Fast and Uncooled Semiconducting Ca-Doped Y-Ba-Cu-O Thin Film-Based Thermal Sensors for Infrared
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Thin Film Deposition and Characterization
2.2. Device Fabrication
2.3. NIR Optical Characterization
3. Pyroelectric Material Properties
4. Pyroelectric Detector Performances: Results and Discussion
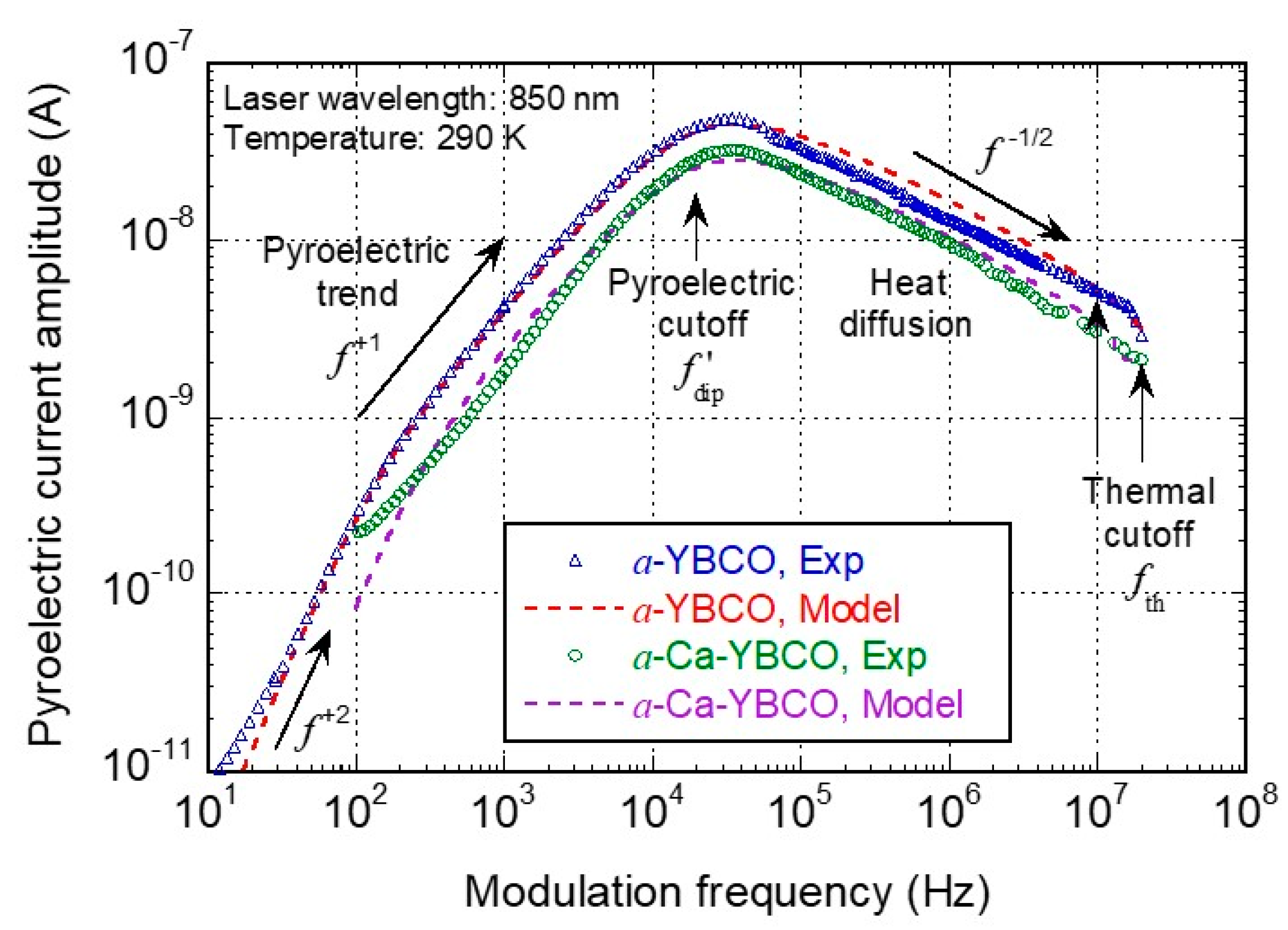
4.1. Device Optical Response
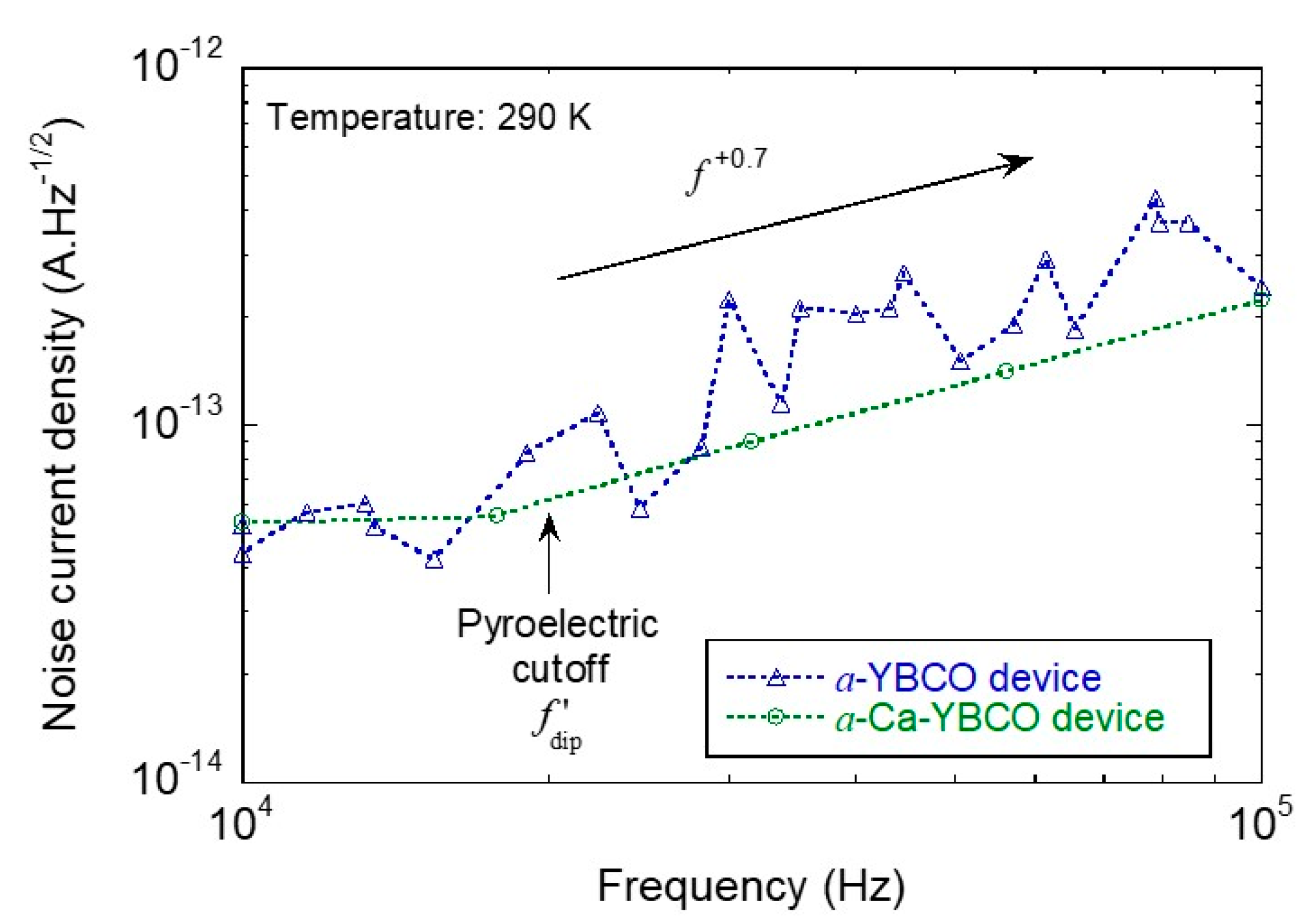
- At very low frequencies (below Hz), a behavior was visible only for the a-YBCO device that is related to a dipolar relaxation due to interfacial effects between the a-YBCO film and gold contact pads [23]. The a-Ca-YBCO device response was too noisy and could not be tested below 100 Hz;
- Between 100 Hz and ~10 kHz, a low-frequency high-pass behavior was identified, which is typical of a pyroelectric response (capacitive effect occurring in this device structure at low frequency). The cutoff at ~20 kHz of this behavior can be related to a second mechanism of dipolar relaxation in both the a-YBCO and a-Ca-YBCO films;
- Between 20 kHz and 80 kHz, a maximum current response was reached, with a lower amplitude for the a-Ca-YBCO device;
- Above 100 kHz, the low-pass behavior, close to , was typical of heat diffusion through the substrate. Measurements were limited to 40 MHz due to the readout preamplifier cutoff.
4.2. Analytical Model and Discussion
4.3. Device Performances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogalski, A. Infrared and Terahertz Detectors, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 223–297. [Google Scholar]
- Hafiz, S.B.; Scimeca, M.; Sahu, A.; Ko, D.-K. Colloidal quantum dots for thermal infrared sensing and imaging. Nano Converg. 2019, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, S.; Muench, J.E.; Ruocco, A.; Balci, O.; van Thourhout, D.; Sorianello, V.; Romagnoli, M.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Goykhman, I.; et al. High-responsivity graphene photodetectors integrated on silicon microring resonators. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koepfli, S.M.; Baumann, M.; Koyaz, Y.; Gadola, R.; Güngör, A.; Keller, K.; Horst, Y.; Nashashibi, S.; Schwanninger, R.; Doderer, M.; et al. Metamaterial graphene photodetector with bandwidth exceeding 500 gigahertz. Science 2023, 380, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik Yadav, P.V.; Yadav, I.; Ajitha, B.; Rajasekar, A.; Gupta, S.; Ashok Kumar Reddy, Y. Advancements of uncooled infrared microbolometer materials: A review. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2023, 342, 113611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranu; Uthra, B.; Sinha, R.; Agarwal, P.B. CMOS compatible pyroelectric materials for infrared detectors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 140, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ni, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X. A front-side microfabricated tiny-size thermopile infrared detector with high sensitivity and fast response. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Murata, A.; Okuyama, M. Miniaturized infrared sensor using silicon diaphragm based on Golay cell. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 1998, 66, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralt, P. Micromachined infrared detectors based on pyroelectric thin films. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2001, 64, 1339–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatmore, R.W. Pyroelectric Crystals, Ceramics, and Thin Films for IR Sensors, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Butler, D.P. Modified lead titanate thin films for pyroelectric infrared detectors on gold electrodes. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, W.; Zeng, X.; Huang, S.; Xie, Q.; Wan, L.; Shuai, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W. Integration and characterization of LiTaO3 single crystal film pyroelectric sensor using mid-infrared metamaterial perfect absorber. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 10381–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suen, J.Y.; Fan, K.; Montoya, J.; Bingham, C.; Stenger, V.; Sriram, S.; Padilla, W.J. Multifunctional metamaterial pyroelectric infrared detectors. Optica 2017, 4, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.P.; Rangrab, K.; Kumara, D. MEMS AlN pyroelectric infrared sensor with medium to long wave IR absorber. Sens. Actuator A 2019, 300, 111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranacher, C.; Consani, C.; Tortschanoff, A.; Rauter, L.; Holzmann, D.; Fleury, C.; Stocker, G.; Fant, A.; Schaunig, H.; Irsigler, P.; et al. A CMOS compatible pyroelectric mid-infrared detector based on aluminium nitride. Sensors 2019, 19, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poberaj, I.; Mihailovic, D. Pyroelectric effect measurements in YBa2Cu3O6+y and La2CuO4 materials. Ferroelectrics 1992, 128, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Çelik-Butler, Z.; Butler, D.P.; Jahanzeb, A. Dielectric and pyroelectric response in Nb/semiconducting Y-Ba-Cu-O/Nb structures. Ferroelectrics 1998, 209, 517–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, P.; Raasch, J.; Scheuring, A.; Hofherr, M.; Il’in, K.; Wünsch, S.; Semenov, A.; Hübers, H.W.; Judin, V.; Müller, A.-S.; et al. Highly responsive Y-Ba-Cu-O thin film THz detectors with picosecond time resolution. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2013, 23, 2400206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladret, R.; Dégardin, A.; Jagtap, V.; Kreisler, A. THz mixing with high-TC hot electron bolometers: A performance modeling assessment for Y-Ba-Cu-O devices. Photonics 2019, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.P.; Celik-Butler, Z.; Jahanzeb, A.; Gray, J.E.; Travers, C.M. Micromachined YBaCuO capacitor structures as uncooled pyroelectric infrared detectors. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreisler, A.J.; Dégardin, A.F.; Galiano, X.; Alamarguy, D. Low noise and fast response of infrared sensing structures based on amorphous Y-Ba-Cu-O semiconducting thin films sputtered on silicon. Thin Solid Films 2016, 617, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheneau, A.; Dégardin, A.F.; Kreisler, A.J. Semiconducting amorphous Y-Ba-Cu-O thin film detectors: Fast room temperature thermal response up to 40 MHz. In Proceedings of the 2022 47th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz), Delft, The Netherlands, 28 August–2 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dégardin, A.F.; Galiano, X.; Gensbittel, A.; Dubrunfaut, O.; Jagtap, V.S.; Kreisler, A.J. Amorphous Y-Ba-Cu-O oxide thin films: Structural, electrical and dielectric properties correlated with uncooled IR pyroelectric detection performances. Thin Solid Films 2014, 553, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awana, V.P.S.; Tulapurkar, A.A.; Malik, S.K.; Narlikar, A.V. Role of Ca in enhancing the superconductivity of YBa2Cu307-y. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, G.; Schmehl, A.; Schulz, R.R.; Goetz, B.; Bielefeldt, H.; Schneider, C.W.; Hilgenkamp, H.; Mannhart, J. Enhanced supercurrent density in polycrystalline YBa2Cu3O(7-δ) at 77 K from calcium doping of grain boundaries. Nature 2000, 407, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augieri, A.; Petrisor, T.; Celentano, G.; Ciontea, L.; Galluzzi, V.; Gambardella, U.; Mancini, A.; Rufoloni, A. Effect of Ca doping in YBCO superconducting thin films. Phys. C 2004, 401, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-i.; Larbalestier, D.C. Influence of variable Ca-doping on the critical current density of low-angle grain boundaries in YBa2Cu3O7-d. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 103905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, V.S.; Dégardin, A.F.; Kreisler, A.J. Low temperature amorphous growth of semiconducting Y-Ba-Cu-O oxide thin films in view of infrared bolometric detection. Thin Solid Film. 2012, 520, 4754–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubourdieu, C.; Sénateur, J.; Thomas, O.; Weiss, F. High quality YBa2Cu3O7-x superconducting thin films grown by MOCVD. J. Phys. IV Proc. 1995, 5, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odon, A.; Szlachta, A. Voltage response of a pyroelectric detector to a single rectangular optical radiation pulse. Sensors 2022, 22, 6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillner, U.; Kessler, E.; Meyer, H.-G. Figures of merit for thermoelectric and bolometric thermal radiation detectors. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2013, 2, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InfraTech. Available online: www.InfraTec.de (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Heinmann Sensor. Available online: www.heimannsensor.com (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Qinqin, W.; Xicai, L.; Xingyu, Y.; Bin, X.; Yuanqing, W. Pyroelectric infrared device with overlap dual capacitor structure sensor. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2018, 282, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
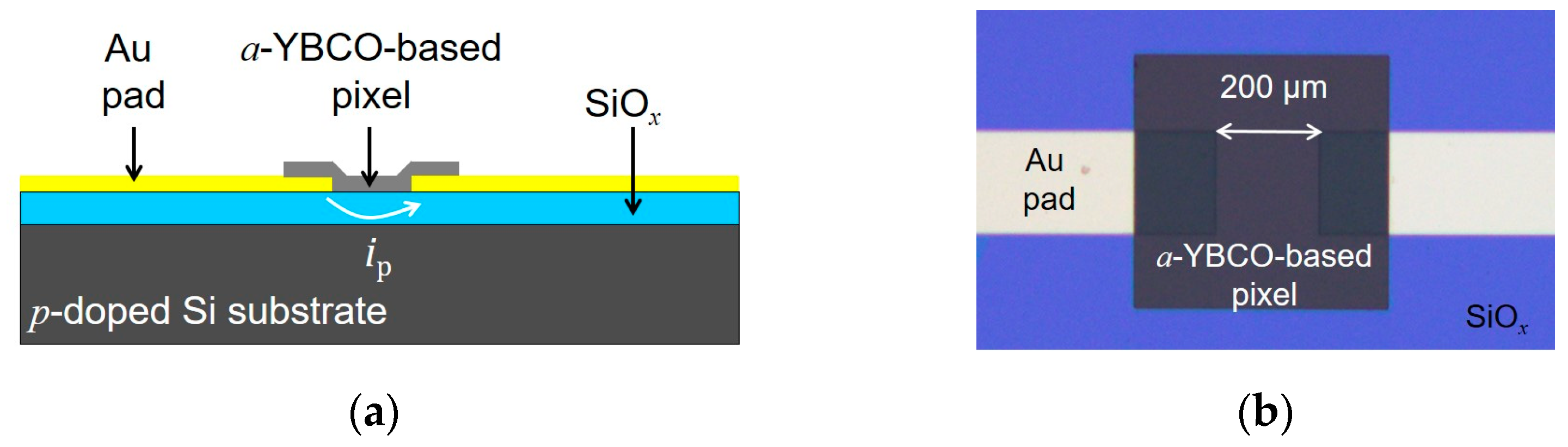

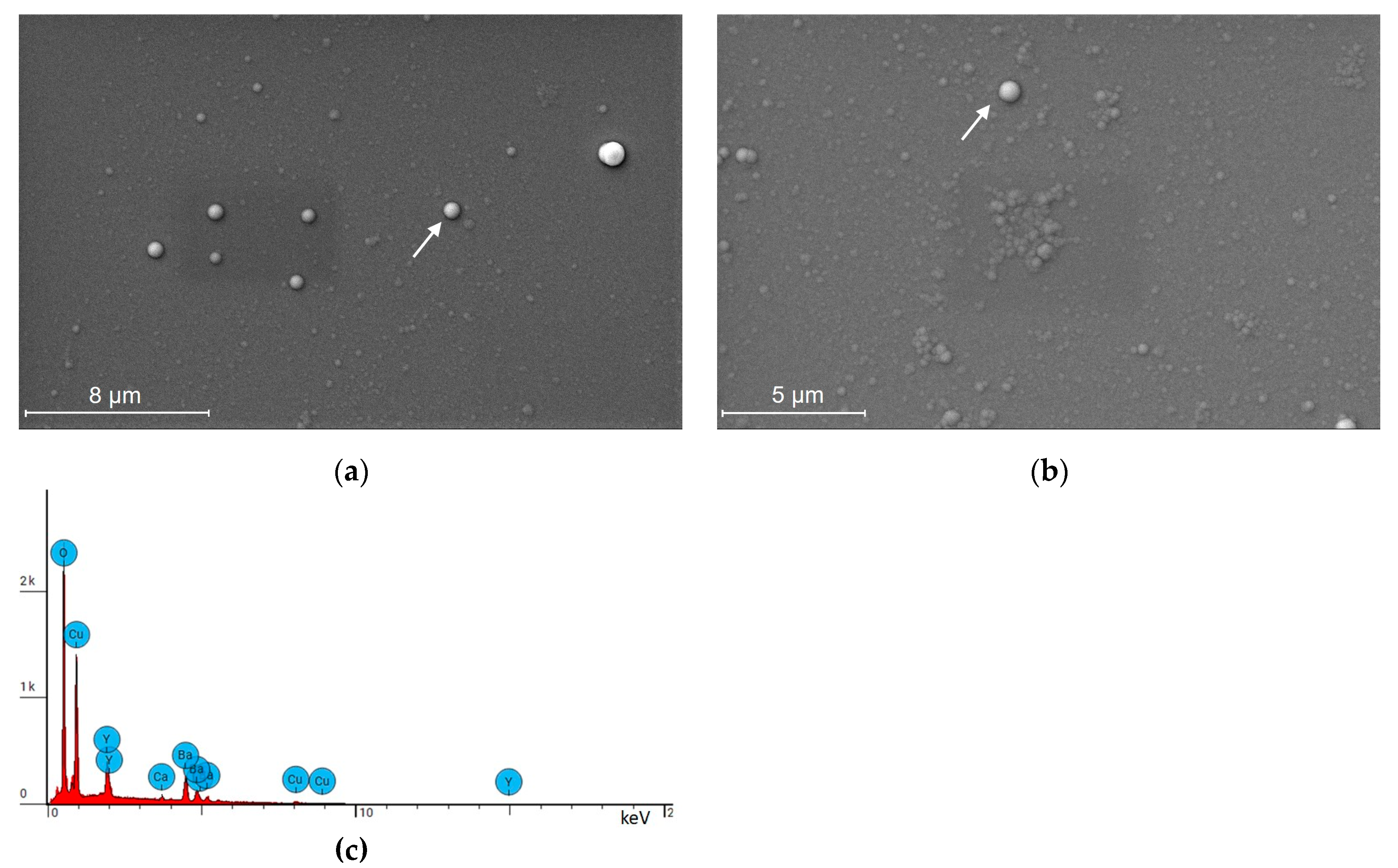
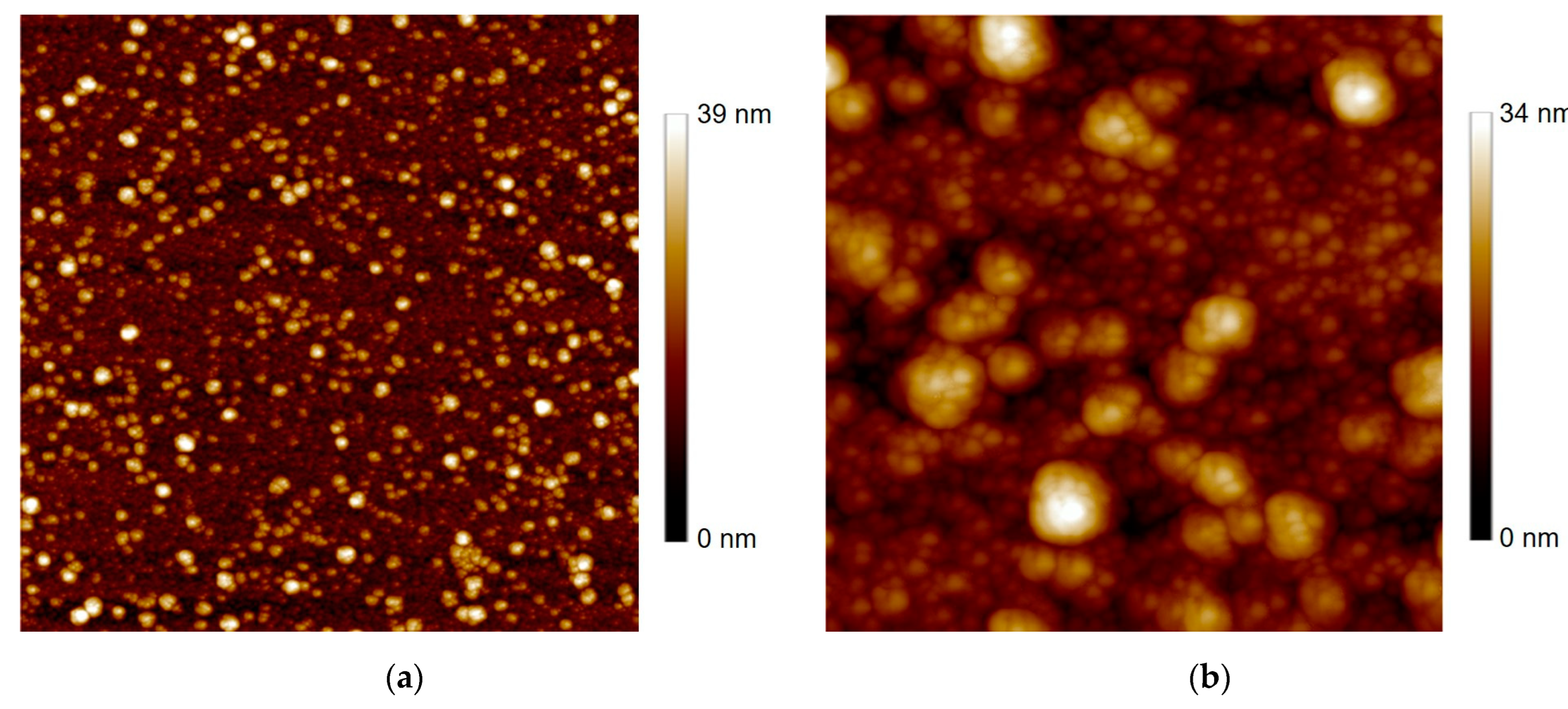
| Type of a-YBCO Film (Thickness) | Atomic % | Cationic Composition | Nominal Composition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Ca | Ba | Cu | |||
| Ca-doped (225 nm) | 6.65 | 0.86 | 14.42 | 21.79 | Y0.89Ca0.11Ba1.92Cu2.90 | Y0.9Ca0.1Ba2Cu3 |
| Ca-doped (900 nm) | 6.73 | 0.77 | 15.7 | 23.16 | Y0.9Ca0.1Ba2.09Cu3.09 | Y0.9Ca0.1Ba2Cu3 |
| Undoped (260 nm) | 3.66 | – | 5.60 | 10.31 | Y1Ba1.84Cu2.82 | Y1Ba2Cu3 |
| Type of a-YBCO Film | (nm rms) | (nm) | (MΩ/☐) | (mS/cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Grains | Small Grains | ||||
| Ca-doped | 4.3 | 270 ± 20 | 50 ± 10 | 158 | 0.07 |
| Undoped | 3 | 55 ± 5 | 2 ± 1 | 6.5 | |
| Parameter | a-Ca-YBCO Device | a-YBCO Device |
|---|---|---|
| 300 Hz | 130 Hz | |
| 20 kHz | 20 kHz | |
| 100 kHz | 100 kHz | |
| 20 MHz | 10 MHz |
| f (Hz) | NEP (W·Hz–1/2) | (cm·Hz1/2·W−1) | (ns) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-Ca-YBCO | a-YBCO | a-Ca-YBCO | a-YBCO | a-Ca-YBCO | a-YBCO | |
| <8 | <16 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dégardin, A.; Alamarguy, D.; Brézard Oudot, A.; Beldi, S.; Chaumont, C.; Boussaha, F.; Cheneau, A.; Kreisler, A. Fast and Uncooled Semiconducting Ca-Doped Y-Ba-Cu-O Thin Film-Based Thermal Sensors for Infrared. Sensors 2023, 23, 7934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187934
Dégardin A, Alamarguy D, Brézard Oudot A, Beldi S, Chaumont C, Boussaha F, Cheneau A, Kreisler A. Fast and Uncooled Semiconducting Ca-Doped Y-Ba-Cu-O Thin Film-Based Thermal Sensors for Infrared. Sensors. 2023; 23(18):7934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187934
Chicago/Turabian StyleDégardin, Annick, David Alamarguy, Aurore Brézard Oudot, Samir Beldi, Christine Chaumont, Faouzi Boussaha, Antoine Cheneau, and Alain Kreisler. 2023. "Fast and Uncooled Semiconducting Ca-Doped Y-Ba-Cu-O Thin Film-Based Thermal Sensors for Infrared" Sensors 23, no. 18: 7934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187934
APA StyleDégardin, A., Alamarguy, D., Brézard Oudot, A., Beldi, S., Chaumont, C., Boussaha, F., Cheneau, A., & Kreisler, A. (2023). Fast and Uncooled Semiconducting Ca-Doped Y-Ba-Cu-O Thin Film-Based Thermal Sensors for Infrared. Sensors, 23(18), 7934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187934







