A Study of Outliers in GNSS Clock Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
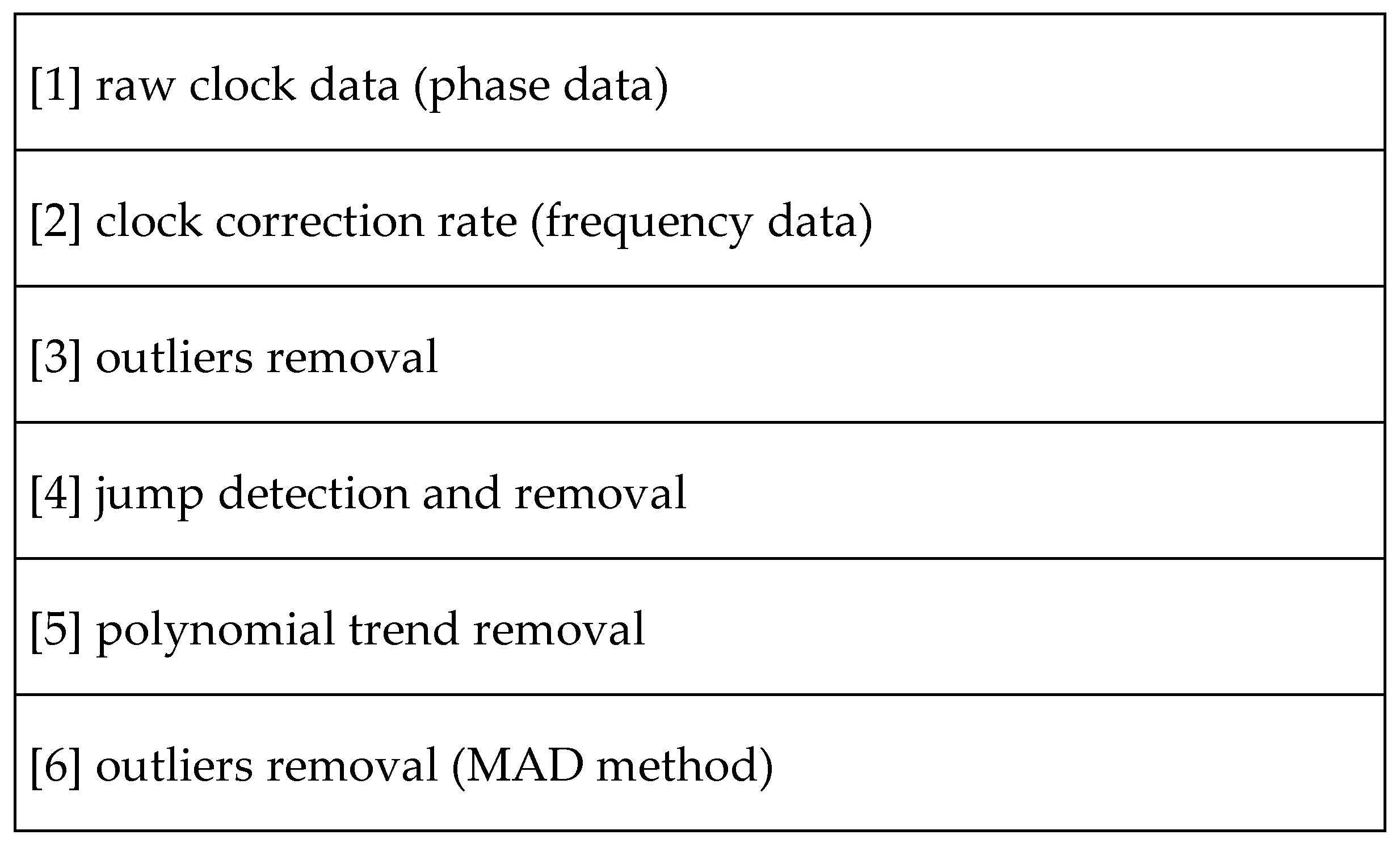
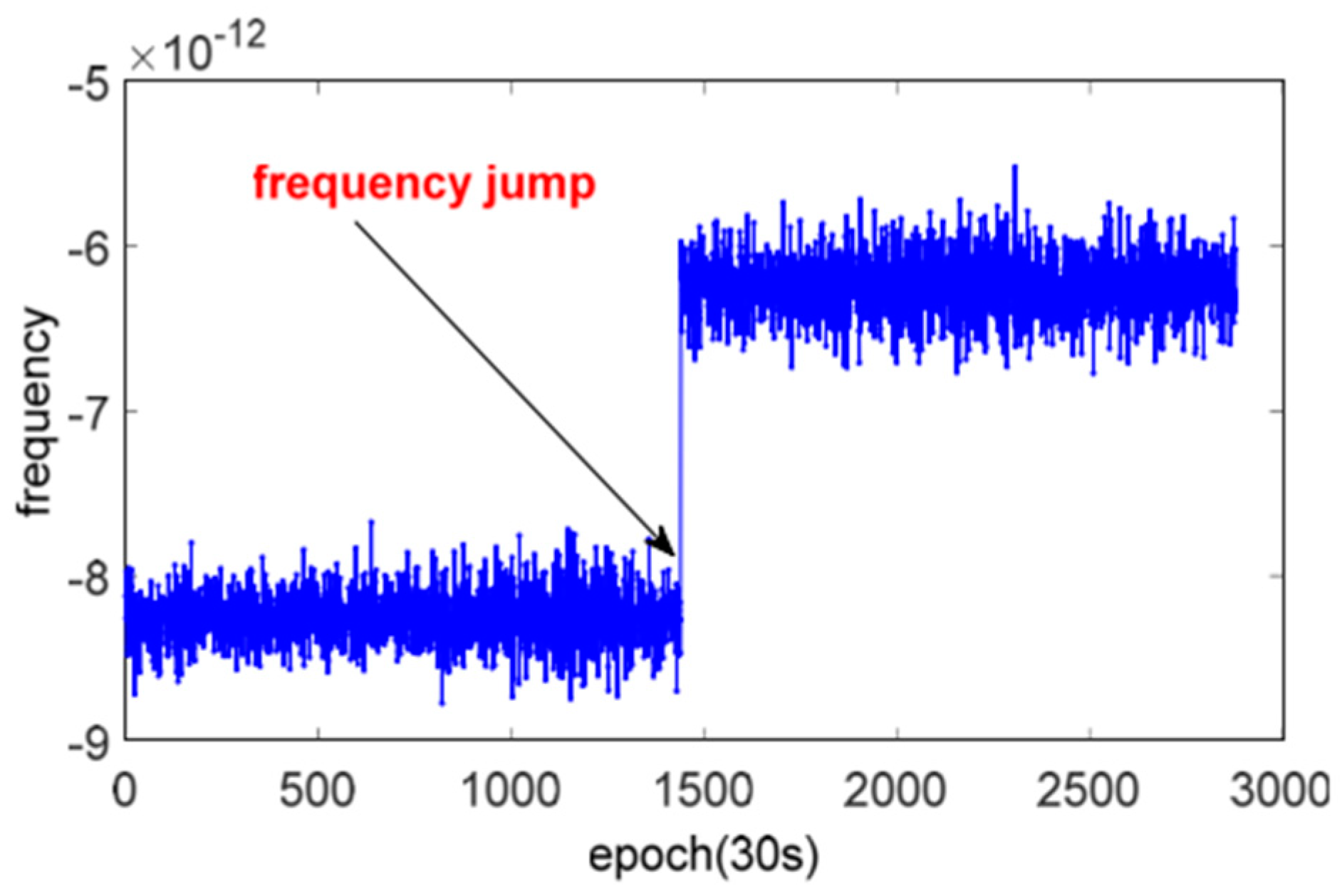
2. Methods
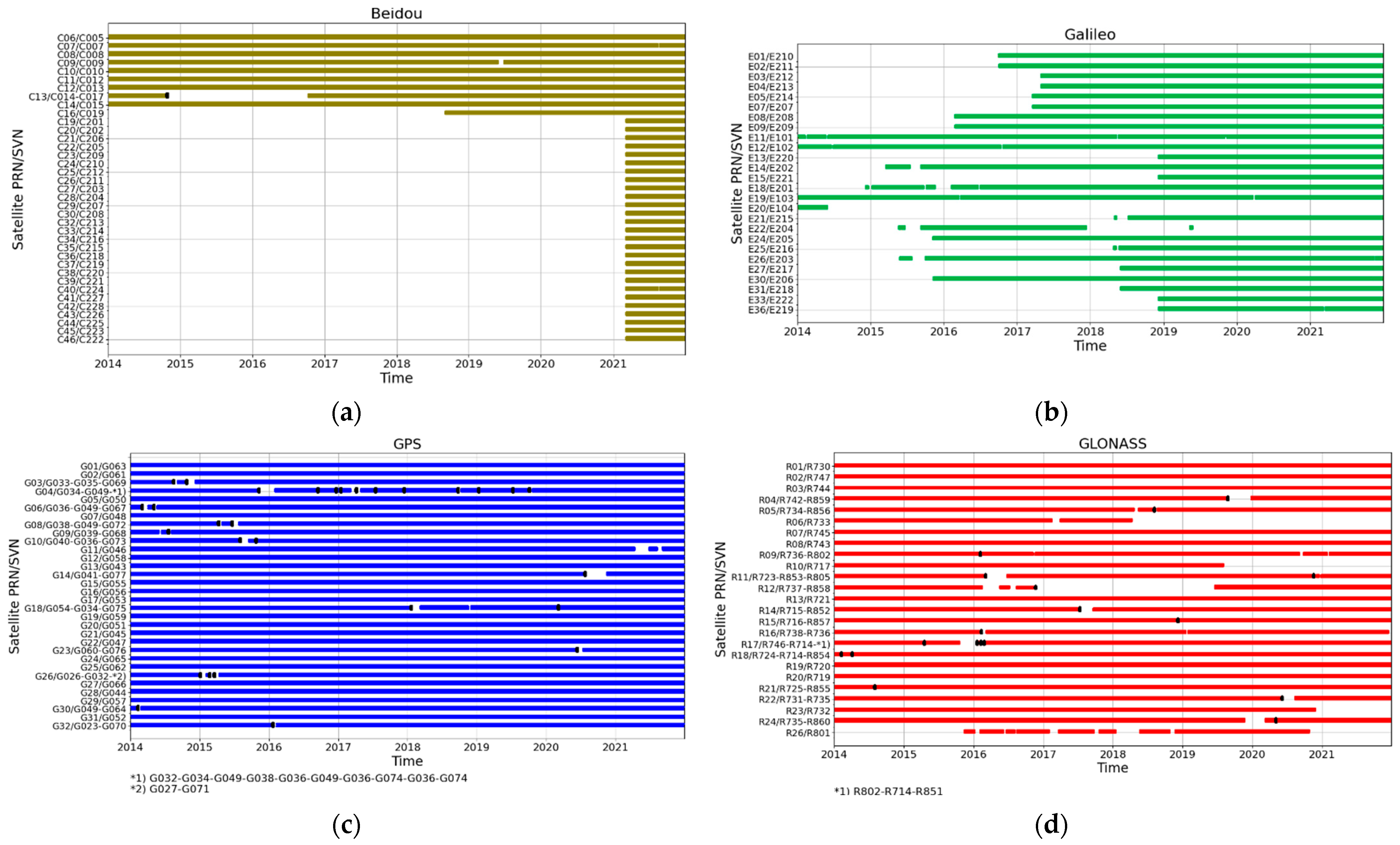
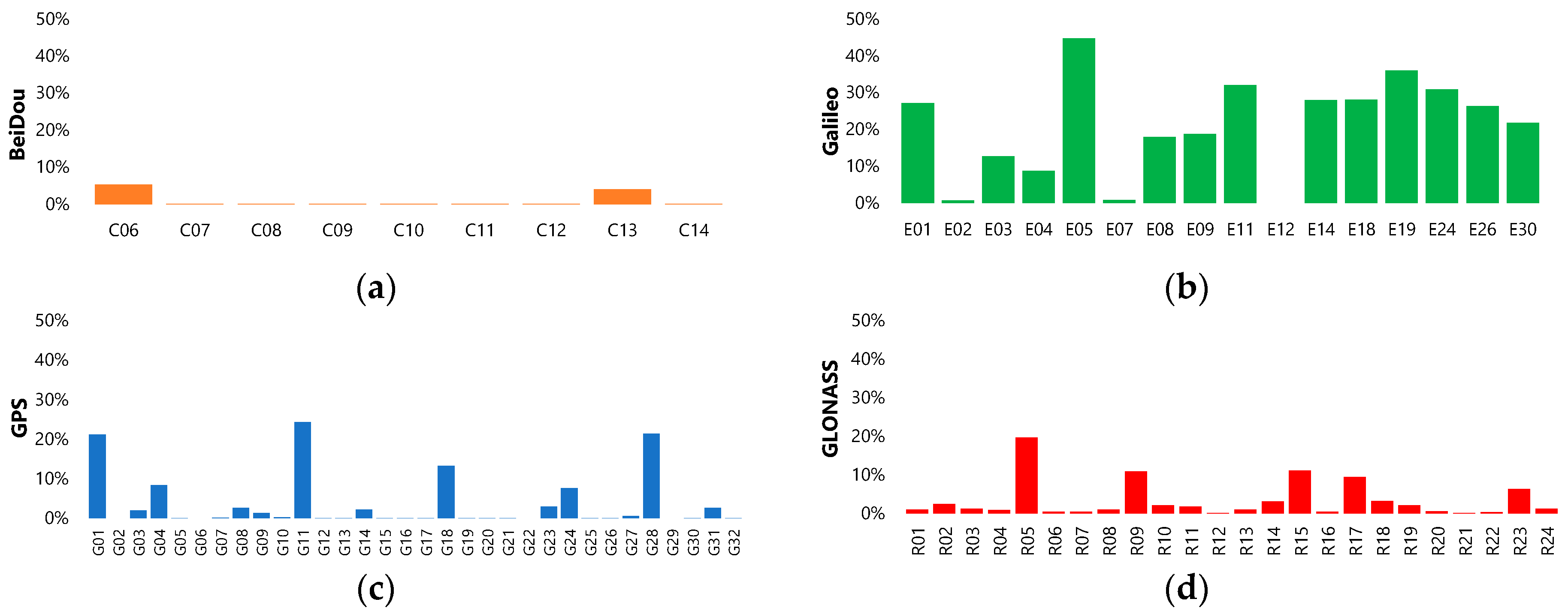
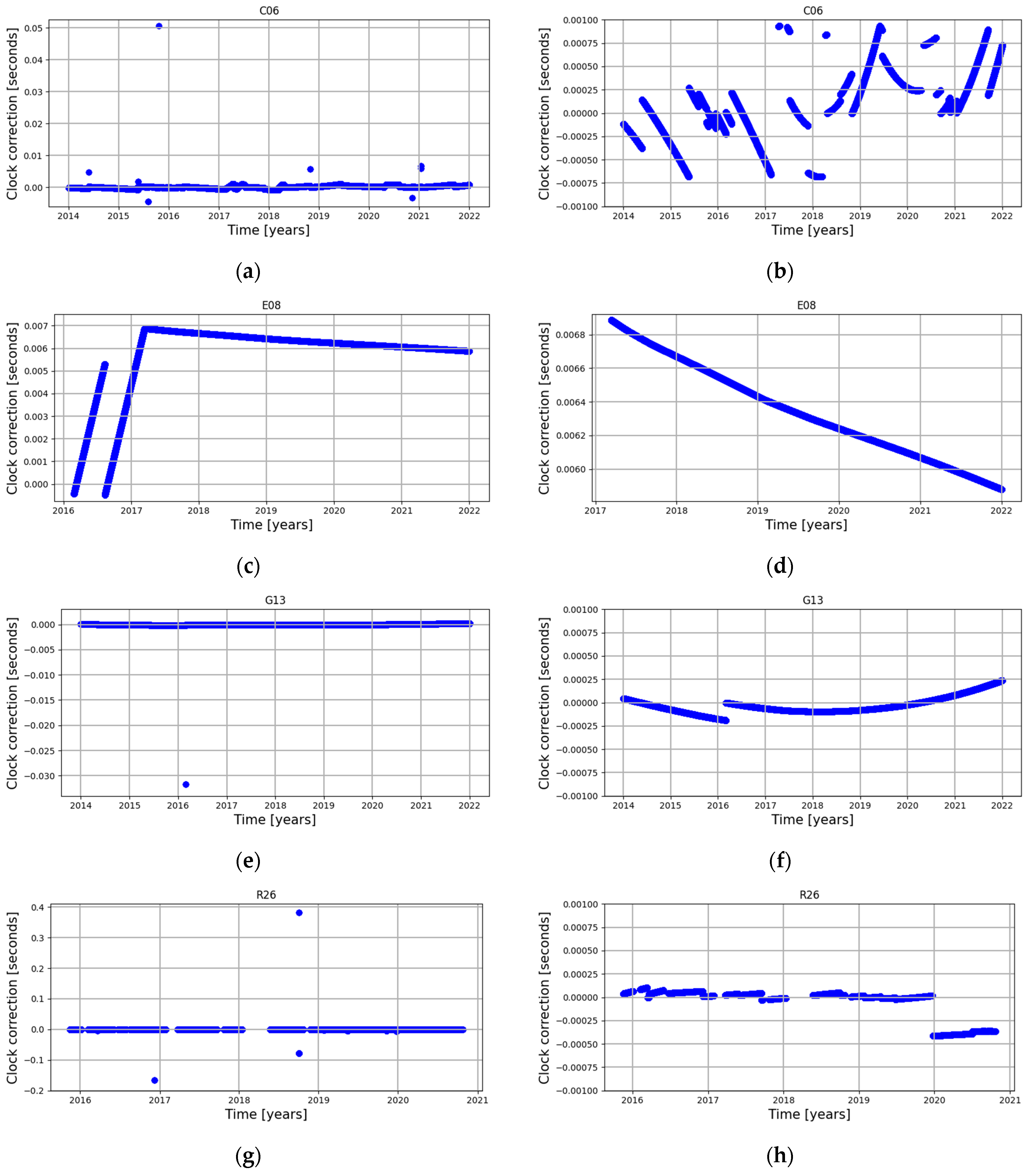
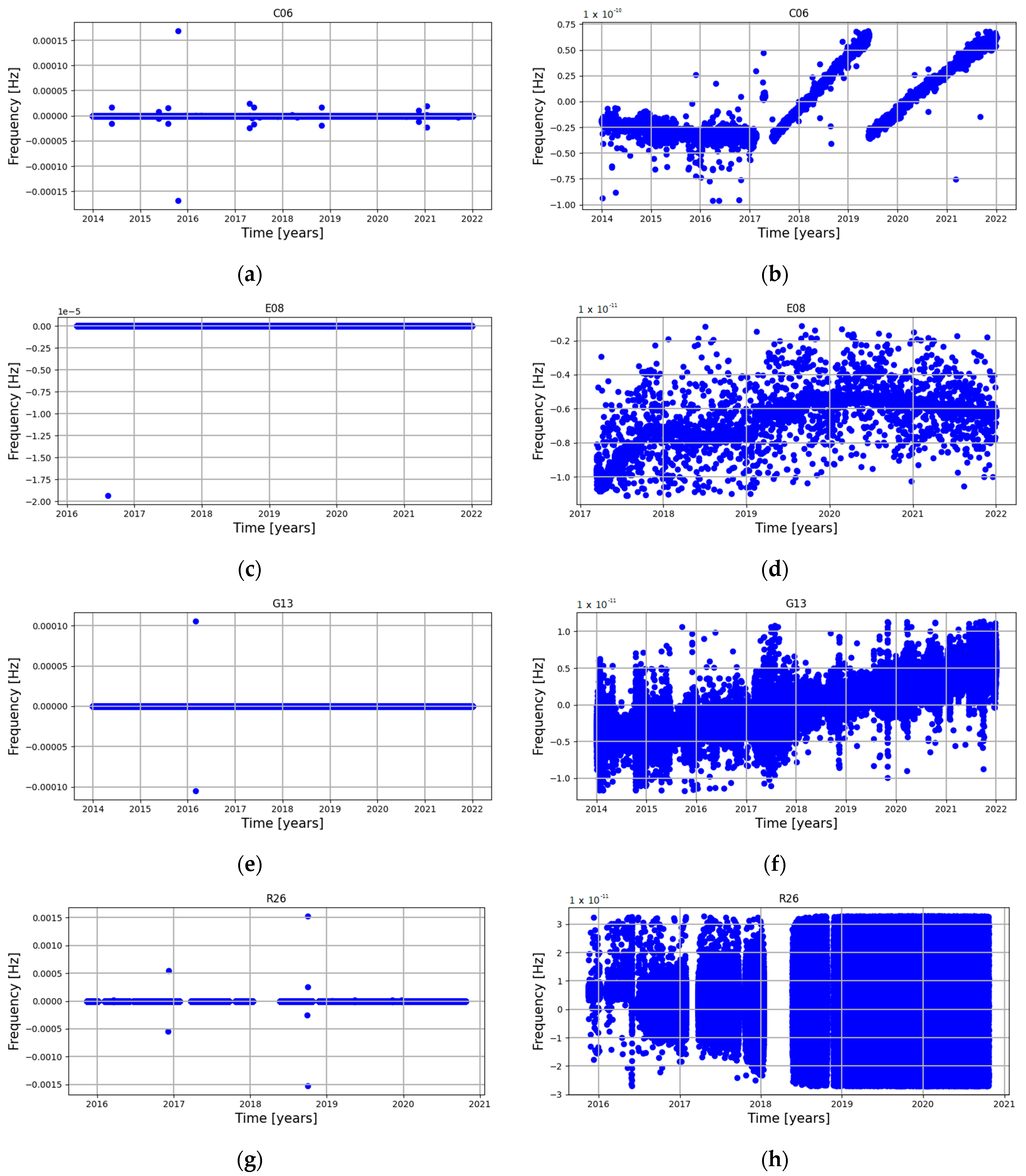
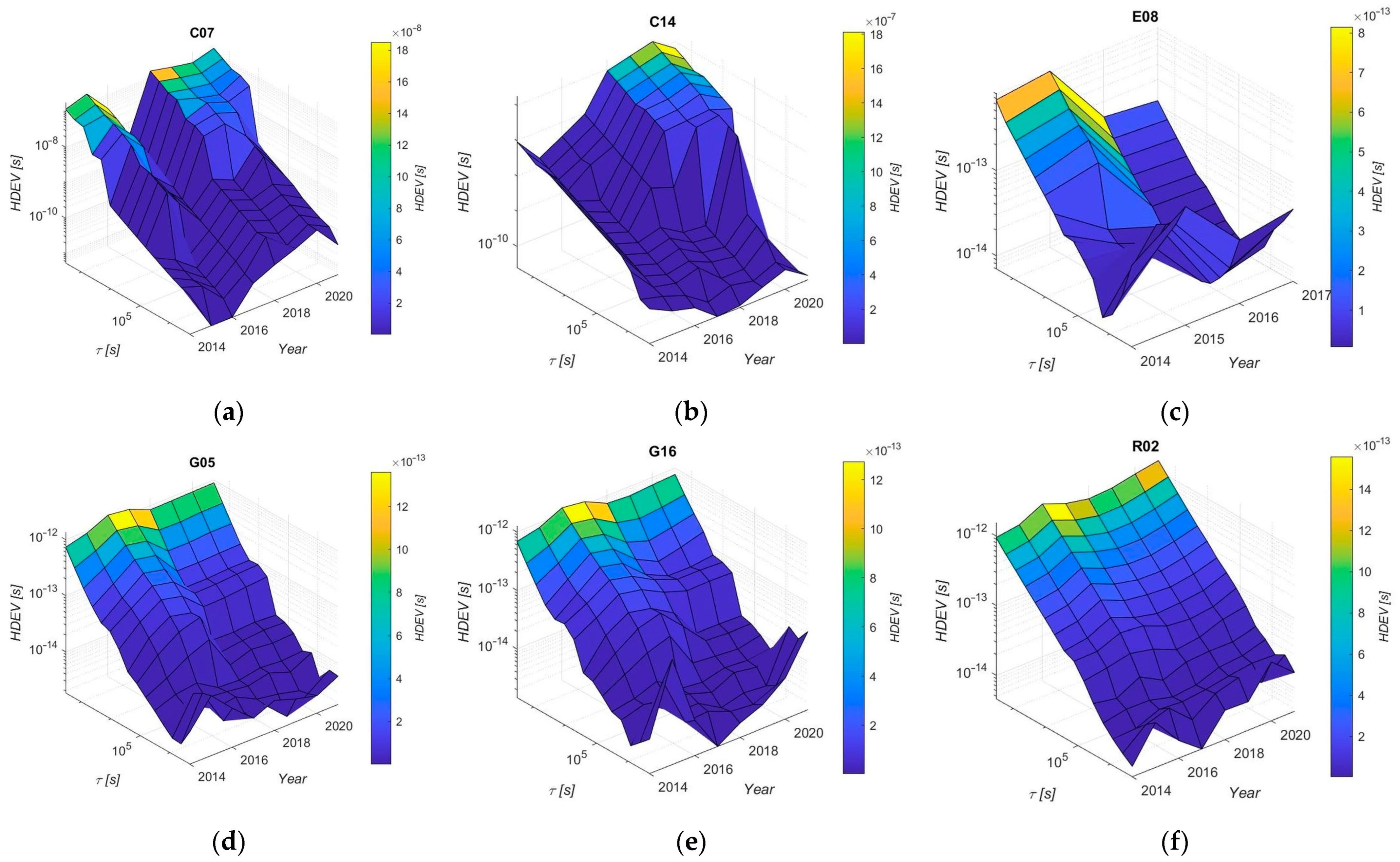
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Specht, M. Experimental Studies on the Relationship Between Hdop and Position Error in the Gps System. Metrol. Meas. Syst. 2022, 29, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiera, W.; Vārna, I.; Mitrofanovs, I.; Silabrieds, G.; Krawczyk, A.; Skorupa, B.; Apollo, M.; Maciuk, K. Accuracy of Code GNSS Receivers under Various Conditions. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leick, A.; Rapoport, L.; Tatarnikov, D. GPS Satellite Surveying, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 9781119018612. [Google Scholar]
- Brach, M. Rapid Static Positioning Using a Four System GNSS Receivers in the Forest Environment. Forests 2022, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Cai, H.; Chen, G.; Jiao, W.; He, Q.; Yang, Y. Multi-GNSS Combined Orbit and Clock Solutions at iGMAS. Sensors 2022, 22, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, L.; Villiger, A.; Sidorov, D.; Schaer, S.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Jäggi, A. Overview of CODE’s MGEX solution with the focus on Galileo. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 2786–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)—Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrinjski, M.; Matika, K.; Barković, Đ. Razvoj i modernizacija GNSS-a. Geod. List 2019, 73, 45–65. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Khachikyan, R.; Weber, G.; Langley, R.B.; Mervart, L.; Hugentobler, U. IGS-MGEX Preparing the Ground for Multi-COnstellation GNSS Science. Inside GNSS 2014, 9, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Maciuk, K. Aging of ground Global Navigation Satellite System oscillators. Eksploat. Niezawodn. 2022, 24, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Song, S.; Zhou, W. Accuracy analysis of gnss hourly ultra-rapid orbit and clock products from shao ac of igmas. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, F.; Shi, C. Multi-GNSS real-time precise clock estimation considering the correction of inter-satellite code biases. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Li, B.; Wu, T.; Jiang, S. Prediction models of GNSS satellite clock errors: Evaluation and application in PPP. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 2470–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Assessment of multi-GNSS precise orbit and clock products from different analysis centers based on precise point positioning. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2021, 18, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Dai, X.; Zhao, Q.; Bao, Z.; Li, C. Multi-GNSS real-time clock estimation using the dual-thread parallel method. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira-Garcia, A.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; González-Casado, G.; Ventura-Traveset, J.; Cacciapuoti, L.; Schoenemann, E. Removing day-boundary discontinuities on GNSS clock estimates: Methodology and results. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Guo, S.; Wang, Z.; Jing, G. Impact of satellite clock offset on differential code biases estimation using undifferenced GPS triple-frequency observations. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, W.J. Handbook of Frequency Stability Analysis; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 31, ISBN 3019753058.
- Jiang, N.; Xu, T.; Xu, Y.; Xu, G.; Schuh, H. Detecting and repairing inter-system bias jumps with satellite clock preprocessing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zeng, T.; Ruan, R.; Mao, Y.; Xiao, G. Atomic clock performance assessment of BeiDou-3 basic system with the noise analysis of orbit determination and time synchronization. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Galileo and QZSS precise orbit and clock determination using new satellite metadata. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, S.; Buda, A.S. The Influence of Zenith Tropospheric Delay on PPP-RTK. J. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2016, 6, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, S.; Buda, A.S. Evaluation of the ambiguity resolution and data products from different analysis centers on zenith wet delay using PPP method. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2017, 14, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Montillet, J.P.; Hua, X.; Yu, K.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, F. Noise analysis for environmental loading effect on GPS position time series. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2017, 14, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, P. An improved QZSS satellite clock offsets prediction based on the extreme learning machine method. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 156557–156568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, L.; Fu, W.; Chen, R.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. A practical adaptive clock offset prediction model for the BeiDou-2 system. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Yang, S.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, S.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.H. Outlier Detection Method for Time Synchronization. J. Position. Navig. Timing 2020, 9, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Huang, G.; Xie, W.; Xie, S.; Wang, H. Assessment and comparison of satellite clock offset between BeiDou-3 and other GNSSs. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2021, 56, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Maciuk, K.; Lewińska, P.; Borowski, Ł. Characteristics of Onefold Clocks of GPS, Galileo, BeiDou and GLONASS Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maciuk, K.; Varna, I.; Krzykowska-Piotrowska, K. A Study of Outliers in GNSS Clock Products. Sensors 2024, 24, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030799
Maciuk K, Varna I, Krzykowska-Piotrowska K. A Study of Outliers in GNSS Clock Products. Sensors. 2024; 24(3):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030799
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaciuk, Kamil, Inese Varna, and Karolina Krzykowska-Piotrowska. 2024. "A Study of Outliers in GNSS Clock Products" Sensors 24, no. 3: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030799
APA StyleMaciuk, K., Varna, I., & Krzykowska-Piotrowska, K. (2024). A Study of Outliers in GNSS Clock Products. Sensors, 24(3), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030799






