Lane Detection Based on ECBAM_ASPP Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
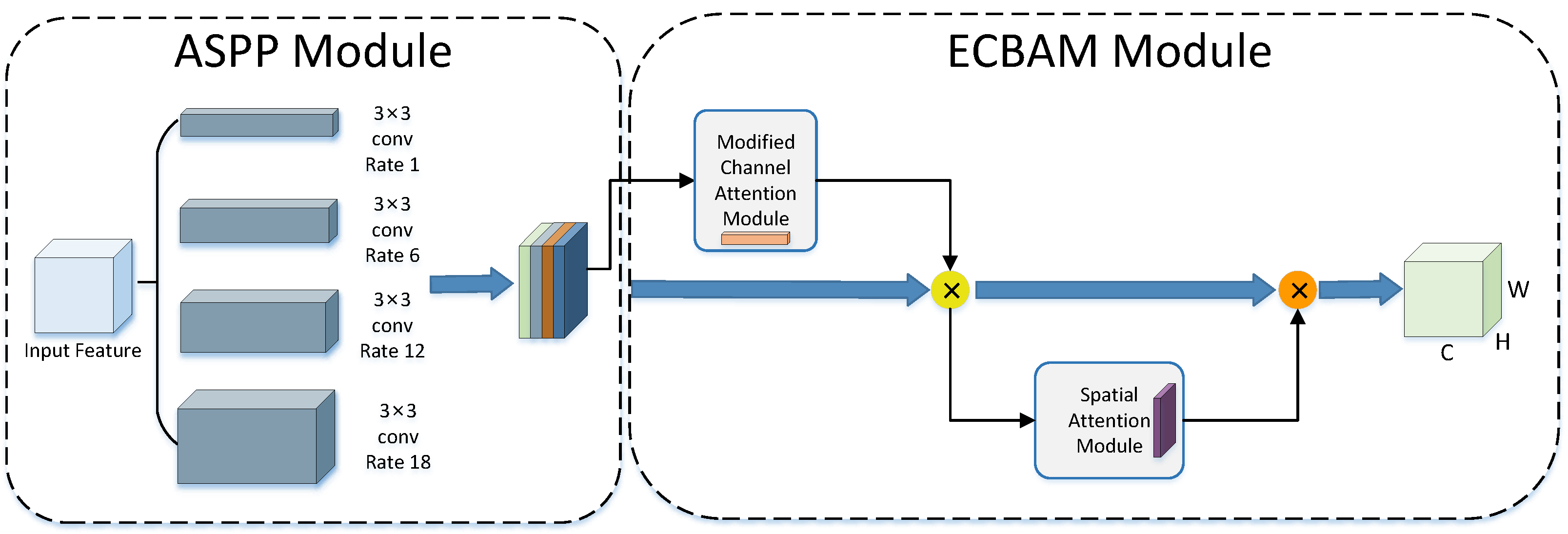
- In this paper, we propose the Efficient Convolutional Block Attention Module (ECBAM), which comprises two submodules: the Efficient Channel Attention Module (ECAM) and the Spatial Attention Module (SAM). ECBAM enhances the traditional Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) by employing a dynamic one-dimensional convolution kernel in place of a shared Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP).
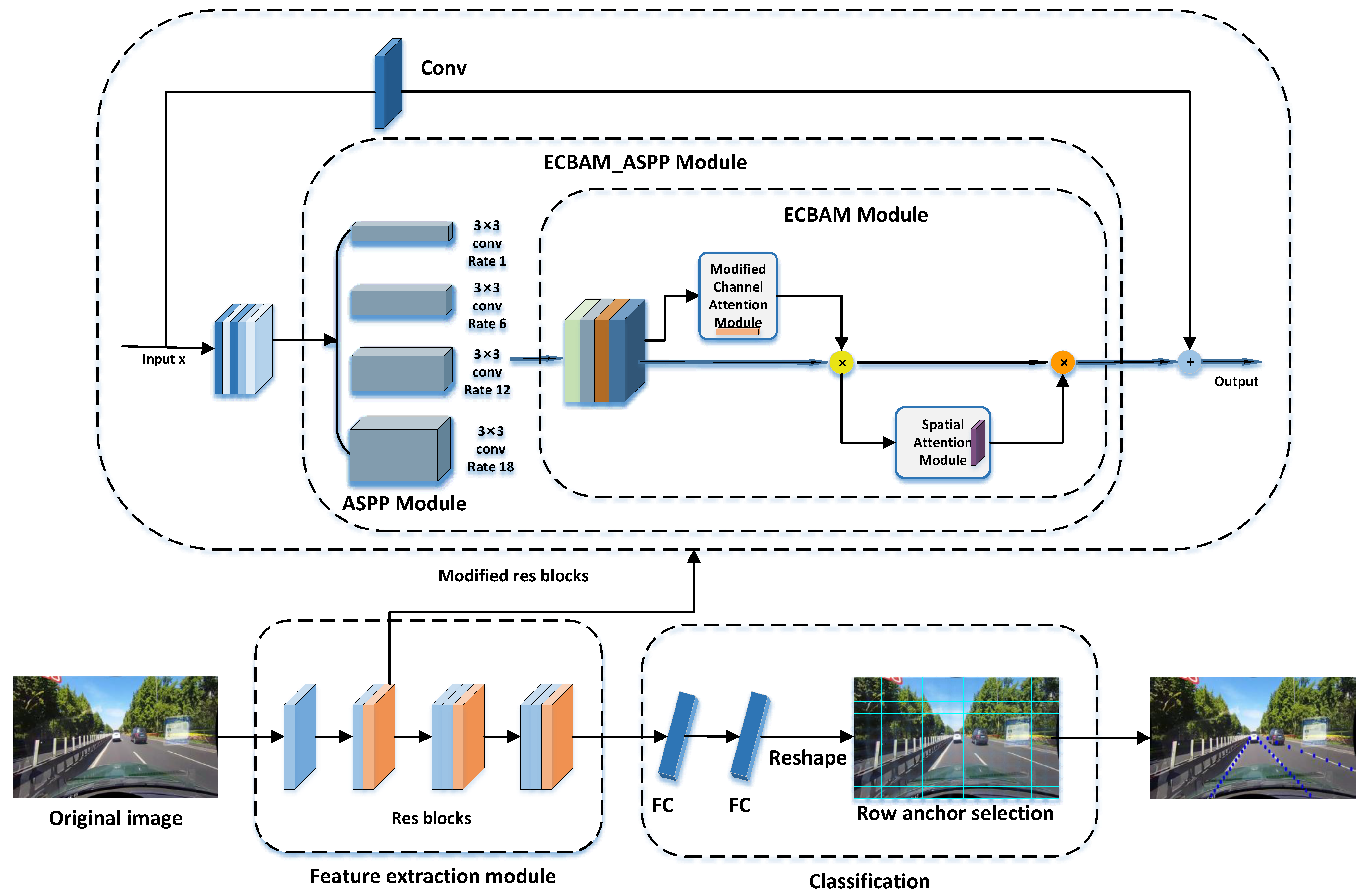
- Building on the ECBAM and ASPP modules, this paper introduces the ECBAM_ASPP model. The ASPP module extracts multi-scale input features by applying different sampling rates, generating richer feature maps. These feature maps are combined with the attention weights generated by the ECBAM module to focus on lane areas while suppressing background interference.
- We evaluated the proposed ECBAM_ASPP model on the TuSimple and CULane datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that the ECBAM_ASPP model significantly enhances frames per second (FPS) while maintaining high accuracy. This indicates that the model ensures reliable lane line recognition while achieving high FPS, enabling vehicles to perceive road conditions in real time and make timely and accurate decisions.
2. Related Work
2.1. Lane Detection Methods Based on Conventional Image Processing
2.2. Lane Detection Methods Based on Deep Learning
2.3. Attention Mechanism
3. Methodology
3.1. Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP)
3.2. Efficient Channel Attention (ECA)
3.3. Efficient Convolution Block Attention Module (ECBAM)
3.3.1. Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM)
3.3.2. Efficient Convolution Block Attention Module (ECBAM)
3.4. ECBAM_ASPP Model
3.5. Lane Detection
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Experimental Environment and Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
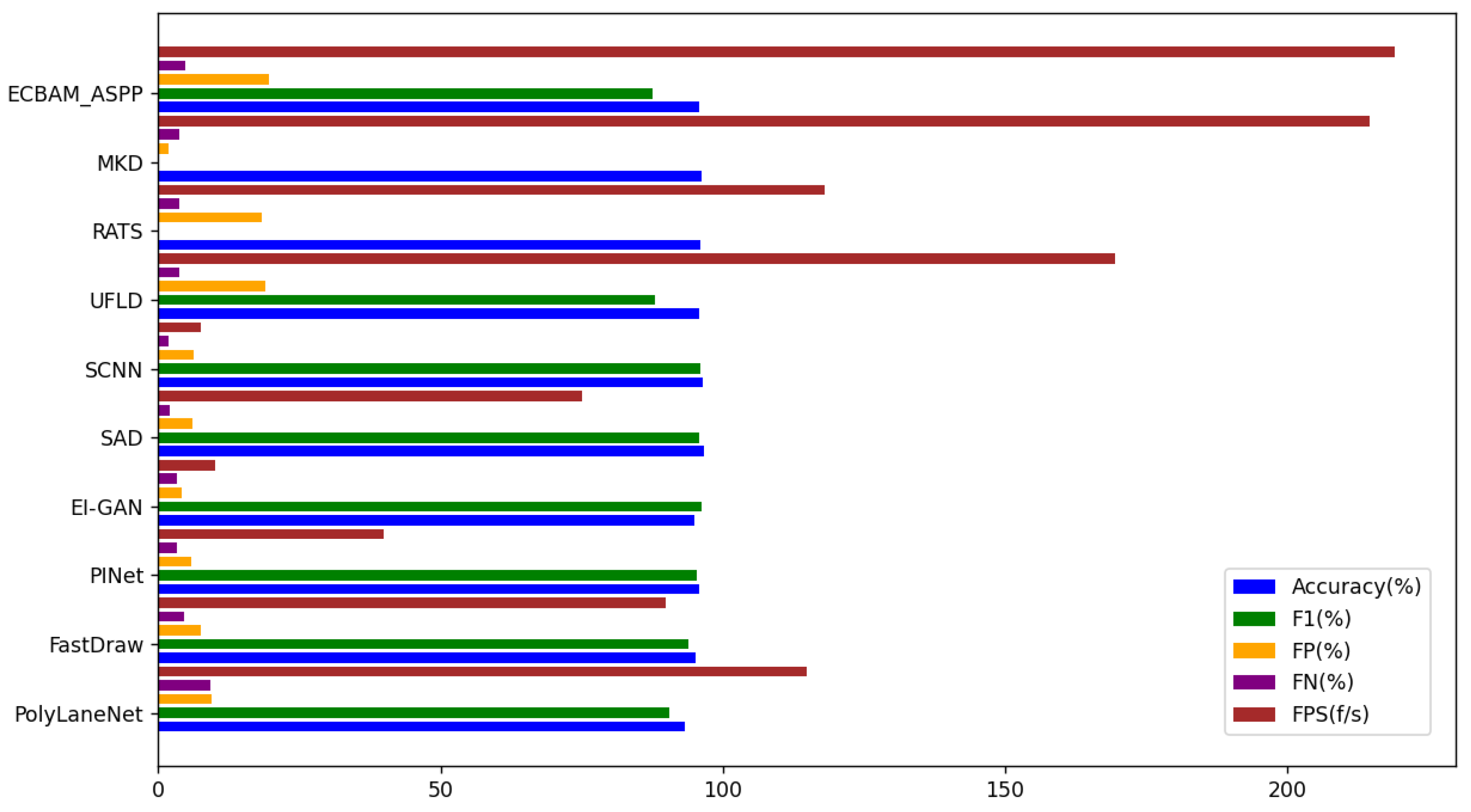
4.4. Comparative Analysis of Experiments
4.4.1. Tusimple Dataset
4.4.2. CULane Dataset
4.5. Ablation Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECBAM | Efficient Convolution Block Attention Module |
| CBAM | Convolutional Block Attention Module |
| ASPP | Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| ECBAM_ASPP | Efficient Convolution Block Attention Module_Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| ECA | Efficient Channel Attention |
References
- Hou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, C.; Loy, C.C. Learning lightweight lane detection cnns by self attention distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1013–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Shin Yoon, J.; Shin, S.; Bailo, O.; Kim, N.; Lee, T.H.; Seok Hong, H.; Han, S.H.; So Kweon, I. Vpgnet: Vanishing point guided network for lane and road marking detection and recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1947–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Neven, D.; De Brabandere, B.; Georgoulis, S.; Proesmans, M.; Van Gool, L. Towards end-to-end lane detection: An instance segmentation approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Changshu, China, 26–30 June 2018; pp. 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cai, D. Resa: Recurrent feature-shift aggregator for lane detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 19–21 May 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3547–3554. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Tan, P. Condlanenet: A top-to-down lane detection framework based on conditional convolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3773–3782. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Huang, S.; Hui, T.; Wang, F.; Qian, C.; Zhang, T. A keypoint-based global association network for lane detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 1392–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Borkar, A.; Hayes, M.; Smith, M.T. A novel lane detection system with efficient ground truth generation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2011, 13, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Luo, S.; Song, K.; Yan, C.W.; Wang, M.C. Improved lane line detection algorithm based on Hough transform. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 2018, 28, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Zheng, L.; Huang, J. Nighttime lane markings recognition based on Canny detection and Hough transform. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Real-Time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Angkor Wat, Cambodia, 6–9 June 2016; pp. 411–415. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, Z.; Feng, W. Research on lane detection and tracking algorithm based on improved hough transform. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference of Intelligent Robotic and Control Engineering (IRCE), Lanzhou, China, 24–27 August 2018; pp. 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Li, S.; Liu, W. Lane detection algorithm based on local feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 2013 Chinese Automation Congress, Changsha, China, 7–8 November 2013; pp. 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Kong, B.; Mei, T.; Wei, H. Lane detection algorithm based on temporal–spatial information matching and fusion. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2017, 2, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satzoda, R.K.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Srikanthan, T.; Sathyanarayana, S. Hierarchical additive Hough transform for lane detection. IEEE Embed. Syst. Lett. 2010, 2, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Wu, K.; Fang, Q. A fast and stable lane detection method based on B-spline curve. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 10th International Conference on Computer-Aided Industrial Design & Conceptual Design, Wenzhou, China, 26–29 November 2009; pp. 1036–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, W.; Qiu, Q. Lanenet: Real-time lane detection networks for autonomous driving. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.01726. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Shi, J.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Spatial as deep: Spatial cnn for traffic scene understanding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Koubia, A.E.; Mohammed, K.A.K. Traffic lane detection using fcn. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08977. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Ultra fast structure-aware deep lane detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXIV 16. pp. 276–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Q.; Jiang, H.; Dai, Q.; Yue, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q. Robust lane detection from continuous driving scenes using deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 69, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, T.; Xiong, Z. End-to-end lane shape prediction with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Online, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3694–3702. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Chang, X.; Sun, W. Multitask knowledge distillation guides end-to-end lane detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 9703–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gong, M.; Du, B.; Qian, G.; Smith-Miles, K. Generating dynamic kernels via transformers for lane detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 6835–6844. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. A fast and accurate lane detection method based on row anchor and transformer structure. Sensors 2024, 24, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective kernel networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tusimple Benchmark Ground Truth. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/manideep1108/Tusimple?resource=download (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- CULane Dataset. Available online: https://xingangpan.github.io/projects/CULane.html (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Tabelini, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixao, T.M.; Badue, C.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. Polylanenet: Lane estimation via deep polynomial regression. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 6150–6156. [Google Scholar]
- Philion, J. Fastdraw: Addressing the long tail of lane detection by adapting a sequential prediction network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11582–11591. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Y.; Lee, Y.; Azam, S.; Munir, F.; Jeon, M.; Pedrycz, W. Key points estimation and point instance segmentation approach for lane detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 8949–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoorian, M.; Nugteren, C.; Baka, N.; Booij, O.; Hofmann, M. El-gan: Embedding loss driven generative adversarial networks for lane detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tabelini, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixao, T.M.; Badue, C.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. Keep your eyes on the lane: Real-time attention-guided lane detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Zhou, R. End-to-end lane detection with one-to-several transformer. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.00675. [Google Scholar]






| Dataset | Frame | Train | Validation | Test | Lane | Resolution | Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tusimple | 6408 | 3268 | 358 | 2782 | 1 | ||
| CULane | 133,235 | 88,880 | 9675 | 34,680 | 9 |
| Method Name | Accuracy (%) | F1 (%) | FP (%) | FN (%) | FPS (f/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyLaneNet | 93.36 | 90.62 | 9.42 | 9.33 | 115 |
| FastDraw | 95.2 | 93.92 | 7.6 | 4.5 | 90 |
| PINet | 95.81 | 95.39 | 5.85 | 3.36 | 40 |
| EL-GAN | 94.9 | 96.26 | 4.12 | 3.36 | 10 |
| SAD | 96.64 | 95.92 | 6.02 | 2.05 | 75 |
| SCNN | 96.53 | 95.97 | 6.17 | 1.8 | 7.5 |
| UFLD | 95.86 | 88.02 | 18.91 | 3.75 | 169.5 |
| RATS | 96.16 | - | 18.3 | 3.62 | 118 |
| MKD | 96.27 | - | 1.79 | 3.8 | 214.6 |
| ECBAM_ASPP | 95.78 | 87.67 | 19.7 | 4.7 | 219 |
| Method Name | Total | Normal | Crowded | Dazzle | Shawdow | No line | Arrow | Curve | Cross | Night | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCNN | 71.6 | 90.6 | 69.7 | 58.5 | 66.9 | 43.4 | 84.1 | 64.4 | 1990 | 66.1 | 7.5 |
| SAD | 70.7 | 89.9 | 68.5 | 59.9 | 67.7 | 42.2 | 83.8 | 66.0 | 1960 | 64.6 | 19.8 |
| UFLD | 72.3 | 90.7 | 70.2 | 59.5 | 69.3 | 44.4 | 85.7 | 69.5 | 2037 | 66.7 | 175.4 |
| LaneATT | 76.68 | 92.14 | 75.03 | 66.47 | 78.15 | 49.39 | 88.38 | 67.72 | 1330 | 70.72 | 129 |
| CondLaneNet | 78.74 | 93.38 | 77.14 | 71.17 | 79.93 | 51.85 | 89.89 | 73.88 | 1387 | 73.92 | 128 |
| GANet | 79.39 | 93.73 | 77.92 | 71.64 | 79.49 | 52.63 | 90.37 | 76.32 | 1368 | 73.67 | 127 |
| O2SFormer | 77.03 | 92.5 | 75.25 | 70.93 | 77.72 | 50.97 | 87.63 | 68.1 | 2749 | 72.88 | - |
| MKD | 79.69 | 93.62 | 78.93 | 61.41 | 80.56 | 61.81 | 88.58 | 76.56 | 3102 | 76.36 | 214.8 |
| ECBAM_ASPP | 78.45 | 94.08 | 77.17 | 68.56 | 79.20 | 51.18 | 88.72 | 75.41 | 2559 | 73.71 | 227.3 |
| Group Number | ASPP Module | ECBAM Module | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 95.06 | ||
| 2 | ✓ | 95.35 | |
| 3 | ✓ | 95.48 | |
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | 95.78 |
| Group Number | CBAM Module | ECBAM Module | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 95.35 | ||
| 2 | ✓ | 95.42 | |
| 3 | ✓ | 95.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, X.; Huang, Q.; Du, C. Lane Detection Based on ECBAM_ASPP Model. Sensors 2024, 24, 8098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248098
Gu X, Huang Q, Du C. Lane Detection Based on ECBAM_ASPP Model. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):8098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248098
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Xiang, Qiwei Huang, and Chaonan Du. 2024. "Lane Detection Based on ECBAM_ASPP Model" Sensors 24, no. 24: 8098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248098
APA StyleGu, X., Huang, Q., & Du, C. (2024). Lane Detection Based on ECBAM_ASPP Model. Sensors, 24(24), 8098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248098






