Operational Modal Analysis of Civil Engineering Structures with Closely Spaced Modes Based on Improved Hilbert–Huang Transform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hilbert–Huang Transform
2.1. EMD
2.2. Hilbert Transform
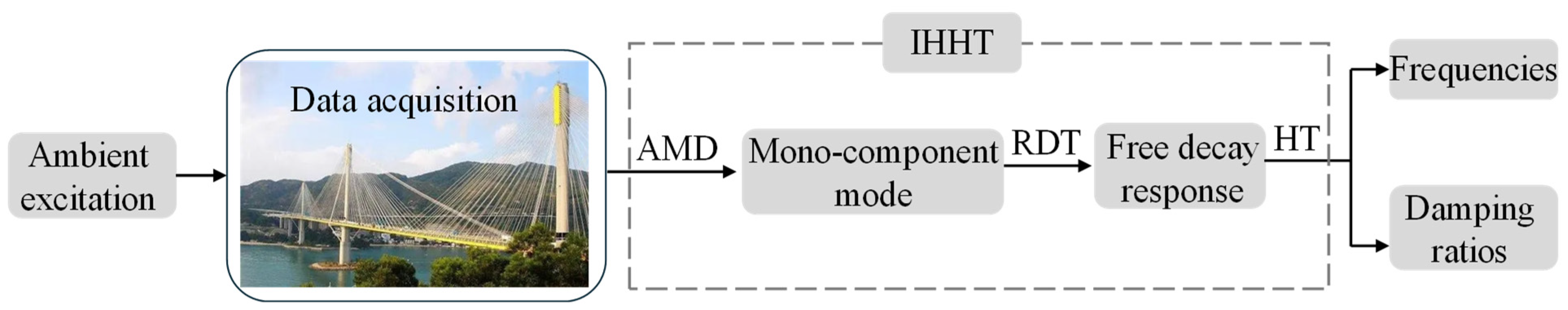
3. Improved HHT for Modal Parameter Identification
3.1. AMD
3.2. RDT
- (1)
- Both zero up-crossings and down-crossings serve as triggering conditions, effectively doubling the number of segments included in the averaging process.
- (2)
- The sampling frequency of the measured response is artificially increased using a curve fitting method to enhance the accuracy of detecting the triggering value.
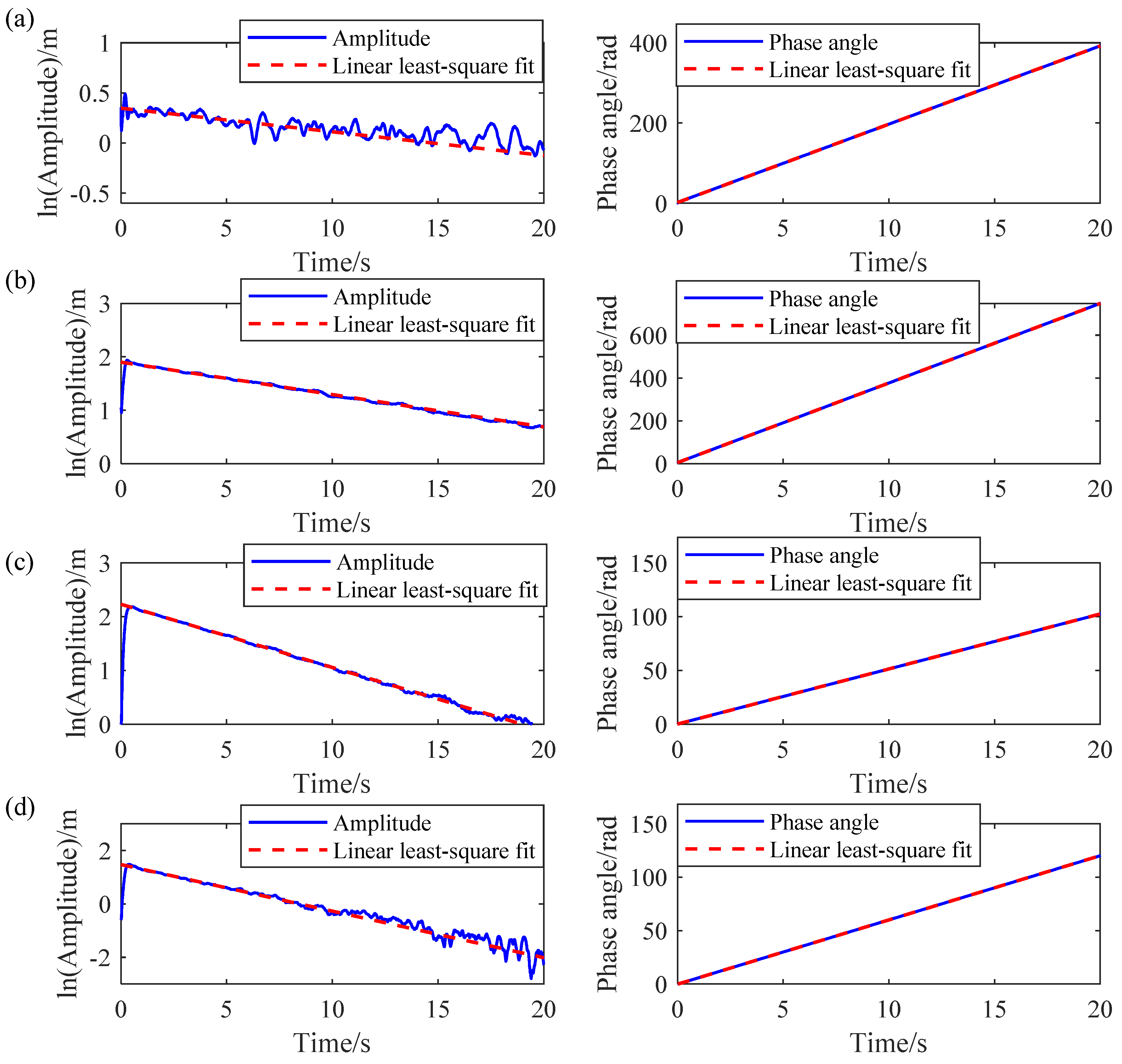
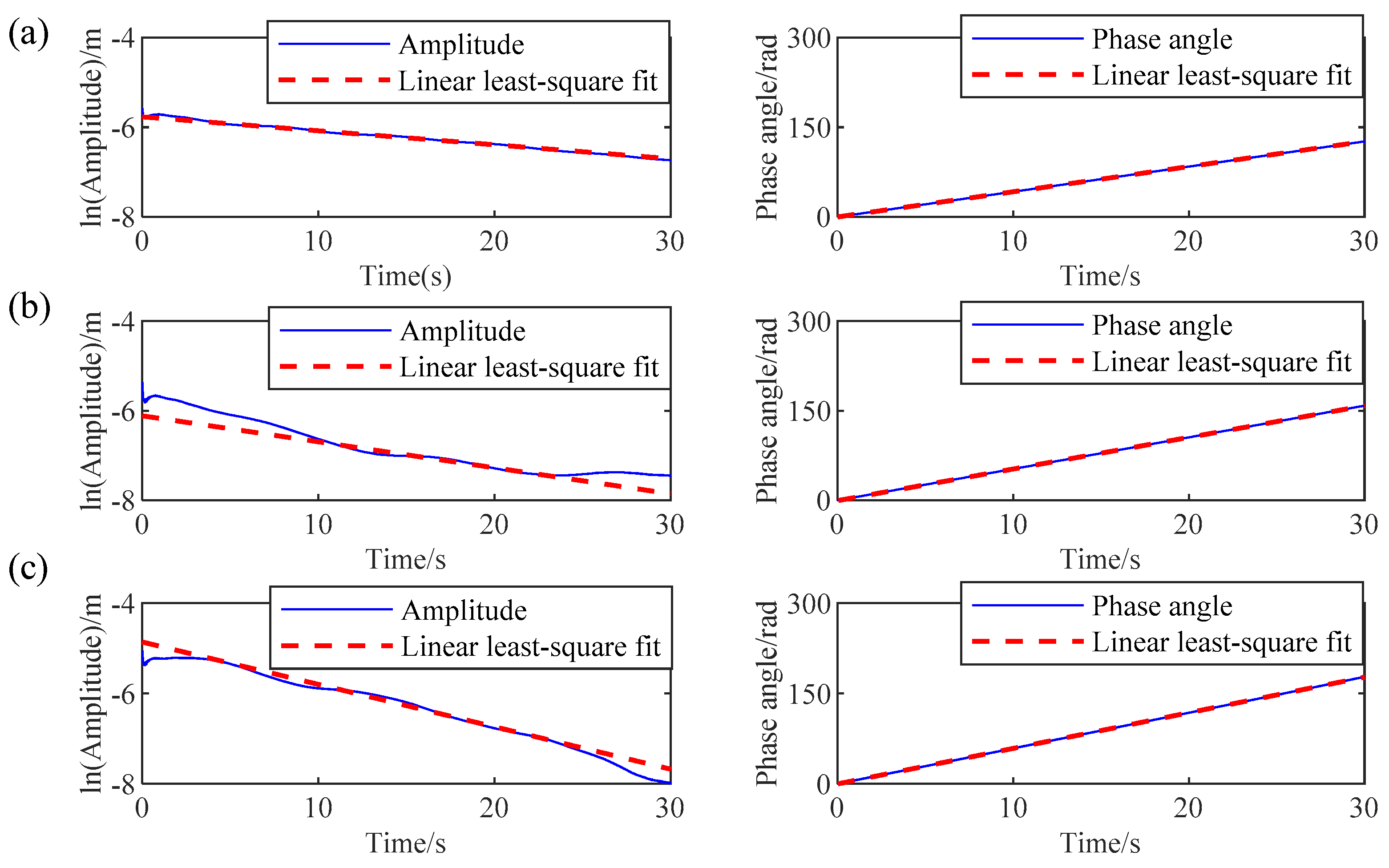
3.3. HT for Modal Parameter Identification
3.4. Procedure of the Proposed Method for Modal Identification
- (1)
- Input the measured response and determine the bisecting frequency of AMD based on the Fourier spectrum.
- (2)
- Use AMD to decompose the measured response into several mono-component modes.
- (3)
- Employ RDT to obtain the free decay response of each mono-component mode.
- (4)
- Apply HT to the free decay responses to identify the frequencies and damping ratios of structures with closely spaced modes.
4. Numerical Examples
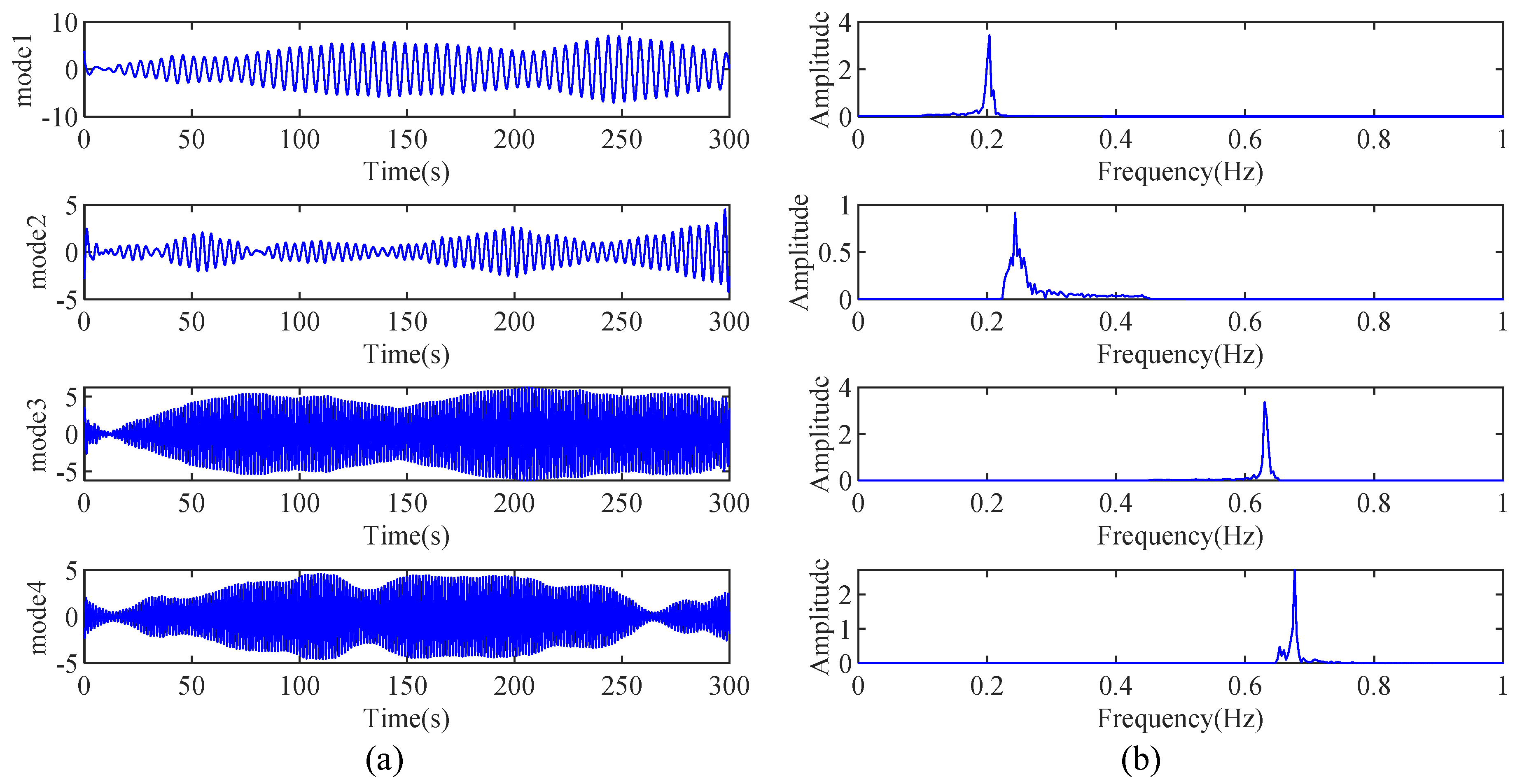
4.1. A 3-DOF Spring-Mass System
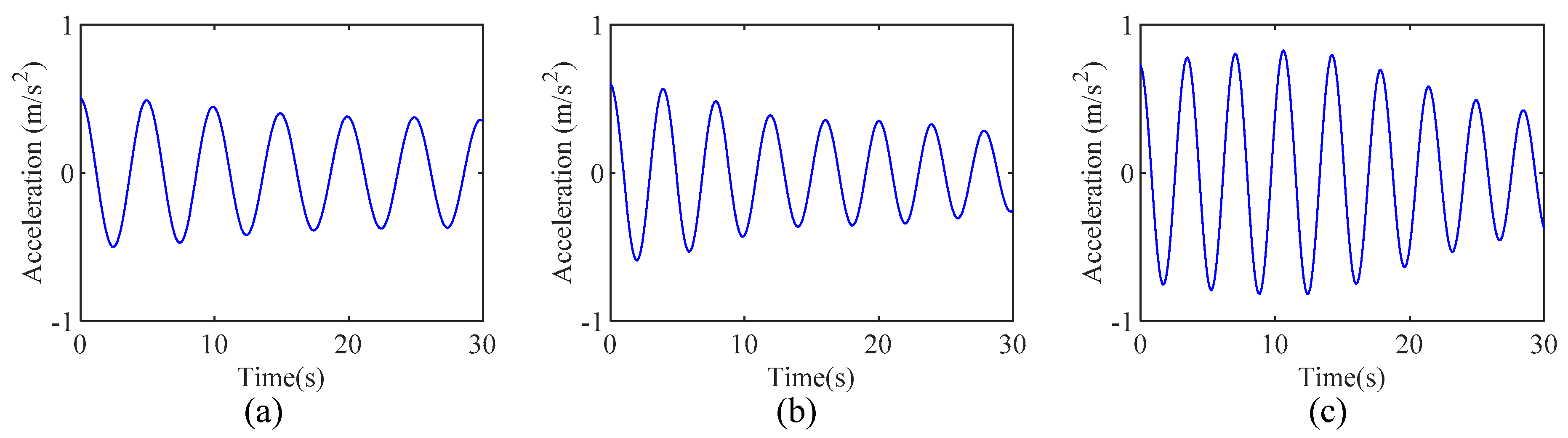
4.2. A High-Rise Building
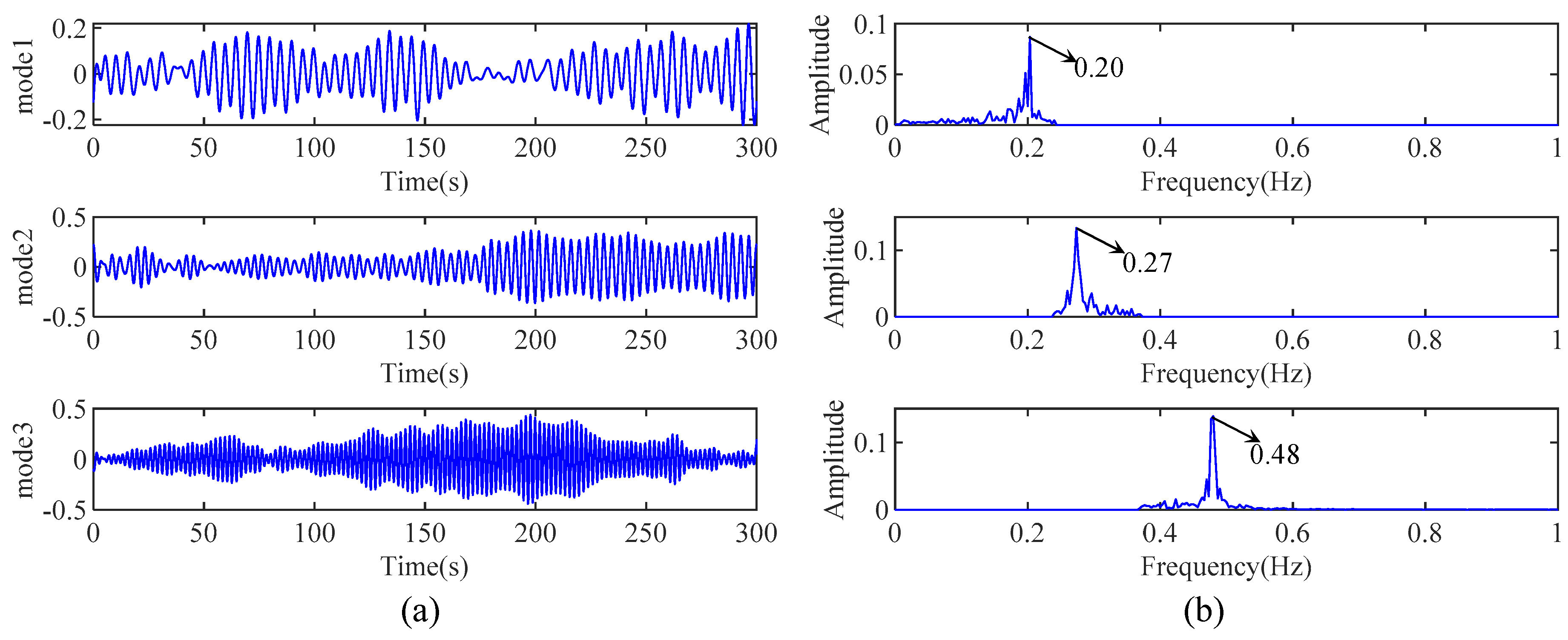
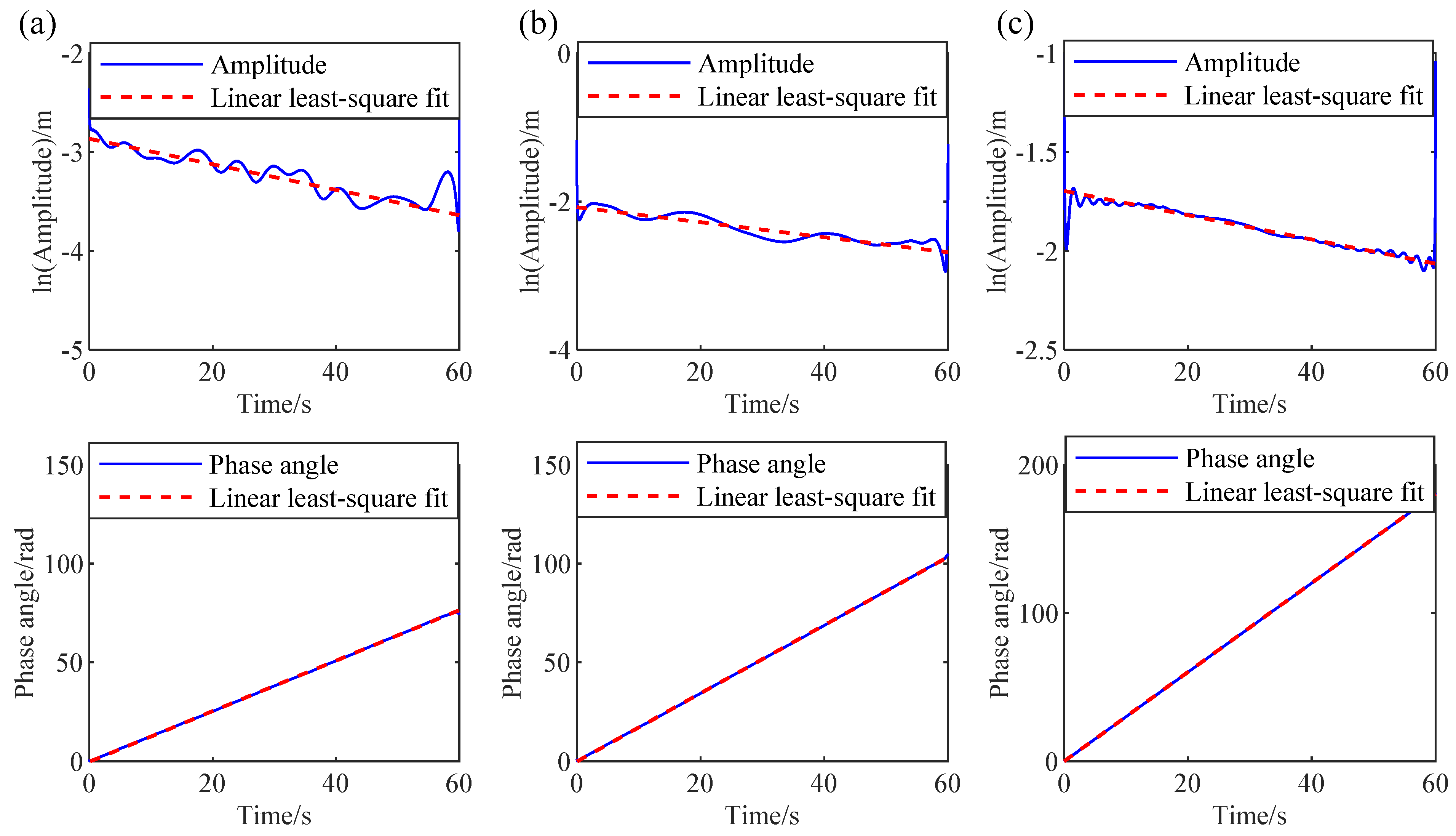
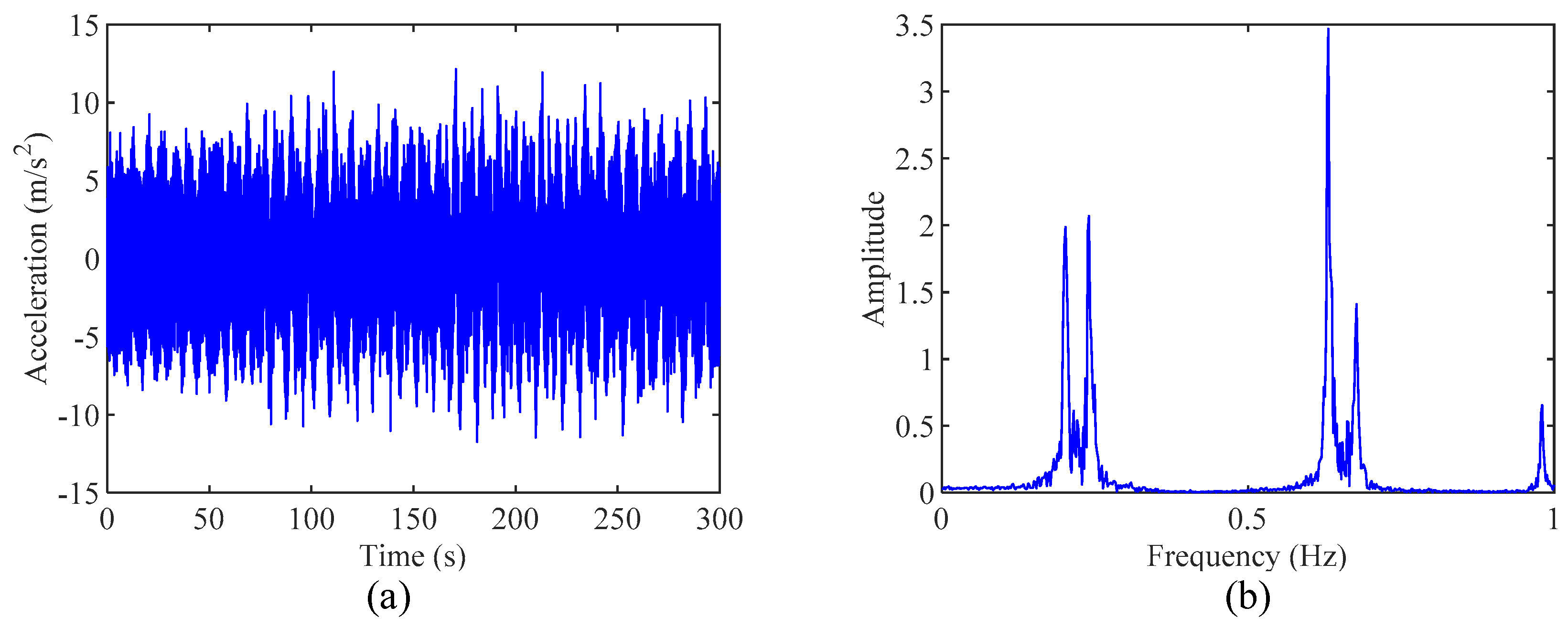
5. Engineering Application in a Long-Span Cable-Stayed Bridge
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Au, S.-K.; Brownjohn, J.M.; Li, B.; Raby, A. Understanding and managing identification uncertainty of close modes in operational modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 147, 107018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Xu, D.; Jankowski, Ł. Structural modal parameter identification with the Power-Exponential window function. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 222, 111771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, G.; Betti, M.; Bartoli, G. A quality-based automated procedure for operational modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 164, 108173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.C.; Lam, H.F.; Zhang, F.L. Assessing uncertainty in fast Bayesian modal identification based on seismic struc-tural responses. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 185, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhi, L.; Zhou, K.; Li, Q.; Kong, F. A novel symplectic geometry-based modal decomposition technique for accurate modal identification of tall buildings with close-spaced modes. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Su, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Zong, H. Identification of closely spaced modes of a long-span suspension bridge based on Bayesian inference. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2023, 23, 2350194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowitz, E.; Brandt, A. Comparison of experimental and operational modal analysis on a laboratory test plate. Measurement 2017, 102, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, S.; Tarazaga, P.A.; Sarlo, R. In situ seismic testing for experimental modal analysis of civil structures. Eng. Struct. 2022, 270, 114773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Pakzad, S.N. Modified natural excitation technique for stochastic modal identification. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, S.D.; Brincker, R. Robust multi-dataset identification with frequency domain decomposition. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 508, 116207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zeng, S. Uncertainty quantification in operational modal analysis of time-varying structures based on time-dependent autoregressive moving average model. J. Sound Vib. 2023, 548, 117549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Tang, B.; Tang, G. An improved stochastic subspace identification for operational modal analysis. Measurement 2012, 45, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Loh, C.; Ni, Y. Stochastic subspace identification for output-only modal analysis: Application to super high-rise tower under abnormal loading condition. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 42, 477–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, E. System identification methods for (operational) modal analysis: Review and comparison. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2012, 19, 51–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, E.; Houbrechts, J.; De Roeck, G. Fully automated (operational) modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 29, 228–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, F.; Cunha, Á. Explaining operational modal analysis with data from an arch bridge. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 1431–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.-K.; Brownjohn, J.M.; Mottershead, J.E. Quantifying and managing uncertainty in operational modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 102, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.M.; Aloisio, A.; Parol, J.; Marano, G.C.; Quaranta, G. Intelligent automatic operational modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 201, 110669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hua, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, F. EMD-based random decrement technique for modal parameter identification of an existing railway bridge. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposi-tion and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.N.; Lei, Y.; Pan, S.; Huang, N. System identification of linear structures based on Hilbert–Huang spectral analysis. Part 1: Normal modes. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2003, 32, 1443–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.N.; Lei, Y.; Lin, S.; Huang, N. Identification of natural frequencies and dampings of in situ tall buildings using ambient wind vibration data. J. Eng. Mech. 2004, 130, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Xie, B.; Li, H.; Zhong, Z.; You, Y. An improved Hilbert–Huang transform method for modal parameter iden-tification of a high arch dam. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 91, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Chen, S.W.; Zhang, R.C. Modal identification of Di Wang Building under Typhoon York using the Hilbert–Huang transform method. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2003, 12, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, O.; Ramezani, S. Enhanced Hilbert-Huang transform and its application to modal identification. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2014, 23, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.-X.; Wang, H.; Feng, D.-M.; Tao, T.-Y.; Zheng, W.-Z. Investigation of dynamic properties of long-span cable-stayed bridges based on one-year monitoring data under normal operating condition. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondra, V.; Sever, I.A.; Schwingshackl, C.W. Identification of complex non-linear modes of mechanical systems us-ing the Hilbert-Huang transform from free decay responses. J. Sound Vibr. 2021, 495, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.-Q.; Huang, T.-L.; Chen, H.-P.; Ren, W.-X.; Lou, M.-L. Recursive variational mode decomposition enhanced by orthogonalization algorithm for accurate structural modal identification. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 197, 110358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.-Q.; Huang, T.-L.; Tang, L.; Chen, H.-P.; Ren, W.-X. Accurate and fast identification of time-varying tension in bridge cables via variational nonlinear chirp mode extraction. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 218, 111574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.-Q.; Tang, L.; Huang, T.-L.; Wang, N.-B.; Ren, W.-X. Time-varying characteristics analysis of bridge under moving vehicle using a modified time-frequency method with limited sensors. Eng. Struct. 2024, 316, 118528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.Q.; Huang, T.L.; Tang, L.; Ren, W.X. An Enhanced Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition for Instantane-ous Frequency Identification of Time-Varying Structures. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2023, 36, 04023050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Xu, D.; Jankowski, Ł.; Liu, Y. Constrained mode decomposition method for modal parameter identification. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2022, 29, e2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Z. A signal decomposition theorem with Hilbert transform and its application to narrowband time series with closely spaced frequency components. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 28, 258–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-C.; Ge, B.; Ren, W.-X.; Hou, J.; Li, D.; He, W.-Y.; Chen, T. Discrete analytical mode decomposition with automatic bisecting frequency selection for structural dynamic response analysis and modal identification. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 484, 115520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Li, T.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Guan, Z.; Chen, G. Application of adaptive wavelet transform based multiple analytical mode decomposition for damage progression identification of Cable-Stayed bridge via shake table test. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 149, 107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Li, Q. Reliability analysis of damping estimation by random decrement technique for high-rise buildings. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 1251–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabamehr, A.; Amani, N.; Bagchi, A. Innovative multi-setup modal analysis using random decrement technique: A novel approach for enhanced structural characterization. Int. J. Struct. Integr. 2024, 15, 902–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, K.; Fatehi, P.; Yazdani, A. On-line system identification of structures using wavelet-Hilbert transform and sparse component analysis. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 870–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Huang, C.S. Identification of instantaneous modal parameter of time-varying systems via a wavelet-based approach and its application. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2014, 29, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.W.; Xia, Y.X. Investigation of mode identifiability of a cable-stayed bridge: Comparison from am-bient vibration responses and from typhoon-induced dynamic responses. Smart. Struct. Syst. 2015, 15, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Methods | Identification Results of Mode 1/Relative Error | Identification Results of Mode 2/Relative Error | Identification Results of Mode 3/Relative Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Freq. (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | Natural Freq. (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | Natural Freq. (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | |
| Theoretical values | 0.199 | 0.19 | 0.275 | 0.34 | 0.479 | 0.45 |
| Proposed IHHT | 0.198/0.5% | 0.18/5.2% | 0.276/0.4% | 0.32/5.8% | 0.477/0.4% | 0.44/2.2% |
| HHT | 0.214/7.5% | 0.25/31.5% | ____ | ____ | ____ | ____ |
| SSI | 0.198/0.5% | 0.21/10.5% | 0.277/0.7% | 0.32/5.8% | 0.476/0.6% | 0.47/4.4% |
| Mode Number | Theoretical Values | Proposed Method/Relative Error | HHT/Relative Error | SSI/Relative Error | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Freq. | Damping Ratio (%) | Natural Freq. | Damping Ratio (%) | Natural Freq. | Damping Ratio (%) | Natural Freq. | Damping Ratio (%) | |
| Mode 1 | 0.202 | 1.00 | 0.204/0.9% | 1.08/8% | 0.187/7.4% | 1.9/90% | 0.201/0.5% | 0.91/9% |
| Mode 2 | 0.243 | 1.00 | 0.244/0.4% | 0.91/9% | ____ | ____ | 0.247/1.6% | 1.24/24% |
| Mode 3 | 0.631 | 1.00 | 0.629/0.3% | 0.89/11% | ____ | ____ | 0.634/0.5% | 1.15/15% |
| Mode 4 | 0.677 | 1.00 | 0.680/0.4% | 0.93/7% | ____ | ____ | 0.673/1.1% | 0.82/18% |
| Mode No. | Finite Element Calculation | Proposed Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Freq. (Hz) | Natural Freq. (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | |
| 1 | 0.170 | 0.166 | 2.27 |
| 2 | 0.226 | 0.227 | 1.76 |
| 3 | 0.262 | 0.263 | 2.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, X.-Q.; Huang, T.-L.; He, Y.-B.; Chen, H.-P. Operational Modal Analysis of Civil Engineering Structures with Closely Spaced Modes Based on Improved Hilbert–Huang Transform. Sensors 2024, 24, 7600. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237600
Shang X-Q, Huang T-L, He Y-B, Chen H-P. Operational Modal Analysis of Civil Engineering Structures with Closely Spaced Modes Based on Improved Hilbert–Huang Transform. Sensors. 2024; 24(23):7600. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237600
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Xu-Qiang, Tian-Li Huang, Yi-Bin He, and Hua-Peng Chen. 2024. "Operational Modal Analysis of Civil Engineering Structures with Closely Spaced Modes Based on Improved Hilbert–Huang Transform" Sensors 24, no. 23: 7600. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237600
APA StyleShang, X.-Q., Huang, T.-L., He, Y.-B., & Chen, H.-P. (2024). Operational Modal Analysis of Civil Engineering Structures with Closely Spaced Modes Based on Improved Hilbert–Huang Transform. Sensors, 24(23), 7600. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237600






