Abstract
Precise monitoring of NOx concentrations in nitric oxide delivery systems is crucial to ensure the safety and well-being of patients undergoing inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Currently, NOx sensing in commercialized iNO instruments predominantly relies on chemiluminescence sensors, which not only drives up costs but also limits their portability. Herein, we developed solid-state gas sensors utilizing Ni-based sensing materials for effectively tracking the levels of NO and NO2 in the NO delivery system. These sensors comprised of NiO-SE or (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE vs. Mn-based RE demonstrated high selectivity toward 100 ppm NO under the interference of 10 ppm NO2 or 3 ppm NO2 under the interference of 100 ppm NO, respectively. Meanwhile, excellent stability, repeatability, and humidity resistance were also verified for the proposed sensors. Sensing mechanisms were thoroughly investigated through assessments of adsorption capabilities and electrochemical reactivity. It turns out that the superior electrochemical reactivity of NiO toward NO, alongside the NO2 favorable adsorption characteristics of (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3), is the primary reason for the high selectivity to NOx. These findings indicate a bright future for the application of these NOx sensors in innovative iNO treatment technologies.
1. Introduction
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a complex and fatal emergency vascular disorder that affects more than 100 million people worldwide, and is mainly found in neonates [1,2]. Compared with oral medicine or injection, inhaled nitric oxide (iNO), a pulmonary vasodilator approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), offers several advantages in the PAH treatment such as noninvasive, targeted, fast onset of action, and less severe systemic adverse effects [3,4,5]. This method, depending on the severity of disease, usually involves the continuous administration of NO gas in the range of 100 ppm by nasal plug or mask [6,7]. However, during treatment, the concentration of NO delivered needs to be tightly controlled in the first place; otherwise, it may cause a rebound in pulmonary arterial pressure and endanger the patient’s life [8]. Additionally, a certain amount of low concentration NO2 may be generated during the transport of NO, which also should be precisely detected timely because such a toxic gas can directly endanger patients’ health when the concentration is above 3 ppm [9,10].
It is worth noting that commercialized iNO systems generally use chemiluminescence devices to measure NO and NO2, which limits portability and leads to very high cost [3,11]. In recent years, with the rapid development of gas sensors, NOx gas sensors based on solid-state YSZ (yttria-stabilized zirconia)-based electrolytes have received extensive attention from researchers due to their high selectivity, desirable sensitivity, and satisfactory stability [12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Moreover, YSZ-based sensors can be fabricated in planar configuration, greatly simplifying the structure of the sensor and facilitating the development of integration for commercially available products [13,19,20]. However, currently reported mixed-potential NOx gas sensors mainly focus on the detection of NO and NO2 in the middle-to-high concentration range of 100–500 ppm in automotive and industrial contexts [21,22,23,24,25], while the iNO treatment instrument normally requires a relatively low NOx detection limit. Furthermore, it is a great challenge to selectively detect 3 ppm NO2 with 100 ppm NO interference, tens times the difference in concentration. Herein, we proposed high-performance YSZ-based NOx sensors by screening out optimal sensing materials. The sensing characteristics of the developed sensors were systematically studied, and we compared the sensors’ performance with some typical NOx gas sensors in Table 1. Moreover, the adsorption capabilities and electrochemical reactivity of these sensors were characteristics to clarify the working principle.

Table 1.
Our work in contrast with the literature.
2. Experimental
2.1. Fabrication of Sensors
Figure 1 depicts the schematic components of the planar sensor. Initially, commercial MnO2 powder (99% purity, Sigma Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Taufkirchen, Germany) was thoroughly mixed with α-terpineol, and the obtained paste was painted on the YSZ plate (length × width × thickness: 2.75 × 0.5 × 0.1 cm3; NIKKATO CORPORATION, Osaka, Japan); after drying at 130 °C for 4 h, the YSZ plate attached with the MnO2 layer was calcined at 1400 °C for 2 h in a muffle furnace to form the Mn-based reference electrode (RE). Various commercial metal oxides (Sigma Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Taufkirchen, Germany, with a purity of 99%) were fabricated with a similar procedure and both were calcined at high temperature for 2 h to form the sensing electrodes (SE).
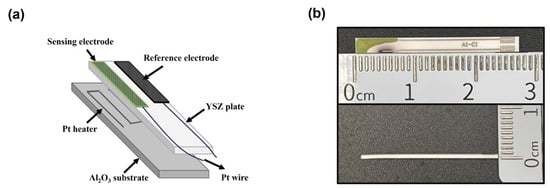
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic illustration of the planar YSZ-based gas sensor; (b) the fabricated miniaturized YSZ-based sensor.
2.2. Evaluation of Sensing Characteristics
The fabricated sensor was set in a quartz tube, and alternatively exposed to the base gas (21 vol.% O2, N2 balance) or the sample gas containing NO, NO2 (total flow rate: 100 mL·min−1) for 5 min. As the sensors are expected to be applied in iNO treatment devices in which the process of NO generation and transportation is tightly controlled, as a result, there are few interference gases excepted NO2 and the concentration of NO2 is below 10 ppm in reality. Moreover, the NO at specific concentrations will be directly inhaled by the patients. Taking these factors into account, in such a specific application, the NO tested concentration range was 10–100 ppm in 21 vol% O2, N2 balance, and the NO2 tested concentration range was 1.5–10 ppm in 21 vol% O2, N2 balance. An adjustable DC power supply (SS-3305D, A-BF, Dongguan, China) controls the Pt heater’s working voltage to provide a high working temperature for the sensors; notably, the temperatures of the experiments mentioned in the following research just represent the temperature of a tiny area (approximately: 0.4 × 0.4 cm2) on the sensor’s surface rather than the whole tests chamber. And there is no significant heat spread, so the temperature of transported gas flow is virtually unaffected. The electrochemical signals were recorded by a Data Acquisition/Switch Unit (34970A, Agilent, Nanjing, China) via Pt wire connected, and the potential difference ΔV (ΔV = VSample gas − VBase gas) represented the sensor’s response to sample gas. The surface morphology of calcined powders was observed by Scanning Electron Microscope (Gemini 360, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) with an excitation voltage of 15 kV, and the crystalline phase was characterized by X-ray diffraction (D8 DaVinci, Bruker, Berlin, Germany). Finally, microcantilever chips and an integrated Gas Sensing System (LoC-GSS 1000, High-End MEMS Technology, Xiamen, China) were utilized to test the sensing materials’ gas adsorption.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening of Nitric Oxide Sensing Materials and Developing a High-Performance NO Sensor
The sensing mechanism of mixed-potential type NOX can be interpreted by mixed potential theory [13], where the electrochemical reactions for NO (NO2) and O2 occur simultaneously at the SE/YSZ interface as follows.
For NO:
For NO2:
It can be seen that NO and NO2 undergo different reactions respectively and the responses to NO and NO2 for YSZ-based NOX sensors are opposite to each other. Generally, the response is negative to NO and positive to NO2.
Several metal oxides were selected as potential candidates for a NO sensing material, and among the examined SEs, In2O3−SE not only gave the highest potential value of 100 ppm NO but also a higher potential value of 10 ppm NO2, resulting in poor NO selectivity (Figure 2). In contrast, NiO-SE showed both desirable NO sensitivity and selectivity in comparison with other examined materials. Consequently, NiO was predicted to be the optimal material for NO detection due to its higher sensitivity and selectivity.
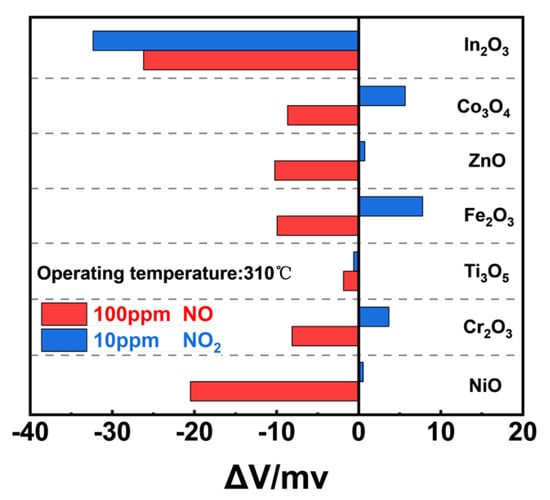
Figure 2.
Comparison of sensing responses to 100 ppm NO and 10 ppm NO2 in air.
The SEM image in Figure 3 shows that the NiO powder annealed at 1200 °C was plate-like and relatively compact. According to former research showing that plate−like metal oxides normally exhibit better selectivity to NO [30,31], we anticipated desirable selectivity for NiO toward NO when against NO2.
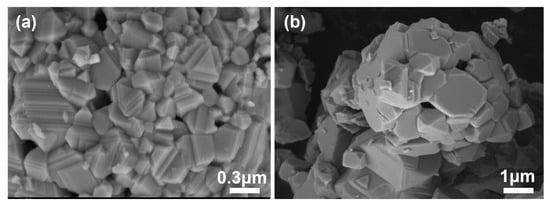
Figure 3.
SEM image of NiO powders after calcination with (a) high magnification; (b) low magnification.
To confirm the practicability of using NiO tracking a high level of NO with high selectivity against 10 ppm NO2, sensing characteristics of the YSZ−based gas sensor comprised of NiO-SE vs. Mn−-based RE were studied. Figure 4a depicts the relationship between the sensor’s response and the operating/calcination temperature for the NiO−SE; it can be confirmed that the optimal response signal was observed for the sensor fabricated at 1200 °C. Moreover, it should be noted the operated temperature of YSZ solid electrolyte must be above 300 °C [32]. And it needs to be clarified that when the operating temperature was below 300 °C, the conductivity of YSZ was greatly reduced, which led to poor recovery characteristics and noticeable noise in the sensor’s response curves. Consequently, the optimal operating/calcination temperature was selected at 310 °C and 1200 °C for the following study. As shown in Figure 4b, the response signal of the sensor varied linearly to the logarithm of the NO concentration in the range of 10–100 ppm. According to the repeated response transients of the sensor that were exposed to 100 ppm NO and 10 ppm NO2 (Figure 4c), it can be concluded that the sensor gave excellent repeatability in the successive runs and high selectivity to 100 ppm NO (24.7 mV) against 10 ppm NO2 (less than 1 mV). In light of the long-term stability, which is a crucial factor in practical applications. A 35-day test to 100 ppm NO was further measured under 310 °C, as shown in Figure 4d, variation in the response value during the tested period was roughly estimated to be less than 3 mV, indicating satisfactory stability of the sensor using NiO-SE and Mn−based RE.
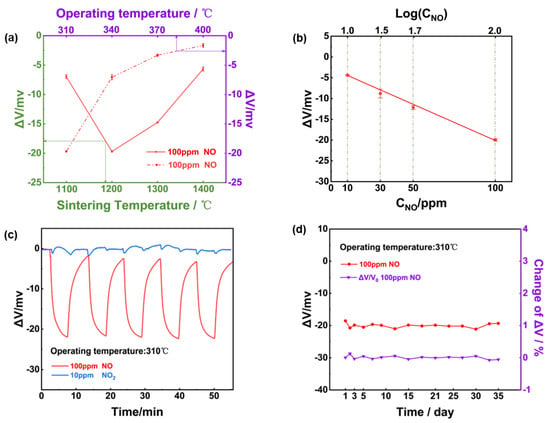
Figure 4.
Sensing characteristics of the NiO−SE NO sensor in 21% O2 with N2 balance: (a) variation of the response signal to 100 ppm NO on the operational/calcination temperature; (b) dependence of the response signal on the logarithm of the NO concentration in the range of 10−100 ppm at 310 °C; (c) repeated response transients to 100 ppm NO and 10 ppm NO2 of the sensor at 310 °C; (d) long−term stability of the sensor to 100 ppm NO within 35−days.
To further justify the NiO-SE sensor’s ability to differentiate NO in a mixture, Figure 5a compared the responses of the sensor to 100 ppm NO interfered with different concentrations of NO2. It could be concluded that the response to 100 ppm NO changed little and the NiO-SE sensor showed excellent anti-interference capability. In addition, the sensor may work under relatively high humidity environments in real practical applications, and Figure 5b illustrates the responses and the change in response values of the NiO-SE sensor at 0%, 24%, 67%, and 91% RH separately to 100 ppm NO at 310 °C. The maximum |ΔV| value was 5% under the range of 0–91% RH, proving that the sensor displays good humidity resistance.
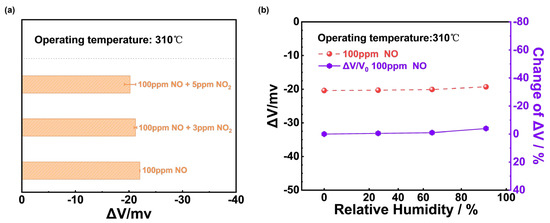
Figure 5.
(a) Sensing behavior of NiO−SE sensor to 100 ppm NO mixed with different concentrations of NO2; (b) humidity effect on the response values of NiO−SE sensor under 0−91% RH to 100 ppm NO at 310 °C.
3.2. Screening of Nitric Dioxide Sensing Materials and Developing a High-Performance NO2 Sensor
It is a great challenge to detect low concentration of NO2 compared to ten times the concentration of NO, and pure metal oxides as sensing materials are hardly able to realize the research target. Recently, spinel−based oxides have proven to be good candidates for NOx sensing. For instance, NiFe2O4 was reported to be a potential NO2 sensing material but the inadequate detection limit (LOD) down to 5 ppm limits its application in iNO treatment technologies [23,33,34]. In order to improve the sensing behavior of NO2, it is believed that adding additives or dopants to NiFe2O4 would effectively extend the LOD [35,36]. In the meantime, Fe2O3 was announced that not only exhibited the same trivalent cation as the NiFe2O4’s AB2O4 general formula but also demonstrated acceptable capability to detect NO2 [37]. Thus, we added Fe2O3 into NiFe2O4 in an attempt to enhance the NO2 detection capacity.
Figure 6 demonstrated the XRD patterns for NiFe2O4, Fe2O3, and (NiFe2O4 + x wt.% Fe2O3) composites after calcined at 1200 °C for 2 h. No impurity peaks were observed, confirming the high purity of the products. However, there were no characteristic diffraction peaks of Fe2O3 for the composite materials; the reason for this could be Fe2O3’s lower loading content and weak crystallization.
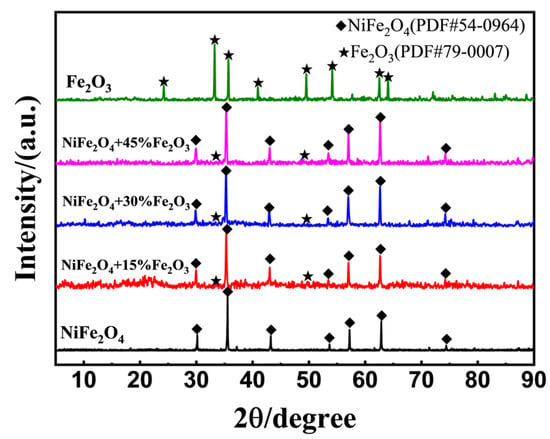
Figure 6.
XRD patterns of NiFe2O4, Fe2O3, and (NiFe2O4 + x wt.% Fe2O3) composites (x = 15%, 30%, 45%), with calcined at 1200 °C for 2 h.
Furthermore, micro-structures of NiFe2O4, Fe2O3, and their composite (e.g., NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3) were characterized via scanning electron microscope (SEM) and presented in Figure 7. In comparison with NiFe2O4 (Figure 7a,b) and Fe2O3 (Figure 7c,d), a certain amount of grains (with a diameter of around 0.6 μm), which could be assigned to NiFe2O4, was observed in the NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3 composite. Moreover, it is reasonable to deduce that the formed composite had a more porous and three-dimensional (3D) structure when compared with that of NiFe2O4. The porous 3D micro-structure would offer more active reaction sites for NO2.

Figure 7.
SEM images of (a,b) NiFe2O4; (c,d) Fe2O3; (e,f) NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3 composite sensing electrodes prepared at 1200 °C in different scales.
Accordingly, sensing behavior to detect 3 ppm NO2 and 100 ppm NO for the YSZ−based gas sensor utilizing NiFe2O4 and its composite-SEs (vs. Mn-based RE) was examined. As shown in Figure 8a, when the amount of Fe2O3 reaches 30%, the sensor gave superior selectivity and sensitivity to 3 ppm NO2 against 100 ppm NO. In other words, the YSZ−based gas sensor using (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE is a good candidate for tracking the trace amount of NO2. Figure 8b suggests the optimal operating/calcination temperature was 390 °C/1200 °C.
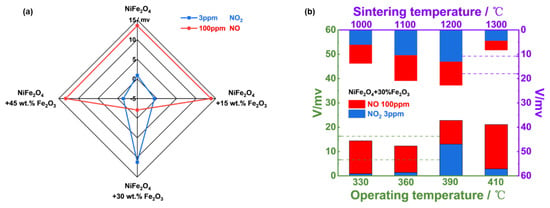
Figure 8.
(a) Response magnitude to 3 ppm NO2 and 100 ppm NO in 21% O2 with N2 balance respectively for the YSZ-based sensors comprising NiFe2O4/Fe2O3 composite SEs and Mn−based RE, operated at 390 °C; (b) effect of change in operating/sintering temperature on the sensing characteristic of the sensor using (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE in 21% O2 with N2 balance.
The dependence of the sensing response on the NO2 concentration in the range of 1.5–10 ppm was examined and a linear relationship between response value and NO2 concentration on a logarithmic scale (Figure 9a). Notably, it can be concluded that after aging for several days (2–3 days), the response signal of the sensor to 100 ppm NO significantly decreased, whereas it maintained a high response value of 3 ppm NO2 (Figure 9b). This phenomenon might be caused by the sensing materials’ gas phase catalytic reaction to NO, whereby a certain amount of NO was converted to NO2 before arriving at the TPB, and both NO and NO2 triggered the electrochemical reaction in reality. Based on the aforementioned Reaction (1)–(4), the measured potential signal was the final response after the response of NO offset the response of NO2. However, in early tests, the mixed materials’ properties were not yet stable, and the conversion efficiency of NO was dynamic. After several days of aging, the NO conversion rate stabilized and the sensor’s response to NO was maintained. Figure 9c,d further indicates the sensor’s excellent repeatability and stability as well as ultra-high selectivity to 3 ppm NO2.
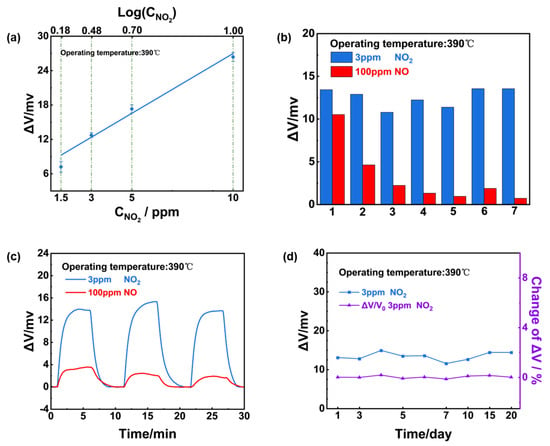
Figure 9.
Sensing characteristics of the YSZ−based gas sensor using (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE: (a) Dependence of the response signal on the logarithm of the NO2 concentration in the range of 1.5–10 ppm at 390 °C; (b) repeated response to 3 ppm NO2 and 100 ppm NO during aging process; (c) repeated response transients to 3 ppm NO2 and 100 ppm NO; (d) long−term stability of the sensor to 3 ppm NO2 within 20 day.
The selectivity to NO2 of (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE could be reinforced in Figure 10a. The responses of the sensor only reduced less than 4 mv even when 3 ppm NO2 was mixed with 90 ppm NO and it could be concluded that the (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE sensor showed excellent selectivity to NO2 at 390 °C. The sensing performance of the (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE sensor on the variation in the water vapor content (0–91% RH) was also studied, and Figure 10b shows that the sensor’s response values to 3 ppm NO2 were hardly affected by the change in humidity, which could be ascribed to the desorption of water at such a high operating temperature.
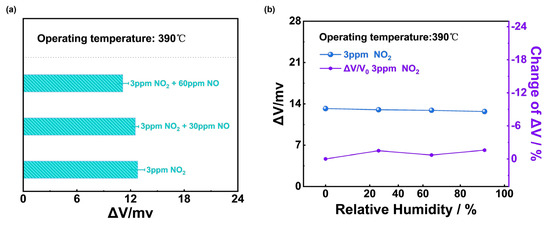
Figure 10.
(a) Sensing behavior of (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE sensor to 3 ppm NO2 mixed with different concentrations of NO; (b) humidity effect on the response values of (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE sensor under 0–91% RH to 3 ppm NO2 at 390 °C.
3.3. Study on the Sensing Mechanism
According to the working principle of an electrochemical gas sensor, the target gas initially selectively adsorbs on the surface of the sensing material and then participates in the following electrochemical reaction. In this case, both adsorption capabilities and electrochemical reactivity contribute to the final response selectivity and response value. To understand which step primarily determines the widely concerned selectivity during NOx sensing, we initially used microgravimetric technology [38,39] to compare the NOx adsorption capabilities of each sensing material. In this study, changes in the microcantilever’s vibration frequency directly reflected the difference in the adsorption capabilities of NO and NO2.
Figure 11 shows the frequency shift to 100 ppm NO and 10 ppm NO2 of NiO, respectively. In repeated tests, the frequency shift to NO was greater than that of NO2, implying that NiO preferred to adsorb NO molecules when exposed to the NOx mixture. In a similar manner, the gas adsorption capabilities of NiFe2O4(+30 wt.% Fe2O3) were examined and are presented in Figure 12. It is reasonable to conclude that (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3) exhibits similar adsorption capability to both 3 ppm NO2 and 100 ppm NO, since only a minor difference in the frequency shift to NO and NO2 was observed.
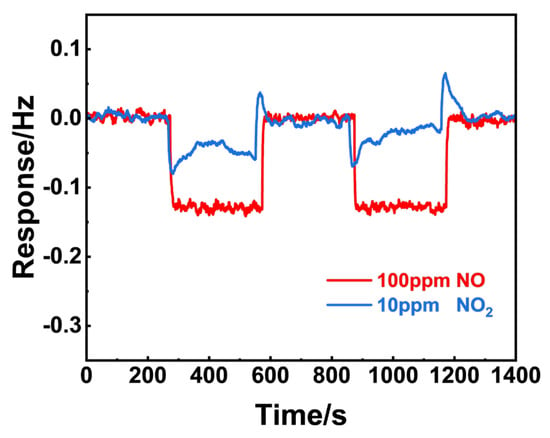
Figure 11.
Comparison of the 100 ppm NO and 10 ppm NO2 gas adsorption for NiO using the resonant microcantilever.

Figure 12.
Comparison of the 100 ppm NO and 3 ppm NO2 gas adsorption for (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3) calcined at 1200 °C using the resonant microcantilever.
To further understand the mechanism for the sensors’ different selectivity, polarization curves were measured in the sample gas (3 ppm NO2, 10 ppm NO2, 10 ppm NO, and 100 ppm NO, in 21% O2, with N2 balanced) and air, which could reflect the reaction rate for the electrochemical reaction that occurred in TPB (triple-phase boundary). Figure 13a shows that when the bias voltage was 0 mV, the current value difference between various sample gases at different concentrations and air was small, and it can be inferred that NiO-SE had poor electrochemical catalytic activity to NO and NO2. On the contrary, an obvious current difference between NO2 and NO is given in Figure 13b. Furthermore, a higher current value of NO2 suggests that the (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE had better electrochemical catalytic activity of NO2, compared with NO.
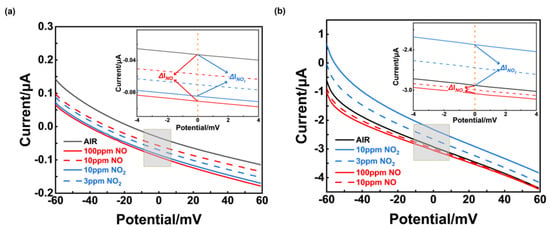
Figure 13.
Polarization curves in different concentrations of NO and NO2 using different sensors: (a) sensor using NiO−SE, operated at 310 °C; (b) sensor using (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.%Fe2O3)−SE, operated at 390 °C (ΔINO and ΔINO2 represent the current value generated from NO or NO2, respectively).
Through a comparative analysis of gas adsorption capabilities and electrochemical reactivity, we can conclude that the response selectivity of the sensor using NiO−SE primarily arises from its strong adsorption affinity for NO (confirmed by Figure 11). Although NiO exhibits similar electrochemical catalytic activity toward both NO and NO2 (Figure 13a), it demonstrates a significant difference in the adsorption of these gases. Conversely, for the sensor utilizing (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE, the notable selectivity for NO2 can be attributed to the high electrochemical reactivity of NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3 with NO2, as only a minor difference was observed in its adsorption capabilities (as presented in Figure 12 and Figure 13b).
4. Conclusions
To precisely track the level of NOx during iNO treatment, we developed YSZ-based gas sensors comprised of Ni-based SEs and Mn-based RE. These sensors using NiO or (NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3)-SE demonstrated high selectivity, desirable stability, and excellent repeatability to high-level NO or low-level NO2. The working principle of these sensors can be summarized that NO preferred to be adsorbed on the surface of NiO, while NiFe2O4 + 30 wt.% Fe2O3 composite demonstrated high electrochemical reactivity to NO2, resulting in satisfactory sensing characteristics for these sensors in tracking the variation of NOx. However, it should be noted that due to the high operational temperature of these sensors, it is necessary to overcome the limitations of high power consumption in practical applications. Additionally, the current response times might not be fast enough for real-time monitoring, and some strategies, such as a porous sensing layer to accelerate the diffusion rates of gases and machine learning for sensors’ response characteristics to recognize the differences in short-term transient response processes, will be further investigated to improve sensors’ efficiency. In summary, these findings mark a bright future for the application of robust and high-performance NOx sensors in innovative iNO treatment technologies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.C., Y.Z. (Yangbo Zhao), Y.Z. (Yuyan Zhang), and H.J.; Data curation, Z.Z. and C.Y.; Formal analysis, Z.Z., C.Y., and H.J.; Investigation, Z.Z., C.Y., and H.J.; Methodology, H.J.; Project administration, H.J.; Resources, T.C. and H.J.; Supervision, H.J.; Validation, Z.Z.; Visualization, Z.Z.; Writing—original draft, Z.Z.; Writing—review and editing, H.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support for this research from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2022YFE0118800, 62227815, 52000133), “the Belt and Road” young scientist exchange program of the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai (Grant No. 20490743000), Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. WF220403061), Sichuan Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2022NSFSC0390, KX002), Oceanic Interdisciplinary Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Grant No. SL2020MS014), and Program of National Key Laboratory (SKLPBS2249).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the application of patents.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Tao Chen, Yangbo Zhao, Yuyan Zhang were employed by the company Nanjing Novlead Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Abman, S.H.; Hansmann, G.; Archer, S.L.; Ivy, D.D.; Adatia, I.; Chung, W.K.; Hanna, B.D.; Rosenzweig, E.B.; Raj, J.U.; Cornfield, D.; et al. Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension. Circulation 2015, 132, 2037–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarz, A.; Kadry, H.; Alobaida, A.; Ahsan, F. Newer approaches and novel drugs for inhalational therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, J.P.; Parker, T.A.; Ivy, D.D.; Abman, S.H. Noninvasive delivery of inhaled nitric oxide therapy for late pulmonary hypertension in newborn infants with congential diaphragmatic hernia. J. Pediatr. 2003, 142, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinose, F.; Roberts, J.D.; Zapol, W.M. Inhaled Nitric Oxide. Circulation 2004, 109, 3106–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, I.R.; Sagliani, K.D.; Roberts, K.E.; Shah, A.M.; DeSouza, S.A.; Howard, W.; Brennan, J.; Hill, N.S. Comparison of Acute Hemodynamic Effects of Inhaled Nitric Oxide and Inhaled Epoprostenol in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barst, R.J.; Channick, R.; Ivy, D.; Goldstein, B. Clinical Perspectives with Long-Term Pulsed Inhaled Nitric Oxide for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2012, 2, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, M.L.; Romer, L.H.; Bembea, M.M. Spectrum of Current Management of Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertensive Crisis. Crit. Care Explor. 2019, 1, e0037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBlasi, R.M.; Myers, T.R.; Hess, D.R. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline: Inhaled nitric oxide for neonates with acute hypoxic respiratory failure. Respir. Care 2010, 55, 1717–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger, B.; Laskin, D.L.; Heck, D.E.; Laskin, J.D. The toxicology of inhaled nitric oxide. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 59, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, D.M.; Bekker, J.M.; Johengen, M.J.; Hendricks-Munoz, K.; Gerrets, R.; Black, S.M.; Fineman, J.R. Inhaled nitric oxide-induced rebound pulmonary hypertension: Role for endothelin-1. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H777–H785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Su, Z.; Yan, Y.; Feng, B.; Mao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; et al. An electrochemical nitric oxide generator for in-home inhalation therapy in pulmonary artery hypertension. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y. Metal oxide gas sensors for detecting NO2 in industrial exhaust gas: Recent developments. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 359, 131579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Sato, T.; Anggraini, S.A.; Ikeda, H.; Zhuiykov, S. A review of mixed-potential type zirconia-based gas sensors. Ionics 2014, 20, 901–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Liu, X.; Jin, H.; Zhan, Z.; Jian, J. NO2 sensing properties of electrode-supported sensor by tape casting and co-firing method. Ionics 2015, 21, 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergus, J. Materials for high temperature electrochemical NOx gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 121, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.O.; Miura, N. Absolute potential analysis of the mixed potential occurring at the oxide/YSZ electrode at high temperature in NO-containing air. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 113, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiyan, K.P.; Mukundan, R. Editors’ Choice—Review—Recent Advances in Mixed Potential Sensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanytsia, I.; Viricelle, J.-P.; Vernoux, P.; Pijolat, C. Application of advanced morphology Au–X (X=YSZ, ZrO2) composites as sensing electrode for solid state mixed-potential exhaust NOx sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; You, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Z.; He, J.; Liu, A.; et al. Compact and planar type rapid response ppb-level SO2 sensor based on stabilized zirconia and SrMoO4 sensing electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhao, J.; Hoa, N.D.; Hieu, N.V.; Ganeev, A.A.; Chuchina, V.; Jouyban, A.; Cui, D.; et al. Integrated Smart Gas Tracking Device with Artificially Tailored Selectivity for Real-Time Monitoring Food Freshness. Sensors 2023, 23, 8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Yan, X.; Sun, P.; Wang, L.; et al. Mixed potential type YSZ-based NO2 sensors with efficient three-dimensional three-phase boundary processed by electrospinning. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 354, 131219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, X.; Hong, X. Medium-Low-Temperature NO2 Sensor Based on YSZ Solid Electrolyte and Mesoporous WO3 Sensing Electrode for Detection of Vehicle Emissions. Nano 2021, 16, 2150083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, B.; Yu, H.; Xia, F.; Xiao, J. Superior sensitive NiFe2O4 electrode for mixed-potential NO2 sensor. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 2962–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, A.; You, R.; Liu, F.; Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Jin, R.; He, J.; Yang, Z.; et al. High-response mixed-potential type planar YSZ-based NO2 sensor coupled with CoTiO3 sensing electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Effects of Electrode Microstructures on the Sensitivity and Response Time of Mixed-Potential NO2 Sensor Based on La0.6Sr0.4CoO3 Sensing Electrode. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 8621–8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Akisada, K.; Wang, J.; Zhuiykov, S.; Ono, T. Mixed-potential-type NOx sensor based on YSZ and zinc oxide sensing electrode. Ionics 2004, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.; Chatterjee, S.; Macam, E.; Wachsman, E. Effect of Electrode Microstructure on the Sensitivity and Response Time of Potentiometric NO Sensors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, N.F.; Du, H.; Akbar, S.A.; Soliman, A.; Dutta, P.K. Microporous zeolite modified yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) sensors for nitric oxide (NO) determination in harsh environments. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 82, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, D.; Zosel, J.; Guth, U. NO sensitivity of perovskite-type electrode materials La0.6Ca0.4B′1−xB″xO3±δ (B′=Mn, Cr; B″=Ni, Fe, Co; x=0, 0.1, …, 0.6) in mixed potential sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Huang, Y.; Jian, J. Plate-like Cr2O3 for highly selective sensing of nitric oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Huang, Y.; Jian, J. Sensing mechanism of the zirconia-based highly selective NO sensor by using a plate-like Cr2O3 sensing electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 219, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Lu, G.; Yamazoe, N. Progress in mixed-potential type devices based on solid electrolyte for sensing redox gases. Solid State Ionics 2000, 136–137, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.-M.; Yang, H.-F.; Shen, G.-L.; Yu, R.-Q. Hydrogen sulfide sensing properties of NiFe2O4 nanopowder doped with noble metals. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 102, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuiykov, S.; Muta, M.; Ono, T.; Hasei, M.; Yamazoe, N.; Miura, N. Stabilized Zirconia-Based NOx Sensor Using ZnFe2O4 Sensing Electrode. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2001, 4, H19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Xiong, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiao, J. Promoted Carbon Monoxide Sensing Performance of a Bi2Mn4O10-Based Mixed-Potential Sensor by Regulating Oxygen Vacancies. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 2978–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Shi, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhang, J. Black Phosphorus–Tungsten Oxide Sandwich-like Nanostructures for Highly Selective NO2 Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangale, S.S.; Jadhav, V.V.; Shaikh, S.F.; Shinde, P.V.; Ghule, B.G.; Raut, S.D.; Tamboli, M.S.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Mane, R.S. Facile one-step hydrothermal synthesis and room-temperature NO2 sensing application of α-Fe2O3 sensor. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeders, K.M.; Colton, J.S.; Bottomley, L.A. Microcantilevers: Sensing Chemical Interactions via Mechanical Motion. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Xu, P.; Zheng, D.; Yu, H.; Li, X. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Resonant-Gravimetric Detection of Trace-Level Xylene Molecules. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12234–12240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).