Augmented Physics-Based Models for High-Order Markov Filtering
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Augmented Physics-Based Model
1.2. Augmented State for High-Order Markov Models
1.3. Contributions
2. Augmented-State APBM for High-Order Markov Models
2.1. Augmented-State APBM
2.2. Approximated-State APBM
3. Numerical Simulations
3.1. AR Model
- Processor (CPU): Intel Core i7-10700KF, 8 cores, 3.80 GHz. The multi-core CPU allowed for efficient parallel processing during data preprocessing.
- Memory (RAM): 32 GB DDR4.
- Storage: 1 TB NVMe SSD.
- Operating System: Windows 11 Pro.
- Software Platform: MATLAB R2023a.
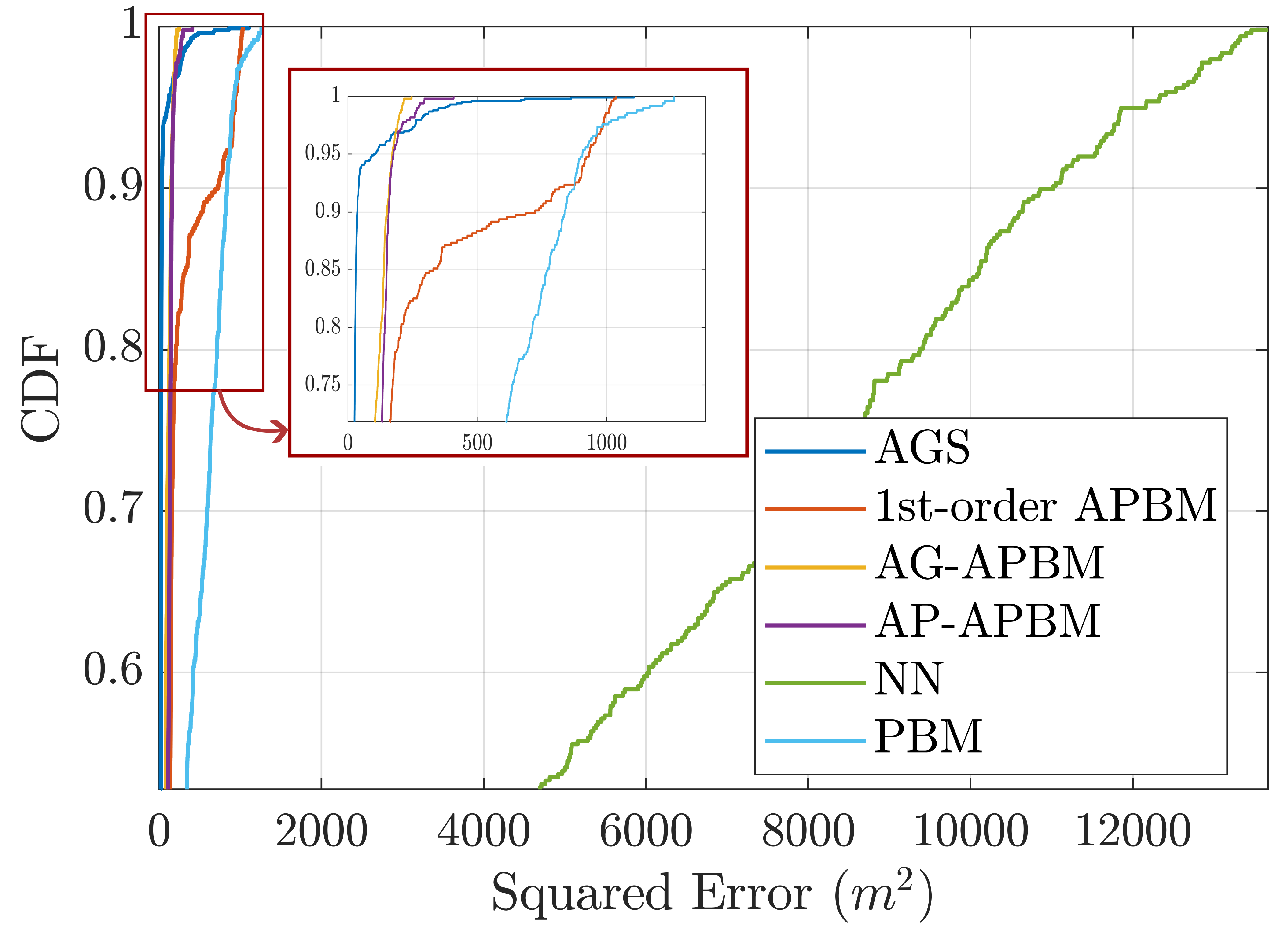
3.2. A Delayed-Feedback Control Nonlinear Model
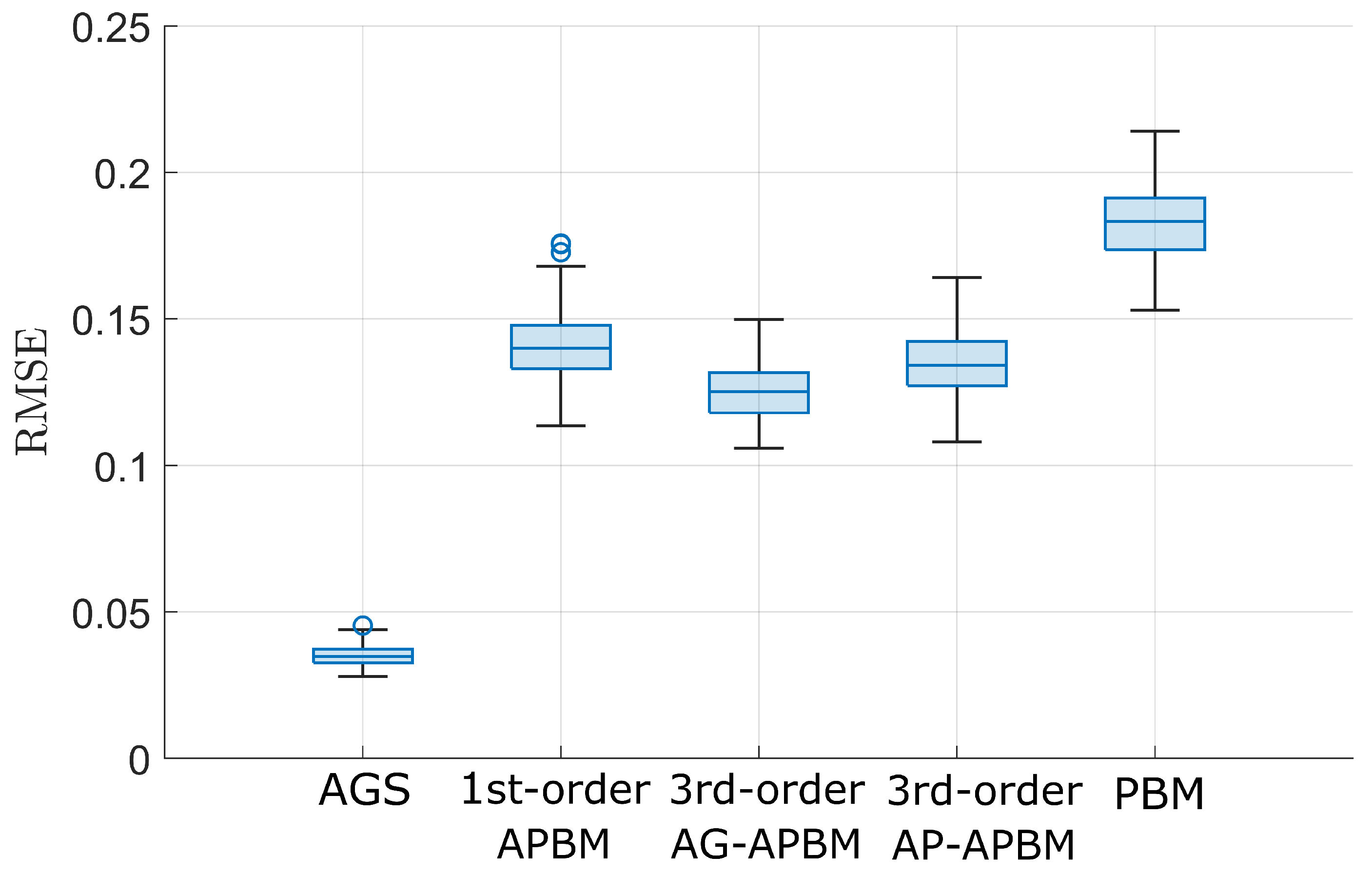
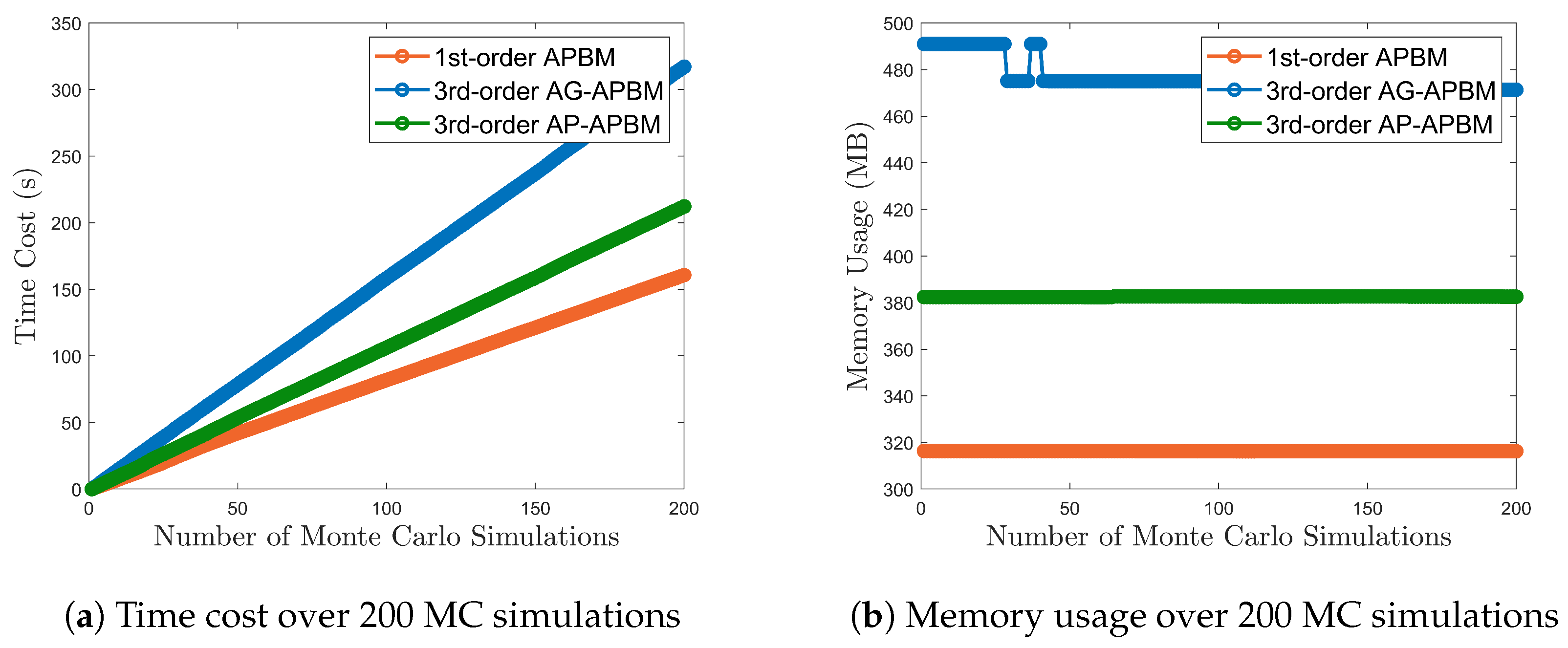
3.3. AG-APBM and AP-APBM Performance
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| State vector at time instance k | |
| Measurement vector at time instance k | |
| Noise of the dynamics model | |
| Noise of the measurement model | |
| Possibly nonlinear measurement model | |
| Possibly nonlinear true dynamics model | |
| Physics-based model (PBM) | |
| Augmented physics-based model (APBM) | |
| Neural network (NN) parameters | |
| Noise of NN parameter dynamics model | |
| Pseudo-measurement for NN parameter regularization | |
| Noise of NN parameter pseudo-measurement model | |
| Augmented state vector at time instance k | |
| Augmented-state APBM (AG-APBM) | |
| Noise of AG-APBM | |
| Estimated state at time instance k | |
| Dirac delta function |
References
- Duník, J.; Biswas, S.K.; Dempster, A.G.; Pany, T.; Closas, P. State Estimation Methods in Navigation: Overview and Application. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2020, 35, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Särkkä, S.; Svensson, L. Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Kalman, R.E. Contributions to the theory of optimal control. Bol. Soc. Mat. Mex. 1960, 5, 102–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, E.A.; Van Der Merwe, R. The unscented Kalman filter. In Kalman Filtering and Neural Networks; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 221–280. [Google Scholar]
- Arasaratnam, I.; Haykin, S. Cubature Kalman filters. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulampalam, M.S.; Maskell, S.; Gordon, N.; Clapp, T. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Gu, Z.; Park, J.H.; Shen, M. Fusion-Based Event-Triggered H-infinity State Estimation of Networked Autonomous Surface Vehicles With Measurement Outliers and Cyber-Attacks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 7541–7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Gao, S.; Qi, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Distributed cubature H-infinity information filtering for target tracking against uncertain noise statistics. Signal Process. 2020, 177, 107725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, F.; Xu, S. State-of-charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on improved H infinity filter algorithm and its novel equalization method. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoqing, L.; Borsoi, R.A.; Imbiriba, T.; Closas, P.; Bermudez, J.C.M.; Erdoğmuş, D. Model-Based Deep Autoencoder Networks for Nonlinear Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbiriba, T.; Wu, P.; LaMountain, G.; Erdoğmuş, D.; Closas, P. Recursive Gaussian Processes and Fingerprinting for Indoor Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Portland, ON, USA, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 933–940. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, L. Application of neural networks in target tracking data fusion. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidehi, V.; Chitra, N.; Krishnan, C.; Chokkalingam, M. Neural network aided Kalman filtering for multitarget tracking applications. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2001, 27, 217–228. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Yan, J.; Zhou, S.; Varshney, P.; Liu, H. Long short-term memory-based deep recurrent neural networks for target tracking. Inf. Sci. 2019, 502, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Wu, L. Training multilayer perceptrons with the extended Kalman algorithm. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1988, 1. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/1988/file/38b3eff8baf56627478ec76a704e9b52-Paper.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Haykin, S. Kalman Filtering and Neural Networks; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Imbiriba, T.; Demirkaya, A.; Duník, J.; Straka, O.; Erdoğmuş, D.; Closas, P. Hybrid neural network augmented physics-based models for nonlinear filtering. In Proceedings of the 2022 25th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Linköping, Sweden, 4–7 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Imbiriba, T.; Straka, O.; Duník, J.; Closas, P. Augmented physics-based machine learning for navigation and tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 2692–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A. An introduction to hidden Markov models for biological sequences. In New Comprehensive Biochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 32, pp. 45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.M.; Lee, J.C. A study on high-order hidden Markov models and applications to speech recognition. In International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 682–690. [Google Scholar]
- Salnikov, V.; Schaub, M.T.; Lambiotte, R. Using higher-order Markov models to reveal flow-based communities in networks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urteaga, I.; Djurić, P.M. Sequential estimation of hidden ARMA processes by particle filtering—Part one. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 65, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric, P.M.; Kay, S.M. Order selection of autoregressive models. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1992, 40, 2829–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M.; Nasrabadi, N.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Raftery, A.E. A model for high-order Markov chains. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1985, 47, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwijn, B.; Porta, J.M.; Kröse, B.J. A particle filter to estimate non-Markovian states. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Autonomous Systems, IAS, Singapore, 22–25 June 2004; Volume 4, pp. 1062–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Guo, J.; He, D.; Guo, W. Adaptive Kalman filtering based on optimal autoregressive predictive model. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway, R.H.; Stoffer, D.S.; Stoffer, D.S. Time Series Analysis and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kerns, A.J.; Shepard, D.P.; Bhatti, J.A.; Humphreys, T.E. Unmanned aircraft capture and control via GPS spoofing. J. Field Robot. 2014, 31, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, M.T.; Lau, D.; Witham, K.L.; Closas, P.; LaMountain, G.M. System for Closed-Loop GNSS Simulation. US Patent Application No. 17/662,822, 10 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Li, X.R.; Kirubarajan, T. Estimation with Applications to Tracking and Navigation: Theory Algorithms and Software; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kost, O.; Duník, J.; Straka, O. Measurement difference method: A universal tool for noise identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, H.; Achilles, F.; DiPietro, R.; Navab, N.; Tombari, F. Long short-term memory Kalman filters: Recurrent neural estimators for pose regularization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5524–5532. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Niu, R. EKFNet: Learning system noise statistics from measurement data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 4560–4564. [Google Scholar]
- Revach, G.; Shlezinger, N.; Ni, X.; Escoriza, A.L.; Van Sloun, R.J.; Eldar, Y.C. KalmanNet: Neural network aided Kalman filtering for partially known dynamics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 1532–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstinsky, A. Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (RNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) network. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2020, 404, 132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. NIPS 2017. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Imbiriba, T.; Duník, J.; Straka, O.; Closas, P. Augmented Physics-Based Models for High-Order Markov Filtering. Sensors 2024, 24, 6132. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186132
Tang S, Imbiriba T, Duník J, Straka O, Closas P. Augmented Physics-Based Models for High-Order Markov Filtering. Sensors. 2024; 24(18):6132. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186132
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Shuo, Tales Imbiriba, Jindřich Duník, Ondřej Straka, and Pau Closas. 2024. "Augmented Physics-Based Models for High-Order Markov Filtering" Sensors 24, no. 18: 6132. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186132
APA StyleTang, S., Imbiriba, T., Duník, J., Straka, O., & Closas, P. (2024). Augmented Physics-Based Models for High-Order Markov Filtering. Sensors, 24(18), 6132. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186132






