Soft DAgger: Sample-Efficient Imitation Learning for Control of Soft Robots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Online control solution: Introduction of an algorithm for online control policy training and optimization using Transfer Learning (TL) and the Dynamic Behavioral Map (DBM) of a soft arm;
- Sample efficiency: A drastic decrease in the training time and samples required to learn to replicate desired expert demonstrations on a soft arm (almost and less samples and episodes required compared to an average Reinforcement Learning (RL) [28,31], and continuous IL algorithm [30], respectively);
- Robustness in the control solution: The ability to tackle excessive variability in expert task demonstrations due to the flexible shape, and reproducing the demonstrations on the soft arm while overcoming their inherent stochastic nature (an approximately decrease in standard deviation of the Student Policy Reproduced Expert Demonstrations (SPREDs).
2. Related Works
2.1. IL and Generalization Capability
2.2. IL and Compounding Error
| Algorithm 1 Policy and Model Optimization (PMO) |
|
2.3. IL for Soft Robotics
3. Preliminaries
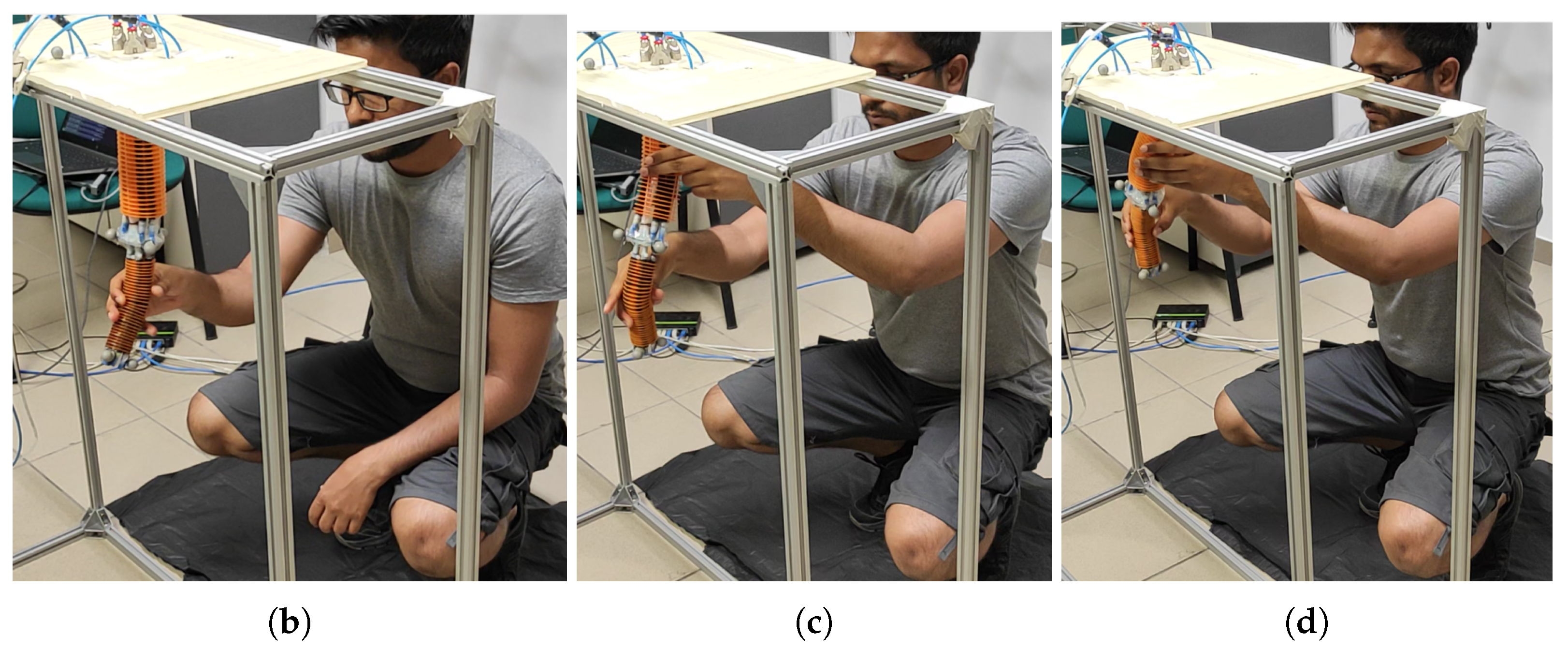
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Task Description
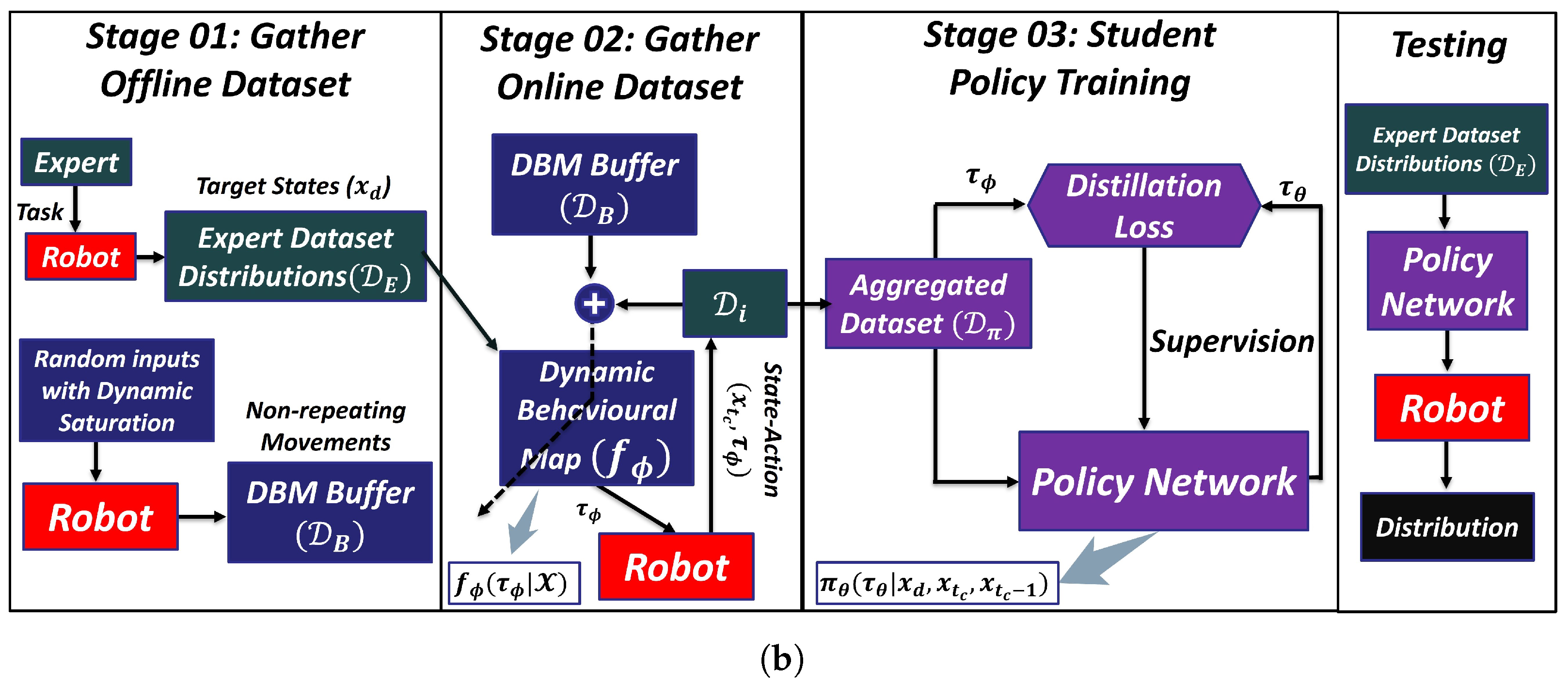
3.3. Soft DAgger with DBM
| Algorithm 2 Student Policy OpTimization (SPOT) |
3.3.1. Dynamic Behavioral Map (DBM)
3.3.2. Soft DAgger
4. Experimental Evaluation
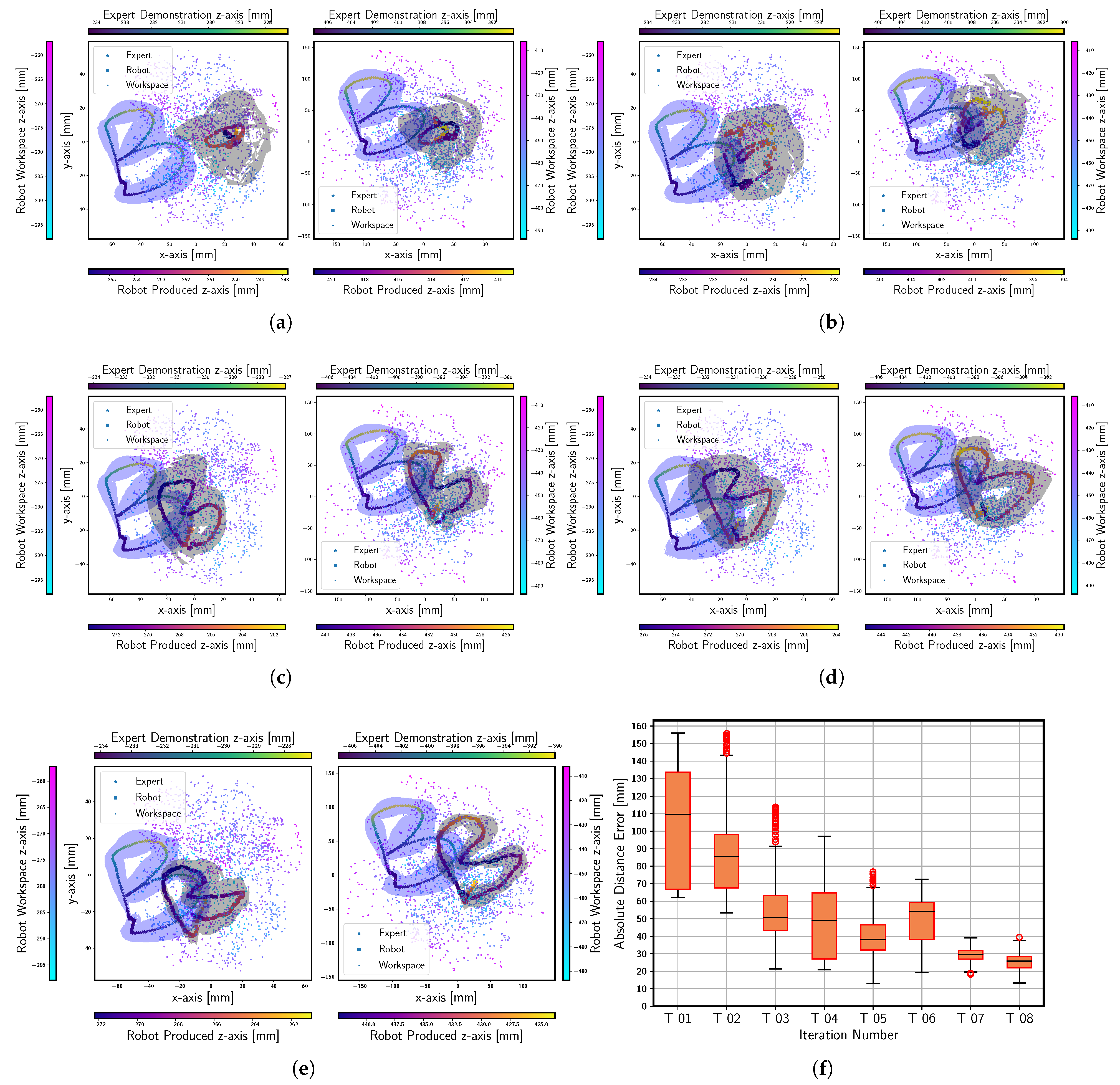
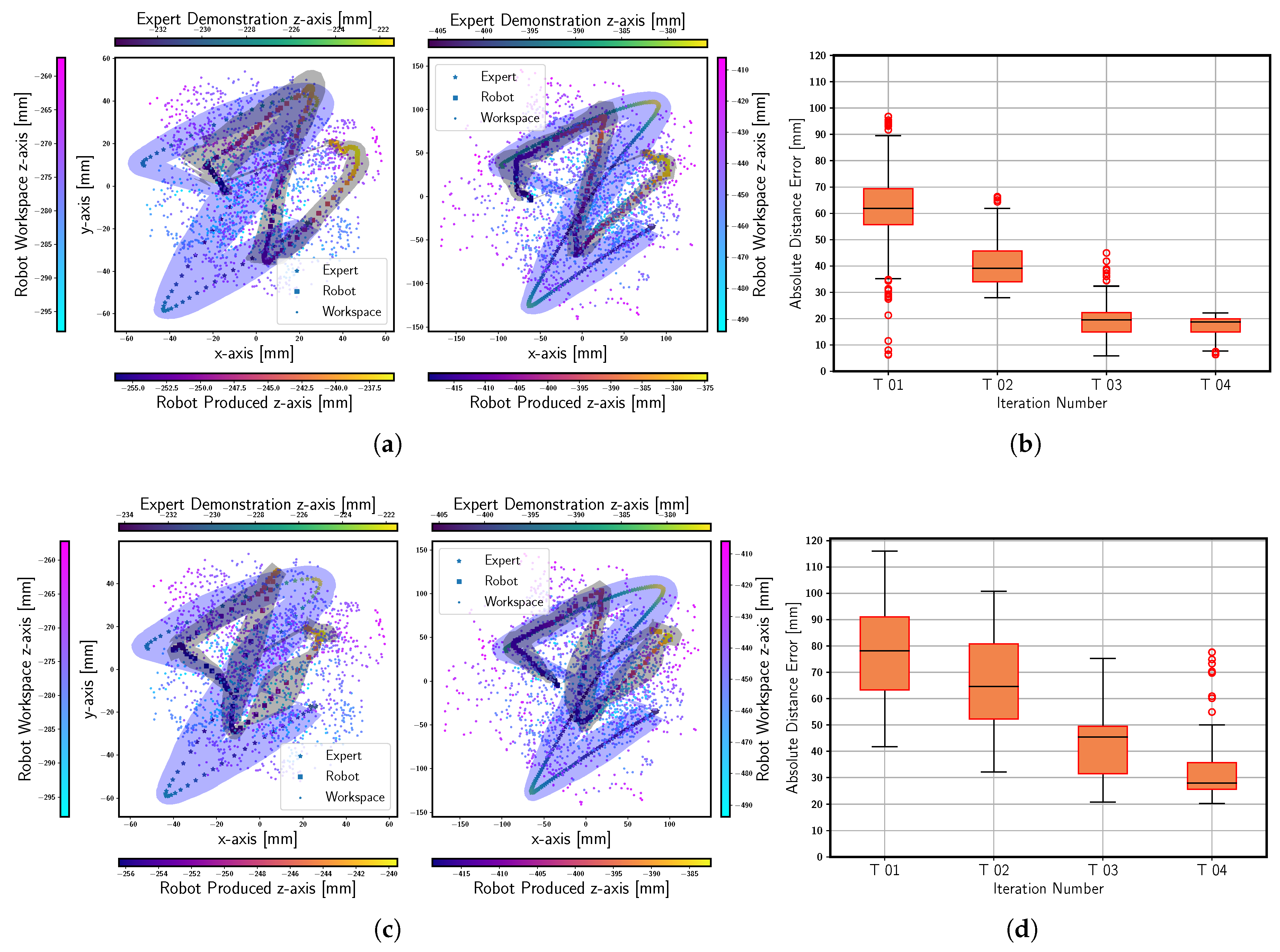
4.1. Student Policy Evaluation Criteria
4.2. Results
4.2.1. Policy and Model Optimization (PMO)
4.2.2. Student Policy OpTimization (SPOT)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DBM | Dynamic Behavioral Map |
| SPREDs | Student Policy Reproduced Expert Demonstrations |
| SPOT | Student Policy OpTimization |
| PMO | Policy and Model Optimization |
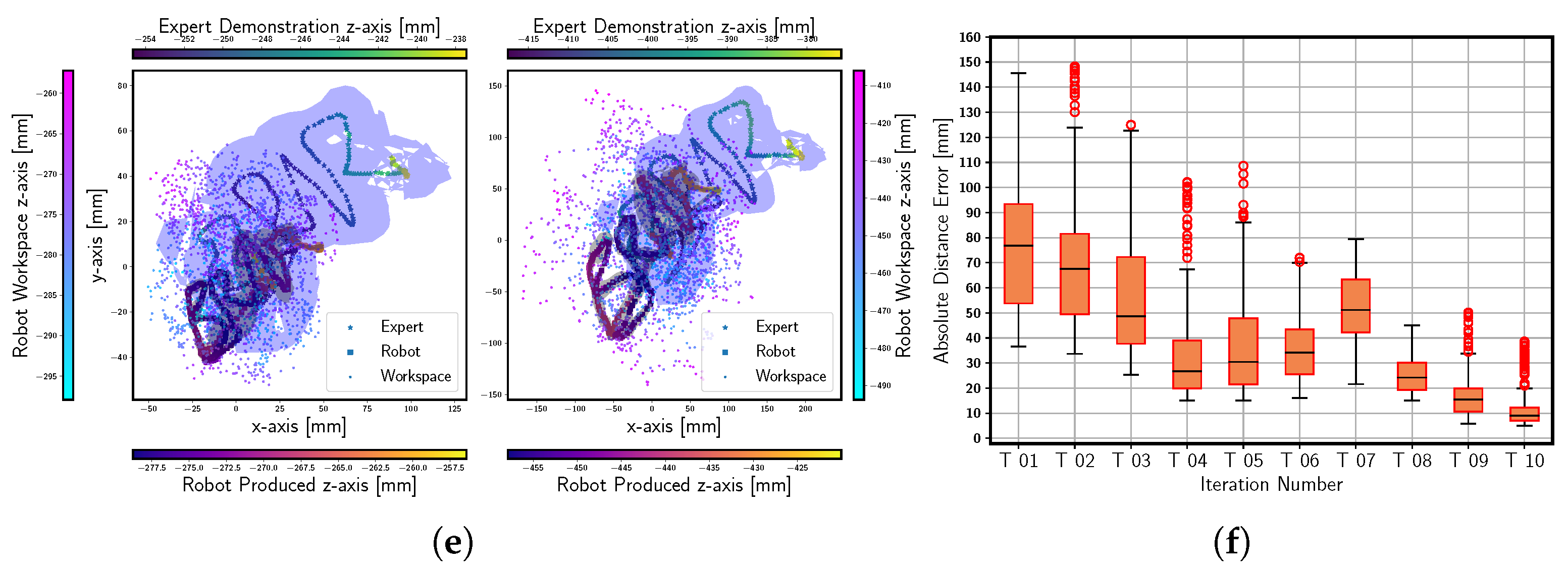
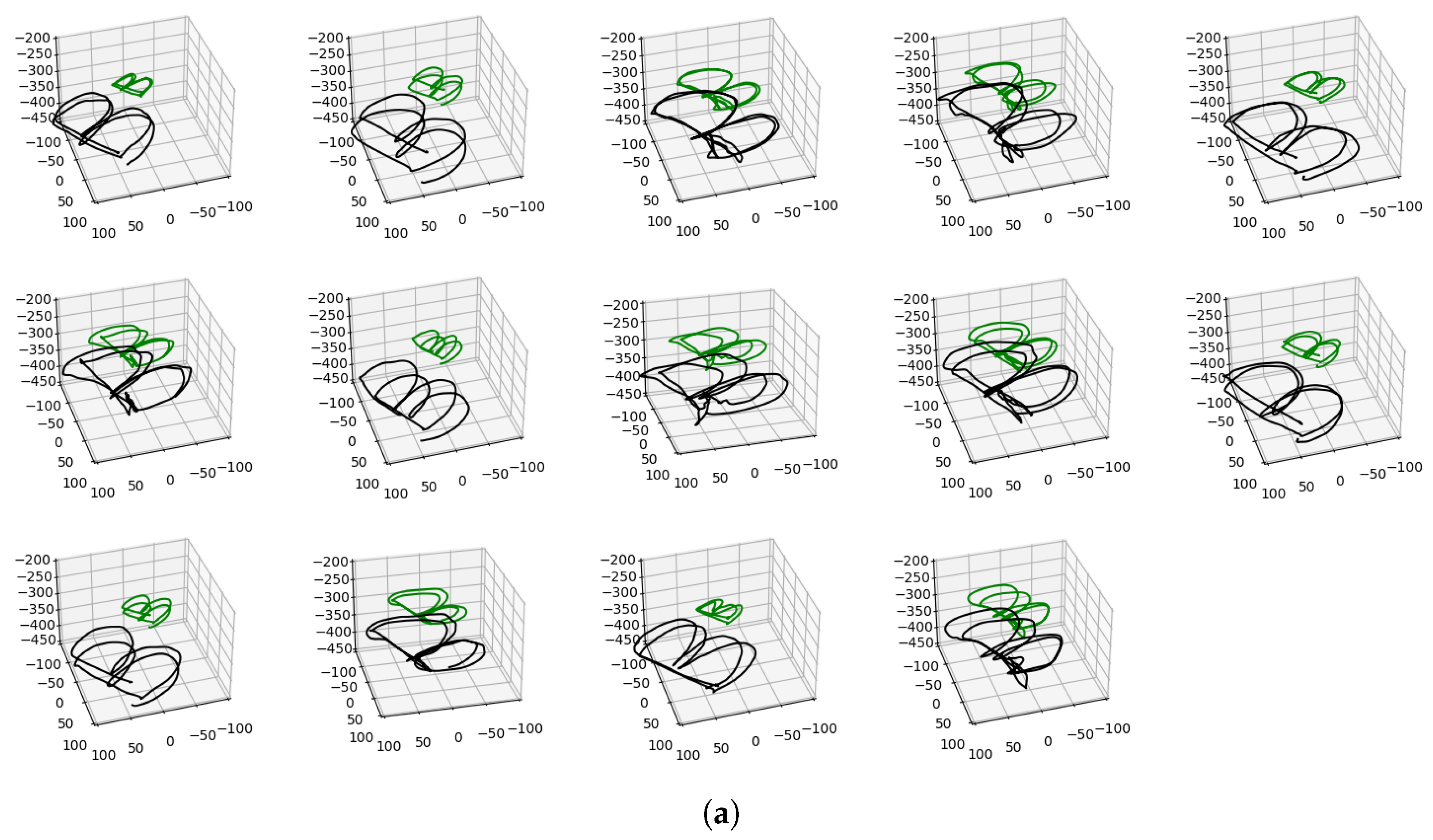
Appendix A. Additional Results with PMO

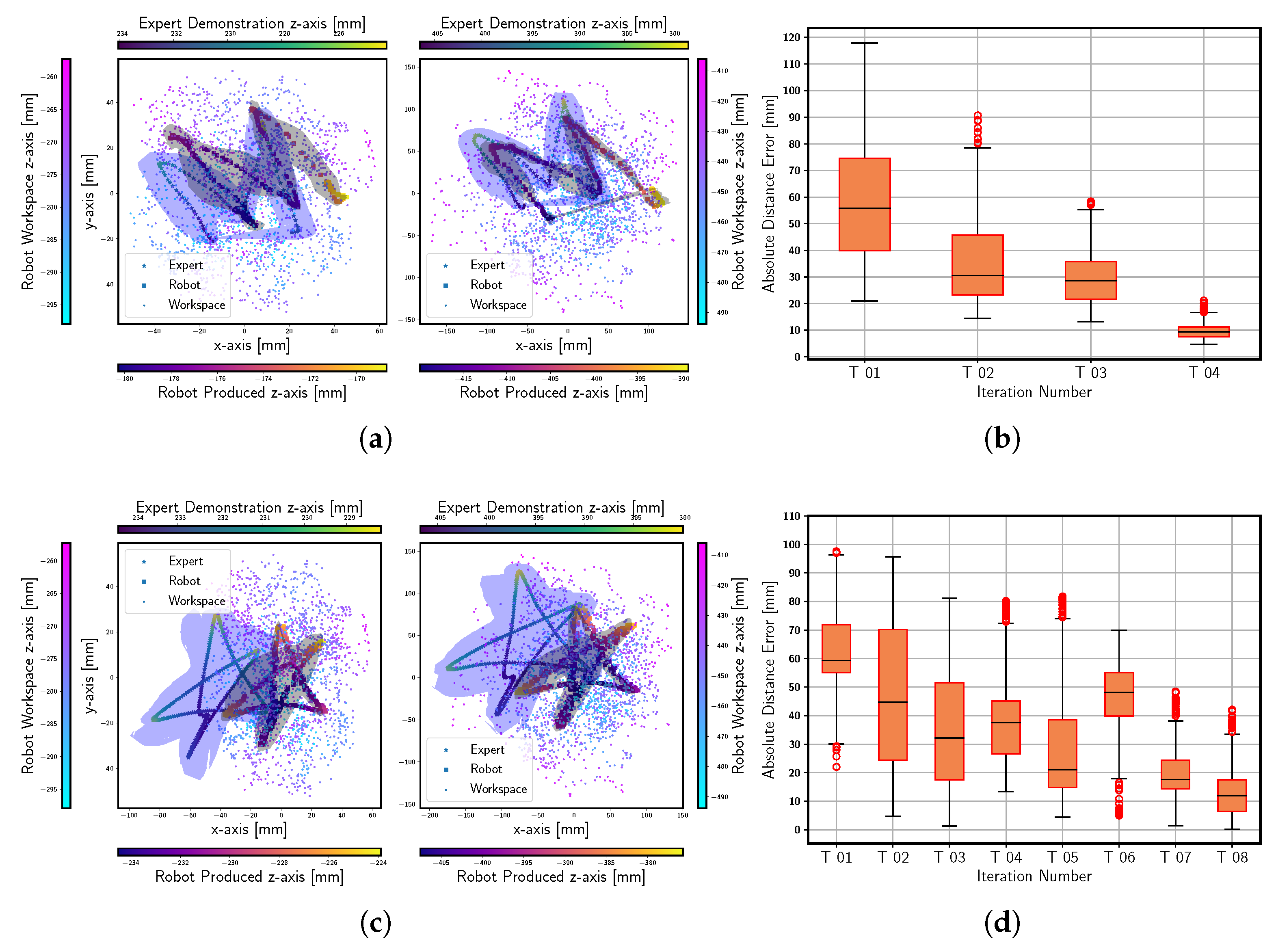
Appendix B. Additional Results with SPOT
References
- Kim, S.; Laschi, C.; Trimmer, B. Soft robotics: A bioinspired evolution in robotics. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanini, C.; Boyer, F.; Mathew, A.T.; Duriez, C.; Renda, F. Soft Robots Modeling: A Structured Overview. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.03645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.J., III; Jones, B. Design and Kinematic Modeling of Constant Curvature Continuum Robots: A Review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Frazelle, C.; Walker, I. A Comparison of Constant Curvature Forward Kinematics for Multisection Continuum Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second IEEE International Conference on Robotic Computing (IRC), Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 31 January–2 February 2018; pp. 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Tucker, R. Nonlinear dynamics of elastic rods using the Cosserat theory: Modelling and simulation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2008, 45, 460–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucker, D.C.; Webster, R.J., III. Statics and Dynamics of Continuum Robots With General Tendon Routing and External Loading. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 27, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, M.; Miguel, E.; Deimel, R.; Malvezzi, M.; Bickel, B.; Brock, O.; Prattichizzo, D. Efficient FEM-Based Simulation of Soft Robots Modeled as Kinematic Chains. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 4206–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schegg, P.; Duriez, C. Review on generic methods for mechanical modeling, simulation and control of soft robots. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0251059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, T.; Kang, B.B.; Lee, M.; Park, W.; Ku, S.; Kim, D.; Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; et al. Review of machine learning methods in soft robotics. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George Thuruthel, T.; Ansari, Y.; Falotico, E.; Laschi, C. Control Strategies for Soft Robotic Manipulators: A Survey. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Thuruthel, T.; Falotico, E.; Manti, M.; Pratesi, A.; Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C. Learning Closed Loop Kinematic Controllers for Continuum Manipulators in Unstructured Environments. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, L.; Falotico, E.; Di Lecce, N.; Dario, P.; Laschi, C. Integrating feedback and predictive control in a Bio-inspired model of visual pursuit implemented on a humanoid robot. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2015, 9222, 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.; Liu, C.; Ataka, A.; Lam, H.K.; Althoefer, K. Kinematic Control of Continuum Manipulators Using a Fuzzy-Model-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5022–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, P.; Dometios, A.; Khamassi, M.; Tzafestas, C.S. Task Driven Skill Learning in a Soft-Robotic Arm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2021), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mahl, T.; Hildebrandt, A.; Sawodny, O. A Variable Curvature Continuum Kinematics for Kinematic Control of the Bionic Handling Assistant. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, M.; Best, C.; Townsend, E.; Wingate, D.; Killpack, M. Learning nonlinear dynamic models of soft robots for model predictive control with neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018; pp. 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuruthel, T.G.; Falotico, E.; Renda, F.; Laschi, C. Learning dynamic models for open loop predictive control of soft robotic manipulators. Bioinspiration Biomimetics 2017, 12, 066003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuruthel, T.G.; Falotico, E.; Manti, M.; Laschi, C. Stable Open Loop Control of Soft Robotic Manipulators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuruthel, T.G.; Falotico, E.; Renda, F.; Laschi, C. Model-Based Reinforcement Learning for Closed-Loop Dynamic Control of Soft Robotic Manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2019, 35, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chepinskiy, S.A.; Wang, J.; Zhilenkov, A.A.; Krasnov, A.Y.; Chernyi, S. Position Control of Cable-Driven Robotic Soft Arm Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Information 2020, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, F.; Kalidindi, H.T.; Fruzzetti, L.; Laschi, C.; Menciassi, A.; Falotico, E. Controlling Soft Robotic Arms Using Continual Learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 5469–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménager, E.; Schegg, P.; Khairallah, E.; Marchal, D.; Dequidt, J.; Preux, P.; Duriez, C. SofaGym: An Open Platform for Reinforcement Learning Based on Soft Robot Simulations. Soft Robot. 2022, 10, 410–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Kwok, K.W. A Survey for Machine Learning-Based Control of Continuum Robots. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, M.C.; Camarillo, D.B. Model-Less Feedback Control of Continuum Manipulators in Constrained Environments. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Lee, K.H.; Ho, J.; Fu, H.; Fu, K.C.D.; Kwok, K.W. Vision-Based Online Learning Kinematic Control for Soft Robots Using Local Gaussian Process Regression. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.; Banerjee, H.; Tse, Z. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Soft, Flexible Robots: Brief Review with Impending Challenges. Robotics 2019, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centurelli, A.; Arleo, L.; Rizzo, A.; Tolu, S.; Laschi, C.; Falotico, E. Closed-Loop Dynamic Control of a Soft Manipulator Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 4741–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koryakovskiy, I.; Kudruss, M.; Vallery, H.; Babuška, R.; Caarls, W. Model-plant mismatch compensation using reinforcement learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, A.; Thananjeyan, B.; Lee, J.; Li, F.; Zahed, A.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Goldberg, K. On-Policy Robot Imitation Learning from a Converging Supervisor. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Osaka, Japan, 30 October–1 November 2019; pp. 24–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kober, J.; Bagnell, J.A.; Peters, J. Reinforcement learning in robotics: A survey. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1238–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, M.; Calinon, S.; Bruno, D.; Caldwell, D. Learning by Imitation with the STIFF-FLOP Surgical Robot: A Biomimetic Approach Inspired by Octopus Movements. Robot. Biomimetics Spec. Issue Med. Robot. 2014, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calinon, S.; Bruno, D.; Malekzadeh, M.; Nanayakkara, T.; Caldwell, D. Human–robot skills transfer interfaces for a flexible surgical robot. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 116, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasagawa, A.; Fujimoto, K.; Sakaino, S.; Tsuji, T. Imitation Learning Based on Bilateral Control for Human–Robot Cooperation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6169–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racinskis, P.; Arents, J.; Greitans, M. A Motion Capture and Imitation Learning Based Approach to Robot Control. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; R.S. Sutton, A.G. Barto (Eds.). Neural Netw. 2000, 13, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osa, T.; Pajarinen, J.; Neumann, G.; Bagnell, J.A.; Abbeel, P.; Peters, J. An Algorithmic Perspective on Imitation Learning. Found. Trends Robot. 2018, 7, 1–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Fan, W.; Lloyd, J.; Yang, C.; Lepora, N.F. One-shot domain-adaptive imitation learning via progressive learning applied to robotic pouring. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Merel, J.; Rusu, A.; Erez, T.; Cabi, S.; Tunyasuvunakool, S.; Kramár, J.; Hadsell, R.; Freitas, N.; et al. Reinforcement and Imitation Learning for Diverse Visuomotor Skills. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.09564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perico, C.A.V.; De Schutter, J.; Aertbeliën, E. Combining Imitation Learning With Constraint-Based Task Specification and Control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, F.; Yohira, T.; Kawaguchi, A. Sample Efficient Imitation Learning for Continuous Control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stadie, B.; Abbeel, P.; Sutskever, I. Third-Person Imitation Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.01703. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, M. Self-Imitation Learning in Sparse Reward Settings. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.06962. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, A.; Gómez, S.; Gulcehre, C.; Desjardins, G.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Pascanu, R.; Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Hadsell, R. Policy Distillation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06295. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Andrychowicz, M.; Stadie, B.; Ho, J.; Schneider, J.; Sutskever, I.; Abbeel, P.; Zaremba, W. One-Shot Imitation Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.07326. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, C.; Yu, T.; Zhang, T.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. One-Shot Visual Imitation Learning via Meta-Learning. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Conference on Robot Learning, Mountain View, CA, USA, 13–15 November 2017; pp. 357–368. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, J.; Choudhury, S.; Venkatraman, A.; Ziebart, B.; Bagnell, J.A. Feedback in imitation learning: The three regimes of covariate shift. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.02872. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.; Gordon, G.; Bagnell, J. A Reduction of Imitation Learning and Structured Prediction to No-Regret Online Learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. Proc. Track 2010, 15, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Sidrane, C.; Driggs-Campbell, K.; Kochenderfer, M.J. HG-DAgger: Interactive Imitation Learning with Human Experts. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 8077–8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskey, M.; Lee, J.; Fox, R.; Dragan, A.; Goldberg, K. DART: Noise Injection for Robust Imitation Learning. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Conference on Robot Learning, Mountain View, CA, USA, 13–15 November 2017; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Menda, K.; Driggs-Campbell, K.; Kochenderfer, M.J. EnsembleDAgger: A Bayesian Approach to Safe Imitation Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Venetian Macao, Macau, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 5041–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, M.; Bruno, D.; Calinon, S.; Nanayakkara, T.; Caldwell, D. Skills Transfer Across Dissimilar Robots by Learning Context-Dependent Rewards. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, P.; Khamassi, M.; Tzafestas, C. Periodic movement learning in a soft-robotic arm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 4586–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, P.; Dometios, A.; Khamassi, M.; Tzafestas, C. Reproduction of Human Demonstrations with a Soft-Robotic Arm based on a Library of Learned Probabilistic Movement Primitives. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manti, M.; Pratesi, A.; Falotico, E.; Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C. Soft assistive robot for personal care of elderly people. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Singapore, 26–29 June 2016; pp. 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatintsi, N.; Dometios, A.; Kardaris, N.; Rodomagoulakis, I.; Koutras, P.; Papageorgiou, X.S.; Maragos, P.; Tzafestas, C.; Vartholomeos, P.; Hauer, K.; et al. I-Support: A robotic platform of an assistive bathing robot for the elderly population. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 126, 103451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, T.; Bursztein, E.; Long, J.; Chollet, F.; Jin, H.; Invernizzi, L.; de Marmiesse, G.; Fu, Y.; Hahn, A.; Mullenbach, J.; et al. KerasTuner. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/keras-team/keras-tuner (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, M.R.U.; de Gusmao, P.P.B.; Almalioglu, Y.; Markham, A.; Trigoni, N. Distilling Knowledge From a Deep Pose Regressor Network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.00858. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazeer, M.S.; Laschi, C.; Falotico, E. Soft DAgger: Sample-Efficient Imitation Learning for Control of Soft Robots. Sensors 2023, 23, 8278. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198278
Nazeer MS, Laschi C, Falotico E. Soft DAgger: Sample-Efficient Imitation Learning for Control of Soft Robots. Sensors. 2023; 23(19):8278. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198278
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazeer, Muhammad Sunny, Cecilia Laschi, and Egidio Falotico. 2023. "Soft DAgger: Sample-Efficient Imitation Learning for Control of Soft Robots" Sensors 23, no. 19: 8278. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198278
APA StyleNazeer, M. S., Laschi, C., & Falotico, E. (2023). Soft DAgger: Sample-Efficient Imitation Learning for Control of Soft Robots. Sensors, 23(19), 8278. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198278






