A Novel Approach for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Co-Located MIMO Radars by Exploiting Extended Array Manifold Vectors
Abstract
1. Introduction
- FPA is designed and implemented for the first time for DOA estimation with a monostatic/co-located MIMO radar system.
- A novel fitness function based on extended array manifold vectors is developed for the optimization of FPA.
- For different scenarios, the design scheme is validated.
- The scheme’s correctness is observed for very small deviations from the reference values.
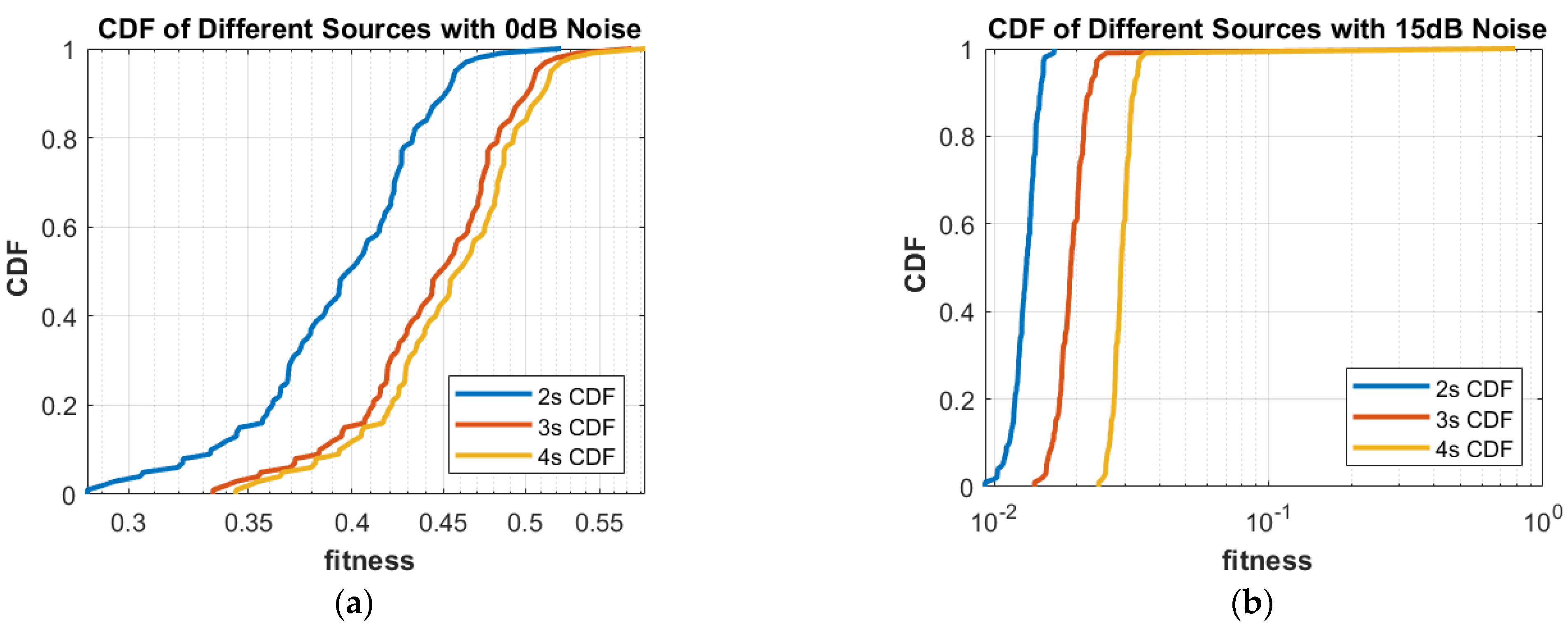
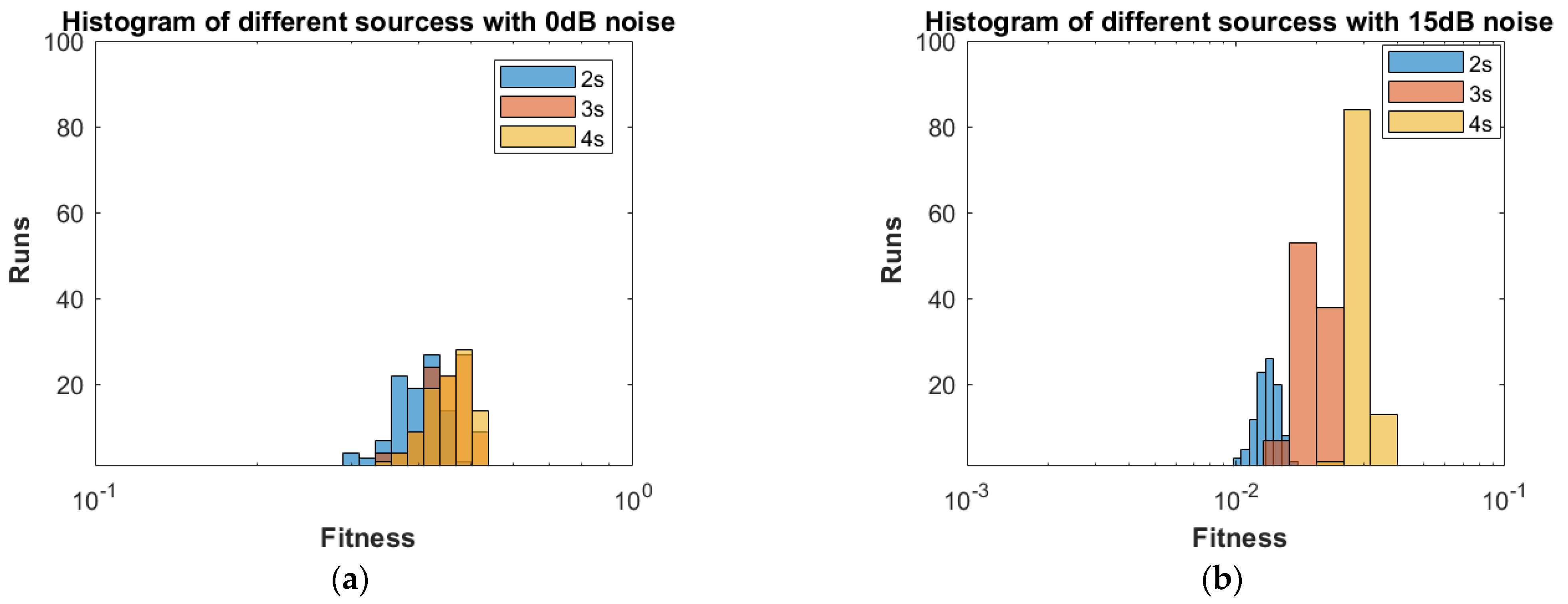
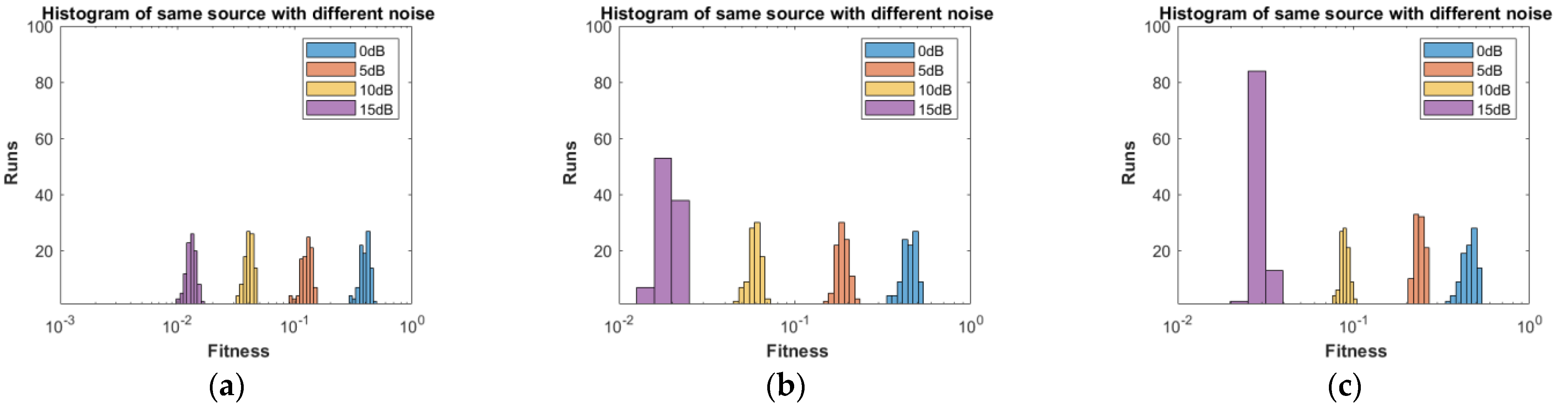
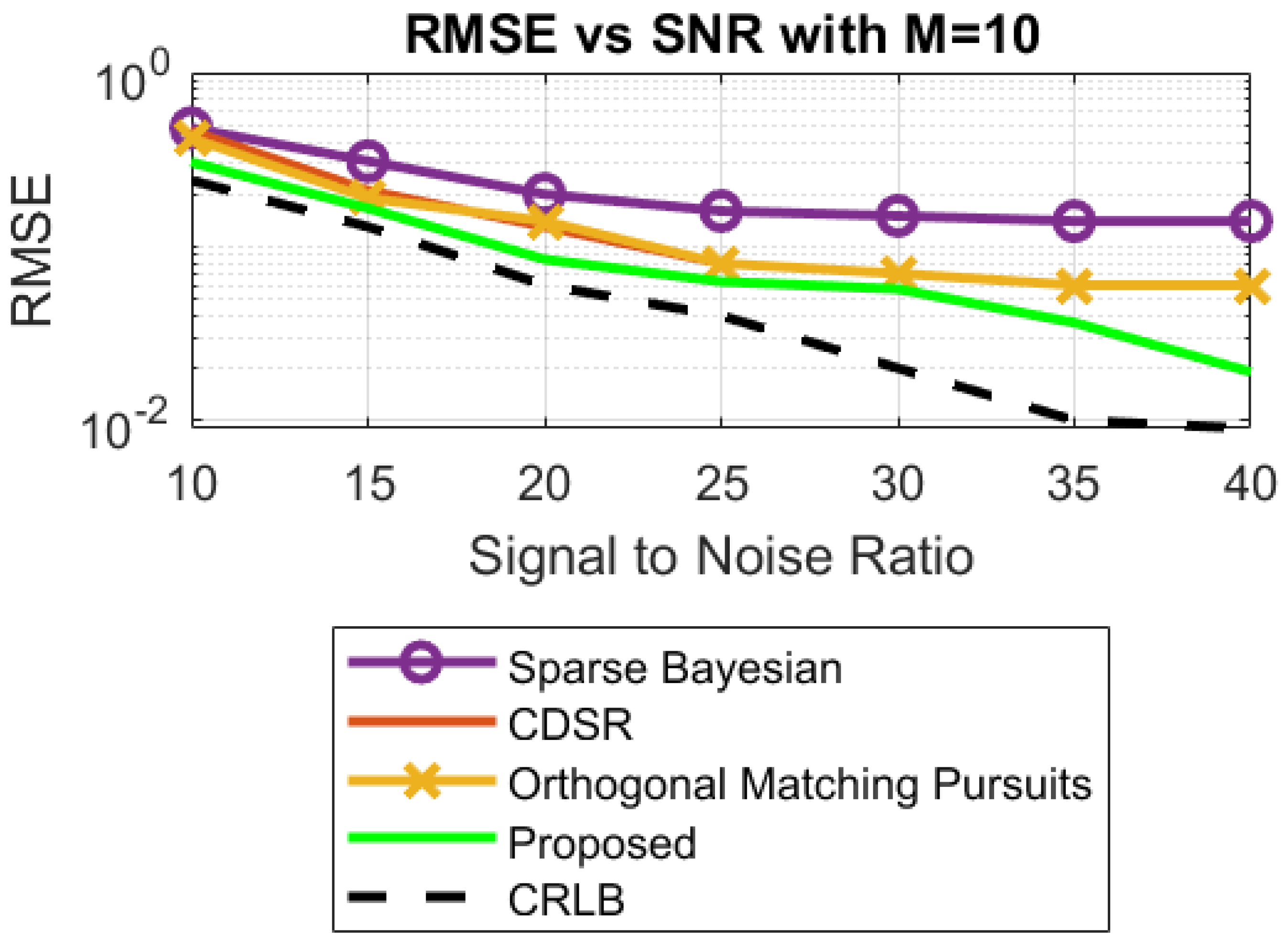
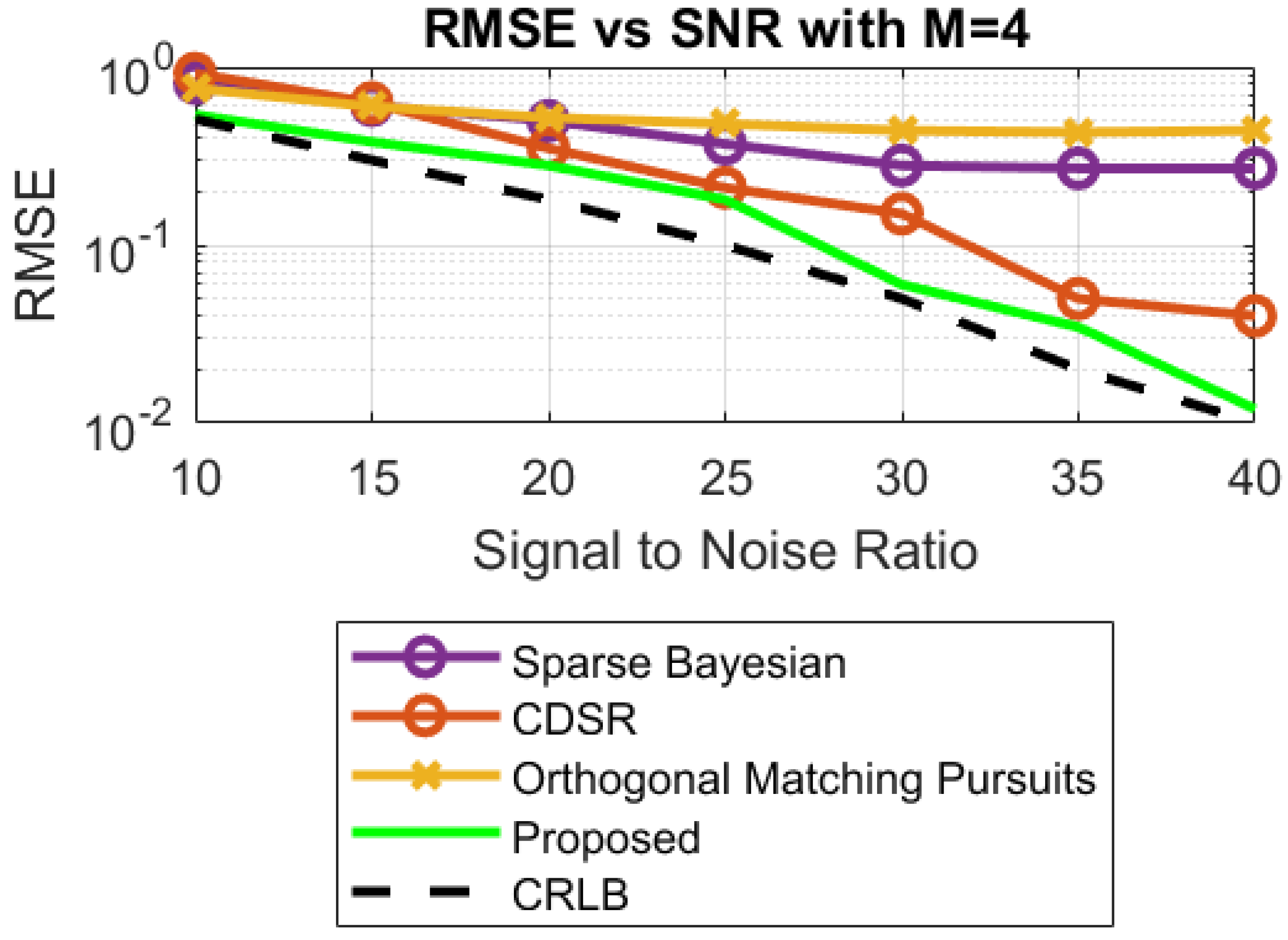
- Different statistical performances, such as RMSE, box plots, CDF and histograms, are used to confirm the reliability, consistency and robustness of the proposed approach.
2. System Model
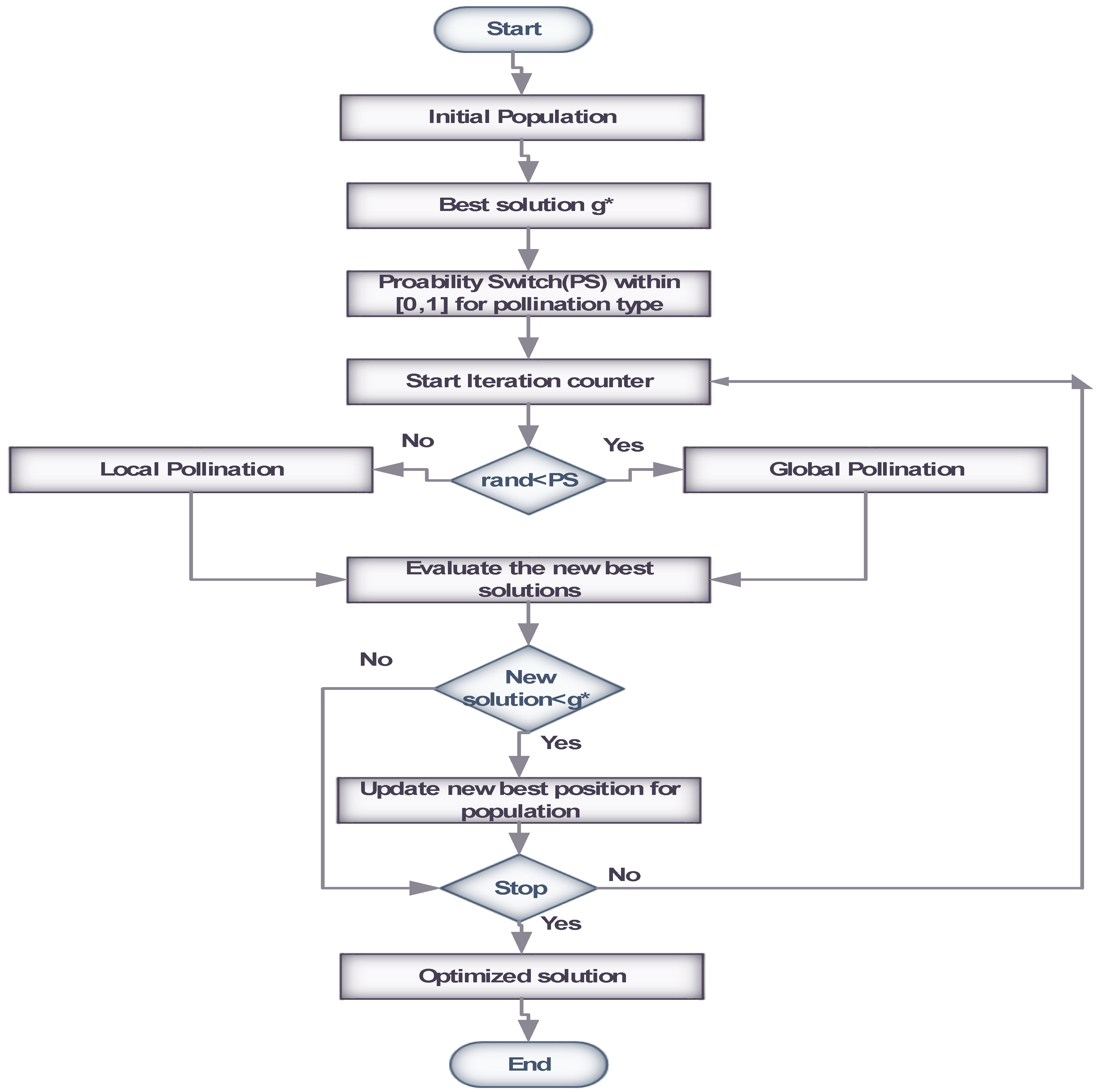
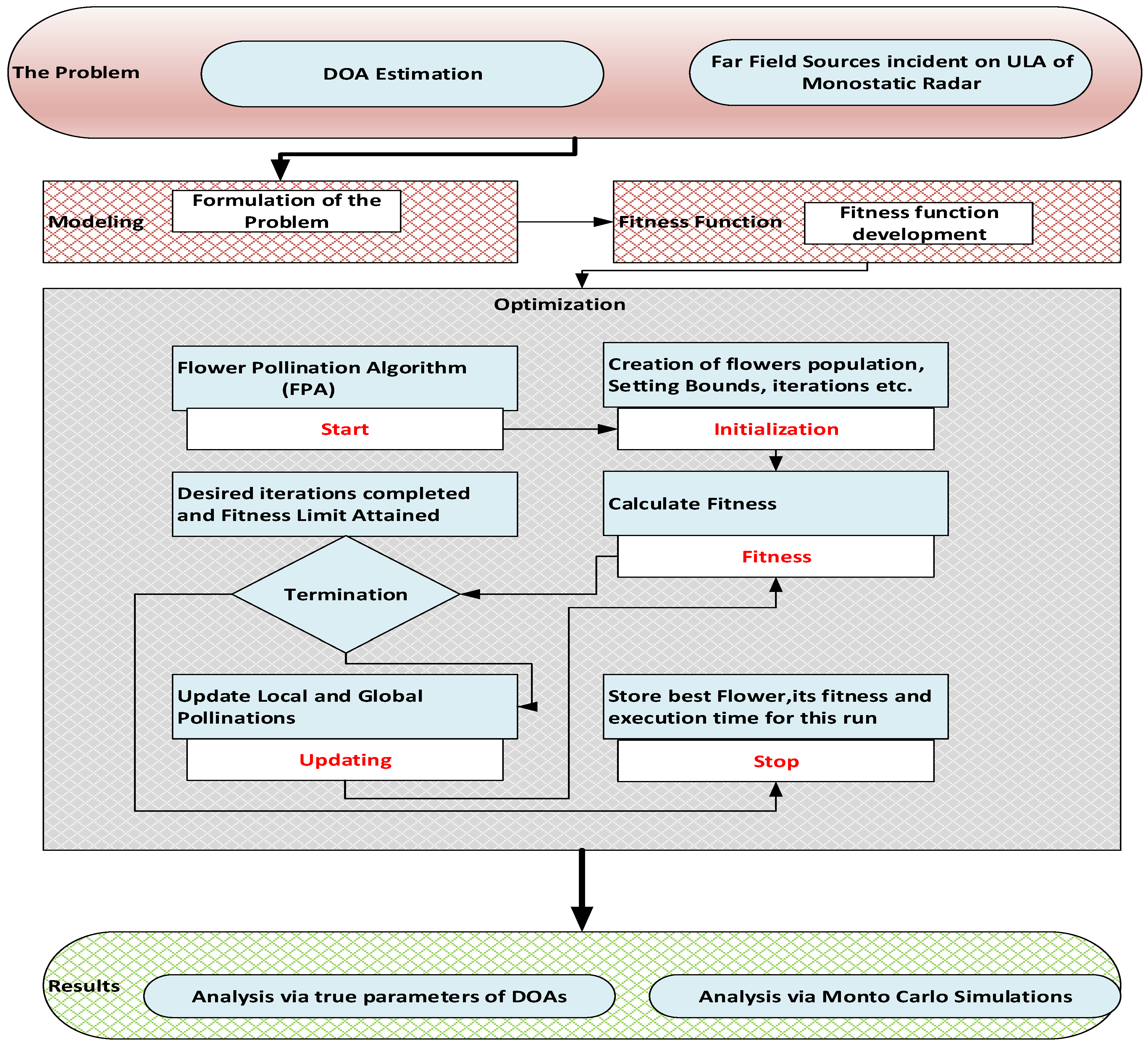
3. Proposed Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravi, K.C.; Kumar, J. Miniaturized Parasitic Loaded High-Isolation MIMO Antenna for 5G Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, W.C.; Sun, J.S. A Novel 5G LTE antenna design for portable devices. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaroudiparchin, N.; Shen, M.; Zhang, S.; Pedersen, G.F. A switchable 3-D-coverage-phased array antenna package for 5G mobile terminals. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, K.C.; Kumar, J. Multi-directional Wideband Unit-element MIMO Antenna for FR-2 Band 5G Array Applications. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2022, 46, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchin, N.O.; Zhang, J.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A.; Pedersen, G.F.; Zhang, S. A planar dual-polarized phased array with broad bandwidth and quasi-endfire radiation for 5G mobile handsets. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 6410–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Petropulu, A.P.; Poor, H.V. MIMO radar for advanced driver-assistance systems and autonomous driving: Advantages and challenges. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikas, A. Beamforming: Sensor Signal Processing for Defence Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2015; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Stoica, P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2007, 24, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimovich, A.M.; Blum, R.S.; Cimini, L.J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2007, 25, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Fu, L.; Lu, Q. Linear prediction-based DOA estimation for directional borehole radar 3-D imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5493–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Stoica, P. MIMO Radar Signal Processing; John and Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Van Veen, B.D.; Buckley, K.M. Beamforming: A versatile approach to spatial filtering. IEEE Assp. Mag. 1988, 5, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenneti, S.V.; Vaidyanathan, P.P. IMUSIC: A family of MUSIC-like algorithms for integer period estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 67, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoun, S.; Usevich, K.; Comon, P. Multidimensional ESPRIT for damped and undamped signals: Algorithm, computations, and perturbation analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 5897–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Nehorai, A. Coarrays, MUSIC, and the Cramér–Rao bound. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 65, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehashi, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Ohgane, T. Prediction of time-varying multi-user MIMO channels based on DOA estimation using compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 68, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P. Compressed sensing-based DOA estimation with antenna phase errors. Electronics 2019, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Determe, J.F.; Louveaux, J.; Jacques, L.; Horlin, F. On the noise robustness of simultaneous orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 65, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L.; Zhang, C. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 61, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, X. A super-resolution DOA estimation method for fast-moving targets in MIMO radar. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4049785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M. Conditional Cramér–Rao lower bounds for DOA estimation and array calibration. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 21, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Khader, A.T.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Yang, X.S. Variants of the Flower Pollination Algorithm: A review. Nat.-Inspired Algorithms Appl. Optim. 2018, 744, 91–118. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, S.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Zaman, F.; Alquhayz, H. Flower Pollination Heuristics for Parameter Estimation of Electromagnetic Plane Waves. CMC Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 68, 2529–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S. Flower Pollination Algorithm for Global Optimization. In International Conference on Unconventional Computing and Natural Computation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 240–249. [Google Scholar]
- Fadzli, A.A.M.; Hadi, M.S.; Eek, R.T.P.; Talib, M.H.A.; Yatim, H.M.; Darus, I.Z.M. PID Controller Based on Flower Pollination Algorithm of Flexible Beam System. In Recent Trends in Mechatronics Towards Industry 4.0; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Shekhar Das, H. Applications of Flower Pollination Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Networking and Image Processing: A Detailed Study. In Applications of Flower Pollination Algorithm and its Variants; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 197–220. [Google Scholar]
- Mahendran, G.; Govindaraju, C. Flower pollination algorithm for distribution system phase balancing considering variable demand. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2020, 74, 103008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Dhal, K.G.; Ray, S.; Galvez, J.; Das, S. Fitness based weighted flower pollination algorithm with mutation strategies for image enhancement. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 28955–28986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedurkar, D.P.; Metkar, S.P.; Al-Turjman, F.; Stephan, T.; Kolhar, M.; Altrjman, C. A Novel Approach for Multichannel Epileptic Seizure Classification Based on Internet of Things Framework Using Critical Spectral Verge Feature Derived from Flower Pollination Algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiroma, H.; Shuib, N.L.M.; Muaz, S.A.; Abubakar, A.I.; Ila, L.B.; Maitama, J.Z. A review of the applications of bio-inspired flower pollination algorithm. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 62, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Javaid, N.; Khan, I.U.; Khan, Z.A.; Chand, A.; Ahmad, N. Optimal Power Flow with Uncertain Renewable Energy Sources Using Flower Pollination Algorithm. In Advanced Information Networking and Applications: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA-2019); Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S.; Karamanoglu, M.; He, X. Flower pollination algorithm: A novel approach for multiobjective optimization. Eng. Optim. 2014, 46, 1222–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Hu, X.; Liu, C.; Peng, M.; Zhong, C. Location Sensing and Beamforming Design for IRS-Enabled Multi-User ISAC Systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 5178–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.A.; Mohjazi, L.; Bariah, L.; Muhaidat, S.; Cui, T.J.; Abbasi, Q.H. (Eds.) Intelligent Reconfigurable Surfaces (IRS) for Prospective 6G Wireless Networks; John and Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, M.; Souza, D.; da Costa, D.B.; Borges, G.; Cavalcante, A.M.; Marquezini, M.; Almeida, I.; Rodrigues, R.; Costa, J.C. Matched-Decision AP Selection for User-Centric Cell-Free Massive MIMO Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| S.No. | Name | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Population Size | 10 members |
| 2. | Probability Switch (PSW) | 0.8 |
| 3. | Number of Iterations | 2000 |
| 4. | Lower Bound | −90° |
| 5. | Upper Bound | 90° |
| S.No. | Name | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Operating System | Windows 10 Enterprise, 64 bit |
| 2. | RAM | 32 GB |
| 3. | Processor | Intel(R) Core (TM) i7-7820HQ CPU @ 2.90 GHz 2.90 GHz |
| 4. | Software | MATLAB R2022b |
| Noise | DOAs | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 dB | −34.6106 | 35.3599 | 0.0318 |
| 5 dB | −35.2284 | 34.8185 | 0.0286 |
| 10 dB | −35.1221 | 35.0787 | 0.0136 |
| 15 dB | −35.1136 | 35.0413 | 0.0267 |
| Noise | DOAs | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 dB | −39.6713 | 41.1235 | 52.2910 | 0.1626 |
| 5 dB | −40.0724 | 40.8380 | 50.4058 | 0.0915 |
| 10 dB | −39.7974 | 40.1003 | 50.1806 | 0.0387 |
| 15 dB | −40.0801 | 39.9033 | 49.6680 | 0.0270 |
| Noise | DOAs | RMSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 dB | −55.9432 | 54.0006 | 65.7209 | −67.0888 | 0.1931 |
| 5 dB | −55.5708 | 55.3826 | 65.1077 | −65.3172 | 0.1802 |
| 10 dB | −56.1675 | 54.1641 | 64.5014 | −67.3498 | 0.1379 |
| 15 dB | −54.9222 | 54.6566 | 65.0776 | −64.6327 | 0.0855 |
| Scheme | RMSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Desired DOA | −30 | 30 | 50 | -- |
| SBL Method [19] | −30.0260 | 29.8147 | 50.6640 | 0.1300 |
| CDSR [20] | −30.0960 | 29.8947 | 50.1740 | 0.4082 |
| OMP Method [18] | −30.0260 | 29.9447 | 50.7040 | 0.3985 |
| Proposed Scheme | −30.0000 | 30.0000 | 50.0000 | 0.0901 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbar, S.; Sohail, M.; Zaman, F.; Khan, M.A.R.; Ajavakom, N.; Phanomchoeng, G. A Novel Approach for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Co-Located MIMO Radars by Exploiting Extended Array Manifold Vectors. Sensors 2023, 23, 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052550
Akbar S, Sohail M, Zaman F, Khan MAR, Ajavakom N, Phanomchoeng G. A Novel Approach for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Co-Located MIMO Radars by Exploiting Extended Array Manifold Vectors. Sensors. 2023; 23(5):2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052550
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbar, Sadiq, Muhammad Sohail, Fawad Zaman, Muhammad Abdul Rehman Khan, Nopdanai Ajavakom, and Gridsada Phanomchoeng. 2023. "A Novel Approach for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Co-Located MIMO Radars by Exploiting Extended Array Manifold Vectors" Sensors 23, no. 5: 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052550
APA StyleAkbar, S., Sohail, M., Zaman, F., Khan, M. A. R., Ajavakom, N., & Phanomchoeng, G. (2023). A Novel Approach for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Co-Located MIMO Radars by Exploiting Extended Array Manifold Vectors. Sensors, 23(5), 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052550







