A Novel Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on MFCC and RACNN
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- With the application of residual and attention mechanisms, we enhance the learning capability, fault tolerance, and emphasis on vital information of networks. This facilitates the suppression of various environmental noises, the extraction of deep abstract features of the signal, and the improvement of sensitivity to critical information.
- (2)
- Compared to other networks, we reduce the number of parameters and effectively highlight crucial information hidden in the time–frequency spectrum. This leads to a reduction in the use of computational resources and an increase in computational efficiency and speed, which makes sense in practical applications.
2. Proposed Method
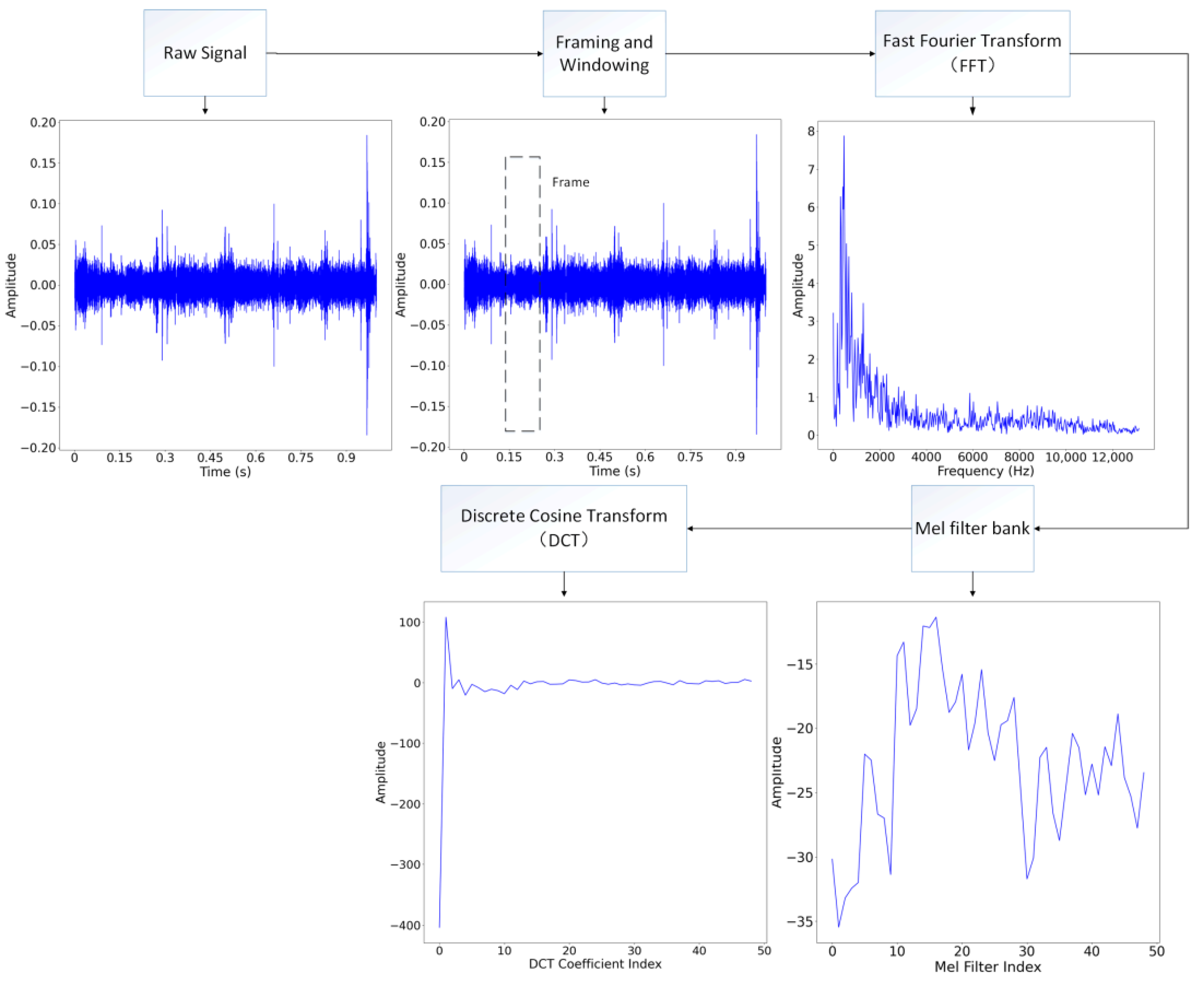
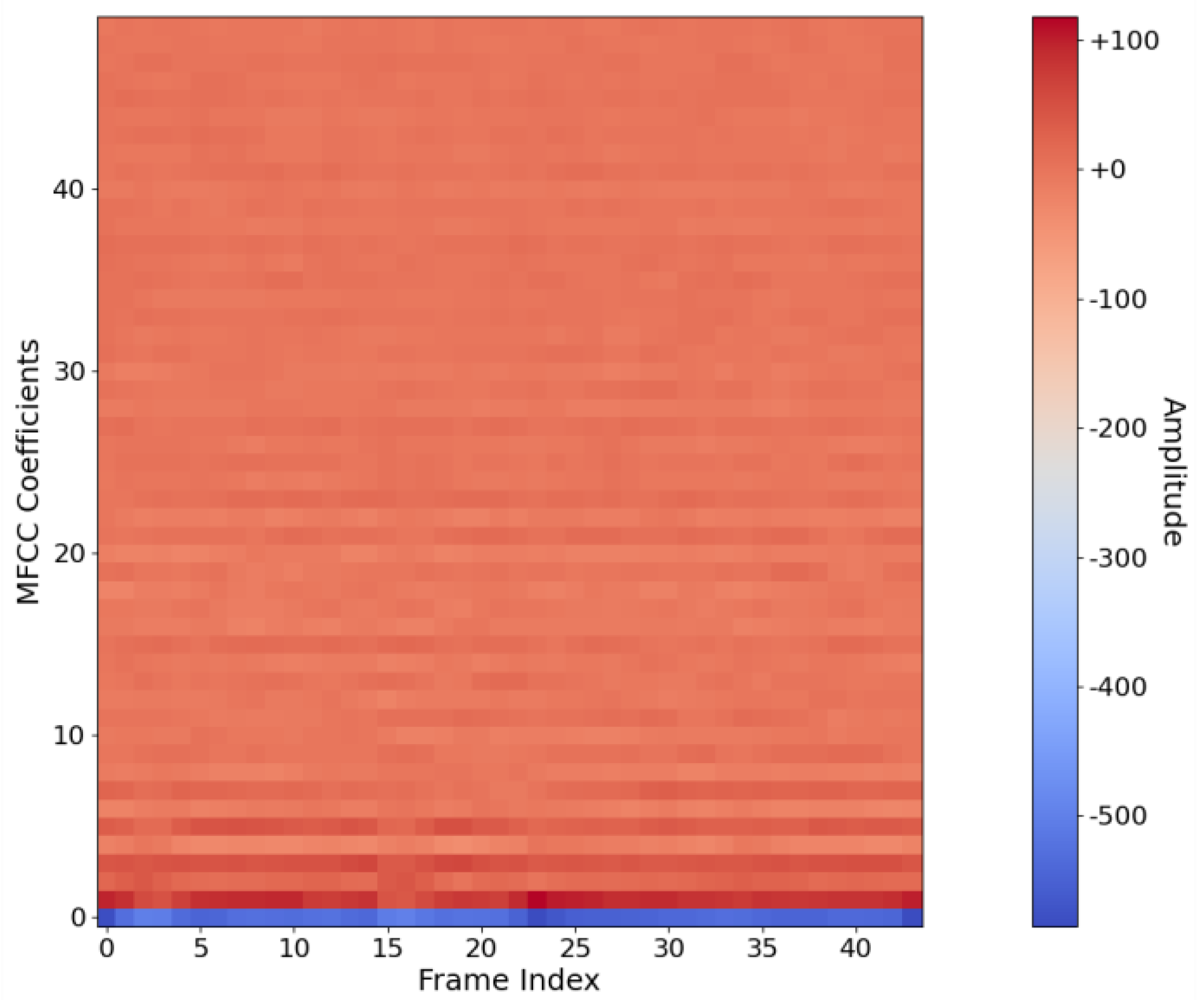
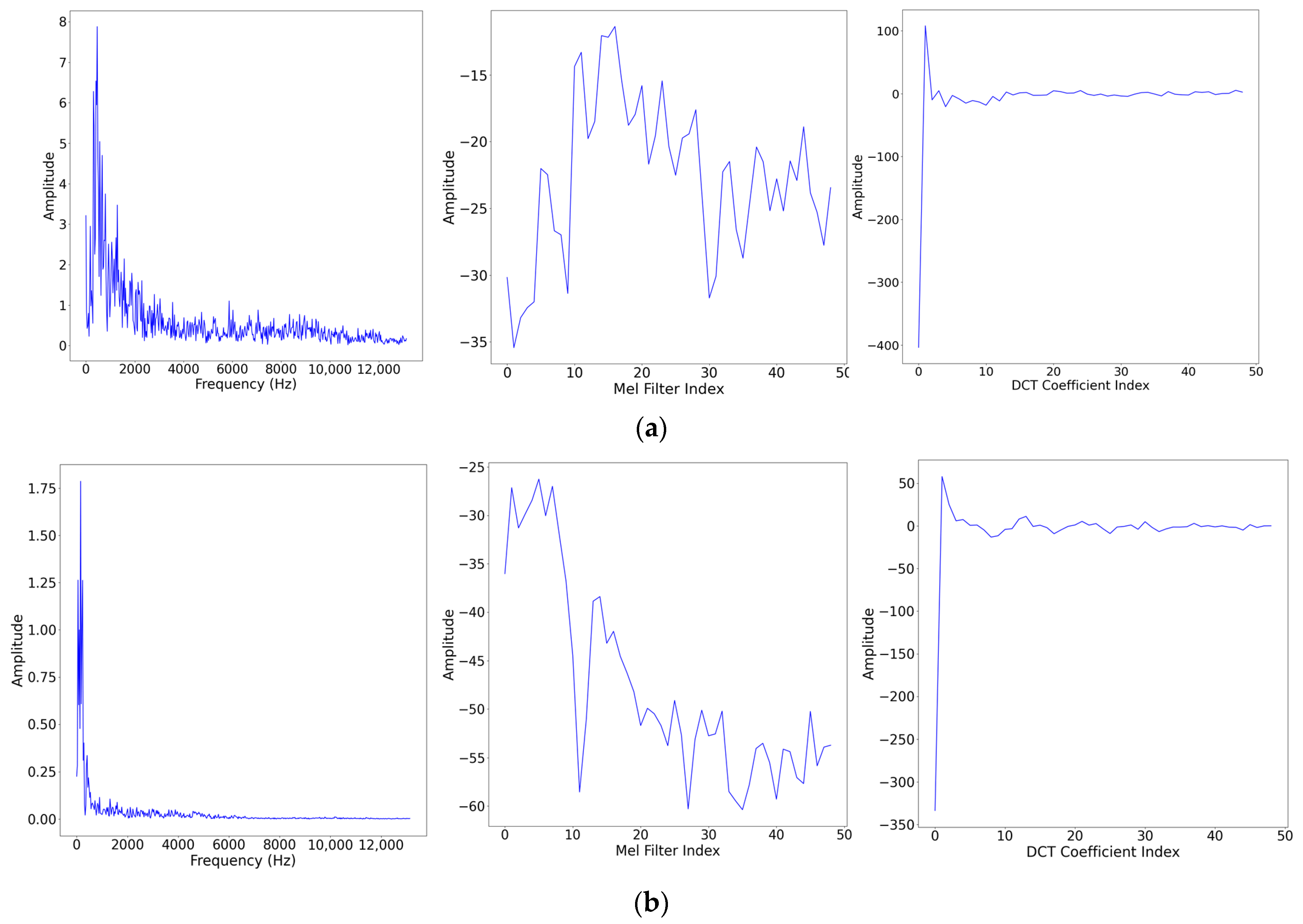
2.1. MFCC Feature Extraction
2.2. Design of Deep Learning Networks
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Experiment Setup and Dataset
3.2. Experiment Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, L.; Liang, H.; Yang, C. Accurate Underwater ATR in Forward-Looking Sonar Imagery Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 125522–125531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, M. An Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on Combined Feature with Automatic Coding and Reconstruction. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 63841–63854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shen, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H. Discriminative Ensemble Loss for Deep Neural Network on Classification of Ship-Radiated Noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Lei, X.; Zhou, C.; Qing, L.; Zhang, Q. Compressed Sensing Multiscale Sample Entropy Feature Extraction Method for Underwater Target Radiation Noise. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 77688–77694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, J.; Yu, H.; Chu, J. Underwater Target Detection Utilizing Polarization Image Fusion Algorithm Based on Unsupervised Learning and Attention Mechanism. Sensors 2023, 23, 5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Shen, T.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, D.; Guo, S. Underwater Target Recognition Using Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks with 3-D Mel-Spectrogram and Data Augmentation. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 178, 107989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J. Anthropogenic and Natural Sources of Ambient Noise in the Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 395, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, H. Bidirectional Denoising Autoencoders-Based Robust Representation Learning for Underwater Acoustic Target Signal Denoising. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, K. Underwater Single-Channel Acoustic Signal Multitarget Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 151, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Shang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q. A LOFAR Spectrum Multi-Sub-Band Matching Method for Passive Target Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Signal Image Processing and Communication (ICSIPC 2022), Qingdao, China, 20–22 May 2022; Cheng, D., Deperlioglu, O., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D. Design and Optimization of 1D-CNN for Spectrum Recognition of Underwater Targets. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2021, 218, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.C.; Ren, C.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y. Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on a Joint Neural Network. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, C.; Celeux, G.; Govaert, G. Assessing a Mixture Model for Clustering with the Integrated Completed Likelihood. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intell. 2000, 22, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Fan, Z. Classify Motion Model via SVM to Track Underwater Maneuvering Target. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Dalian, China, 20–22 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Han, X.; Zhu, Z. Feature extraction of underwater target signal using mel frequency cepstrum coefficients based on acoustic vector sensor. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 7864213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, T.; Huang, M.; Xu, X. An Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on Spectrograms with Different Resolutions. JMSE 2021, 9, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Bae, K.; Hwang, C.; Lee, H. Classification of Underwater Transient Signals Using MFCC Feature Vector. In Proceedings of the 2007 9th International Symposium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 12–15 February 2007; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-C. Underwater Acoustic Localisation by GMM Fingerprinting with Noise Reduction. Int. J. Sens. Netw. 2019, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Khishe, M.; Ravakhah, S. Underwater Targets Classification Using Local Wavelet Acoustic Pattern and Multi-Layer Perceptron Neural Network Optimized by Modified Whale Optimization Algorithm. Ocean Eng. 2020, 219, 108415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Feng, R.; Chen, J. An Improved Pretraining Strategy-Based Scene Classification with Deep Learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, H. Seismic Facies Analysis Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Qiu, M.; Shi, J.; Liu, L. Deep Learning Methods for Underwater Target Feature Extraction and Recognition. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, F. Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition: A Combination of Multi-Dimensional Fusion Features and Modified Deep Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, V.-S.; Huynh-The, T.; Kim, D.-S. Underwater Acoustic Target Classification Based on Dense Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atal, B.S.; Hanauer, S.L. Speech analysis and synthesis by linear prediction of the speech wave. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1971, 50, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, H.; Munson, W.A. Loudness, its definition, measurement and calculation. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1933, 12, 377–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Domínguez, D.; Torres-Guijarro, S.; Cardenal-López, A.; Pena-Gimenez, A. ShipsEar: An Underwater Vessel Noise Database. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 113, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, S. An Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on AMNet. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 5501105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Class A | Class B | Class C | Class D | Class E | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train samples Number | 912 | 1500 | 1248 | 3416 | 1964 | 9040 |
| Test samples Number | 288 | 375 | 312 | 854 | 491 | 2260 |
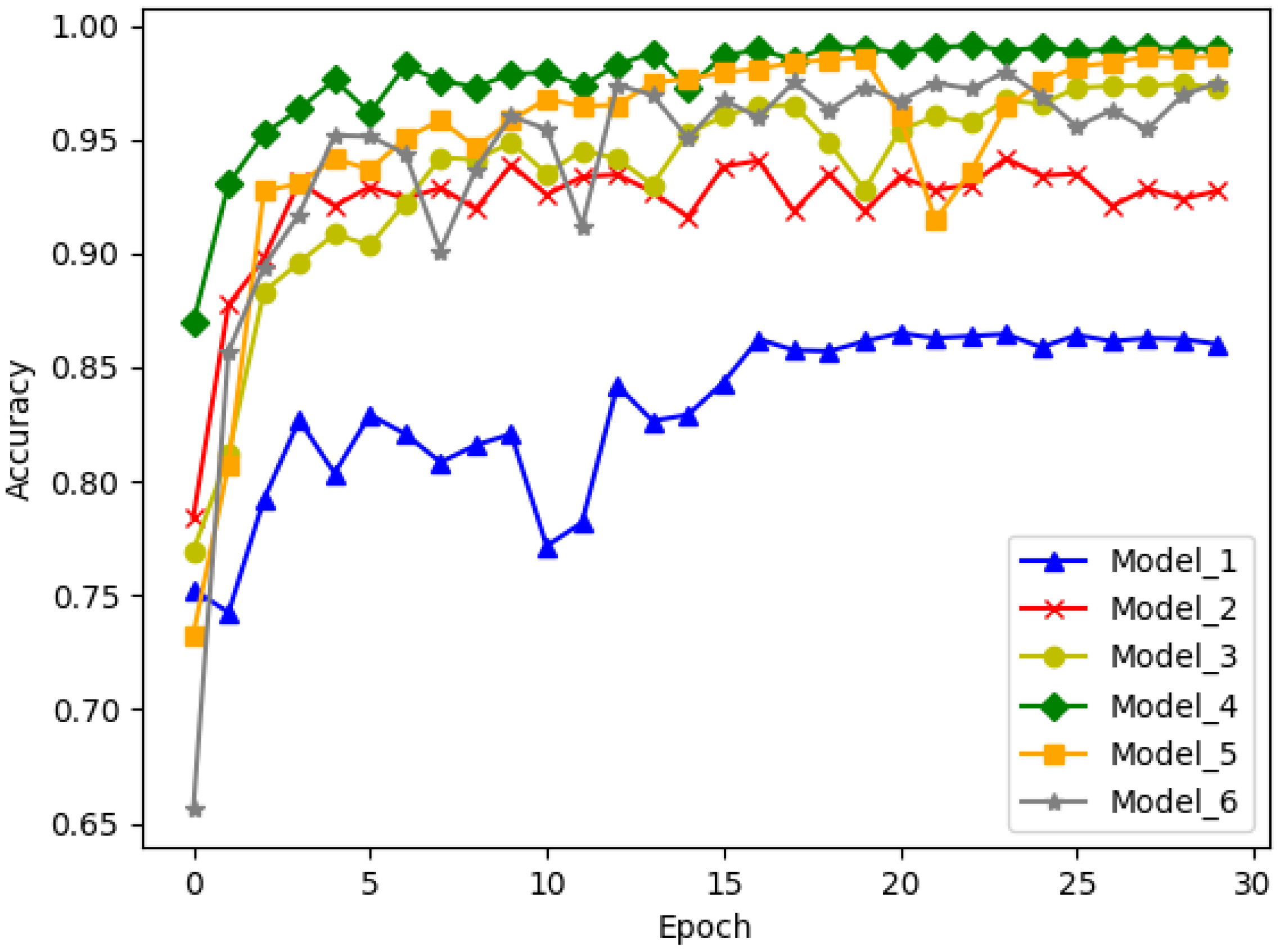
| Model | Block_A | Block_B | FC | Acc | Params |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model_1 | 1 | 1 | None | 0.8414 | 249 K |
| Model_2 | 1 | 1 | 512 | 0.9544 | 18 M |
| Model_3 | 3 | 2 | None | 0.9646 | 79 K |
| Model_4 | 3 | 2 | 256 | 0.9934 | 149 K |
| Model_5 | 4 | 3 | None | 0.9807 | 99 K |
| Model_6 | 4 | 3 | 64 | 0.9783 | 101 K |
| Name | Kernel Size | Activate | Accuracy | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model_4 | 1 × 3 | Relu | 0.9903 | 149 K |
| Model_4 | 1 × 3 | Sigmoid | 0.9792 | 149 K |
| Model_4 | 1 × 3 | Elu | 0.9934 | 149 K |
| Model_4 | 1 × 5 | Elu | 0.9850 | 193 K |
| Model_4 | 1 × 7 | Elu | 0.9929 | 237 K |
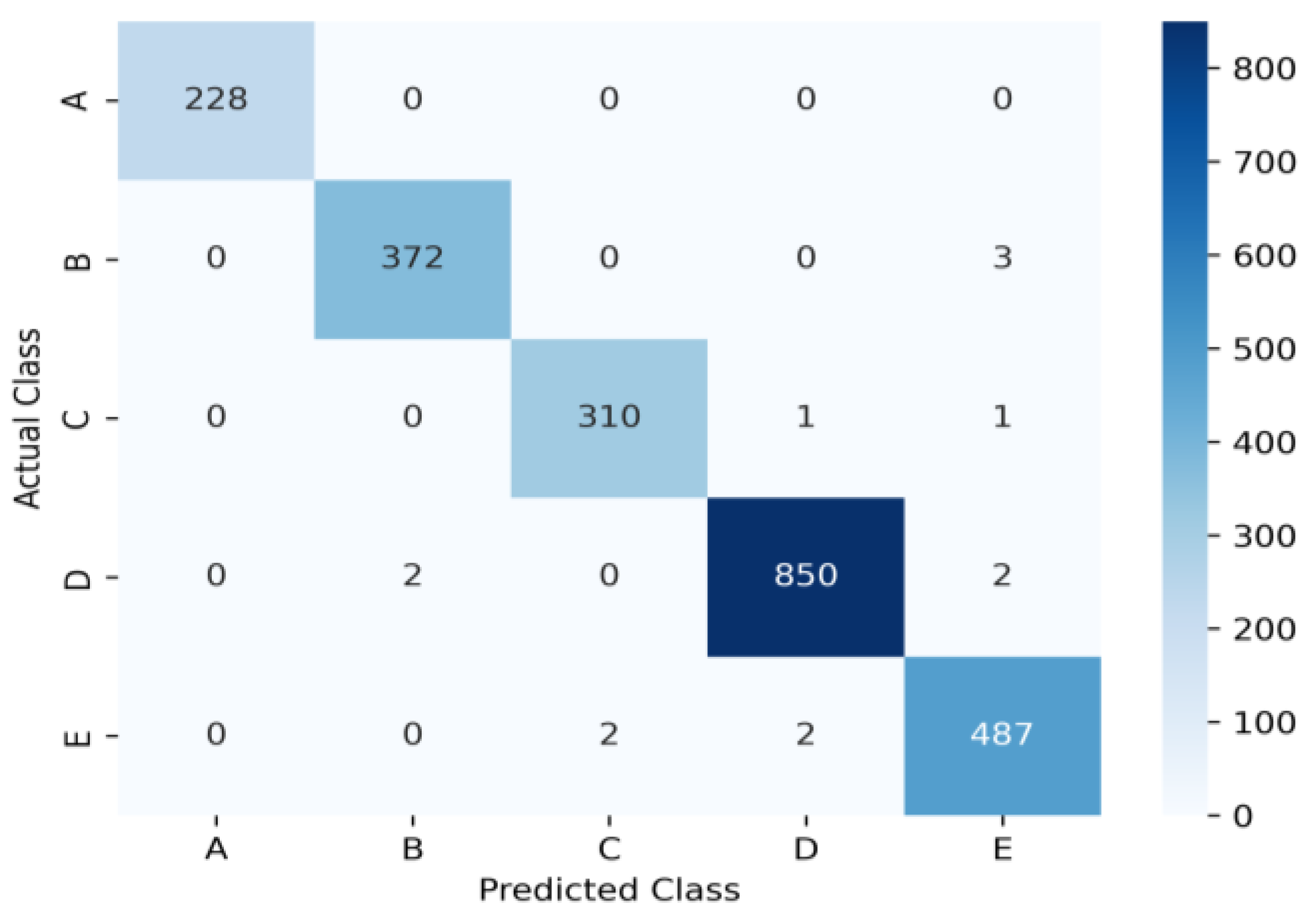
| Dataset | Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShipsEar | A | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 228.0 |
| B | 0.9946 | 0.9920 | 0.9933 | 372.0 | |
| C | 0.9936 | 0.9936 | 0.9936 | 312.0 | |
| D | 0.9964 | 0.9953 | 0.9958 | 850.0 | |
| E | 0.9878 | 0.9918 | 0.9898 | 487.0 | |
| Ave | 0.9944 | 0.9945 | 0.9945 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Yang, H.; Hou, W.; Wang, B. A Novel Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on MFCC and RACNN. Sensors 2024, 24, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010273
Liu D, Yang H, Hou W, Wang B. A Novel Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on MFCC and RACNN. Sensors. 2024; 24(1):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dali, Hongyuan Yang, Weimin Hou, and Baozhu Wang. 2024. "A Novel Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on MFCC and RACNN" Sensors 24, no. 1: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010273
APA StyleLiu, D., Yang, H., Hou, W., & Wang, B. (2024). A Novel Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on MFCC and RACNN. Sensors, 24(1), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010273






