Design and Experimental Study of a Hybrid Micro-Vibration Isolation System Based on a Strain Sensor for High-Precision Space Payloads
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Study
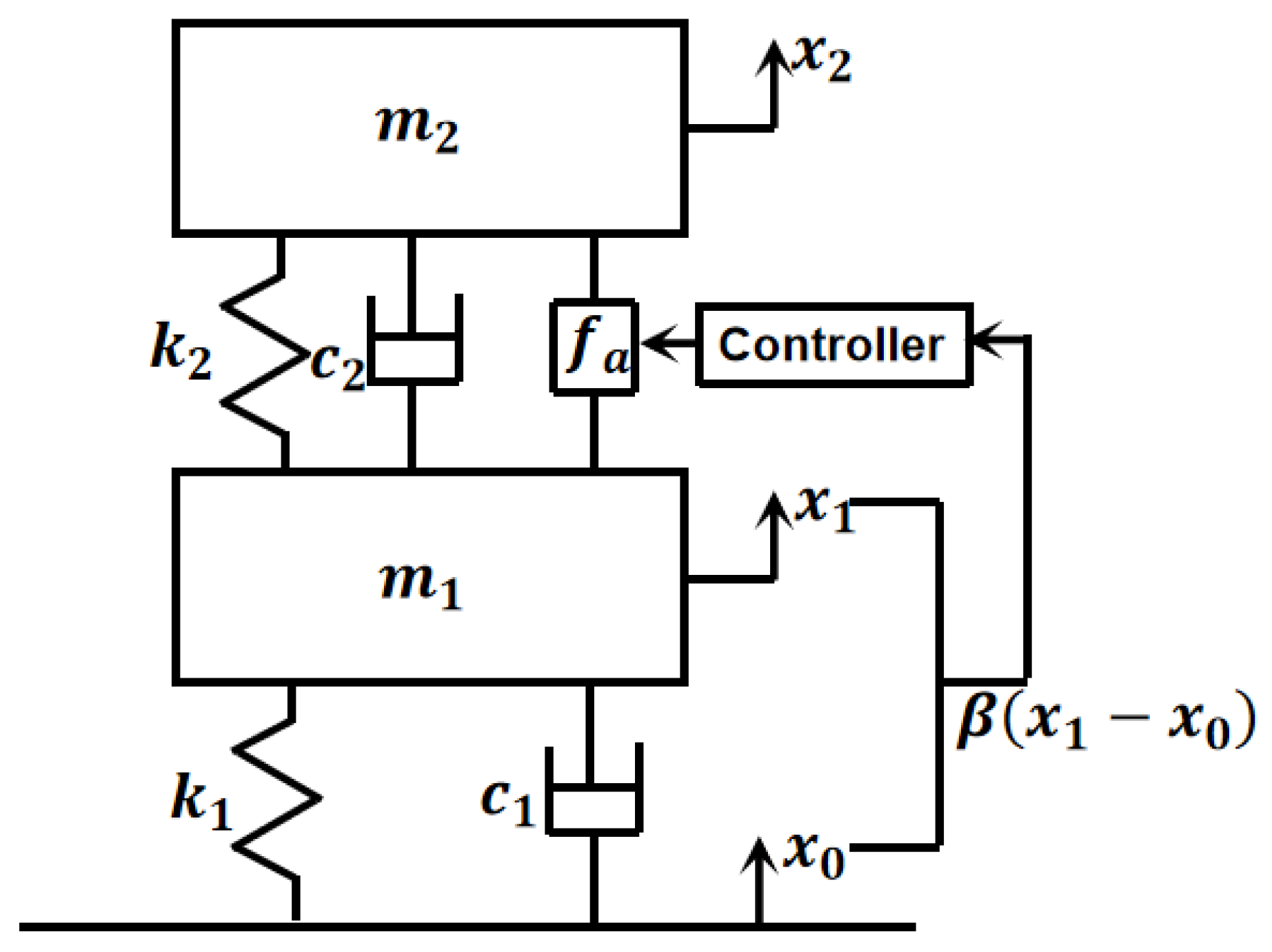
2.1. Theoretical Model
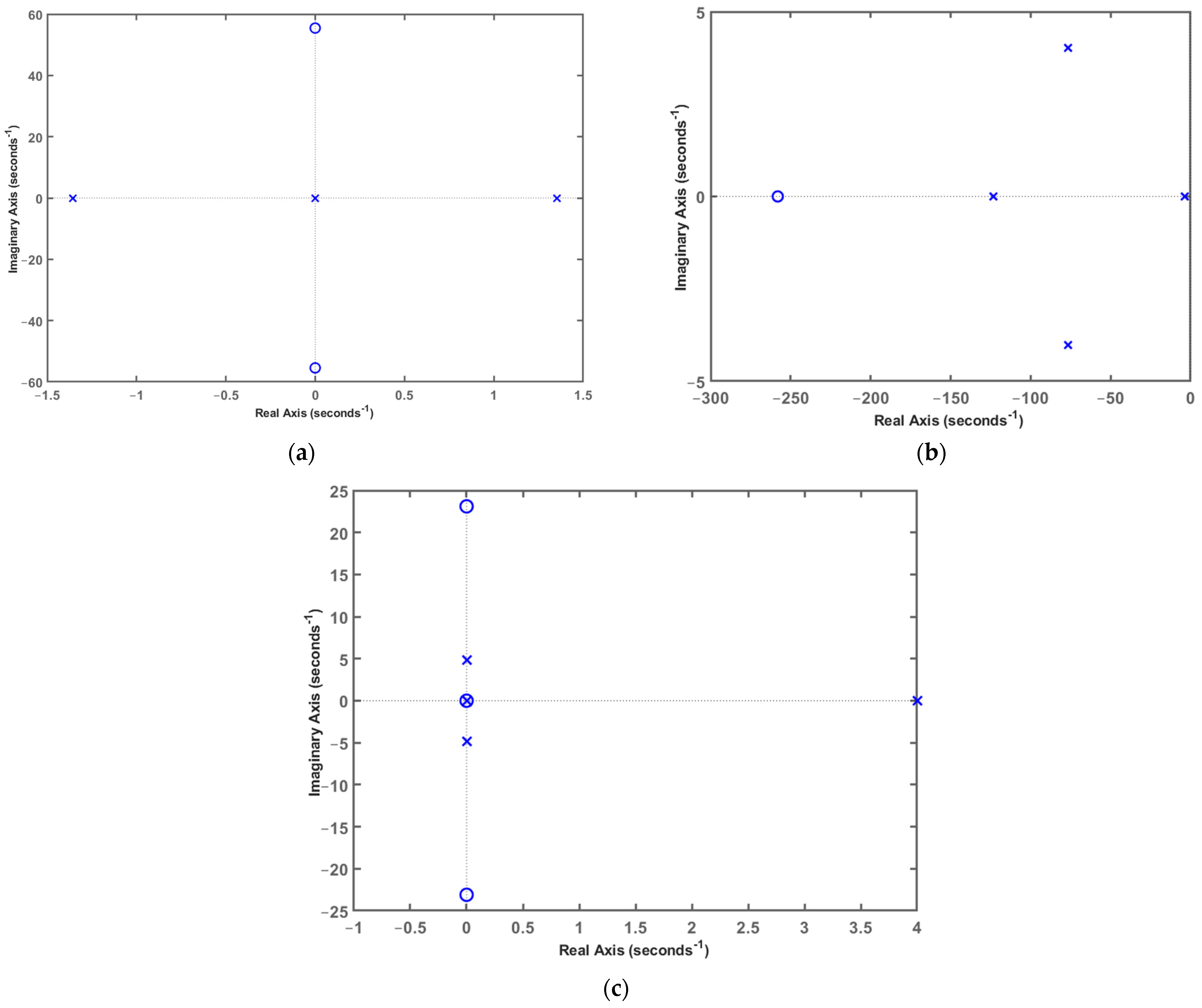
2.2. Controller Design
3. Experimental Study
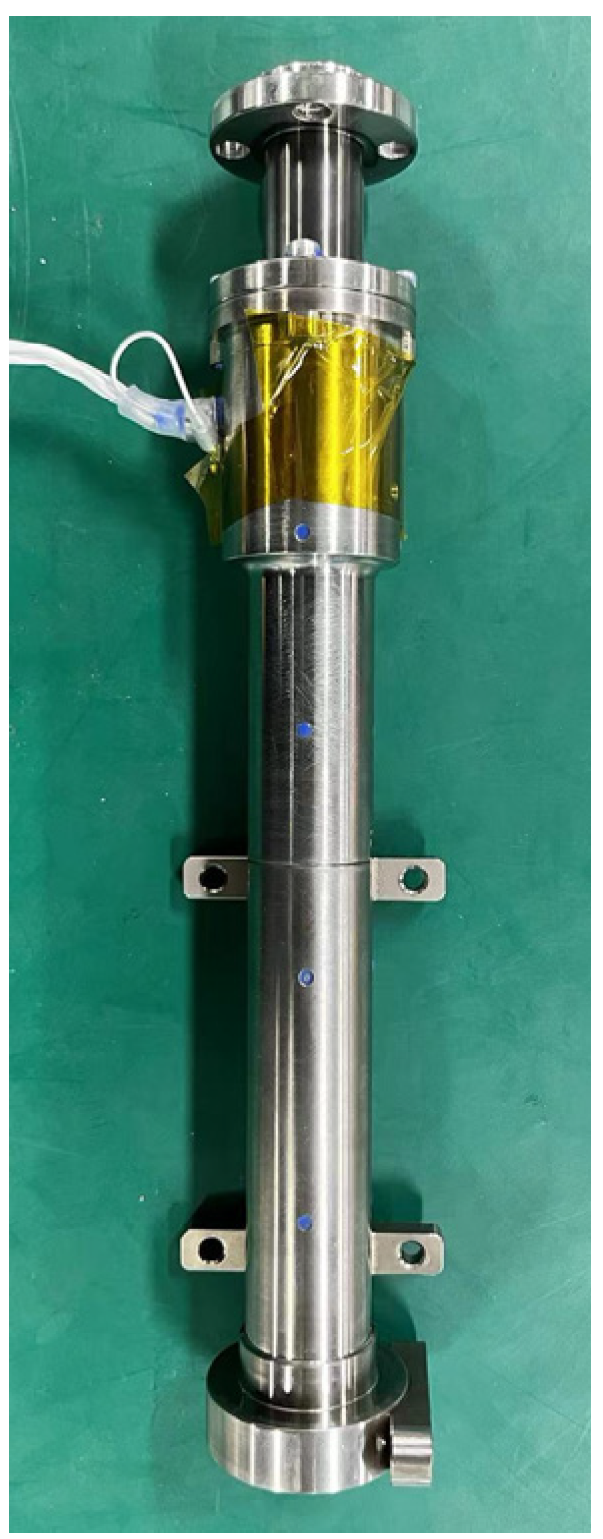
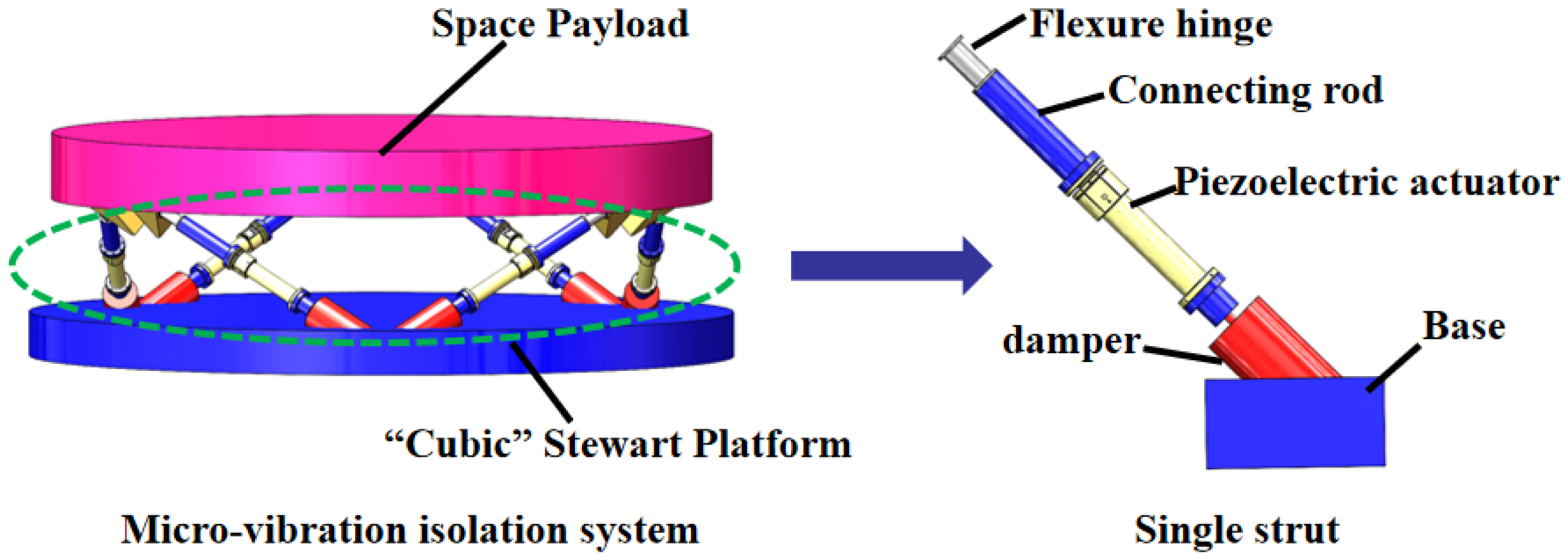
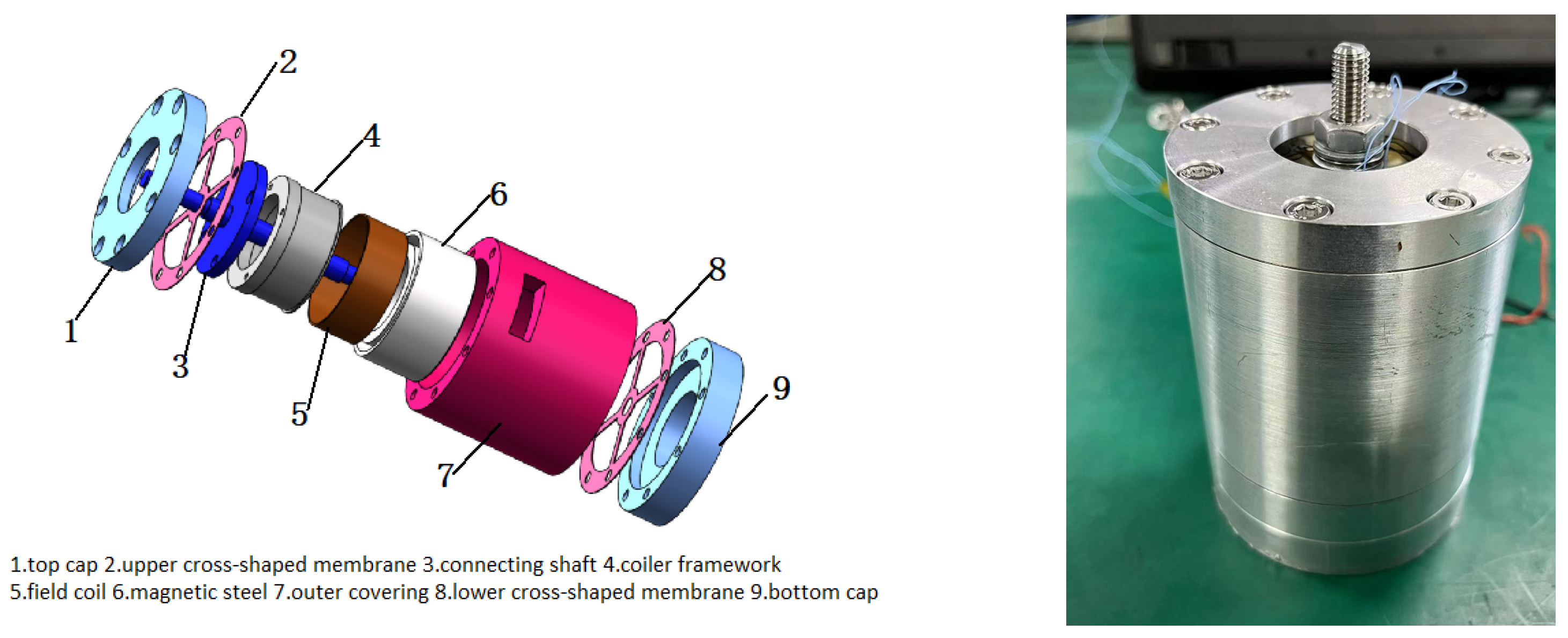
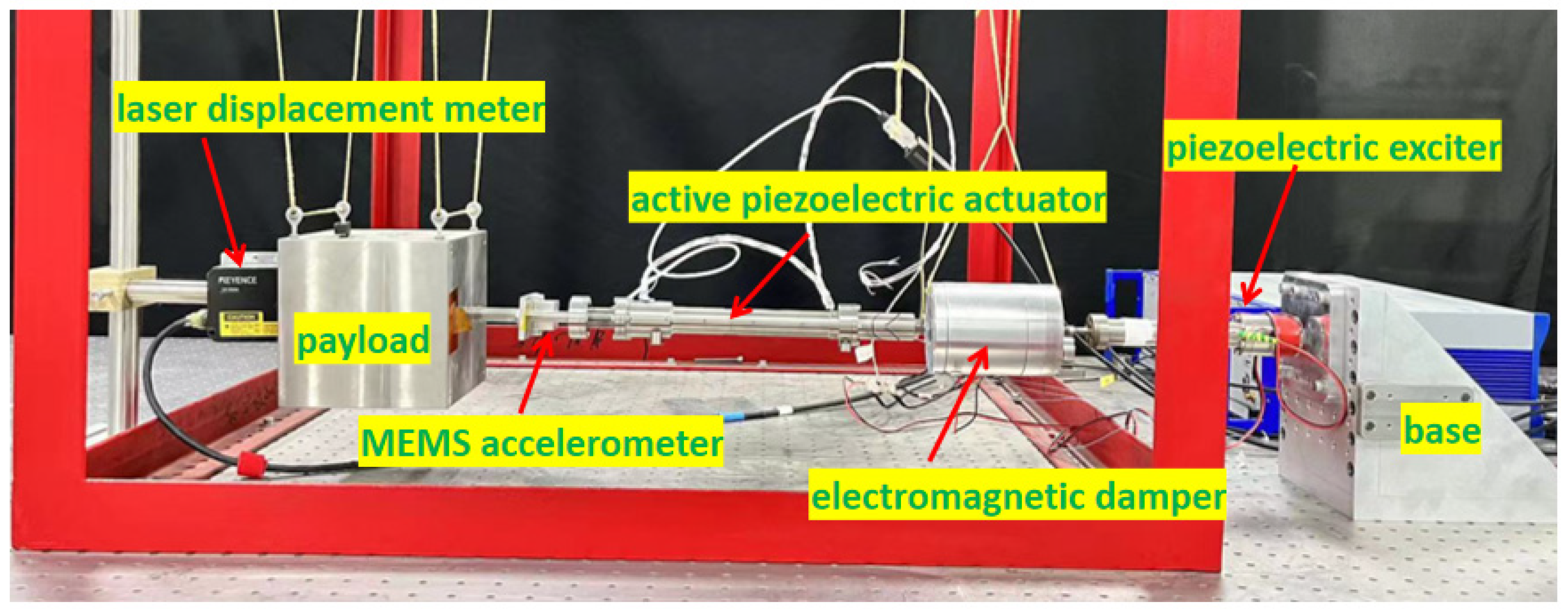
3.1. Electromagnetic Damper Design
3.2. Active Piezoelectric Actuator Design
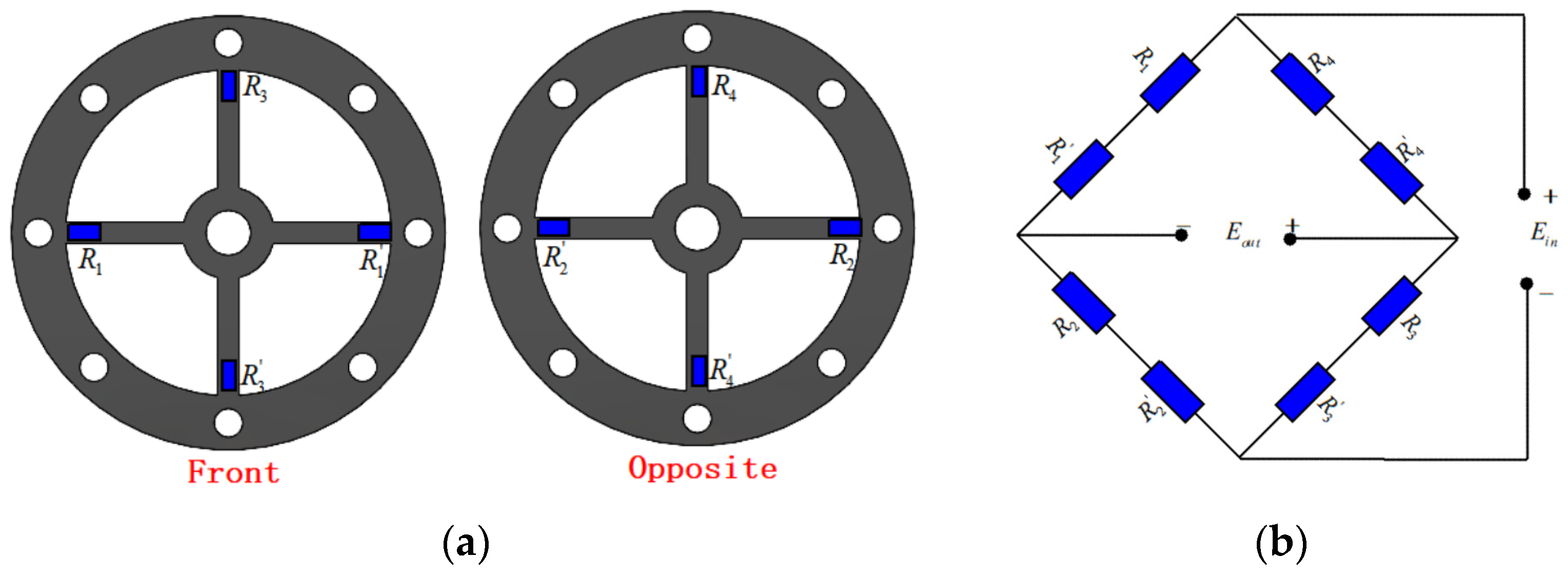
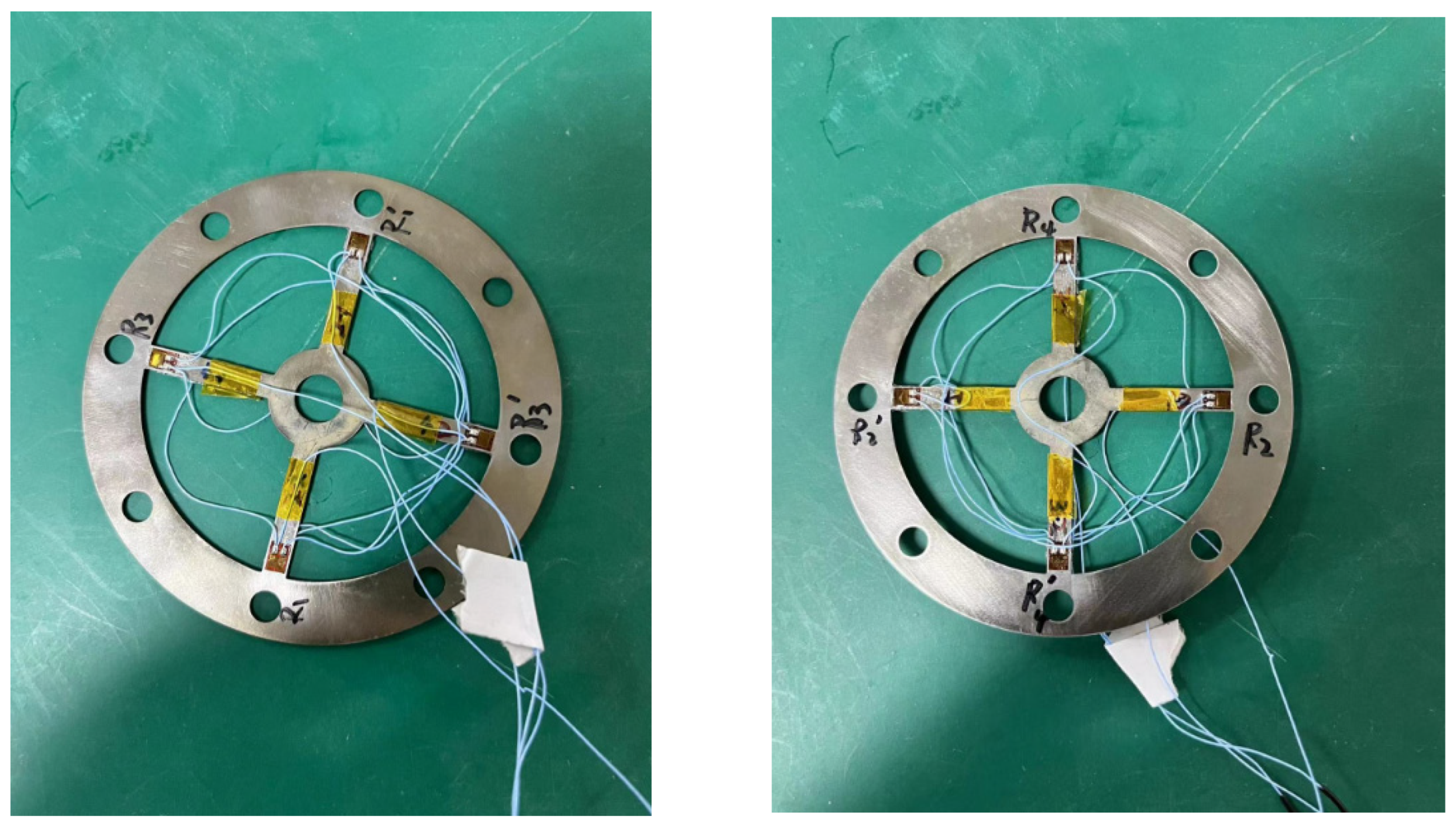
3.3. Strain Sensor Design
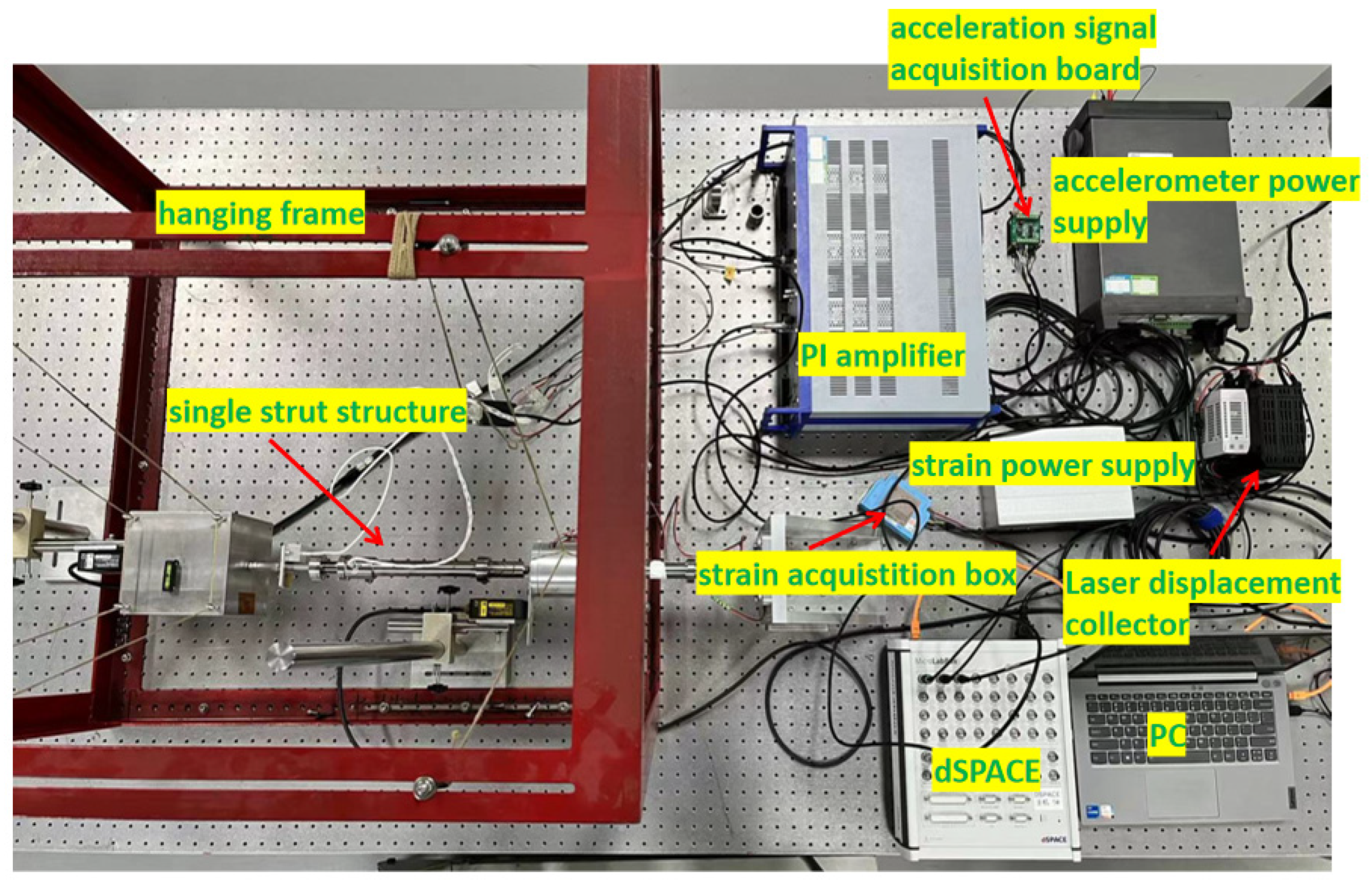
3.4. Experimental System Design
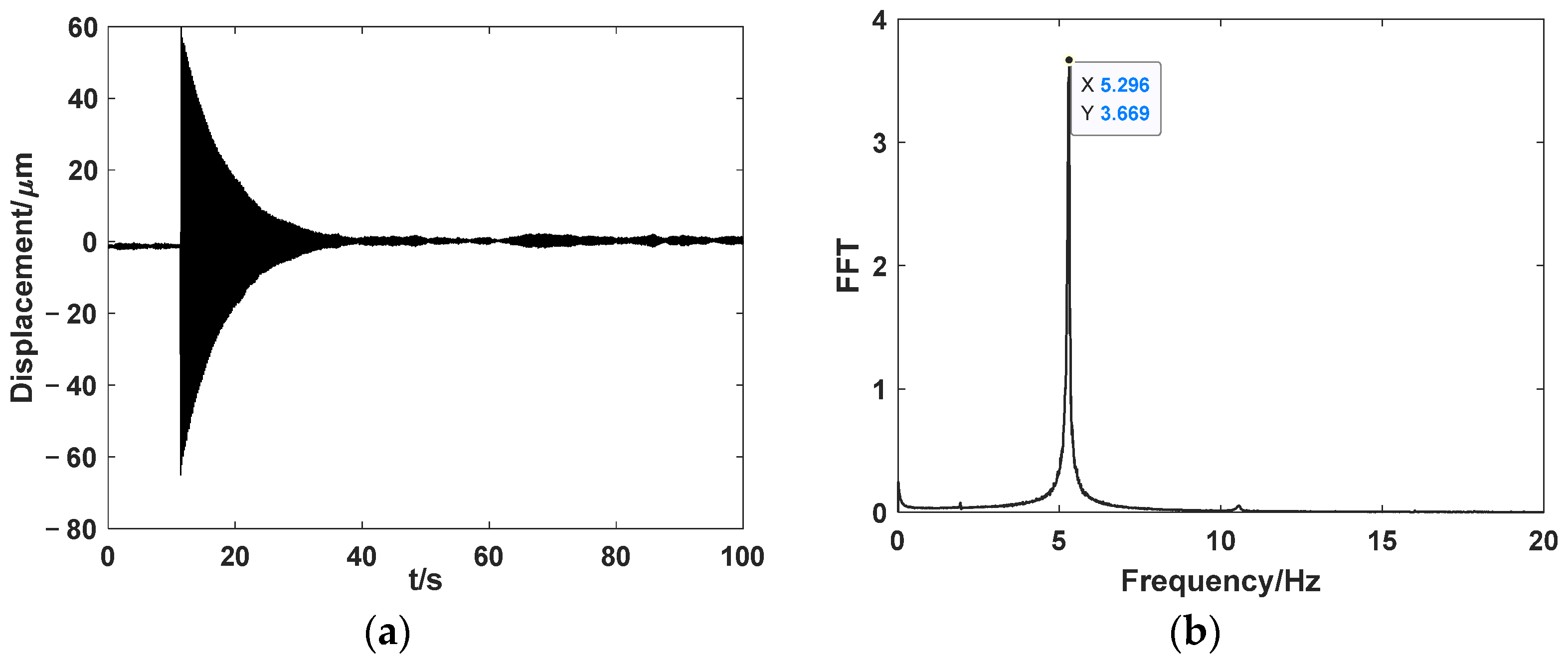
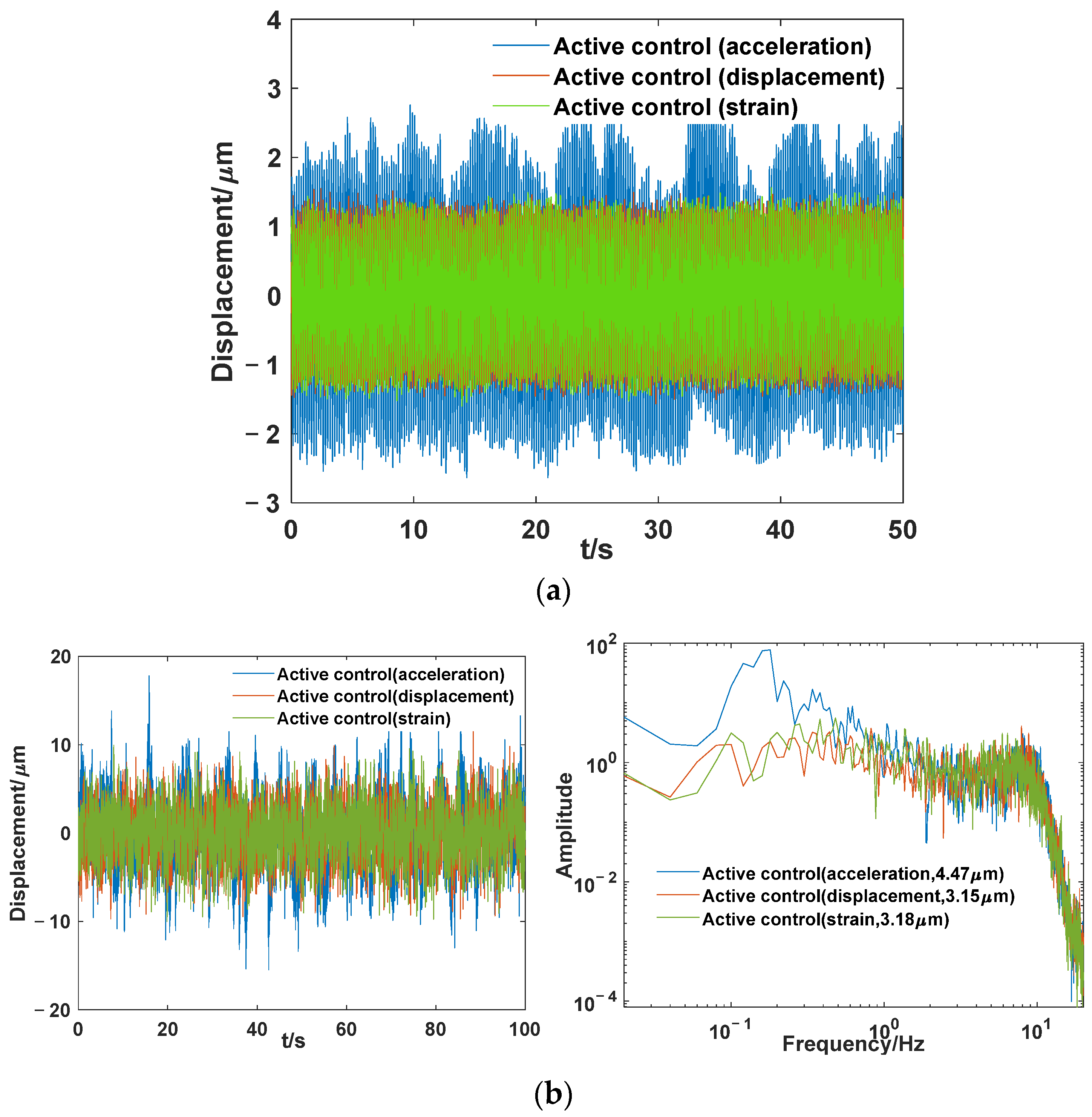
3.5. Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The designed electromagnetic damper effectively reduces the response at the fundamental frequency of the system. The control algorithm developed using strain sensing achieves effective damping control and minimizes the payload response. The algorithm demonstrates stability according to both theoretical analysis and experimental results.
- (2)
- In the hybrid isolation system, the control effect of the acceleration sensor is inferior to those of the displacement and strain sensors, and the control effects of the displacement and strain sensors are comparable. However, the strain sensor method holds more potential to meet the needs of practical aerospace applications than the displacement sensor.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bronowicki, A.J. Vibration Isolator for Large Space Telescopes. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2006, 43, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannibale, V.; Ortiz, G.G.; Farr, W.H. A Sub-Hertz Vibration Isolation Platform for a Deep space Communication Transceiver. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7199, 719901-1–719901-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Eltohamy, F.; Abd-Elrazek, A.; Hanafy, M.E. Assessment of Micro-Vibration Effect on the Quality of Remote Sensing Satellites Images. Int. J. Image Date Fusion 2023, 14, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.T.; Abubakar, M.; Bai, X.T.; Luo, Z. Vibration Isolation Methods in Spacecraft: A Review of Current Techniques. Adv. Space Res. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.C.; Jo, M.S.; Ko, D.H.; Oh, H.U. Viscoelastic Multilayered Blade-type Passive Vibration Isolation System for a Spaceborne Cryogenic Cooler. Cryogenics 2020, 105, 102982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xuan, M.; Xin, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Design and Experiment of Dual Micro-vibration Isolation System for Optical Satellite Flywheel. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 179, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanieh, A.A. Active Isolation and Damping of Vibrations via Stewart Platform; Universite Libre De Bruxelles: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.U.; Onoda, J.; Minesugi, K. Characterisitics of a Liquid-Crystal Type ER-Fluid Variable Damper for Semiactive Vibration Suppression. J. Vib. Acoust. 2000, 122, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Rui, X.; Zhu, W.; Yang, F.; Gu, J. Control and Experimental Study of 6-Dof Vibration Isolation Platform with Magnetorheological Damper. Mechatronics 2022, 81, 102706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.C.; Jing, X.J.; Cheng, L. A Magnetorheological Fluid Embedded Pneumatic Vibration Isolator Allowing Independently Adjustable Stiffness and Damping. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 085025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillon, L.; Petitjean, B.; Frapard, B.; Lebihan, D. Active Isolation in Space Truss Structures: From Concept to Implementation. Smart Mater. Struct. 1999, 8, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, H.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, X.; Bai, Y. Design and Experiments of an Active Isolator for Satellite Micro-Vibration. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Investigation on Active Vibration Isolation of a Stewart Platform with Piezoelectric Actuators. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 383, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preumont, A.; Horodinca, M.; Romanescu, I.; de Marneffe, B.; Avraam, M.; Deraemaeker, A.; Bossens, F.; Abu Hanieh, A. A Six-axis Single-stage Active Vibration Isolator Based on Stewart Platform. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 300, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Active-Passive Integrated Vibration Control for Control Moment Gyros and Its Application to Satellites. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 394, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, S.W. Control of a Hybrid Active-passive Vibration Isolation System. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 5711–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shao, S.; Tian, Z.; Xu, M.; Xie, S. Active-passive Hybrid Vibration Isolation with Magnetic Negative Stiffness Isolator based on Maxwell Normal Stress. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 123, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.H.; Fumo, J.P.; Erwin, R.S. Satellite Ultraquiet Isolation Technology Experiment (SUITE). In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Proceedings (Cat. No.00TH8484), Big Sky, MT, USA, 25 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Babuska, V.; Erwin, R.S.; Sullivan, L.A. System Identification of the SUITE Isolation Platform: Comparison of Ground and Flight Experiments. In Proceedings of the 44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Norfolk, VA, USA, 7–10 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, R.G.; Sullivan, J.M.; Das, A.; Davis, L.P.; Hyde, T.T.; Davis, T.; Rahman, Z.H.; Spanos, J.T. Vibration Isolation and Suppression System for Precision Payloads in Space. Smart Mater. Struct. 1999, 8, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.D.; Jung, H.J.; Shin, Y.H.; Moon, S.J.; Moon, Y.J.; Oh, J. Feasibility Study on a Hybrid Mount System with Air Springs and Piezo-stack Actuators for Microvibration Control. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2011, 23, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Yasuda, M.; Fujita, T. Development of Active Six-Degrees-of-Freedom Micro-Vibration Control System Using Hybrid Actuators Comprising Air Actuators and Giant Magnetostrictive Actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiao, Y. A Hybrid Vibration Isolator: Design, Control, and Experiments. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2015, 25, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Values | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke | ±40 | μm |
| Voltage | 0~100 | V |
| Tension force | 200 | N |
| Thrust force | 1000 | N |
| Weight | 420 | g |
| Length | 241 | mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Tang, G. Design and Experimental Study of a Hybrid Micro-Vibration Isolation System Based on a Strain Sensor for High-Precision Space Payloads. Sensors 2024, 24, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051649
Guo Q, Zhou J, Li L, Xu M, Tang G. Design and Experimental Study of a Hybrid Micro-Vibration Isolation System Based on a Strain Sensor for High-Precision Space Payloads. Sensors. 2024; 24(5):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051649
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qiwei, Jian Zhou, Liang Li, Minglong Xu, and Guoan Tang. 2024. "Design and Experimental Study of a Hybrid Micro-Vibration Isolation System Based on a Strain Sensor for High-Precision Space Payloads" Sensors 24, no. 5: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051649
APA StyleGuo, Q., Zhou, J., Li, L., Xu, M., & Tang, G. (2024). Design and Experimental Study of a Hybrid Micro-Vibration Isolation System Based on a Strain Sensor for High-Precision Space Payloads. Sensors, 24(5), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051649





