Solid Particle Swarm Measurement in Jet Fuel Based on Mie Scattering Theory and Extinction Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
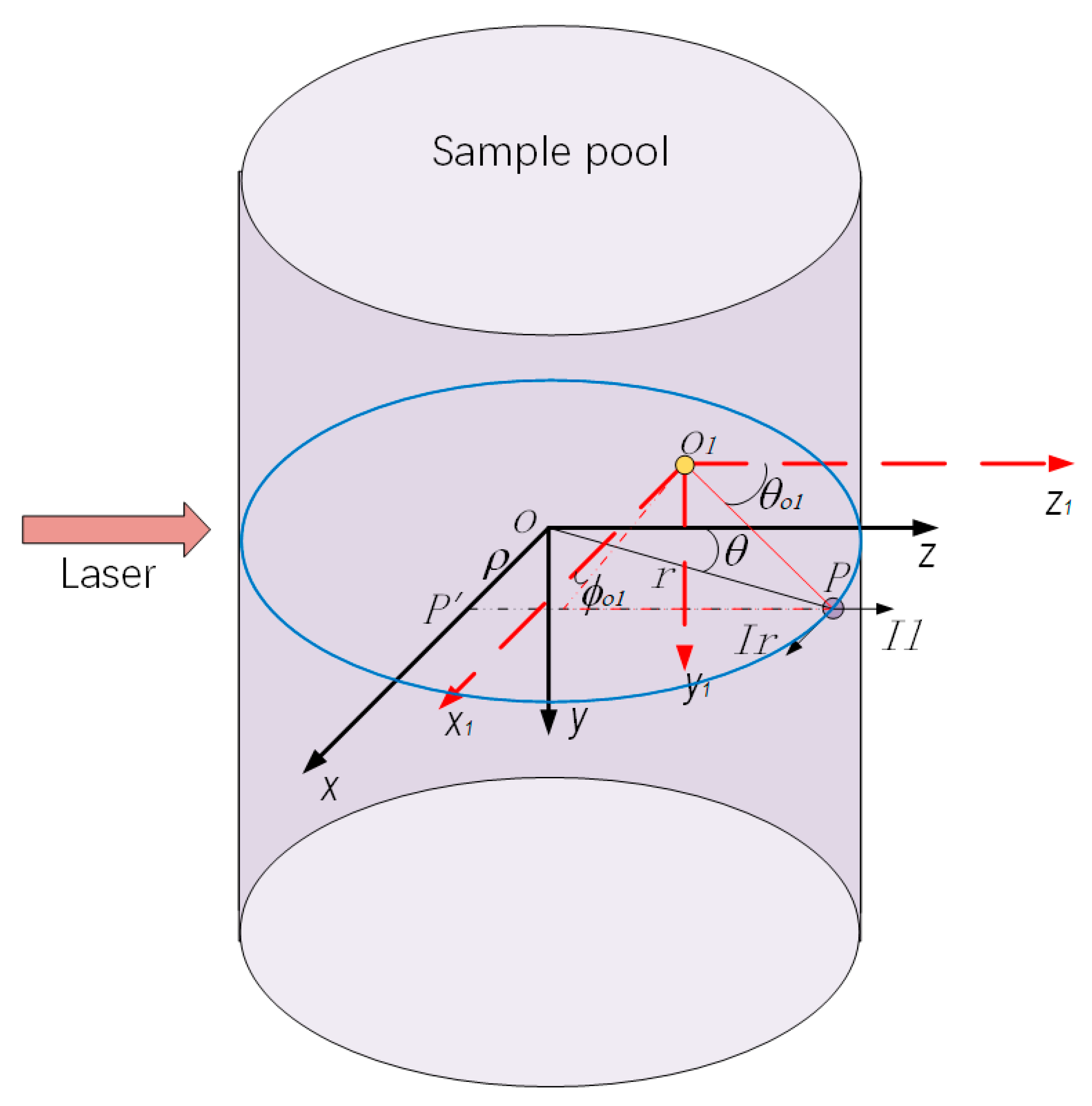
2.1. Experimental Method
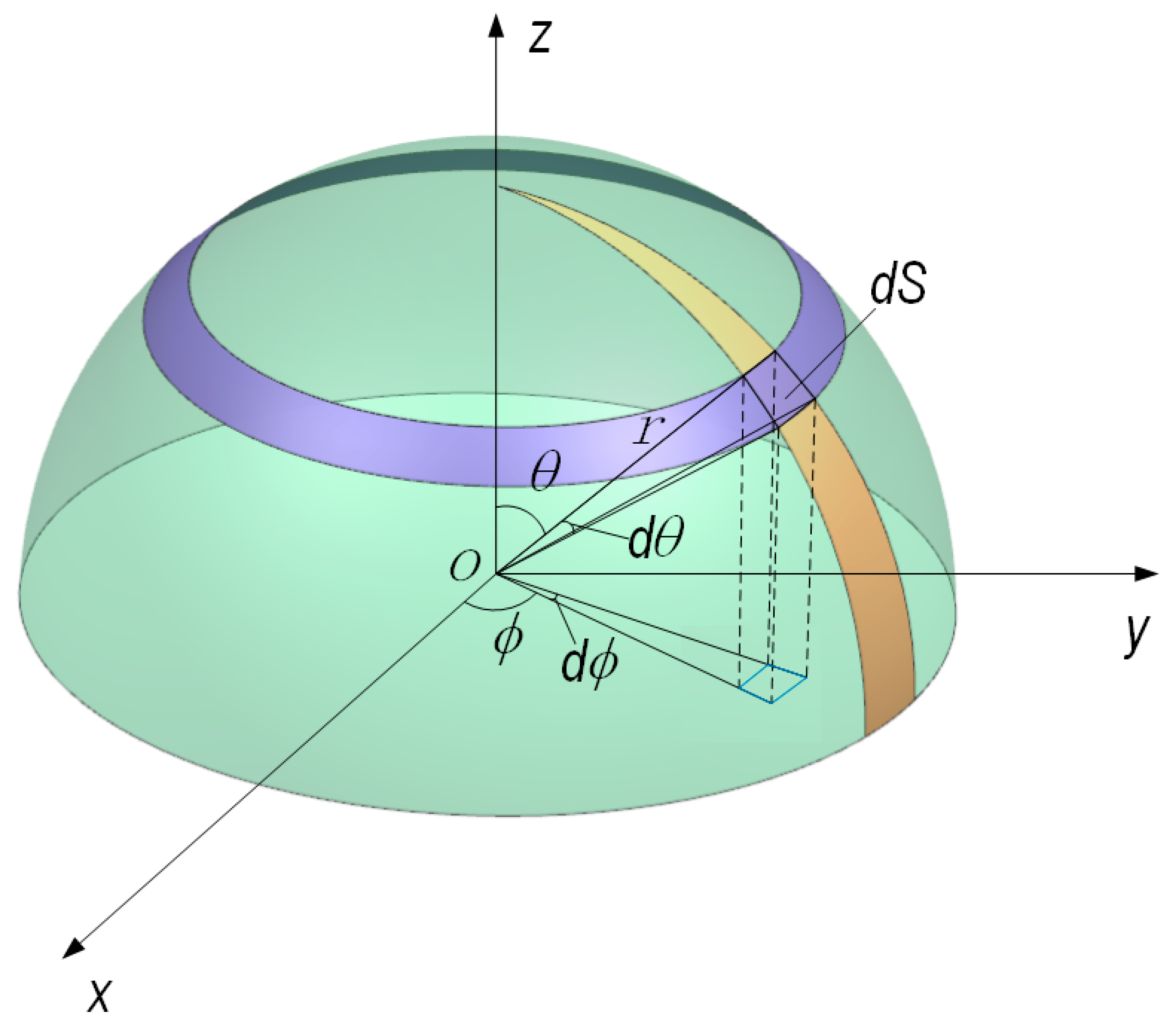
2.2. Theory Method
2.3. Experimental Material
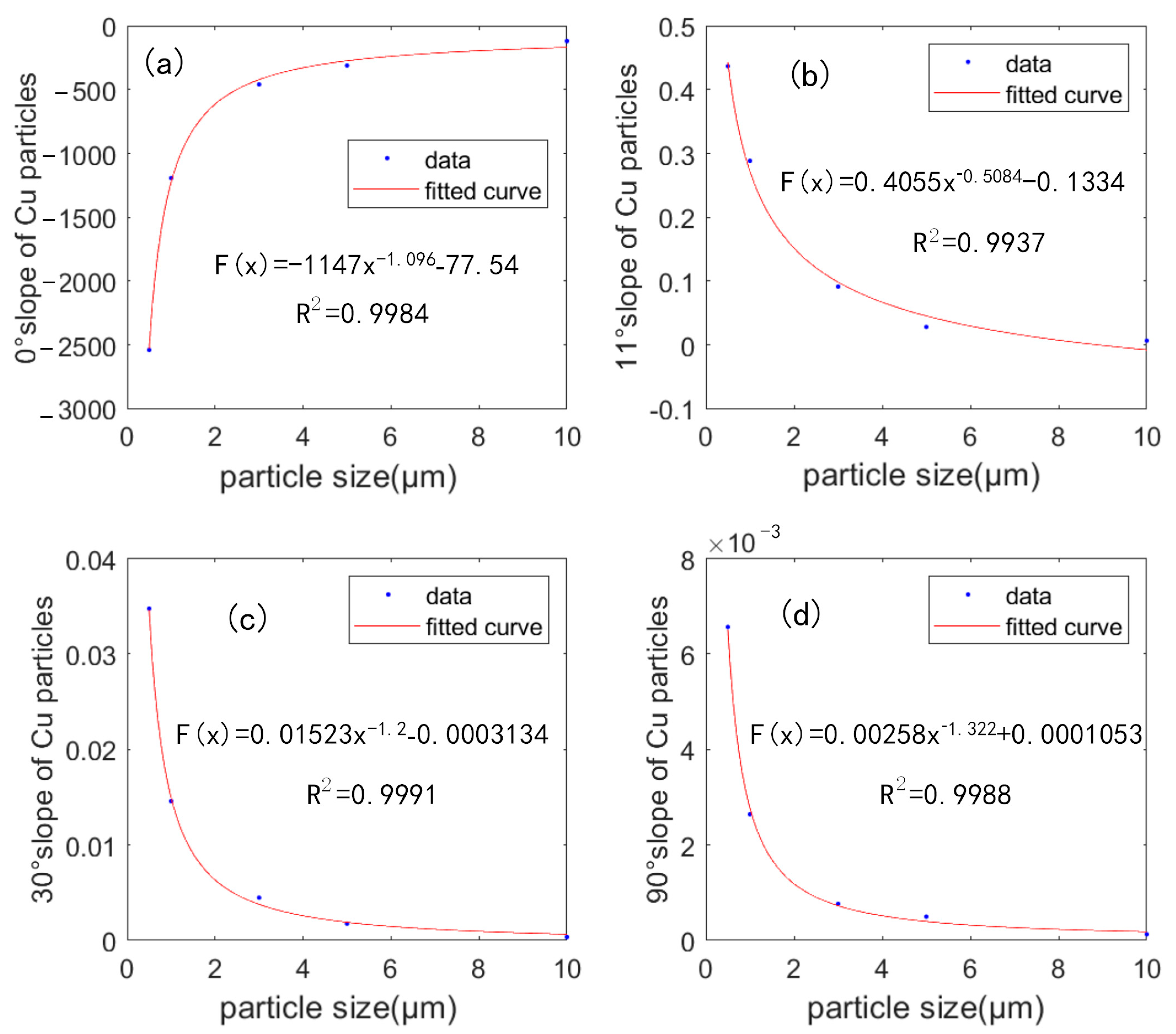
3. Simulation Processes and Results
3.1. Calculation of Complex Refractive Index for Jet Fuel
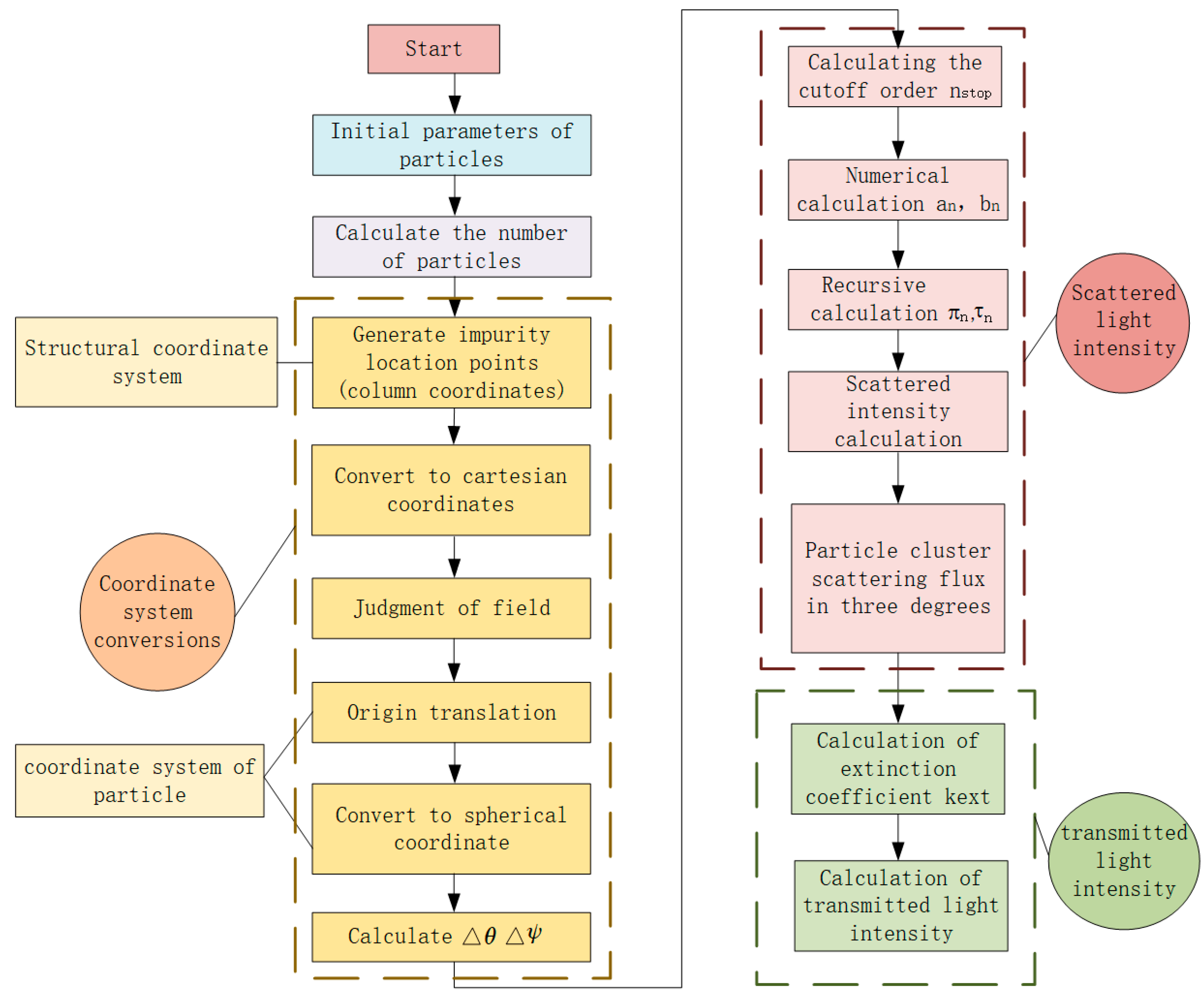
3.2. Simulationprocedure
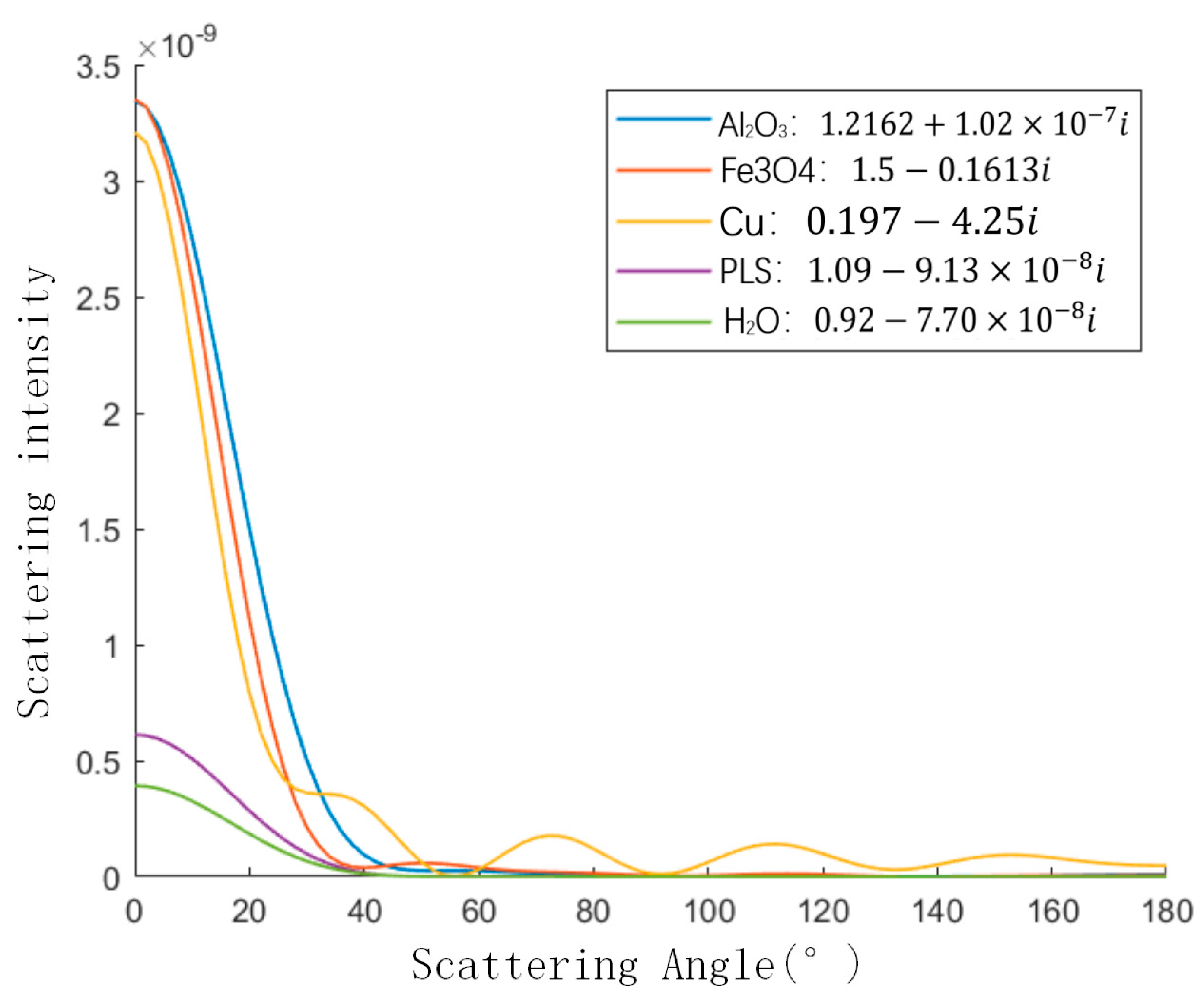
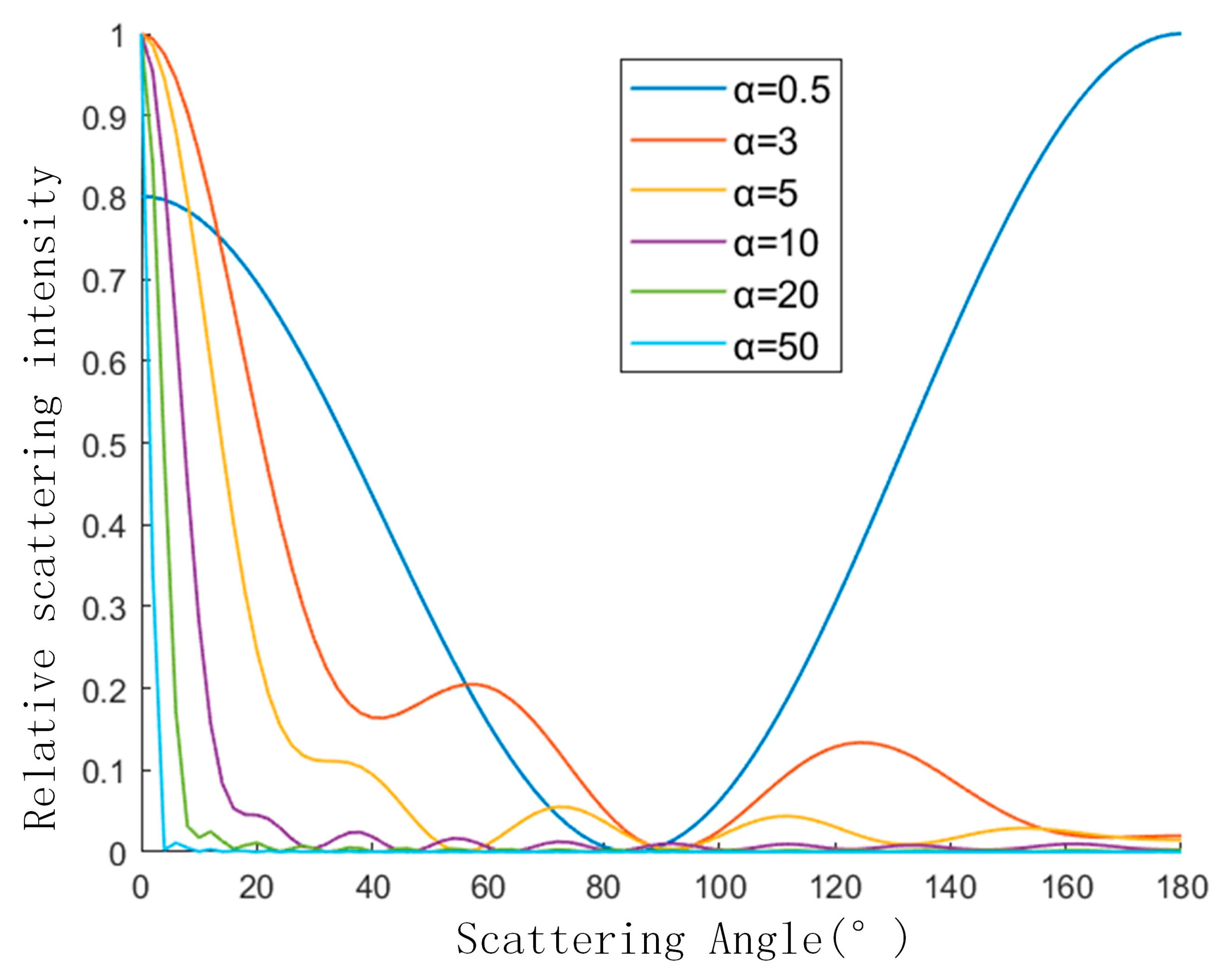
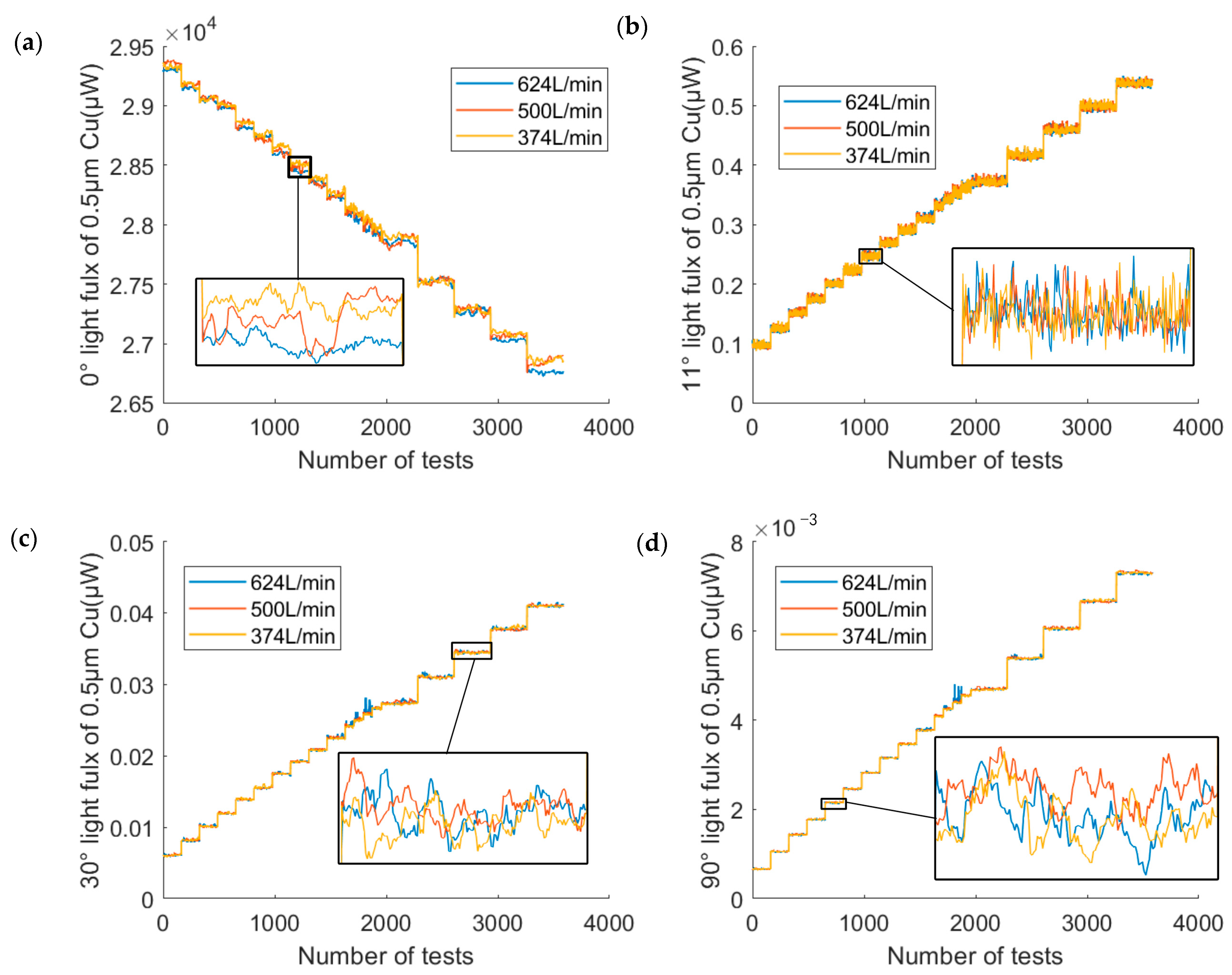
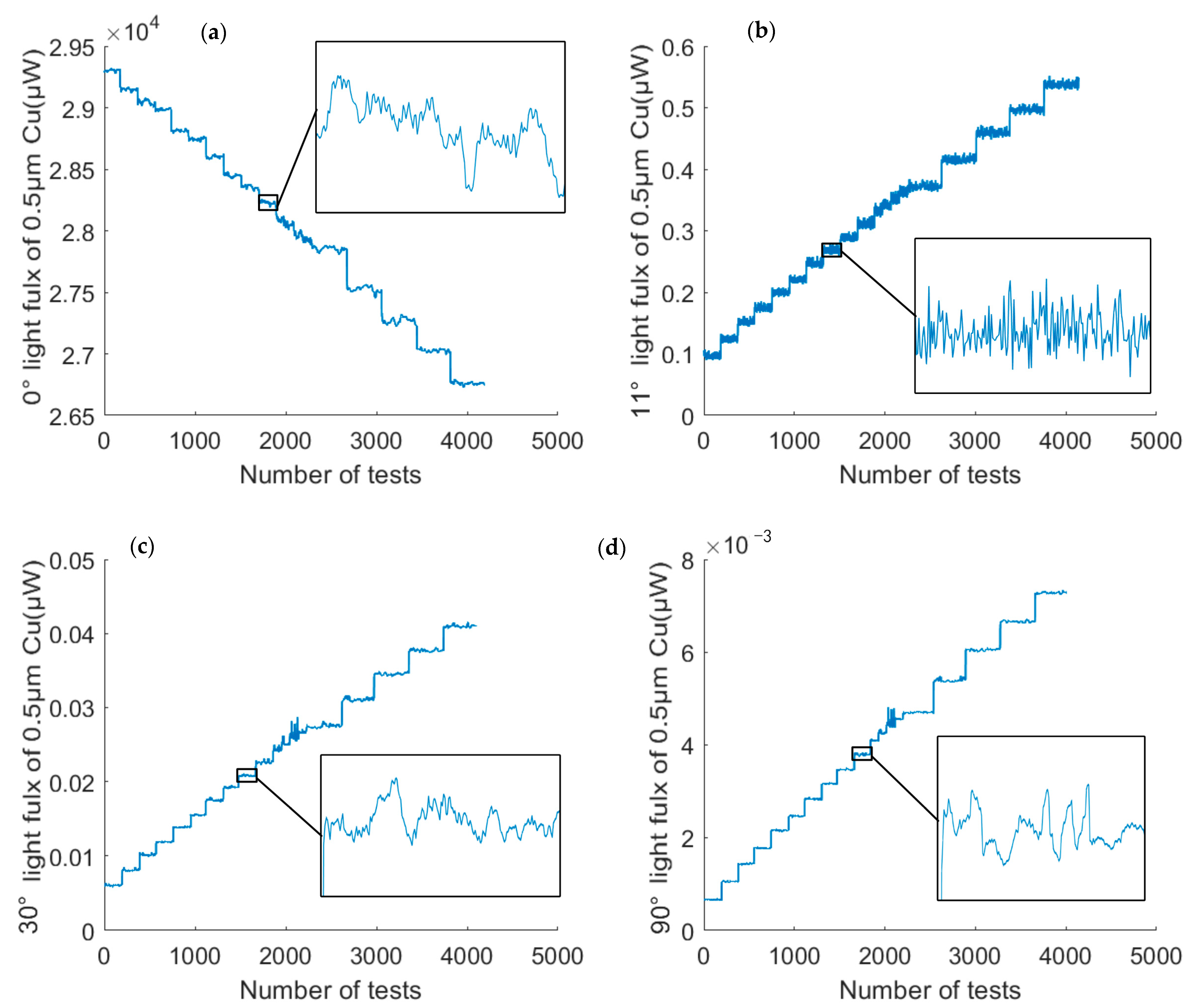
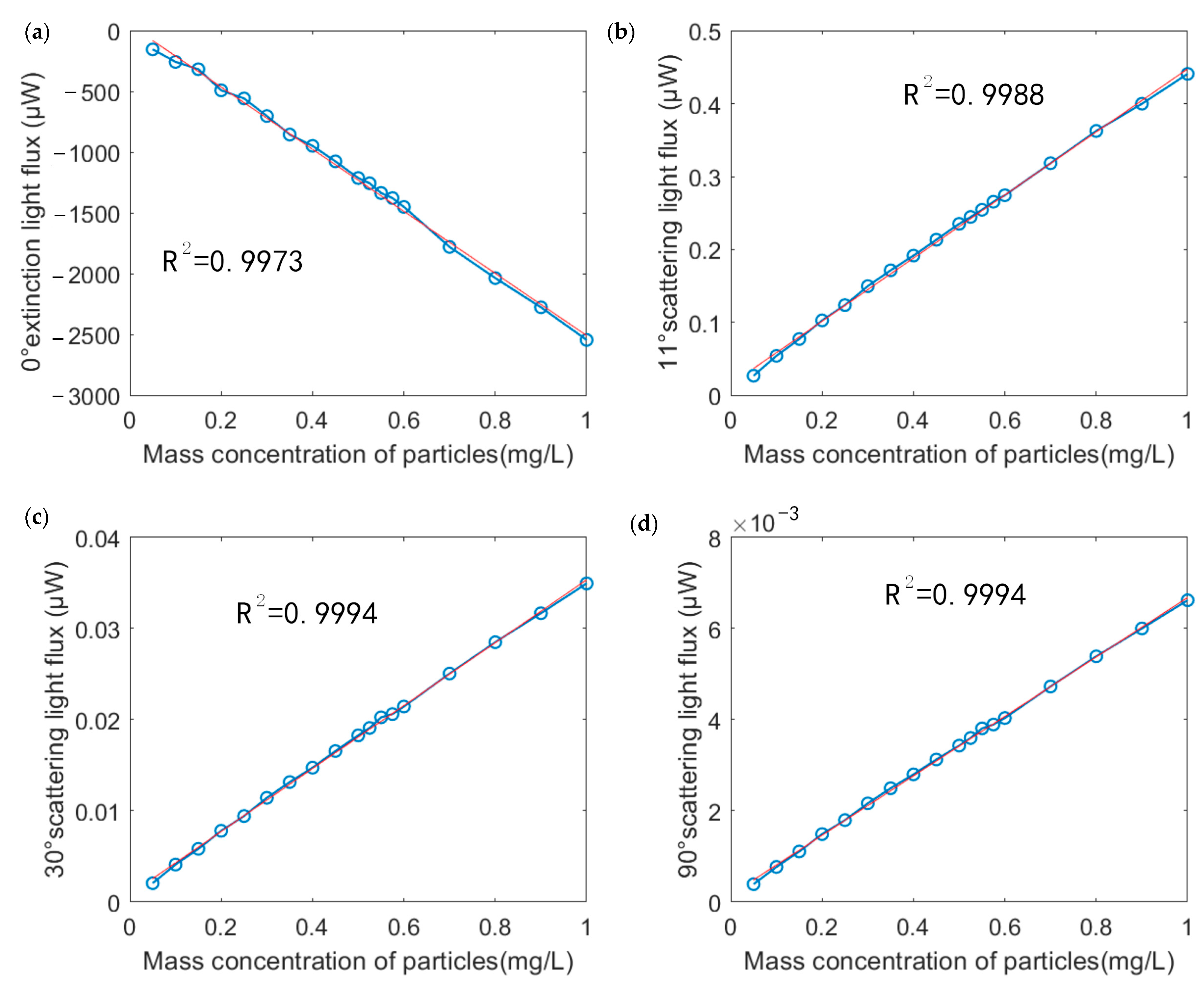
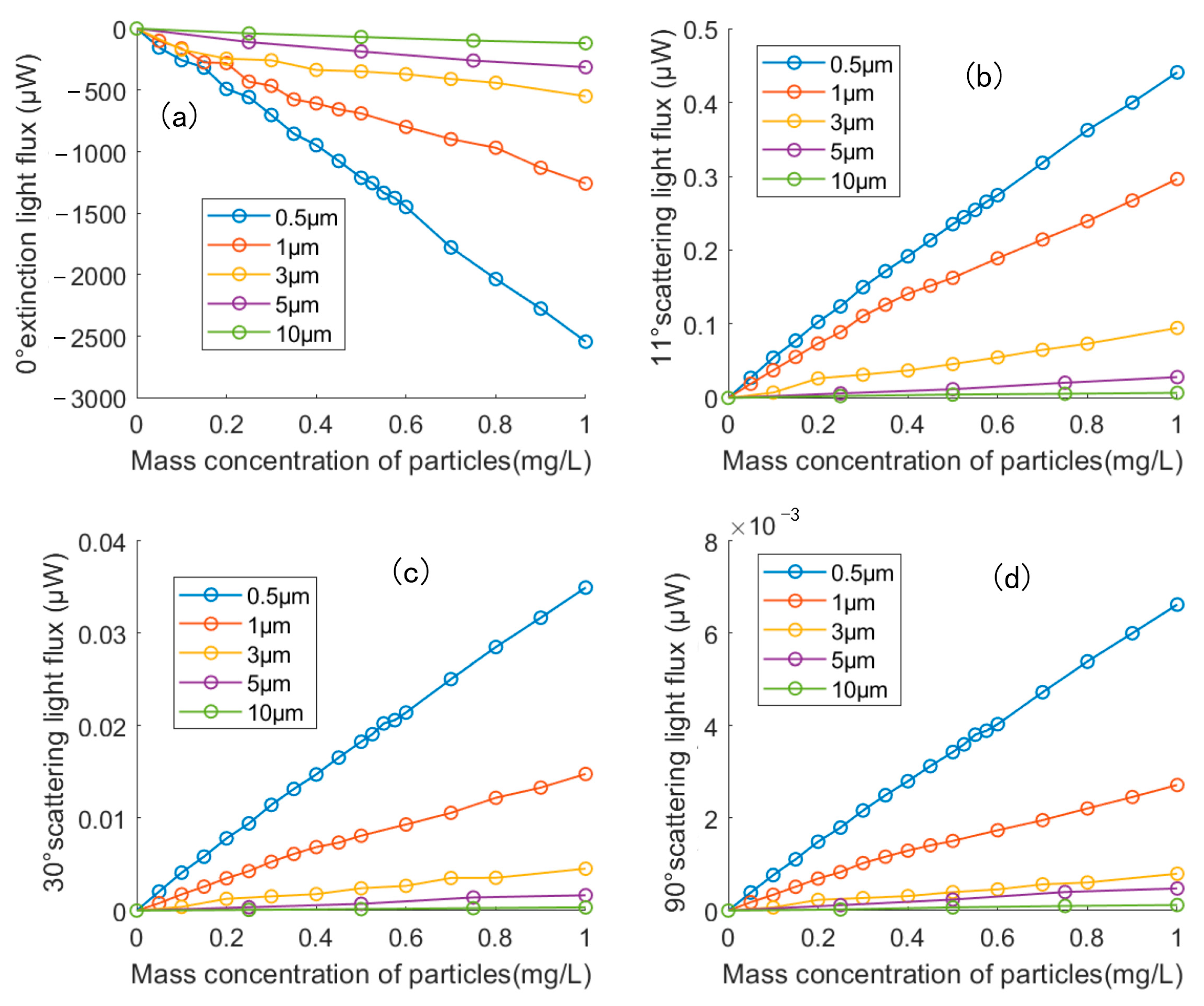
3.3. Scattering Characteristics Analysis
4. Experiment
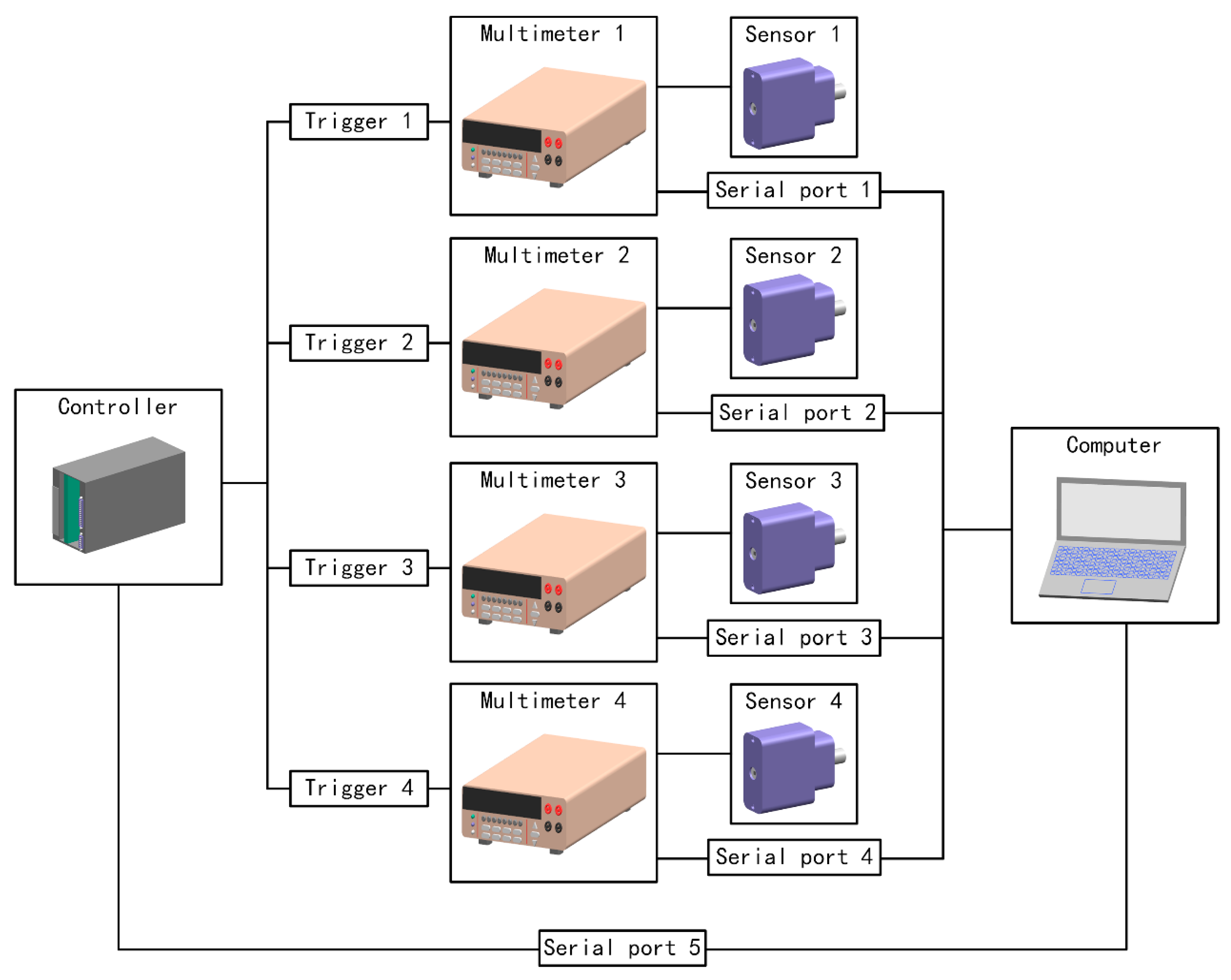
4.1. Prototype Setup
4.2. Optical System
4.3. Data Acquisition System
4.4. Experimental Sample
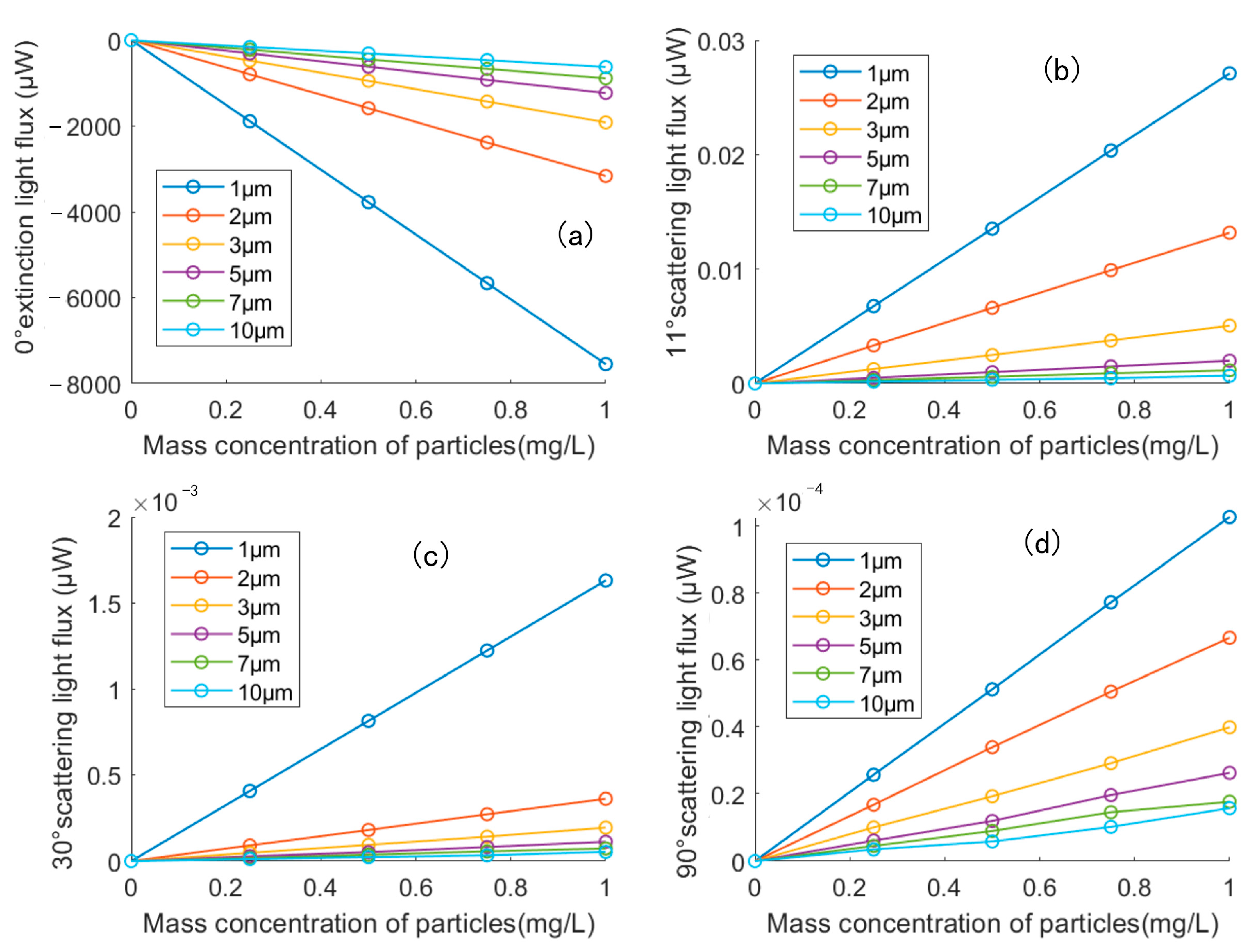
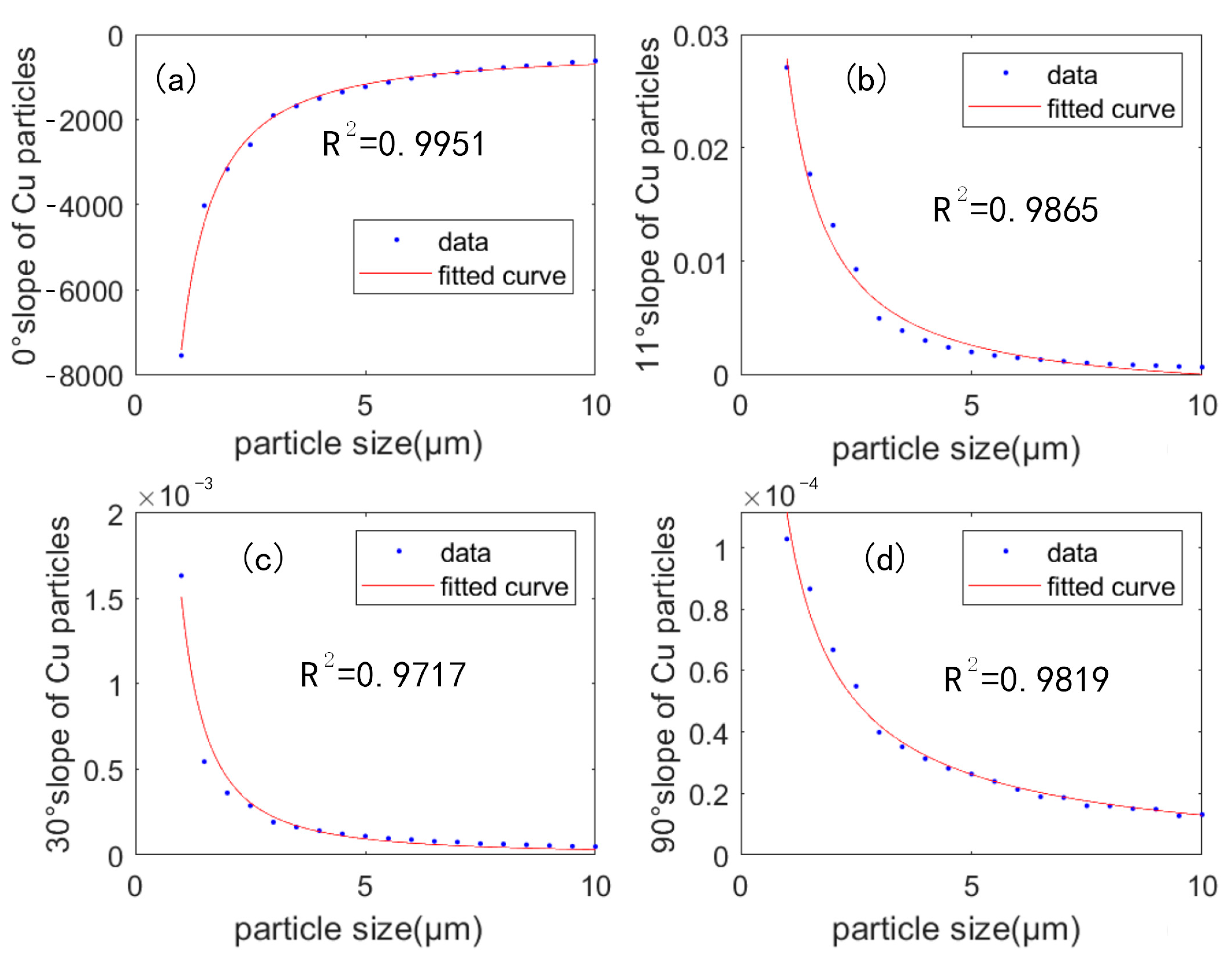
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oster, C.V., Jr.; Strong, J.S.; Zorn, C.K. Analyzing aviation safety: Problems, challenges, opportunities. Res. Transp. Econ. 2013, 43, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsi, M.; Najmi, K.; Najafifard, F.; Hassani, S.; McLaury, B.S.; Shirazi, S.A. A comprehensive review of solid particle erosion modeling for oil and gas wells and pipelines applications. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 21, 850–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yan, B.; Chen, G. Technical review on jet fuel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Antonio, C.; Gómez-Castro, F.; de Lira-Flores, J.; Hernández, S. A review on the production processes of renewable jet fuel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 709–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ail, S.S.; Dasappa, S. Biomass to liquid transportation fuel via Fischer Tropsch synthesis–Technology review and current scenario. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumo Wang, J.H.; Li, W.; Zhou, D.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Yu, D.; Gong, J. Discussion on quality assurance in the process of aviation kerosene storage and transportation. Oil Gas Storage Transp. 2020, 39-9, 971–979. [Google Scholar]
- Adekitan, A.I. Safeguards: A key process safety tool in jet fuel management from refinery to aircraft wings. Process Saf. Prog. 2018, 37, 518–524. [Google Scholar]
- Rejowski, R., Jr.; Pinto, J.M. Scheduling of a multiproduct pipeline system. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2003, 27, 1229–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Chinese Jet Fuel; China Petrochemical Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wojdat, C. Security of military aviation flight operations concerning the quality of fuel supplied to aircraft. Zesz. Naukowe. Transp./Politech. Śląska 2017, 94, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y. Aviation Fuel Analysis and Testing; China Petrochemical Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Neilson, J.; Gilchrist, A. An experimental investigation into aspects of erosion in rocket motor tail nozzles. Wear 1968, 11, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Yoshida, T. Practical estimation of erosion damage caused by solid particle impact: Part 2: Mechanical properties of materials directly associated with erosion damage. Wear 2005, 259, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.; Tabakoff, W. Erosion prediction in turbomachinery resulting from environmental solid particles. J. Aircr. 1975, 12, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogsøe, K.; Eriksen, R.L.; Henneberg, M. Performance of a light extinction based wear particle counter under various contamination levels. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 112956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitigal, J. Light Obscuration Particle Counter Fuel Contamination Limits; US Army TARDEC Warren United States: Warren, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Krogsøe, K.; Henneberg, M.; Eriksen, R.L. Model of a light extinction sensor for assessing wear particle distribution in a lubricated oil system. Sensors 2018, 18, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowicz, K.M.; Chiliński, M.T. Evaluation of two low-cost optical particle counters for the measurement of ambient aerosol scattering coefficient and Ångström exponent. Sensors 2020, 20, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousan, S.; Regmi, S.; Park, Y.M. Laboratory evaluation of low-cost optical particle counters for environmental and occupational exposures. Sensors 2021, 21, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J. Scattering on scattering. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuillier, G.; Zhu, P.; Snow, M.; Zhang, P.; Ye, X. Characteristics of solar-irradiance spectra from measurements, modeling, and theoretical approach. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruma, Y.; Sakaguchi, T.; Sakurai, H. Mass-measurement-type optical particle counting method for determination of number concentration of liquid-borne particles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabe, J.; Zubia, J.; Gorritxategi, E. Photonic low cost micro-sensor for in-line wear particle detection in flowing lube oils. Sensors 2017, 17, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Mao, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Xie, Y. A new on-line visual ferrograph. Tribol. Trans. 2009, 52, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Chuttani, R.; Pleskow, D.K.; Turzhitsky, V.; Khan, U.; Zakharov, Y.N.; Zhang, L.; Berzin, T.M.; Yee, E.U.; Sawhney, M.S. Multispectral light scattering endoscopic imaging of esophageal precancer. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 17174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Perring, A.; Thornberry, T.; Rollins, A.; Schwarz, J.; Ciciora, S.; Fahey, D. A high-sensitivity low-cost optical particle counter design. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Determination of the refractive index and size distribution of aerosol from dual-scattering-angle optical particle counter measurements. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 3864–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulst, H.C.; van de Hulst, H.C. Light Scattering by Small Particles; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Duthon, P.; Colomb, M.; Bernardin, F. Light transmission in fog: The influence of wavelength on the extinction coefficient. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, S.D.; Pacey, G.E. Detection of water in jet fuel using layer-by-layer thin film coated long period grating sensor. Talanta 2009, 78, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, M.-C.; Briard, V.; Michel, F. Optical parameters of milk fat globules for laser light scattering measurements. Lait 2001, 81, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiscombe, W.J. Improved Mie scattering algorithms. Appl. Opt. 1980, 19, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, M.J. “Refractive Index” in Handbook of Laser Science and Technology, Volume IV, Optical Materials: Part 2; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Querry, M. Optical Constants, Contractor Report; US Army Chemical Research, Development and Engineering Center (CRDC): Harford County, MD, USA, 1985; p. 418. [Google Scholar]
- Rakić, A.D.; Djurišić, A.B.; Elazar, J.M.; Majewski, M.L. Optical properties of metallic films for vertical-cavity optoelectronic devices. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 5271–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanova, N.; Kasarova, S.; Nikolov, I. Dispersion proper ties of optical polymers. Acta Phys. Pol. Ser. A Gen. Phys. 2009, 116, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, G.M.; Querry, M.R. Optical constants of water in the 200-nm to 200-μm wavelength region. Appl. Opt. 1973, 12, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Particles | Complex Refractive Index (940 nm) | Density (mg/mm3) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| particles | 1.7569 | 3.99 | Malitson et al. 1972 [34] |
| particles | 2.168–0.223i | 5.18 | Querry 1985 [35] |
| Cu particles | 0.28419–6.1375i | 8.96 | Rakić et al. 1998 [36] |
| PLS particles | 1.5739 | 1.06 | Sultanova et al. 2009 [37] |
| particles | 1.3274 | 1 | Hale et al. 1973 [38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, P.; Wang, X.; Lin, G. Solid Particle Swarm Measurement in Jet Fuel Based on Mie Scattering Theory and Extinction Method. Sensors 2023, 23, 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052837
He L, Wu H, Li J, Li B, Sun Y, Jiang P, Wang X, Lin G. Solid Particle Swarm Measurement in Jet Fuel Based on Mie Scattering Theory and Extinction Method. Sensors. 2023; 23(5):2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052837
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Limin, Heng Wu, Jifeng Li, Bingqiang Li, Yulai Sun, Peng Jiang, Xiaoxu Wang, and Guanyu Lin. 2023. "Solid Particle Swarm Measurement in Jet Fuel Based on Mie Scattering Theory and Extinction Method" Sensors 23, no. 5: 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052837
APA StyleHe, L., Wu, H., Li, J., Li, B., Sun, Y., Jiang, P., Wang, X., & Lin, G. (2023). Solid Particle Swarm Measurement in Jet Fuel Based on Mie Scattering Theory and Extinction Method. Sensors, 23(5), 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052837






