Sensitive Coatings Based on Molecular-Imprinted Polymers for Triazine Pesticides’ Detection †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Designing Sensitive Coatings for Detecting Pesticides
2.3.1. Effect of Acid Content on Sensitivity of Sensor Coatings
2.3.2. Template Removal
2.3.3. IR Analysis for Template Removal
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reeves, W.R.; McGuire, M.K.; Stokes, M.; Vicini, J.L. Assessing the safety of pesticides in food: How current regulations protect human health. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Tan, P.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Advances in organophosphorus pesticides pollution: Current status and challenges in ecotoxicological, sustainable agriculture, and degradation strategies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, S.; Kour, J.; Singh, A.D.; Devi, K.; Tikoria, R.; Ali, M.; Kumar, D.; Ohri, P.; Bhardwaj, R. Impact of pesticide application on the food chain and food web. In Pesticides in a Changing Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 87–118. [Google Scholar]
- Onyeaka, H.; Ghosh, S.; Obileke, K.; Miri, T.; Odeyemi, O.A.; Nwaiwu, O.; Tamasiga, P. Preventing chemical contaminants in food: Challenges and prospects for safe and sustainable food production. Food Control 2024, 155, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Nadeem, M.A.; Nawaz, H.; Amin, M.M.; Abbasi, G.H.; Nadeem, M.; Ali, M.; Ameen, M.; Javaid, M.M.; Maqbool, R. Pesticides: Impacts on agriculture productivity, environment, and management strategies. In Emerging Contaminants and Plants: Interactions, Adaptations and Remediation Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 109–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Ahmad, F.A.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Zeyaullah, M.; AlShahrani, A.M.; Muzammil, K.; Saati, A.A.; Wahab, S.; Elbendary, E.Y.; Kambal, N. Pesticides impacts on human health and the environment with their mechanisms of action and possible countermeasures. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Moreno, A.C.; Mejia-Grau, K.; Puente-DelaCruz, L.; Codling, G.; Villa, A.L.; Ríos-Marquez, O.; Patequiva-Chauta, L.; Cobo, M.; Johnson-Restrepo, B. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (pbdes), polychlorinated biphenyls (pcbs), organochlorine pesticides (ocps) in human breast milk from colombia: A probabilistic risk assessment approach. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.A.; Mahmood, D.; Abd Elmoneim, O.E.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Khan, M.I.; Ashfaq, F.; Patel, M.; Snoussi, M.; Kieliszek, M.; Adnan, M. Exposure to pesticide residues in honey and its potential cancer risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 180, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yao, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, N.; Hu, X.; Lv, H.; Mu, B.; Wang, J. Fosthiazate, a soil-applied nematicide, induces oxidative stress, neurotoxicity and transcriptome aberrations in earthworm (Eisenia fetida). J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 463, 132865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sánchez, E.D.; Ortiz, G.G.; Reyes-Uribe, E.; Torres-Jasso, J.H.; Salazar-Flores, J. Effect of pesticides on phosphorylation of tau protein, and its influence on alzheimer’s disease. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polaka, S.; Raji, S.; Singh, A.; Katare, P.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 26—connecting link between pesticides and parkinson’s disease. In Public Health and Toxicology Issues in Drug Research; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 735–754. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, D.; Verma, R.K.; Sharma, V.; Kaur, A.; Rai, A.R.; Kumari, P.; Nagar, V.; Sankhla, M.S.; Parihar, K. Associations between high levels pesticide and adverse reproductive outcomes in females: A comprehensive review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 95, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; Crespi, C.; Vergara, X.; Kheifets, L. Pesticides as a potential independent childhood leukemia risk factor and as a potential confounder for electromagnetic fields exposure. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 116899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Q.; Jia, Y.; Lin, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Fang, T.; Jiang, W. The associations between organophosphate pesticides (ops) and respiratory disease, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease: A review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Toxics 2023, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilden, R.C.; Harris, R.L.; Friedmann, E.J.; Han, M.; Hackney, A.J.; Olorunyemi, E.; Spanier, A.J. Systematic review: Association of pesticide exposure and child wheeze and asthma. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2023, 19, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanmohammadi, A.; Jalili Ghazizadeh, A.; Hashemi, P.; Afkhami, A.; Arduini, F.; Bagheri, H. An overview to electrochemical biosensors and sensors for the detection of environmental contaminants. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 17, 2429–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Sequeira, R.; Starbird-Pérez, R.; Rojas-Carillo, O.; Vargas-Villalobos, S. What are the main sensor methods for quantifying pesticides in agricultural activities? A review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayivi, R.D.; Obare, S.O.; Wei, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers as chemosensors for organophosphate pesticide detection and environmental applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsounidi, D.; Soulis, D.; Manoli, F.; Klinakis, A.; Tsekenis, G. Ache-based electrochemical biosensor for pesticide detection in vegetable oils: Matrix effects and synergistic inhibition of the immobilized enzyme. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, S.; Latif, U.; Dickert, F.L. Plastic antibodies as chemical sensor material for atrazine detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmont, A.-S.; Jaeger, S.; Knopp, D.; Niessner, R.; Gauglitz, G.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymer films for reflectometric interference spectroscopic sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3267–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vállez-Gomis, V.; Exojo-Trujillo, S.; Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A. Stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction by a poly(methacrylic acid-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate)-based magnetic sorbent for the determination of tricyclic antidepressants and their main active metabolites in human urine. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, U.; Mujahid, A.; Lieberzeit, P.; Afzal, A.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Iqbal, N.; Roshan, S. Molecularly imprinted polymeric coatings for sensitive and selective gravimetric detection of artemether. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 34355–34363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarev, O.A.; Polyakova, I.V. Molecularly imprinted polymers based on methacrylic acid and ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate for l-lysine recognition. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 130, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, A.M.; Karlsson, B.C.G.; Nicholls, I.A. Consequences of morphology on molecularly imprinted polymer-ligand recognition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, U.; Seifner, A.; Dickert, F.L. Selective detection of erythrocytes with qcms—abo blood group typing. Sensors 2023, 23, 7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeen, A.; Shaji, L.K.; Nair, A.K.; Kalarikkal, N. Chapter 12—morphological characterization of nanomaterials. In Characterization of Nanomaterials; Mohan Bhagyaraj, S., Oluwafemi, O.S., Kalarikkal, N., Thomas, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 335–364. [Google Scholar]
- Dickert, F.L.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Achatz, P.; Palfinger, C.; Fassnauer, M.; Schmid, E.; Werther, W.; Horner, G. Qcm array for on-line-monitoring of composting procedures. Analyst 2004, 129, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, J.-H.; Tian, H.-W.; Ma, R.; Wang, Z.-H.; Pan, Y.-C.; Hu, X.-Y.; Guo, D.-S. Calixarene-based supramolecular sensor array for pesticide discrimination. Sensors 2024, 24, 3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsibande, S.A.; Forbes, P.B. Development of a quantum dot molecularly imprinted polymer sensor for fluorescence detection of atrazine. Luminescence 2019, 34, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahshoor, Z.; Ho, K.-V.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; de Cortalezzi, M.F. Detection of atrazine and its metabolites by photonic molecularly imprinted polymers in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 12, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Shrivastav, A.M.; Gupta, B.D. Surface plasmon resonance based optical fiber sensor for atrazine detection using molecular imprinting technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Feng, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. Rapid determination of atrazine in apple juice using molecularly imprinted polymers coupled with gold nanoparticles-colorimetric/sers dual chemosensor. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Zanoni, C.; Spina, S.; Magnaghi, L.R.; Biesuz, R. Mip-based screen-printed potentiometric cell for atrazine sensing. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattach, Y.; Garnier, F.; Remita, S. Influence of chemical and structural properties of functionalized polythiophene-based layers on electrochemical sensing of atrazine. Chemphyschem 2012, 13, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Shin, H.-K.; Hong, S.W.; Park, J.Y. Lithographically patterned molecularly imprinted polymer for gravimetric detection of trace atrazine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, M.; Mo, Y.; Qu, J.; Feng, Y. Thickness-shear mode acoustic sensor for atrazine using molecularly imprinted polymer as recognition element. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 428, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Piletska, E.V.; Bossi, A.; Karim, K.; Lowe, P.; Turner, A.P. Substitution of antibodies and receptors with molecularly imprinted polymers in enzyme-linked and fluorescent assays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, J.; Takayose, M.; Akamatsu, K.; Nawafune, H.; Tamaki, K.; Sugimoto, N. Molecularly imprinted nanocomposites for highly sensitive spr detection of a non-aqueous atrazine sample. Analyst 2009, 134, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Lah, N.F.; Ahmad, A.L.; Low, S.C.; Zaulkiflee, N.D. Isotherm and electrochemical properties of atrazine sensing using pvc/mip: Effect of porogenic solvent concentration ratio. Membranes 2021, 11, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, I.; Shoji, R.; Fuchiwaki, Y.; Suzuki, H. Atrazine sensing chip based on molecularly imprinted polymer layer. Electrochemistry 2008, 76, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


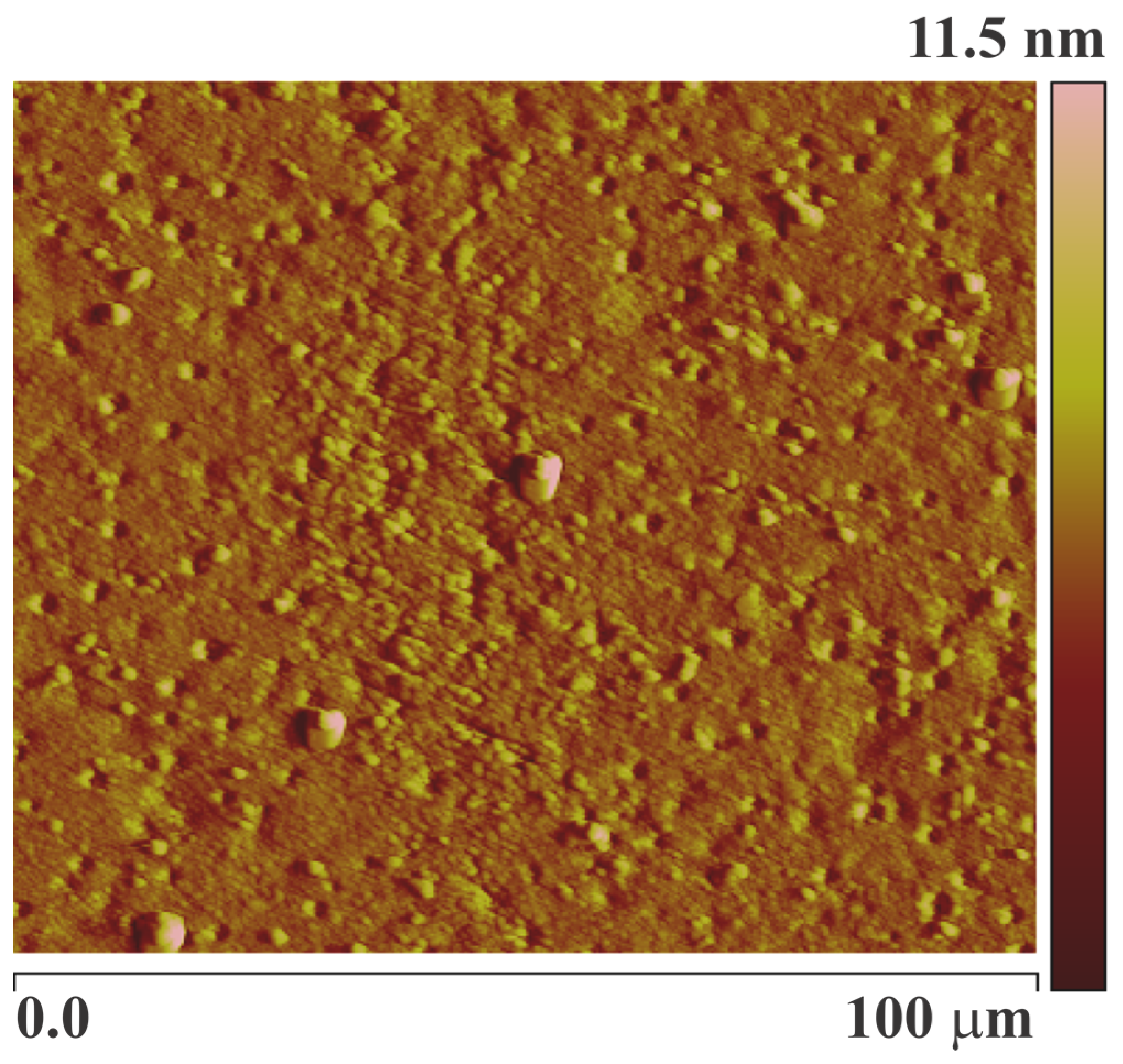
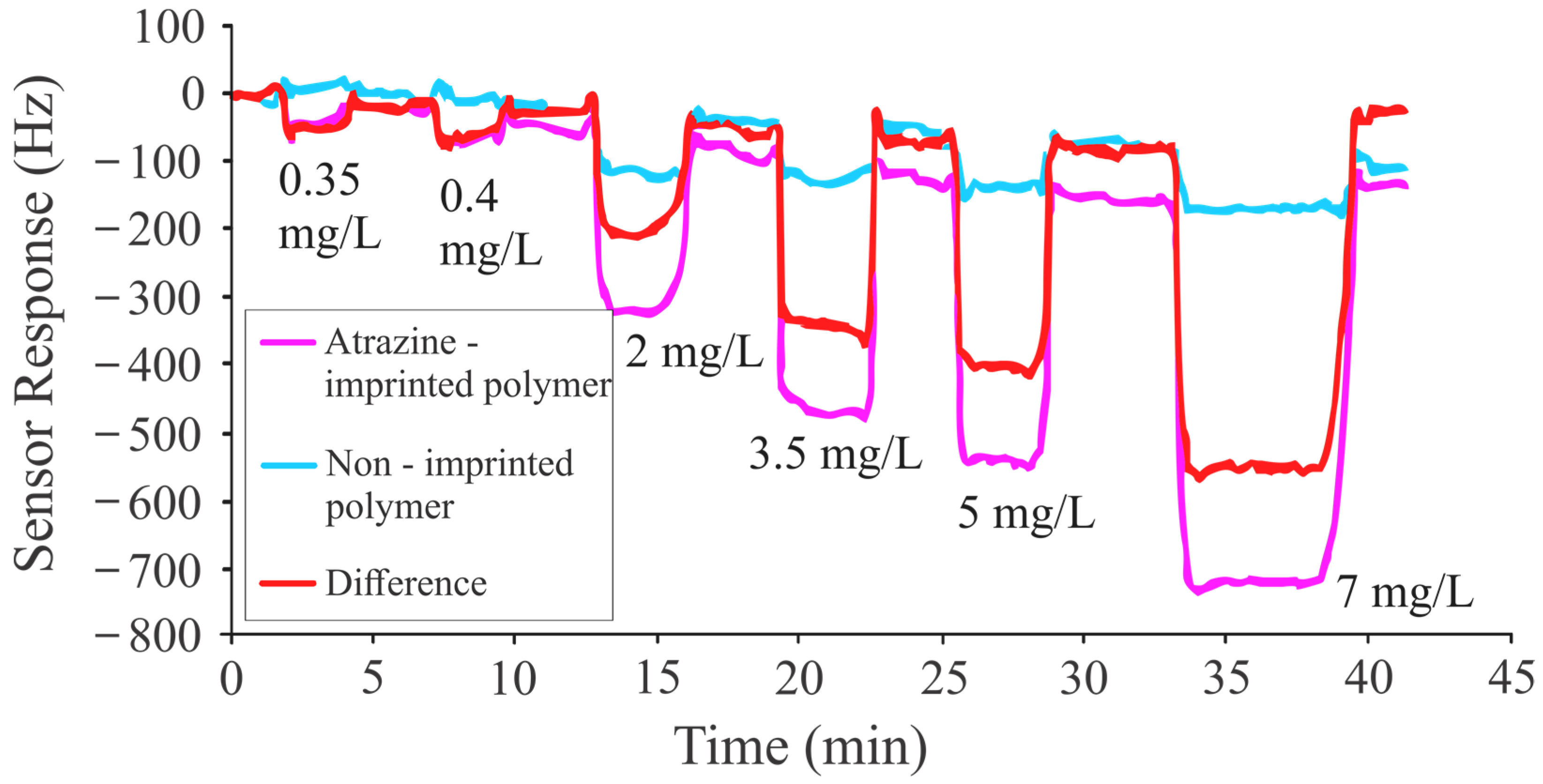

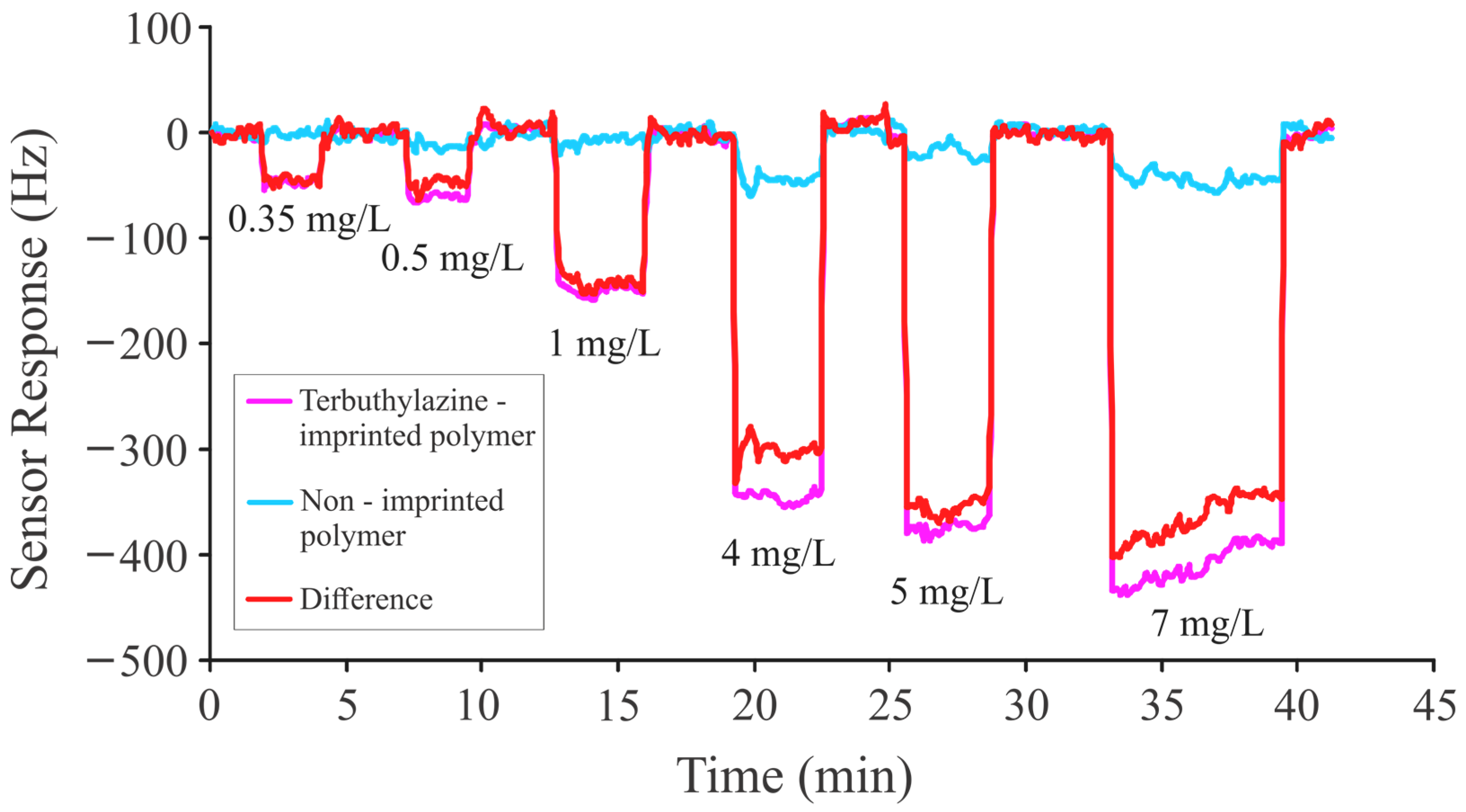


| MAA:EGDMA | Layer Height (kHz) | Net Frequency Shift (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 28:72 | 8 | 200 |
| 30:70 | 10 | 354 |
| 33:67 | 6 | 198 |
| 35:65 | 5.2 | 314 |
| 40:60 | 5 | 408 |
| 46:54 | 6.25 | 546 |
| 50:50 | 4 | 180 |
| 60:40 | 4.2 | 84 |
| Sr. No. | Recognition Element | Pesticide | Detection Method | Detection Range | LOD | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CdSeTe/ZnS (QD)@MIP | Atrazine | Fluorescence | 2–20 mol/L | 0.8 × 10−7 mol/L | [30] |
| 2 | Acrylic acid, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate | ATR, DEA and de-isopropyl atrazine (DIA) | Photonic MIP | 0.1 to 10 ppb | 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 ppb for ATR, DEA, and DIA, respectively | [31] |
| 3 | 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate | Atrazine | Surface plasmon resonance | 10−12 to 10−7 M | 1.92 × 10−14 M | [32] |
| 4 | Methacrylic acid, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate and AuNPs | Atrazine | Colorimetric and SERS | 0.005 mg/L to 1 mg/L | <0.01 mg/L (Colorimetric) 0.0012 mg/L (SERS) | [33] |
| 5 | Methacrylic acid, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate | Atrazine | Electrochemical | 5 × 10−7 to 5 × 10−6 M | 4 × 10−7 M | [34] |
| 6 | Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxy thiophene-co-3-thiophene acetic acid | Atrazine | Electrochemical | 10−8 to 10−4 mol/L | 10−9 mol/L | [35] |
| 7 | Methacrylic acid, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate | Atrazine, propazine, terbuthylazine, des-ethyl atrazine | Mass sensitive | 0.35 mg/L to 7 mg/L | 0.1 to 0.2 mg/L for ATR, PRO, and TBA 0.1 mg/L or less for DEA | This Study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latif, U.; Yaqub, S.; Dickert, F.L. Sensitive Coatings Based on Molecular-Imprinted Polymers for Triazine Pesticides’ Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 5934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185934
Latif U, Yaqub S, Dickert FL. Sensitive Coatings Based on Molecular-Imprinted Polymers for Triazine Pesticides’ Detection. Sensors. 2024; 24(18):5934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185934
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatif, Usman, Sadaf Yaqub, and Franz L. Dickert. 2024. "Sensitive Coatings Based on Molecular-Imprinted Polymers for Triazine Pesticides’ Detection" Sensors 24, no. 18: 5934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185934
APA StyleLatif, U., Yaqub, S., & Dickert, F. L. (2024). Sensitive Coatings Based on Molecular-Imprinted Polymers for Triazine Pesticides’ Detection. Sensors, 24(18), 5934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185934






