Blind Video Quality Assessment for Ultra-High-Definition Video Based on Super-Resolution and Deep Reinforcement Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. BVQA
2.2. Deep Reinforcement Learning
3. Proposed Method
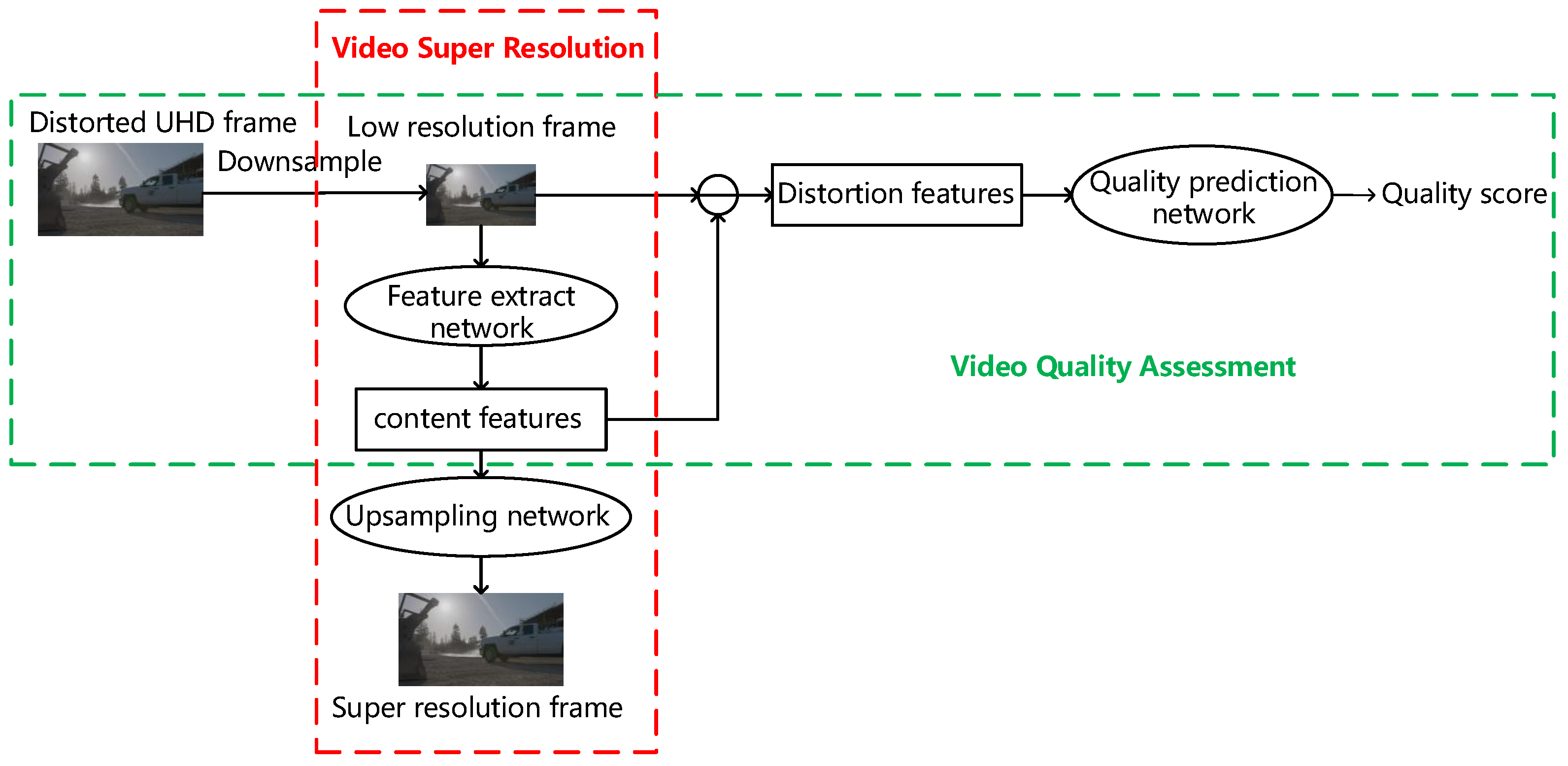
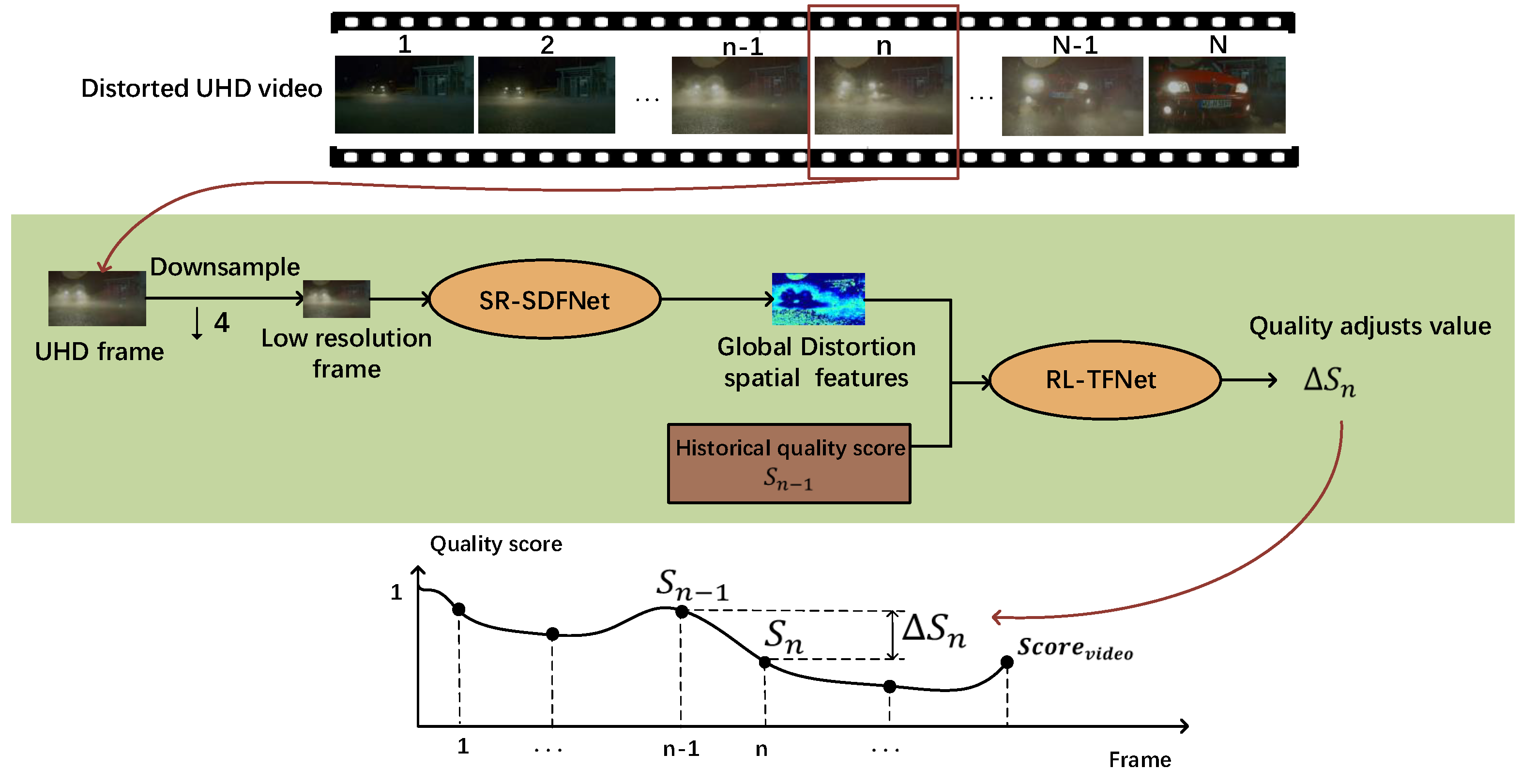
3.1. BVQA-SR&DRL
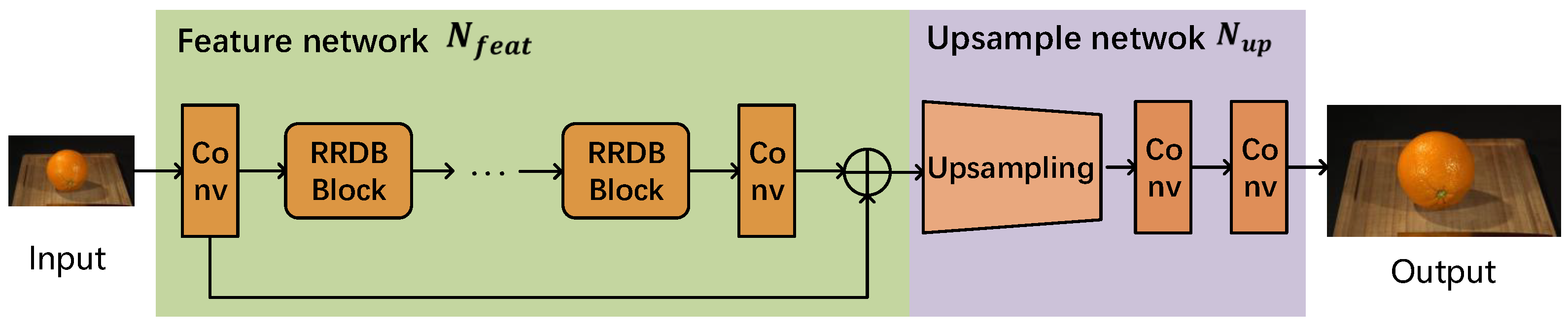
3.2. Spatial Distortion Feature Network Based on a Super-Resolution Model (SR-SDFNet)
3.3. Time Fusion Network Based on Reinforcement Learning (RL-TFNet)
3.3.1. State Space
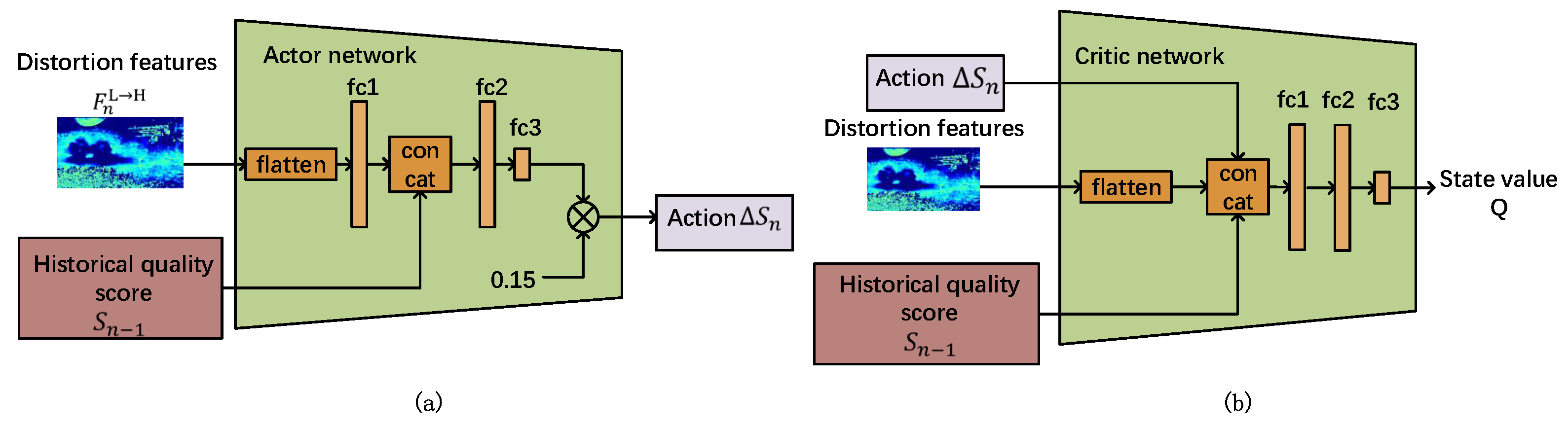
3.3.2. Action Space
3.3.3. Reward Function
3.3.4. Network Introduction
| Algorithm 1 RL-TFNet Algorithm |
| Randomly set the initialize weights of the actor network and critic network . Initialize copy network weights , . Initial quality score
|
3.4. Training Procedure
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Databases and Evaluation Criteria
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Comparisons with the State of the Art
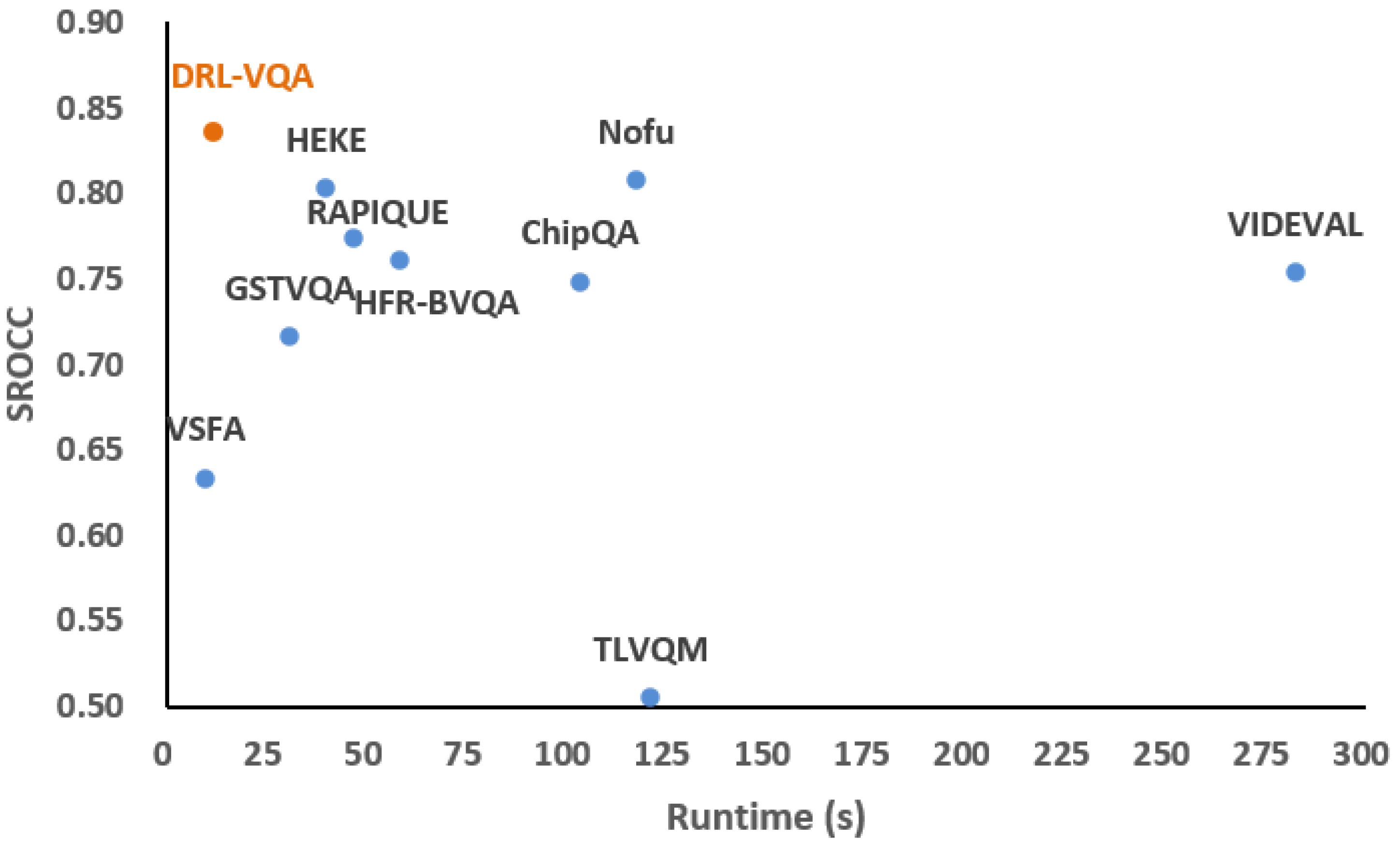
4.4. Performance on Computation Complexity and Runtime
4.5. Visual Analysis
4.6. Ablation Study
4.6.1. SR-SDFNet
4.6.2. RL-TFNet
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madhusudana, P.C.; Birkbeck, N.; Wang, Y.; Adsumilli, B.; Bovik, A.C. St-greed: Space-time generalized entropic differences for frame rate dependent video quality prediction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7446–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W.; Shi, G.; Lin, W. Quality assessment for video with degradation along salient trajectories. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 2738–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appina, B.; Dendi, S.V.R.; Bovik, A.C. Study of subjective quality and objective blind quality prediction of stereoscopic videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 5027–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, J.; Su, Y.; You, J. Blind natural video quality prediction via statistical temporal features and deep spatial features. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Raake, A.; Borer, S.; Satti, S.M.; Gustafsson, J.; Rao, R.R.R.; Medagli, S.; List, P.; Göring, S.; Bitto, R. Multi-model standard for bitstream-, pixel-based and hybrid video quality assessment of uhd/4k: Itu-t p.1204. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193020–193049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göring, S.; Rao, R.R.R.; Feiten, B.; Raake, A. Modular framework and instances of pixel-based video quality models for uhd-1/4k. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 31842–31864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Tian, M.; Zhai, G.; Wang, X. Blindly assess quality of in-the-wild videos via quality-aware pre-training and motion perception. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 5944–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahankali, N.S.; Raghavan, M.; Channappayya, S.S. No-reference video quality assessment using voxel-wise fmri models of the visual cortex. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, L.; Dong, W.; Zhang, J.; Shi, G. Spatiotemporal representation learning for blind video quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 3500–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Birkbeck, N.; Adsumilli, B.; Bovik, A.C. Rapique: Rapid and accurate video quality prediction of user generated content. IEEE Open J. Signal Process. 2021, 2, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Tu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, X.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference quality assessment of variable frame-rate videos using temporal bandpass statistics. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 1795–1799. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; He, L.; Lu, W.; He, R. Blind video quality assessment with weakly supervised learning and resampling strategy. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 29, 2244–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Su, L.; Huang, Q. Cnn-mr for no reference video quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering (ICISCE), Changsha, China, 21–23 July 2017; pp. 224–228. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Su, L.; Zhang, W. Come for no-reference video quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), Miami, FL, USA, 10–12 April 2018; pp. 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Li, L.; Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Shi, G. Rirnet: Recurrent-in-recurrent network for video quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendi, S.V.R.; Channappayya, S.S. No-reference video quality assessment using natural spatiotemporal scene statistics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 5612–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, J.P.; Shang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wei, H.; Sethuraman, S.; Bovik, A.C. Chipqa: No-reference video quality prediction via space-time chips. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 8059–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, L.; Li, G.; Lu, F.; Fan, H.; Wang, S. Learning generalized spatial-temporal deep feature representation for no-reference video quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z. Perceptual quality assessment of internet videos. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual Event, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 1248–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, D. No-reference video quality assessment using the temporal statistics of global and local image features. Sensors 2022, 22, 9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X. Study on no-reference video quality assessment method incorporating dual deep learning networks. Multim. Tools Appl. 2022, 82, 3081–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, W.; Lan, C.; Zhao, T. Saliency-aware spatio-temporal artifact detection for compressed video quality assessment. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.01069. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Graves, A.; Antonoglou, I.; Wierstra, D.; Riedmiller, M.A. Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.5602. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lin, M.; Wang, J.; Luo, P.; Ren, J. Learning a reinforced agent for flexible exposure bracketing selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1817–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Xiao, J.; Lim, E.G. Iterative shrinking for referring expression grounding using deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14060–14069. [Google Scholar]
- Nauata, N.; Hosseini, S.; Chang, K.-H.; Chu, H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Furukawa, Y. House-gan++: Generative adversarial layout refinement network towards intelligent computational agent for professional architects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13627–13636. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Shen, J.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Pantic, M. Dynamic face video segmentation via reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6957–6967. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Fu, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Jia, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. Rtn: Reinforced transformer network for coronary ct angiography vessel-level image quality assessment. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022, Proceedings, Part I; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.U.; Fu, Y.; Stavrinides, V.; Baum, Z.M.C.; Yang, Q.; Rusu, M.; Fan, R.E.; Sonn, G.A.; Noble, J.A.; Barratt, D.C.; et al. Image quality assessment for machine learning tasks using meta-reinforcement learning. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 78, 102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Dong, C.; Shan, Y. Real-esrgan: Training real-world blind super-resolution with pure synthetic data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1905–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Netix. Netix Vmaf. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/Netflix/vmaf (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Sheikh, H.R.; Bovik, A.C. Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillicrap, T.; Hunt, J.; Pritzel, A.; Heess, N.; Erez, T.; Tassa, Y.; Silver, D.; Wierstra, D. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.02971. [Google Scholar]
- Cheon, M.; Lee, J.-S. Subjective and objective quality assessment of compressed 4k uhd videos for immersive experience. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.R.R.; Göring, S.; Robitza, W.; Feiten, B.; Raake, A. Avt-vqdb-uhd-1: A large scale video quality database for uhd-1. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 December 2019; pp. 17–177. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Bovik, A.C. A feature-enriched completely blind image quality evaluator. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Tao, D. dipiq: Blind image quality assessment by learning-to-rank discriminable image pairs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3951–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, M. Quality assessment of in-the-wild videos. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 2351–2359. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, J. Two-level approach for no-reference consumer video quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 5923–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Birkbeck, N.; Adsumilli, B.; Bovik, A.C. Ugc-vqa: Benchmarking blind video quality assessment for user generated content. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4449–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosu, V.; Hahn, F.; Jenadeleh, M.; Lin, H.; Men, H.; Szirányi, T.; Li, S.; Saupe, D. The konstanz natural video database (konvid-1k). In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Erfurt, Germany, 31 May–2 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y.R. Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, D.; Szirányi, T. No-reference video quality assessment via pretrained cnn and lstm networks. Signal Image Video Process. 2019, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Method | ALL | AVC | HEVC | VP9 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | |
| VSFA | 0.633 | 0.708 | 1.751 | 0.757 | 0.834 | 1.613 | 0.614 | 0.655 | 1.892 | 0.295 | 0.575 | 1.399 |
| TLVQM | 0.505 | 0.577 | 2.050 | 0.607 | 0.629 | 1.936 | 0.487 | 0.526 | 2.156 | 0.462 | 0.449 | 1.790 |
| VIDEVAL | 0.753 | 0.686 | 1.808 | 0.751 | 0.828 | 1.625 | 0.811 | 0.834 | 1.384 | 0.698 | 0.704 | 1.244 |
| GSTVQA | 0.716 | 0.830 | 1.382 | 0.740 | 0.855 | 1.513 | 0.774 | 0.850 | 1.319 | 0.588 | 0.682 | 1.251 |
| RAPIQUE | 0.774 | 0.758 | 1.617 | 0.781 | 0.763 | 1.887 | 0.818 | 0.828 | 1.402 | 0.726 | 0.779 | 1.074 |
| ChipQA | 0.748 | 0.753 | 1.636 | 0.755 | 0.738 | 1.821 | 0.792 | 0.791 | 1.565 | 0.702 | 0.753 | 1.068 |
| Nofu | 0.808 | 0.803 | 1.544 | 0.832 | 0.803 | 1.674 | 0.838 | 0.824 | 1.502 | 0.726 | 0.754 | 1.068 |
| HEKE | 0.803 | 0.834 | 1.487 | 0.816 | 0.811 | 1.657 | 0.810 | 0.845 | 1.485 | 0.722 | 0.755 | 1.065 |
| HFR-BVQA | 0.761 | 0.775 | 1.600 | 0.808 | 0.780 | 1.828 | 0.836 | 0.847 | 1.463 | 0.712 | 0.696 | 1.456 |
| Proposed | 0.836 | 0.878 | 1.189 | 0.874 | 0.841 | 1.387 | 0.869 | 0.896 | 1.110 | 0.733 | 0.789 | 1.050 |
| Method | ALL | TEST1 | TEST2 | TEST3 | TEST4 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | SRCC | PLCC | RMSE | |
| VSFA | 0.607 | 0.601 | 0.826 | 0.715 | 0.692 | 0.768 | 0.754 | 0.789 | 0.641 | 0.696 | 0.729 | 0.738 | 0.536 | 0.596 | 0.737 |
| TLVQM | 0.488 | 0.509 | 0.977 | 0.501 | 0.501 | 0.992 | 0.510 | 0.524 | 0.963 | 0.516 | 0.537 | 0.987 | 0.469 | 0.477 | 0.921 |
| VIDEVAL | 0.715 | 0.724 | 0.686 | 0.704 | 0.722 | 0.738 | 0.739 | 0.756 | 0.668 | 0.747 | 0.757 | 0.711 | 0.668 | 0.679 | 0.641 |
| GSTVQA | 0.679 | 0.701 | 0.737 | 0.536 | 0.655 | 0.803 | 0.777 | 0.835 | 0.573 | 0.780 | 0.814 | 0.626 | 0.688 | 0.731 | 0.626 |
| RAPIQUE | 0.674 | 0.729 | 0.708 | 0.500 | 0.696 | 0.763 | 0.837 | 0.866 | 0.521 | 0.767 | 0.797 | 0.651 | 0.680 | 0.757 | 0.599 |
| ChipQA | 0.725 | 0.745 | 0.667 | 0.714 | 0.761 | 0.716 | 0.766 | 0.718 | 0.703 | 0.740 | 0.778 | 0.691 | 0.652 | 0.689 | 0.637 |
| Nofu | 0.731 | 0.701 | 0.774 | 0.798 | 0.745 | 0.709 | 0.795 | 0.746 | 0.741 | 0.748 | 0.682 | 0.823 | 0.632 | 0.600 | 0.803 |
| HEKE | 0.762 | 0.775 | 0.641 | 0.780 | 0.801 | 0.680 | 0.805 | 0.819 | 0.617 | 0.760 | 0.745 | 0.703 | 0.684 | 0.707 | 0.638 |
| HFR-BVQA | 0.711 | 0.750 | 0.671 | 0.750 | 0.756 | 0.721 | 0.717 | 0.764 | 0.661 | 0.709 | 0.720 | 0.757 | 0.723 | 0.733 | 0.615 |
| Proposed | 0.816 | 0.803 | 0.616 | 0.849 | 0.859 | 0.652 | 0.878 | 0.866 | 0.521 | 0.807 | 0.847 | 0.572 | 0.717 | 0.729 | 0.628 |
| Method | Implement | Runtimes (s) | Parameters (Millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TLVQM | Matlab-CPU | 121.20 | - |
| VIDEVAL | Matlab-CPU | 282.46 | - |
| RAPIQUE | Matlab-CPU | 46.54 | 96.4 |
| HFR-BVQA | Matlab-CPU | 58.12 | 97.1 |
| ChipQA | Python-CPU | 103.40 | - |
| Nofu | Python-CPU | 117.52 | - |
| VSFA | Python-GPU | 9.74 | 100 |
| GSTVQA | Python-GPU | 30.88 | 580.4 |
| HEKE | Python-GPU | 39.90 | 377.6 |
| Proposed | Python-GPU | 12.08 | 6.2 |
| Method | MCML | AVT | Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRCC | PLCC | SRCC | PLCC | ||
| VGG16 | 0.795 | 0.818 | 0.788 | 0.772 | 528 M |
| Mobilenetv2 | 0.762 | 0.786 | 0.723 | 0.738 | 5.2 M |
| Resnet-50 | 0.813 | 0.854 | 0.793 | 0.774 | 97.8 M |
| RCAN | 0.829 | 0.870 | 0.811 | 0.789 | 59.7 M |
| SR-SDFNet | 0.836 | 0.878 | 0.816 | 0.803 | 4.9 M |
| Time Process Strategies | MCML | AVT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRCC | PLCC | SRCC | PLCC | |
| Average Pooling | 0.792 | 0.795 | 0.767 | 0.773 |
| LSTM | 0.802 | 0.820 | 0.781 | 0.772 |
| RL-TFNet | 0.836 | 0.878 | 0.816 | 0.803 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, Z.; Pan, D.; Shi, P. Blind Video Quality Assessment for Ultra-High-Definition Video Based on Super-Resolution and Deep Reinforcement Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031511
Ying Z, Pan D, Shi P. Blind Video Quality Assessment for Ultra-High-Definition Video Based on Super-Resolution and Deep Reinforcement Learning. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031511
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Zefeng, Da Pan, and Ping Shi. 2023. "Blind Video Quality Assessment for Ultra-High-Definition Video Based on Super-Resolution and Deep Reinforcement Learning" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031511
APA StyleYing, Z., Pan, D., & Shi, P. (2023). Blind Video Quality Assessment for Ultra-High-Definition Video Based on Super-Resolution and Deep Reinforcement Learning. Sensors, 23(3), 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031511









