Roman Urdu Hate Speech Detection Using Transformer-Based Model for Cyber Security Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- To develop a first-ever Roman Urdu pre-trained BERT Model (BERT-RU), trained on the largest Roman Urdu dataset in the hate speech domain.
- 2.
- To explore the efficacy of transfer learning (by freezing pre-trained layers and fine-tuning) for Roman Urdu hate speech classification using state-of-the-art deep learning models.
- 3.
- To examine the transformer-based model for the classification task of Roman Urdu hate speech and compare its effectiveness with state-of-the-art machine learning, deep learning, and pre-trained transformer-based models.
- 4.
- To show the robustness and generalization of the transformer-based model and other comparison models on a cross-domain dataset.
2. Related Work
2.1. English Hate Speech Detection
2.2. Non-English Hate Speech Detection
3. Proposed Methodology
- Same-Domain Testing.
- Cross-Domain Testing.
3.1. Dataset Selection
3.2. Preprocessing
3.3. Normalization
3.4. Features Extraction/Embeddings
3.5. Contextual Classification of Hate Speech Using Transformer-Based Model
3.6. Training Phase
3.7. Cross-Validation of Proposed Model
3.8. Testing Phase
3.8.1. Same Domain Testing
3.8.2. Cross-Domain Testing
4. Experimental Settings
4.1. Experimental Setting for Baseline (Traditional Machine Learning) Models
4.2. Experimental Setting for Deep Learning Models
4.3. Experimental Setting for Transformer-Based Model
4.4. Experimental Setting for Transfer Learning
4.4.1. Transfer Learning by Using Pre-Trained Embeddings
4.4.2. Transfer Learning by Fine-Tuning
4.5. Training Setup
4.5.1. Pre-Training of BERT on Roman Urdu (BERT-RU)
4.5.2. Training of Underlying Models
- Experiment No.1: Transformer Model.
- Experiment No.2: BERT-RU + BILSTM (by Transfer Learning).
- Experiment No.3: BERT-RU + BILSTM (by Fine Tuning).
- Experiment No.4: BERT-RU + BILSTM + Attention (by Transfer Learning).
- Experiment No.5: BERT-RU + BILSTM + Attention (by Fine Tuning).
- Experiment No.6: BERT-English + BILSTM (by Transfer Learning).
- Experiment No.7: BERT-English + BILSTM (by Fine Tuning).
- Experiment No.8: BERT-English + BILSTM + Attention (by Transfer Learning).
- Experiment No.9: BERT-English + BILSTM + Attention (by Fine Tuning).
- Experiment No.10 BERT-Multilingual + BILSTM (by Transfer Learning).
- Experiment No.11 BERT-Multilingual + BILSTM (by Fine Tuning).
- Experiment No.12: BERT-Multilingual + BILSTM + Attention (by Transfer Learning).
- Experiment No.13: BERT-Multilingual + BILSTM + Attention (by Fine Tuning).
4.5.3. Cross-Validation of Models
4.6. Testing Setup
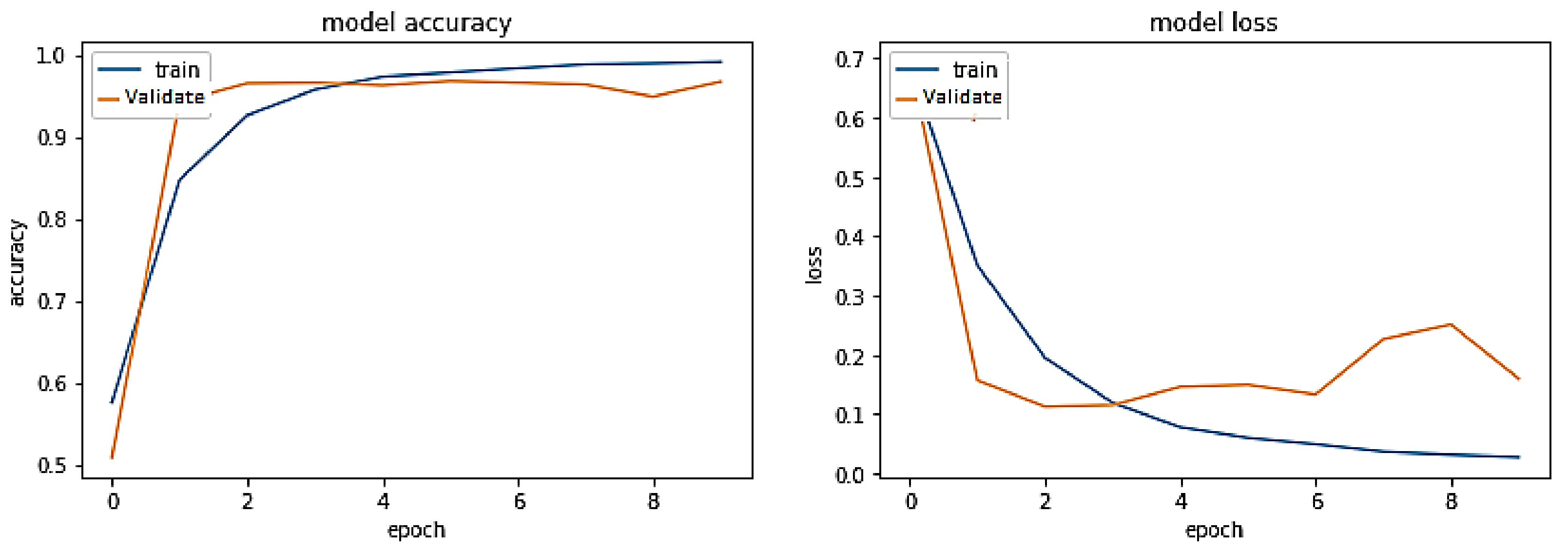
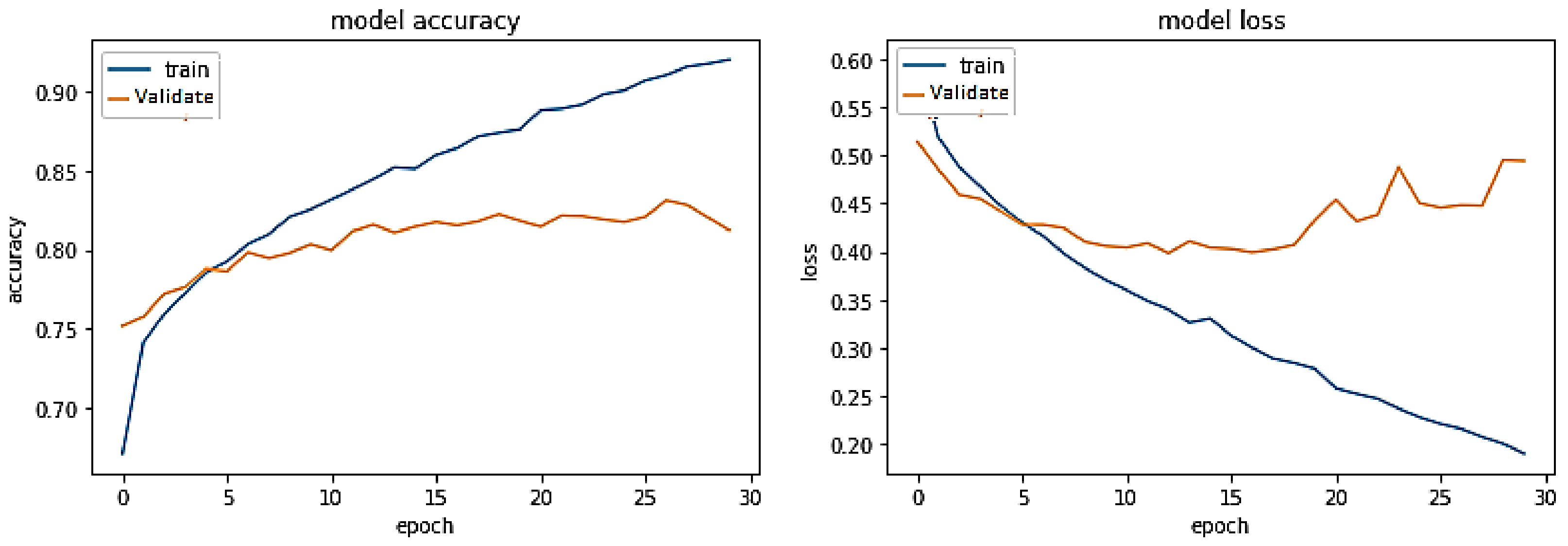
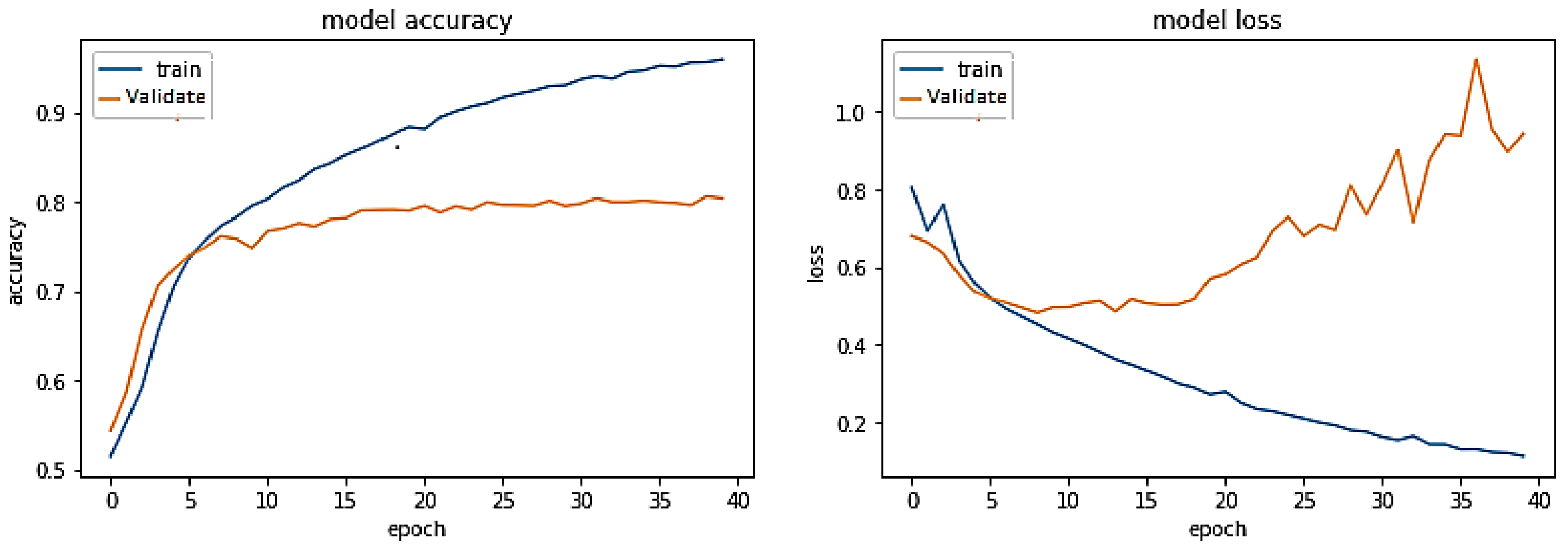
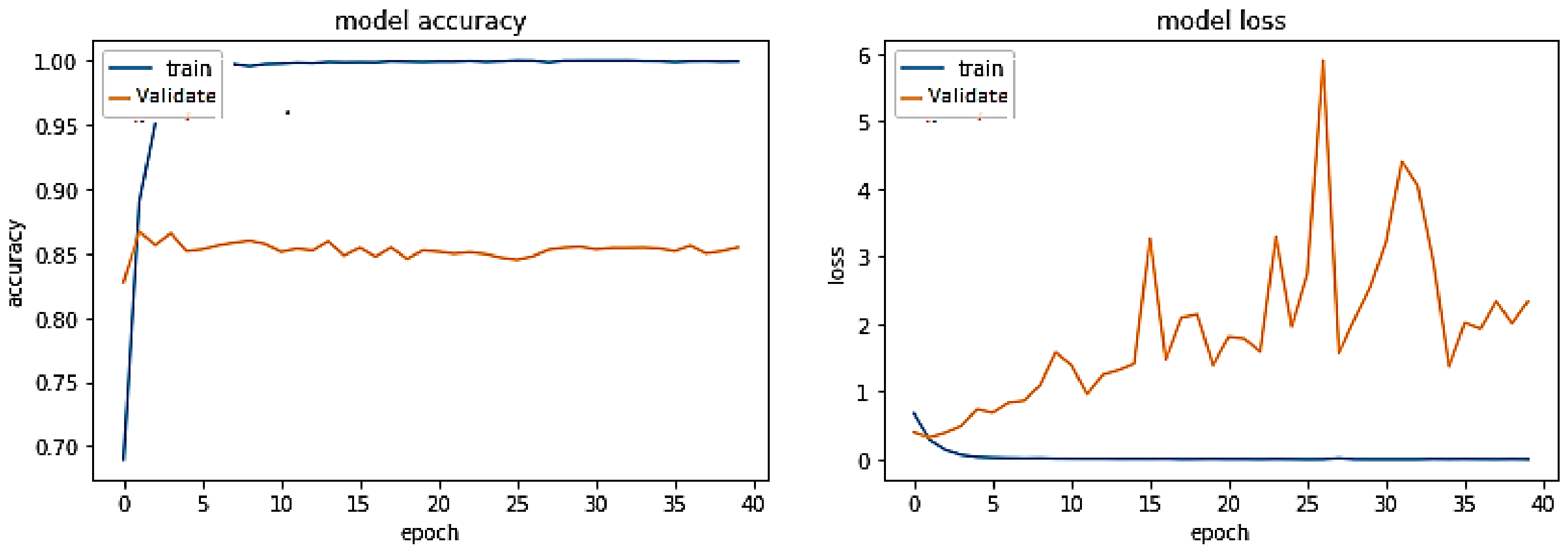
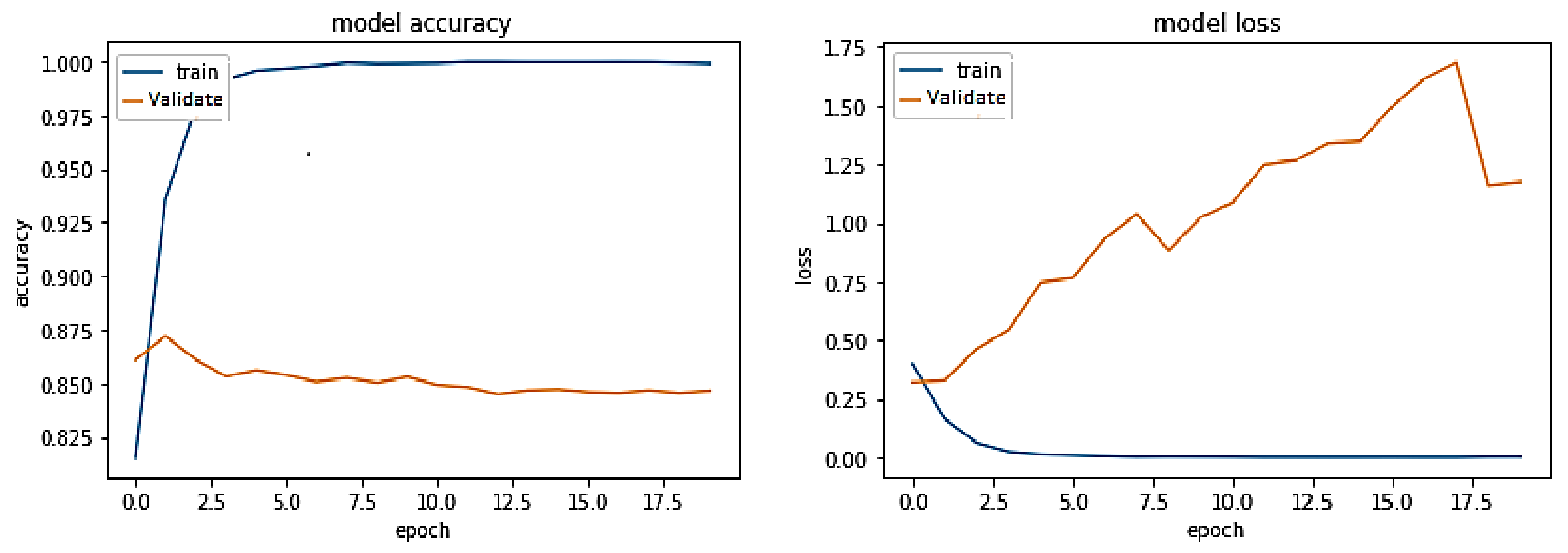
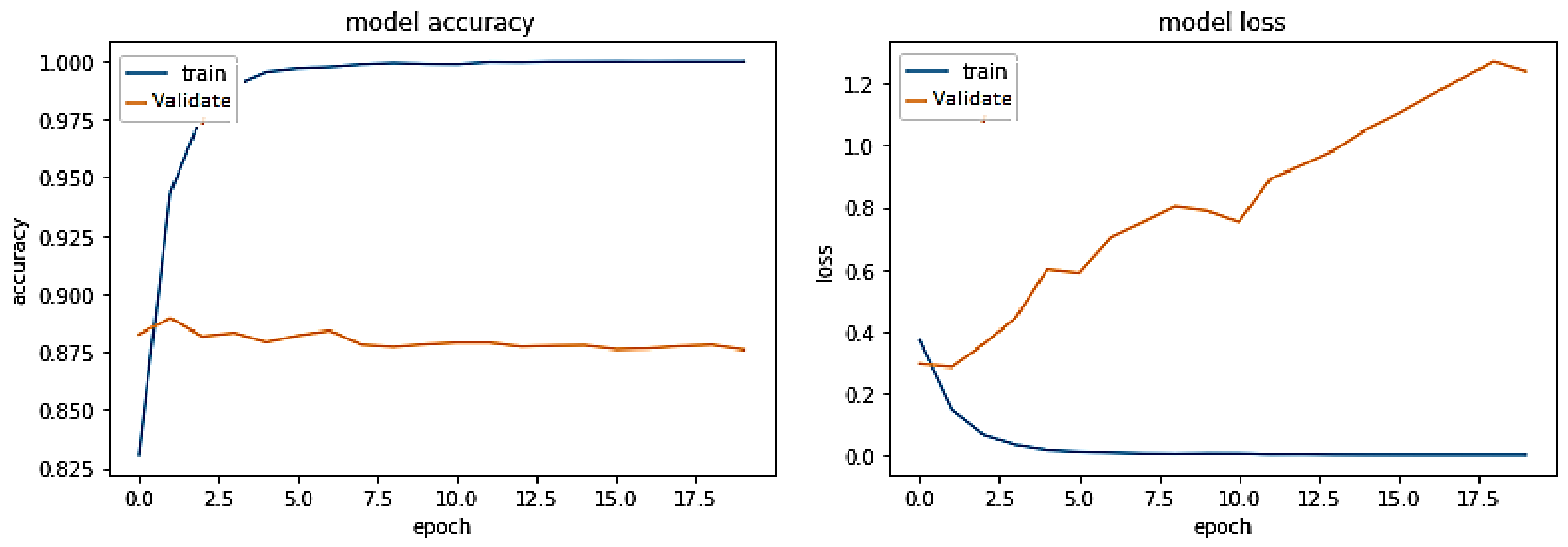
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Discussion on Experimental Results
5.2. Results of all Models on Cross Domain Dataset
- Accuracy.
- Precision.
- Recall.
- F-Measure.
6. Conclusions
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv Prepr. 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, M.A.; Mamoon, S.; Tao, S.K.; Ali, Z.; Adil, M.; Lu, J. Lexical Variation and Sentiment Analysis of Roman Urdu Sentences with Deep Neural Networks. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutanga, R.T.; Naicker, N.; Olugbara, O.O. Hate speech detection in twitter using transformer methods. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.; Warmsley, D.; Macy, M.; Weber, I. Automated hate speech detection and the problem of offensive language. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media; AAAI: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 512–515. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; McKeever, S.; Delany, S.J. A comparison of classical versus deep learning techniques for abusive content detection on social media sites. In International Conference on Social Informatics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Abro, S.; Shaikh, S.; Khand, Z.H.; Zafar, A.; Khan, S.; Mujtaba, G. Automatic hate speech detection using machine learning: A comparative study. Mach. Learn. 2020, 11, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Shahzad, K.; Malik, M.K. Hate speech detection in roman urdu. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. (TALLIP) 2021, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröndahl, T.; Pajola, L.; Juuti, M.; Conti, M.; Asokan, N. All you need is ”love” evading hate speech detection. In Proceedings of the 11th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Toronto, Canada, 15–19 October 2018; pp. 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, L. Hate speech detection: A solved problem? the challenging case of long tail on twitter. Semantic Web. 2019, 10, 925–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badjatiya, P.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, M.; Varma, V. Deep learning for hate speech detection in tweets. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 759–760. [Google Scholar]
- Gitari, N.D.; Zuping, Z.; Damien, H.; Long, J. A lexicon-based approach for hate speech detection. Int. J. Multimed. Ubiquitous Eng. 2015, 10, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAvaney, S.; Yao, H.R.; Yang, E.; Russell, K.; Goharian, N.; Frieder, O. Hate speech detection: Challenges and solutions. PloS ONE 2019, 14, e0221152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talat, Z.; Thorne, J.; Bingel, J. the gaps: Multi task learning for domain transfer of hate speech detection. In Online Harassment; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 29–55. [Google Scholar]
- Di Capua, M.; Di Nardo, E.; Petrosino, A. Unsupervised cyber bullying detection in social networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 432–437. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.; Argueta, C.; Chen, Y.L. Automatic detection of hate speech on facebook using sentiment and emotion analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Okinawa, Japan, 11–13 February 2019; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, S.; Awekar, A. Deep learning for detecting cyberbullying across multiple social media platforms. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Retrieval, Grenoble, France, 25–29 March 2018; pp. 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mollas, I.; Chrysopoulou, Z.; Karlos, S.; Tsoumakas, G. Ethos: An online hate speech detection dataset. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2006.08328. [Google Scholar]
- Baydogan, C. Deep-Cov19-Hate: A textual-based novel approach for automatic detection of hate speech in online social networks throughout COVID-19 with shallow and deep learning models. Tehnički Vjesnik 2022, 29, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Mozafari, M.; Farahbakhsh, R.; Crespi, N. Hate speech detection and racial bias mitigation in social media based on BERT model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swamy, S.D.; Jamatia, A.; Gambäck, B. Studying generalisability across abusive language detection datasets. In Proceedings of the 23rd Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL), Hong Kong, China, 3–4 November 2019; pp. 940–950. [Google Scholar]
- Alshalan, R.; Al-Khalifa, H. A deep learning approach for automatic hate speech detection in the saudi twittersphere. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldjanabi, W.; Dahou, A.; Al-qaness, M.A.; Elaziz, M.A.; Helmi, A.M.; Damaševičius, R. Arabic offensive and hate speech detection using a cross-corpora multi-task learning model. Informatics 2021, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.H.; Nguyen, V.A.; Doan, L.B.; Tran, N.N.; Thanh, T.M. From universal language model to downstream task: Improving RoBERTa-based Vietnamese hate speech detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE), Can Tho City, Vietnam, 12–14 November 2020; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, H.; Lee, H. Mc-bert4hate: Hate speech detection using multi-channel bert for different languages and translations. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Beijing, China, 8–11 November 2019; pp. 551–559. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Lin, C.J. Tocp: A dataset for chinese profanity processing. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying, Marseille, France, 16 May 2020; pp. 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sreelakshmi, K.; Premjith, B.; Soman, K.P. Detection of hate speech text in Hindi-English code-mixed data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 171, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velankar, A.; Patil, H.; Gore, A.; Salunke, S.; Joshi, R. Hate and offensive speech detection in Hindi and Marathi. arXiv Prepr. 2021, arXiv:2110.12200. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.; Saha, P.; Mathew, B.; Mukherjee, A. HateCheckHIn: Evaluating Hindi Hate Speech Detection Models. arXiv Prepr. 2022, arXiv:2205.00328. [Google Scholar]
- Rizwan, H.; Shakeel, M.H.; Karim, A. Hate-speech and offensive language detection in roman Urdu. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 2512–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, L.; Amjad, A.; Ashraf, N.; Chang, H.T. Multi-class sentiment analysis of urdu text using multilingual BERT. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Farooq, U.; Arshad, U.; Shahzad, W.; Beg, M.O. Hate speech detection on Twitter using transfer learning. Comput. Speech Lang. 2022, 74, 101365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Khan, A.; Jan, S.; Musa, S. Context-aware deep learning model for detection of roman urdu hate speech on social media platform. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 121133–121151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharf, Z.; Rahman, S.U. Lexical normalization of roman Urdu text. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2017, 17, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Sharf, Z.; Rahman, S.U. Performing natural language processing on roman urdu datasets. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2018, 18, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, M.P.; Jiangbin, Z.; Naqvi, I.R.; Abdelmajeed, M.; Sadiq, M.T. Automatic detection of offensive language for urdu and roman urdu. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91213–91226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





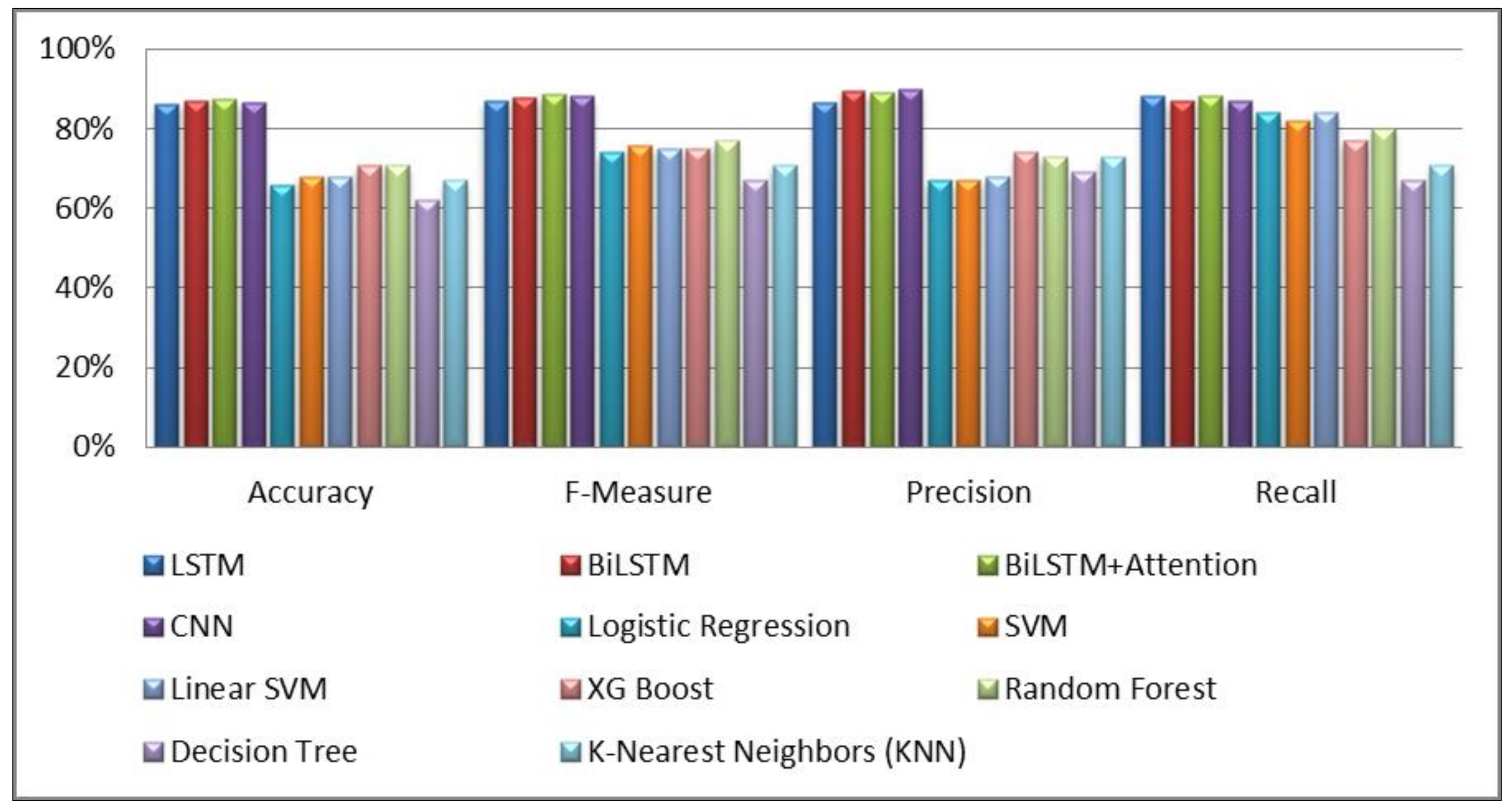








| Classifier Model | Accuracy | F-Measure | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep Learning Models | ||||
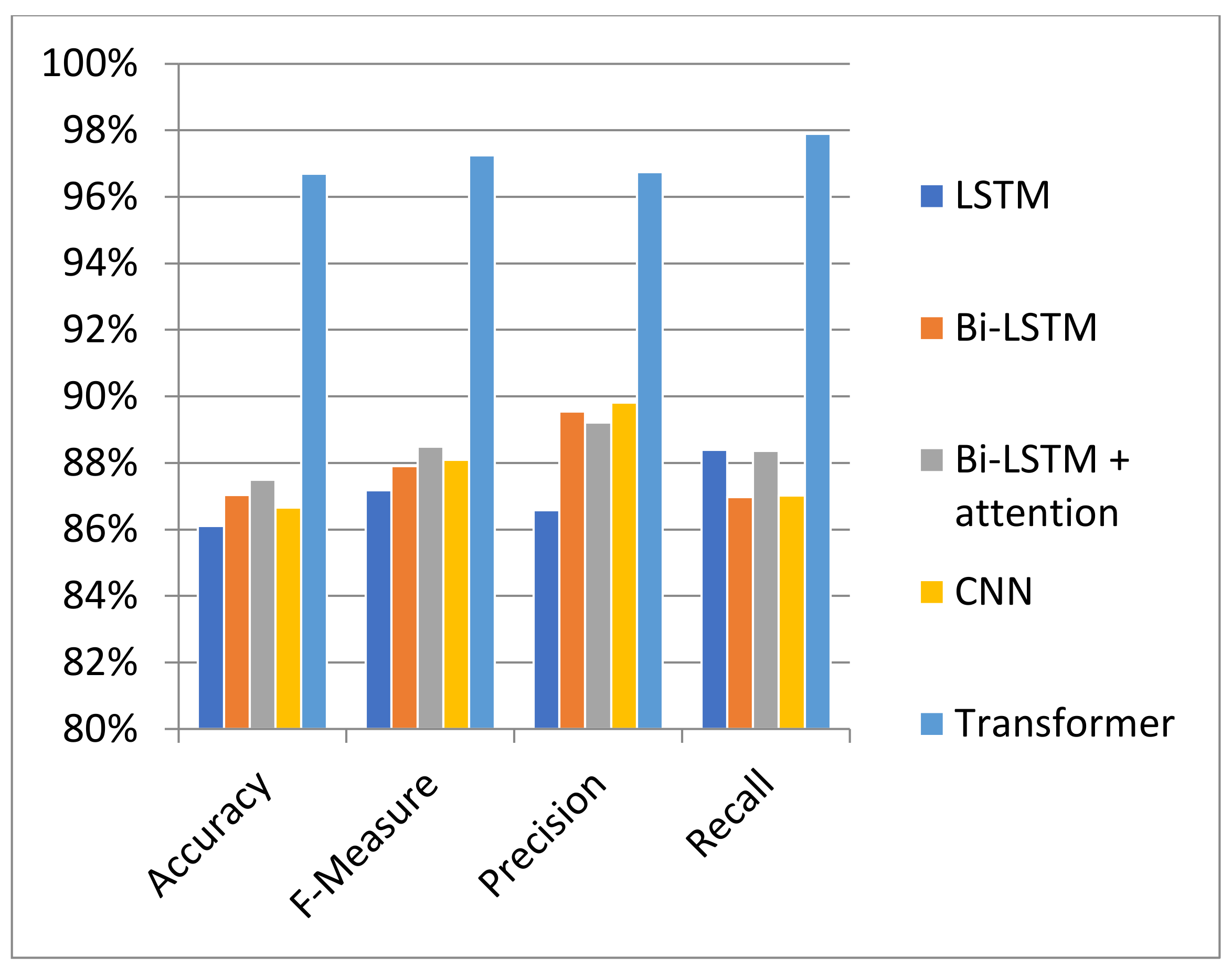
| LSTM | 86.11% | 87.18% | 86.58% | 88.40% |
| BiLSTM | 87.03% | 87.91% | 89.54% | 86.97% |
| BiLSTM + attention | 87.50% | 88.48% | 89.22% | 88.36% |
| CNN | 86.66% | 88.10% | 89.82% | 87.02% |
| Traditional Machine Learning Models | ||||
| Logistic Regression | 66% | 74% | 67% | 84% |
| SVM | 68% | 76% | 67% | 82% |
| Linear SVM | 68% | 75% | 68% | 84% |
| XG Boost | 71% | 75% | 74% | 77% |
| Random Forest | 71% | 77% | 73% | 80% |
| Decision Tree | 62% | 67% | 69% | 67% |
| K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) | 67% | 71% | 73% | 71% |
| Classifier Models | Accuracy | F-Measure | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer-based Model | 96.70% | 97.25% | 96.74% | 97.89% |
| Transfer Learning | ||||
| BERT-RU + BiLSTM (Transfer Learning) | 82.53% | 82.37% | 83.22% | 82.47% |
| BERT-RU + BiLSTM (Fine Tuning) | 82.77% | 82.43% | 81.95% | 83.88% |
| BERT-RU + (BILSTM + Attention) (Transfer Learning) | 80.54% | 80.66% | 79.45% | 82.81% |
| BERT-RU + (BILSTM + Attention) (Fine-Tuning) | 85.46% | 85.42% | 84.08% | 87.54% |
| BERT Multilingual + BiLSTM (Transfer Learning) | 84.31% | 83.86% | 83.30% | 85.35% |
| BERT-Multilingual + BiLSTM (Fine Tuning) | 85.27% | 84.86% | 85.07% | 85.51% |
| BERT-Multilingual + (BiLSTM + Attention) (Transfer Learning) | 80.09% | 80.13% | 79.71% | 81.55% |
| BERT-Multilingual + (BiLSTM + Attention) (Fine Tuning) | 83.41% | 83.36% | 82.68% | 85.08% |
| BERT-English + BiLSTM (Transfer Learning) | 82.07% | 81.63% | 82.19% | 81.99% |
| BERT-English + BiLSTM (Fine Tuning) | 87.29% | 87.85% | 85.66% | 89.59% |
| BERT-English + (BiLSTM + Attention) (Transfer Learning) | 83.23% | 83.55% | 80.84% | 87.39% |
| BERT-English + (BiLSTM + Attention) (Fine Tuning) | 85.73% | 85.58% | 84.39% | 87.54% |
| Classifier Models | Accuracy | F-Measure | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 79.45% | 78.49% | 77.47% | 81.05% |
| BiLSTM | 80.16% | 78.81% | 77.15% | 81.98% |
| BiLSTM + Attention Layer | 80.90% | 79.48% | 78.02% | 82.42% |
| CNN | 79.90% | 78.65% | 76.96% | 81.95% |
| Transformer Model | 81.04% | 79.64% | 77.96% | 82.82% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilal, M.; Khan, A.; Jan, S.; Musa, S.; Ali, S. Roman Urdu Hate Speech Detection Using Transformer-Based Model for Cyber Security Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083909
Bilal M, Khan A, Jan S, Musa S, Ali S. Roman Urdu Hate Speech Detection Using Transformer-Based Model for Cyber Security Applications. Sensors. 2023; 23(8):3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083909
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilal, Muhammad, Atif Khan, Salman Jan, Shahrulniza Musa, and Shaukat Ali. 2023. "Roman Urdu Hate Speech Detection Using Transformer-Based Model for Cyber Security Applications" Sensors 23, no. 8: 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083909
APA StyleBilal, M., Khan, A., Jan, S., Musa, S., & Ali, S. (2023). Roman Urdu Hate Speech Detection Using Transformer-Based Model for Cyber Security Applications. Sensors, 23(8), 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083909







