Accuracy Validation of a Sensor-Based Inertial Measurement Unit and Motion Capture System for Assessment of Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Older Adults—A Novel and Convenient Measurement Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Participants and Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Method
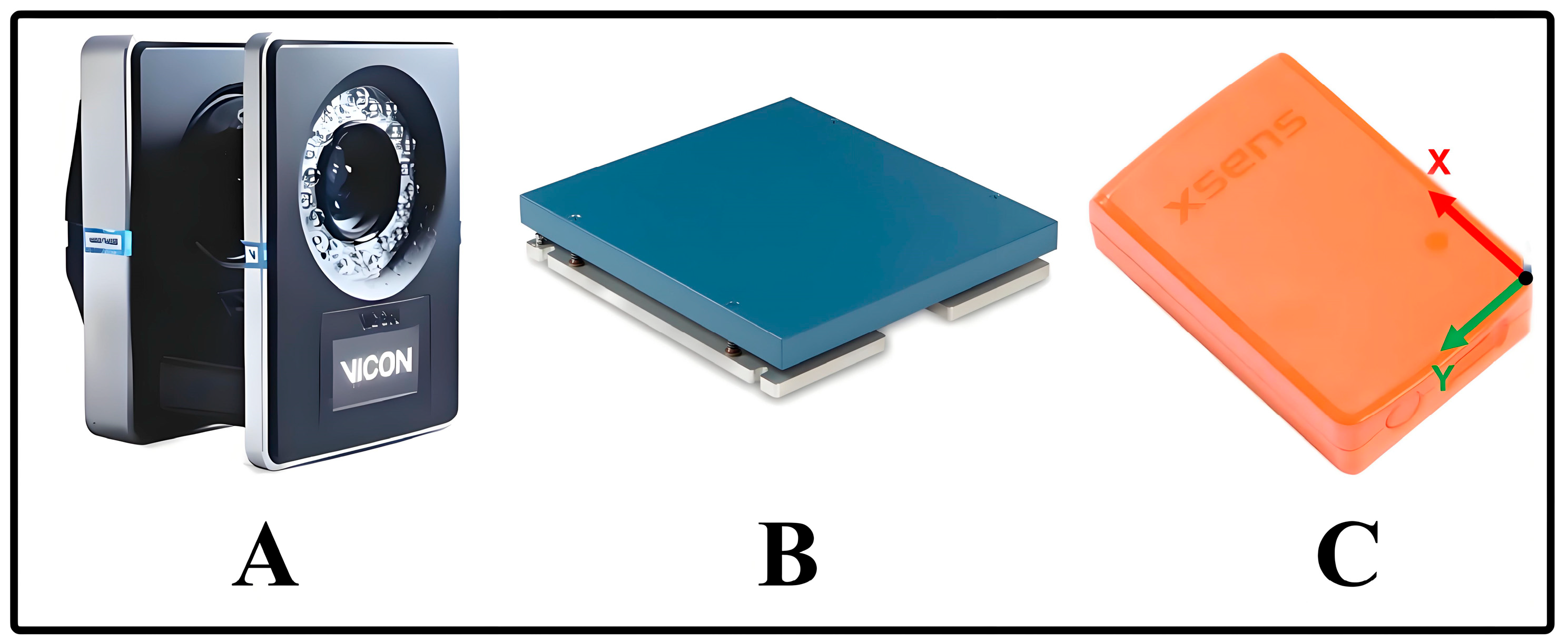
2.2.1. Instrumentation
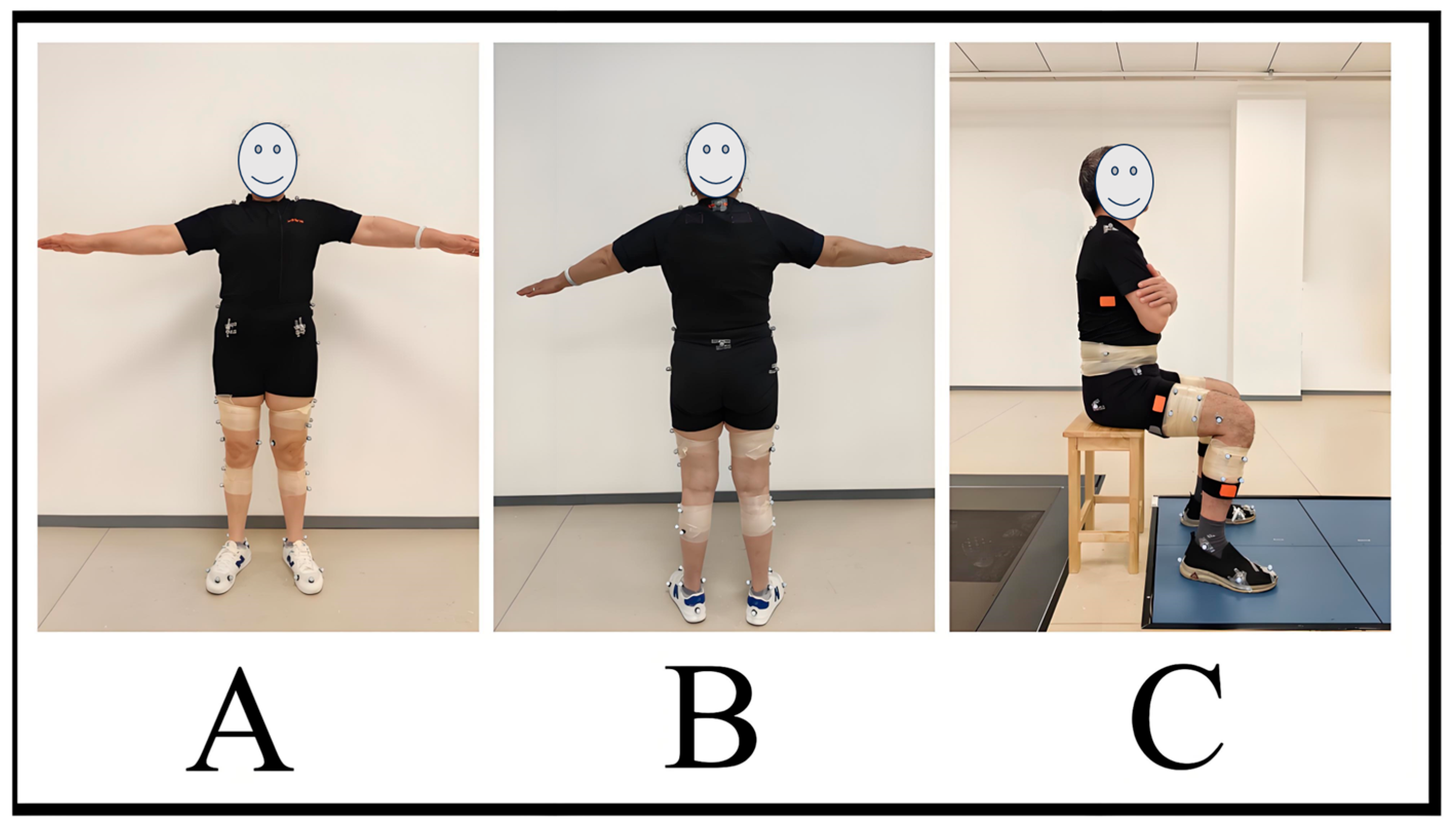
2.2.2. Test Protocols
2.2.3. Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
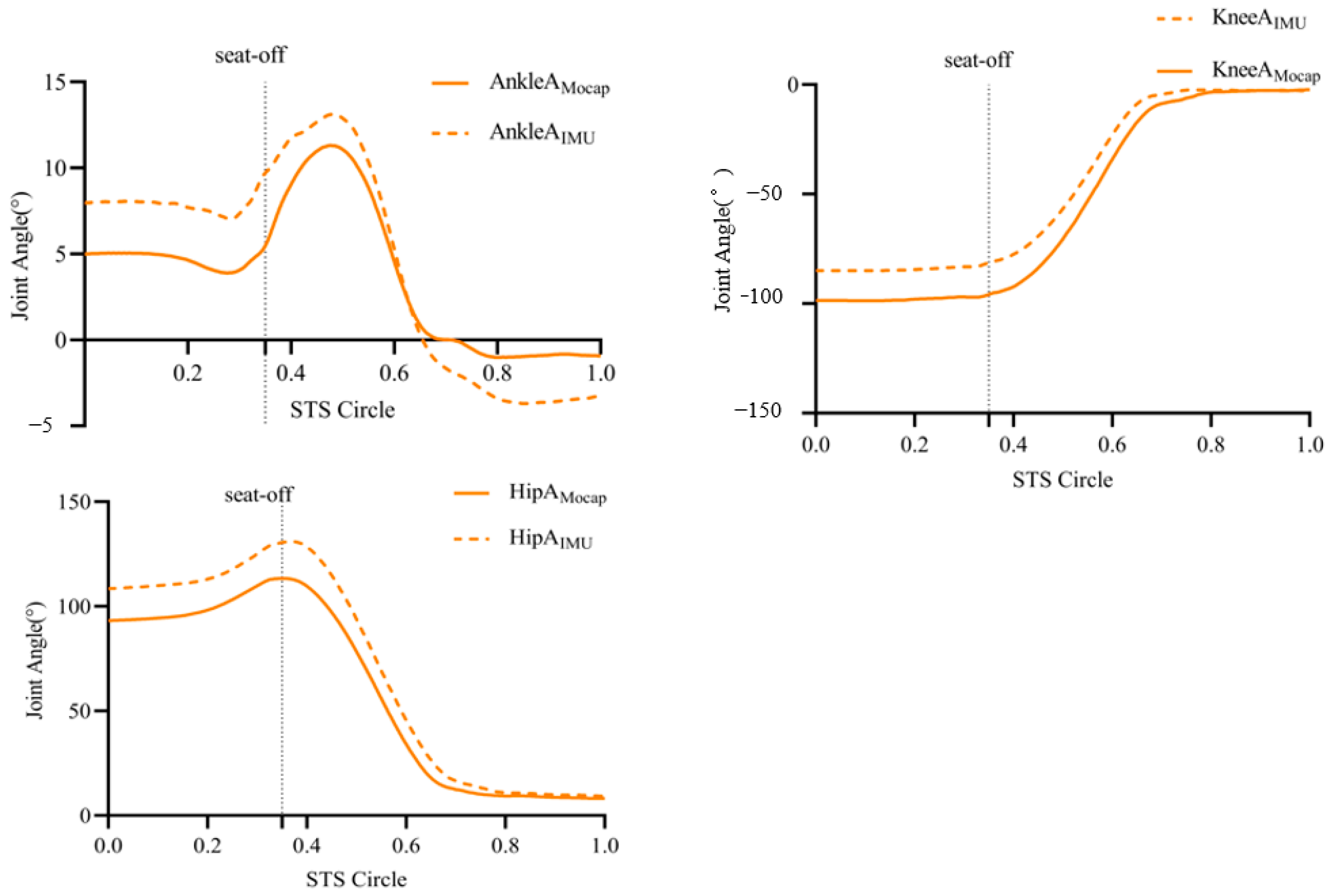
3.1. Peak Joint Angle Results within the Sagittal Plane of the Hip, Knee, and Ankle Joints Captured by the Two Systems
3.2. Results of Peak Joint Moments in the Sagittal Plane of the Hip, Knee, and Ankle Joints Collected by the Two Systems
3.2.1. Consistency Test
3.2.2. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regterschot, G.R.; Folkersma, M.; Zhang, W.; Baldus, H.; Stevens, M.; Zijlstra, W. Sensitivity of sensor-based sit-to-stand peak power to the effects of training leg strength, leg power and balance in older adults. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irisawa, H.; Mizushima, T. Assessment of changes in muscle mass, strength, and quality and activities of daily living in elderly stroke patients. International journal of rehabilitation research. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2022, 45, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H. Tools for assessing fall risk in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Ambrose, T.; Davis, J.C.; Best, J.R.; Dian, L.; Madden, K.; Cook, W.; Hsu, C.L.; Khan, K.M. Effect of a Home-Based Exercise Program on Subsequent Falls among Community-Dwelling High-Risk Older Adults After a Fall: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschung Pfister, P.; de Bruin, E.D.; Sterkele, I.; Maurer, B.; de Bie, R.A.; Knols, R.H. Manual muscle testing and hand-held dynamometry in people with inflammatory myopathy: An intra- and interrater reliability and validity study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Ciesla, N.D.; Truong, A.D.; Bhoopathi, V.; Zeger, S.L.; Needham, D.M. Inter-rater reliability of manual muscle strength testing in ICU survivors and simulated patients. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Odasso, M.; van der Velde, N.; Martin, F.C.; Petrovic, M.; Tan, M.P.; Ryg, J.; Aguilar-Navarro, S.; Alexander, N.B.; Becker, C.; Blain, H.; et al. World guidelines for falls prevention and management for older adults: A global initiative. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Ha, S.; Lee, K.; Hong, S.; Shin, H.; Lee, G. Development of a sit-to-stand assistive device with pressure sensor for elderly and disabled: A feasibility test. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2021, 44, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, C.; Fairhall, N.J.; Wallbank, G.K.; Tiedemann, A.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Howard, K.; Clemson, L.; Hopewell, S.; Lamb, S.E. Exercise for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 1, CD012424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcazar, J.; Losa-Reyna, J.; Rodriguez-Lopez, C.; Alfaro-Acha, A.; Rodriguez-Mañas, L.; Ara, I.; García-García, F.J.; Alegre, L.M. The sit-to-stand muscle power test: An easy, inexpensive and portable procedure to assess muscle power in older people. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 112, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, S.; Nagano, A.; Hay, D.C.; Fukashiro, S. The minimum required muscle force for a sit-to-stand task. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-de-Villa, S.; Ruiz, L.R.; Neira, G.G.; Alvarez, M.N.; Huertas-Hoyas, E.; Del-Ama, A.J.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, M.C.; Seco, F.; Jimenez, A.R. Validation of an IMU-based Gait Analysis Method for Assessment of Fall Risk Against Traditional Methods. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.J.; Wong, N.L.; Law, M.C.; Lam, F.M.; Wong, H.C.; Chan, T.O.; Wong, K.N.; Zheng, Y.P.; Huang, Q.Y.; Wong, A.Y.; et al. Reliability, Validity, and Identification Ability of a Commercialized Waist-Attached Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) Sensor-Based System in Fall Risk Assessment of Older People. Biosensors 2023, 13, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Lebel, K.; Bogard, S.; Goubault, E.; Boissy, P.; Duval, C. Using Inertial Sensors to Automatically Detect and Segment Activities of Daily Living in People with Parkinson’s Disease. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanko, R.M.; Outerleys, J.B.; Laende, E.K.; Selbie, W.S.; Deluzio, K.J. Comparison of Concurrent and Asynchronous Running Kinematics and Kinetics from Marker-Based and Markerless Motion Capture Under Varying Clothing Conditions. J. Appl. Biomech. 2024, 40, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altai, Z.; Boukhennoufa, I.; Zhai, X.; Phillips, A.; Moran, J.; Liew, B.X.W. Performance of multiple neural networks in predicting lower limb joint moments using wearable sensors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1215770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koska, D.; Gaudel, J.; Hein, T.; Maiwald, C. Validation of an inertial measurement unit for the quantification of rearfoot kinematics during running. Gait Posture 2018, 64, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristianslund, E.; Krosshaug, T.; van den Bogert, A.J. Effect of low pass filtering on joint moments from inverse dynamics: Implications for injury prevention. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Ye, M. Noninvasive Estimation of Joint Moments with Inertial Sensor System for Analysis of STS Rehabilitation Training. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 6570617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Cutti, A.G.; Cappello, A. A new formulation of the coefficient of multiple correlation to assess the similarity of waveforms measured synchronously by different motion analysis protocols. Gait Posture 2010, 31, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Cárdenas, J.D.; Montemurro, A.; Martínez-García, M.D.M.; Rodríguez-Juan, J.J. Sit-to-Stand Video Analysis-Based App for Diagnosing Sarcopenia and Its Relationship with Health-Related Risk Factors and Frailty in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Diagnostic Accuracy Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e47873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedian-Nasab, N.; Jaberi, A.; Shirazi, F.; Kavousipor, S. Effect of virtual reality exercises on balance and fall in elderly people with fall risk: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, J.M.; Nakaishi, A.P.M.; Cangussu-Oliveira, L.M.; Freire Júnior, R.C.; Spilla, S.B.; Abreu, D.C.C. Relationship between grip strength and global muscle strength in community-dwelling older people. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 82, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochicchio, G.; Ferrari, L.; Bottari, A.; Lucertini, F.; Scarton, A.; Pogliaghi, S. Temporal, Kinematic and Kinetic Variables Derived from a Wearable 3D Inertial Sensor to Estimate Muscle Power during the 5 Sit to Stand Test in Older Individuals: A Validation Study. Sensors 2023, 23, 4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Iizuka, T.; Irisawa, K.; Imura, S. Detection of Movement Events of Long-Track Speed Skating Using Wearable Inertial Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, H.; Jehu, D.A.; Daneshjoo, A.; Shakoor, E.; Razeghi, M.; Amani, A.; Hakim, M.N.; Yusof, A. Effects of 8 Weeks of Balance Training, Virtual Reality Training, and Combined Exercise on Lower Limb Muscle Strength, Balance, and Functional Mobility among Older Men: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sports Health 2021, 13, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, D.; Hassett, L.; Schurr, K.; Fairhall, N.J.; Cameron, I.D.; Sherrington, C. Mobility training for increasing mobility and functioning in older people with frailty. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 6, CD010494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.T.; Liang, P.J.; Lee, S.C. Differences in walking-to-turning characteristics between older adult fallers and nonfallers: A prospective and observational study using wearable inertial sensors. International journal of rehabilitation research. Internationale Zeitschrift fur Rehabilitationsforschung. Rev. Int. Rech. Readapt. 2022, 45, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Larsson, S.C. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: Prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2023, 144, 155533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemson, L.; Stark, S.; Pighills, A.C.; Fairhall, N.J.; Lamb, S.E.; Ali, J.; Sherrington, C. Environmental interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 3, CD013258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalumiere, M.; Villeneuve, C.; Bellavance, C.; Goyette, M.; Bourbonnais, D. Patterns of lower limb muscular activity and joint moments during directional efforts using a static dynamometer. BMC Biomed. Eng. 2020, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McComb, A.; Warkentin, L.M.; McNeely, M.L.; Khadaroo, R.G. Development of a reconditioning program for elderly abdominal surgery patients: The Elder-friendly Approaches to the Surgical Environment-BEdside reconditioning for Functional ImprovemenTs (EASE-BE FIT) pilot study. World J. Emerg. Surg. WJES 2018, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, A.I.; Majumder, S.; Mondal, T.; Cowan, D.; Naseh, S.; Deen, M.J. Monitoring Methods of Human Body Joints: State-of-the-Art and Research Challenges. Sensors 2019, 19, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, J.; Yang, C. Effective adaptive Kalman filter for MEMS-IMU/magnetometers integrated attitude and heading reference systems. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7151–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number of Persons (Male/Female) | Age (Years) | Height (m) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | SPPB (Score) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 (13/15) | 64.79 ± 4.58 | 1.61 ± 0.07 | 63.15 ± 7.69 | 24.3 ± 1.96 | 10.6 ± 0.9 |
| Joint | P-Amocap (°) | P-AIMU (°) | RMSE (°) | p-Value | r | ICC (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankle | 10.67 ± 2.98 | 13.02 ± 2.84 | 2.5 | 0.091 | 0.96 * | 0.885 (0.862, 0.904) |
| Knee | −99.2 ± 15.37 | −85.95 ± 18.67 | 10.2 | 0.125 | 0.99 * | 0.989 (0.987, 0.991) |
| Hip | 113.3 ± 19.18 | 130.4 ± 19.60 | 12.4 | 0.372 | 0.99 * | 0.990 (0.988, 0.992) |
| Joint | P-Mmocap (N/kg) | P-MIMU (N/kg) | RMSE (N/kg) | p-Value | r | ICC (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankle | −0.27 ±0.12 | −0.31 ± 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.85 * | 0.89 (0.77, 0.95) |
| Knee | 0.83 ± 0.13 | 0.96 ± 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.68 | 0.96 * | 0.92 (0.87, 0.97) |
| Hip | −0.86 ± 0.18 | −0.90 ± 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.92 | 0.92 * | 0.94 (0.90, 0.98) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, N. Accuracy Validation of a Sensor-Based Inertial Measurement Unit and Motion Capture System for Assessment of Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Older Adults—A Novel and Convenient Measurement Approach. Sensors 2024, 24, 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186040
Zhu Y, Li H, Wu X, Chen N. Accuracy Validation of a Sensor-Based Inertial Measurement Unit and Motion Capture System for Assessment of Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Older Adults—A Novel and Convenient Measurement Approach. Sensors. 2024; 24(18):6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186040
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Ye, Haojie Li, Xie Wu, and Nan Chen. 2024. "Accuracy Validation of a Sensor-Based Inertial Measurement Unit and Motion Capture System for Assessment of Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Older Adults—A Novel and Convenient Measurement Approach" Sensors 24, no. 18: 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186040
APA StyleZhu, Y., Li, H., Wu, X., & Chen, N. (2024). Accuracy Validation of a Sensor-Based Inertial Measurement Unit and Motion Capture System for Assessment of Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Older Adults—A Novel and Convenient Measurement Approach. Sensors, 24(18), 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186040







