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1998, 402, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CST Computer Simulation Technology, Studio Suite. Dassault SystÉmes Simulia, 2022.
- Bilanishvili, S.; Zobov, M. Capacitive BPM electromagnetic design optimisation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2687, 072004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, H.O.C.; Sanfelici, L.; Marques, S.R. Design and impedance optimization of the SIRIUS BPM button. In Proceedings of the IBIC2013, Oxford, UK, 16–19 September 2013; pp. 365–368. [Google Scholar]
- El Ajjouri, M.; Alves, F.; Gamelin, A.; Hubert, N. Preliminary studies for the SOLEIL upgrade BPM. In Proceedings of the International Beam Instrumentation Conference (10th), Pohang, Republic of Korea, 24–28 May 2021; pp. 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ajjouri, M.; Hubert, N.; Gamelin, A.; Alves, F. Design of the beam position monitor for SOLEIL II. In Proceedings of the International Beam Instrumentation Conference (11th), Kraków, Poland, 11–15 September 2022; pp. 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleva, S.; Bassanese, S.; Brajnik, G.; Cudin, I.; De Monte, R.; Loda, G.; Pangon, G.; Comisso, M.; Passarelli, A.; Maletta, C.; et al. Button type beam position monitor design for the Elettra 2.0 storage ring. In Proceedings of the 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference, Venice, Italy, 7–12 May 2023; pp. 4621–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


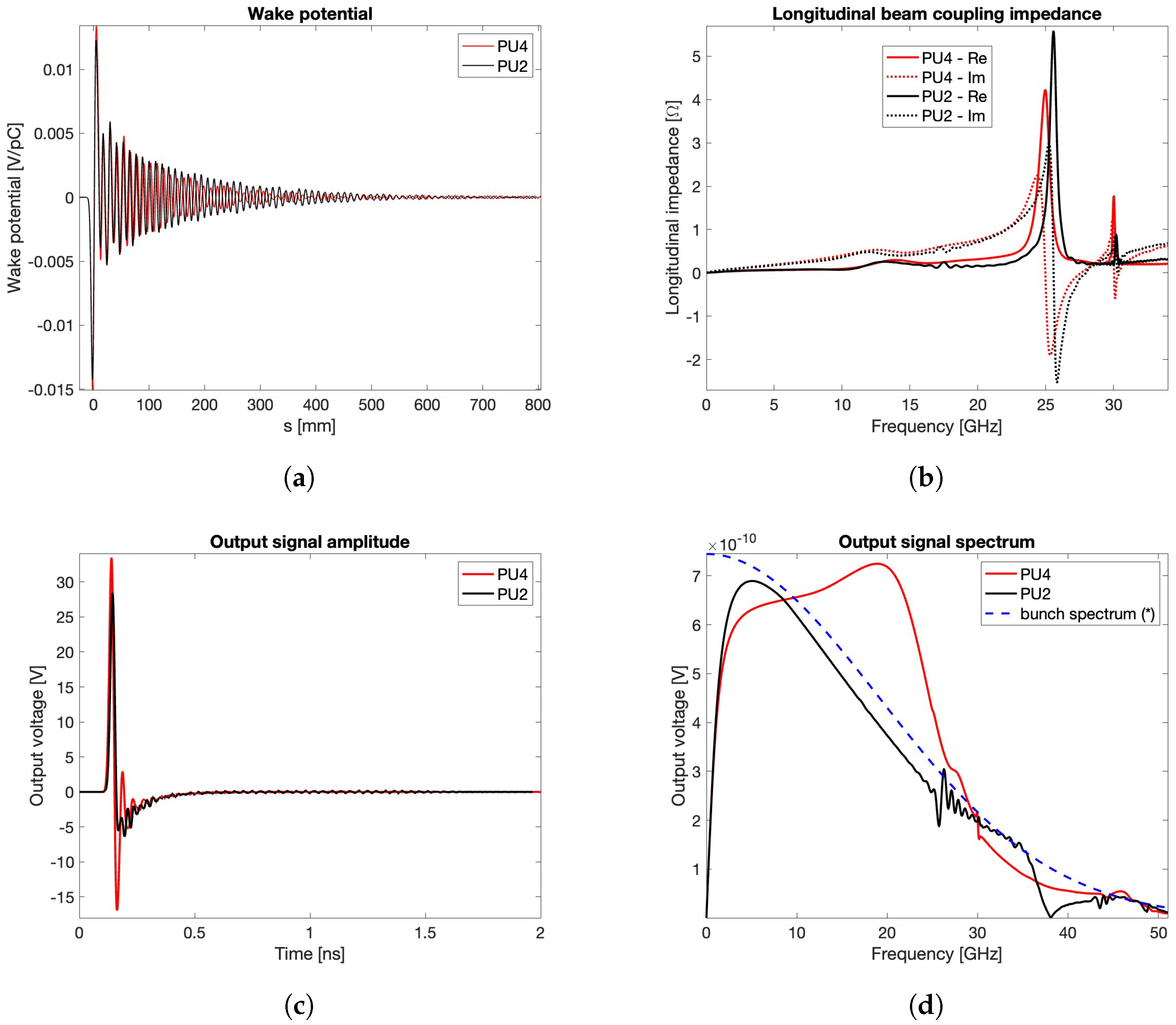
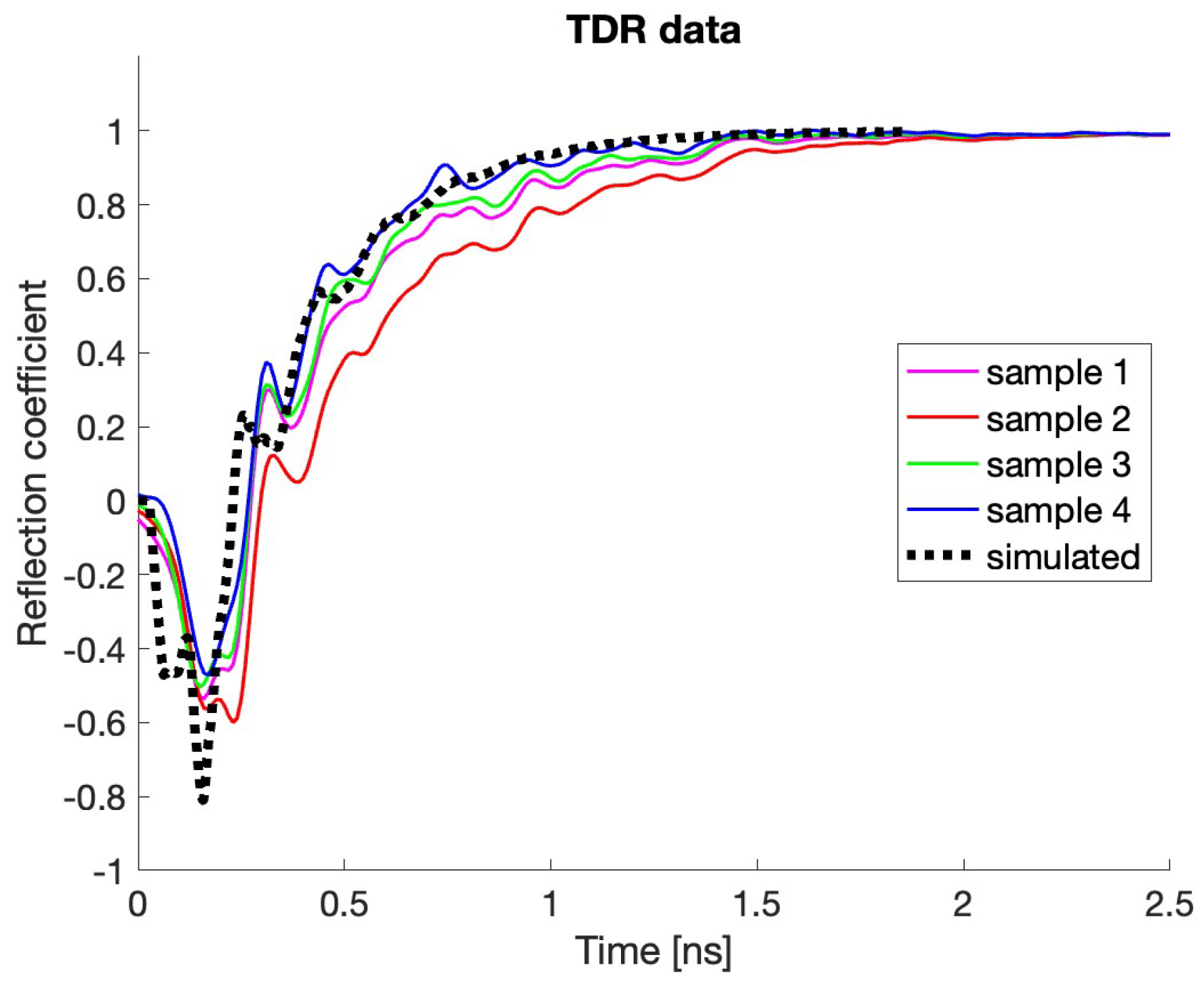

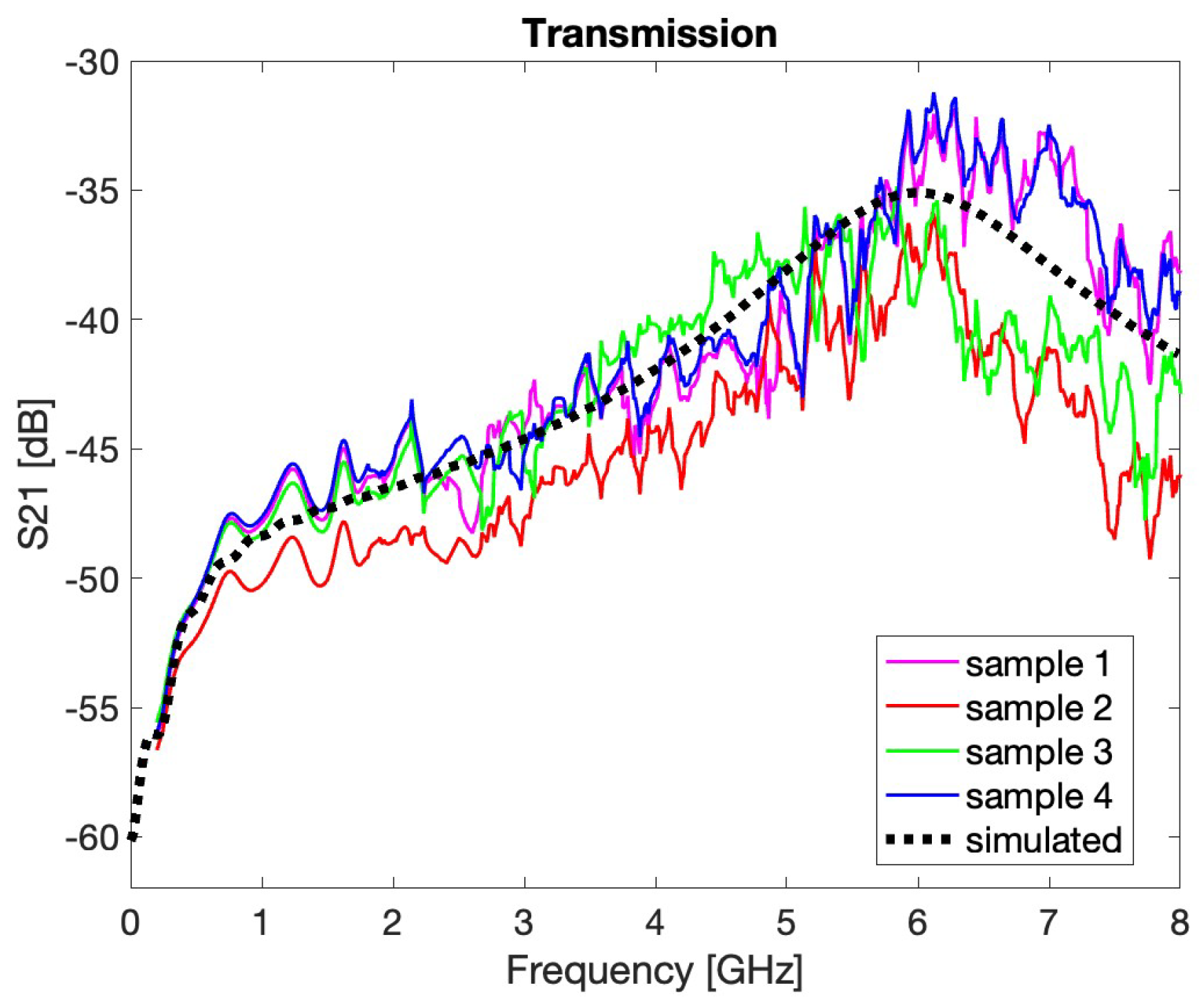
| PU1 | PU2 | PU3 | PU4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.7 | 4.1 | 6.7 | 6.7 | |
| [mV/pC] | 4.40 | 3.90 | 5.06 | 4.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cleva, S.; Bassanese, S.; Comisso, M.; El Ajjouri, M.; Sergo, R.; Morello, C.; Passarelli, A. Button-Type Beam Position Monitor Development for Fourth-Generation Synchrotron Light Sources: Numerical Modeling and Test Bench Measurements. Sensors 2024, 24, 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092726
Cleva S, Bassanese S, Comisso M, El Ajjouri M, Sergo R, Morello C, Passarelli A. Button-Type Beam Position Monitor Development for Fourth-Generation Synchrotron Light Sources: Numerical Modeling and Test Bench Measurements. Sensors. 2024; 24(9):2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092726
Chicago/Turabian StyleCleva, Stefano, Silvano Bassanese, Massimiliano Comisso, Moussa El Ajjouri, Rudi Sergo, Christian Morello, and Andrea Passarelli. 2024. "Button-Type Beam Position Monitor Development for Fourth-Generation Synchrotron Light Sources: Numerical Modeling and Test Bench Measurements" Sensors 24, no. 9: 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092726
APA StyleCleva, S., Bassanese, S., Comisso, M., El Ajjouri, M., Sergo, R., Morello, C., & Passarelli, A. (2024). Button-Type Beam Position Monitor Development for Fourth-Generation Synchrotron Light Sources: Numerical Modeling and Test Bench Measurements. Sensors, 24(9), 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092726






