Multi-Modal Multi-Array Electrochemical and Optical Sensor Suite for a Biological CubeSat Payload
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Prior Research and Limitations
1.3. Main Purpose and Scope of This Work
2. Materials and Methods
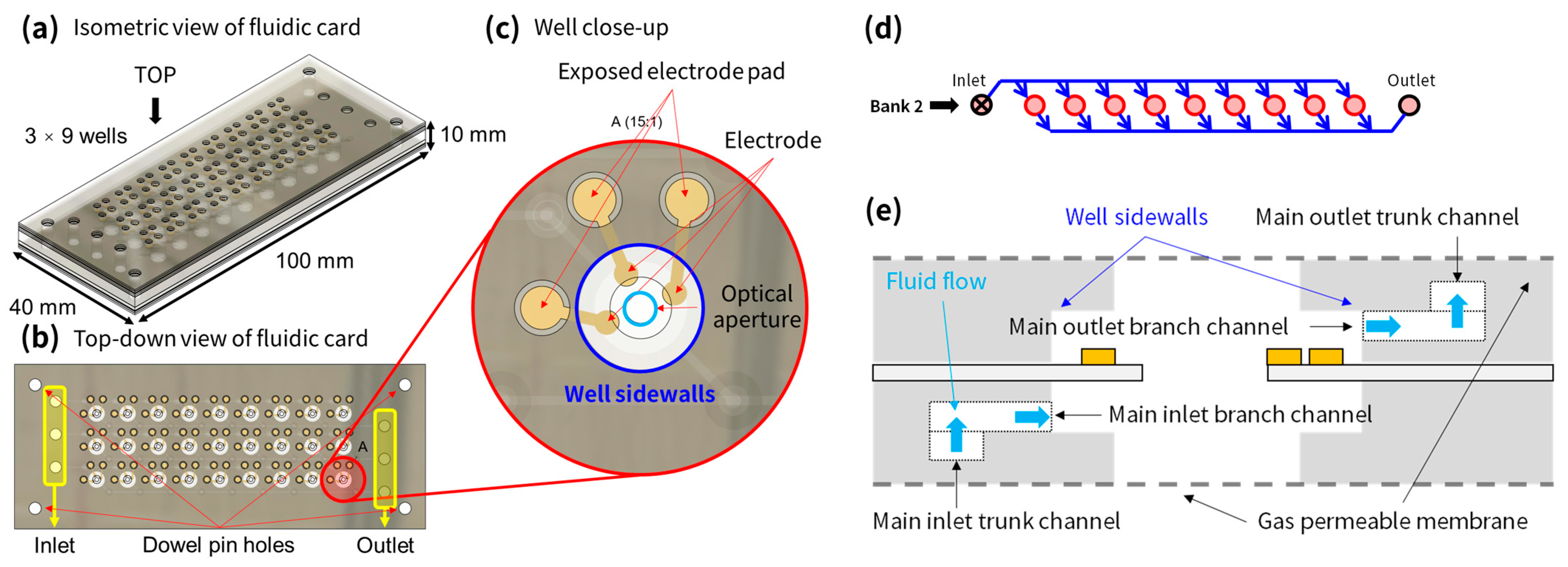
2.1. Fluidic Card
2.1.1. Design
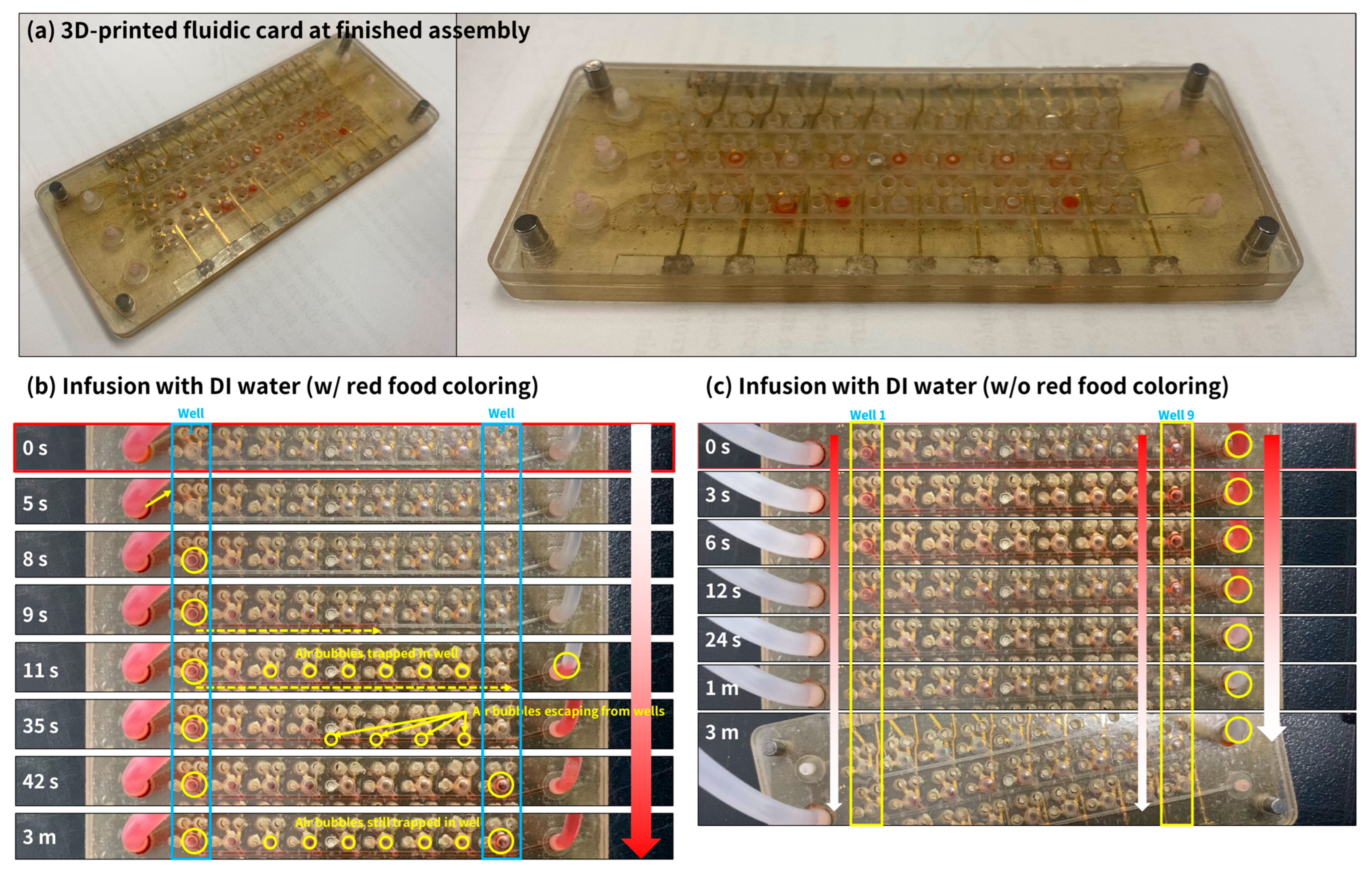
2.1.2. Fabrication and Assembly
2.1.3. Flow and Leakage Test Process
- Criterion 1: Leakage
- a.
- Intra-bank leakage: liquid leakage from one bank well into other features such as pogo-pin holes or other wells within the same bank.
- b.
- Inter-bank leakage: liquid from one bank leaking into another bank.
- c.
- Overall leakage: liquid within the fluidic card well and channels leaking out of the card from the sides.
- Criterion 2: Critical flow-rate
- a.
- The highest flow-rate a system can handle before experiencing rupture or leakage.
- Criterion 3: Well fill
- a.
- Whether the wells fill completely with liquid is crucial, as trapped air bubbles can prevent the electrochemical sensor electrodes from making proper contact with the test liquid.
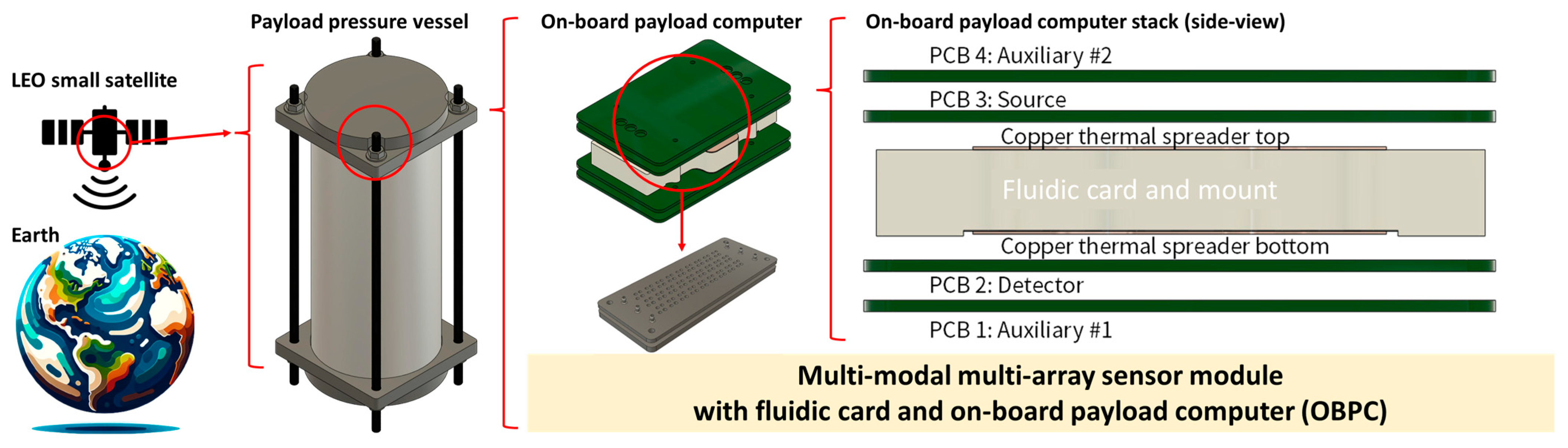
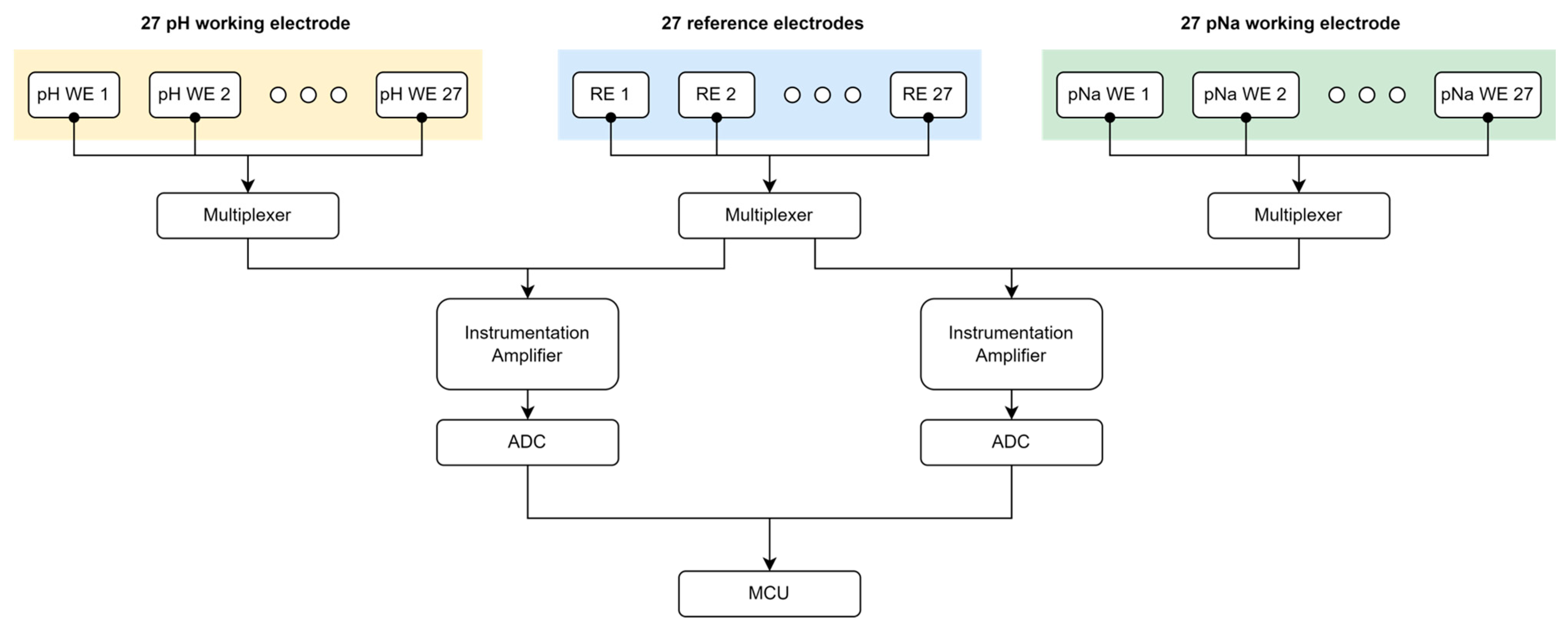
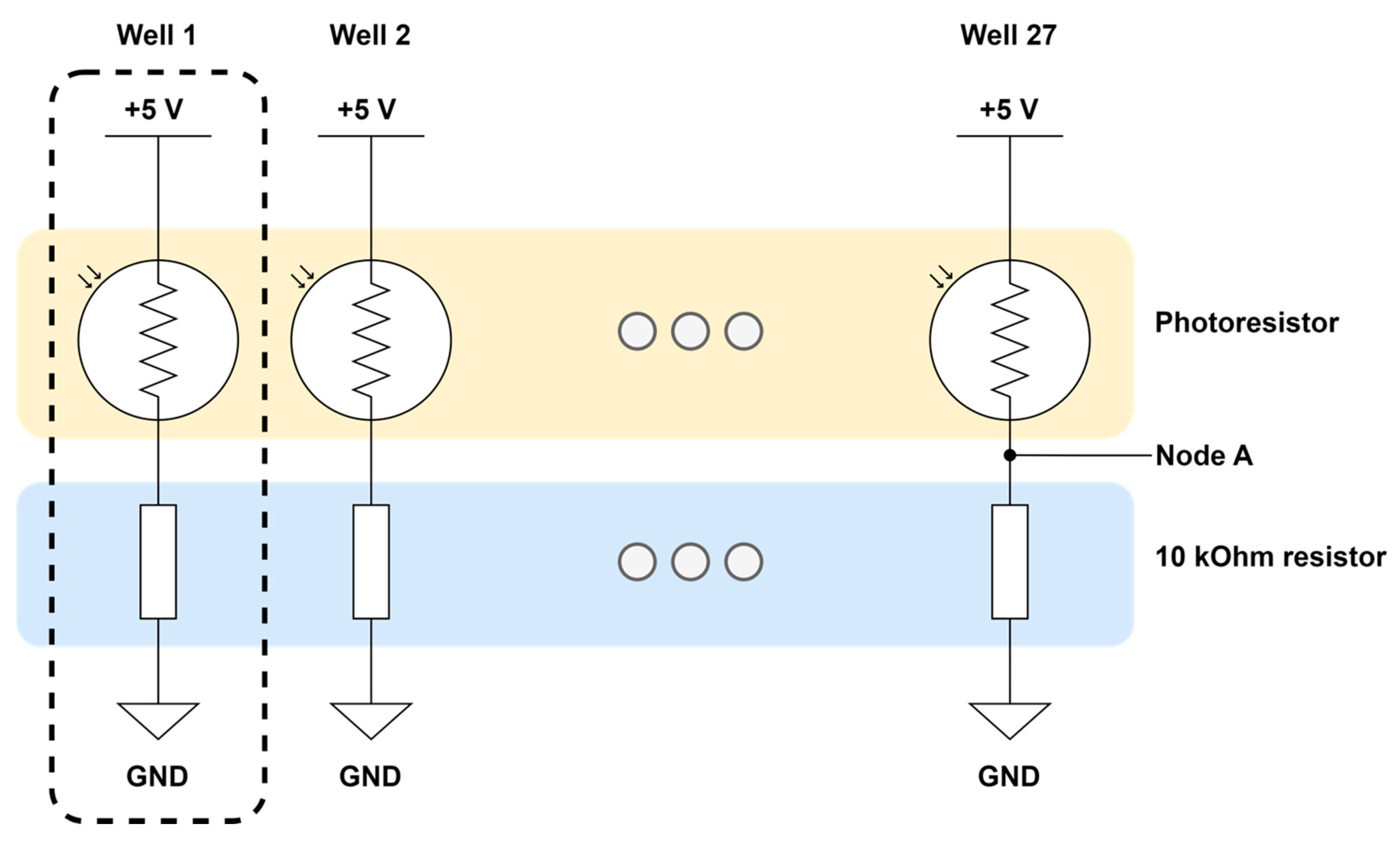
2.2. Multi-Modal Multi-Array Electrochemical Electrode and Optical Sensor Module
2.2.1. Design
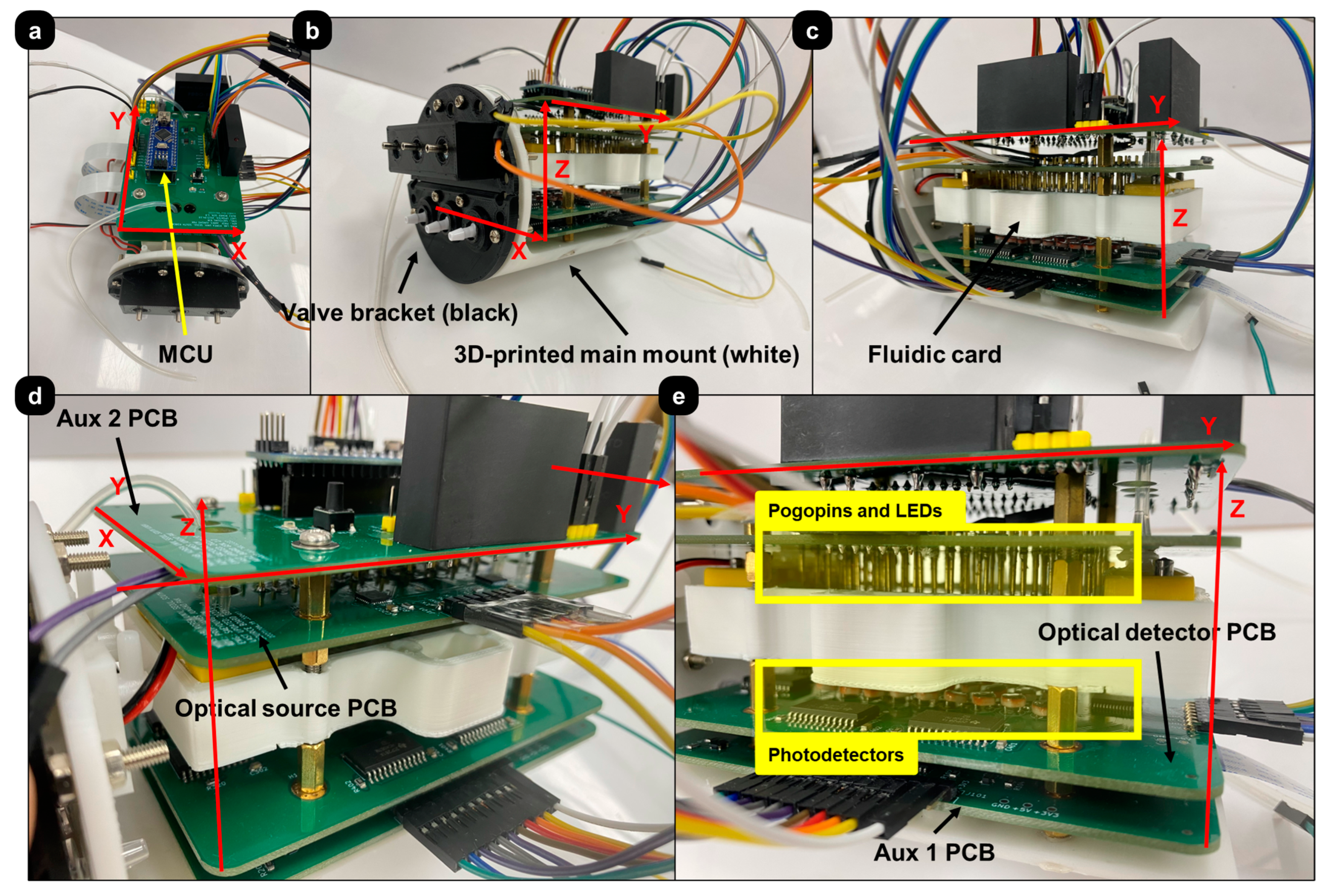
2.2.2. Fabrication and Assembly
2.2.3. Performance Evaluation
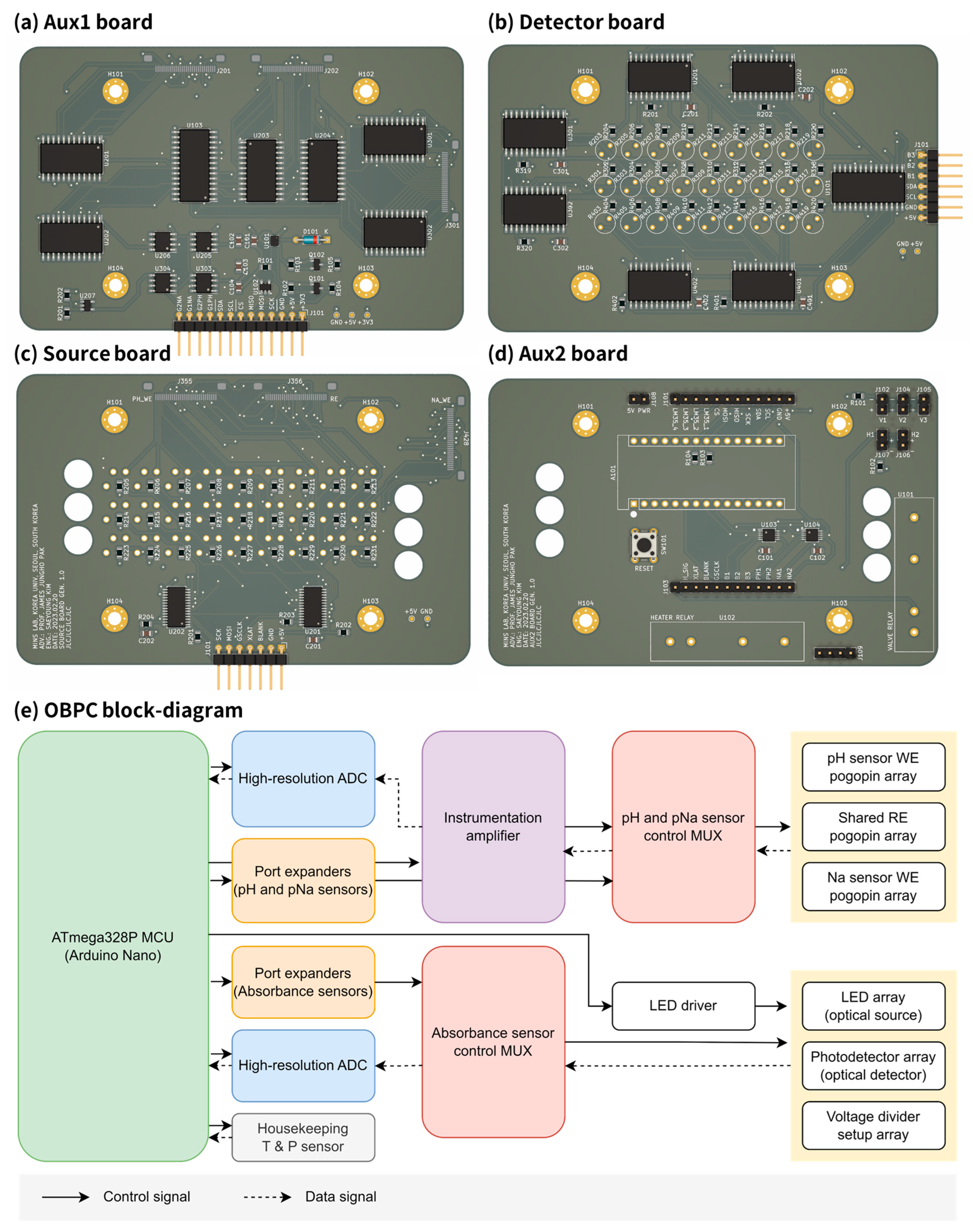
2.3. On-Board Payload Computer
2.3.1. Circuitry
2.3.2. Firmware
2.3.3. OBPC Functional Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fluidic Card Flow and Leakage Test Results
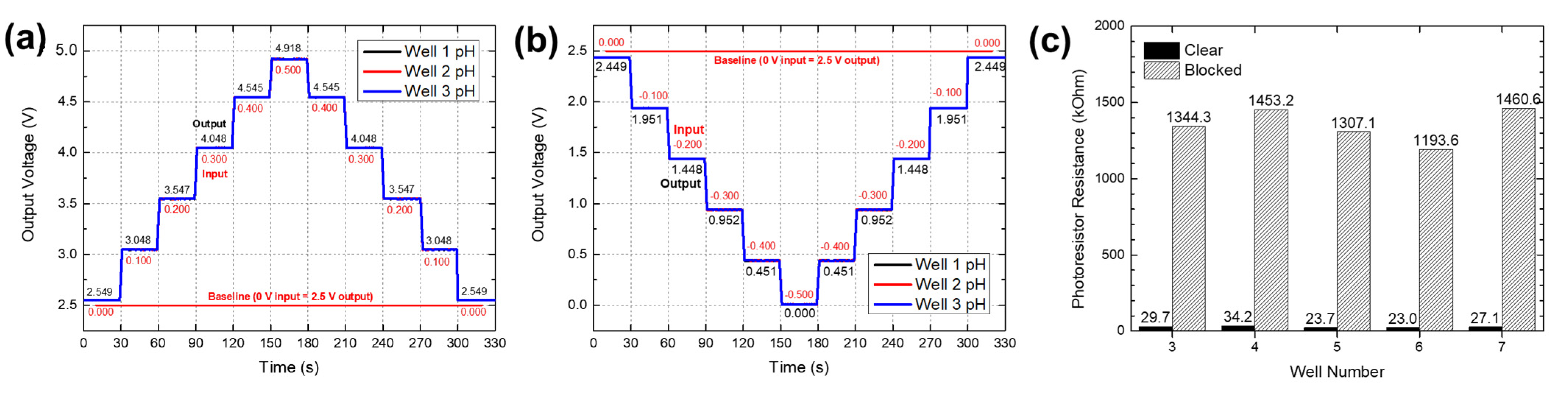
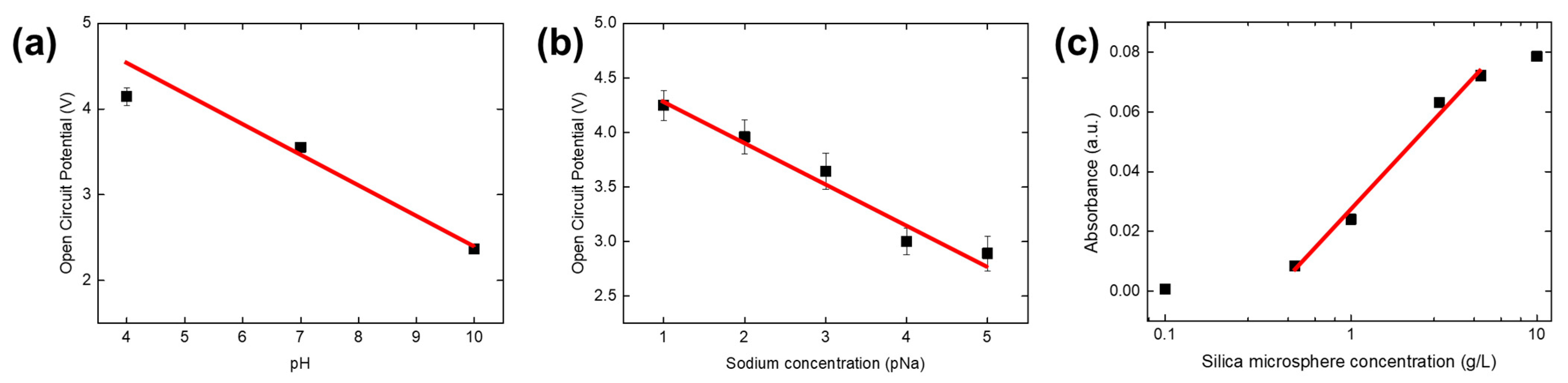
3.2. Multi-Modal Multi-Array Electrochemical Electrode Performance Evaluation
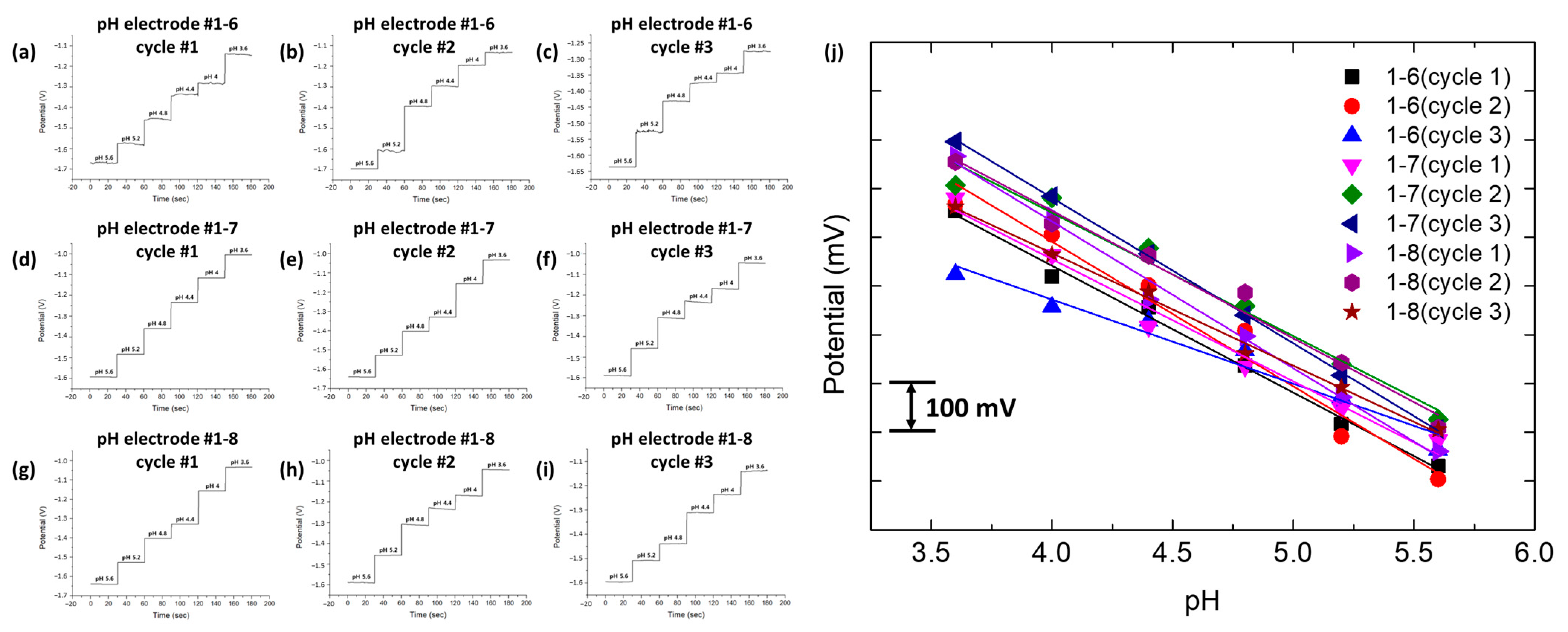
3.2.1. Stand-Alone Single-Well Ag/AgCl RE Evaluation
3.2.2. Multi-Array Electrochemical Electrode Evaluation
3.3. OBPC Functional Test Results
3.4. Discussion and Potential Future Work
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- California Polytechnic State. Cubesat Design Specification. In The CubeSat Program; Cal Poly: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 14, p. 34. Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5418c831e4b0fa4ecac1bacd/t/62193b7fc9e72e0053f00910/1645820809779/CDS+REV14_1+2022-02-09.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Zea, L.; Maria, S.R.S.; Ricco, A.J. CubeSats for Microbiology and Astrobiology Research; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, D.J.; Cappelletti, C. Biomedical payloads: A maturing application for CubeSats. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 191, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, D. CubeSats and Science Return CubeSats (aka canisterized Nanosats). In Proceedings of the National Academies’ Meeting on Achieving Science Goals with CubeSats, Virtual, 17 November 2015; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, D.C.; Longley, J.; Kingston, J.; Lee, D.; Black, M.; Pearson, D.; Waring, C.; Pink, R. BAMMsat—A platform for beyond LEO space environments studies on biological systems in CubeSats and CubeSat-like payloads. In Proceedings of the 5th Interplanetary CubeSat workshop (iCubeSat), Oxford, UK, 24–25 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Poghosyan, A.; Golkar, A. CubeSat evolution: Analyzing CubeSat capabilities for conducting science missions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2016, 88, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.; Korsmeyer, D. A Review of NASA Ames CubeSat Program. 2015. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20160007401.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Crusan, J.; Galica, C. NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative: Enabling broad access to space. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 157, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapstone, L.J.; Leite, M.N.; Purton, S.; Crawford, I.A.; Dartnell, L. Cyanobacteria and microalgae in supporting human habitation on Mars. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 59, 107946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belz, S.; Helisch, H.; Keppler, J.; Detrell, G. Microalgae cultivation in space for future exploration missions: Results of the preparatory activities for a spaceflight experiment on the International Space Station ISS. In Proceedings of the International Astronautical Congress, IAC, Washington, DC, USA, 5 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Revellame, E.D.; Aguda, R.; Chistoserdov, A.; Fortela, D.L.; Hernandez, R.A.; Zappi, M.E. Microalgae cultivation for space exploration: Assessing the potential for a new generation of waste to human life-support system for long duration space travel and planetary human habitation. Algal Res. 2021, 55, 102258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkolnik, E.L. On the verge of an astronomy CubeSat revolution. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitts, C.; Ronzano, K.; Rasay, R.; Mas, I.; Williams, P.; Mahacek, P.; Minelli, G.; Hines, J.; Agasid, E.; Friedericks, C.; et al. Flight Results from the GeneSat-1 Biological Microsatellite Mission. In Proceedings of the 2007 AIAA Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 11–14 August 2007; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2007; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Minelli, G.; Kitts, C.; Ronzano, K.; Beasley, C.; Rasay, R.; Mas, I.; Williams, P.; Mahacek, P.; Shepard, J.; Acain, J.; et al. Extended Life Flight Results from the GeneSat-1 Biological Microsatellite Mission. In Proceedings of the USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 11–14 August 2007; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2008; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kitts, C.; Hines, J.; Agasid, E.; Ricco, A.; Yost, B.; Ronzano, K.; Puig-Suari, J. The GeneSat-1 Microsatellite Mission: A Challenge in Small Satellite Design. In Proceedings of the AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 14–17 August 2006; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kitts, C.; Ronzano, K.; Rasay, R.; Mas, I.; Acain, J.; Neumann, M.; Bica, L.; Mahacek, P.; Minelli, G.; Beck, E.; et al. Initial Flight Results from the PharmaSat Biological Microsatellite Mission. In Proceedings of the 23nd Annual AIAA/USU Conf on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ricco, A.; Parra, M.; Niesel, D.; McGinnis, M.; Ly, D.; Kudlicki, A.; Hines, J.; Piccini, M.; Timucin, L.; Beasley, C.; et al. Pharmasat: Drug Dose Dependence Results from An Autonomous Microsystem-Based Small Satellite in Low Earth Orbit. In Proceedings of the 2010 Solid-State, Actuators, and Microsystems Workshop Technical Digest, Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 6–10 June 2010; Transducer Research Foundation: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, A.; Parra, M.; Niesel, D.; Piccini, M.; Ly, D.; McGinnis, M.; Kudlicki, A.; Hines, J.W.; Timucin, L.; Beasley, C.; et al. PharmaSat: Drug dose response in microgravity from a free-flying integrated biofluidic/optical culture-and-analysis satellite. In Proceedings of the Microfluidics, BioMEMS, and Medical Microsystems IX, San Francisco, CA, USA, 14 February 2011; Becker, H., Gray, B.L., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2011; p. 79290T. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfreund, P.; Ricco, A.; Squires, D.; Kitts, C.; Agasid, E.; Bramall, N.; Bryson, K.; Chittenden, J.; Conley, C.; Cook, A.; et al. The O/OREOS mission—Astrobiology in low Earth orbit. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 93, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, G.; Ricco, A.; Beasley, C.; Hines, J. O/OREOS Nanosatellite: A Multi-Payload Technology Demonstration. In Proceedings of 24th AIAAl/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 9–12 August 2010; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mattioda, A.L.; Cook, A.M.; Ehrenfreund, P.; Quinn, R.C.; Ricco, A.J.; Squires, D.; Bramall, N.; Bryson, K.; Chittenden, J.; Minelli, G.; et al. The O/OREOS Mission: First Science Data from the Space Environment Viability of Organics (SEVO) Payload. Astrobiology 2012, 12, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, W.L.; Ricco, A.J.; Agasid, E.; Beasley, C.; Diaz-Aguado, M.; Ehrenfreund, P.; Friedericks, C.; Ghassemieh, S.; Henschke, M.; Hines, J.W.; et al. The O/OREOS Mission: First Science Data from the Space Environment Survivability of Living Organisms (SESLO) Payload. Astrobiology 2011, 11, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgen, M. EcAMSat and BioSentinel: Autonomous Bio Nanosatellites Addressing Strategic Knowledge Gaps for Manned Spaceflight Beyond LEO. In Proceedings of the SUNY Polytechnic Institute (College of Nanoscale Science + Engineering) CNSE Colloquium Series, Albany, NY, USA, 24 March 2017; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Padgen, M.R.; Lera, M.P.; Parra, M.P.; Ricco, A.J.; Chin, M.; Chinn, T.N.; Cohen, A.; Friedericks, C.R.; Henschke, M.B.; Snyder, T.V.; et al. EcAMSat spaceflight measurements of the role of σs in antibiotic resistance of stationary phase Escherichia coli in microgravity. Life Sci. Space Res. 2019, 24, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgen, M.R.; Chinn, T.N.; Friedericks, C.R.; Lera, M.P.; Chin, M.; Parra, M.P.; Piccini, M.E.; Ricco, A.J.; Spremo, S.M. The EcAMSat fluidic system to study antibiotic resistance in low earth orbit: Development and lessons learned from space flight. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 173, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, B.; Chartres, J.; Sanchez, H. BioSentinel—A Deep Space Radiation BioSensor Mission. CubeSat Developers Workshop 2017. 2017. Available online: http://mstl.atl.calpoly.edu/~workshop/archive/2017/Spring/Day%201/Session%203/2_RobertHanel.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Santa Maria, S.R.; Marina, D.B.; Parra, M.P.; Boone, T.D.; Tan, M.; Ricco, A.J.; Straume, T.N.; Lusby, T.C.; Harkness, T.; Reiss-Bubenheim, D.; et al. BioSentinel: Developing a space radiation biosensor Santa. In Proceedings of the American Society for Gravitational and Space Research Conference, Pasadena, CA, USA, 23–26 October 2019; p. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tieze, S.M.; Liddell, L.C.; Maria, S.R.S.; Bhattacharya, S. BioSentinel: A Biological CubeSat for Deep Space Exploration. Astrobiology 2023, 23, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricco, A.J.; Hanel, R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Boone, T.; Tan, M.; Mousavi, A.; Padgen, M.; Gentry, D.; Rademacher, A.; Schooley, A.; et al. The biosentinel bioanalytical microsystem: Characterizing DNA radiation damage in living organisms beyond earth orbit. In Proceedings of the 2016 Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Workshop, Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 5–9 June 2016; pp. 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, A.J.; Maria, S.R.S.; Hanel, R.P.; Bhattacharya, S. BioSentinel: A 6U Nanosatellite for Deep-Space Biological Science. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2020, 35, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Salmi, M.L.; Wan Salim, W.W.A.; Rademacher, A.; Wickizer, B.; Schooley, A.; Benton, J.; Cantero, A.; Argote, P.F.; Ren, M.; et al. An autonomous lab on a chip for space flight calibration of gravity-induced transcellular calcium polarization in single-cell fern spores. Lab. Chip. 2017, 17, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, E.D.; Bebout, B.M.; Tan, M.X.; Selch, F.; Ricco, A.J. Biological system development for GraviSat: A new platform for studying photosynthesis and microalgae in space. Life Sci. Space Res. 2014, 3, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SporeSat 1, 2—Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/sporesat.htm (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Cypionka, H.; Reese, J.O. Recording and Simulating Proton-Related Metabolism in Bacterial Cell Suspensions. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 654065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Song, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xia, J.; Bai, R.; Kong, X. Sodium Dynamics in the Cellular Environment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10522–10532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Hsu, L.H.-H.; Kavanagh, P.; Barrière, F.; Lens, P.N.L.; Lapinsonnière, L.; V, J.H.L.; Schröder, U.; Jiang, X.; Leech, D. The ins and outs of microorganism–electrode electron transfer reactions. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, G.C. Organic Acid Metabolism of Yeasts During Fermentation of Alcoholic Beverages—A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 1976, 82, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskirchen, S.; Schröder, S.K.; Buhl, E.M.; Weiskirchen, R. A Beginner’s Guide to Cell Culture: Practical Advice for Preventing Needless Problems. Cells 2023, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J. Understanding and Managing Cell Culture Contamination; Corning Incorporated: Acton, MA, USA, 2002; Available online: https://safety.fsu.edu/safety_manual/supporting_docs/Understanding%20and%20Managing%20Cell%20Culture%20Contamination.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Mazzara, F.; Patella, B.; D’agostino, C.; Bruno, M.G.; Carbone, S.; Lopresti, F.; Aiello, G.; Torino, C.; Vilasi, A.; O’riordan, A.; et al. Pani-based wearable electrochemical sensor for ph sweat monitoring. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, I.A.; Lakard, S.; Lakard, B. Flexible Sensors Based on Conductive Polymers. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Cho, W.J. Highly sensitive and selective sodium ion sensor based on silicon nanowire dual gate field-effect transistor. Sensors 2021, 21, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.-R.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kwon, S.; Mahmood, M.; Kwon, Y.-T.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.M.; Yeo, W.-H. Wireless, flexible, ion-selective electrode system for selective and repeatable detection of sodium. Sensors 2020, 20, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubei KENTO Electronic Co., Ltd. KT-0603R Specification. Available online: https://datasheet.lcsc.com/lcsc/1810231112_Hubei-KENTO-Elec-KT-0603R_C2286.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Nanyang Senba Optical & Electronic Co., Ltd. GL5537 LDR Sensor Datasheet. Available online: https://www.kth.se/social/files/54ef17dbf27654753f437c56/GL5537.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Kasmi, M.; Chatti, A.; Hamdi, M.; Trabelsi, I. Eco-friendly process for soft drink industries wastewater reuse as growth medium for Saccharomyces cerevisiae production. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 2265–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| CubeSat Name | Organism | Size | Measured Parameters | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GeneSat-1 | E. coli | 3U | Optical absorbance | 2006 | [13,14,15] |
| PharmaSat 1 | S. cerevisiae | 3U | Optical absorbance | 2009 | [16,17,18] |
| O/OREOS | B. subtilis | 3U | Optical absorbance | 2010 | [19,20,21,22] |
| SporeSat-1 | Ceratopteris richardii | 3U | Calcium ions | 2014 | [31] |
| GraviSat | Cyanobacteria/Algal Cultures | 3U | Optical absorbance | Not launched | [32] |
| SporeSat-2 | Ceratopteris richardii | 3U | Optical absorbance | Not launched | [33] |
| EcAMSat | E. coli | 6U | Optical absorbance | 2017 | [23,24,25] |
| BioSentinel | S. cerevisiae | 6U | Optical absorbance | 2022 | [26,27,28,29,30] |
| Ingredient | % | Weight or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium ionophore X | 1 wt% | 18.18 mg |
| sodium tetrakis [3,5 bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl] borate (Na-TFPB) | 0.55 wt% | 10 mg |
| polyvinylchloride (PVC) | 33 wt% | 600 mg |
| bis(2-ethylehexyl) sebacate (DOS) | 65.45 wt% | 1.3 mL |
| tetrahydrofuran | 660 uL | 12 mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Park, S.; Pak, J.J. Multi-Modal Multi-Array Electrochemical and Optical Sensor Suite for a Biological CubeSat Payload. Sensors 2024, 24, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010265
Kim S, Park S, Pak JJ. Multi-Modal Multi-Array Electrochemical and Optical Sensor Suite for a Biological CubeSat Payload. Sensors. 2024; 24(1):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010265
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Saeyoung, Sanghyun Park, and James Jungho Pak. 2024. "Multi-Modal Multi-Array Electrochemical and Optical Sensor Suite for a Biological CubeSat Payload" Sensors 24, no. 1: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010265
APA StyleKim, S., Park, S., & Pak, J. J. (2024). Multi-Modal Multi-Array Electrochemical and Optical Sensor Suite for a Biological CubeSat Payload. Sensors, 24(1), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010265






