The Adaption of Recent New Concepts in Neural Radiance Fields and Their Role for High-Fidelity Volume Reconstruction in Medical Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce the emerging concept of NeRF, originally developed for natural images, into the medical domain to explore their potential applicability and utilities;
- We evaluate four state-of-the-art NeRF techniques by optimizing them to four distinct medical image datasets to identify their strengths and limitations;
- We conduct a comprehensive analysis with the traditional filtered back project (FDK) alternative [15] that is commonly employed for reconstructing medical images.
2. Related Works
2.1. Medical Volume Reconstruction
2.2. Neural Radiance Field
3. Comparative NeRF Methods and Optimization to Medical Domains
3.1. NeRF
3.2. Attenuation Field
3.3. Uniform Sampling
3.4. Three Variations of the Vanilla NeRF
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation
4.3. Evaluation Metric
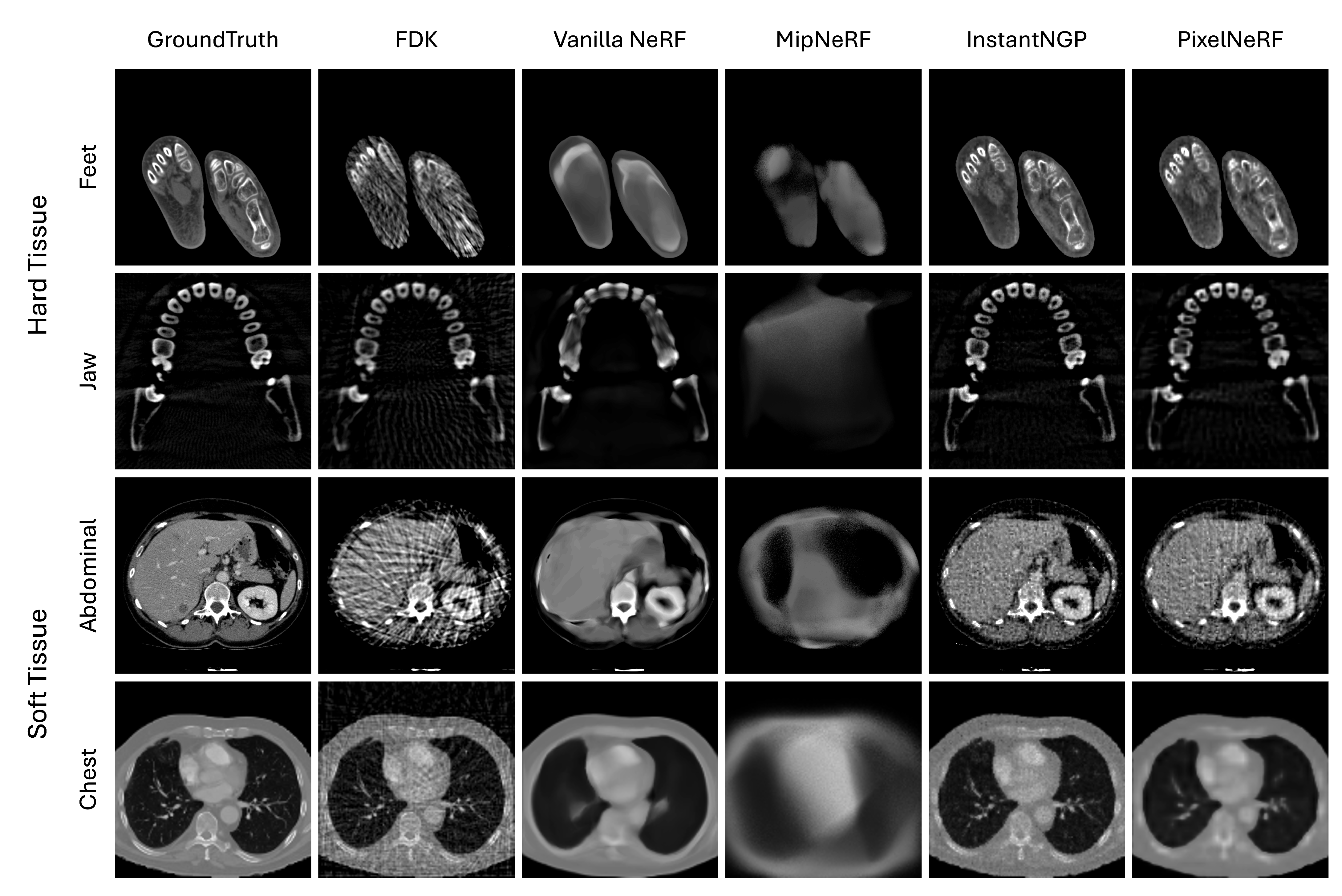
5. Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Häggström, I.; Schmidtlein, C.R.; Campanella, G.; Fuchs, T.J. DeepPET: A deep encoder–decoder network for directly solving the PET image reconstruction inverse problem. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 54, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.L. Medical Image Reconstruction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 530. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Cai, J.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, J. Cnn-based real-time dense face reconstruction with inverse-rendered photo-realistic face images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 1294–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Lv, S.; Dong, F.; Takei, M. Image reconstruction based on convolutional neural network for electrical resistance tomography. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 19, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, S.; Ye, J.C.; Fessler, J.A. Image reconstruction: From sparsity to data-adaptive methods and machine learning. Proc. IEEE 2019, 108, 86–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnema, J.; Wolff, J.; Koivisto, J.; Lucka, F.; Batenburg, K.J.; Forouzanfar, T.; van Eijnatten, M. Comparison of convolutional neural network training strategies for cone-beam CT image segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 207, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Li, J.; Pomykala, K.L.; Kleesiek, J.; Alves, V.; Egger, J. GAN-based generation of realistic 3D volumetric data: A systematic review and taxonomy. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 93, 103100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 2021, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, A.; Aminimehr, A.; Tavakoli, A.; Kazerouni, A.; Azad, B.; Azad, R.; Merhof, D. Implicit neural representation in medical imaging: A comparative survey. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 2381–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Tancik, M.; Hedman, P.; Martin-Brualla, R.; Srinivasan, P.P. Mip-nerf: A multiscale representation for anti-aliasing neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 5855–5864. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, T.; Evans, A.; Schied, C.; Keller, A. Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding. ACM Trans. Graph. (Tog) 2022, 41, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Ye, V.; Tancik, M.; Kanazawa, A. pixelnerf: Neural radiance fields from one or few images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4578–4587. [Google Scholar]
- Feldkamp, L.A.; Davis, L.C.; Kress, J.W. Practical cone-beam algorithm. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1984, 1, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzler, P.; Rasche, V.; Ropinski, T.; Ritschel, T. Single-image tomography: 3D volumes from 2D cranial X-rays. In Proceedings of the Computer Graphics Forum, Bintan Island, Indonesia, 11–14 June 2018; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 37, pp. 377–388. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Liu, J.Z.; Cauley, S.F.; Rosen, B.R.; Rosen, M.S. Image reconstruction by domain-transform manifold learning. Nature 2018, 555, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.; Guo, H.; Ma, K.; Wu, J.; Weng, Z.; Zheng, Y. X2CT-GAN: Reconstructing CT from biplanar X-rays with generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10619–10628. [Google Scholar]
- Ratul, M.A.R.; Yuan, K.; Lee, W. CCX-rayNet: A class conditioned convolutional neural network for biplanar X-rays to CT volume. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), IEEE, Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 1655–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Tancik, M.; Srinivasan, P.; Mildenhall, B.; Fridovich-Keil, S.; Raghavan, N.; Singhal, U.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Barron, J.; Ng, R. Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 7537–7547. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Tancik, M.; Abbeel, P. Putting nerf on a diet: Semantically consistent few-shot view synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 5885–5894. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. NAF: Neural attenuation fields for sparse-view CBCT reconstruction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 442–452. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Mei, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Cui, Z.; Shen, D. Snaf: Sparse-view cbct reconstruction with neural attenuation fields. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.17048. [Google Scholar]
- Swinehart, D.F. The beer-lambert law. J. Chem. Educ. 1962, 39, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osirix-DICOM Image Library. Available online: https://www.osirix-viewer.com/resources/dicom-image-library/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Open Scientific Visualization Datasets. Available online: https://klacansky.com/open-scivis-datasets/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Soler, L.; Hostettler, A.; Agnus, V.; Charnoz, A.; Fasquel, J.B.; Moreau, J.; Osswald, A.B.; Bouhadjar, M.; Marescaux, J. 3D Image Reconstruction for Comparison of Algorithm Database. 2010. Available online: https://www.ircad.fr/research/data-sets/liver-segmentation-3d-ircadb-01 (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Armato III, S.G.; McLennan, G.; Bidaut, L.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; Zhao, B.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A.; et al. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): A completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biguri, A.; Dosanjh, M.; Hancock, S.; Soleimani, M. TIGRE: A MATLAB-GPU toolbox for CBCT image reconstruction. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2016, 2, 055010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Bovik, A.C. Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 23, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, B.; Cresson, T.; de Guise, J.A.; Vazquez, C. X-ray to DRR images translation for efficient multiple objects similarity measures in deformable model 3D/2D registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 42, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Fan, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Xiao, D.; Ai, D.; Fu, T.; Song, H.; Yuan, K.; Duan, F.; et al. DSC-Recon: Dual-Stage Complementary 4D Organ Reconstruction from X-ray Image Sequence for Intraoperative Fusion. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type | Dataset | Volume Size | Voxel Size (mm) | Number of X-ray Images | Viewing Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Tissue | Feet | 512 × 512 × 250 | 0.4023 × 0.4023 × 0.5 | 50 | 0–360° |
| Jaw | 256 × 256 × 256 | 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 | 50 | 0–360° | |
| Soft Tissue | Abdominal | 512 × 512 × 129 | 0.57 × 0.57 × 1.6 | 50 | 0–360° |
| Chest | 128 × 128 × 128 | 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 | 50 | 0–360° |
| Type | Dataset | Models | 3D PSNR↑ | 3D SSIM↑ | LPIPS↓ | GMSD↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Tissue | Feet | FDK | 28.9 | 0.790 | 0.382 | |
| Vanilla NeRF | 28.9 | 0.905 | 0.099 | |||
| MipNeRF | 24.5 | 0.832 | 0.220 | |||
| Instant-NGP | 37.6 | 0.975 | 0.037 | |||
| PixelNeRF | 35.4 | 0.965 | 0.047 | |||
| Jaw | FDK | 30.3 | 0.857 | 0.266 | ||
| Vanilla NeRF | 30.1 | 0.872 | 0.351 | |||
| MipNeRF | 22.5 | 0.609 | 0.690 | |||
| Instant-NGP | 34.4 | 0.941 | 0.143 | |||
| PixelNeRF | 31.9 | 0.913 | 0.303 | |||
| Soft Tissue | Abdominal | FDK | 24.0 | 0.735 | 0.441 | |
| Vanilla NeRF | 26.6 | 0.891 | 0.230 | |||
| MipNeRF | 17.3 | 0.709 | 0.512 | |||
| Instant-NGP | 32.3 | 0.942 | 0.183 | |||
| PixelNeRF | 29.2 | 0.888 | 0.237 | |||
| Chest | FDK | 25.8 | 0.744 | 0.256 | ||
| Vanilla NeRF | 27.9 | 0.885 | 0.164 | |||
| MipNeRF | 15.1 | 0.497 | 0.543 | |||
| Instant-NGP | 31.6 | 0.943 | 0.090 | |||
| PixelNeRF | 28.7 | 0.912 | 0.121 |
| Model | Hard Tissue (sec) | Soft Tissue (sec) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feet | Jaw | Abdominal | Chest | |
| FDK | 0.652 | 1.284 | 1.911 | 0.872 |
| Vanilla NeRF | 2.183 | 9.023 | 10.729 | 5.103 |
| MipNeRF | 2.748 | 10.162 | 11.285 | 5.394 |
| Instant-NGP | 1.016 | 4.201 | 4.978 | 2.591 |
| PixelNeRF | 2.189 | 9.657 | 10.878 | 5.493 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, H.; Khan, J.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.; Jung, Y. The Adaption of Recent New Concepts in Neural Radiance Fields and Their Role for High-Fidelity Volume Reconstruction in Medical Images. Sensors 2024, 24, 5923. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185923
An H, Khan J, Kim S, Choi J, Jung Y. The Adaption of Recent New Concepts in Neural Radiance Fields and Their Role for High-Fidelity Volume Reconstruction in Medical Images. Sensors. 2024; 24(18):5923. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185923
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Haill, Jawad Khan, Suhyeon Kim, Junseo Choi, and Younhyun Jung. 2024. "The Adaption of Recent New Concepts in Neural Radiance Fields and Their Role for High-Fidelity Volume Reconstruction in Medical Images" Sensors 24, no. 18: 5923. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185923
APA StyleAn, H., Khan, J., Kim, S., Choi, J., & Jung, Y. (2024). The Adaption of Recent New Concepts in Neural Radiance Fields and Their Role for High-Fidelity Volume Reconstruction in Medical Images. Sensors, 24(18), 5923. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185923







