Advancements in Smart Wearable Mobility Aids for Visual Impairments: A Bibliometric Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Overview of the Results of the Bibliometric Analysis
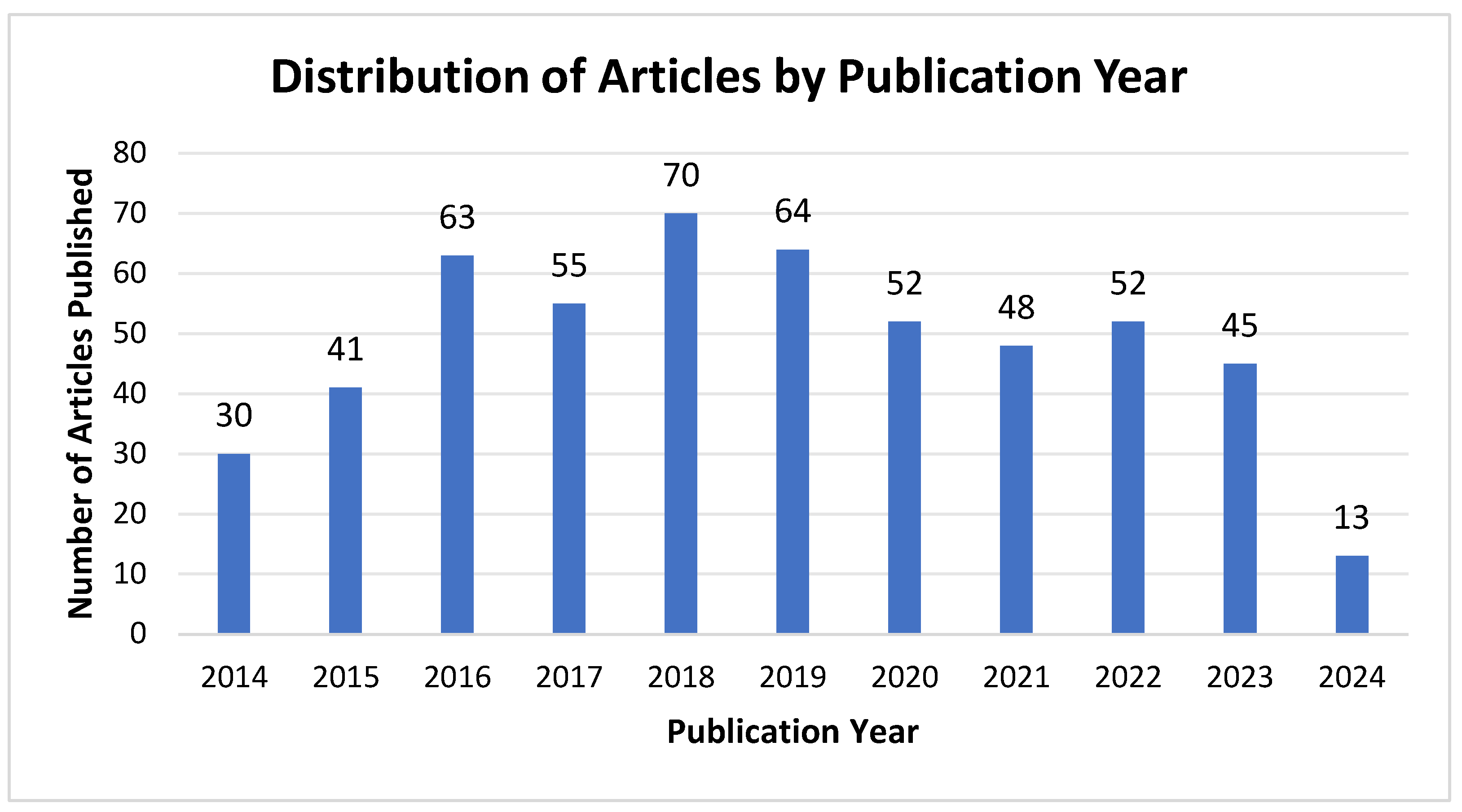
3.1.1. Analysis of Annual Publications
3.1.2. Most Influential Journals: A Co-Citation Analysis
3.1.3. Analysis of the Author Collaboration Network
3.1.4. Analysis of Co-Citation Reference Network
3.1.5. Keyword Co-Occurrence and Clustering
3.2. Wearable Assistive Devices for the Visually Impaired Based on Sensory Substitution Technology
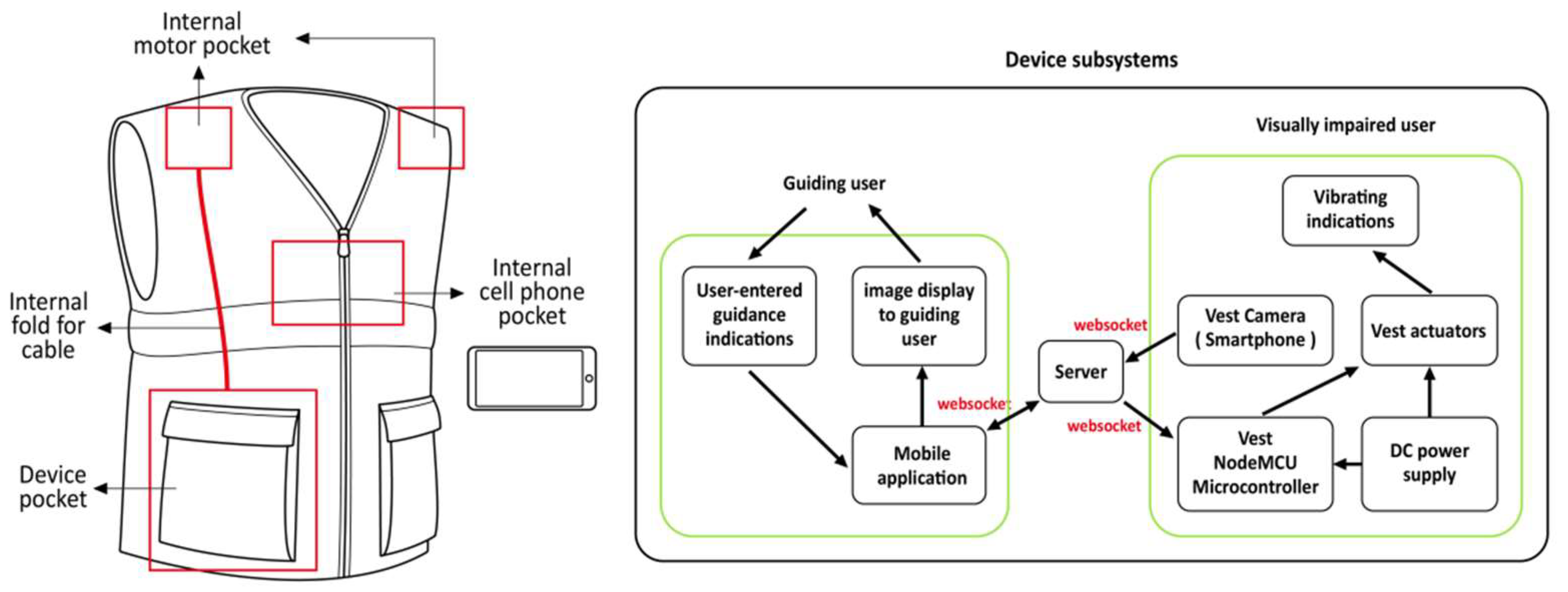
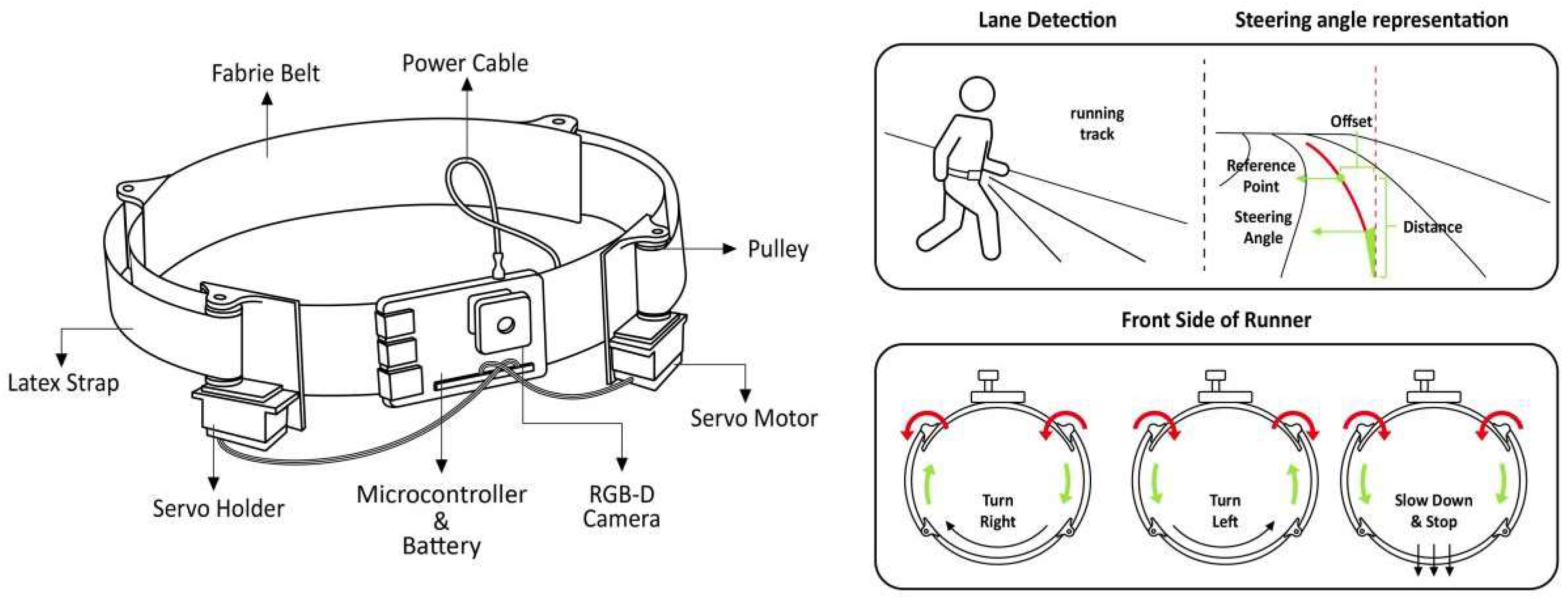
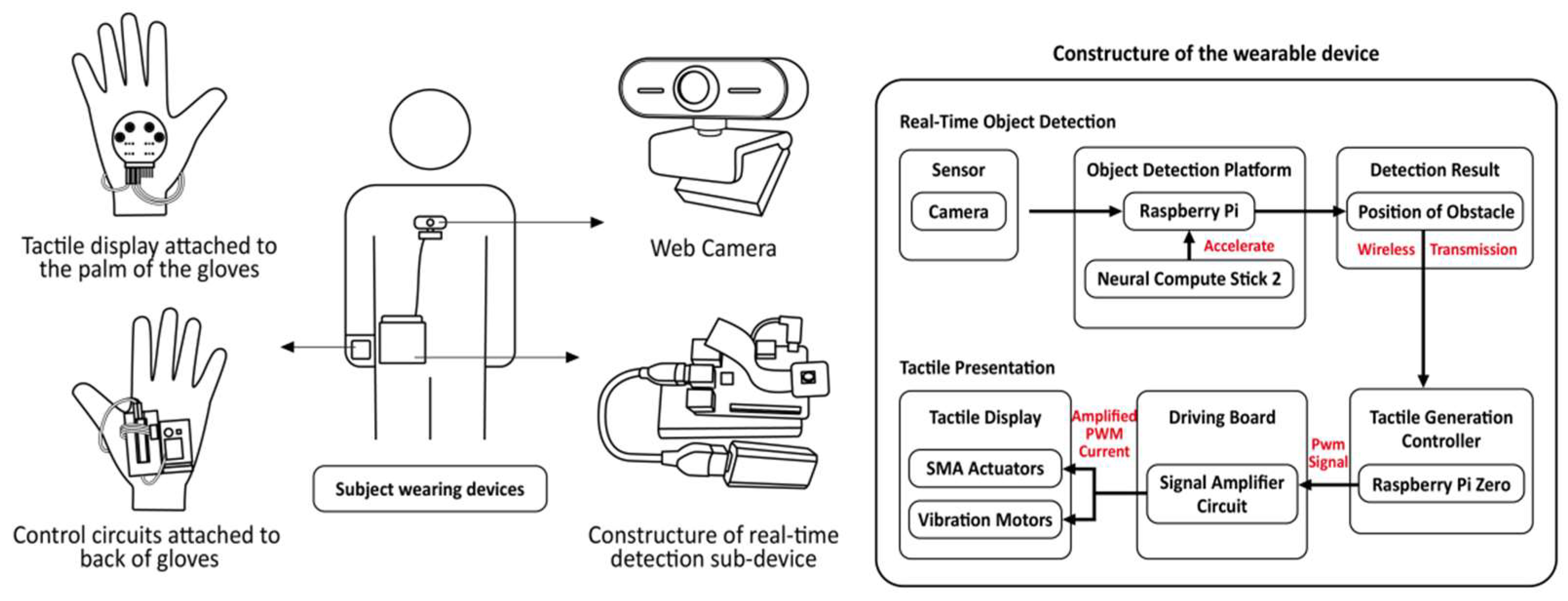
3.2.1. Haptic Feedback Devices
3.2.2. Auditory Feedback Devices
3.2.3. Application of Smart Materials
3.2.4. Conflicting Interests of the Individual and Society
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of the Results of the Bibliometric Analysis
4.2. Optimizing Haptic and Auditory Information Transmission While Multitasking
4.3. Advancing the Cross-Disciplinary Application of Smart Materials in Wearable Devices
4.4. Balancing the Interests of the Individual and Society
4.5. Two Future Developments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhowmick, A.; Hazarika, S.M. An insight into assistive technology for the visually impaired and blind people: State-of-the-art and future trends. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2017, 11, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindness and Vision Impairment. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-impairment (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Trillo, A.H.; Dickinson, C.M. The Impact of Visual and Nonvisual Factors on Quality of Life and Adaptation in Adults with Visual Impairment. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4234–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Profita, H.P. Designing Wearable Assistive Computing Devices to Support Social Acceptability and Personal Expression. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.M. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, R.R.; Flaxman, S.R.; Braithwaite, T.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J.H.; Leasher, J.; Limburg, H. Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e888–e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladrén, A.; López-Nicolás, G.; Puig, L.; Guerrero, J.J. Navigation Assistance for the Visually Impaired Using RGB-D Sensor with Range Expansion. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 10, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmannai, W.; Elleithy, K. Sensor-Based Assistive Devices for Visually-Impaired People: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Directions. Sensors 2017, 17, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismark Kweku, A.A. Development of a Wearable Assistive Device for Navigation for the Visually Impaired with Command and Request Support. Ph.D. Thesis, Soka University, Tokyo, Japan, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Almajdoub, R.A.; Shiba, O.S. An Assistant System for Blind To Avoid Obstacles Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques. Int. J. Eng. Inf. Technol. (IJEIT) 2024, 12, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, M.; Dhankhar, A.; Rajoria, H.; Soreng, J.; Batsyas, R.; Kharangarh, P.R. Innovations in Flexible Sensory Devices for the Visually Impaired. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 077011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Li, Y.; Bunarto, D.; Lee, E.; Wang, O.H.; Rodriguez, A.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Froehlich, J.E. Towards AI-Powered AR for Enhancing Sports Playability for People with Low Vision: An Exploration of ARSports. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct), Bellevue, WA, USA, 21–25 October 2024; pp. 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.D.B.; Sai, B.U.; Karthik, S.S. AI-Integrated Smart Glasses for Enhancing Reading and Guidance Independence for the Visually Impaired. J. Trends Comput. Sci. Smart Technol. 2024, 6, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, B.; Zhu, M.; Shi, P. Multi-sensory visual-auditory fusion of wearable navigation assistance for people with impaired vision. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutny, R. Exploring space: User interfaces for blind and visually impaired people for spatial and non-verbal information. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computers Helping People with Special Needs, Linz, Austria, 8–12 July 2024; pp. 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Duanmu, D.; Xu, T.; Li, X.; Cao, X.; Huang, W.; Hu, Y. Perceptual Feedback through Multisensory Fusion in Hand Function Rehabilitation by A Machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Virtual Environments for Measurement Systems and Applications (CIVEMSA), Xi’an, China, 14–16 June 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ghose, S.; Roy, K.; Prevost, J.J. SoundEYE: AI-Driven Sensory Augmentation System for Visually Impaired Individuals through Natural Sound. In Proceedings of the 2024 19th Annual System of Systems Engineering Conference (SoSE), Tacoma, WA, USA, 23–26 June 2024; pp. 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- ST, A.; Amarnath, R.N.; Gopi, B.; Selvakumar, R.; Ganesh, E.; Sujatha, S. IoT-Embedded Smart Clothing with CNN for Improved Spatial Awareness in the Visually Impaired. In Proceedings of the 2024 Second International Conference on Intelligent Cyber Physical Systems and Internet of Things (ICoICI), Coimbatore, India, 28–30 August 2024; pp. 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Agrimi, E.; Battaglini, C.; Bottari, D.; Gnecco, G.; Leporini, B. Game accessibility for visually impaired people: A review. Soft Comput. 2024, 28, 10475–10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach-y-Rita, P.; Kercel, S.W. Sensory substitution and the human-machine interface. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2003, 7, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bark, K.; Wheeler, J.; Shull, P.; Savall, J.; Cutkosky, M. Rotational Skin Stretch Feedback: A Wearable Haptic Display for Motion. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2010, 3, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, B.; Panchanathan, S. Haptics for Sensory Substitution; Springer International Publishing Ag: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Boljanić, T.; Baljić, M.; Kostić, M.; Barralon, P.; Došen, S.; Štrbac, M. Psychometric evaluation of high-resolution electrotactile interface for conveying 3D spatial information. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, M.; Forsyth, J.; Deportes, L.; Castaneda, D. Braille Learning using Haptic Feedback. In Proceedings of the 2024 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS), Charlottesville, VA, USA, 3 May 2024; pp. 460–465. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa-Hernandez, A.G.; Perdomo-Vasquez, C.; Gomez-Escobar, D.; Galvis-Pedraza, H.; Medina-Castañeda, J.F.; González-Vargas, A.M. Haptic Interface for Remote Guidance of People with Visual Disabilities. In Proceedings of the Latin American Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Florianópolis, Brazil, 24–28 October 2022; pp. 681–689. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, F.; Xian, S.F.; Yang, R.N.; Wu, C.C.; Lu, X. A Wearable Visually Impaired Assistive System Based on Semantic Vision SLAM for Grasping Operation. Sensors 2024, 24, 3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulimowski, P.; Strumiłło, P.; Trygar, S.; Trygar, W. Haptic Display of Depth Images in an Electronic Travel Aid for the Blind: Technical Indoor Trials. In Proceedings of the Polish Conference on Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, Lodz, Poland, 27–29 September 2023; pp. 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- Sultania, C.; Singhal, D.; Kabra, M.; Madurwar, A.; Pawar, S.; Rao, M. Wearable Haptic Braille Device for Enhancing Classroom Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Conference, Vienna, Austria, 29 October–1 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; ACM. Learning Music Blind: Understanding the Application of Technology to Support BLV Music Learning. In Proceedings of the 24th International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility (ASSETS), Athens, Greece, 23–26 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Khusro, S. An insight into smartphone-based assistive solutions for visually impaired and blind people: Issues, challenges and opportunities. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2021, 20, 265–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; McConville, R.; Metatla, O.; Chang, M.; Han, C.; Lee, J.; Roudaut, A. Outdoor localization using BLE RSSI and accessible pedestrian signals for the visually impaired at intersections. Sensors 2022, 22, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhan, O.; Samur, E.; IEEE. A Wearable Haptic Guidance System Based on Skin Stretch around the Waist for Visually-Impaired Runners. In Proceedings of the IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–24 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
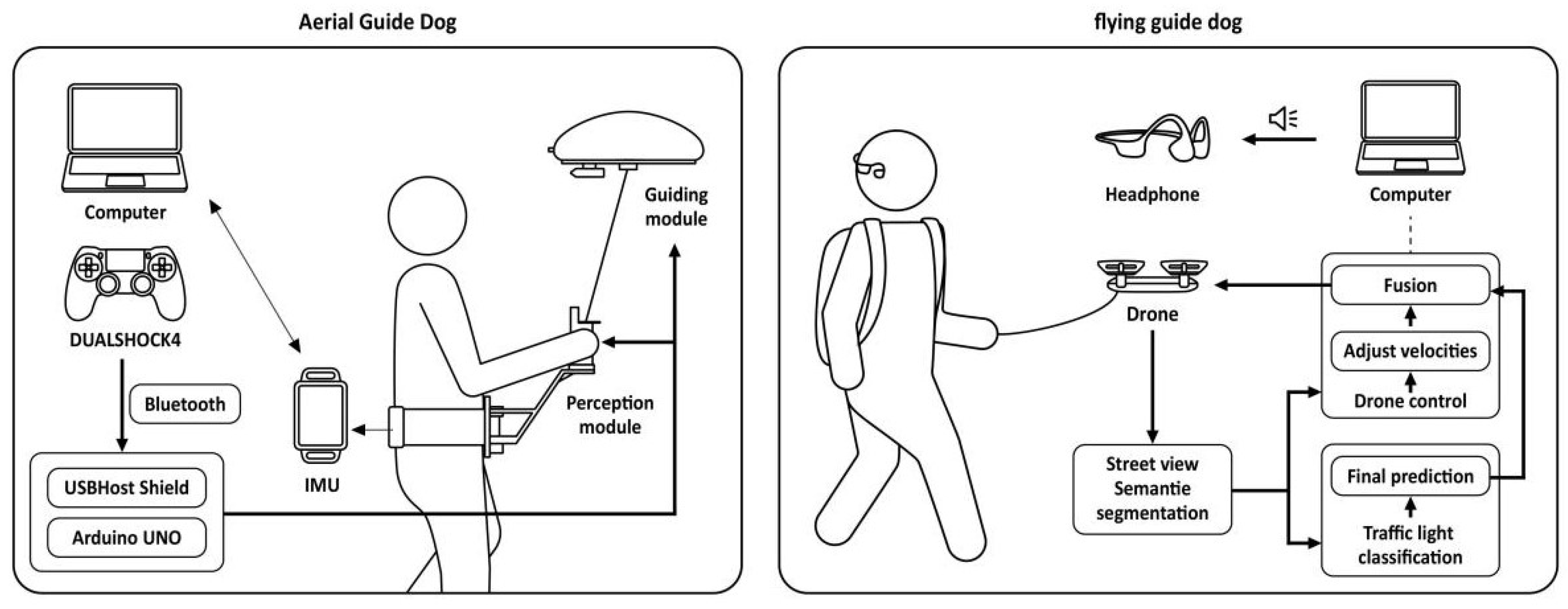
- Zhang, X.; Pan, Z.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Ding, S. The aerial guide dog: A low-cognitive-load indoor electronic travel aid for visually impaired individuals. Sensors 2024, 24, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Chen, C.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Seibold, C.; Yang, K.; Stiefelhagen, R. Flying guide dog: Walkable path discovery for the visually impaired utilizing drones and transformer-based semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Sanya, China, 27–31 December 2021; pp. 1123–1128. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Wang, R.L.; Xu, X.H.; Assoc Comp, M. PneuFetch: Supporting Blind and Visually Impaired People to Fetch Nearby Objects via Light Haptic Cues. In Proceedings of the ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, E.D.Z.; Siu, A.F.; Boadi-Agyemang, A.; Kim, G.S.H.; Gonzalez, E.J.; Follmer, S.; ACM. PantoGuide: A Haptic and Audio Guidance System To Support Tactile Graphics Exploration. In Proceedings of the 22nd International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility (ASSETS), Electr Network, New York, NY, USA, 26–28 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, P.; Chauhan, A.; IEEE. Sensory Vision Substitution using Tactile Stimulation. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Electr Network, Pune, India, 2–4 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alsuhibany, S.A. Vibration-Based Pattern Password Approach for Visually Impaired People. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2022, 40, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalraj, R.; Vasant, M.; Akoparna, B.; Haris, P.; Subiksha, J. Human-Centric Design and Machine Learning Integration in Smart Footwear for Visually Impaired Individuals. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Manag. 2024, 6, 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- Chouvardas, V.G.; Miliou, A.N.; Hatalis, M.K. Tactile displays: Overview and recent advances. Displays 2008, 29, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Fazli, P.; Jeong, H. Artificial Intelligence in Virtual Reality for Blind and Low Vision Individuals: Literature Review. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2024, 10711813241266832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barontini, F.; Catalano, M.G.; Pallottino, L.; Leporini, B.; Bianchi, M. Integrating wearable haptics and obstacle avoidance for the visually impaired in indoor navigation: A user-centered approach. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2020, 14, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T. Towards the Design of Wearable Assistive Technologies to Address the Privacy and Security Concerns of People with Visual Impairments. Ph.D. Thesis, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Okolo, G.I.; Althobaiti, T.; Ramzan, N. Assistive systems for visually impaired persons: Challenges and opportunities for navigation assistance. Sensors 2024, 24, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, D.K.X. A Finger-Mounted Obstacle Detector for People with Visual Impairment. Master’s Thesis, Swinburne, Melbourne, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, M.J.; Ohm, Y.; Chin, K.; Majidi, C. Composites of functional polymers: Toward physical intelligence using flexible and soft materials. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 37, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, P.B.; Damian, D.D. Haptic wearables as sensory replacement, sensory augmentation and trainer—A review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.; Ndukwe, C.; Virdee, B.; Djemai, R. Image recognition tools for blind and visually impaired users: An emphasis on the design considerations. ACM Trans. Access. Comput. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Kan, Z. Sensing and navigation of wearable assistance cognitive systems for the visually impaired. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022, 15, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalvini, F.; Bordeau, C.; Ambard, M.; Migniot, C.; Dubois, J. Outdoor Navigation Assistive System Based on Robust and Real-Time Visual-Auditory Substitution Approach. Sensors 2024, 24, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarika, M.; Santhoshkumar, R.; Dharson, R.; Jayamani, S. Assistive Voice Guidance System for Blind Individuals using Deep Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications Theme: Healthcare and Internet of Things (AIMLA), Namakkal, India, 15–16 March 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar, D. Voice Assisted Facial Emotion Recognition System for Blind Peoples with Tensorflow Model. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Students’ Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science (SCEECS), Bhopal, India, 24–25 February 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. Hearing the World: A Pilot Study Design on Spatial Audio for the Visually Impaired. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 27th International Academic Mindtrek Conference, Tampere, Finland, 8–11 October 2024; pp. 244–248. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.U.; Ranganath, S.; Ashwin, T.; Reddy, G.R.M. A Google glass based real-time scene analysis for the visually impaired. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 166351–166369. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Singh, M.; Chauhan, N.; Chauhan, A.S. A Novel Approach for Complete Aid to Blinds Using Voice Assisted Smart Glasses. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Sustainable Emerging Innovations in Engineering and Technology (ICSEIET), Ghaziabad, India, 14–15 September 2023; pp. 365–369. [Google Scholar]
- Bastola, A.; Gluck, A.; Brinkley, J. Feedback mechanism for blind and visually impaired: A review. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2023, 67, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, G. Auditory Feedback to compensate audible instructions to support people with visual impairment. In Proceedings of the 23rd International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility, Online, 18–22 October 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- van der Bie, J.; Ben Allouch, S.; Jaschinski, C. Communicating multimodal wayfinding messages for visually impaired people via wearables. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services, Taipei, Taiwan, 1–4 October 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ghodrat, S.; Sandhir, P.; Huisman, G. Exploring shape memory alloys in haptic wearables for visually impaired people. Front. Comput. Sci. 2023, 5, 1012565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Hinchet, R.; Shea, H.; Majidi, C. Wearable soft technologies for haptic sensing and feedback. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, M. Smart Memory Alloy Actuated Slave System for Medical Robotics, with Haptic Feedback. DCT Report 2003. Master’s Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, W.Y.E. Dynamic Compression for Novel Haptic Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.J.; Chen, Y.W.; Sawada, H. A Wearable Assistive Device for Blind Pedestrians Using Real-Time Object Detection and Tactile Presentation. Sensors 2022, 22, 4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Sawada, H. A wearable assistive system for the visually impaired using object detection, distance measurement and tactile presentation. Intell. Robot. 2023, 3, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Tang, L. Recent Advances of Soft Actuators in Smart Wearable Electronic-Textile. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-H.; Chang, S.-H. PVDF-based ferroelectric polymers and dielectric elastomers for sensor and actuator applications: A review. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2019, 1, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torras, N.; Zinoviev, K.; Camargo, C.; Campo, E.M.; Campanella, H.; Esteve, J.; Marshall, J.; Terentjev, E.; Omastová, M.; Krupa, I. Tactile device based on opto-mechanical actuation of liquid crystal elastomers. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 208, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z. Wearable Pressure Sensors and Their Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Computer Applications (ICIPCA), Shenyang, China, 28–30 June 2024; pp. 446–449. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.C.; Hu, S.G.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Chen, T.P.; Yin, Y.; et al. Braille recognition by E-skin system based on binary memristive neural network. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Shin, H.; Jekal, M. Braille glove design toward interdisciplinary approach for visually impaired people: Developing independent sensing design with MXene and embroidery. Fash. Text. 2024, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, S.M.; Zhang, K.J.; Zhao, D.Z.; Pi, Y.C.; Guan, X.; Peng, Z.C.; Zhong, Q.Z.; Zhong, J.W. Electrostatic Smart Textiles for Braille-To-Speech Translation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 10, 2313518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, M.N.; Abdalla, I.; Zhu, M.M.; Wei, X.D.; Yu, J.Y.; Li, Z.L.; Ding, B. Highly Wearable, Breathable, and Washable Sensing Textile for Human Motion and Pulse Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19965–19973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbaud, R.; Najafi, M.; Gandarias, J.M.; Lorenzini, M.; Paul, U.C.; Zych, A.; Athanassiou, A.; Cataldi, P.; Ajoudani, A. Toward Sustainable Haptics: A Wearable Vibrotactile Solar-Powered System with Biodegradable Components. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, N.; Gilbert, S. The WEAR scale: Developing a measure of the social acceptability of a wearable device. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; pp. 2864–2871. [Google Scholar]
- Denning, T.; Dehlawi, Z.; Kohno, T. In situ with bystanders of augmented reality glasses: Perspectives on recording and privacy-mediating technologies. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Toronto, ON, Canada, 26 April–1 May 2014; pp. 2377–2386. [Google Scholar]
- Profita, H.; Albaghli, R.; Findlater, L.; Jaeger, P.; Kane, S.K.; ACM. The AT Effect: How Disability Affects the Perceived Social Acceptability of Head-Mounted Display Use. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI4GOOD), San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; pp. 4884–4895. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.J.; Yurchisin, J.; Hodges, N.; Watchravesringkan, K.; Ackerman, T. An investigation of self-concept, clothing selection motivation, and life satisfaction among disabled consumers. Fam. Consum. Sci. Res. J. 2013, 42, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ding, X.; Yu, C.; Gao, L.; Chi, X.; Shi, Y. “I Bought This for Me to Look More Ordinary” A Study of Blind People Doing Online Shopping. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wickens, C.D.; Gordon, S.E.; Liu, Y.; Lee, J. An Introduction to Human Factors Engineering; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Căilean, A.-M.; Avătămăniței, S.-A.; Beguni, C. Design and Experimental Evaluation of a Visible Light Communications-Based Smart Backpack for Visually Impaired Persons’ Assistance. In Proceedings of the 2023 31st Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 21–22 November 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, N.; Khalid, A.; Mutalib, A.A. Evaluation of Cohesive Affective Design Model for People with Visual Challenges Through Expert Review Method. TEM J. 2024, 13, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Escobar, L.M.; Chavarria, M.A.; Schönenberger, K.; Hurst, S.; Stein, M.A.; Mugeere, A.; Rivas Velarde, M. Assessing the implementation of user-centred design standards on assistive technology for persons with visual impairments: A systematic review. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2023, 4, 1238158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapu, R.; Mocanu, B.; Zaharia, T. Wearable assistive devices for visually impaired: A state of the art survey. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 137, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodnik, J.; Jakus, G.; Tomažič, S. Multiple spatial sounds in hierarchical menu navigation for visually impaired computer users. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2011, 69, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Cho, S.; Choe, A.; Yeom, J.; Ro, Y.G.; Kim, J.; Kang, D.-H.; Lee, S.; Ko, H. Soft Sensors and Actuators for Wearable Human–Machine Interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 1464–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.D.P.; Suzuki, A.H.G.; Medola, F.O.; Vaezipour, A. A systematic review of wearable devices for orientation and mobility of adults with visual impairment and blindness. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 162306–162324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maćkowski, M.; Brzoza, P.; Kawulok, M.; Meisel, R.; Spinczyk, D. Multimodal presentation of interactive audio-tactile graphics supporting the perception of visual information by blind people. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2023, 19, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.-K.; Gohil, K.; Huster, R.J.; Beste, C. On the effects of multimodal information integration in multitasking. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OhnBar, E.; Kitani, K.; Asakawa, C. Personalized dynamics models for adaptive assistive navigation systems. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Zürich, Switzerland, 29–31 October 2018; pp. 16–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Ryoo, H.-Y.; Shin, B.-S. Sustainable wearables: Wearable technology for enhancing the quality of human life. Sustainability 2016, 8, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.R.; Kim, H.S.; Qazi, R.; Kwon, Y.T.; Jeong, J.W.; Yeo, W.H. Advanced soft materials, sensor integrations, and applications of wearable flexible hybrid electronics in healthcare, energy, and environment. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Shu, L.; Yang, Y.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, W. Smart textile-integrated microelectronic systems for wearable applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chortos, A.; Liu, J.; Bao, Z. Pursuing prosthetic electronic skin. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lin, J.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, B. Customized surface adhesive and wettability properties of conformal electronic devices. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 6289–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Lee, M.Y.; Park, C.H.; Lee, H.R.; Oh, J.H. Toward environmentally robust organic electronics: Approaches and applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
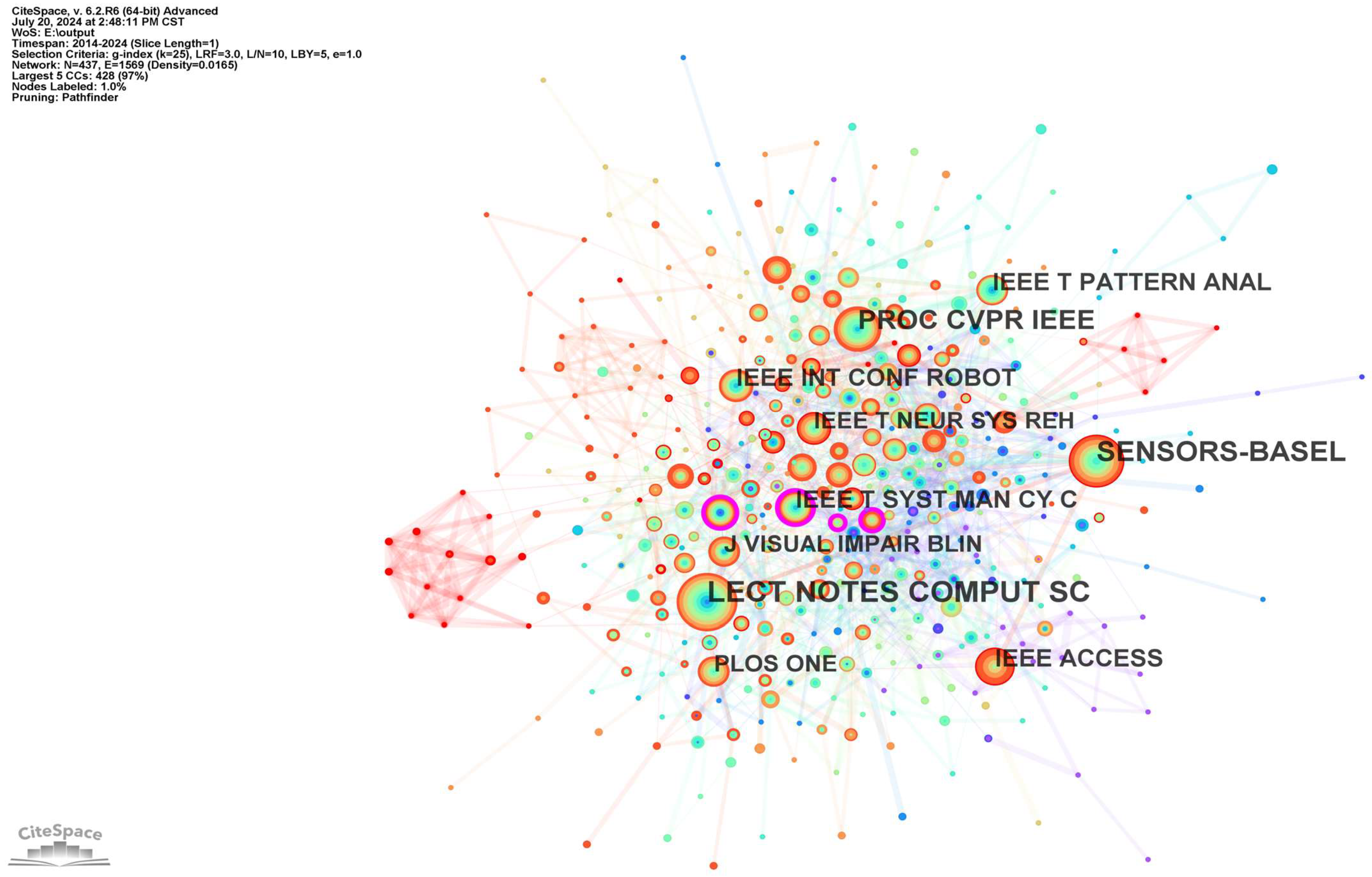
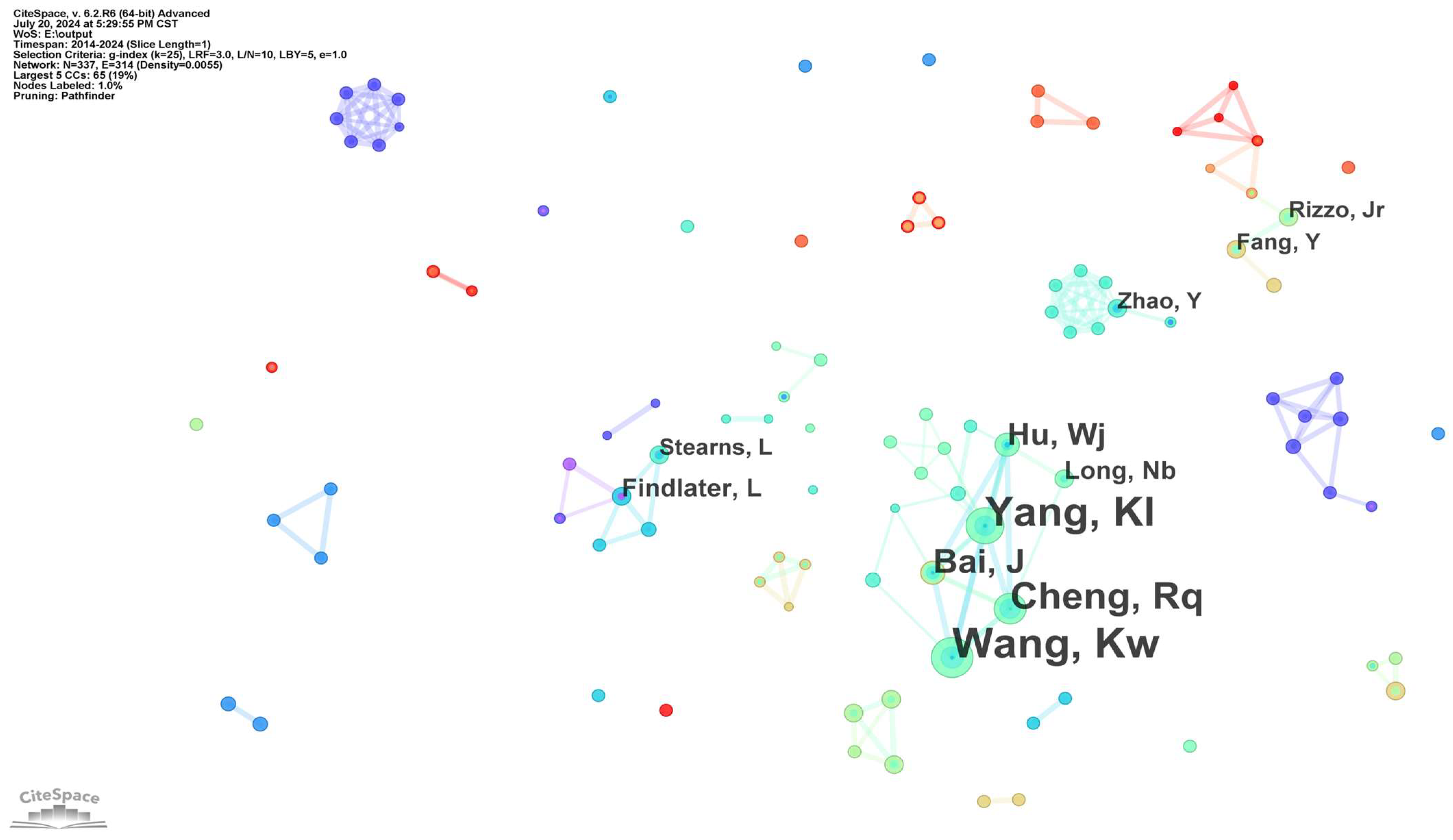
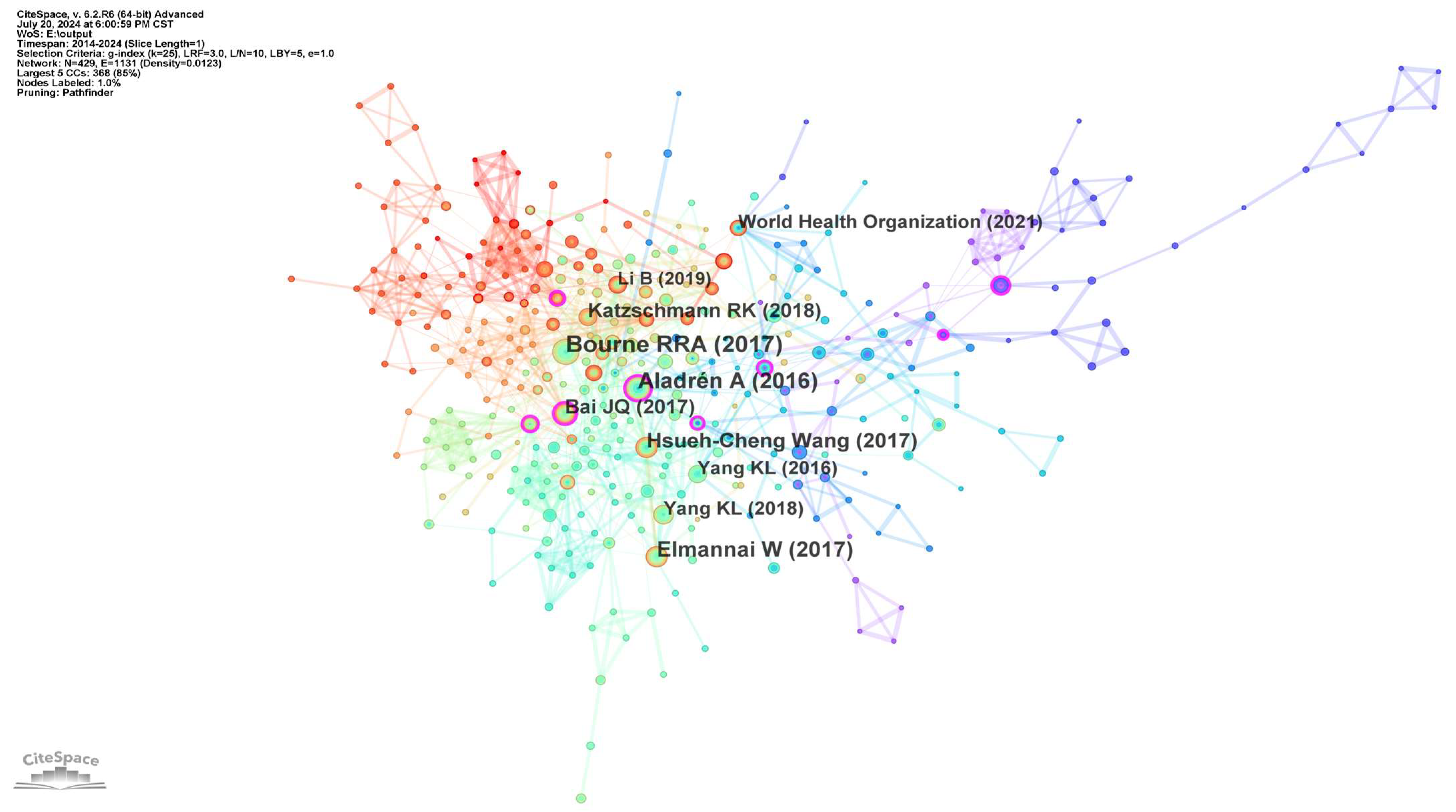
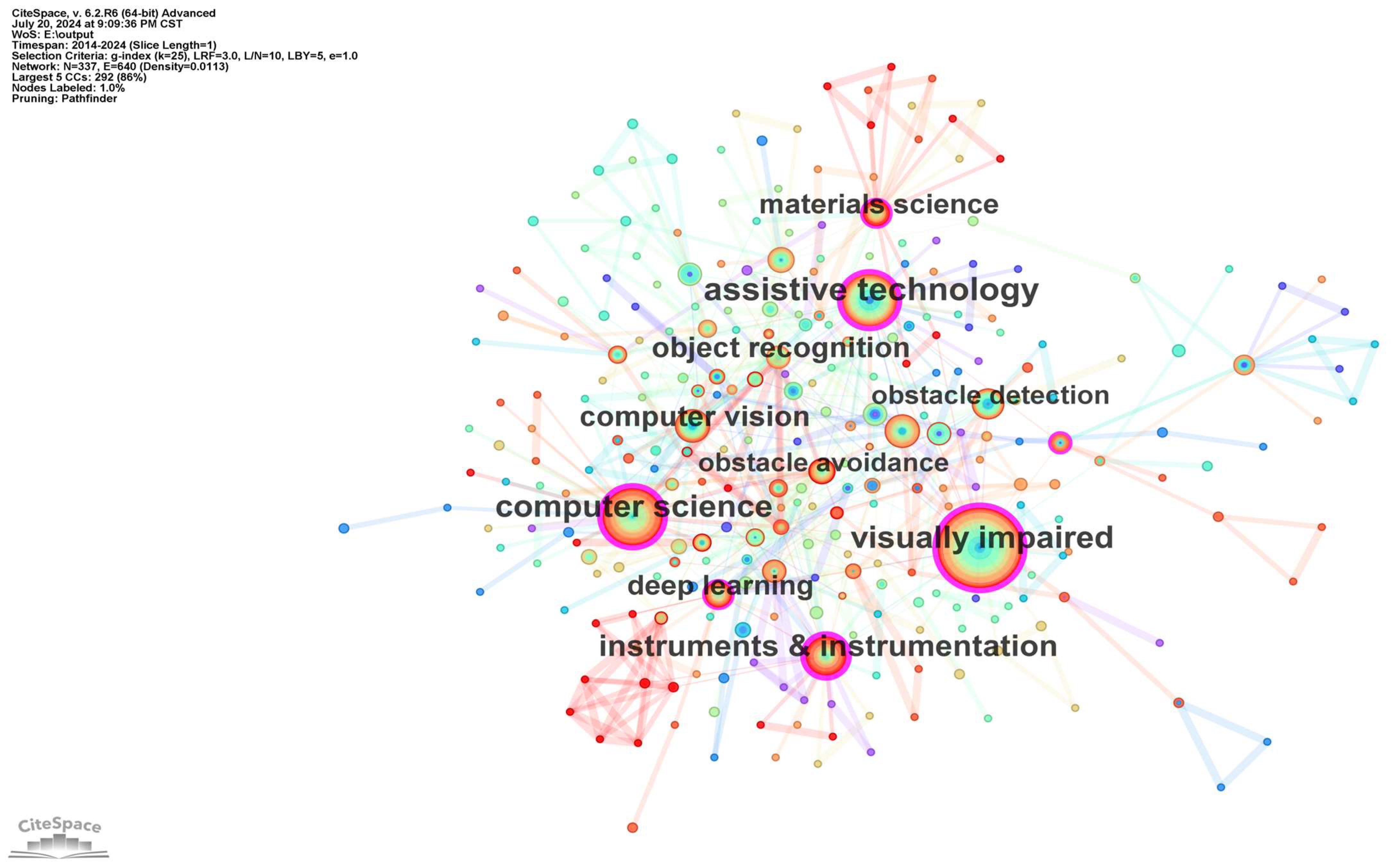
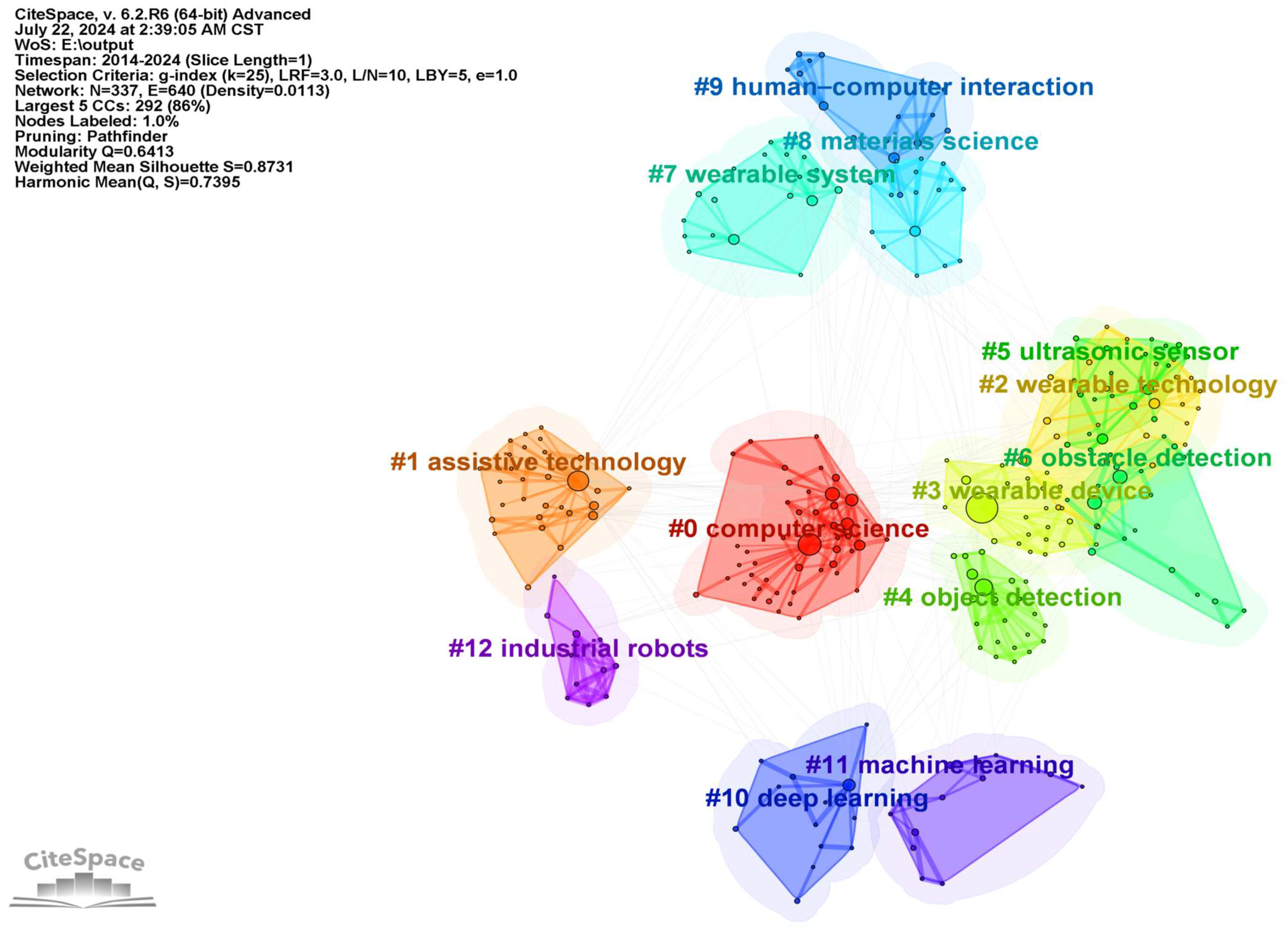
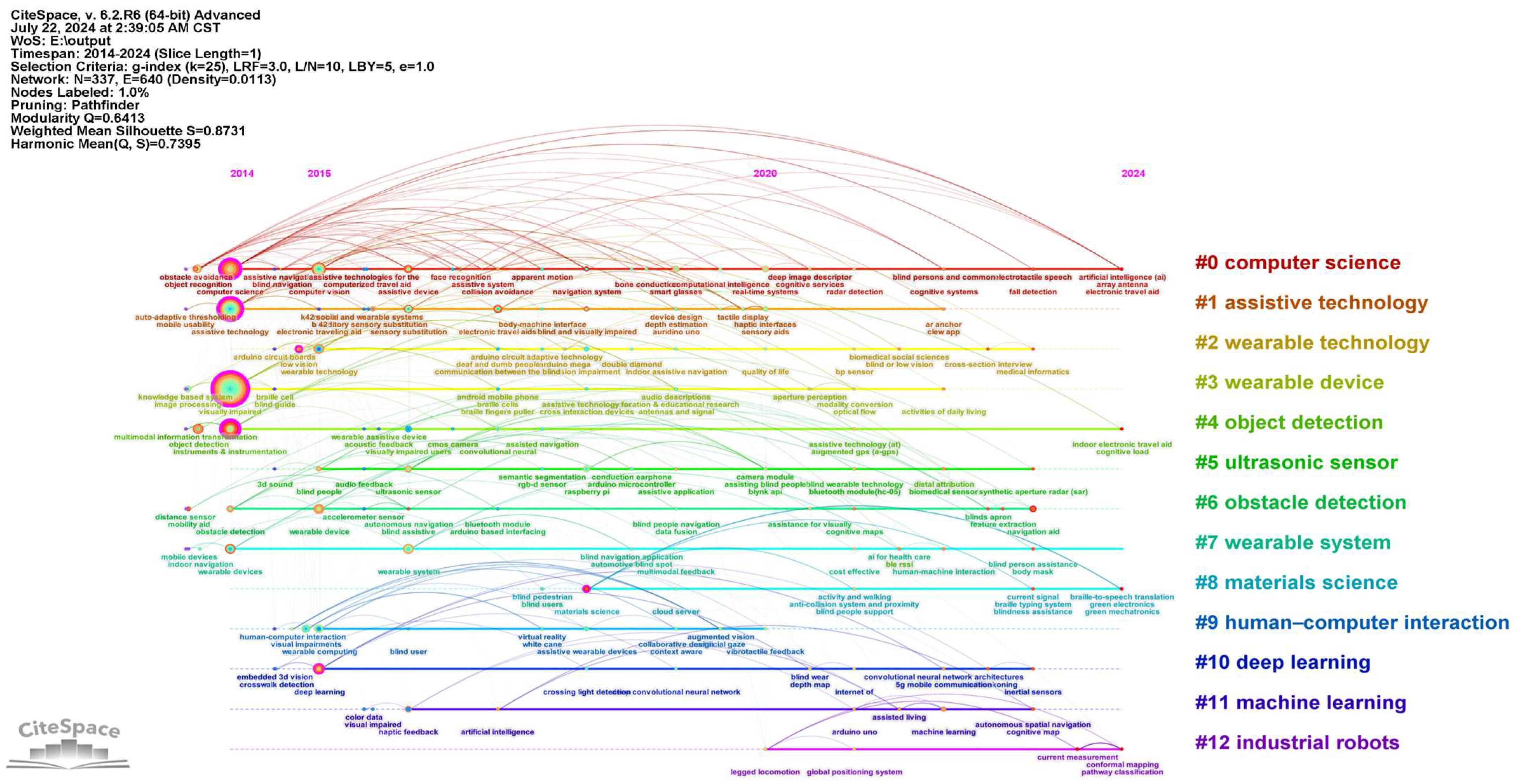



| Rank | Number of Articles Published | Centrality | Year | Journal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 205 | 0.03 | 2014 | Lecture Notes in Computer Science |
| 2 | 168 | 0.07 | 2014 | Sensors |
| 3 | 127 | 0.05 | 2014 | IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Proceedings |
| 4 | 85 | 0.11 | 2014 | IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems |
| 5 | 76 | 0.06 | 2014 | IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation |
| 6 | 75 | 0.02 | 2014 | IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence |
| 7 | 74 | 0.02 | 2019 | IEEE Access |
| 8 | 66 | 0.04 | 2015 | IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering |
| 9 | 64 | 0.06 | 2014 | Journal of Visual Impairment and Blindness |
| 10 | 63 | 0.05 | 2015 | Public Library of Science ONE |
| Rank | Number of Articles Published | Author |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | Kaiwei Wang |
| 2 | 18 | Kailun Yang |
| 3 | 14 | Ruiqi Cheng |
| 4 | 10 | Jinqiang Bai |
| 5 | 8 | Weijian Hu |
| 6 | 5 | Ningbo Long |
| 7 | 5 | Leah Findlater |
| 8 | 5 | Liang-Bi Chen |
| 9 | 5 | Wan-Jung Chang |
| 10 | 4 | Lee Stearns |
| Rank | Freq | Centrality | Year | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35 | 0.02 | 2017 | Magnitude, Temporal Trends, and Projections of the Global Prevalence of Blindness and Distance and Near Vision Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis |
| 2 | 33 | 0.16 | 2016 | Navigation Assistance for the Visually Impaired Using RGB-D Sensor With Range Expansion |
| 3 | 28 | 0.05 | 2017 | Sensor-Based Assistive Devices for Visually Impaired People: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Directions |
| 4 | 24 | 0.06 | 2017 | Enabling Independent Navigation for Visually Impaired People Through a Wearable Vision-Based Feedback System |
| 5 | 20 | 0.11 | 2017 | Smart Guiding Glasses for Visually Impaired People in Indoor Environments |
| 6 | 19 | 0.08 | 2018 | Safe Local Navigation for Visually Impaired Users With a Time-of-Flight and Haptic Feedback Device |
| 7 | 18 | 0.01 | 2018 | Unifying Terrain Awareness for the Visually Impaired Through Real-Time Semantic Segmentation |
| 8 | 18 | 0.09 | 2016 | Expanding the Detection of Traversable Area With RealSense for the Visually Impaired |
| 9 | 17 | 0.09 | 2021 | World Health Organization, 2021, Blindness and Vision Impairment |
| 10 | 16 | 0.04 | 2019 | Vision-Based Mobile Indoor Assistive Navigation Aid for Blind People |
| Rank | Count | Centrality | Year | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 151 | 0.3 | 2014 | visually impaired |
| 2 | 73 | 0.21 | 2014 | computer science |
| 3 | 70 | 0.39 | 2014 | assistive technology |
| 4 | 48 | 0.21 | 2014 | instruments and instrumentation |
| 5 | 31 | 0.1 | 2015 | computer vision |
| 6 | 28 | 0.06 | 2015 | wearable device |
| 7 | 26 | 0.08 | 2014 | obstacle detection |
| 8 | 22 | 0.11 | 2015 | deep learning |
| 9 | 21 | 0.09 | 2014 | object recognition |
| 10 | 18 | 0.08 | 2014 | obstacle avoidance |
| 11 | 17 | 0.14 | 2018 | materials science |
| 12 | 17 | 0.09 | 2016 | ultrasonic sensor |
| 13 | 15 | 0.09 | 2016 | assistive device |
| 14 | 15 | 0.02 | 2014 | object detection |
| 15 | 13 | 0.09 | 2016 | wearable system |
| Rank | Centrality | Count | Year | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.39 | 70 | 2014 | assistive technology |
| 2 | 0.3 | 151 | 2014 | visually impaired |
| 3 | 0.21 | 73 | 2014 | computer science |
| 4 | 0.21 | 48 | 2014 | instruments and instrumentation |
| 5 | 0.14 | 17 | 2018 | materials science |
| 6 | 0.11 | 22 | 2015 | deep learning |
| 7 | 0.11 | 7 | 2015 | low vision |
| 8 | 0.1 | 31 | 2015 | computer vision |
| 9 | 0.09 | 21 | 2014 | object recognition |
| 10 | 0.09 | 17 | 2016 | ultrasonic sensor |
| 11 | 0.09 | 15 | 2016 | assistive device |
| 12 | 0.09 | 13 | 2016 | wearable system |
| 13 | 0.08 | 26 | 2014 | obstacle detection |
| 14 | 0.08 | 18 | 2014 | obstacle avoidance |
| 15 | 0.08 | 12 | 2015 | wearable technology |
| Cluster ID | Size | Silhouette | Year | Top Terms (LSI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 46 | 0.796 | 2018 | computer science; object recognition; assistive technology; real-time systems; impaired people/smart glasses; obstacle avoidance; assistive devices; collision avoidance; legged locomotion |
| 1 | 31 | 0.946 | 2017 | assistive technology; computer science; wearable computers; navigation device; wearable system/electronic travel aids; computer vision; visual impairment; patent analysis; vision impairment |
| 2 | 25 | 0.892 | 2018 | wearable technology; sport assistance; augmented reality; impaired people; navigation aids/symptom monitoring; medical informatics; cross-section interview; health data; mhealth technology |
| 3 | 23 | 0.921 | 2017 | assistive technology; computer science; wearable device; obstacle detection; electronic travel aids/visual impairment; information technology; daily living; visual odometry; stair detection |
| 4 | 22 | 0.903 | 2017 | object detection; haar transformation; positional analysis; cmos camera; object recognition/visual impairment; convolutional neural; wearable assistive system; ground segmentation; three-dimensional displays |
| 5 | 20 | 0.87 | 2017 | obstacle detection; wearable device; assistive device; Bluetooth module; navigation aid/computer science; mobility aid; blind assistive; feature fusion; multilayer gru |
| 6 | 20 | 0.79 | 2018 | ultrasonic sensor; audio feedback; visual impairment; object recognition; smart system/object recognition; raspberry pi; computer science; blind people; navigation device |
| 7 | 19 | 0.919 | 2018 | wearable system; computer vision; navigational aid; indoor navigation; radar detection/handicapped aids; radar detection; signal processing algorithm; millimeter wave radar; frequency-modulated continuous wave radar system |
| 8 | 17 | 0.776 | 2018 | human-computer interaction; computer science; wearable computing; augmented vision; sensory augmentation/visual impairments; virtual reality; auditory feedback; assistive wearable devices; collaborative design |
| 9 | 17 | 0.851 | 2022 | materials science; other topics; braille typing system; current signal; blindness assistance/fall detection; indoor navigation monitoring; anti-collision system; blind people support; non-contact triboelectric sensor |
| 10 | 13 | 0.925 | 2019 | machine learning; wireless sensor networks; heuristic algorithms; sensing systems; assistive technology/positioning systems; visual impairment; user acceptance; vehicles opportunities; cognitive map |
| 11 | 13 | 0.807 | 2019 | deep learning; computer science; object detection; mobile edge; wireless communication/assistive technology; crosswalk detection; pedestrian detection; crossing light detection; dead reckoning |
| 12 | 11 | 0.893 | 2023 | deep learning; industrial robots; impedance measurement; surface impedance; terrain classification/legged locomotion; current measurement; humanoid robots; mono-filament issues; deep learning |
| 13 | 5 | 1 | 2022 | bio-inspired navigation; visual localization; navigation assistive; devices; artificial place cells; artificial grid cells; artificial head; direction cells |
| 14 | 4 | 1 | 2023 | viola jones algorithm; haar cascades; opencv; py-yolov5 algorithm; onnx; model; deep neural networks; eigen faces; principal component; analysis; azure maps; octa-polar segmentation; dimensional ratio; similarity; py-tesseract; paddle ocr |
| 15 | 3 | 1 | 2017 | wvns; a combinatorial planner; aiming-tracking mechanism; autoregressive; model; dynamic weighted a* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Ding, Y.; Long, L.; Li, W.; Xu, X. Advancements in Smart Wearable Mobility Aids for Visual Impairments: A Bibliometric Narrative Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 7986. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247986
Zhang X, Huang X, Ding Y, Long L, Li W, Xu X. Advancements in Smart Wearable Mobility Aids for Visual Impairments: A Bibliometric Narrative Review. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):7986. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247986
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaochen, Xiaoyu Huang, Yiran Ding, Liumei Long, Wujing Li, and Xing Xu. 2024. "Advancements in Smart Wearable Mobility Aids for Visual Impairments: A Bibliometric Narrative Review" Sensors 24, no. 24: 7986. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247986
APA StyleZhang, X., Huang, X., Ding, Y., Long, L., Li, W., & Xu, X. (2024). Advancements in Smart Wearable Mobility Aids for Visual Impairments: A Bibliometric Narrative Review. Sensors, 24(24), 7986. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247986