Quantitative Colorimetric Sensing of Carbidopa in Anti-Parkinson Drugs Based on Selective Reaction with Indole-3-Carbaldehyde
Abstract
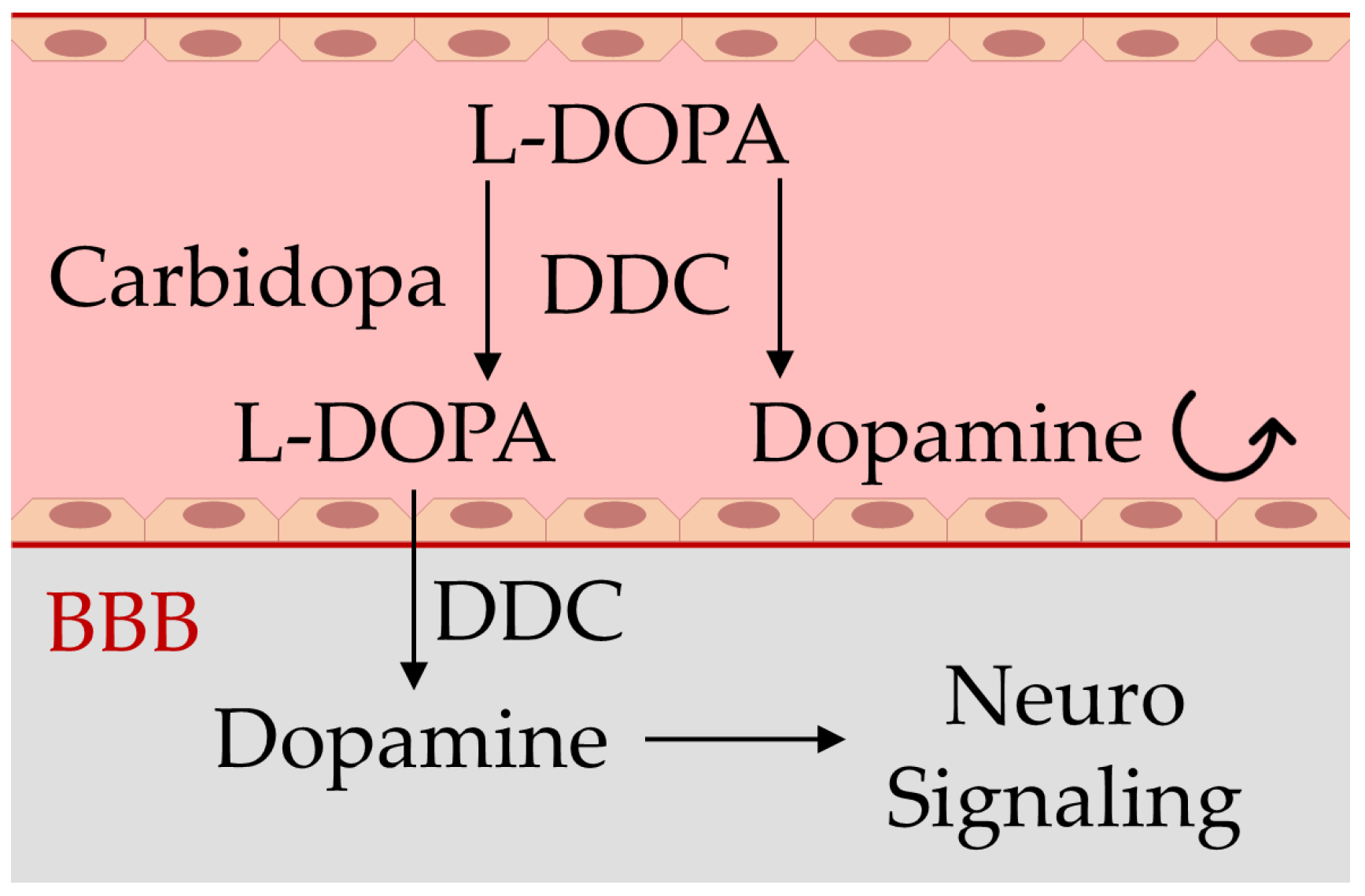
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Methods
2.2. Visible Spectroscopy
2.3. LC–MS
3. Results and Discussion
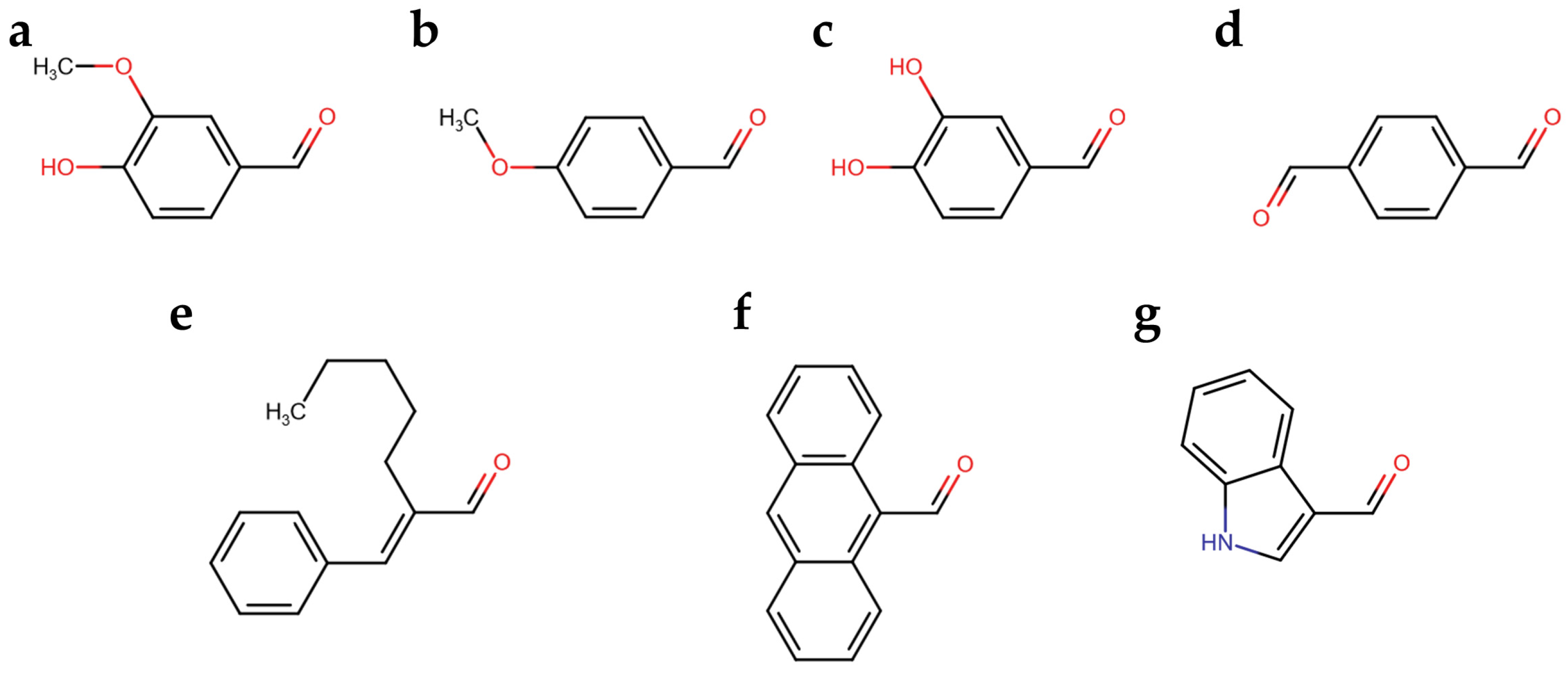
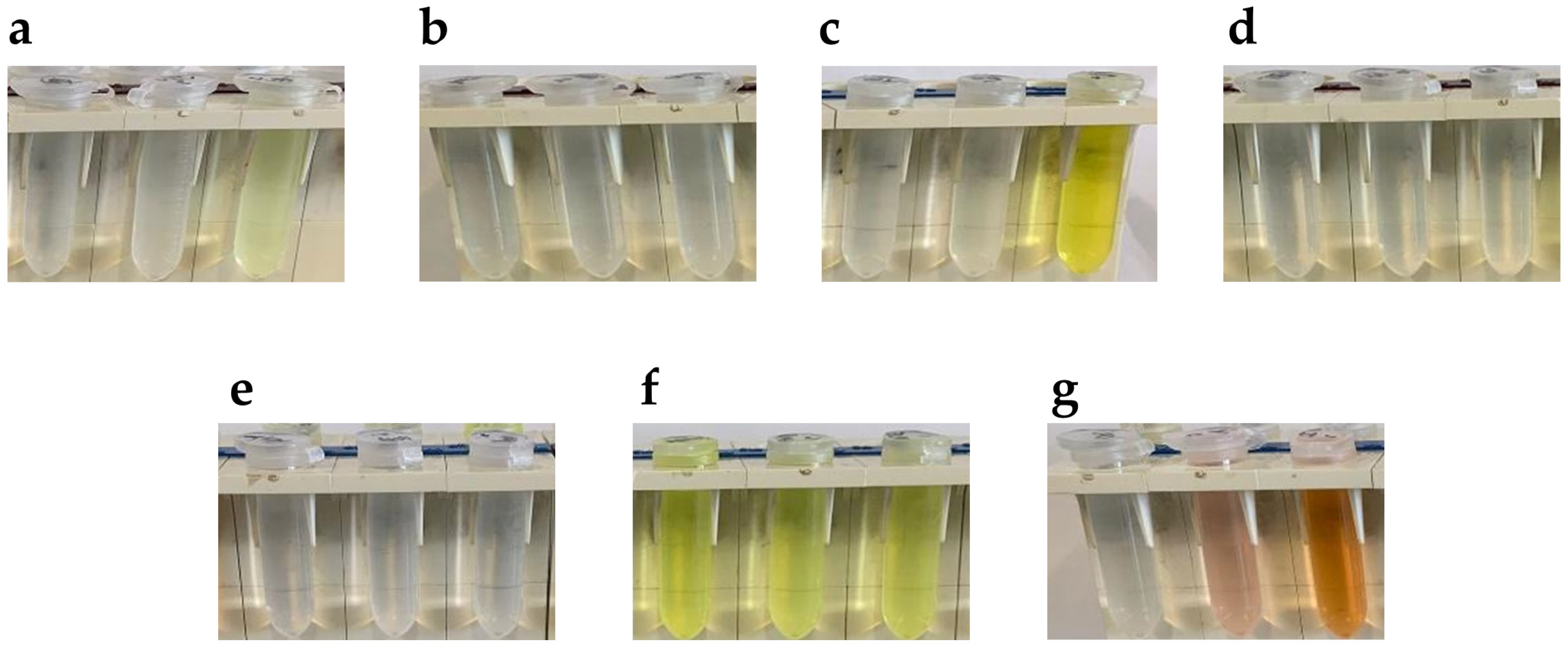
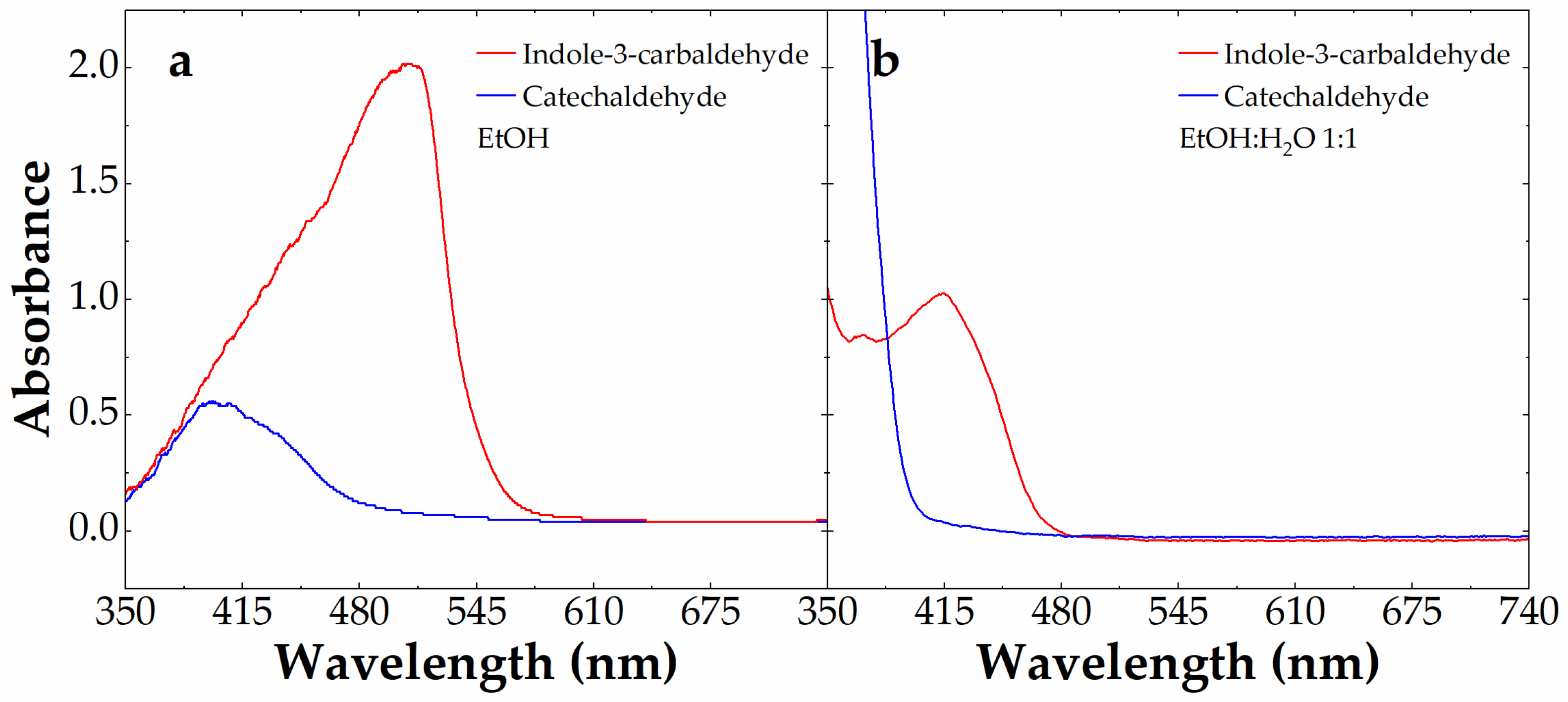
3.1. Aldehyde Selection for Aldazine Formation upon Reaction with Carbidopa
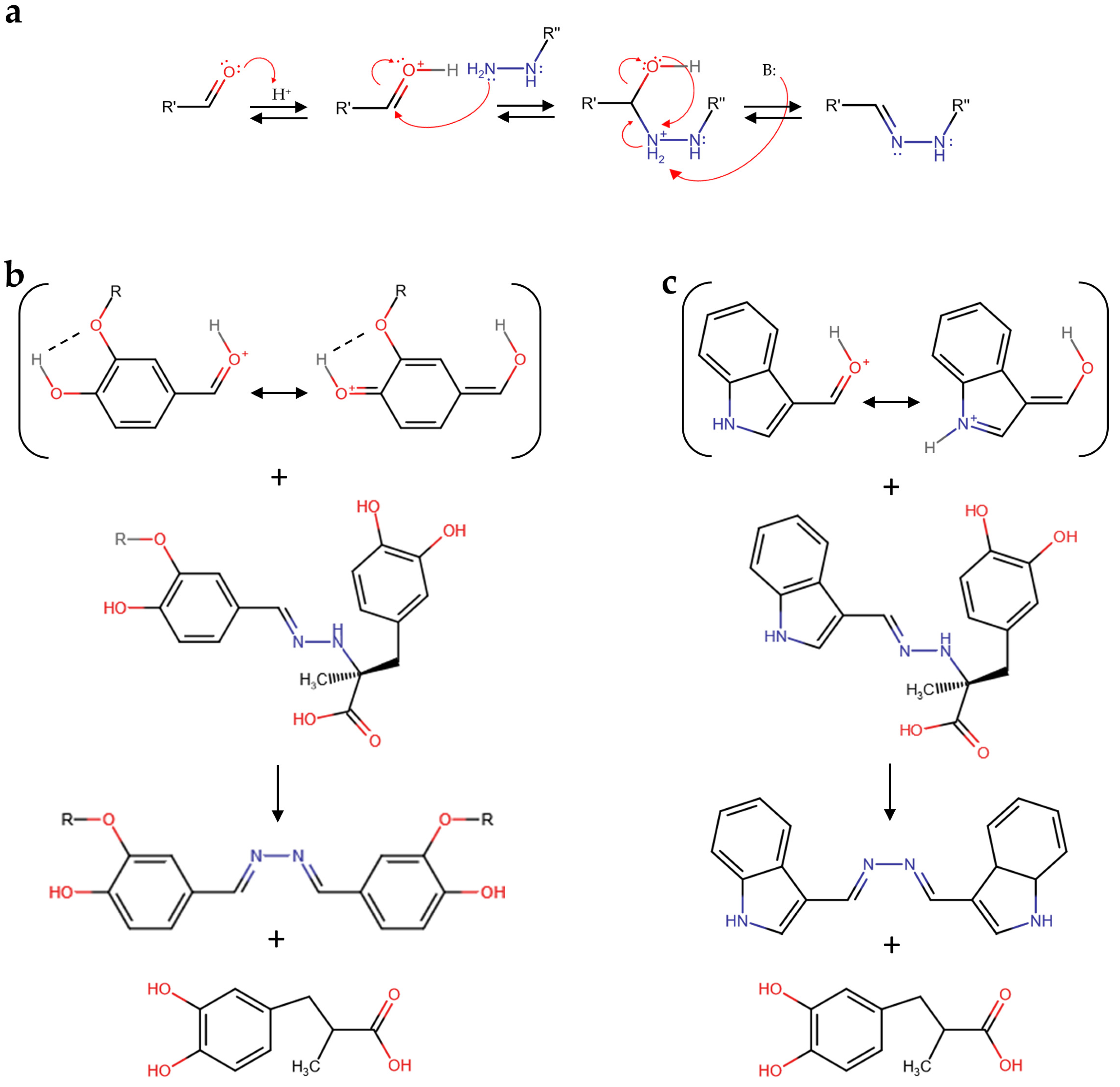
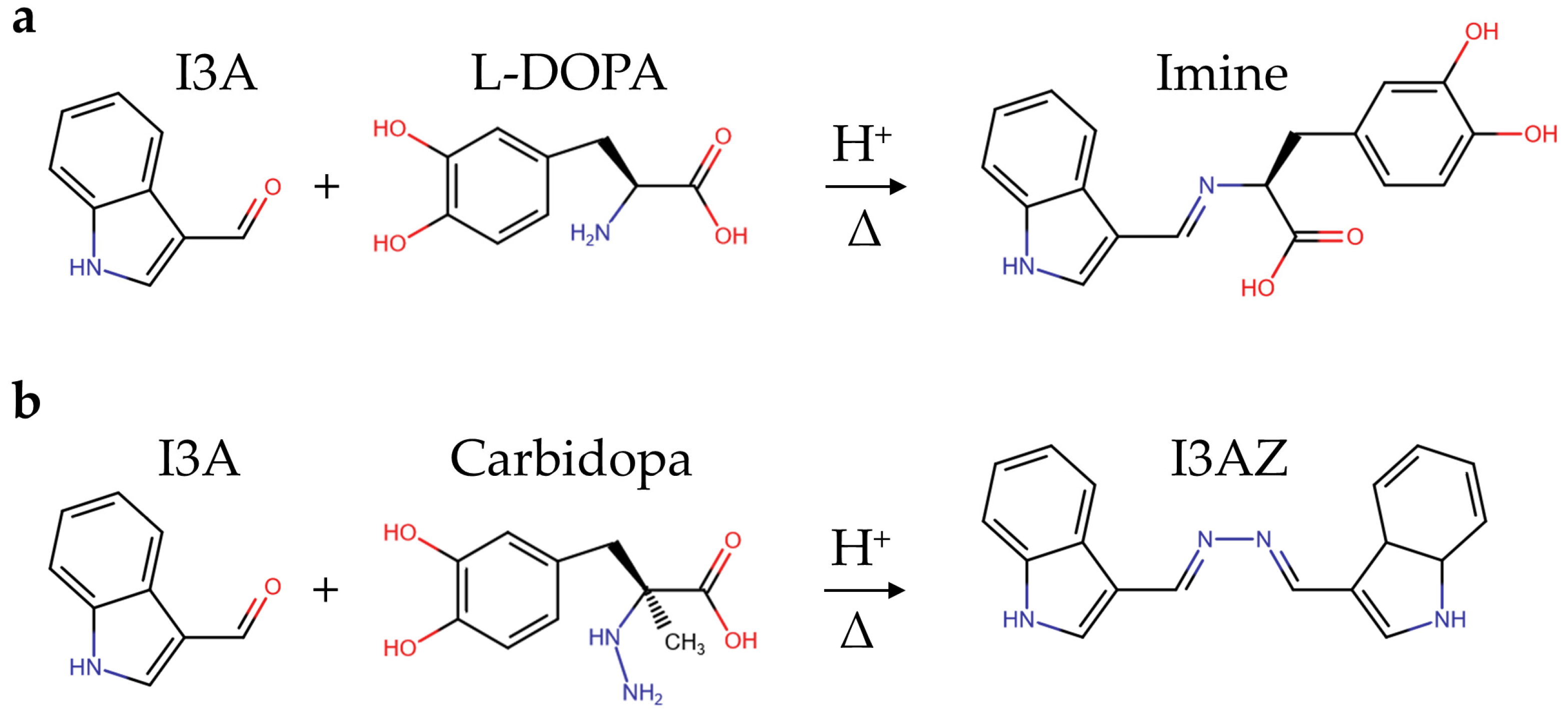
3.2. Proposed Mechanism of Reaction of Selected Aldehydes and Carbidopa
3.3. Visible Spectroscopy of Carbidopa/Aldehyde Reaction Products
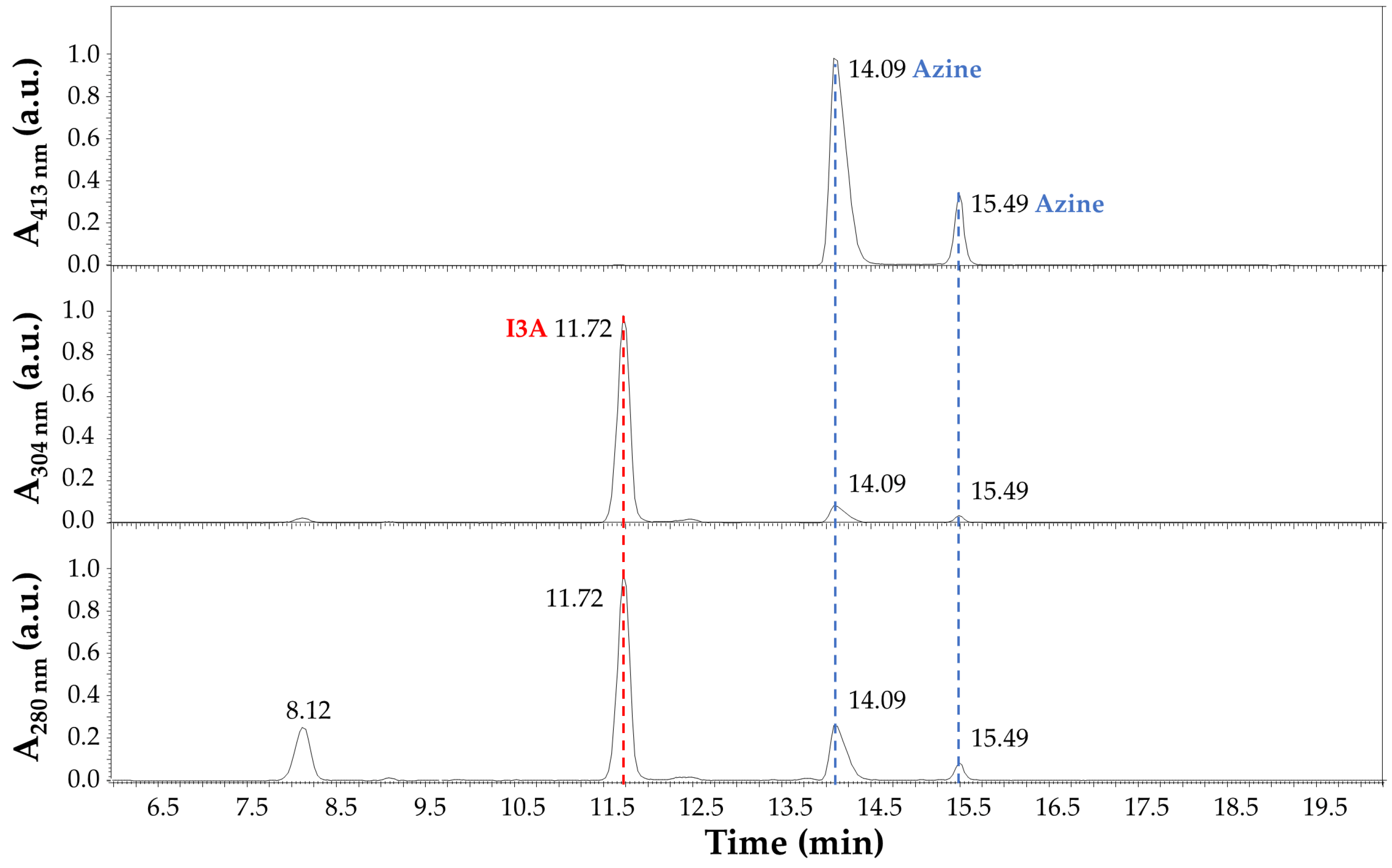
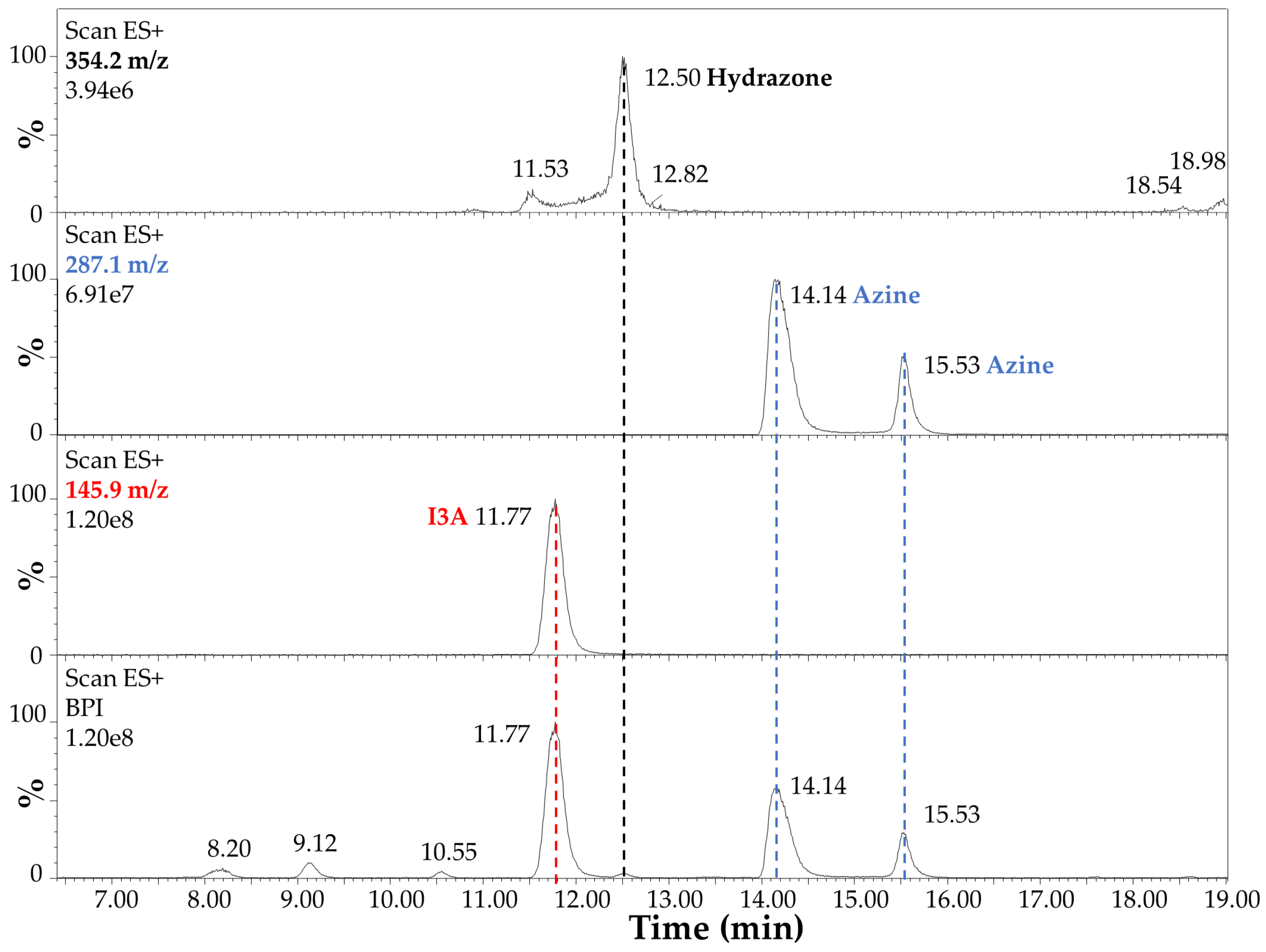
3.4. LC–MS Analysis of Carbidopa/I3A Reaction Products
3.5. Colorimetric Quantification of Carbidopa in Tablets by Using of I3A Azine as a Molecular Probe
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mhyre, T.R.; Boyd, J.T.; Hamill, R.W.; Maguire-Zeiss, K.A. Parkinson’s disease. Subcell. Biochem. 2012, 65, 389–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereczki, D. The description of all four cardinal signs of Parkinson’s disease in a Hungarian medical text published in 1690. Park. Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisaglia, M.; Filograna, R.; Beltramini, M.; Bubacco, L. Are dopamine derivatives implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease? Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 13, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeitner, T.M.; Kalogiannis, M.; Krasnikov, B.F.; Gomlin, I.; Peltier, M.R.; Moran, G.R. Linking inflammation and Parkinson disease: Hypochlorous acid generates parkinsonian poisons. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 151, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel, W.H. Recent advances in treating Parkinson’s disease. F1000Research 2017, 6, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, B.S.; Lang, A.E. Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vascellari, S.; Manzin, A. Parkinson’s disease: A prionopathy? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, I.; Nayeem, S.M. Effect of osmolytes on conformational behavior of intrinsically disordered protein α-synuclein. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, V.; Palladino, P.; Tizzano, B.; Negro, A.; Berisio, R.; Zagari, A. The effect of the osmolyte trimethylamine N-oxide on the stability of the prion protein at low pH. Biopolymers 2006, 82, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Parkinson’s Foundation. Available online: https://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/statistics (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Al-Zaid, F.S.; Hurley, M.J.; Dexter, D.T.; Gillies, G.E. Neuroprotective role for RORA in Parkinson’s disease revealed by analysis of post-mortem brain and a dopaminergic cell line. Npj Parkinson’s Dis. 2023, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, S.; Javed, H.; Khan, I.; Jaber, F.; Sohail, A.; Zaib, Z.; Mehboob, T.; Tabassam, N.; Ogaly, H.A. Neurodegenerative Diseases: Their Onset, Epidemiology, Causes and Treatment. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202300225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Q.; Feng, Z.; Dai, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yo, Q.-D.; Xu, X. Medicinal chemistry perspective on cGAS-STING signaling pathway with small molecule inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 244, 114791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Mei, J.; Huang, L.; Lou, X.; Zhao, S.-M.; Song, L.; Chen, W.; et al. The cyclopeptide astin C specifically inhibits the innate immune CDN sensor STING. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3405–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.; Zanotti, G.; Saviano, M.; Iacovino, R.; Palladino, P.; Saviano, G.; Amodeo, P.; Tancredi, T.; Laccetti, P.; Corbier, C.; et al. New antitumour cyclic astin analogues: Synthesis, conformation and bioactivity. J. Petp. Sci. 2004, 10, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollmer, E.; Klein, S. Development and Validation of a Robust and Efficient HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Levodopa, Carbidopa, Benserazide and Entacapone in Complex Matrices. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 20, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanali, S.; Pucci, V.; Sabbioni, C.; Raggi, M.A. Quality control of benserazide-levodopa and carbidopa-levodopa tablets by capillary zone electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 2432–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, G.; Chai, H.; Qu, L.; Zhang, X. Flexible biosensors based on colorimetry, fluorescence, and electrochemistry for point-of-care testing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 753692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Hu, X.; Tong, W.; Leng, Y.; Xiong, Y. Recent advances in colorimetry/fluorimetry-based dual-modal sensing technologies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, M.; Mobedi, E.; Garmarudi, A.B.; Mobedi, H.; Kargosha, K. Simultaneous determination of levodopa and carbidopa in levodopa-carbidopa tablets by ATR-FTIR spectrometry. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2007, 12, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamsaz, M.; Safavi, A.; Fadaee, J. Simultaneous kinetic-spectrophotometric determination of carbidopa, levodopa and methyldopa in the presence of citrate with the aid of multivariate calibration and artificial neural networks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 603, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, P.C.; Moschetti, A.C.; Rovetto, A.J.; Benavente, F.; Olivieri, A.C. Design and optimization of a chemometrics-assisted spectrophotometric method for the simultaneous determination of levodopa and carbidopa in pharmaceutical products. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 543, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintino, M.S.M.; Yamashita, M.; Angnes, L. Voltammetric studies and determination of levodopa and carbidopa in pharmaceutical products. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, M.; Emanuele, R.; Scarano, S.; Palladino, P.; Minunni, M. Melanochrome-based colorimetric assay for quantitative detection of levodopa in co-presence of carbidopa and its application to relevant anti-Parkinson drugs. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, M.; Scarano, S.; Palladino, P.; Minunni, M. Colorimetric determination of carbidopa in anti-Parkinson drugs based on 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldazine formation by reaction with vanillin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 6911–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettieri, M.; Spinelli, M.; Caponi, L.; Scarano, S.; Palladino, P.; Amoresano, A.; Minunni, M. Sensing of Catecholamine in Human Urine Using a Simple Colorimetric Assay Based on Direct Melanochrome and Indolequinone Formation. Sensors 2023, 23, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, S.; Stuart, E.K. Spectrofluorometric Determination of Carbidopa [L-(−)-a-Hydrazino-3,4-dihydroxy-a-methylhydrocinnamic Acid] in Plasma. J. Pharm. Sci. 1973, 62, 1550–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, S.; Stuart, E.K.; Hucker, H.B. Further studies on the metabolism of carbidopa, (-)-L-alpha-hydrazino-3,4-dihydroxy-alpha-methylbenzenepropanoic acid monohydrate, in the human, Rhesus monkey, dog, and rat. J. Med. Chem. 1975, 18, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Datta, S.; Mora, A.K.; Modak, B.; Nath, S.; Palit, D.K. Dynamics of hydrogen bond reorganization in the S1 (ππ*) state of 9-Anthracenecarboxaldehyde. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2023, 436, 114379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gąsowska-Bajger, B.; Frąckowiak-Wojtasek, B.; Koj, S.; Cichoń, T.; Smolarczyk, R.; Szala, S.; Wojtasek, H. Oxidation of carbidopa by tyrosinase and its effect on murine melanoma. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3507–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizal, M.R.; Ali, H.M.; Ng, S.W. 1H-Indole-3-carbaldehyde azine. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Struct. Rep. 2008, 64, o555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Brånalt, J.; Perry, M.; Tyrchan, C. The Role of Allylic Strain for Conformational Control in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7733–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Merbel, N.C.; Bronsema, K.J.; Gorman, S.H.; Bakhtiar, R. Sensitivity improvement of the LC–MS/MS quantification of carbidopa in human plasma and urine by derivatization with 2,4-pentanedione. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1064, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus, D.C.; August, T.F.; Yeh, K.C.; Eisenhandler, R.; Bayne, W.F.; Musson, D.G. Simultaneous high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of carbidopa, levodopa and 3-O-methyldopa in plasma and carbidopa, levodopa and dopamine in urine using electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1990, 534, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.; Carl, J.L.; Loftin, S.; Perlmutter, J.S. Modified high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection method for plasma measurement of levodopa, 3-O-methyldopa, dopamine, carbidopa and 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl acetic acid. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 836, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebpour, Z.; Haghgoo, S.; Shamsipur, M. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analysis for simultaneous determination of levodopa, carbidopa and methyldopa in human serum and pharmaceutical formulations. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 603, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 1 Sample | Aldehyde | 2 m (L g−1) | R2 | 3 LOD (mg L−1) | 4 LOQ (mg L−1) | 5 avRSD (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-DOPA:CD | I3A | 52.3 ± 2.5 | 0.993 | 0.114 ± 0.006 | 0.379 ± 0.018 | 2.1 | This work |
| Vanillin | 13.2 ± 0.3 | 0.987 | 0.184 ± 0.005 | 0.615 ± 0.015 | 3.5 | [25] | |
| Brand drug | I3A | 50.7 ± 2.5 | 0.993 | 0.099 ± 0.005 | 0.329 ± 0.016 | 3.7 | This work |
| Vanillin | 13.4 ± 0.2 | 0.996 | 0.215 ± 0.003 | 0.778 ± 0.010 | 3.7 | [25] | |
| Generic drug | I3A | 50.8 ± 2.4 | 0.994 | 0.089 ± 0.003 | 0.296 ± 0.009 | 3.5 | This work |
| Vanillin | 13.2 ± 0.2 | 0.995 | 0.342 ± 0.006 | 1.140 ± 0.019 | 3.4 | [25] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palladino, P.; Rainetti, A.; Lettieri, M.; Pieraccini, G.; Scarano, S.; Minunni, M. Quantitative Colorimetric Sensing of Carbidopa in Anti-Parkinson Drugs Based on Selective Reaction with Indole-3-Carbaldehyde. Sensors 2023, 23, 9142. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229142
Palladino P, Rainetti A, Lettieri M, Pieraccini G, Scarano S, Minunni M. Quantitative Colorimetric Sensing of Carbidopa in Anti-Parkinson Drugs Based on Selective Reaction with Indole-3-Carbaldehyde. Sensors. 2023; 23(22):9142. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229142
Chicago/Turabian StylePalladino, Pasquale, Alberto Rainetti, Mariagrazia Lettieri, Giuseppe Pieraccini, Simona Scarano, and Maria Minunni. 2023. "Quantitative Colorimetric Sensing of Carbidopa in Anti-Parkinson Drugs Based on Selective Reaction with Indole-3-Carbaldehyde" Sensors 23, no. 22: 9142. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229142
APA StylePalladino, P., Rainetti, A., Lettieri, M., Pieraccini, G., Scarano, S., & Minunni, M. (2023). Quantitative Colorimetric Sensing of Carbidopa in Anti-Parkinson Drugs Based on Selective Reaction with Indole-3-Carbaldehyde. Sensors, 23(22), 9142. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229142








