Flexible Self-Powered Low-Decibel Voice Recognition Mask
Abstract
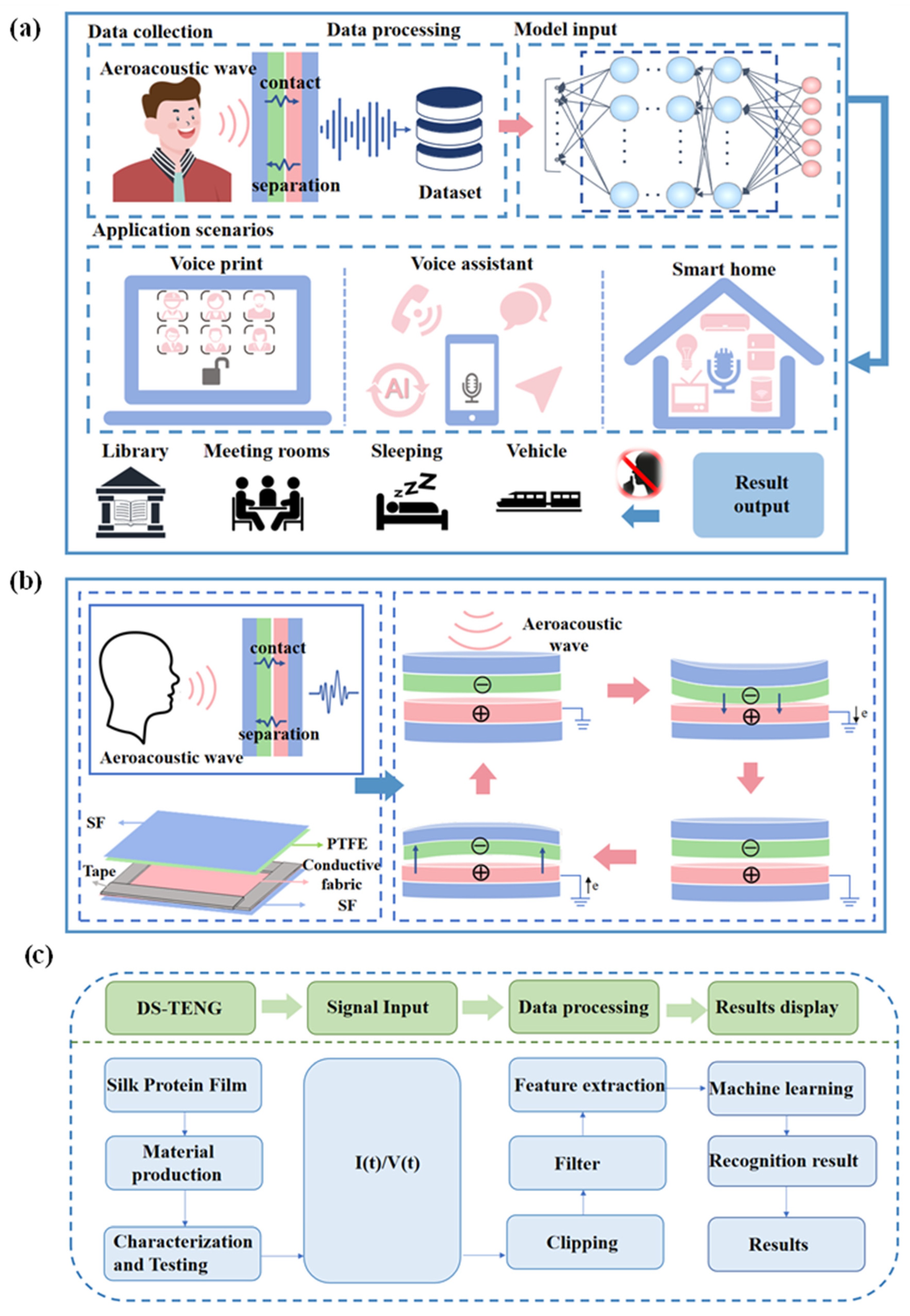
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
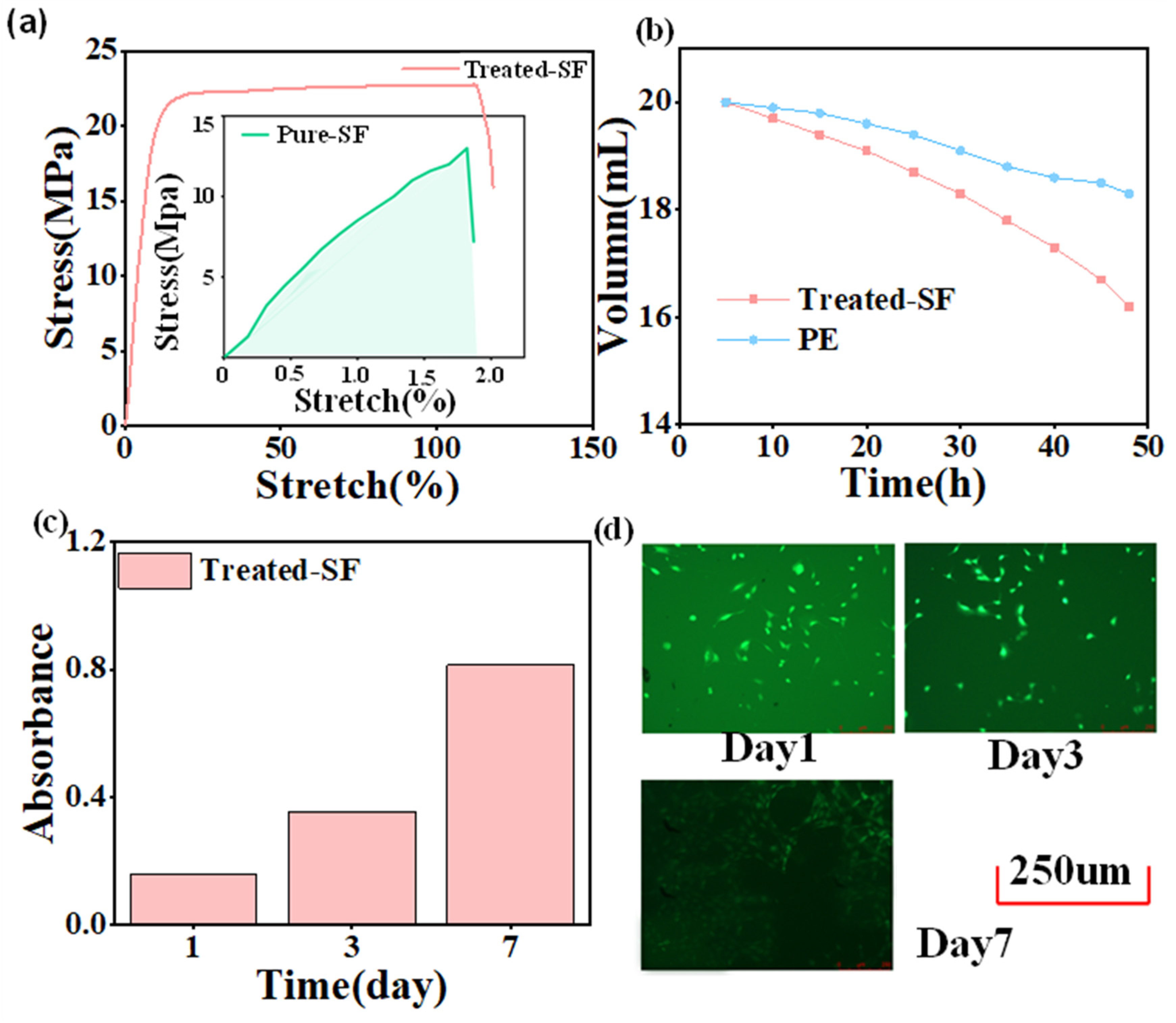
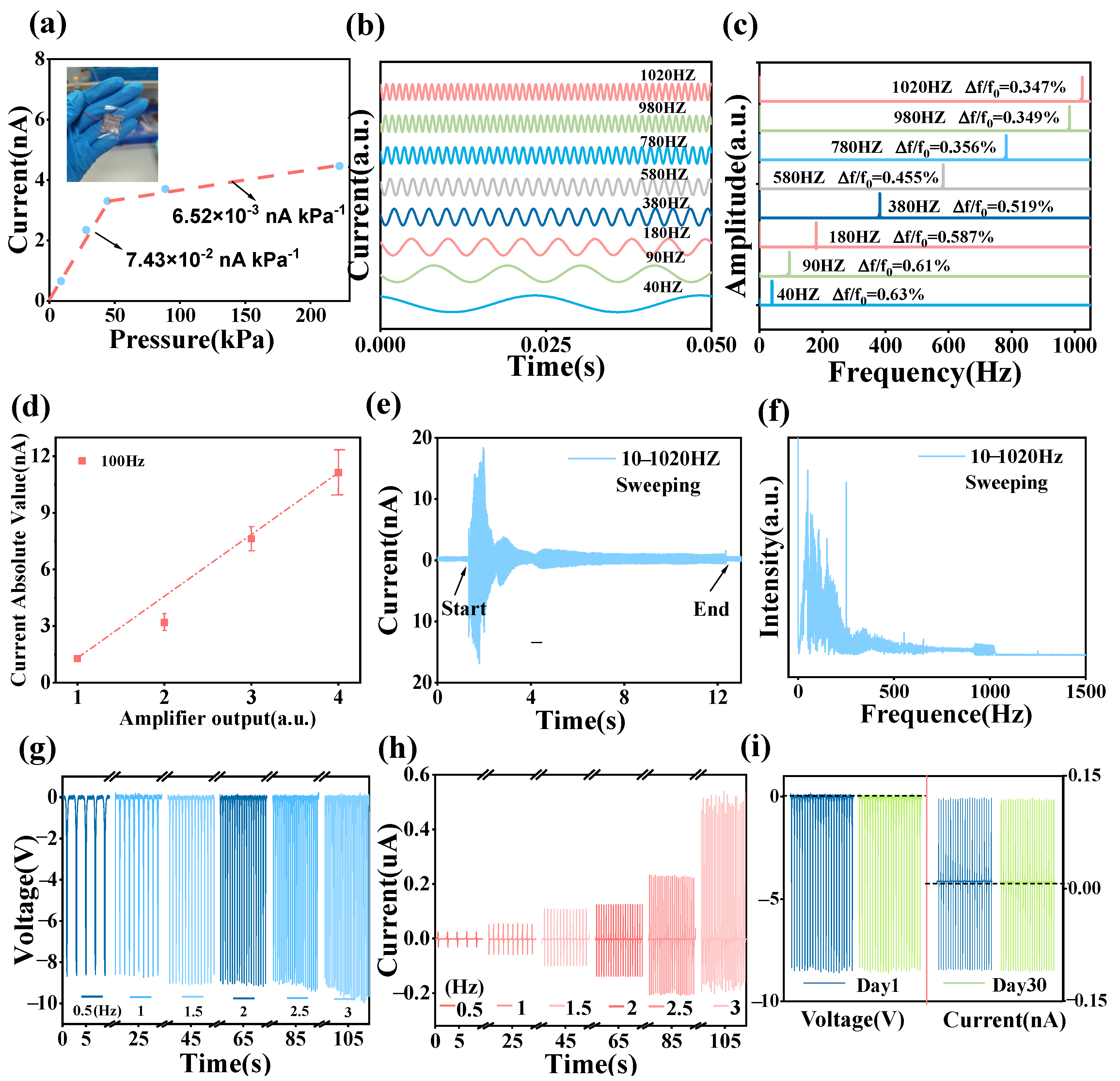
3.1. Performance of CS-TENG
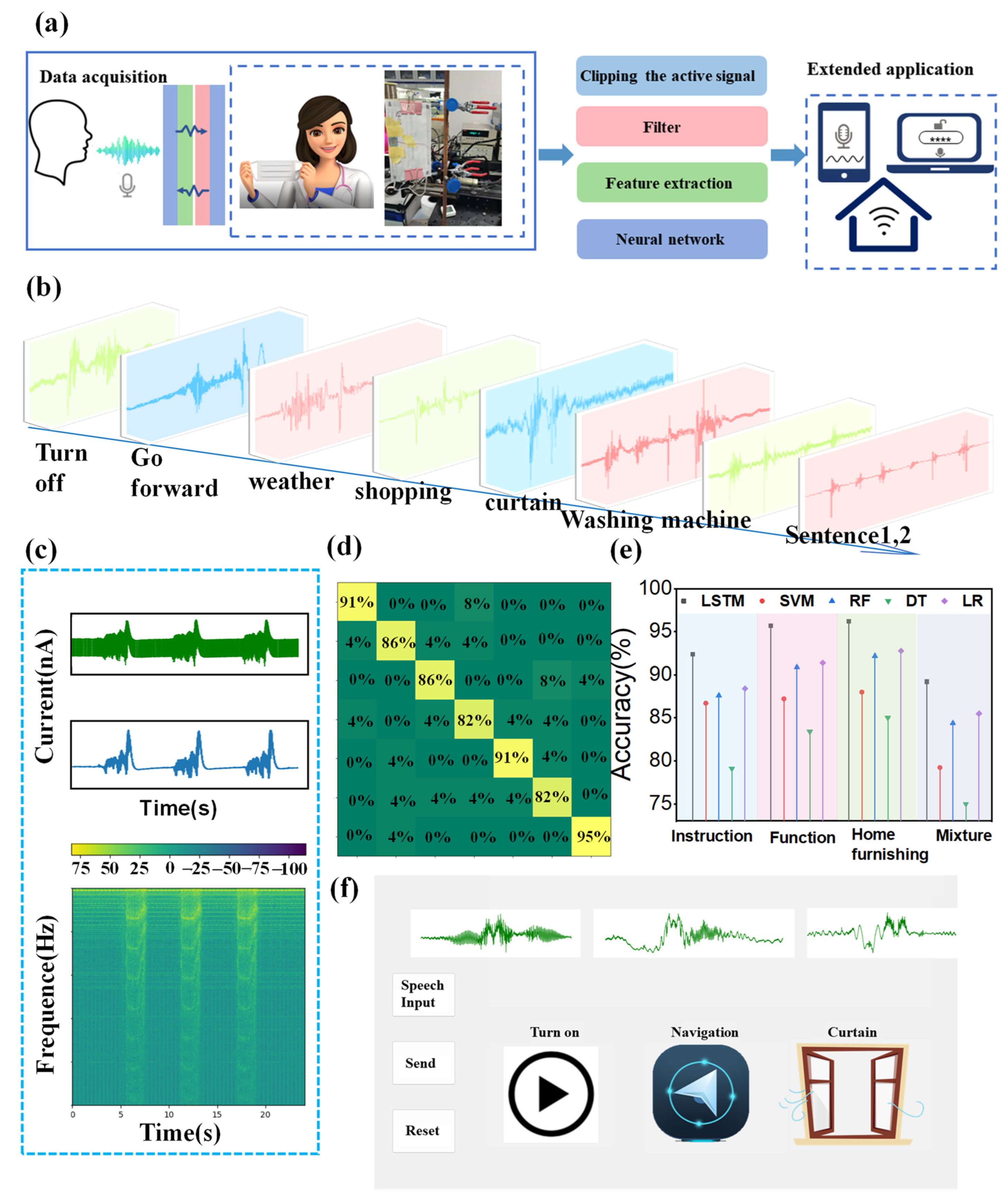
3.2. Speech Recognition Function of CS-TENG
3.3. Identification and Security Defenses
4. Conclusions
5. Experimental Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Reviving Vibration Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensing by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Joule 2017, 1, 480–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, G.; Maria Joseph Raj, N.P.; Kim, S.J. Materials Beyond Conventional Triboelectric Series for Fabrication and Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.G.; Kim, D.W.; Tcho, I.W.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, Y.K. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: Structure, Mechanism, and Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 258–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, B.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Z. Wearable and Implantable Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, T.; Wu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, D. Triboelectric Nanogenerator with a Seesaw Structure for Harvesting Ocean Energy. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, F.; Tian, J.; Li, S.; Fu, E.; Nie, J.; Lei, R.; Ding, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Electro-Tactile System for Virtual Tactile Experiences. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Liu, T.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qian, C.; Lin, T. Recent Progress on the Wearable Devices Based on Piezoelectric Sensors. Ferroelectrics 2018, 531, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Cho, S.; Kim, M.; Ao, C.K.; Soh, S.; Sohn, C.; Jeong, C.K.; Lee, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: From Technological Progress to Commercial Applications. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 11087–11219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Ni, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Fan, Y.; Li, Z. Progress in Self-Powered Health Monitoring and Physiological Function Regulation Devices. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 2367–2385. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shu, M.; Ai, Z.; Lou, Z.; Sou, K.W.; Lu, C.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, C. A Highly Sensitive Triboelectric Vibration Sensor for Machinery Condition Monitoring. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2201132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, H.; Yang, S.; Wen, G. Pagoda-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator with High Reliability for Harvesting Vibration Energy and Measuring Vibration Frequency in Downhole. IEEE Sensors J. 2020, 20, 13999–14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W. Nanogenerator as New Energy Technology for Self-Powered Intelligent Transportation System. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Schütz, U.; Tu, K.; Koch, S.M.; Roman, G.; Stucki, S.; Chen, F.; Ding, Y.; Yan, W.; Wu, C. Scalable and sustainable wood for efficient mechanical energy conversion in buildings via triboelectric effects. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, B.; Yang, J.; Hu, Y.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. A Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerator Driven by Bidirectional Swing for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Small 2023, 19, 2304412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ni, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.L. Self-healing and elastic triboelectric nanogenerators for muscle motion monitoring and photothermal treatment. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14653–14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, N.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Shi, J.; Xie, L.; Jiang, H.; Bao, D. A wrinkled PEDOT: PSS film based stretchable and transparent triboelectric nanogenerator for wearable energy harvesters and active motion sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, T.; Luo, B.; Cai, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, J.; Fatehi, P.; Qin, C.; Nie, S. Cellulosic triboelectric materials for stable energy harvesting from hot and humid conditions. Nano Energy 2023, 111, 108426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, P.; Qiao, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Multi-layered triboelectric nanogenerator incorporated with self-charge excitation for efficient water wave energy harvesting. Appl. Energy 2023, 336, 120792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Liao, J.; Qin, Y.; Ali, A.; Li, C. Solid-Liquid triboelectric nanogenerator based on curvature effect for harvesting mechanical and wave energy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Zhou, B.; Li, J.; Gao, C.; Guo, J. Orange peel-like triboelectric nanogenerators with multiscale micro-nano structure for energy harvesting and touch sensing applications. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Huang, X.; Shi, R.; Yang, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhou, J.; He, X.; Li, J.; Zen, Y.; Jiao, Y. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Enabled Sweat Extraction and Power Activation for Sweat Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2310777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.-Z.; Wang, D.-Y.; Xu, Z.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B. Flexible single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator with MWCNT/PDMS composite film for environmental energy harvesting and human motion monitoring. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 3117–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Long, Y.; Bai, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Tan, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Miao, Y. Variable stiffness triboelectric nano-generator to harvest high-speed railway bridge’s vibration energy. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 268, 115969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wei, X.; Li, R.; Kong, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. A capsule-shaped triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered health monitoring of traffic facilities. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Xiao, Z.; Wan, J.; Xiang, Y.; Dai, G.; Li, H.; Yang, J. A rolling-mode Al/CsPbBr3 Schottky junction direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting mechanical and solar energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yang, W.; Dong, L.; Che, L.; Wang, G. A self-powered and high sensitivity acceleration sensor with V-Q-a model based on triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, T. Research on Throat Speech Signal Detection Based on a Flexible Graphene Piezoresistive Sensor. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 3549–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Jiao, W.; Wu, K.; Qian, L.; Yu, X.; Xia, Q.; Mao, K.; Yuan, S.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y. Nanoparticle Monolayer-Based Flexible Strain Gauge with Ultrafast Dynamic Response for Acoustic Vibration Detection. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Liang, X.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X.; Heidari, H.; Ghannam, R.; Zhang, X. Speech Recognition Using Intelligent Piezoresistive Sensor Based on Polystyrene Sphere Microstructures. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Xia, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, H.; Diao, C.; Yue, G.; Zi, Y. A Novel Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Nanofibers for Effective Acoustic Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Multifunctional Sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, Q.; Xie, Y. A 3d-Printed Acoustic Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Quarter-Wavelength Acoustic Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Edge Sensing. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xiao, X.; Xu, P.; Zhao, T.; Song, L.; Pan, X.; Mi, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.L. Dual-Tube Helmholtz Resonator-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Highly Efficient Harvesting of Acoustic Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Li, R.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Vibration-driven triboelectric nanogenerator for vibration attenuation and condition monitoring for transmission lines. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 5584–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Guo, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, P. Development of a high temperature resistant downhole vibration sensor based on the triboelectric nanogenerator. Drill. Eng. 2022, 49, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, K.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Xu, D. Bow-type bistable triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting energy from low-frequency vibration. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yang, T.; Fang, J.; Pu, X.; Shang, K.; Tian, G.; Lu, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, W.; Qian, L. Tensegrity-inspired triboelectric nanogenerator for broadband and impact-resistive vibration sensing. Nano Energy 2023, 109, 108279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Shen, D.; Xi, Z.; Yu, H.; Dong, F.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, M.; Zou, Y.; Sun, P.; Xu, M. Highly adaptive and broadband triboelectric energy harvester with stretching silicone rubber strip for variable harmonic frequency vibration. Nano Res. 2023, 17, 4089–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, K.; Cui, M.; Ao, T.; Zhang, J.; Ban, D.; Zheng, H. Intelligent Sound Monitoring and Identification System Combining Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensor with Deep Learning Technique. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Du, J.; Yang, P.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Human-Machine Interaction via Dual Modes of Voice and Gesture Enabled by Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Machine Learning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 17009–17018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.-Y.; Long, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zi, Y.; Tao, L.-Q.; Li, C.-H.; Sun, H.; Li, J. Laser-Induced Graphene (Lig)-Based Pressure Sensor and Triboelectric Nanogenerator Towards High-Performance Self-Powered Measurement-Control Combined System. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Pu, X.; Wang, Z.L. Ultralight Iontronic Triboelectric Mechanoreceptor with High Specific Outputs for Epidermal Electronics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Qiu, X.; Yang, X.; Shao, H.; Tang, C.; Zhang, X. Mechanoluminescent-triboelectric bimodal sensors for self-powered sensing and intelligent control. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z. Ultrastretchable Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Ecoflex/Porous Carbon for Self-Powered Gesture Recognition. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ji, H.; Yi, J.; Jiang, P.; Li, Z.; Shen, L.; Sun, X.; Wen, Z. Flexible microfluidic triboelectric sensor for gesture recognition and information encoding. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-S.; Song, W.-Z.; Wu, L.-X.; Li, C.-L.; Chen, T.; Sun, D.-J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, T.-T.; Zhang, J.; Ramakrishna, S. The influence of in-plane electrodes on TENG’s output and its application in the field of IoT intelligent sensing. Nano Energy 2023, 110, 108313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, C.; Dharmasena, I.; Ni, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, H.; Huang, S.-L.; Ding, W. Triboelectric nanogenerators enabled internet of things: A survey. Intell. Converg. Netw. 2020, 1, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhu, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; He, T.; Lee, C. Triboelectric nanogenerator enabled wearable sensors and electronics for sustainable internet of things integrated green earth. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, R. Fibrous triboelectric nanogenerators: Fabrication, integration, and application. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 15881–15905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liang, R.; He, H.; Zeng, Y.; Hou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Luo, B.; Zhang, S.; Cai, C. Nanocellulosic triboelectric materials with micro-mountain arrays for moisture-resisting wearable sensors. Nano Energy 2023, 112, 108480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanh, T.D.; Meena, J.S.; Choi, S.B.; Kim, J.-W. Breathable, self-healable, washable and durable all-fibrous triboelectric nanogenerator for wearable electronics. Mater. Today Adv. 2023, 20, 100427. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Tian, Z.; Gao, X.Z.; Zhao, H.Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Yu, Z.Z.; Yang, D. All-Weather Self-Powered Intelligent Traffic Monitoring System Based on a Conjunction of Self-Healable Piezoresistive Sensors and Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2308845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y. Waterbomb-origami inspired triboelectric nanogenerator for smart pavement-integrated traffic monitoring. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5450–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Pan, J.; Claesson, P.; Larsson, R.; Shi, Y. Self-powered, long-durable, and highly selective oil–solid triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and intelligent monitoring. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Guo, H.; Zhai, W.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Dai, K. Template-Assisted Electrospun Ordered Hierarchical Microhump Arrays-Based Multifunctional Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Tactile Sensing and Animal Voice-Emotion Identification. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Zhao, L.; Shi, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Lei, W.; Chen, H. Self-powered speech recognition system for deaf users. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Cao, Y.; Qu, X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, W.; Pu, X.; Shi, B.; Li, Z. Hybrid nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting, motion state detection, and pulse sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Systems of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jie, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators Driven Self-Powered Electrochemical Processes for Energy and Environmental Science. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, C.Y.; Rao, S.J.; Yang, S.; Tian, H.; Qu, D.H. An Ultrastrong and Highly Stretchable Polyurethane Elastomer Enabled by a Zipper-Like Ring-Sliding Effect. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2000345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, A.; Qiu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Cai, W. An All-Protein Multisensory Highly Bionic Skin. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 4579–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Xu, Z.; Qiu, W.; Wu, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Guo, W. A Biodegradable and Stretchable Protein-Based Sensor as Artificial Electronic Skin for Human Motion Detection. Small 2019, 15, e1805084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, Z.; Qiu, W.; Chen, F.; Meng, Z.; Hou, C.; Guo, W.; Liu, X.Y. Stretchable and Heat-Resistant Protein-Based Electronic Skin for Human Thermoregulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Qiu, W.; Fan, X.; Shi, Y.; Gong, H.; Huang, J.; Patil, A.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Lin, H.; et al. Stretchable, Stable, and Degradable Silk Fibroin Enabled by Mesoscopic Doping for Finger Motion Triggered Color/Transmittance Adjustment. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12429–12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Gao, X.; Guo, L.Y.; Tao, L.Q.; Guo, Z.H.; Shao, Y.; Cui, T.; Yang, Y.; Pu, X.; Ren, T.L. Graphene-based dual-function acoustic transducers for machine learning-assisted human-robot interfaces. InfoMat 2023, 5, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tian, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, F.; Liu, B.; Wei, S.; Ji, L.; Wang, Z.L. Decoding lip language using triboelectric sensors with deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.P.; Jang, H.; Jang, Y.; Song, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, P.S.; Kim, J. Encoding of multi-modal emotional information via personalized skin-integrated wireless facial interface. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Jing, Q.; Li, Z.; Yi, F.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Eardrum-inspired active sensors for self-powered cardiovascular system characterization and throat-attached anti-interference voice recognition. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xi, Y.; Wang, Z.L. High-sensitive and ultra-wide spectrum multifunctional triboelectric acoustic sensor for broad scenario applications. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Acero, A.; Hon, H.-W.; Reddy, R. Spoken Language Processing: A Guide to Theory, Algorithm, and System Development; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bilmes, J.A. Graphical models and automatic speech recognition. In Mathematical Foundations of Speech and Language Processing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 191–245. [Google Scholar]
- Denby, B.; Schultz, T.; Honda, K.; Hueber, T.; Gilbert, J.M.; Brumberg, J.S. Silent speech interfaces. Speech Commun. 2010, 52, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herff, C.; Schultz, T. Automatic speech recognition from neural signals: A focused review. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 204946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier-Hein, L.; Metze, F.; Schultz, T.; Waibel, A. Session independent non-audible speech recognition using surface electromyography. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Cancun, Mexico, 27 November–1 December 2005; pp. 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Meltzner, G.S.; Sroka, J.J.; Heaton, J.T.; Gilmore, L.D.; Colby, G.; Roy, S.H.; Chen, N.; De Luca, C.J. Speech recognition for vocalized and subvocal modes of production using surface EMG signals from the neck and face. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, Brisbane, Australia, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 2667–2670. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Fan, Z. A novel feature optimization for wearable human-computer interfaces using surface electromyography sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, C.; Binsted, K. Web Browser Control Using EMG Based Sub Vocal Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 38th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 6 January 2005; p. 294c. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X. Fundamentals of Speech Recognition. Available online: https://slpcourse.github.io/materials/lecture_notes/Xiao_Guest_lecture_ASR.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2024).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Ye, M.; Guo, W. Flexible Self-Powered Low-Decibel Voice Recognition Mask. Sensors 2024, 24, 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103007
Li J, Shi Y, Chen J, Huang Q, Ye M, Guo W. Flexible Self-Powered Low-Decibel Voice Recognition Mask. Sensors. 2024; 24(10):3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianing, Yating Shi, Jianfeng Chen, Qiaoling Huang, Meidan Ye, and Wenxi Guo. 2024. "Flexible Self-Powered Low-Decibel Voice Recognition Mask" Sensors 24, no. 10: 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103007
APA StyleLi, J., Shi, Y., Chen, J., Huang, Q., Ye, M., & Guo, W. (2024). Flexible Self-Powered Low-Decibel Voice Recognition Mask. Sensors, 24(10), 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103007





