MPI System with Bore Sizes of 75 mm and 100 mm Using Permanent Magnets and FMMD Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation, FFL Generation Magnets and FMMD Coils
2.2. Operational Condition, Sensitivity and Spatial Resolution
2.3. Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Images
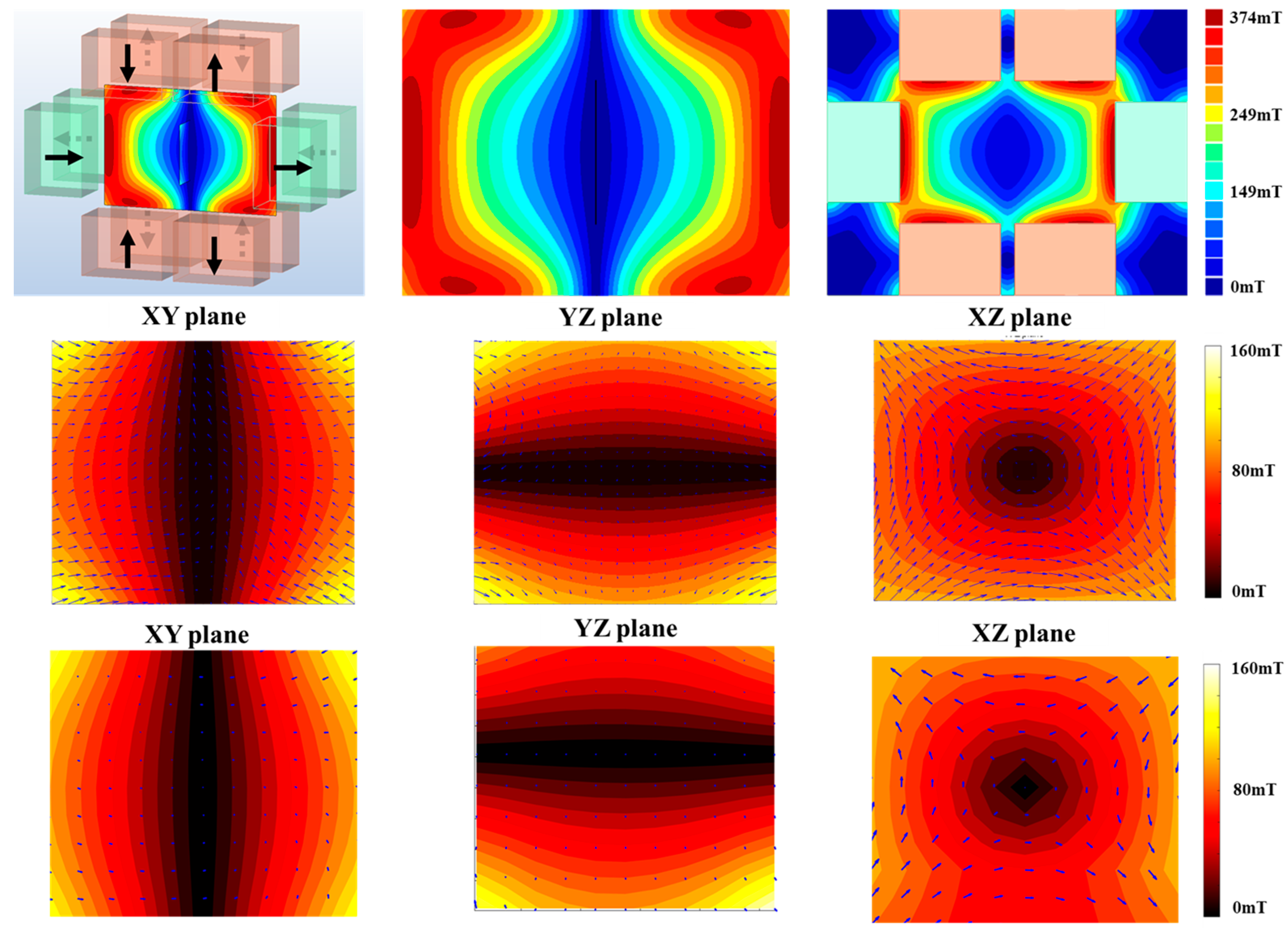
3. Results
3.1. Instrumentation, FFL Generation Magnets, and FMMD Coils
3.2. Sensitivity
3.3. Spatial Resolution
3.4. Three-Dimensional MPI Image Using Phantom Sample
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleich, B.; Weizenecker, J. Tomographic imaging using the nonlinear response of magnetic particles. Nature 2005, 435, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulte, J.W.M. Superparamagnetic iron oxides as MPI tracers: A primer and review of early applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.C.; Zhang, Y.; Steinberg, G.; Qu, H.; Huang, S.; Cheng, M.; Bliss, T.; Du, F.; Rao, J.; Song, G.; et al. A Review of Magnetic Particle Imaging and Perspectives on Neuroimaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Shao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; Han, S.; Li, H. Applications of Magnetic Particle Imaging in Biomedicine: Advancements and Prospects. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 898426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.Y.; Bishop, M.; Zheng, B.; Ferguson, R.M.; Khandhar, A.P.; Kemp, S.J.; Krishnan, K.M.; Goodwill, P.W.; Conolly, S.M. Magnetic Particle Imaging: A Novel in Vivo Imaging Platform for Cancer Detection. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, L.M.; Situ, S.F.; Griswold, M.A.; Samia, A.C.S. Magnetic Particle Imaging Tracers: State-of-the-Art and Future Directions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, T.P.T.; Doan, L. Surface Modifications of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Polyvinyl Alcohol, Chitosan, and Graphene Oxide as Methylene Blue Adsorbents. Coatings 2023, 13, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.M.; El-Safty, S.; Tounsi, A.; Shenashen, M. A review of magnetic nanoparticles used in nanomedicine. APL Mater. 2024, 12, 010601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablico-Lansigan, M.H.; Situ, S.F.; Samia, A.C. Magnetic particle imaging: Advancements and perspectives for real-time in vivo monitoring and image-guided therapy. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4040–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgert, J.; Schmidt, J.D.; Schmale, I.; Rahmer, J.; Bontus, C.; Gleich, B.; David, B.; Eckart, R.; Woywode, O.; Weizenecker, J.; et al. Fundamentals and applications of magnetic particle imaging. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2012, 6, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Jeong, J.C.; Seo, B.S.; Krause, H.J.; Hong, H.B. A Novel Field-Free Line Generator for Mechanically Scanned Magnetic Particle Imaging. Sensors 2024, 24, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Lim, J.; Choi, C.-J.; Shin, S.-W.; Krause, H.-J. Magnetic particle imaging with a planar frequency mixing magnetic detection scanner. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, H.-J.; Wolters, N.; Zhang, Y.; Offenhäusser, A.; Miethe, P.; Meyer, M.H.F.; Hartmann, M.; Keusgen, M. Magnetic particle detection by frequency mixing for immunoassay applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzug, T.M.; Bringout, G.; Erbe, M.; Gräfe, K.; Graeser, M.; Grüttner, M.; Halkola, A.; Sattel, T.F.; Tenner, W.; Wojtczyk, H.; et al. Magnetic particle imaging: Introduction to imaging and hardware realization. Z. Med. Phys. 2012, 22, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weizenecker, J.; Gleich, B.; Borgert, J. Magnetic particle imaging using a field free line. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmer, J.; Weizenecker, J.; Gleich, B.; Borgert, J. Signal encoding in magnetic particle imaging: Properties of the system function. BMC Med. Imaging 2009, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, T.; Gdaniec, N.; Möddel, M. Magnetic particle imaging: From proof of principle to preclinical applications. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, R124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwill, P.W.; Saritas, E.U.; Croft, L.R.; Kim, T.N.; Krishnan, K.M.; Schaffer, D.V.; Conolly, S.M. X-space MPI: Magnetic nanoparticles for safe medical imaging. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3870–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-M.; Jeong, J.-C.; Kim, J.; Lim, E.-G.; Kim, C.-B.; Park, S.-J.; Song, D.-Y.; Krause, H.-J.; Hong, H.; Kweon, I.S. A novel three-dimensional magnetic particle imaging system based on the frequency mixing for the point-of-care diagnostics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, P.; Rückert, M.A.; Greiner, C.; Günther, J.; Reichl, T.; Kampf, T.; Bley, T.A.; Behr, V.C.; Herz, S. iMPI: Portable human-sized magnetic particle imaging scanner for real-time endovascular interventions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, C.; Langley, M.; Warrington, G.; Mashali, F.; Johnson, J.A. Magnetic Particle Imaging: Current and Future Applications, Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis Methods and Safety Measures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Jia, X.; Yin, L.; Yang, Z.; Hui, H.; Li, J.; Huang, W.; Tian, J.; Zhang, S. Advances in magnetic particle imaging and perspectives on liver imaging. iLIVER 2022, 1, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeser, M.; Thieben, F.; Szwargulski, P.; Werner, F.; Gdaniec, N.; Boberg, M.; Griese, F.; Möddel, M.; Ludewig, P.; van de Ven, D.; et al. Human-sized magnetic particle imaging for brain applications. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, A.E.; Heuser, A.; Moenninghoff, C.; Surov, A.; Borggrefe, J.; Kroeger, J.R.; Niehoff, J.H. Does bore size matter?—A comparison of the subjective perception of patient comfort during low field (0.55 Tesla) and standard (1.5 Tesla) MRI imaging. Medicine 2023, 102, e36069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.A.; Bui, M.P.; Yoon, J. Development of Small-Rabbit-Scale Three-Dimensional Magnetic Particle Imaging System with Amplitude-Modulation-Based Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 3167–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 75 mm | LF Coil | HF Coil | Det. Coil |
| Width (mm) | 116.5 | 116.5 | 40 |
| Inner radius (mm) | 47.3 | 46.5 | 37.5 |
| Height (mm) | 4 | 0.8 | 1.8 |
| Wire diameter (mm) | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| No. of layers | 10 | 2 | 6 |
| No. of windings | 233 | 223 | 126 |
| 100 mm | LF Coil | HF Coil | Det. Coil |
| Width (mm) | 116.5 | 116.5 | 40 |
| Inner radius (mm) | 62.6 | 61 | 50 |
| Height (mm) | 4 | 0.8 | 1.8 |
| Wire diameter (mm) | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| No. of layers | 10 | 2 | 6 |
| No. of windings | 233 | 223 | 126 |
| Current (mA) | Magnetic Field (mT) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LF | HF | LF | HF | |
| 75 mm | 56.18 | 80.34 | 7.15 | 0.64 |
| 100 mm | 37.16 | 66.38 | 4.41 | 0.33 |
| 75 mm | |||||||||||
| Position | Conc. (mg/mL) | 25.00 | 12.50 | 6.25 | 3.13 | 1.56 | 0.78 | 0.39 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0 |
| Edge | Average (µV) | 3948.1 | 1765.4 | 916.6 | 501.3 | 290.2 | 180.1 | 131.0 | 106.5 | 95.1 | 86.2 |
| STDEV (µV) | 210.0 | 19.7 | 14.1 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 1.9 | |
| Center | Average (µV) | 2006.5 | 917.2 | 500.2 | 291.0 | 189.0 | 132.8 | 108.4 | 96.3 | 90.5 | 29.4 |
| STDEV (µV) | 87.9 | 8.5 | 5.2 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 49.2 | |
| 100 mm | |||||||||||
| Position | Conc. (mg/mL) | 25.00 | 12.50 | 6.25 | 3.13 | 1.56 | 0.78 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0 |
| Edge | Average (µV) | 1338.1 | 695.5 | 406.8 | 277.2 | 206.2 | 169.2 | 152.0 | 143.1 | 138.9 | 135.5 |
| STDEV | 16.7 | 13.9 | 15.7 | 7.6 | 7.1 | 6.3 | 6.0 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 4.6 | |
| Center | Average (µV) | 562.4 | 330.3 | 234.7 | 186.1 | 161.3 | 148.2 | 141.7 | 138.2 | 136.6 | 135.2 |
| STDEV | 7.1 | 9.9 | 7.7 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 4.5 | 4.5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, J.C.; Kim, T.Y.; Cho, H.S.; Seo, B.S.; Krause, H.J.; Hong, H.B. MPI System with Bore Sizes of 75 mm and 100 mm Using Permanent Magnets and FMMD Technique. Sensors 2024, 24, 3776. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123776
Jeong JC, Kim TY, Cho HS, Seo BS, Krause HJ, Hong HB. MPI System with Bore Sizes of 75 mm and 100 mm Using Permanent Magnets and FMMD Technique. Sensors. 2024; 24(12):3776. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123776
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Jae Chan, Tae Yi Kim, Hyeon Sung Cho, Beom Su Seo, Hans Joachim Krause, and Hyo Bong Hong. 2024. "MPI System with Bore Sizes of 75 mm and 100 mm Using Permanent Magnets and FMMD Technique" Sensors 24, no. 12: 3776. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123776
APA StyleJeong, J. C., Kim, T. Y., Cho, H. S., Seo, B. S., Krause, H. J., & Hong, H. B. (2024). MPI System with Bore Sizes of 75 mm and 100 mm Using Permanent Magnets and FMMD Technique. Sensors, 24(12), 3776. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123776






