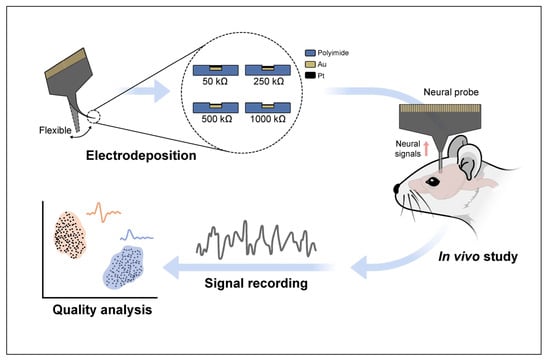
Impact of Impedance Levels on Recording Quality in Flexible Neural Probes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pt Electrodeposition and Measurement of Impedance of the Neural Probe
2.2. In Vivo Electrophysiological Recordings and Analysis
3. Results
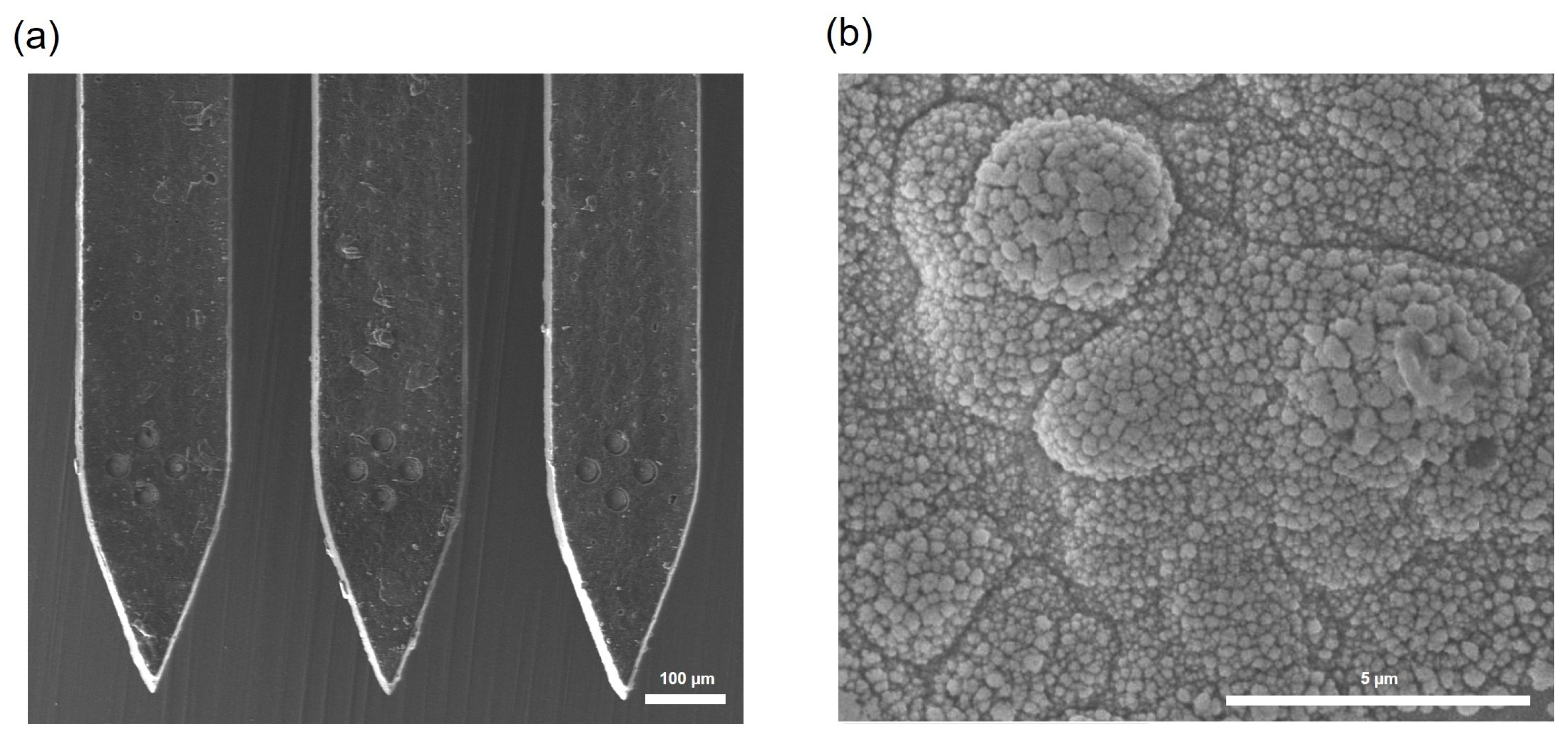
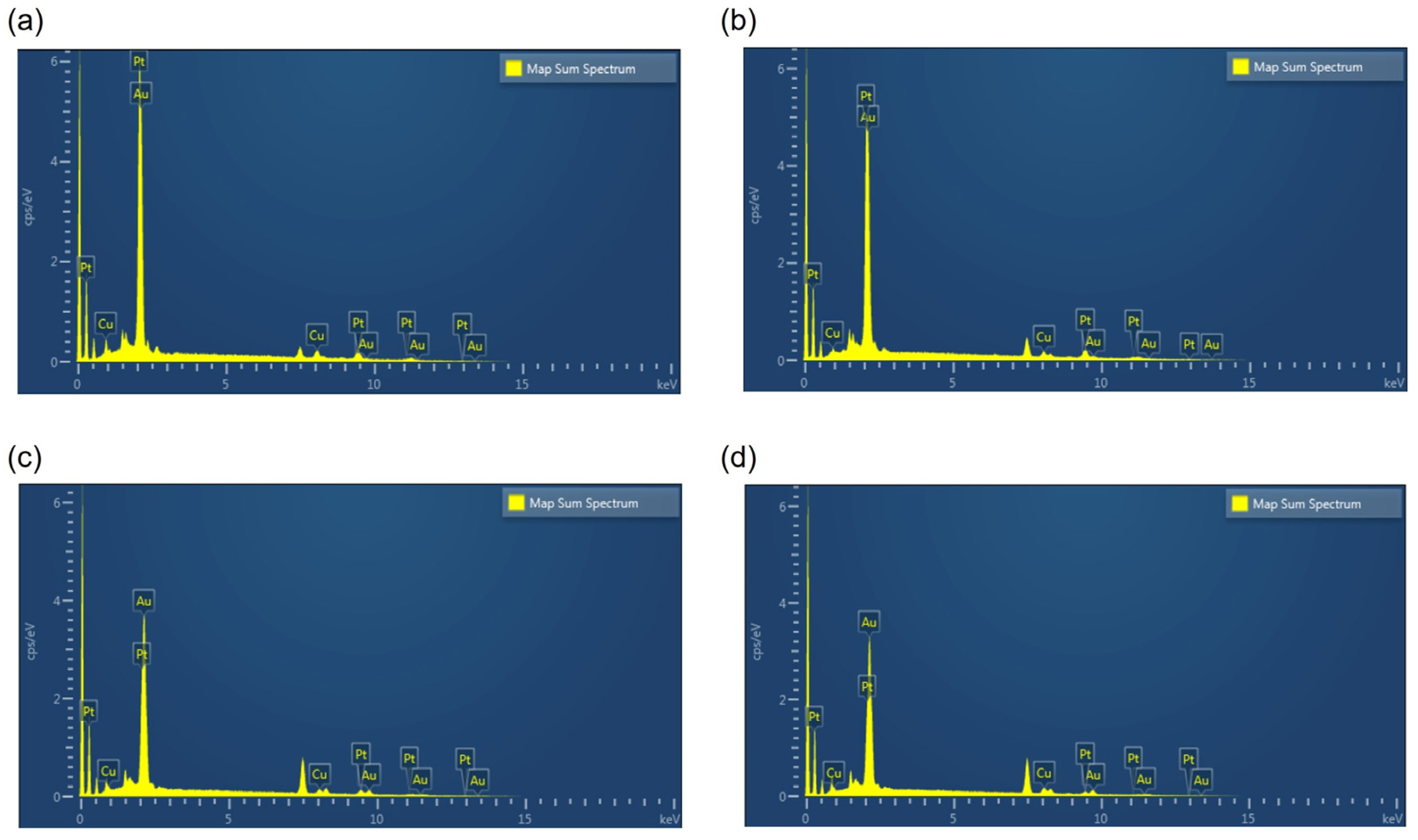
3.1. Pt Electrodeposition and Measurement of Impedance of the Neural Probe
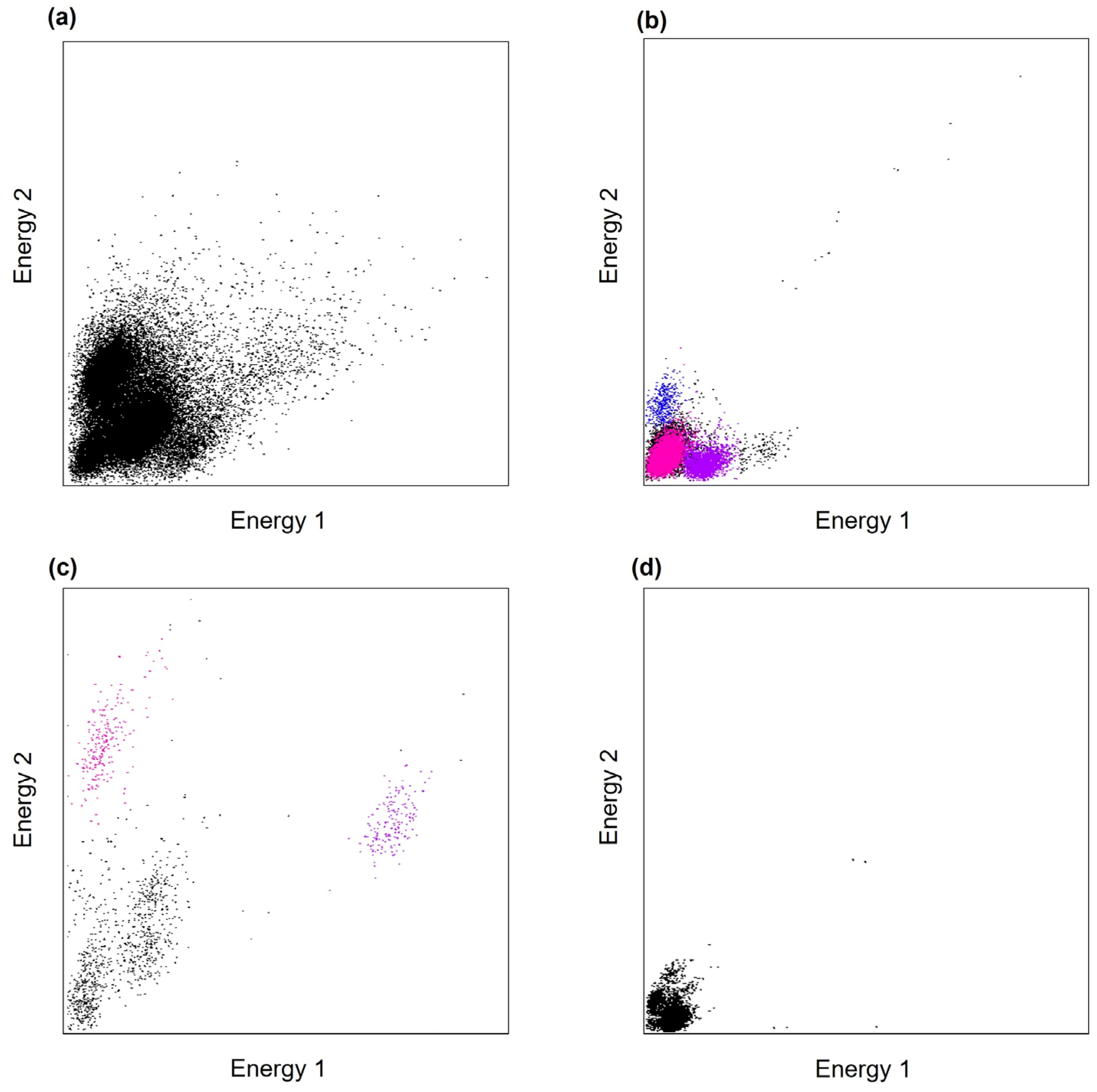
3.2. In Vivo Electrophysiological Recordings and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Luo, J.; Xue, N.; Chen, J. A Review: Research Progress of Neural Probes for Brain Research and Brain-Computer Interface. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorfi, M.; Skousen, J.L.; Weder, C.; Capadona, J.R. Progress towards biocompatible intracortical microelectrodes for neural interfacing applications. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HajjHassan, M.; Chodavarapu, V.; Musallam, S. NeuroMEMS: Neural Probe Microtechnologies. Sensors 2008, 8, 6704–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, K.I.; Lim, J.M.; Paik, S.J.; Park, J.; Byun, S.; Lee, A.; Park, S.; Song, T.; Choi, H.; Jeong, M.J. Multifunctional Probe for Chemical Stimulation and Neural Signal Recording. Sens. Mater. 2005, 17, 087–095. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, J.R.; Pimenta, S.; Santos, D.J.; Esteves, B.; Gomes, N.M.; Correia, J.H. Flexible Neural Probe Fabrication Enhanced with a Low-Temperature Cured Polyimide and Platinum Electrodeposition. Sensors 2022, 22, 9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novais, A.; Calaza, C.; Fernandes, J.; Fonseca, H.; Monteiro, P.; Gaspar, J.; Jacinto, L. Hybrid Multisite Silicon Neural Probe with Integrated Flexible Connector for Interchangeable Packaging. Sensors 2021, 21, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Bellamkonda, R.V.; Sun, W.; Levenston, M.E. Biomechanical analysis of silicon microelectrode-induced strain in the brain. J. Neural Eng. 2005, 2, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Tsang, W.M.; Park, W.T.; Merugu, S. Surface Characteristics, Biodegradability and Biocompatibility of Porous Silicon for Microfabricated Neural Electrode. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 2821–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltman, A.; Yoo, J.; Meng, E. Flexible, Penetrating Brain Probes Enabled by Advances in Polymer Microfabrication. Micromachines 2016, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, G.; Pas, J.; Markovic, K.; Scancar, J.; O’Connor, R.P. PEDOT:PSS-coated platinum electrodes for neural stimulation. APL Bioeng. 2023, 7, 046117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Lycke, R.; Ganji, M.; Xie, C.; Luan, L. Ultraflexible Neural Electrodes for Long-Lasting Intracortical Recording. iScience 2020, 23, 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Huang, L.; Zheng, J.; Xi, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yan, W.; Tao, G.; Qiu, J.; So, K.F.; et al. Flexible Fiber Probe for Efficient Neural Stimulation and Detection. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousche, P.J.; Pellinen, D.S.; Pivin, D.P., Jr.; Williams, J.C.; Vetter, R.J.; Kipke, D.R. Flexible polyimide-based intracortical electrode arrays with bioactive capability. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Gong, R.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J. In Vivo Neural Recording and Electrochemical Performance of Microelectrode Arrays Modified by Rough-Surfaced AuPt Alloy Nanoparticles with Nanoporosity. Sensors 2016, 16, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozai, T.D.; Du, Z.; Gugel, Z.V.; Smith, M.A.; Chase, S.M.; Bodily, L.M.; Caparosa, E.M.; Friedlander, R.M.; Cui, X.T. Comprehensive chronic laminar single-unit, multi-unit, and local field potential recording performance with planar single shank electrode arrays. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 242, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, J.; Cao, B.; Li, Y.; Pang, S.W. Electrode modifications to lower electrode impedance and improve neural signal recording sensitivity. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 056018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.A.; Uram, J.D.; Yang, J.; Martin, D.C.; Kipke, D.R. Chronic neural recordings using silicon microelectrode arrays electrochemically deposited with a poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) film. J. Neural Eng. 2006, 3, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, S.F. Neural stimulation and recording electrodes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 275–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, S.; Chung, H.W.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Kang, C.Y.; Lee, S.H. Flexible deep brain neural probe for localized stimulation and detection with metal guide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.A.; Rolston, J.D.; Guo, L.; Potter, S.M. Improving impedance of implantable microwire multi-electrode arrays by ultrasonic electroplating of durable platinum black. Front. Neuroeng. 2010, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woeppel, K.; Dhawan, V.; Shi, D.; Cui, X.T. Nanotopography-enhanced biomimetic coating maintains bioactivity after weeks of dry storage and improves chronic neural recording. Biomaterials 2023, 302, 122326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, H.K.; Chen, S.; Ridder, M.C.; Sah, P.; Li, N.; Yang, Z.; Hasanbegovic, H.; Gao, Z.; Gerfen, C.R.; Svoboda, K. A midbrain-thalamus-cortex circuit reorganizes cortical dynamics to initiate movement. Cell 2022, 185, 1065–1081.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccino, A.P.; Kuchta, M.; Jæger, K.H.; Ness, T.V.; Berthet, P.; Mardal, K.A.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Tveito, A. How does the presence of neural probes affect extracellular potentials? J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 026030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.P.; Baião, P.; Lopes, G.; Frazão, J.; Nogueira, J.; Fortunato, E.; Barquinha, P.; Kampff, A.R. Does Impedance Matter When Recording Spikes with Polytrodes? Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okun, M.; Lak, A.; Carandini, M.; Harris, K.D. Long Term Recordings with Immobile Silicon Probes in the Mouse Cortex. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, M.K.; Bakkum, D.J.; Rompani, S.B.; Hierlemann, A. Recording large extracellular spikes in microchannels along many axonal sites from individual neurons. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.C.; Borden, P.Y.; Liew, Y.J.; Bolus, M.F.; Stoy, W.M.; Forest, C.R.; Stanley, G.B. Rapid Cortical Adaptation and the Role of Thalamic Synchrony during Wakefulness. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 5421–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.; Chavez, J.; Bramian, A.; Igarashi, K.M. Protocol for remapping of place cells in disease mouse models. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimanski, L.A.; Lipa, P.; Barnes, C.A. Tracking the course of hippocampal representations during learning: When is the map required? J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 3094–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oşan, R.; Chen, G.; Feng, R.; Tsien, J.Z. Differential consolidation and pattern reverberations within episodic cell assemblies in the mouse hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswam, V.; Obien, M.E.J.; Franke, F.; Frey, U.; Hierlemann, A. Optimal Electrode Size for Multi-Scale Extracellular-Potential Recording From Neuronal Assemblies. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Otto, K.J.; Kipke, D.R. Repeated voltage biasing improves unit recordings by reducing resistive tissue impedances. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2005, 13, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, D.R.; Tresco, P.A. Impedance characterization of microarray recording electrodes in vitro. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suner, S.; Fellows, M.R.; Vargas-Irwin, C.; Nakata, G.K.; Donoghue, J.P. Reliability of signals from a chronically implanted, silicon-based electrode array in non-human primate primary motor cortex. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2005, 13, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.E.; Boldt, C.; Redish, A.D. Creating low-impedance tetrodes by electroplating with additives. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 156, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obien, M.E.; Deligkaris, K.; Bullmann, T.; Bakkum, D.J.; Frey, U. Revealing neuronal function through microelectrode array recordings. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, D.; Erö, C.; Markram, H. Cell Densities in the Mouse Brain: A Systematic Review. Front. Neuroanat. 2018, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, V.; Patrick, E.; Dieme, R.; Sanchez, J.C.; Prasad, A.; Nishida, T. Electrode impedance analysis of chronic tungsten microwire neural implants: Understanding abiotic vs. biotic contributions. Front. Neuroeng. 2014, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.A.; Langhals, N.B.; Joseph, M.D.; Richardson-Burns, S.M.; Hendricks, J.L.; Kipke, D.R. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) polymer coatings facilitate smaller neural recording electrodes. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozai, T.D.; Catt, K.; Du, Z.; Na, K.; Srivannavit, O.; Haque, R.U.; Seymour, J.; Wise, K.D.; Yoon, E.; Cui, X.T. Chronic In Vivo Evaluation of PEDOT/CNT for Stable Neural Recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Choi, J.; Jeong, H.; Park, D.; Cheong, E.; Sung, J.; Choi, H.-J. Impact of Impedance Levels on Recording Quality in Flexible Neural Probes. Sensors 2024, 24, 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24072300
Han J, Choi J, Jeong H, Park D, Cheong E, Sung J, Choi H-J. Impact of Impedance Levels on Recording Quality in Flexible Neural Probes. Sensors. 2024; 24(7):2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24072300
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Juyeon, Jungsik Choi, Hyeonyeong Jeong, Daerl Park, Eunji Cheong, Jaesuk Sung, and Heon-Jin Choi. 2024. "Impact of Impedance Levels on Recording Quality in Flexible Neural Probes" Sensors 24, no. 7: 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24072300
APA StyleHan, J., Choi, J., Jeong, H., Park, D., Cheong, E., Sung, J., & Choi, H.-J. (2024). Impact of Impedance Levels on Recording Quality in Flexible Neural Probes. Sensors, 24(7), 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24072300