TDDFusion: A Target-Driven Dual Branch Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A detection-driven fusion framework for infrared and visible light images is proposed. By backpropagating feedback from the detection module to the fusion module, this framework efficiently achieves exceptional performance in both image fusion and downstream detection tasks.
- A novel objective loss function for the fusion task is introduced, designed to balance intensity and detail features in target regions. This effectively enhances fusion quality in these areas.
- A dual-branch feature extraction network is designed, incorporating Global Semantic Extractor (GST) and Local Texture Encoder (LTE) modules to handle global and local features, respectively. This design effectively enhances the model’s ability to extract both semantic and detailed information.
2. Related Work
2.1. AE and GAN Based Fusion Network
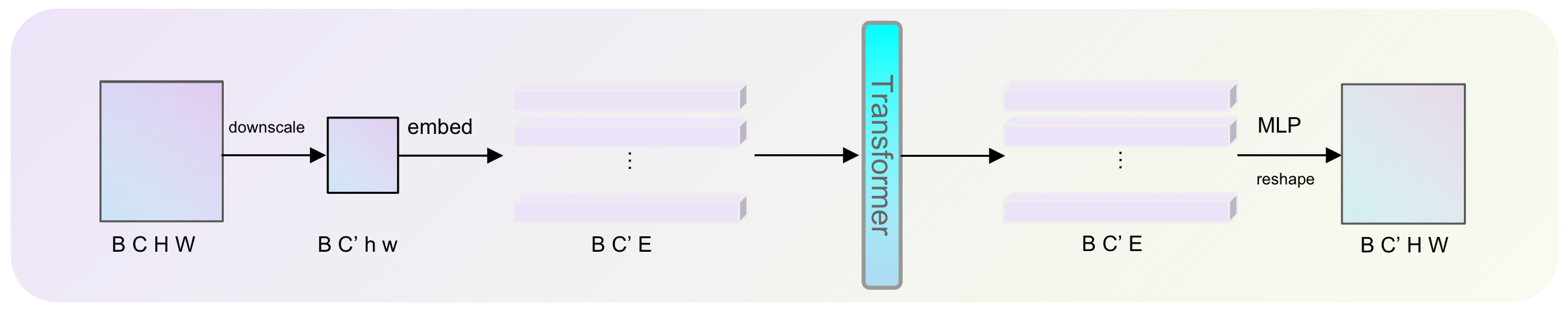
2.2. Vision Transformer
2.3. The High-Level Vision Tasks
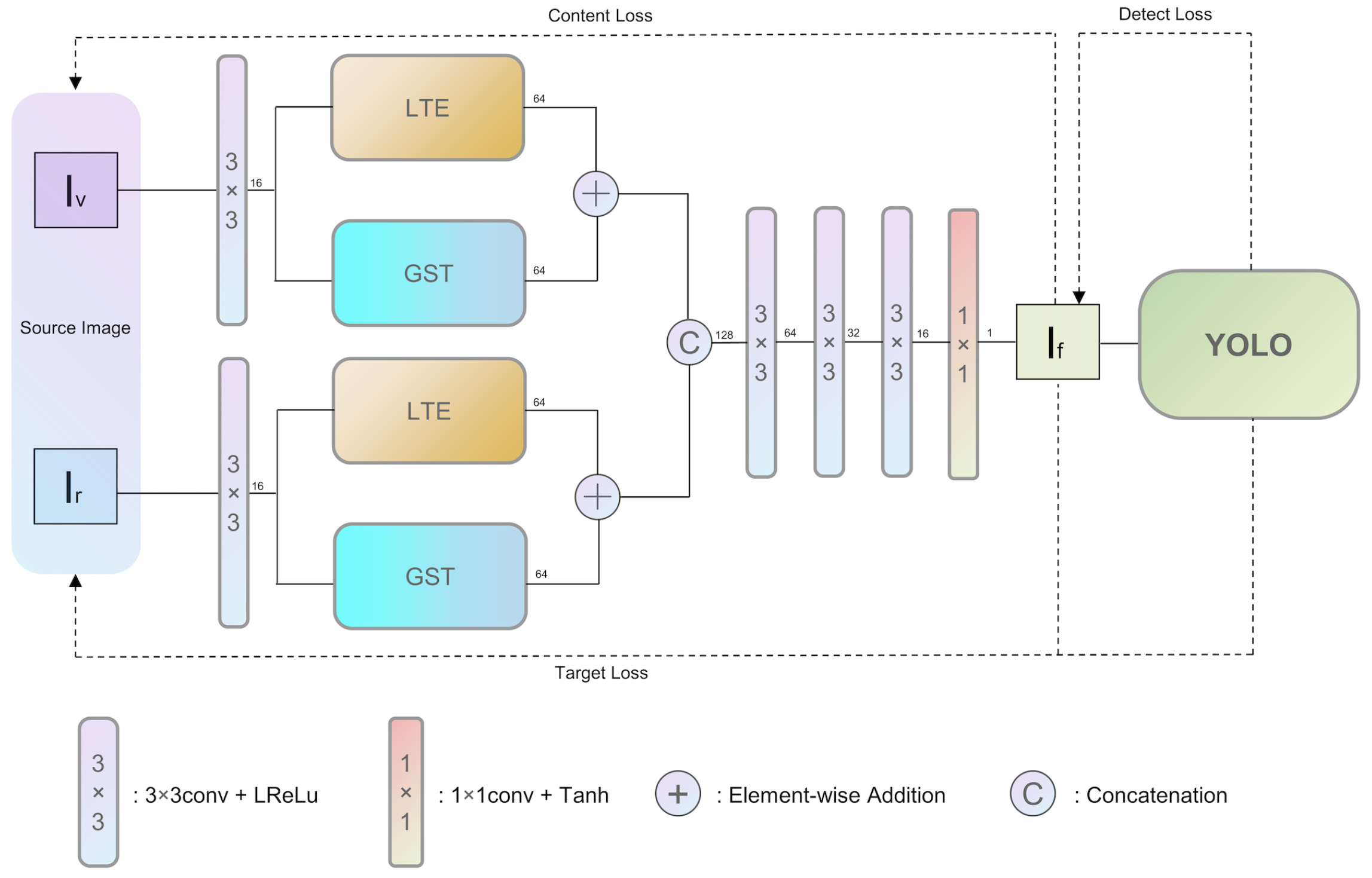
3. Proposed Method
3.1. General Framework
3.2. Loss Function
3.2.1. Content Loss
3.2.2. Detection Loss
3.2.3. Target Loss
3.3. Network Architecture
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Configuration and Implementation Details
| Algorithm 1 Training procedure |
|
4.2. Comparison Methods and Evaluation Indicators
4.3. Comparative Experiment
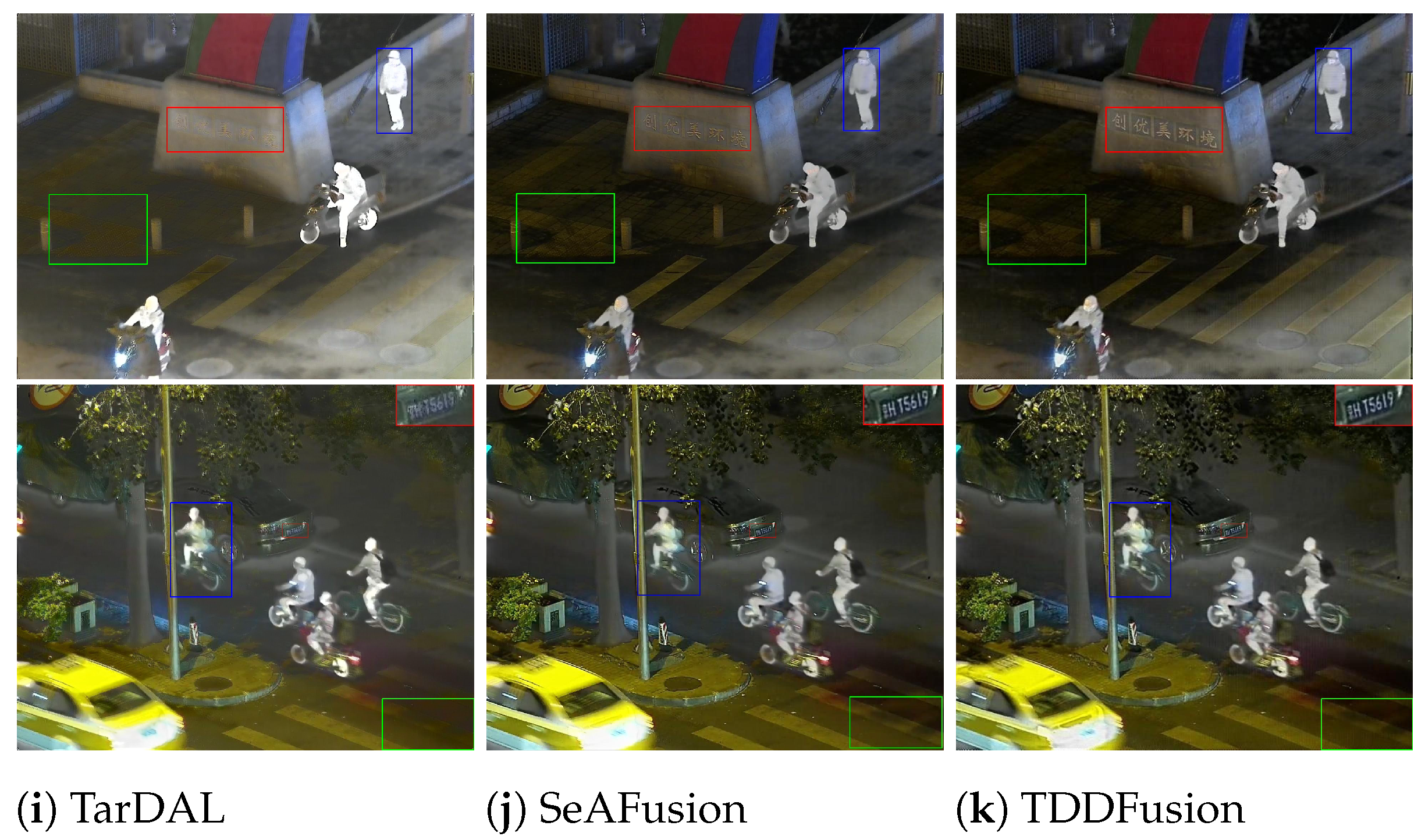
4.3.1. Qualitative Results
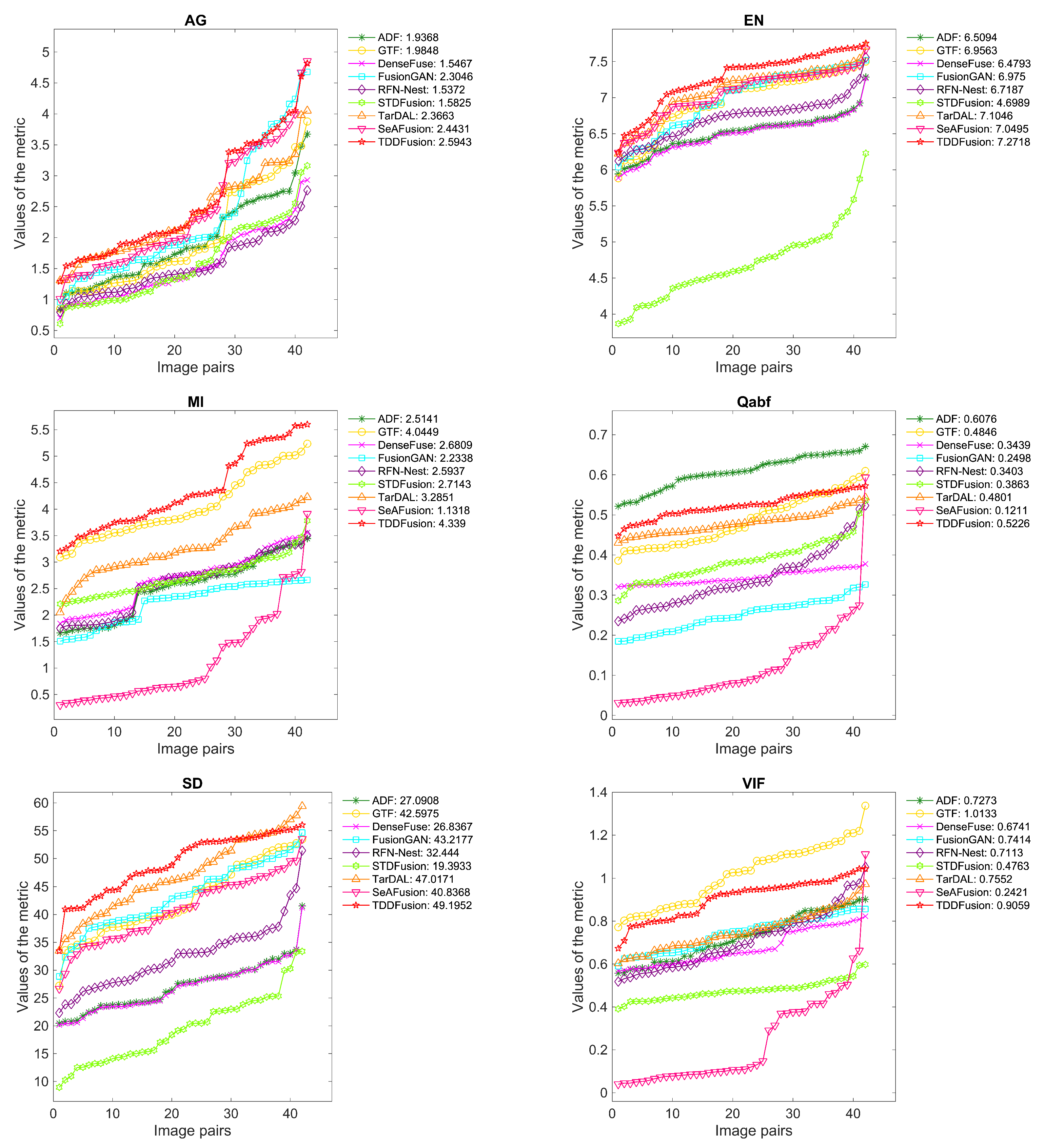
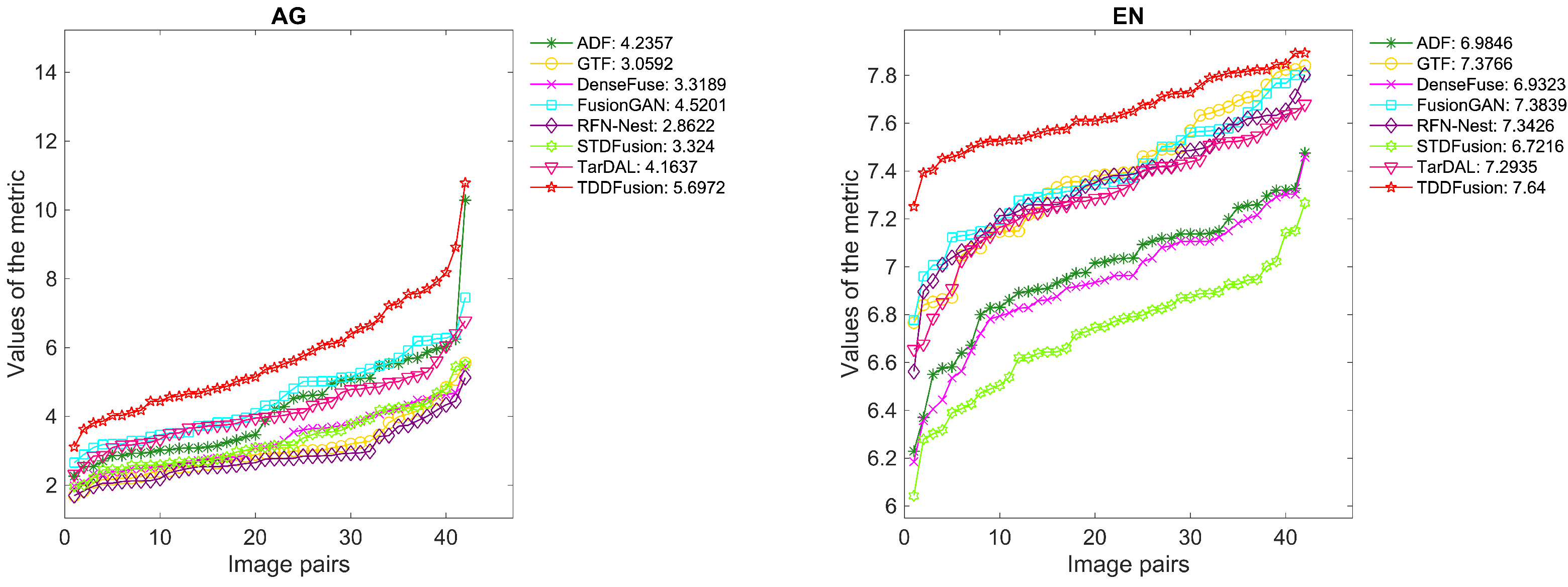
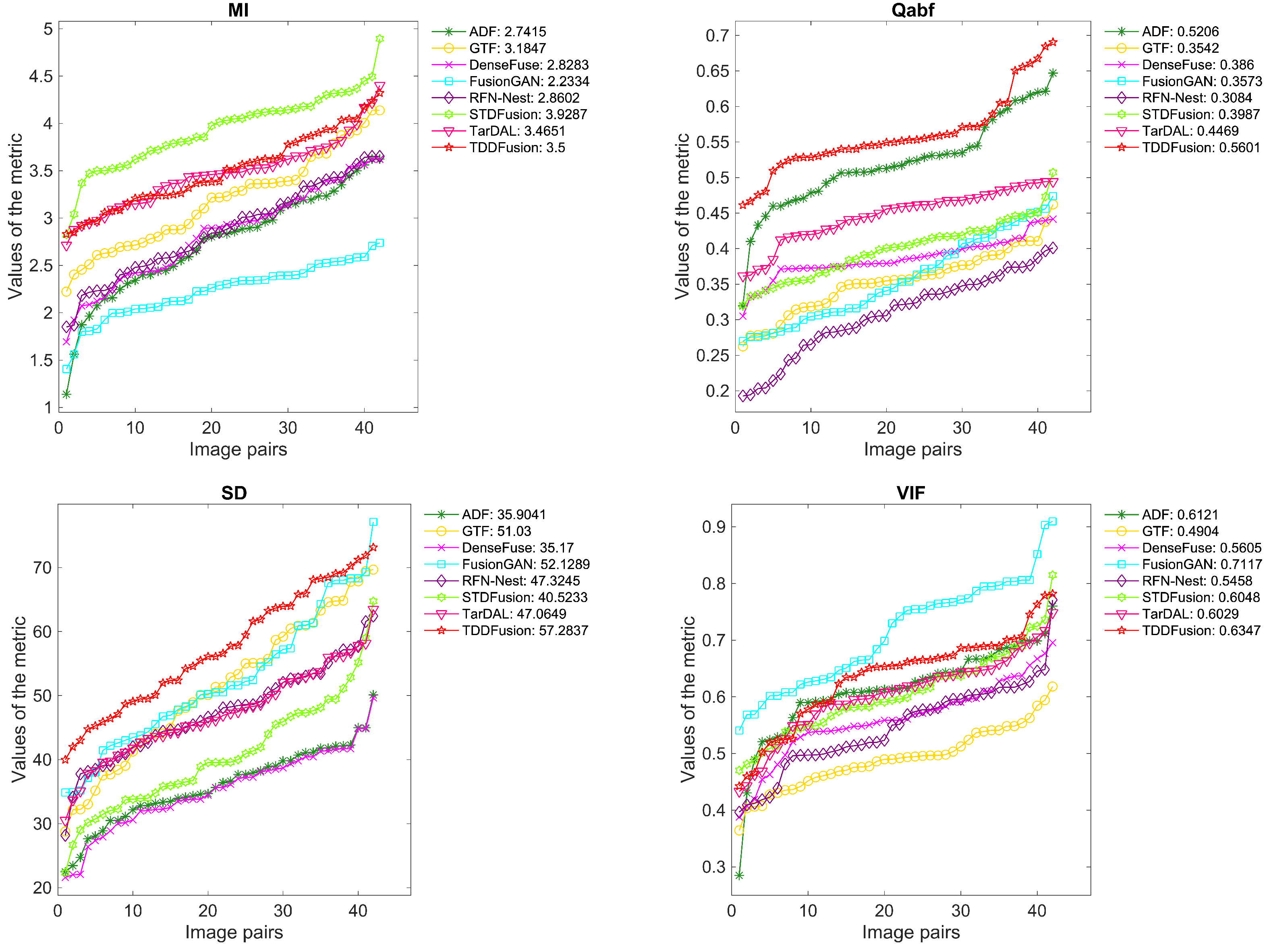
4.3.2. Quantitative Result
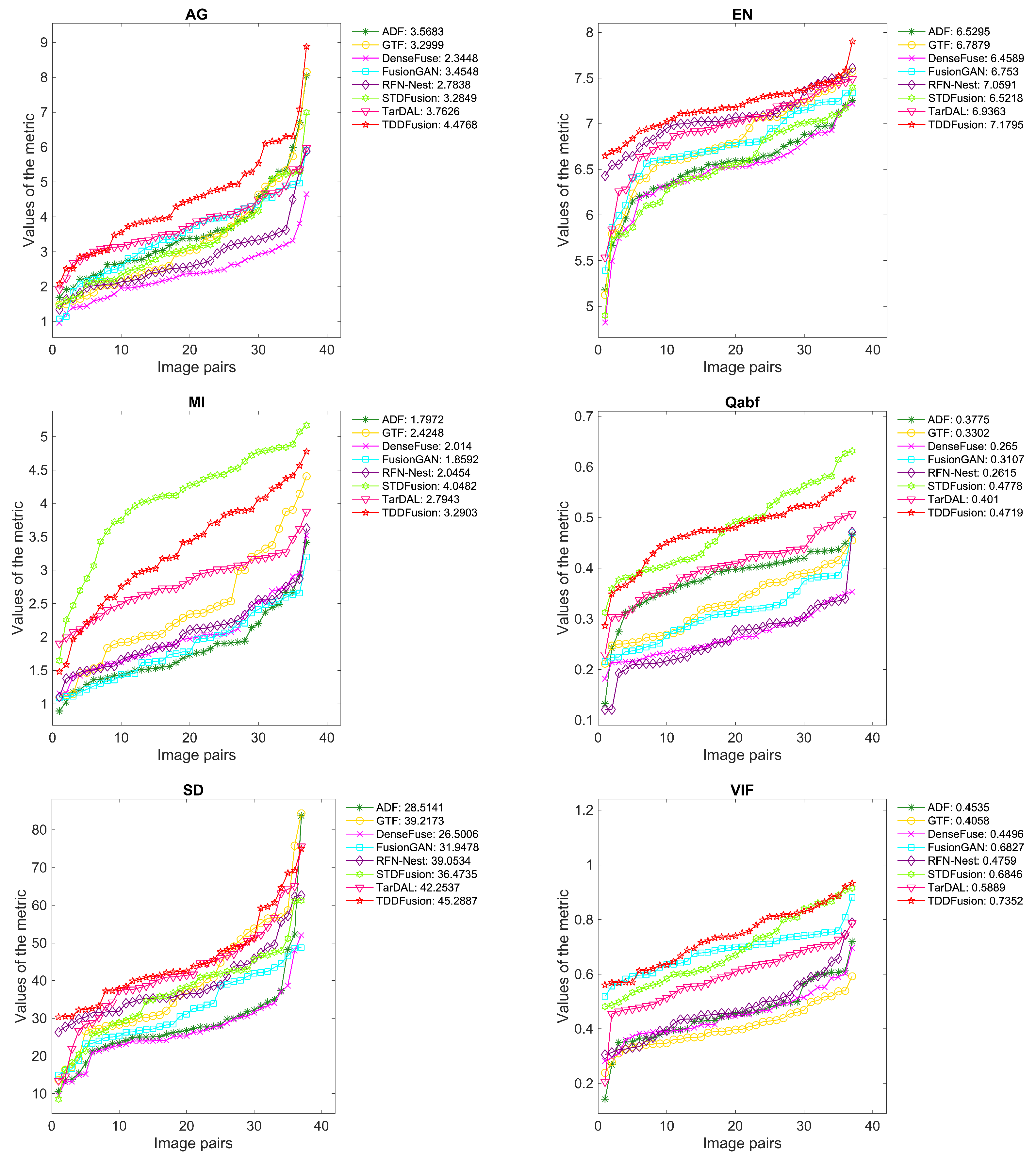
4.4. Generalization Experiment
4.4.1. Results of TNO
4.4.2. Results of RoadScene
4.5. Detection Performance
4.6. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, C.; Miao, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhan, X.; Hao, D.; Ma, C. Lift: Learning 4D lidar image fusion transformer for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17172–17181. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Guan, D.; Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Qiao, Y. Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multispectral feature learning using deep neural networks. Inf. Fusion 2019, 46, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, W. Illumination-Guided RGBT Object Detection With Inter-and Intra-Modality Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Tang, X.; Shen, H.; Zhang, H. Adaptive fusion CNN features for RGBT object tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 7831–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, W. CBFM: Contrast Balance Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Contrast-Preserving Guided Filter. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, T.; Smith, M. Image fusion technology for security and surveillance applications. In Optics and Photonics for Counterterrorism and Crime Fighting II; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6402, pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Cheng, B.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, D. Object classification using CNN-based fusion of vision and LIDAR in autonomous vehicle environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4224–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ma, J.; Le, Z.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X. Fusiondn: A unified densely connected network for image fusion. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12484–12491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; He, D.; Liu, Z.; Pan, X. DPACFuse: Dual-Branch Progressive Learning for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion with Complementary Self-Attention and Convolution. Sensors 2023, 23, 7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y. YDTR: Infrared and visible image fusion via Y-shape dynamic transformer. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 5413–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Yang, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X. DSA-Net: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Dual-Stream Asymmetric Network. Sensors 2023, 23, 7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. Efficient and model-based infrared and visible image fusion via algorithm unrolling. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, J. DIDFuse: Deep image decomposition for infrared and visible image fusion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09210. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, R.; Fan, X. Smoa: Searching a modality-oriented architecture for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Y. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradientlet filter. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 197, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X.-P. DDcGAN: A dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.; Wu, D.; Han, M.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Lei, T.; Zhou, C.; Bai, H.; Xing, L. AT-GAN: A generative adversarial network with attention and transition for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 92, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, W.; Ma, J.; Zhou, H. A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion based on semantic segmentation. Entropy 2021, 23, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Xiang, T.; Lin, M.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, P. Real-Time Semantics-Driven Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network. Sensors 2023, 23, 6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Han, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Visual Saliency Map and Image Contrast Enhancement. Sensors 2022, 22, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wu, D.; Gao, G. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Method Using Salience Detection and Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Zhou, W. LLVIP: A visible-infrared paired dataset for low-light vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; Virtual Conference. pp. 3496–3504. [Google Scholar]
- Toet, A. The TNO multiband image data collection. Data Brief 2017, 15, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Durrani, T.S. Infrared and visible image fusion with ResNet and zero-phase component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Durrani, T. NestFuse: An infrared and visible image fusion architecture based on nest connection and spatial/channel attention models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9645–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Luo, X.; Tong, X.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y. Infrared and visible image fusion based on a two-stage class conditioned auto-encoder network. Neurocomputing 2023, 544, 126248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Li, B.; Lang, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, R.; Ge, M. Infrared and visible image fusion based on infrared background suppression. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023, 164, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Huo, H.; Yang, X.; Li, J. An attention-guided and wavelet-constrained generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 129, 104570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ding, J.; Yu, Y.; Gong, W. THFuse: An infrared and visible image fusion network using transformer and hybrid feature extractor. Neurocomputing 2023, 527, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. “Attention is all you need”. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Hugo, T.; Cord, M.; Matthijs, D.; Francisco, M.; Alexandre, S.; Herve, J. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18 July 2021; pp. 10347–10357. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiang, T.; Torr, P.H.; et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6881–6890. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shao, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. SwinFuse: A residual swin transformer fusion network for infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y. TCCFusion: An infrared and visible image fusion method based on transformer and cross correlation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 137, 109295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Lin, Z.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Cddfuse: Correlation-driven dual-branch feature decomposition for multi-modality image fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 5906–5916. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, D. Aod-net: All-in-one dehazing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4770–4778. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Chen, M.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, X. High-level task-driven single image deraining: Segmentation in rainy days. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing: 27th International Conference, ICONIP 2020, Bangkok, Thailand, 23–27 November 2020; Part I 27 2020. pp. 350–362. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Fan, X. An interactively reinforced paradigm for joint infrared-visible image fusion and saliency object detection. Inf. Fusion 2023, 98, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Chaurasia, A.; Changyu, L.; Hogan, A.; Hajek, J.; Diaconu, L.; Kwon, Y.; Defretin, Y.; et al. ultralytics/yolov5: v5. 0-YOLOv5-P6 1280 models, AWS, Supervise. ly and YouTube integrations. Zenodo. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Dhuli, R. Fusion of infrared and visible sensor images based on anisotropic diffusion and Karhunen-Loeve transform. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 16, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.W.; Van Aardt, J.A.; Ahmed, F.B. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023522. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, G.; Zhang, D.; Yan, P. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, X. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fusion 2013, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| mAP@0.5 | mAP@[0.5:0.95] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | Car | All | Person | Car | All | |
| IR | 0.7793 | 0.5076 | 0.6605 | 0.4375 | 0.2323 | 0.3537 |
| VI | 0.5293 | 0.7435 | 0.6172 | 0.2646 | 0.3689 | 0.3075 |
| ADF | 0.7427 | 0.7236 | 0.7355 | 0.3935 | 0.3418 | 0.3713 |
| GTF | 0.7639 | 0.7118 | 0.7297 | 0.4139 | 0.3359 | 0.3472 |
| DenseFuse | 0.7421 | 0.7419 | 0.7420 | 0.4005 | 0.3793 | 0.3721 |
| FusionGAN | 0.7469 | 0.7223 | 0.7298 | 0.4045 | 0.3515 | 0.3649 |
| RFN-Nest | 0.7616 | 0.7194 | 0.7368 | 0.4108 | 0.3422 | 0.3680 |
| STDFusion | 0.7745 | 0.7265 | 0.7547 | 0.4125 | 0.3779 | 0.3791 |
| TarDAL | 0.7821 | 0.7638 | 0.7712 | 0.4201 | 0.3721 | 0.3826 |
| SeAFusion | 0.7681 | 0.7305 | 0.7403 | 0.4022 | 0.3716 | 0.3692 |
| TDDFusion | 0.8026 | 0.7621 | 0.7863 | 0.4306 | 0.3775 | 0.4027 |
| AG | EN | MI | Qabf | SD | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 2.4336 | 7.0705 | 3.826 | 0.5203 | 47.1083 | 1.0175 |
| M2 | 2.3059 | 6.8137 | 2.6172 | 0.5203 | 47.1083 | 0.7218 |
| M3 | 2.3059 | 6.8137 | 2.6172 | 0.3235 | 41.3274 | 0.6130 |
| M4 | 2.5297 | 7.2501 | 4.287 | 0.5221 | 48.9597 | 0.9021 |
| M5 | 2.5299 | 7.2479 | 4.293 | 0.5214 | 48.9503 | 0.9027 |
| M6 | 2.5360 | 7.2569 | 4.291 | 0.5223 | 48.9528 | 0.9033 |
| M7 | 2.1792 | 6.7932 | 3.475 | 0.4375 | 46.2759 | 0.7559 |
| Ours | 2.5943 | 7.2718 | 4.3390 | 0.5226 | 49.1952 | 0.9059 |
| mAP@50 | mAP@[0.5:0.95] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | Car | All | Person | Car | All | |
| M1 | 0.7625 | 0.7526 | 0.7569 | 0.4127 | 0.3761 | 0.3794 |
| M2 | 0.8013 | 0.7461 | 0.7401 | 0.4152 | 0.3694 | 0.3680 |
| M3 | 0.7472 | 0.7197 | 0.7304 | 0.4046 | 0.3517 | 0.3657 |
| M4 | 0.7718 | 0.7594 | 0.7628 | 0.4139 | 0.3726 | 0.3831 |
| M5 | 0.7716 | 0.7593 | 0.7627 | 0.4139 | 0.3726 | 0.3832 |
| M6 | 0.7735 | 0.7601 | 0.7701 | 0.4196 | 0.3694 | 0.3835 |
| M7 | 0.7723 | 0.7318 | 0.7591 | 0.4203 | 0.3689 | 0.3729 |
| Ours | 0.8026 | 0.7621 | 0.7863 | 0.4306 | 0.3775 | 0.4027 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, S.; Ye, X.; Rao, J.; Li, F.; Liu, S. TDDFusion: A Target-Driven Dual Branch Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Sensors 2024, 24, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010020
Lu S, Ye X, Rao J, Li F, Liu S. TDDFusion: A Target-Driven Dual Branch Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Sensors. 2024; 24(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Siyu, Xiangzhou Ye, Junmin Rao, Fanming Li, and Shijian Liu. 2024. "TDDFusion: A Target-Driven Dual Branch Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion" Sensors 24, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010020
APA StyleLu, S., Ye, X., Rao, J., Li, F., & Liu, S. (2024). TDDFusion: A Target-Driven Dual Branch Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Sensors, 24(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24010020





