A Different Processing of Time-Domain Induced Polarisation: Application for Investigating the Marine Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer in the SE Iberian Peninsula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Influence of Electromagnetic (EM) Coupling
2.2. Measurements in the Time Domain
3. Materials and Methods
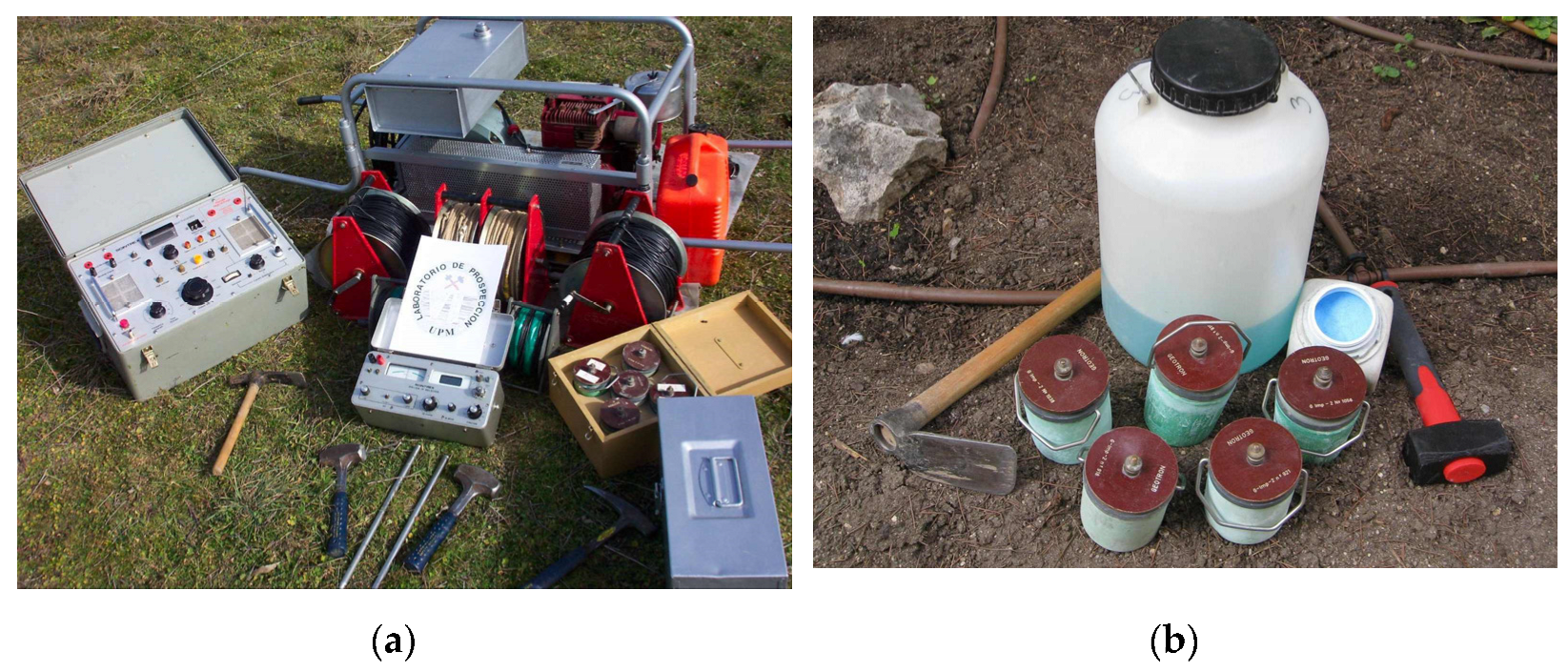
3.1. Data Acquisition
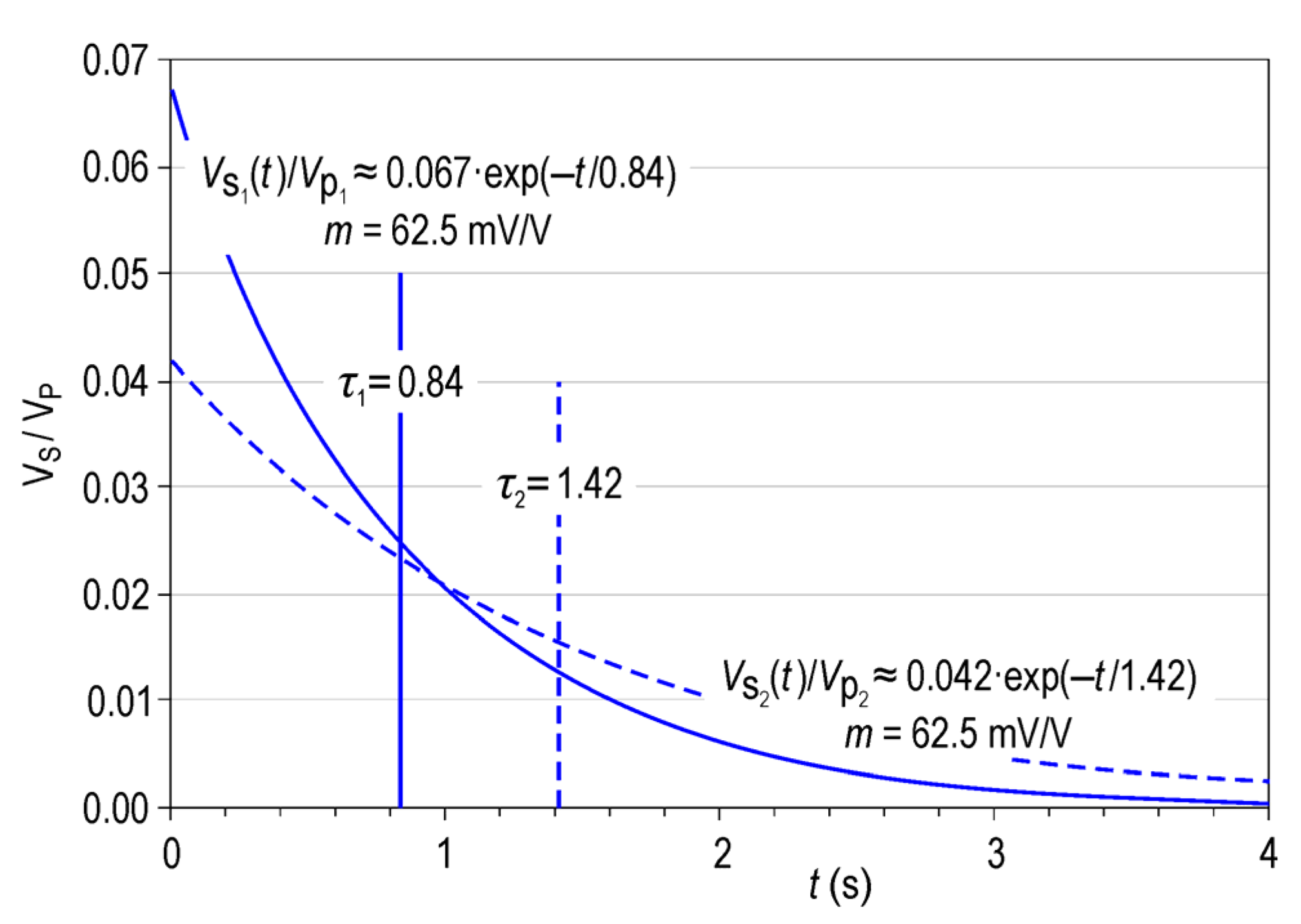
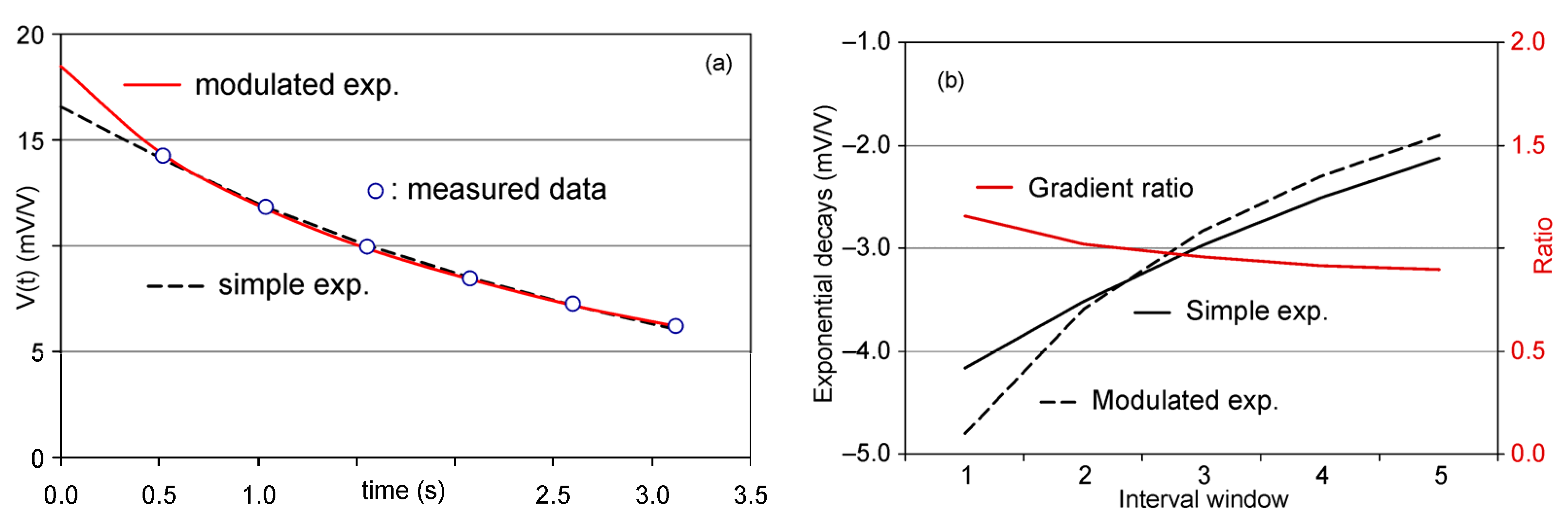
3.2. Analysis of the Decay Curves
3.3. VES-IPS Inversion
4. Application for Investigating the Marine Intrusion in the Almuñécar Coastal Aquifer
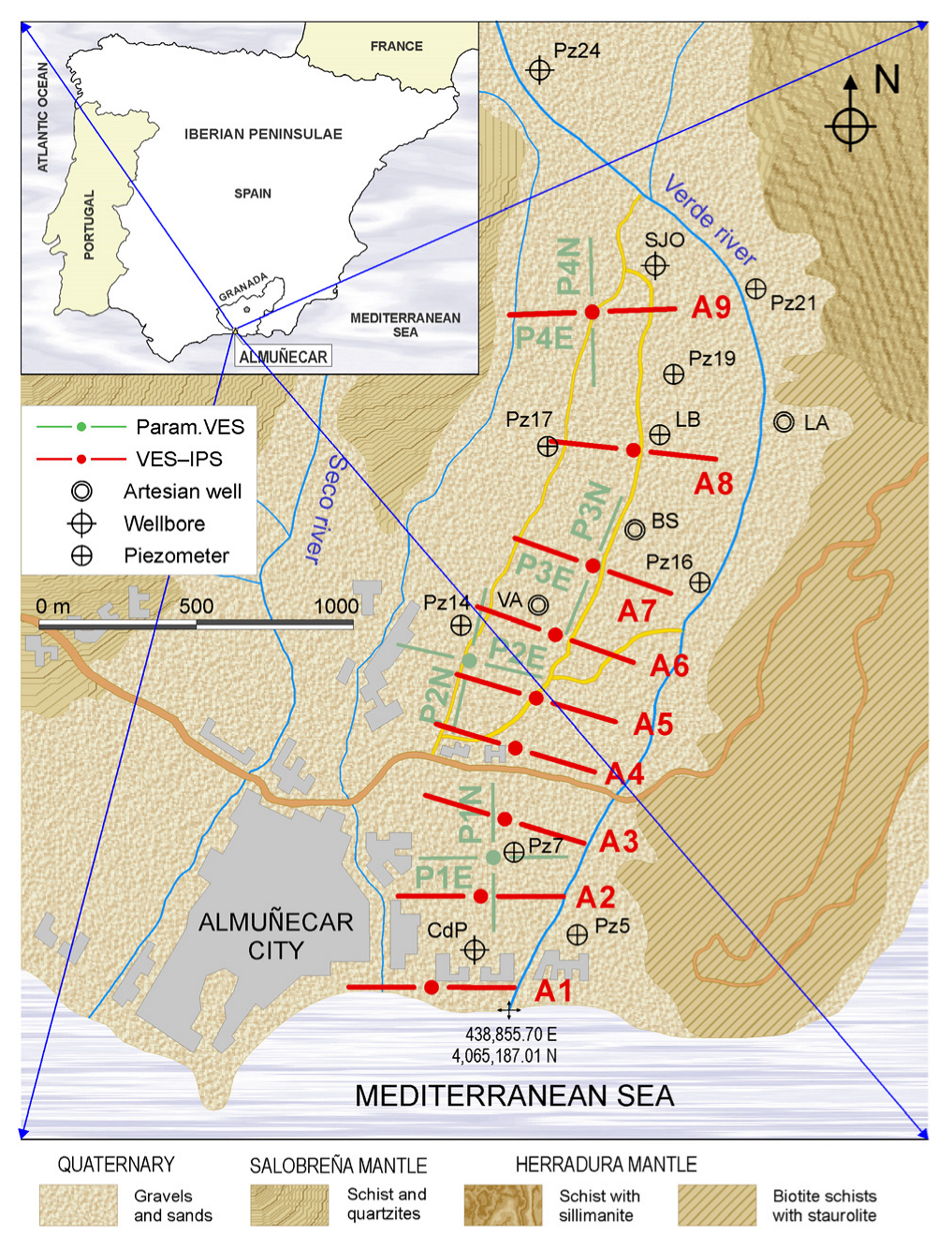
4.1. Overview of the Study Area and Field Survey
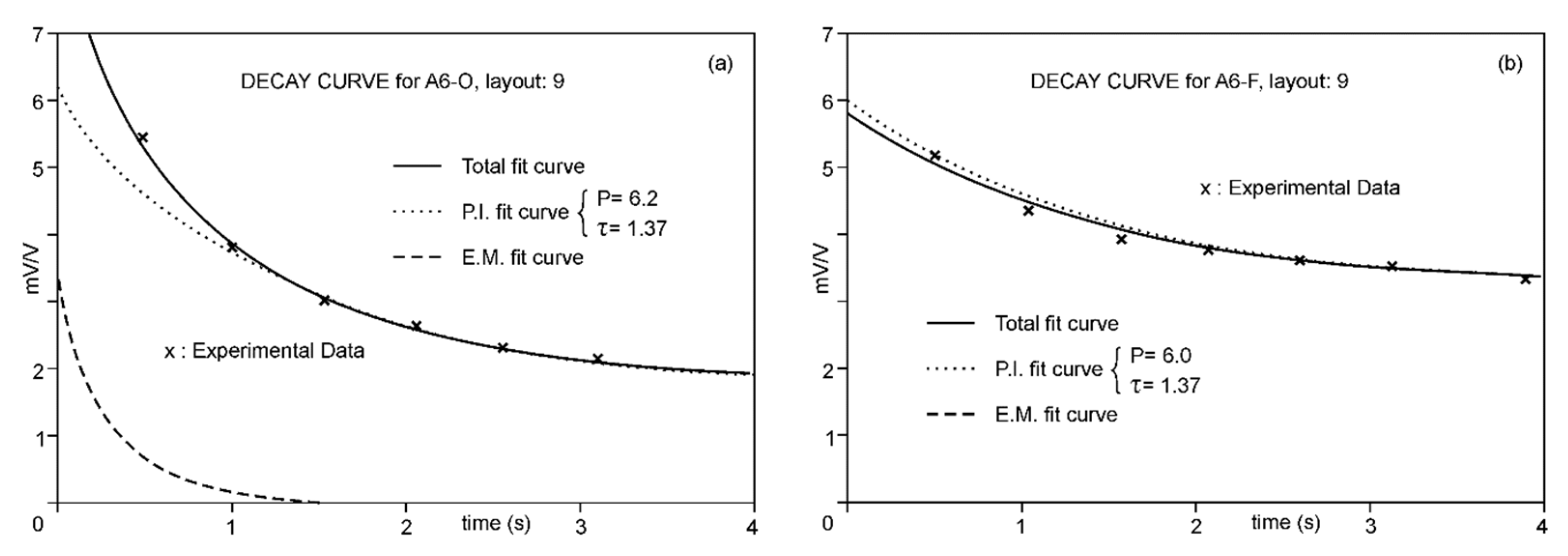
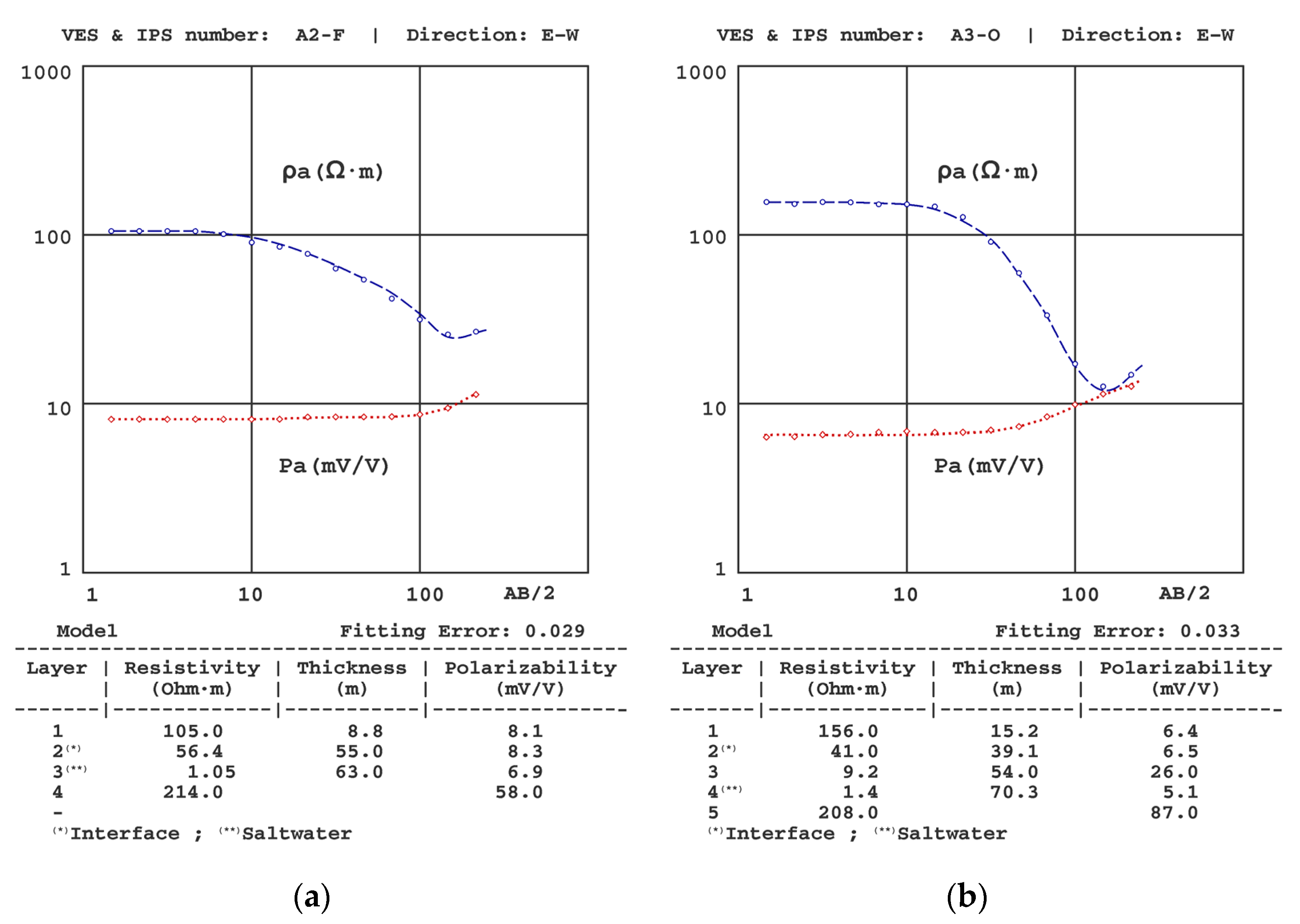
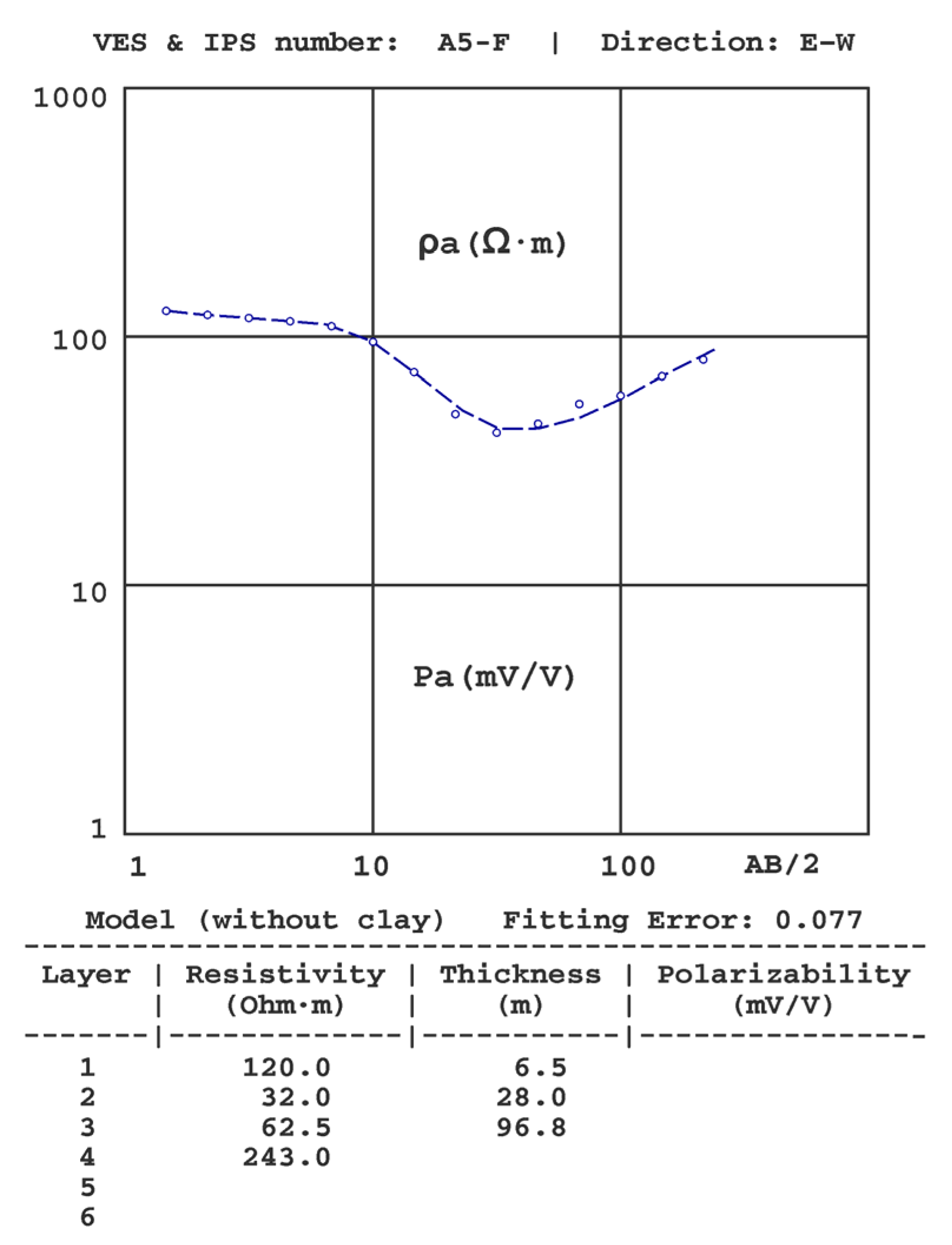
4.2. Analysis of the VES-IPS Results
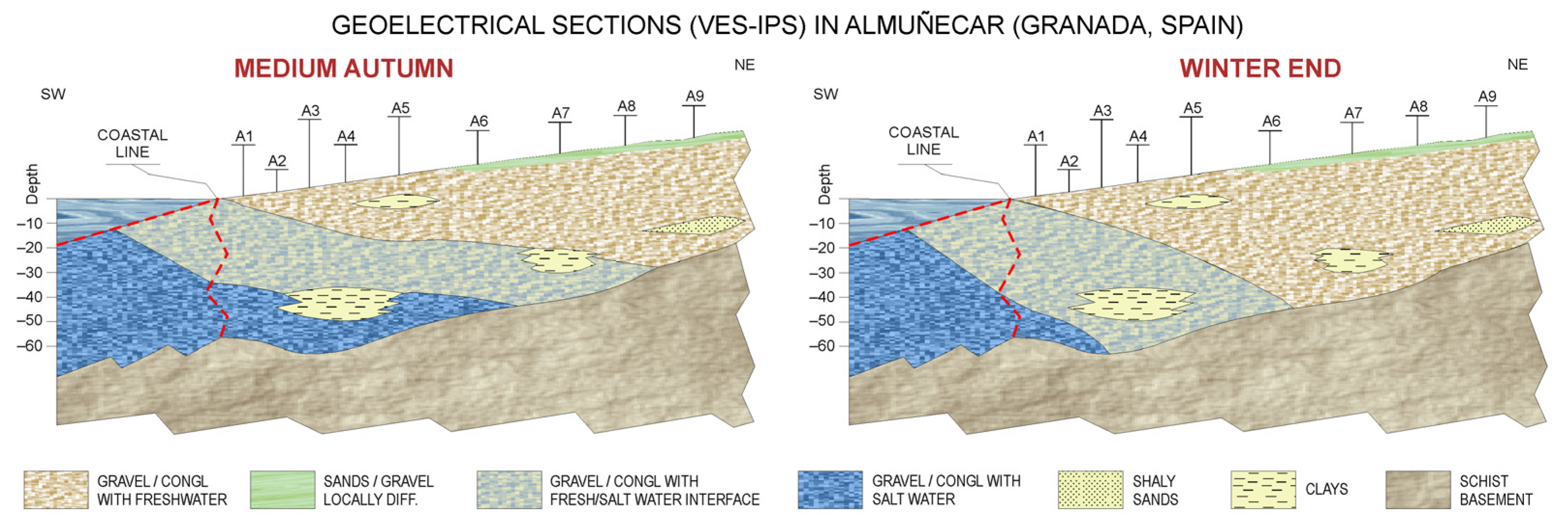
4.3. Seasonal Variation of the Freshwater/Saltwater Interface
5. Discussion
Error Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlumberger, C. Etude sur la prospection electrique du sous-sol; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1920. [Google Scholar]
- Titov, K.; Komarov, V.; Tarasov, V.; Levitski, A. Theoretical and experimental study of time domain-induced polarization in water-saturated sands. J. Appl. Geophy. 2002, 50, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angoran, Y.; Madden, T.R. Induced polarization: A preliminary study of its chemical basis. Geophysics 1977, 42, 788–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grow, L.M. Induced polarization for geophysical exploration. Lead Edge 1982, 1, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, A.; Börner, F.D. Measurements of spectral induced polarization for environmental purposes. Environ. Geol. 1996, 27, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, A.; Brune, S.; Hennig, T.; Kansy, A. Spectral induced polarization at a medieval smelting site. In Proceedings of the EEGS-ES 2000 Annual Meeting, Bochum, Germany, 3–7 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Seigel, H.O. Mathematical formulation and type curves for induced polarization. Geophysics 1959, 24, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.H. Resistivity and Induced Polarization Methods. In Geotechnical an Environmental Geophysics: Volume I: Review and Tutorial; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1990; pp. 147–190. [Google Scholar]
- Fiandaca, G.; Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V.; Gazoty, A. Time-domain-induced polarization: Full-decay forward modeling and 1D laterally constrained inversion of Cole-Cole parameters. Geophysics 2012, 77, E213–E225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, J.; Loeb, J. Transients and field behaviour in induced polarization. Geophys. Prospect. 1969, 17, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics. 1-Alternating current fields. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, W.H.; Ward, S.H.; Hallof, P.G.; Sill, W.R.; Nelson, P.H. Mineral discrimination and removal of inductive coupling with multifrequency IP. Geophysics 1978, 43, 588–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombs, J.M.C. The feasibility of making spectral IP measurements in the time domain. Geoexploration 1981, 19, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, I.M. Spectral induced polarization parameters as determined through time-domain measurements. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1993–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, K.; Calver, H.T. An examination of the relationship between time domain integral chargeability and the Cole-Cole impedance model. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, F.M.; Plata, J.L. Nueva campaña geofísica en el acuífero aluvial del río Verde (Almuñecar, Granada). Boletín Geológico y Minero 2002, 113, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Hönig, M.; Tezkan, B. 1-D and 2-D Cole-Cole inversion of time domain induced polarization data. Geophys. Prospect. 2007, 55, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, T.; Leroux, V.; Nissen, J. Measuring techniques in induced polarisation imaging. J. Appl. Geophys. 2002, 50, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvy, R.D.; Meldrum, P.I.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P.B.; Chambers, J.E.; Sen, M.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Gisbert, J.; Jorreto, S.; Frances, I.; et al. Automated monitoring of coastal aquifers with electrical resistivity tomography. Near Surf. Geophys. 2009, 7, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleil, D.F. Induced polarization: A method of geophysical prospecting. Geophysics 1953, 18, 636–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frische, R.H.; Von Buttlar, H. A Theoretical Study of Induced Electrical Polarization. Geophysics 1957, 22, 688–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wait, J.R. Discussions on a theoretical study of induced electrical polarization. Geophysics 1958, 23, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.J.; Madden, T.R. Induced polarization, a study of its causes. Geophysics 1959, 24, 790–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacquier, V.; Holmes, C.R.; Kintzinger, P.R.; Lavergne, M. Prospecting for ground water by induced electrical polarization. Geophysics 1957, 22, 660–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, S.K. Examples of resolution improvement in geoelectrical soundings applied to groundwater investigations. Geophys. Prospect. 1993, 41, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L.D.; Lesmes, D. IP interpretation in environmental investigations. Geophysics 2002, 67, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevnin, V.; Delgado-Rodríguez, O.; Mousatov, A.; Ryjov, A. Estimation of soil hydraulic conductivity on clay content, determined from resistivity data. In Proceedings of the 19th EEGS Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems, European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, Seattle, WA, USA, 2 April 2006; pp. 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, A.; Slater, L.; Nordsiek, S. On the relationship between induced polarization and surface conductivity: Implications for petrophysical interpretation of electrical measurements. Geophysics 2013, 78, D315–D325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, I.; Acworth, R.I. Intrinsic Negative Chargeability of Soft Clays. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2003, 2003, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L.; Ntarlagiannis, D.; Wishart, D. On the relationship between induced polarization and surface area in metal-sand and clay-sand mixtures. Geophysics 2006, 71, A1–A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, T.; Loke, M.H. Negative apparent chargeability in time-domain induced polarisation data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 123, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börner, F.; Weller, A.; Schopper, J. Evaluation of Transport and Storage Properties in the Soil And Groundwater zone from Induced Polarization Measurements. Geophys. Prospect. 1996, 44, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L.D.; Glaser, D.R. Controls on induced polarization in sandy unconsolidated sediments and application to aquifer characterization. Geophysics 2003, 68, 1547–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.B.T.; Barker, R.D. Determining pore-throat size in Permo-Triassic sandstones from low-frequency electrical spectroscopy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Slater, L.D.; Fukes, M.; Cassiani, G. Relationship between spectral induced polarization and hydraulic properties of saturated and unsaturated sandstone. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, P.F.; Collar, F.A. Relevance of induced polarization to quantitative formation evaluation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1984, 1, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.D.; Sill, W.R. Electrical properties of artificial claybearing sandstone. Geophysics 1982, 47, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinegar, H.J.; Waxman, M.H. Induced polarization of shaly sands. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1267–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhala, H.; Peltoniemi, M. Spectral IP studies of Finnish ore prospects. Geophysics 1992, 57, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.K.; Bhattacharyya, J.; Mukherjee, K.K. Resistivity and induced polarisation sounding for location of saline water pockets. Explor. Geophys. 1995, 25, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, E.; Almeida, F.; Senos, M.J. An experimental study of organic pollutant effects on time domain induced polarization measurements. J. Appl. Geophys. 2006, 60, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seara, J.L.; Granda, A. Interpretation of IP time domain/resistivity soundings for delineating sea-water intrusions in some coastal areas of the northeast of Spain. Geoexploration 1987, 24, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, E.; Almeida, F.; Matias, M.J. Time-domain induced polarization in the determination of the salt/freshwater interface (Aveiro-Portugal). In Groundwater and Saline Intrusion; Araguás, L., Custodio, E., Manzano, M., Eds.; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Sastry, R.G.; Tesfakiros, H.G. Neural network based interpretation algorithm for combined induced polarization and vertical electrical soundings of coastal zones. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2006, 11, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwa, M.; Günther, T.; Grinat, M.; Binot, F. Evaluation of DC, FDEM and SIP resistivity methodsfor imaging a perched saltwater and shallow channel within coastal tidal sediments, Germany. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwa, M.; Ali, H. Resistivity Characterization of Aquifer in Coastal Semiarid Areas: An Approach for Hydrogeological Evaluation. In Groundwater in the Nile Delta; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladejana, J.A.; Kalin, R.M.; Sentenac, P.; Hassan, I. Hydrostratigraphic characterisation of shallow coastal aquifers of Eastern Dahomey Basin, S/W Nigeria, using integrated hydrogeophysical approach; implication for saltwater intrusion. Geosciences 2020, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwa, M.; El Mahmoudi, A.; Elshennawey, A.; Günther, T.; Altahrany, A.; Mohamed, L. Soil Characterization Using Joint Interpretation of Remote Sensing, Resistivity and Induced Polarization Data along the Coast of the Nile Delta. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 3407–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, S.; Cengiz, M.; Balkaya, Ç.; Aysal, N. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Seawater Intrusion (SWI) inferred from geophysical methods as an ecological indicator; A case study from Dikili, NW Izmir, Turkey. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 189, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aal, G.A.; Slater, L.D.; Atekwana, E.A. Induced-polarization measurements on unconsolidated sediments from a site of active hydrocarbon biodegradation. Geophysics 2006, 71, H13–H24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustra, A.; Slater, L.; Ntarlagiannis, D.; Elis, V. Spectral induced polarization (SIP) signatures of clayey soils containing toluene. Near Surf. Geophys. 2012, 10, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores Orozco, A.F.; Kemna, A.; Oberdörster, C.; Zschornack, L.; Leven, C.; Dietrich, P.; Weiss, H. Delineation of subsurface hydrocarbon contamination at a former hydrogenation plant using spectral induced polarization imaging. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2012, 136, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazoty, A.; Fiandaca, G.; Pedersen, J.; Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V. Mapping of landfills using time domain spectral induced polarization data: The Eskelund case study. Near Surf. Geophys. 2012, 10, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, S.; Fiandaca, G.; Dahlin, T. Influence of non-aqueous phase liquid configuration on induced polarization parameters: Conceptual models applied to a time-domain field case study. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 123, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntarlagiannis, D.; Robinson, J.; Soupios, P.; Slater, L. Field-scale electrical geophysics over an olive oil mill waste deposition site: Evaluating the information content of resistivity versus induced polarization (IP) images for delineating the spatial extent of organic contamination. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 135, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid, V.; Sharabi, I.; Frid, M.; Averbakh, A. Leachate detection via statistical analysis of electrical resistivity and induced polarization data at a waste disposal site (Northern Israel). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, G. Theory and Application of Spectral Induced Polarization; Geophysical Monograph Series No. 8; Society of Exporation Geophysicists (USA): Houston, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.N.B.; Jones, D.; Cheng, D.; Schlindwein, F.S. A new method to discriminate between a valid IP response and EM coupling effects. Geophys. Prospect. 2002, 50, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Yizhong Jiang, Y. A time-domain induced-polarization method for estimating permeability in a shaly sand reservoir. Geophys. Prospect. 2006, 54, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.C. Stretched exponential relaxation arising from a continuous sum of exponential decays. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 184430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Oldenburg, D.W. Inversions of time-domain spectral induced polarization data using stretched exponential. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 219, 1851–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Oldenburg, D.W.; Heagy, L.J. Detecting induced polarisation effects in time-domain data: A modelling study using stretched exponentials. Explor. Geophys. 2020, 51, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.P. The application of linear filter theory to the direct interpretation of geoelectrical resistivity sounding measurements. Geophys. Prospect. 1971, 19, 192–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Poddar, M. A simple derivation of Seigel’s time domain induced polarization formula. Geophys. Prospect. 1981, 29, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, J.; Terrón, E. Características hidroquímicas del acuífero aluvial litoral de Castell de Ferro (Granada); III Simposio de Hidrogeología: Madrid, Spain, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Rubio, R. Proceso de salinización-desalinización en el acuífero costero del Río Verde (Almuñécar-Granada); Simposio El Agua en Andalucía: Granada, Spain, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Rubio, R.; Benavente Herrera, J.; Chalons Abellan, C. Hidrogeología de los acuíferos del sector occidental de la costa de Granada. In Proceedings of the Simposio Internacional TIAC’88 Tecnología de la Intrusión en Acuíferos Costeros, Granada, Spain, June 1988; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1988; pp. 239–265. [Google Scholar]
- Calvache, M.L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Effects of geology and human activity on the dynamics of salt-water intrusion in three coastal aquifers in southern Spain. Environ. Geol. 1997, 30, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Curiel, J.; Martín Sánchez, D.; Maldonado Zamora, A.; Gómez Martos, M. Red de control σ/T para el estudio de intrusión marina en Almuñécar (Granada). Boletín Geológico y Minero 1995, 106, 358–372. [Google Scholar]
- IGME. Acuífero costero de Almuñecar. Síntesis de trabajos realizados, situación actual y perspectivas futuras. Informe técnico. 1992; 61p. Available online: https://info.igme.es/SidPDF/038000/237/38237_0001.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Benavente, J. Contribución al conocimiento hidrogeológico de los acuíferos costeros de la Provincia de Granada. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Granada, Granada, Spain, 1982; 435p. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Rubio, R.; Jalón, M. Nuevos datos sobre el proceso salinización-desalinización del acuífero aluvial de Río Verde (Almuñecar). In Proceedings of the Simposio Internacional TIAC’88 Tecnología de la Intrusión en Acuíferos Costeros, Granada, Spain, June 1988; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1988; pp. 413–425. [Google Scholar]
- Calvache, M.L.; Benavente, J. Nuevos datos sobre la geometría del acuífero costero de Almuñecar (Granada). Aportación al conocimiento de la porosidad eficaz y de las reservas. In Proceedings of the Simposio Internacional TIAC’88 Tecnología de la Intrusión en Acuíferos Costeros, Granada, Spain, June 1988; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1988; pp. 375–393. [Google Scholar]
- Calvache, M.L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Saltwater intrusion into a small coastal aquifer (Rio Verde, Almuñecar, southern Spain). J. Hydrol. 1991, 129, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, S. Comparación de la aplicación de distintos modelos matemáticos sobre acuíferos costeros detríticos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Granada, Granada, Spain, 2005; 304p. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, A.; Díaz Castro, J.M.; Rosillo, J.A. Datos referentes al control de la explotación del acuífero detrítico del Río Verde, Almuñecar (Granada). In Proceedings of the Simposio Internacional TIAC’88 Tecnología de la Intrusión en Acuíferos Costeros, Granada, Spain, June 1988; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1988; pp. 395–412. [Google Scholar]
- IGME. Estudio Hidrogeológico de la Cuenca del Guadalfeo y Sectores Adyacentes (T.VII: Definición y Funcionamiento de las Unidades Hidrogeológicas. Acuífero Costero de Almuñécar); Málaga, IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1985; pp. 96–114. [Google Scholar]

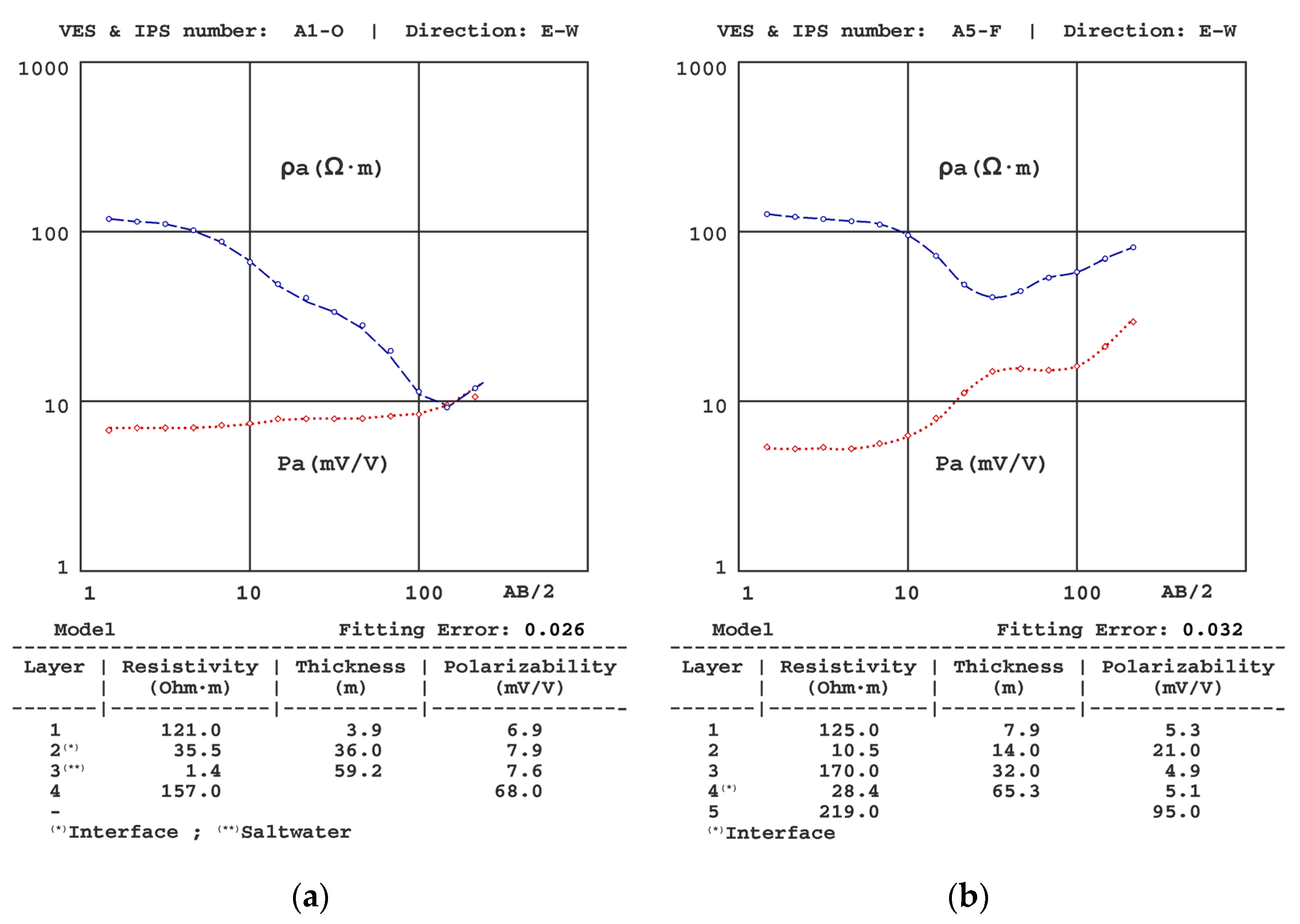
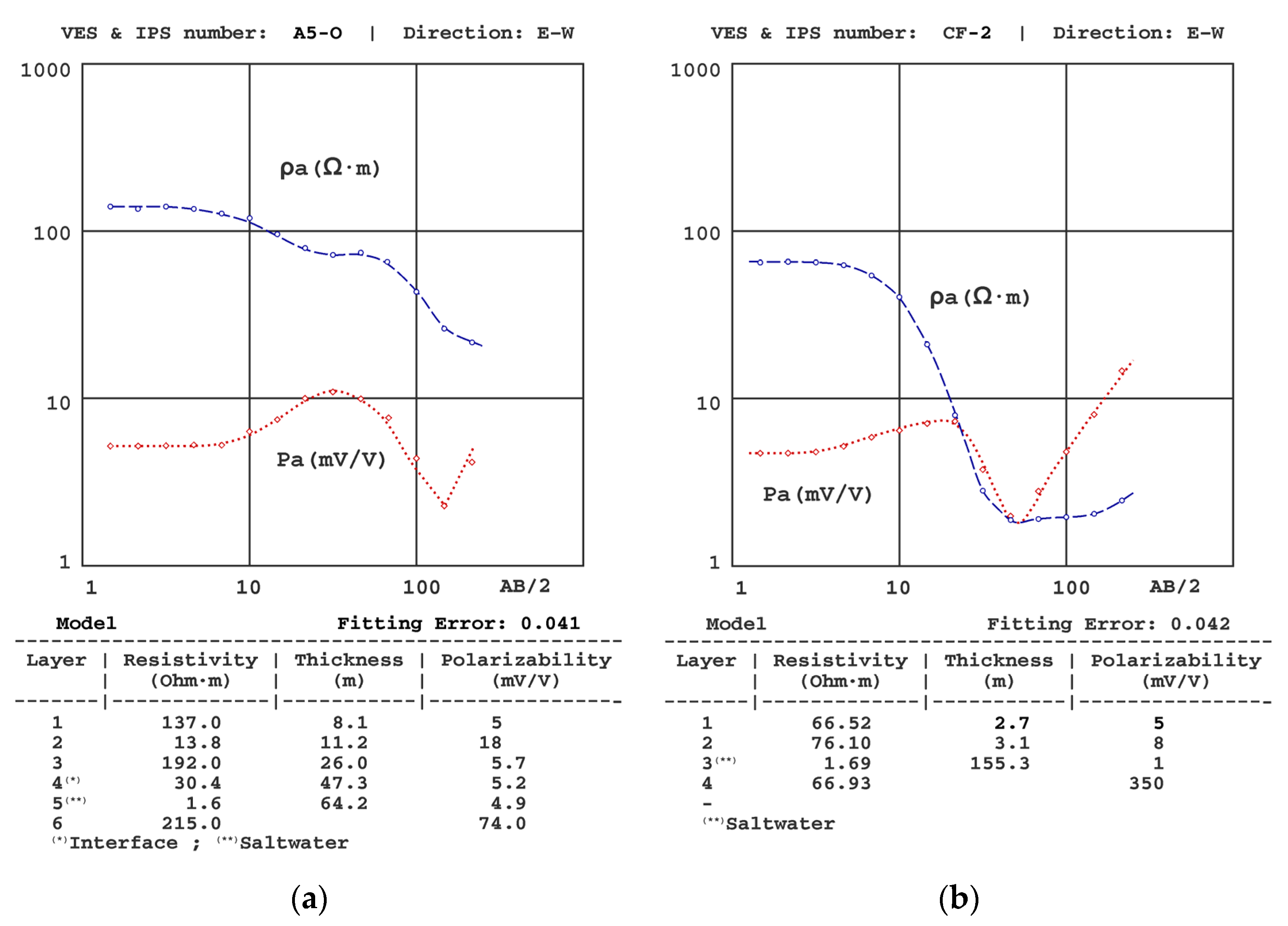
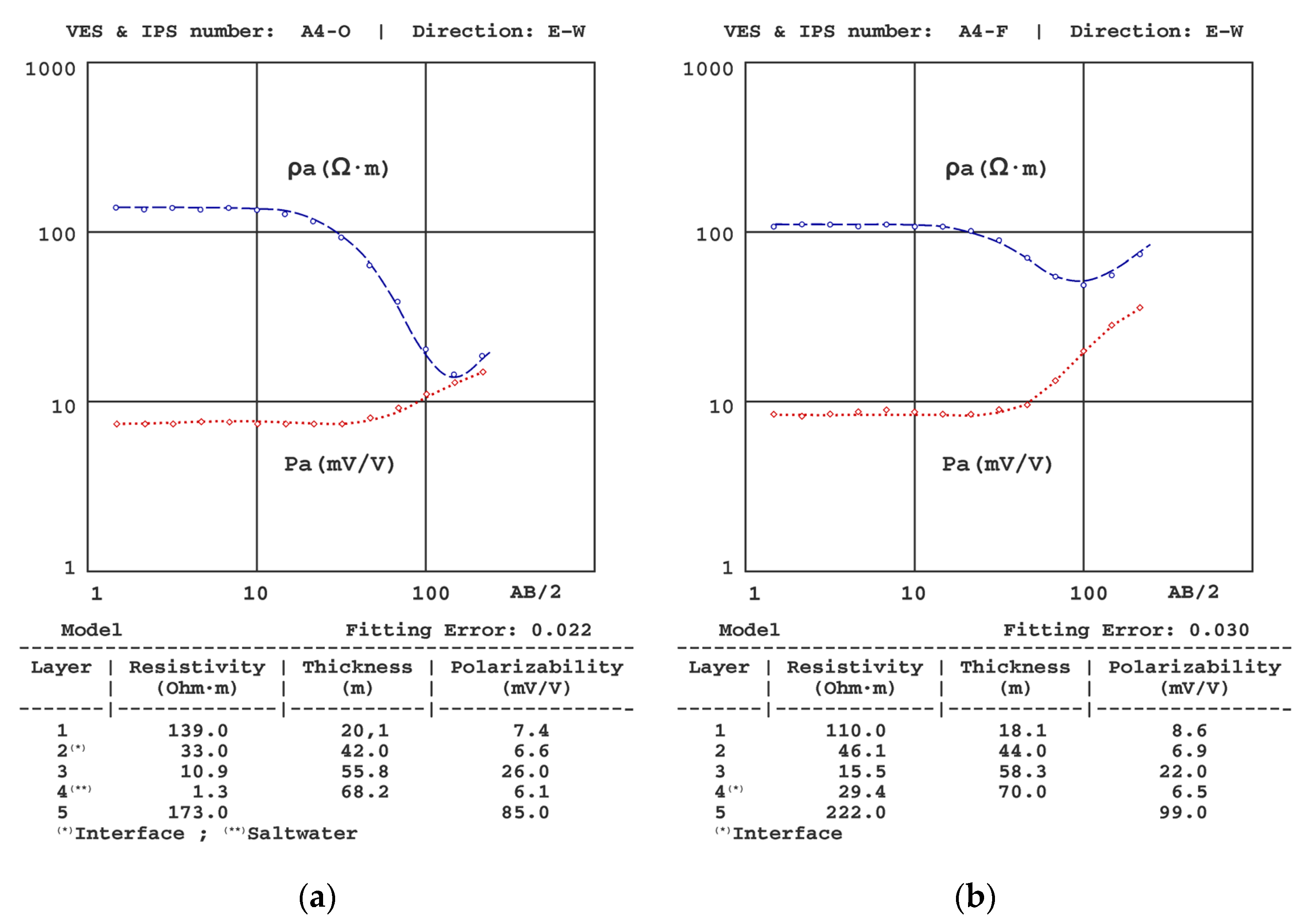
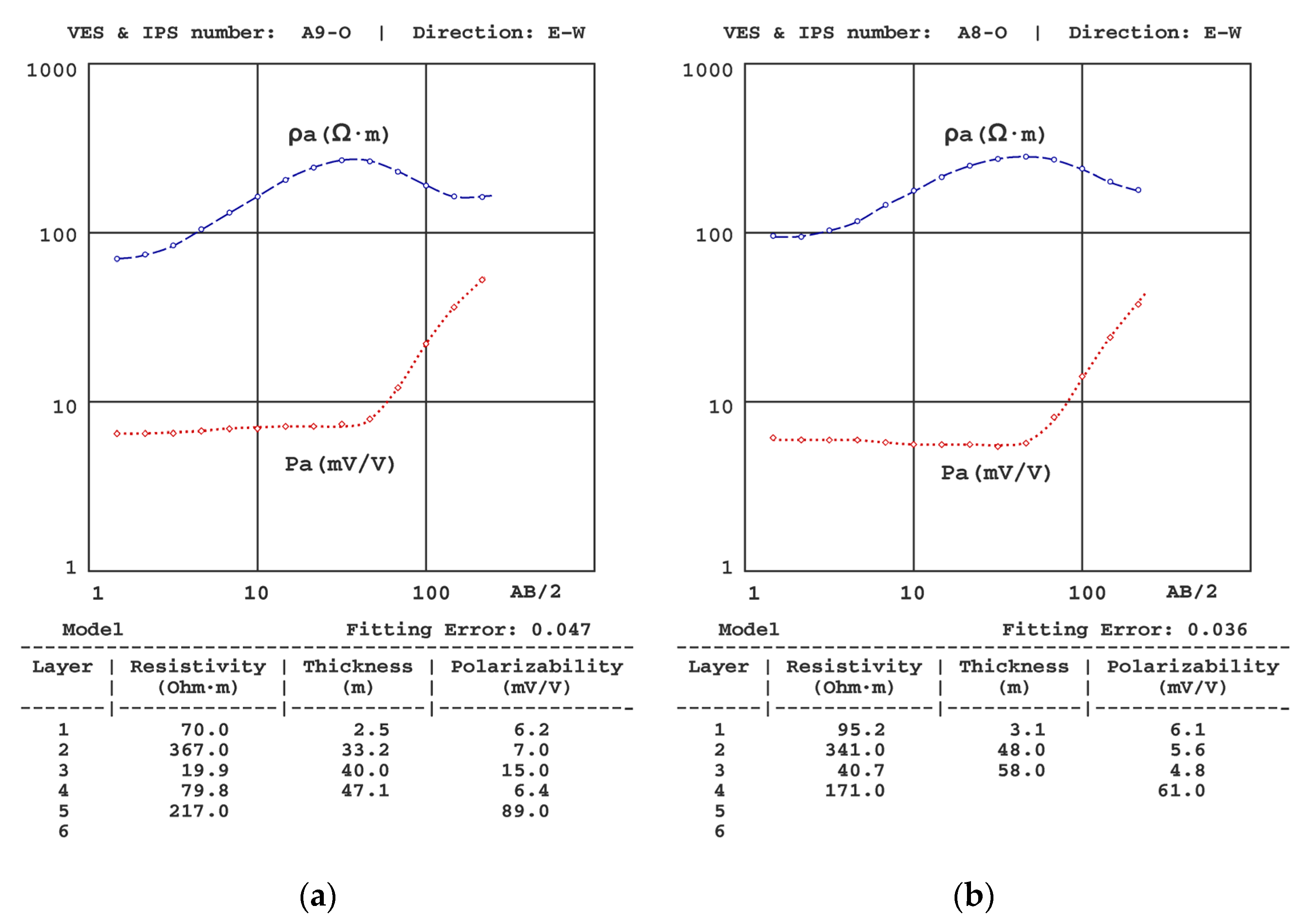
| Sondeo | T (°C) | σ (μS/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| CDP | 16.9 | 31,504 |
| Pz5 | 15.4 | 18,701 |
| Pz7 | 17.4 | 4063 |
| Pz14 | 17.4 | 23,551 |
| VA | 18.8 | 2868 |
| Pz16 | 18.7 | 6767 |
| BS | 19.2 | 13,546 |
| Pz17 | 19.6 | 2056 |
| LB | 21.9 | 6686 |
| LA | 25.5 | 1249 |
| SJO | 22.3 | 1796 |
| Pz21 | 19.07 | 934 |
| Pz24 | 18.4 | 882 |
| Pz19 | 20.2 | 5546 |
| CDP | 16.9 | 31,504 |
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z | ρ | P | z | ρ | P | z | ρ | P | z | ρ | P | z | ρ | P |
| 3.9 | 121 | 6.9 | 9.5 | 132 | 6.4 | 15 | 156 | 6.4 | 20 | 139 | 7.4 | 8.1 | 137 | 5.1 |
| 36 | 35.5 | 7.9 | 41 | 47.9 | 7.0 | 39 | 41 | 6.5 | 42 | 33.0 | 6.6 | 11 | 13.8 | 18 |
| 59 | 1.36 | 7.6 | 60 | 0.95 | 6.5 | 54 | 9.0 | 26 | 56 | 10.9 | 26 | 26 | 192 | 5.7 |
| -- | 157 | 68 | -- | 174 | 87 | 70 | 1.4 | 5.1 | 68 | 1.3 | 6.1 | 47 | 30.0 | 5.2 |
| -- | 208 | 87 | -- | 173 | 85 | 64 | 1.6 | 4.9 | ||||||
| 215 | 74 | |||||||||||||
| A6 | A7 | A8 | A9 | |||||||||||
| z | ρ | P | z | ρ | P | z | ρ | P | z | ρ | P | |||
| 2.7 | 112 | 6.7 | 3.8 | 155 | 7.2 | 3.1 | 95.2 | 6.1 | 2.5 | 70.3 | 6.2 | |||
| 32 | 241 | 5.7 | 38 | 312 | 7.9 | 48 | 341 | 5.6 | 33 | 367 | 7.0 | |||
| 49 | 37 | 6.3 | 45 | 10.2 | 20 | 58 | 40.7 | 4.8 | 40 | 19.9 | 15 | |||
| 60 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 59 | 41.5 | 6.3 | -- | 172 | 61 | 47 | 79.8 | 6.4 | |||
| -- | 171 | 91 | -- | 193 | 87 | -- | 217 | 89 | ||||||
| ρ→ | 121 | 367 | Gravels/conglomerates Fresh water | 30 | 48 | Gravels/conglomerates Interface | 1.0 | 1.6 | Gravels/conglomerates Salt water | 9.0 | 14 | Clay | 157 | 217 | Schist (Substrate) |
| 40 | 1.2 | 10 | |||||||||||||
| P→ | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 25 | 60 | 90 | |||||
| 6 | 6 | 6 | 22 | 75 | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Curiel, J.; Biosca, B.; Arévalo-Lomas, L.; Miguel, M.J. A Different Processing of Time-Domain Induced Polarisation: Application for Investigating the Marine Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer in the SE Iberian Peninsula. Sensors 2023, 23, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020708
Díaz-Curiel J, Biosca B, Arévalo-Lomas L, Miguel MJ. A Different Processing of Time-Domain Induced Polarisation: Application for Investigating the Marine Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer in the SE Iberian Peninsula. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020708
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Curiel, Jesús, Bárbara Biosca, Lucía Arévalo-Lomas, and María Jesús Miguel. 2023. "A Different Processing of Time-Domain Induced Polarisation: Application for Investigating the Marine Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer in the SE Iberian Peninsula" Sensors 23, no. 2: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020708
APA StyleDíaz-Curiel, J., Biosca, B., Arévalo-Lomas, L., & Miguel, M. J. (2023). A Different Processing of Time-Domain Induced Polarisation: Application for Investigating the Marine Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer in the SE Iberian Peninsula. Sensors, 23(2), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020708









