Real-Time Bucket Pose Estimation Based on Deep Neural Network and Registration Using Onboard 3D Sensor
Abstract
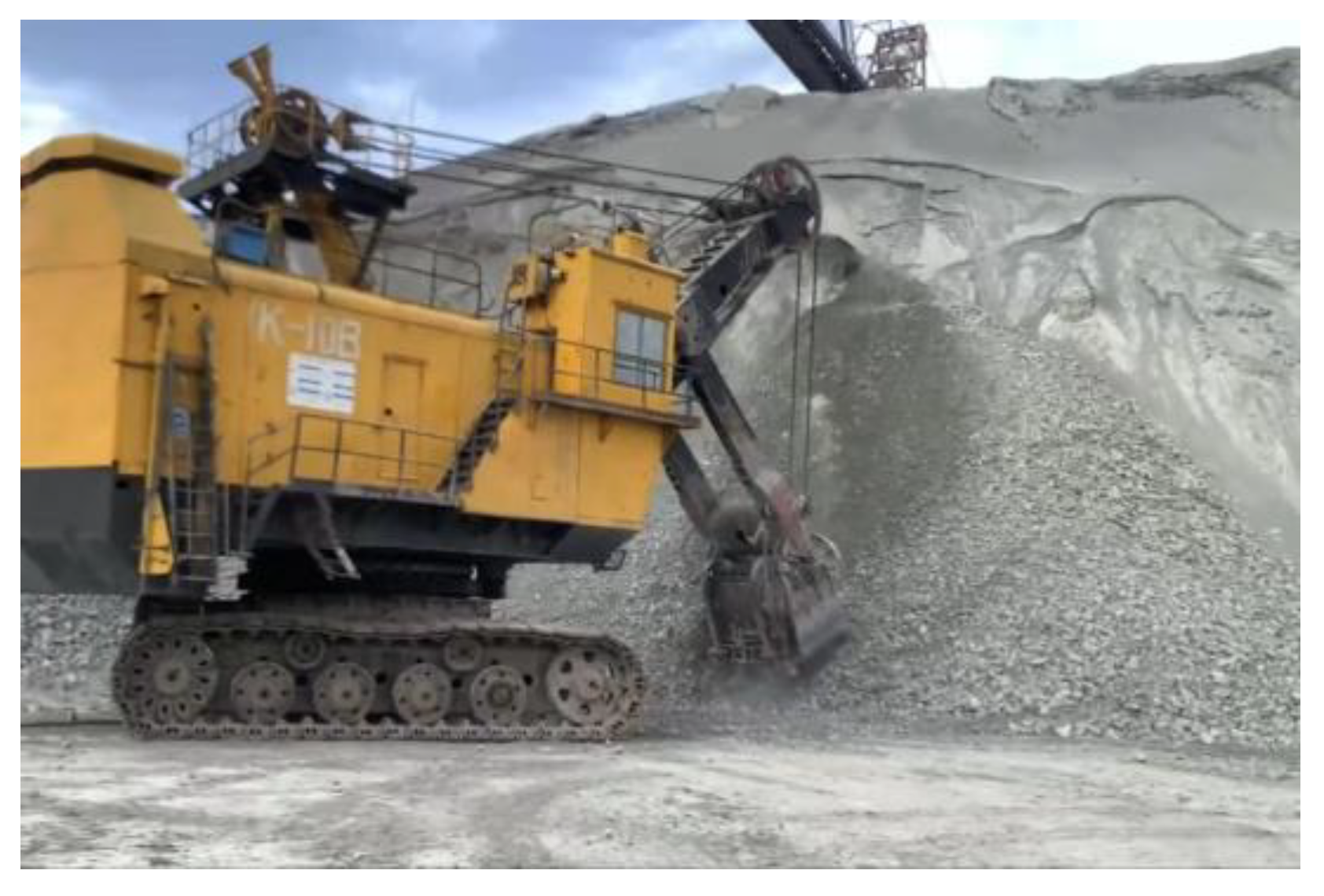
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
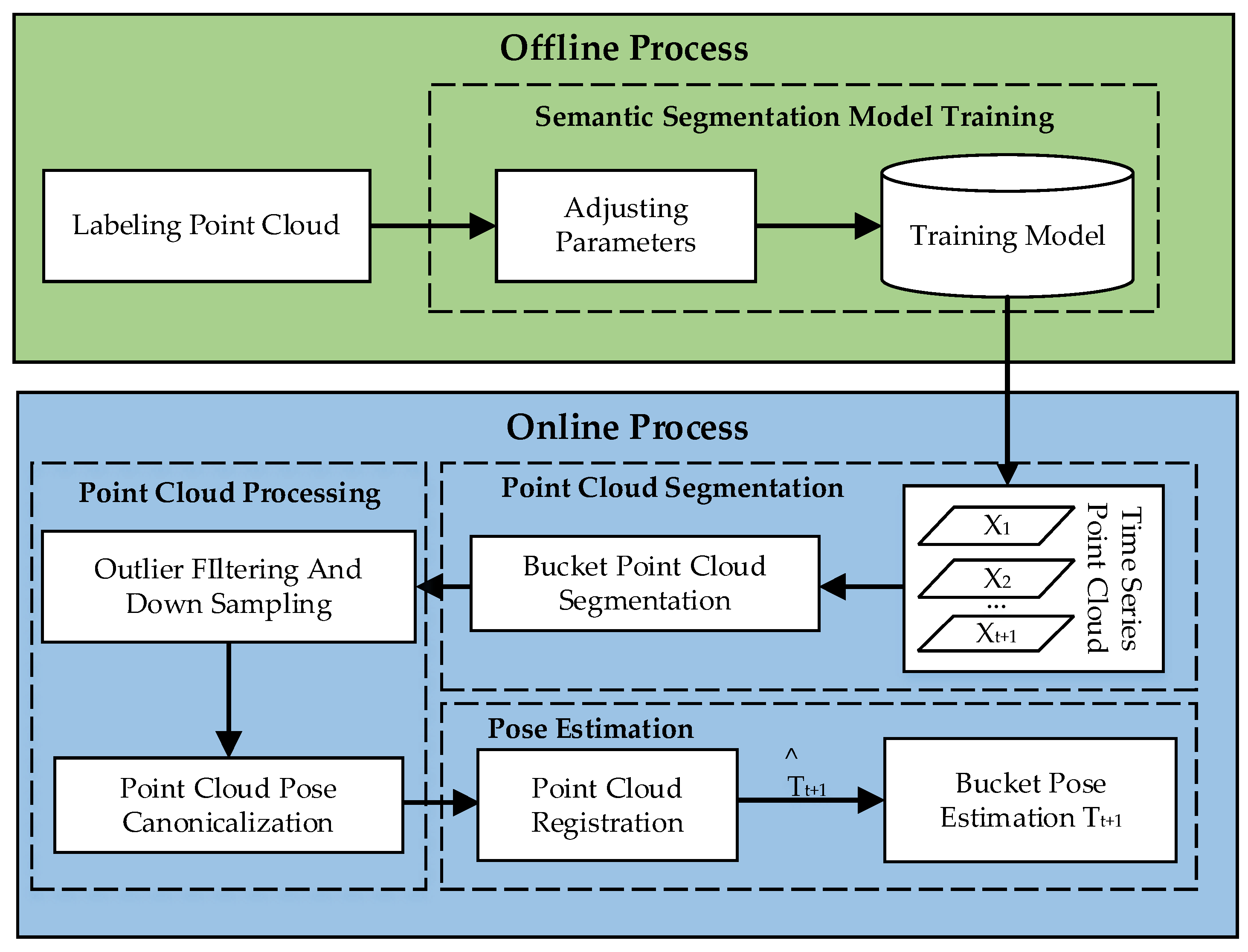
3. Methods
3.1. Semantic Segmentation
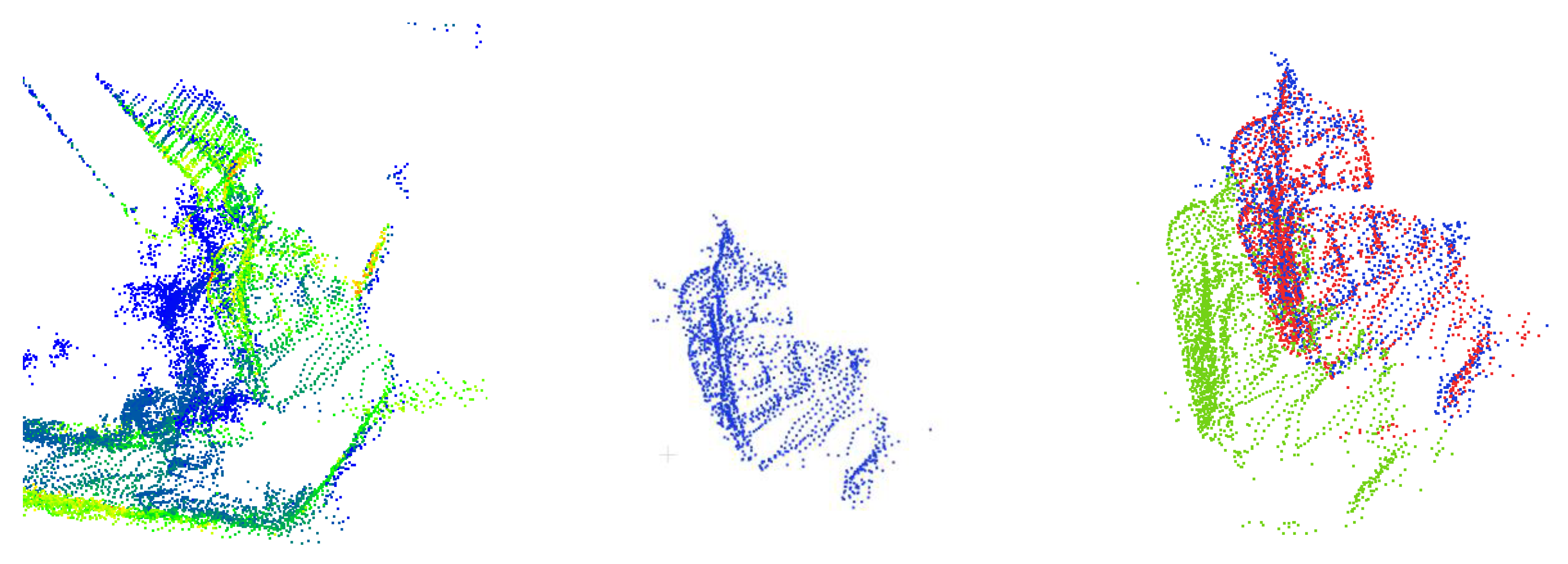
3.2. Pose Estimation
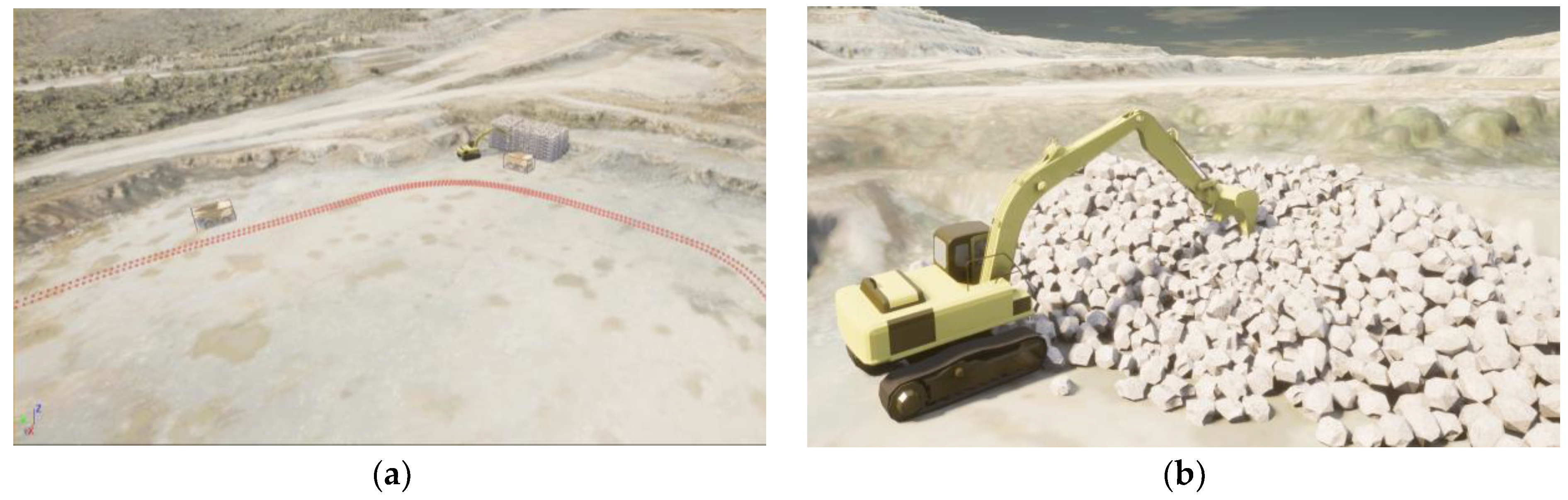
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset
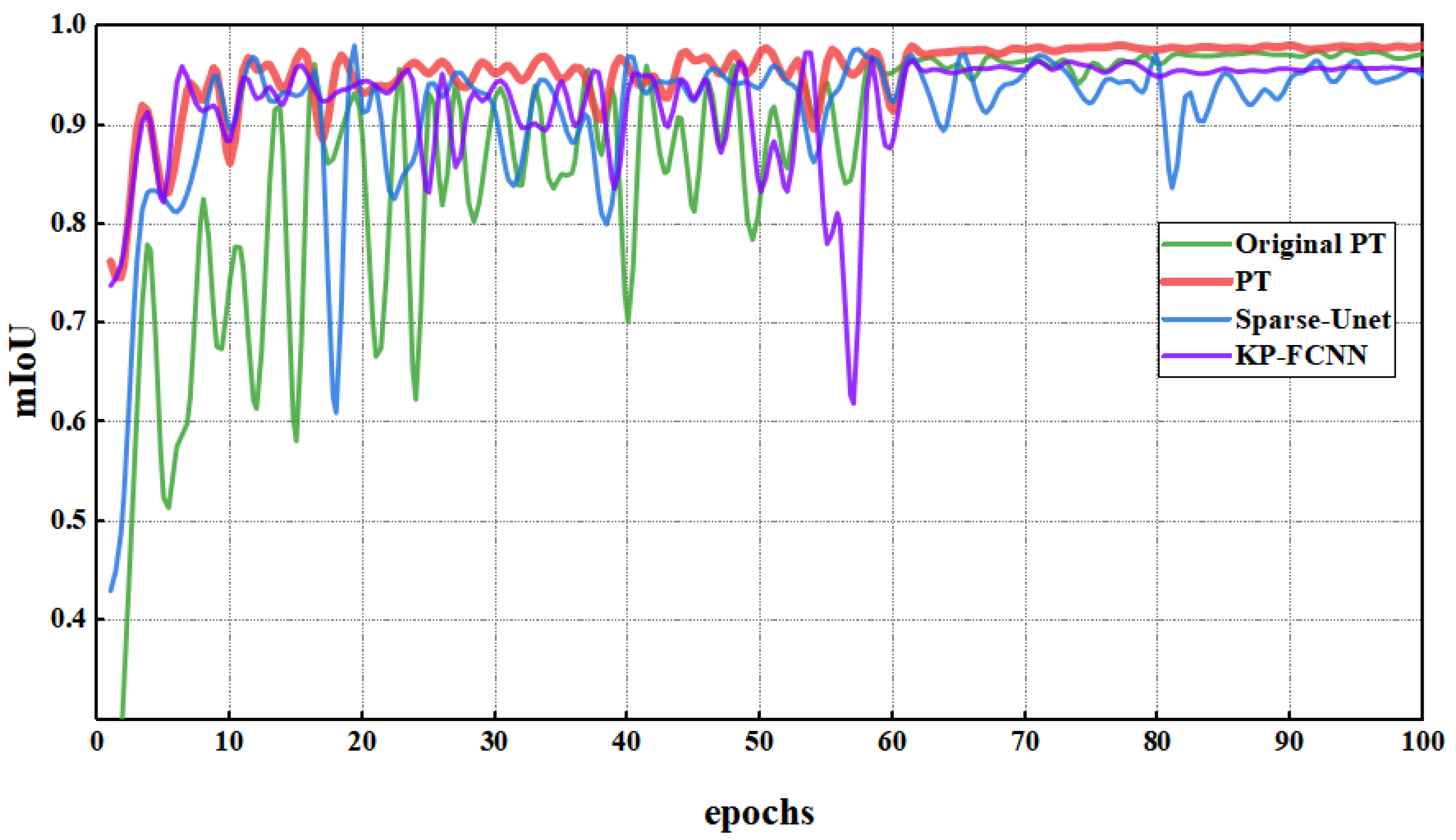
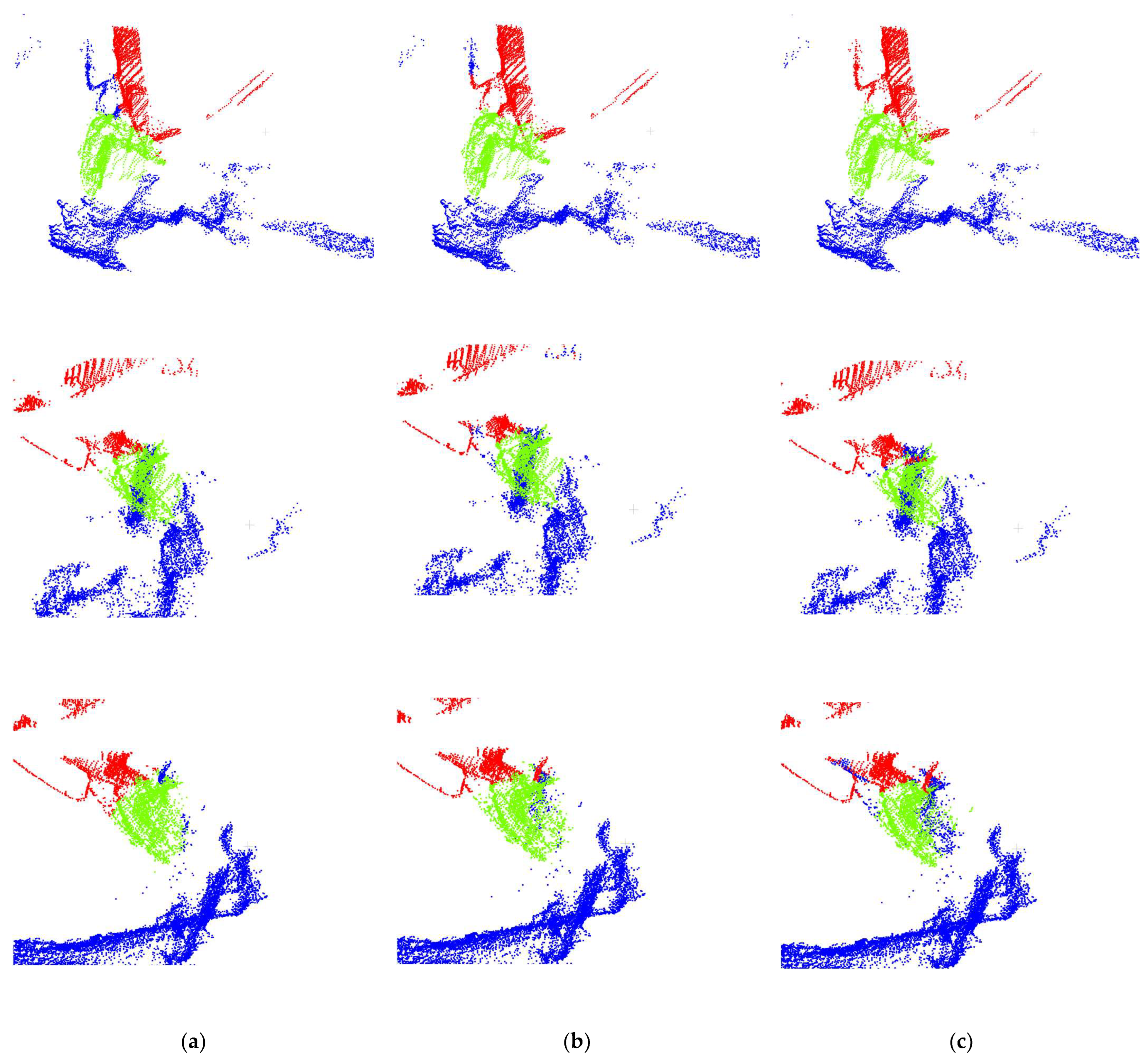
4.2. Semantic Segmentation
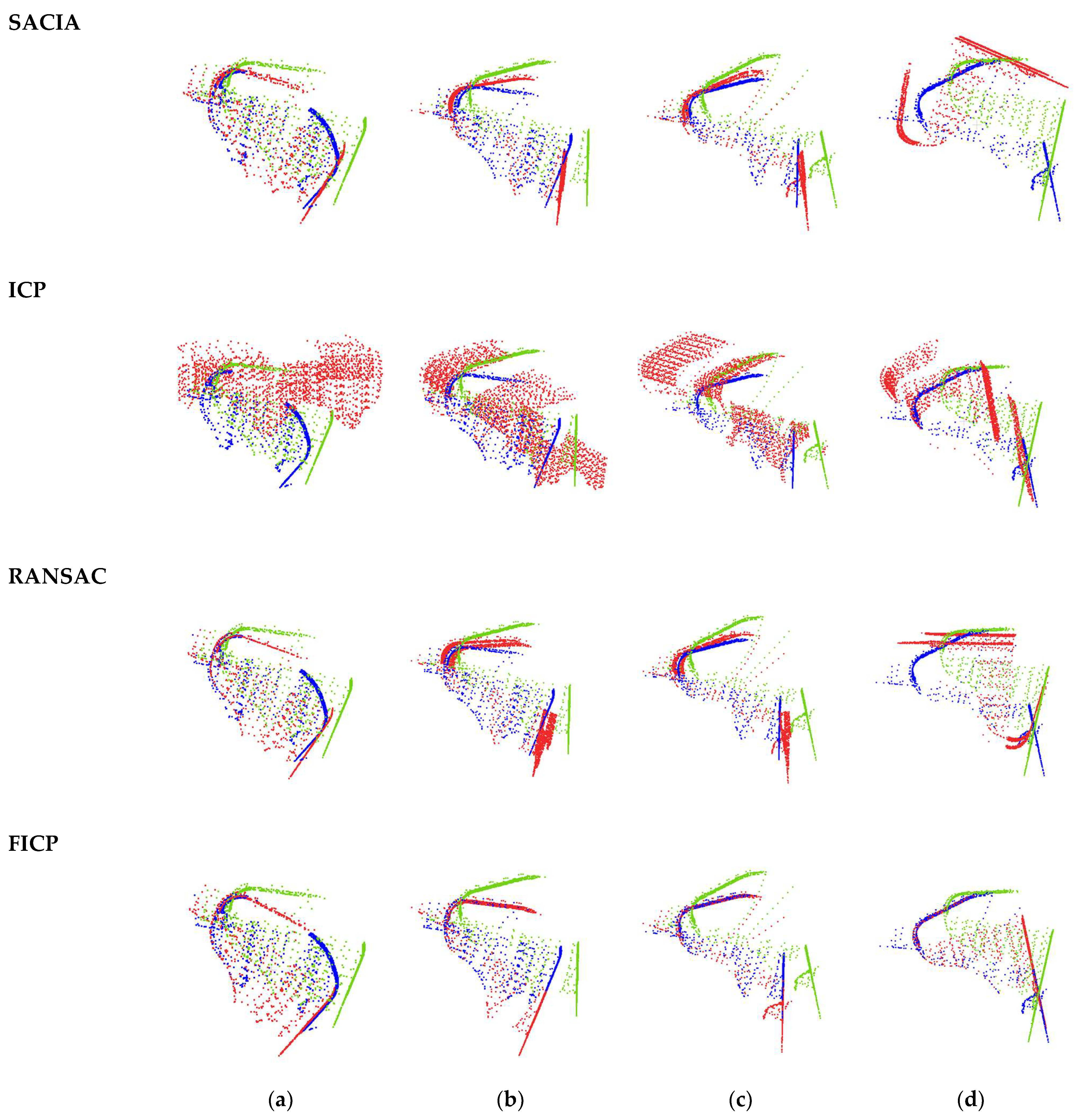
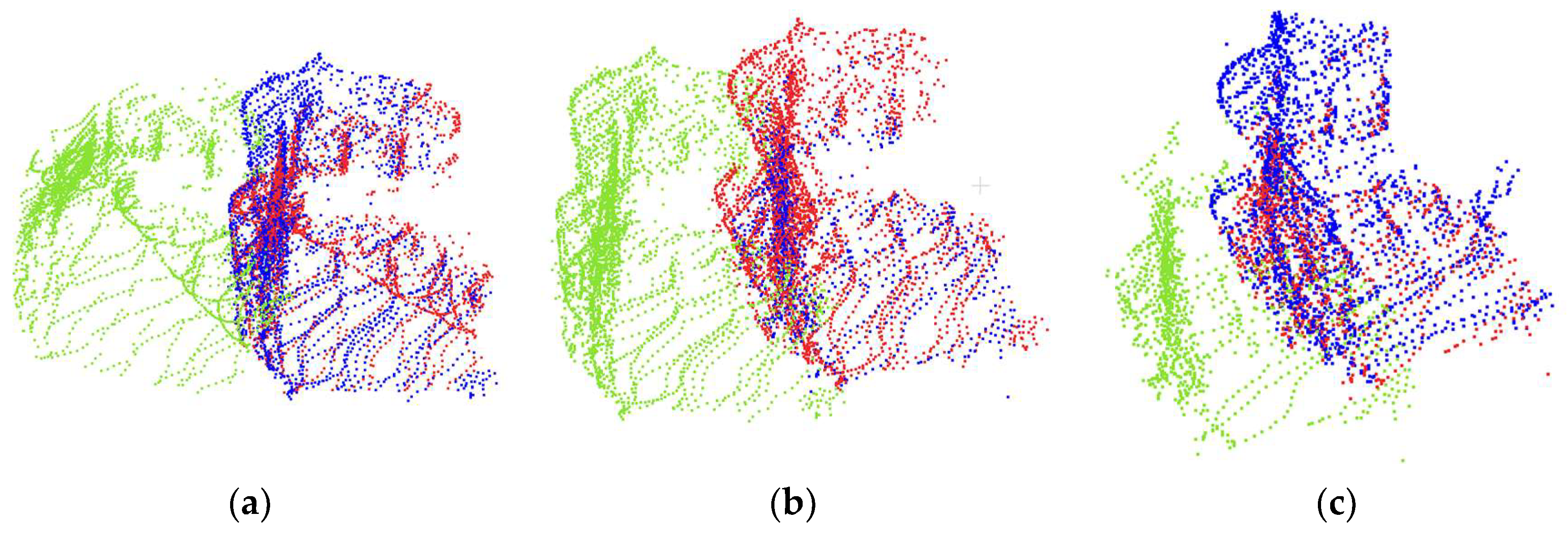
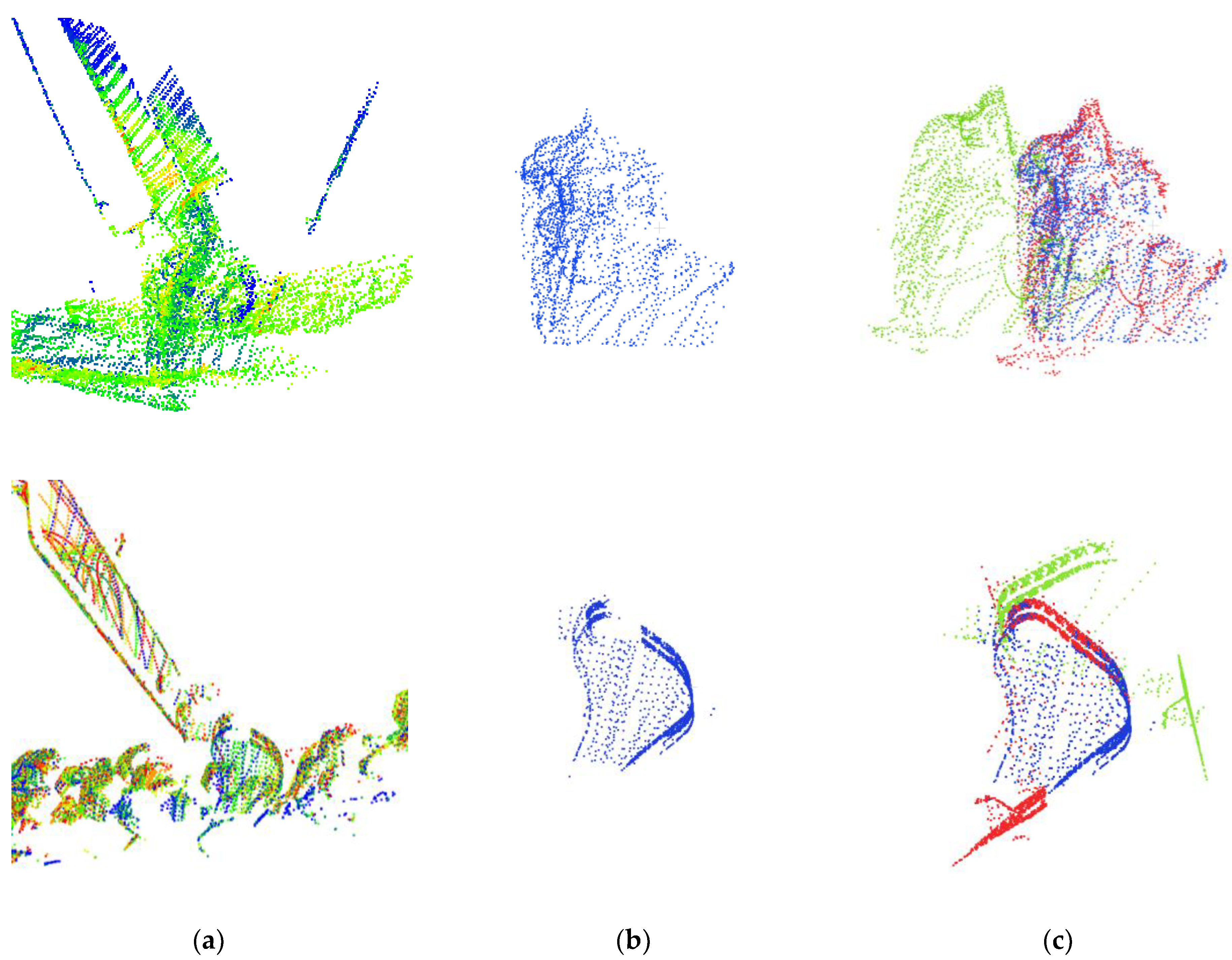
4.3. Pose Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Lu, C.; Jiang, S.; Shan, L.; Xiong, N.N. An Unmanned Intelligent Transportation Scheduling System for Open-Pit Mine Vehicles Based on 5G and Big Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 135524–135539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. TaskNet: A Neural Task Planner for Autonomous Excavator. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rasul, A.; Seo, J.; Oh, K.; Khajepour, A.; Reginald, N. Predicted Safety Algorithms for Autonomous Excavators Using a 3D LiDAR Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Systems Conference (SysCon), Montreal, QC, Canada, 24 August–20 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shariati, H.; Yeraliyev, A.; Terai, B.; Tafazoli, S.; Ramezani, M. Towards autonomous mining via intelligent excavators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Stentz, A.; Bares, J.; Singh, S.; Rowe, P. A robotic excavator for autonomous truck loading. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Innovations in Theory, Practice and Applications (Cat. No.98CH36190), Victoria, BC, Canada, 17 October 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Son, B.; Kim, C.; Kim, C.; Lee, D. Expert-Emulating Excavation Trajectory Planning for Autonomous Robotic Industrial Excavator. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bewley, A.; Upcroft, B.; Lever, P.; Leonard, S. Automatic In-Bucket Volume Estimation for Dragline Operations; The Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Carlton, VIC, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Niu, T.; Qin, T.; Yang, L. Machine Vision Based Autonomous Loading Perception for Super-huge Mining Excavator. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Chengdu, China, 1–4 August 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sandzimier, R.J.; Asada, H.H. A Data-Driven Approach to Prediction and Optimal Bucket-Filling Control for Autonomous Excavators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 2682–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Long, P.; Wang, L.; Qian, L.; Lu, F.; Song, X.; Manocha, D.; Zhang, L. AES: Autonomous Excavator System for Real-World and Hazardous Environments. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.04848. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Lever, P.J.A. On-line trajectory planning for autonomous robotic excavation based on force/torque sensor measurements. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on MFI’94. Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2–5 October 1994; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Haga, M.; Hiroshi, W.; Fujishima, K. Digging control system for hydraulic excavator. Mechatronics 2001, 11, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Ji, C.; Jang, S.; Lee, S.; No, J.; Han, C.; Han, J.; Kang, M. Analysis of the Position Recognition of the Bucket Tip According to the Motion Measurement Method of Excavator Boom, Stick and Bucket. Sensors 2020, 20, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Kim, D.; Liu, M.; Lee, S. 3D Excavator Pose Estimation Using Projection-Based Pose Optimization for Contact-Driven Hazard Monitoring. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2023, 37, 04022048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, B.; Han, S.; Seo, J. Implementation experiments on convolutional neural network training using synthetic images for 3D pose estimation of an excavator on real images. Autom. Constr. 2022, 133, 103996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, M.; Luo, H.; Wong, P.K.Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Cheng, J.C. Full-body pose estimation for excavators based on data fusion of multiple onboard sensors. Autom. Constr. 2023, 147, 104694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; An, Y.; Sun, W.; Hu, H.; Song, X. Memory-Augmented Point Cloud Registration Network for Bucket Pose Estimation of the Intelligent Mining Excavator. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Gao, J.; Feng, L. Recognition and 3D Pose Estimation for Underwater Objects Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network and Point Cloud Registration. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), Kagawa, Japan, 31 August–3 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.M.; Tsai, C.Y.; Lai, Y.C.; Li, S.A.; Wong, C.C. Visual Object Recognition and Pose Estimation Based on a Deep Semantic Segmentation Network. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9370–9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.M.; Kee, V.; Le, T.; Wagner, S.; Mariottini, G.L.; Schneider, A.; Hamilton, L.; Chipalkatty, R.; Hebert, M.; Johnson, D.M.; et al. SegICP: Integrated deep semantic segmentation and pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; IEEE: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pramatarov, G.; De Martini, D.; Gadd, M.; Newman, P. BoxGraph: Semantic Place Recognition and Pose Estimation from 3D LiDAR. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, J.; Jing, F.; Liu, Z.; Tan, M. A pose estimation system based on deep neural network and ICP registration for robotic spray painting application. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. In SPIE 1611, Proceedings of the Sensor Fusion IV: Control Paradigms and Data Structures, Boston, MA, USA, 12–15 November 1991; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Yu, K.T.; Song, S.; Suo, D.; Walker, E.; Rodriguez, A.; Xiao, J. Multi-view self-supervised deep learning for 6D pose estimation in the Amazon Picking Challenge. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.Y. 3D Object Detection and 6D Pose Estimation Using RGB-D Images and Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Shen, B. Active Pose Estimation of Daily Objects. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Changchun, China, 5–8 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Van Tran, L.; Lin, H.Y. BiLuNetICP: A Deep Neural Network for Object Semantic Segmentation and 6D Pose Recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 11748–11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, N.; Belagiannis, V.; Dietmayer, K. Point Transformer. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 134826–134840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Deng, B. Fast and Robust Iterative Closest Point. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2022, 44, 3450–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, H.F.; Ni, P. Anderson acceleration for fixed-point iterations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2011, 49, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Qin, Y.; Duan, Y.; Fan, Q.; Chen, B.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. CAPTRA: CAtegory-level Pose Tracking for Rigid and Articulated Objects from Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.; Mitash, C.; Ren, B.; Bekris, K.E. se(3)-TrackNet: Data-driven 6D Pose Tracking by Calibrating Image Residuals in Synthetic Domains. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Ji, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fox, D. DeepIM: Deep Iterative Matching for 6D Pose Estimation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Category | Parameters | Original PT | Optimized PT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model Performance | mIoU | 0.9756 | 0.9813 |
| Optimal Training Epoch | 94 | 90 | |
| Self-Attention Hyperparameters | Neighboring Points | 16 | 8 |
| Weight-Encoding | GVA | GVA | |
| Groups | (12, 24, 48) | (6, 12, 24) | |
| Network Hyperparameters | Network Layers | (2, 6, 2) | (2, 6, 2) |
| Feature Output Dimensions | (96, 192, 384) | (96, 192, 384) | |
| Parameter Scale | 3.9 million | 3.8 million | |
| Training Hyperparameters | Batch Size | 6 | 6 |
| Dropout Rate | 0 | 0.5 |
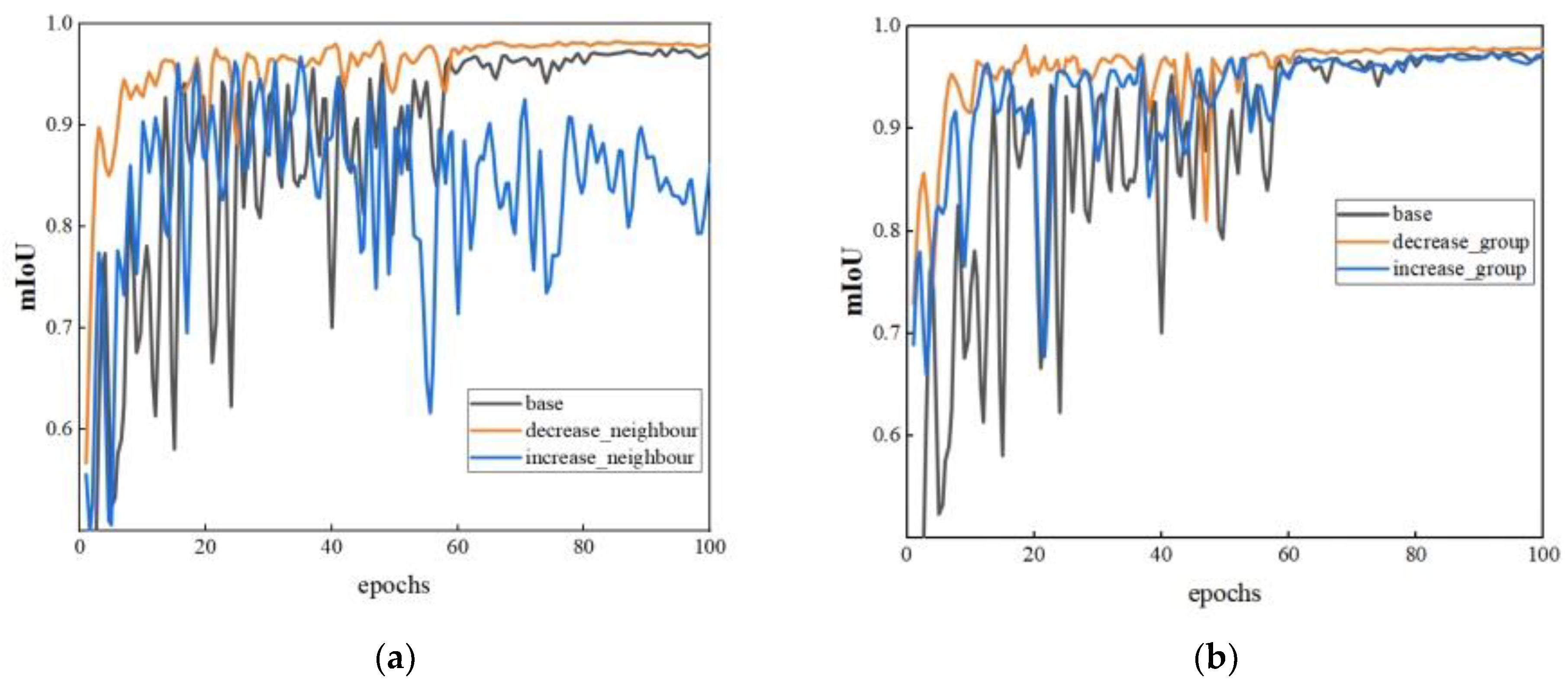
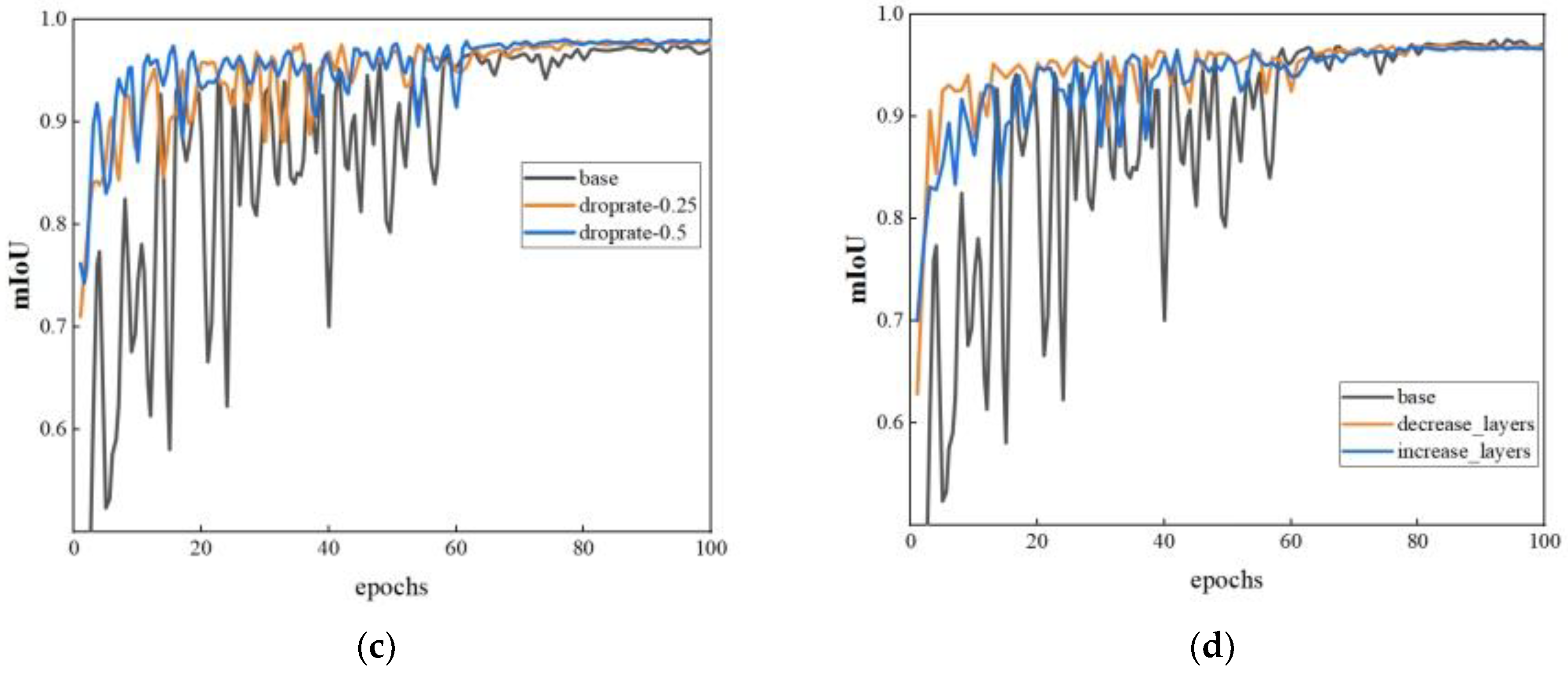
| Parameters | Base | Neighboring Points | Groups | Dropout Rate | Network Layers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU | 0.9756 | 0.9677 | 0.9826 | 0.9736 | 0.9796 | 0.9791 | 0.9813 | 0.9691 | 0.9705 |
| Neighboring Points | 16 | 32 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Groups | (12, 24, 48) | (12, 24, 48) | (12, 24, 48) | (24, 48, 96) | (6, 12, 24) | (12, 24, 48) | (12, 24, 48) | (12, 24, 48) | (12, 24, 48) |
| Network Layers | (2, 6, 2) | (2, 6, 2) | (2, 6, 2) | (2, 6, 2) | (2, 6, 2) | (2, 6, 2) | (2, 6, 2) | (3, 8, 3) | (1, 4, 1) |
| Parameter Scale | 3.9 million | 3.9 million | 3.9 million | 4 million | 3.8 million | 3.9 million | 3.9 million | 5.34 million | 2.47 million |
| Batch size | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Dropout Rate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Method | OA | mA | mIoU | Background | Boom | Bucket |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sparse-Unet | 0.9932 | 0.9781 | 0.9693 | 0.9924 | 0.9845 | 0.9309 |
| OPT | 0.9947 | 0.9863 | 0.9777 | 0.9954 | 0.9849 | 0.9529 |
| PT | 0.9956 | 0.9873 | 0.9816 | 0.9960 | 0.9882 | 0.9605 |
| Method | OA | mA | mIoU | Background | Boom | Bucket |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sparse-Unet | 0.9645 | 0.9433 | 0.8960 | 0.9637 | 0.8953 | 0.8290 |
| OPT | 0.9269 | 0.8568 | 0.8012 | 0.9161 | 0.8599 | 0.6276 |
| PT | 0.9595 | 0.9144 | 0.8853 | 0.9533 | 0.8321 | 0.8703 |
| Method | RE (◦) | TE (m) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAC-IA | 12.0196 | 0.2195 | 725 |
| ICP | 20.2733 | 0.4019 | 1140 |
| RANSAC | 8.9154 | 0.6853 | 4386 |
| SIFT+RANSAC | 4.0621 | 0.0559 | 1011 |
| GICP | 2.0621 | 0.0312 | 20 |
| FICP | 1.2058 | 0.0251 | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Bi, L.; Zhao, Z. Real-Time Bucket Pose Estimation Based on Deep Neural Network and Registration Using Onboard 3D Sensor. Sensors 2023, 23, 6958. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156958
Xu Z, Bi L, Zhao Z. Real-Time Bucket Pose Estimation Based on Deep Neural Network and Registration Using Onboard 3D Sensor. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6958. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156958
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zijing, Lin Bi, and Ziyu Zhao. 2023. "Real-Time Bucket Pose Estimation Based on Deep Neural Network and Registration Using Onboard 3D Sensor" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6958. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156958
APA StyleXu, Z., Bi, L., & Zhao, Z. (2023). Real-Time Bucket Pose Estimation Based on Deep Neural Network and Registration Using Onboard 3D Sensor. Sensors, 23(15), 6958. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156958





