Design, Implementation, and Characterization of a Signal Acquisition Chain for SADino: The Precursor of the Italian Low-Frequency Telescope Named the Sardinia Aperture Array Demonstrator (SAAD)
Abstract
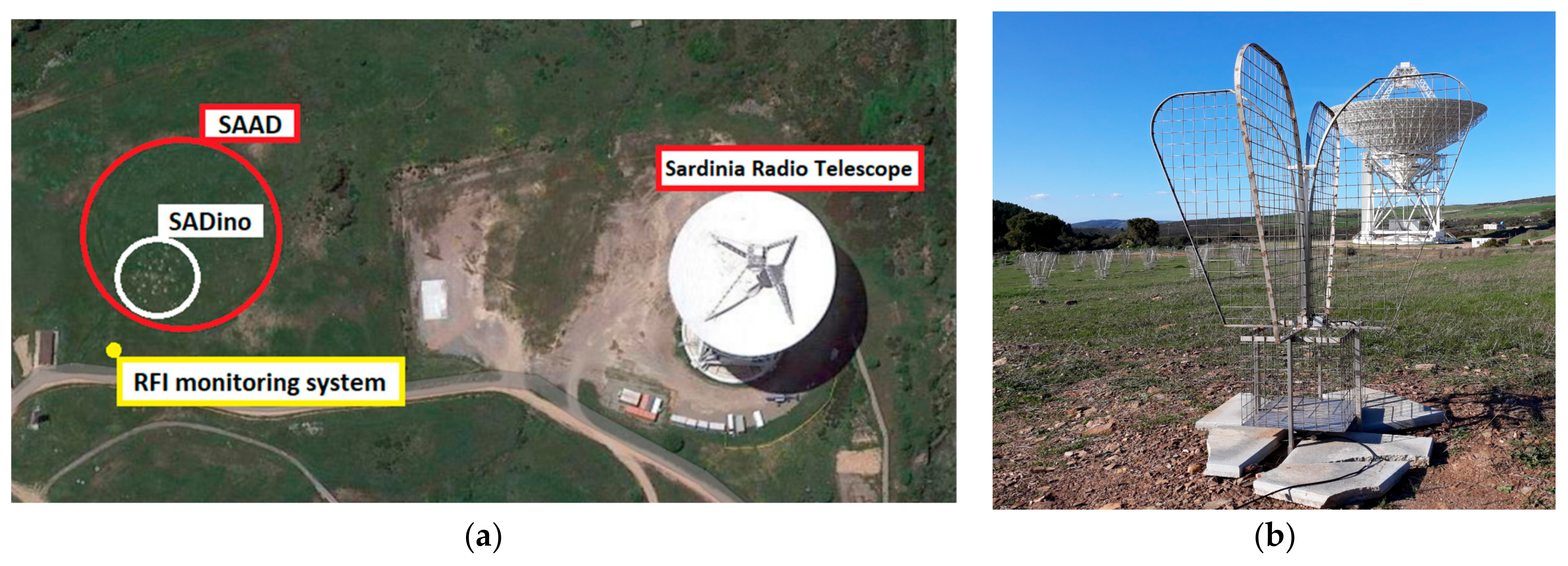
:1. Introduction
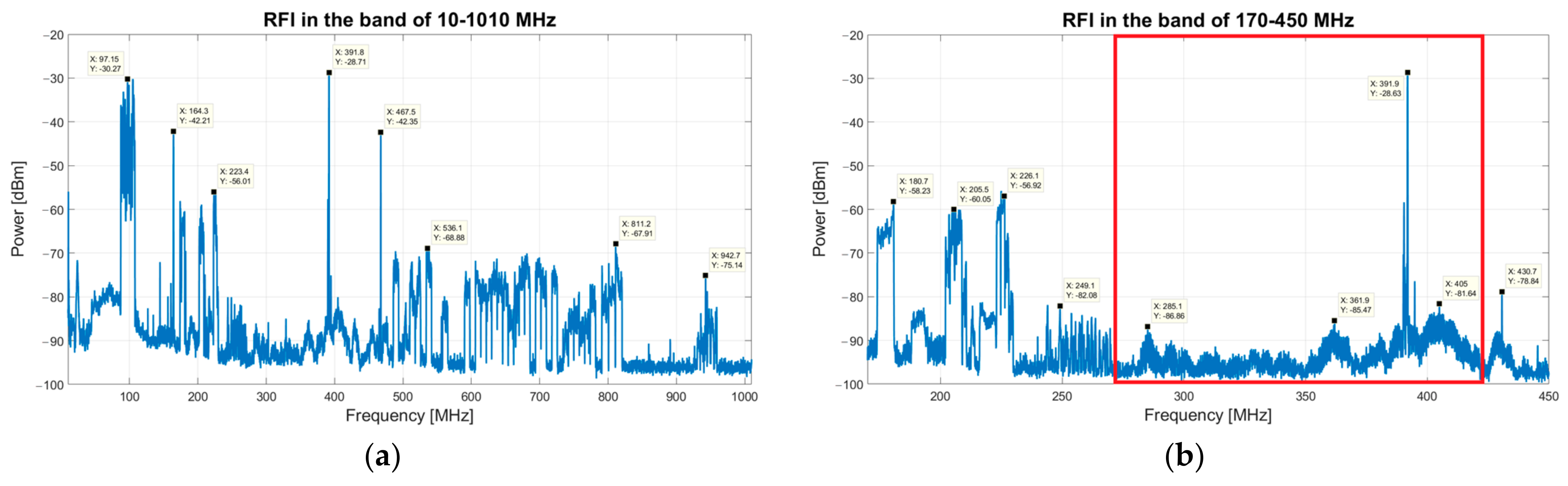
2. Preliminary Measurements Campaign of Radio Frequency Interference
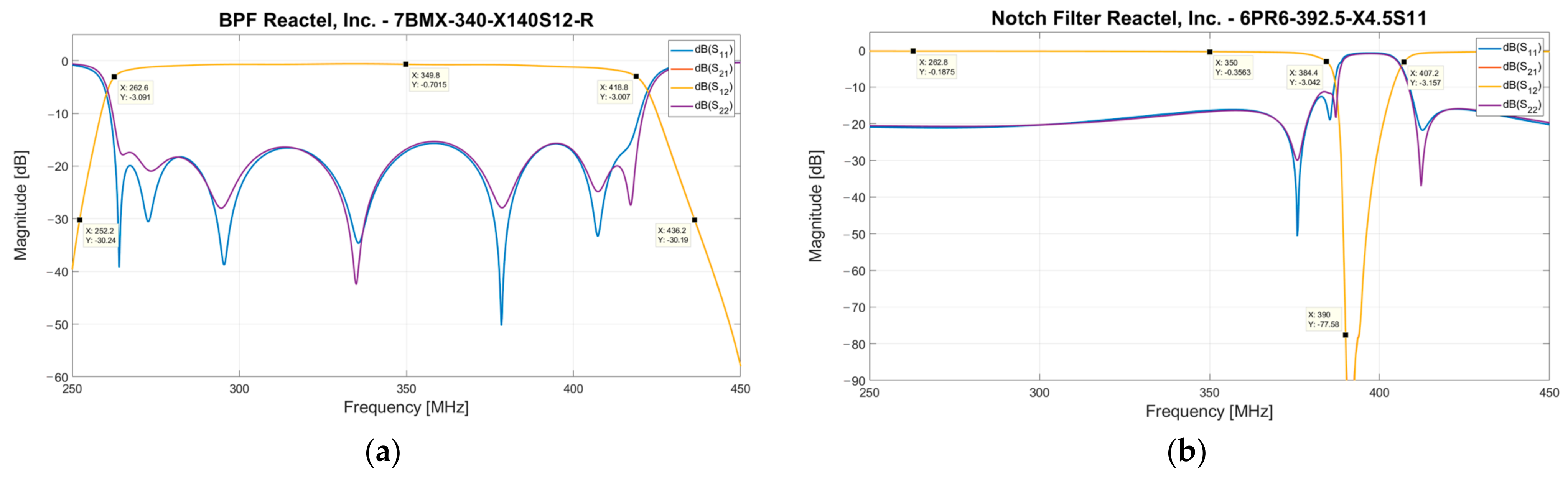
3. Design and Implementation of a Signal Acquisition Chain for SADino
3.1. Vivaldi Antenna
- High flexibility: the mechanical design consists of a mesh steel structure of 16 kg and size of 962 × 962 × 1370 mm. This design guarantees wind resistance with speeds up to 130 km/h. The antenna is fixed to the soil using four tiles (500 × 500 × 40 mm and 21 kg each) at its base in order to guarantee enough robustness and stability. By removing the tiles, the array configuration can be easily changed [36,37,38,39];
- Half power beam width (HPBW) of approximately 45 degrees: the radiation pattern of the Vivaldi antenna was characterized with a UAV-based measurement system, showing an antenna gain at the zenith of 7.8 dBi at 250 MHz and 8.6 dBi at 450 MHz [39];
- Unbalanced 50-ohm excitation through the use of two coaxial cables directly connected to the radiators: the inner part of the coaxial connector is linked to one wing, while the external one is embedded in the opposite wing. In this manner, coupled currents on the cable are not present;
- Linear dual-polarization (i.e., X and Y polarizations);
- Low cross-polarization on the principal axes: each antenna is equipped with a cubic cavity under the four wings to reduce the back lobes and improve the directivity and sensitivity;
- Reflection coefficient (S11) of about −9 dB in the frequency band of 250–450 MHz [39].
3.2. INAF Low Noise Amplifier
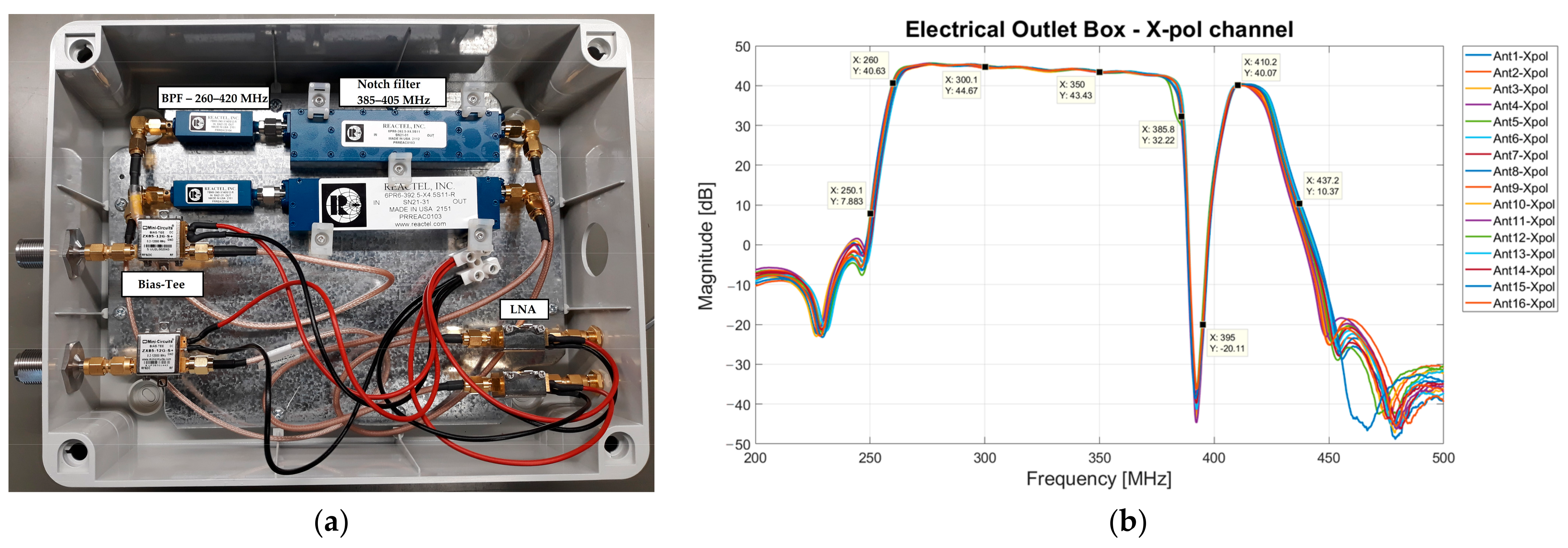
3.3. Electrical Outlet Box
3.4. 70-m Coaxial Cable
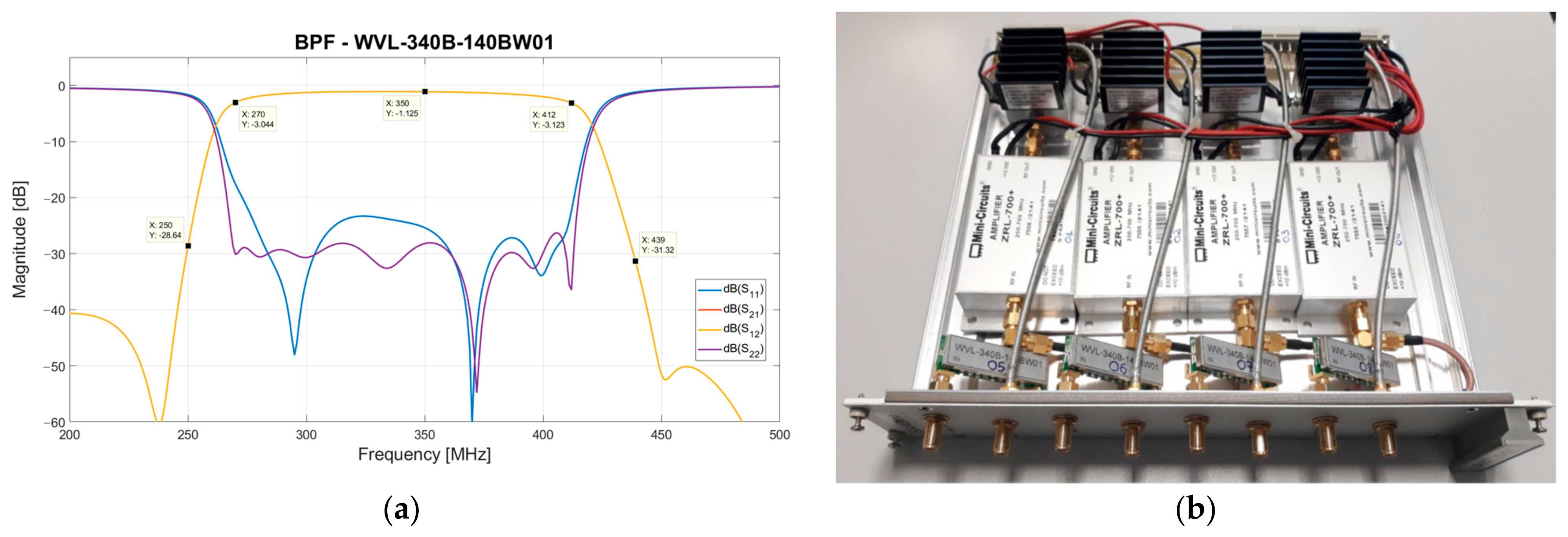
3.5. Interior Rack
4. Results and Discussion: Laboratory Characterization and Real Spectrum Acquisition
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burke, B.F. An Introduction to Radio Astronomy, 4th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Govoni, F.; Bolli, P.; Buffa, F.; Caito, L.; Carretti, E.; Comoretto, G.; Fierro, D.; Melis, A.; Murgia, M.; Navarrini, A.; et al. The high-frequency upgrade of the Sardinia Radio Telescope. In Proceedings of the 2021 XXXIVth General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI GASS), Rome, Italy, 28 August–4 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, D.D.; Horneffer, A.; Beck, R.; Heald, G.; Fletcher, A.; Scaife, A.; Röttgering, H.J.A. The nature of the low-frequency emission of M 51. First observations of a nearby galaxy with LOFAR. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 568, A72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, D.D.; Horneffer, A.; Beck, R.; Krause, M.; Schmidt, P.; Basu, A.; Titterington, D. Investigation of the cosmic ray population and magnetic field strength in the halo of NGC 891. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 615, A98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahori, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Sofue, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Ichiki, K.; Ideguchi, S.; Kameya, O.; Kudoh, T.; Kudoh, Y.; Machida, M.; et al. Cosmic magnetism in centimeter- and meter-wavelength radio astronomy. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 70, R2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.H.; Fan, X.; White, R.L.; Strauss, M.A.; Narayanan, V.K.; Lupton, R.H.; York, D.G. Evidence for Reionization at Z ~ 6: Detection of a Gunn-Peterson trough in a Z = 6.28 Quasar. Astron. J. 2001, 122, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offringa, A.R.; Trott, C.M.; Hurley-Walker, N.; Johnston-Hollitt, M.; McKinley, B.; Barry, N.; Beardsley, A.P.; Bowman, J.D.; Briggs, F.; Carroll, P.; et al. Parametrizing Epoch of Reionization foregrounds: A deep survey of low-frequency point-source spectra with the Murchison Widefield Array. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelles, A.; Schellart, P.; Buitink, S.; Corstanje, A.; De Vries, K.D.; Enriquez, J.E.; Zarka, P. Measuring a Cherenkov ring in the radio emission from air showers at 110–190 MHz with LOFAR. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 65, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.; James, C.W.; Tingay, S.J.; McSweeney, S.J.; Ord, S.M. An Ultra-High Time Resolution Cosmic-Ray Detection Mode for the Murchison Widefield Array. J. Astron. Instrum. 2021, 10, 2150003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, E.P.; Baldovin, C.; Benthem, P.; Bisi, M.M.; Fallows, R.A.; Gallagher, P.T.; Barnes, D. Radio observatories and instrumentation used in space weather science and operations. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2020, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimwell, T.W.; Röttgering, H.J.A.; Best, P.N.; Williams, W.L.; Dijkema, T.J.; de Gasperin, F.; Zwart, J.T.L. The LOFAR Two-metre Sky Survey, I. Survey description and preliminary data release. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 598, A104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, E.F.; Johnston, S.; Bhandari, S.; Barr, E.; Bhat, N.D.R.; Burgay, M.A.R.T.A.; Bassa, C. The host galaxy of a fast radio burst. Nature 2016, 530, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, N.D.R.; Tremblay, S.E.; Kirsten, F.; Meyers, B.W.; Sokolowski, M.; Van Straten, W.; Wu, C. Observations of Low-frequency Radio Emission from Millisecond Pulsars and Multipath Propagation in the Interstellar Medium. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 238, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, A.C. Antenna Theory, Analysis and Design, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Colllin, E.R. Antennas and Radio Wave Propagation, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Xue, S.; Hu, X.; Lian, P.; Xu, Q.; Wang, N.; Wang, C. Progress and Challenges in Electromechanical Coupling of Radio Telescopes. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2022, 2022, 4728303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, G.; McKean, J.; Pizzo, R. Low Frequency Radio Astronomy and the LOFAR Observatory, 1st ed.; Springer international Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Cappellen, W.A.; Wijnholds, S.J.; Bregman, J.D. Sparse antenna array configurations in large aperture synthesis radio telescopes. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Radar Conference, Manchester, UK, 13–15 September 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, M.; Gunst, A.W.; Nijboer, R. The LOFAR Telescope: System Architecture and Signal Processing. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnholds, S.J.; van Cappellen, W.A. In Situ Antenna Performance Evaluation of the LOFAR Phased Array Radio Telescope. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunst, A.W.; van Haarlem, M.P.; Vermeulen, R.C. LOFAR: A digital aperture array radio telescope. In Proceedings of the 2011 XXXth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 20 October 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, S.W.; Clarke, T.E.; Cohen, A.; Craig, J.; Kassim, N.E.; Pihlstrom, Y.; Taylor, G.B. The Long Wavelength Array. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.B.; Ellingson, S.W.; Kassim, N.E.; Craig, J.; Dowell, J.; Wolfe, C.N.; Wood, D.L. First Light for the First Station of the Long Wavelength Array. J. Astron. Instrum. 2012, 1, 1250004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, C.J.; Cappallo, R.J.; Morales, M.F.; Briggs, F.H.; Benkevitch, L.; Bowman, J.D.; Williams, C. The Murchison Widefield Array: Design Overview. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingay, S.J.; Goeke, R.; Bowman, J.D.; Emrich, D.; Ord, S.M.; Mitchell, D.A.; Wyithe, J.S.B. The Murchison Widefield Array: The Square Kilometre Array Precursor at Low Radio Frequencies. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2013, 30, E007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayth, R.B.; Tingay, S.J.; Trott, C.M.; Emrich, D.; Johnston-Hollitt, M.; McKinley, B.; Wyithe, J.S.B. The Phase II Murchison Widefield Array: Design overview. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2018, 35, E033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SKA-Low: Exploring the Universe from Australia. Available online: https://www.skao.int/en/explore/telescopes/ska-low (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- McMullin, J.; Diamond, P.; Caiazzo, M.; Casson, A.; Cheetham, T.; Dewdney, P.; Pearce, S. The Square Kilometre Array project update. In Proceedings of the SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation, Montréal, QC, Canada, 29 August 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnes, J.; Mort, B.; Dulwich, F.; Salvini, S.; Armour, W. Science Pipelines for the Square Kilometre Array. Galaxies 2018, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labate, M.G.; Braun, R.; Dewdney, P.; Waterson, M.; Wagg, J. SKA1-LOW: Design and scientific objectives. In Proceedings of the 2017 XXXIInd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI GASS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–26 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario, G.; Pupillo, G.; Bernardi, G.; Bolli, P.; Di Ninni, P.; Comoretto, G.; Bhushan, R. Characterization of the SKA1-Low prototype station Aperture Array Verification System 2. J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 2022, 8, 011014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virone, G.; Sarkis, R.; Craeye, C.; Addamo, G.; Peverini, O.A. Gridded Vivaldi Antenna Feed System for the Northern Cross Radio Telescope. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catelani, M.; Scarano, V.L.; Singuaroli, R.; Montebugnoli, S.; Bianchi, G.; Perini, F.; Trotta, I. Northern Cross Radiotelescope: Test and Measurements of Reliability Performance on Radioreceiver Chains. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 58, 3769–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, P.; Perini, F.; Montebugnoli, S.; Pelosi, G.; Poppi, S. Basic Element for Square Kilometer Array Training (BEST): Evaluation of the Antenna Noise Temperature. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2008, 50, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladu, A.; Schirru, L.; Gaudiomonte, F.; Marongiu, P.; Angius, G.; Perini, F.; Vargiu, G.P. Upgrading of the L-P Band Cryogenic Receiver of the Sardinia Radio Telescope: A Feasibility Study. Sensors 2022, 22, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, M.; Bianchi, G.; Bolli, P.; Comoretto, G.; Dallacasa, D.; Farooqui, M.Z.; Zanichelli, A. Sardinia Aperture Array Demonstrator. In Proceedings of the SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation, Montreal, QC, Canada, 22–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, P.; Comoretto, G.; Dallacasa, D.; Farooqui, M.Z.; Fierro, D.; Gaudiomonte, F.; Zanichelli, A. Sardinia Array Demonstrator: Instrument overview and status. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), Turin, Italy, 7–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, P.; Pupillo, G.; Virone, G.; Farooqui, M.Z.; Lingua, A.; Mattana, A.; Tibaldi, A. From MAD to SAD: The Italian experience for the low-frequency aperture array of SKA1-LOW. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virone, G.; Lingua, A.M.; Piras, M.; Cina, A.; Perini, F.; Monari, J.; Tascone, R. Antenna Pattern Verification System Based on a Micro Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladu, A.; Schirru, L.; Melis, A.; Perini, F.; Gaudiomonte, F.; Rusticelli, S.; Schiaffino, M.; Concu, R.; Mattana, A.; Murgia, M. Preliminary tests to design an ad hoc signal acquisition chain for the Sardinia Aperture Array Demonstrator. In Proceedings of the 34th General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI GASS), Rome, Italy, 28 August–4 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- iTPM ADFE—Multi-Channel Digital Beamformer. Available online: https://www.sanitaseg.com/project/itpm-adfe/ (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Gaudiomonte, F.; Ladu, A.; Schirru, L.; Melis, A.; Concu, R.; Perini, F.; Murgia, M. Sardinia Aperture Array Demonstrator: Measurement Campaigns of Radio Frequency Interferences. In Proceedings of the SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation, Online, 13 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- The European Table of Frequency Allocations and Applications in the Frequency Range 8.3 kHz to 3000 GHz (ECA TABLE). Available online: https://docdb.cept.org/download/4316 (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Fanti, A.; Schirru, L.; Casu, S.; Lodi, M.B.; Riccio, G.; Mazzarella, G. Improvement and Testing of Models for Field Level Evaluation in Urban Environment. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 4038–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilia, M. The Low Frequency Perspective on Fast Radio Bursts. Universe 2022, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirru, L.; Pisanu, T.; Podda, A. The Ad Hoc Back-End of the BIRALET Radar to Measure Slant-Range and Doppler Shift of Resident Space Objects. Electronics 2021, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntoni, G.; Montisci, G.; Pisanu, T.; Andronico, P.; Valente, G. Crowded Space: A Review on Radar Measurements for Space Debris Monitoring and Tracking. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losacco, M.; Di Lizia, P.; Massari, M.; Naldi, G.; Pupillo, G.; Bianchi, G.; Siminski, J. Initial orbit determination with the multibeam radar sensor BIRALES. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 167, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirru, L.; Pisanu, T.; Navarrini, A.; Urru, E.; Gaudiomonte, F.; Ortu, P.; Montisci, G. Advantages of Using a C-band Phased Array Feed as a Receiver in the Sardinia Radio Telescope for Space Debris Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 2nd Ukraine Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (UKRCON), Lviv, Ukraine, 2–6 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirru, L.; Ladu, A.; Gaudiomonte, F. Radio Frequency Interference Measurements to Determine the New Frequency Sub-Bands of the Coaxial L-P Cryogenic Receiver of the Sardinia Radio Telescope. Universe 2023, 9, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, D.R.; Gough, R.G.; Bunton, J.D.; Cornwell, T.J.; Beresford, R.J.; Johnston, S.; Boyle, B.J. Australian SKA Pathfinder: A High-Dynamic Range Wide-Field of View Survey Telescope. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1507–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qorvo SPF-5122Z MMIC Amplifier. Available online: https://www.qorvo.com/products/p/SPF5122Z (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Perini, F.; Schiaffino, M.; Mariotti, S.; Monari, J. INAF/IRA AAlo AAVS0 LNA. INAF Technical Reports—Rapporti Tecnici; INAF: Rome, Italy, 2012; Volume 463, Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12386/25786 (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Mini-Circuits—Bias-Tee ZX85-12G+. Available online: https://www.minicircuits.com/pdfs/ZX85-12G+.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Reactel, Inc. Available online: https://reactel.com/ (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Mini-Circuits—Low Noise Amplifier—ZX60-P103LN+. Available online: https://www.minicircuits.com/pdfs/ZX60-P103LN%2B.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Bel Power Solutions, Inc.—HB5-OVP-AG. Available online: https://www.belfuse.com/product/part-details?partn=HB5-3/OVP-AG (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Huber+Suhner: Flexible RF Cable—Model SPUMA_400-FR-01. Available online: https://www.mouser.it/datasheet/2/829/HUBER_2bSUHNER_SPUMA_400_FR_01_DataSheet-1489459.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Wevercomm—Products. Available online: http://wevercomm.com/?utm_source=everythingrf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Mini-Circuits—Low Noise Amplifier—ZRL-700+. Available online: https://www.minicircuits.com/pdfs/ZRL-700+.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Bel Power Solutions, Inc.—HE12-10.2-AG. Available online: https://www.belfuse.com/product/part-details?partn=HE12-10.2-AG (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Mini-Circuits—Low Noise Amplifier—ZFL-2500VH+. Available online: https://www.minicircuits.com/pdfs/ZFL-2500VH+.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Condor DC Power Supply—F15-15-A+G (15V, 15A). Available online: https://www.mouser.it/datasheet/2/373/Linears_DS-14479.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Hérique, A.; Agnus, B.; Asphaug, E.; Barucci, A.; Beck, P.; Bellerose, J.; Zine, S. Direct observations of asteroid interior and regolith structure: Science measurement requirements. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 2141–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




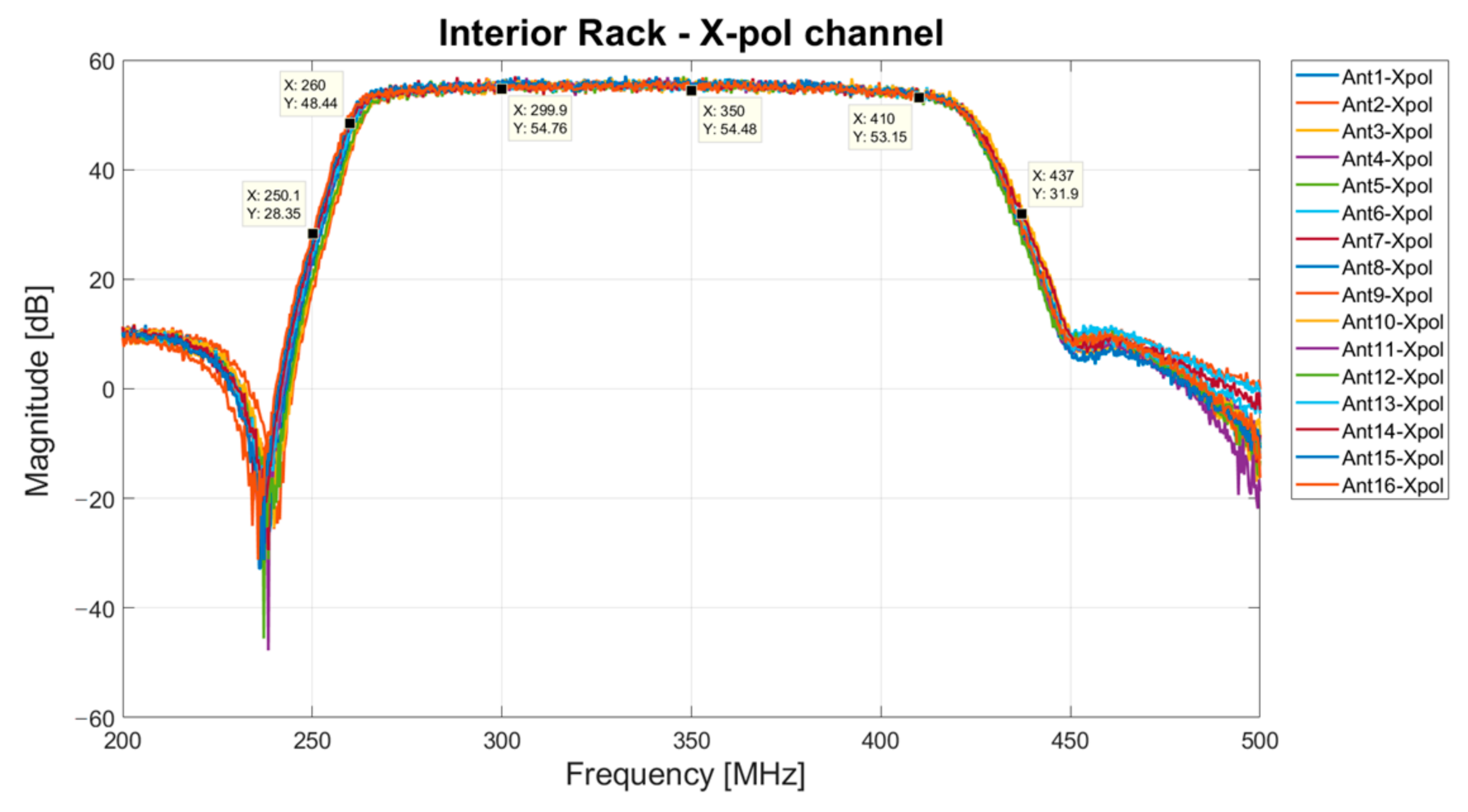
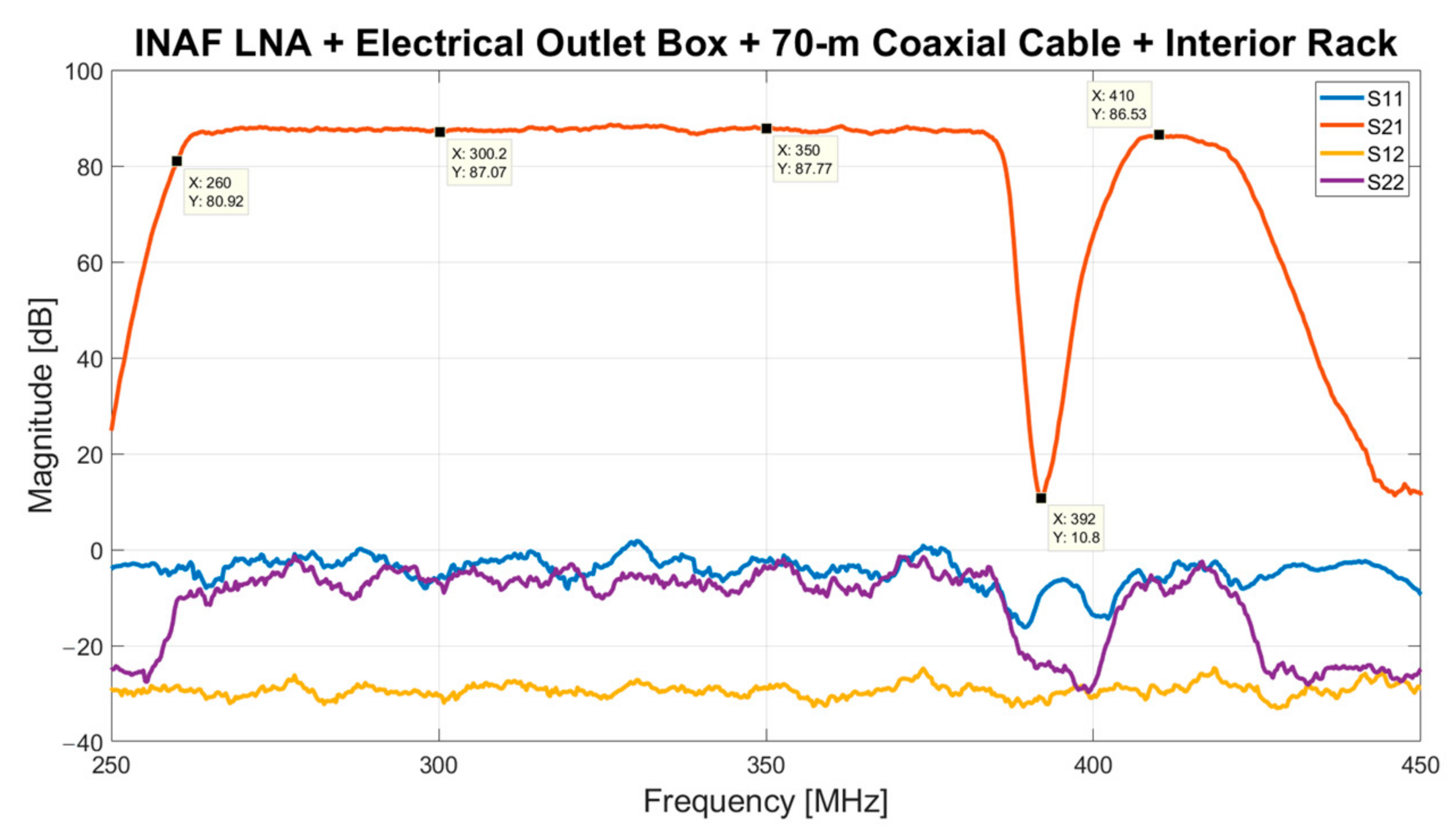
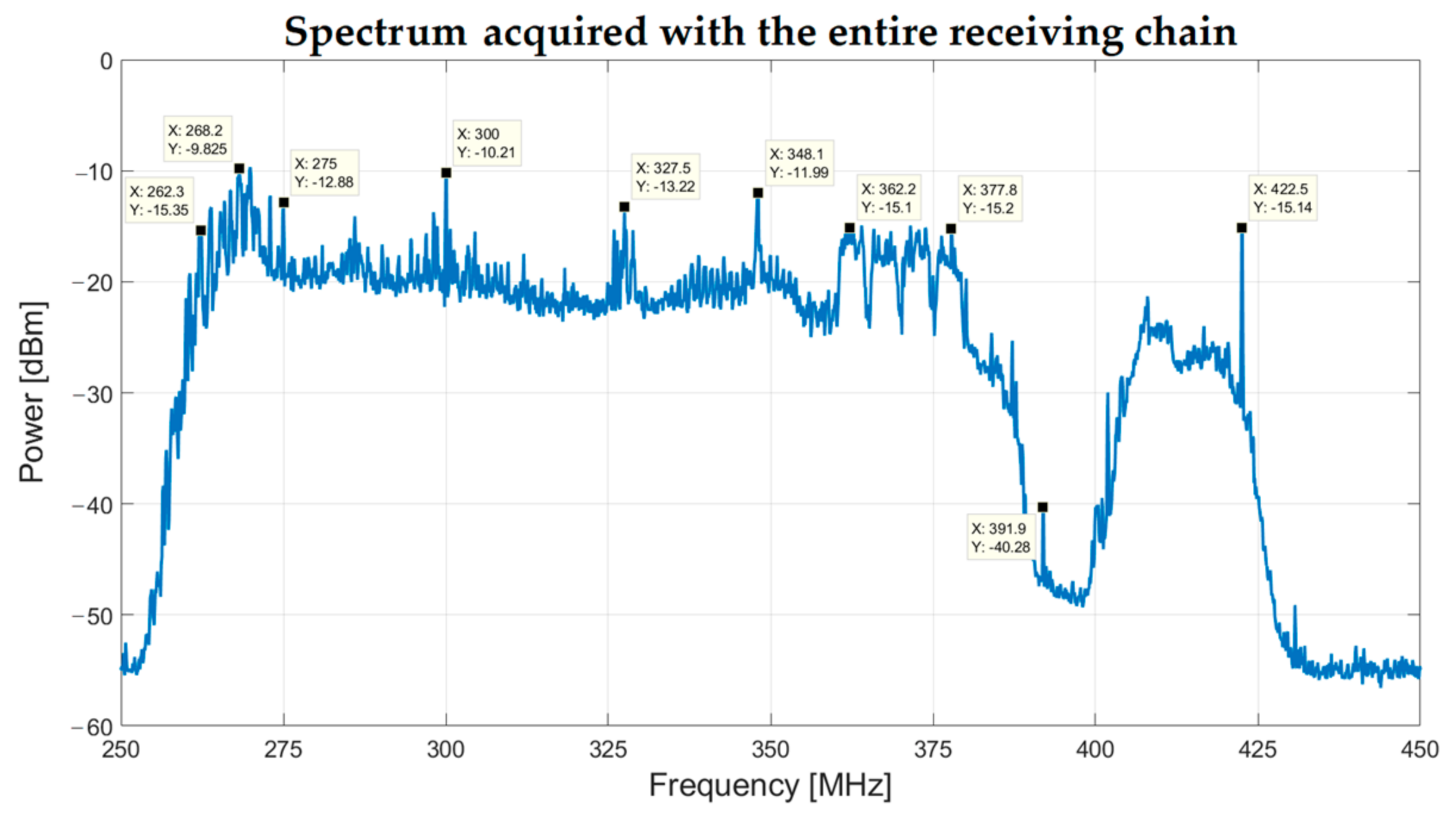
| Receiving Chain Components | Max Attenuation [dB] | Gain [dB] | Noise Figure [dB] |
|---|---|---|---|
| INAF LNA | – | 23 | 0.5 |
| Bias-Tee, ZX85-12G-S+, Mini-Circuits | 0.6 | – | – |
| BPF, 7BMX-340-X140S12-R, Reactel, Inc. | 0.7 | – | – |
| Notch filter, 6PR6-392.5-X4.5S11, Reactel, Inc. | 0.3 | – | – |
| LNA, ZX60-P103LN+, Mini-circuits | – | 20 | 0.5 |
| 70-m coaxial cable, Spuma_400-FR-01, Huber+Suhner | 5.5 | – | – |
| BPF, WVL-340B-140BW01, Wevercomm | 1.1 | – | – |
| LNA, ZRL-700+, Mini-circuits | – | 31 | 2 |
| LNA, ZFL-2500VH+, Mini-circuits | – | 20 | 5.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ladu, A.; Schirru, L.; Pili, M.; Vargiu, G.P.; Gaudiomonte, F.; Perini, F.; Melis, A.; Concu, R.; Murgia, M. Design, Implementation, and Characterization of a Signal Acquisition Chain for SADino: The Precursor of the Italian Low-Frequency Telescope Named the Sardinia Aperture Array Demonstrator (SAAD). Sensors 2023, 23, 9151. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229151
Ladu A, Schirru L, Pili M, Vargiu GP, Gaudiomonte F, Perini F, Melis A, Concu R, Murgia M. Design, Implementation, and Characterization of a Signal Acquisition Chain for SADino: The Precursor of the Italian Low-Frequency Telescope Named the Sardinia Aperture Array Demonstrator (SAAD). Sensors. 2023; 23(22):9151. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229151
Chicago/Turabian StyleLadu, Adelaide, Luca Schirru, Mauro Pili, Gian Paolo Vargiu, Francesco Gaudiomonte, Federico Perini, Andrea Melis, Raimondo Concu, and Matteo Murgia. 2023. "Design, Implementation, and Characterization of a Signal Acquisition Chain for SADino: The Precursor of the Italian Low-Frequency Telescope Named the Sardinia Aperture Array Demonstrator (SAAD)" Sensors 23, no. 22: 9151. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229151
APA StyleLadu, A., Schirru, L., Pili, M., Vargiu, G. P., Gaudiomonte, F., Perini, F., Melis, A., Concu, R., & Murgia, M. (2023). Design, Implementation, and Characterization of a Signal Acquisition Chain for SADino: The Precursor of the Italian Low-Frequency Telescope Named the Sardinia Aperture Array Demonstrator (SAAD). Sensors, 23(22), 9151. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229151





