Self-Enhanced Mixed Attention Network for Three-Modal Images Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- As far as we know, it is the first time that three-modal images are used as input for few-shot semantic segmentation. The effectiveness of the three-modal fusion mechanism designed by us is proved by ablation experiments.
- (2)
- We make a novel V-D-T few-shot semantic segmentation dataset VDT-2048-5i and conduct many comparison experiments with the existing methods. We also prove that the effectiveness and necessity of three-modal few-shot semantic segmentation.
- (3)
- We design a novel Self-Enhanced Mixed Attention Network (SEMANet). It includes an SE (Self-Enhanced) module for enhancing three-modal features and a MA (Mixed Attention) module for fusing three-modal features. The experimental results prove that the proposed SEMANet achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Single-Modal Segmentation
2.2. Multi-Modal Segmentation
2.3. Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
3. Methods
3.1. Problem Setting
- (1)
- , represents the visible image, and represents the infrared image, represents the depth image, and all three are pixel-level corresponding pictures of the same scene. represents the corresponding mask of the base class images. represents the base class in the training, and represents the number of base images.
- (2)
- , represents the number of sets of visible, infrared, and depth image pairs. By comparing the predicted results of the model with its corresponding ground truth image, we can test the performance of the model.
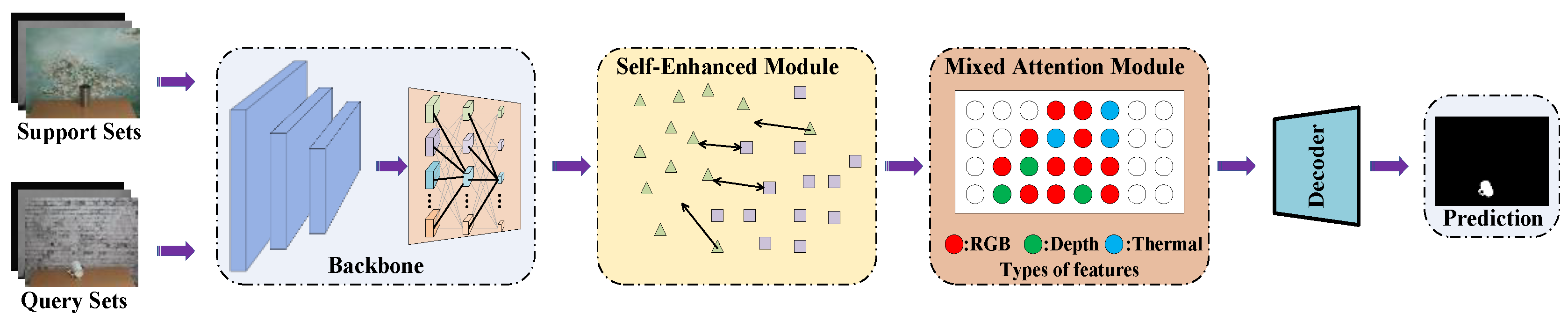
3.2. The Proposed Model
3.3. Feature Extraction
3.4. Self-Enhanced Module
3.5. Self-Enhanced Module
3.6. Our Network
4. Dataset
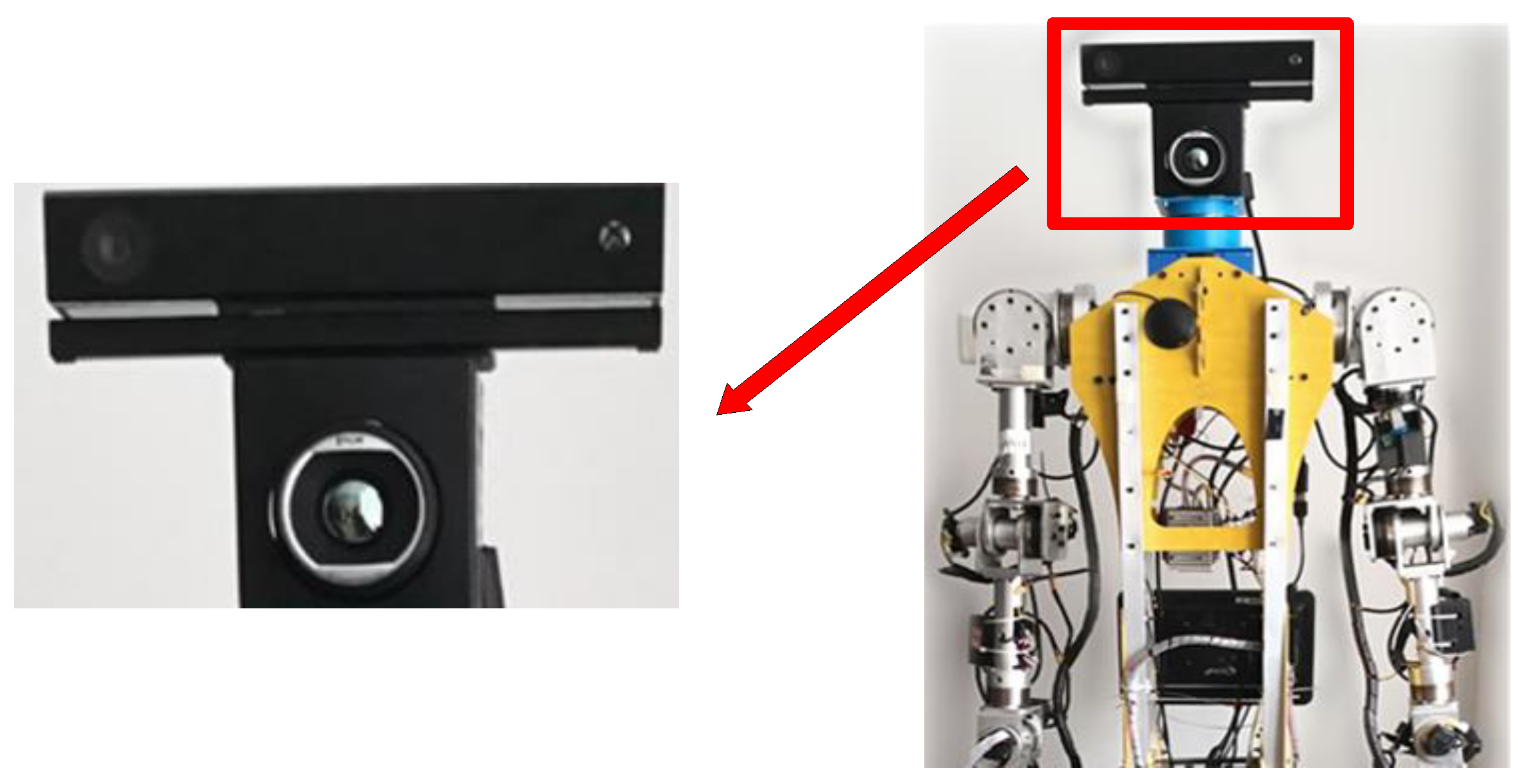
4.1. Composition of the Hardware
4.2. Construction of the Dataset
5. Experiment
5.1. Setup Details
5.2. Evaluation Metrics
5.3. Results and Analysis
5.4. Ablation Study
5.4.1. Ablation Study on Three-Modal Data
5.4.2. Ablation Study on the Proposed Module
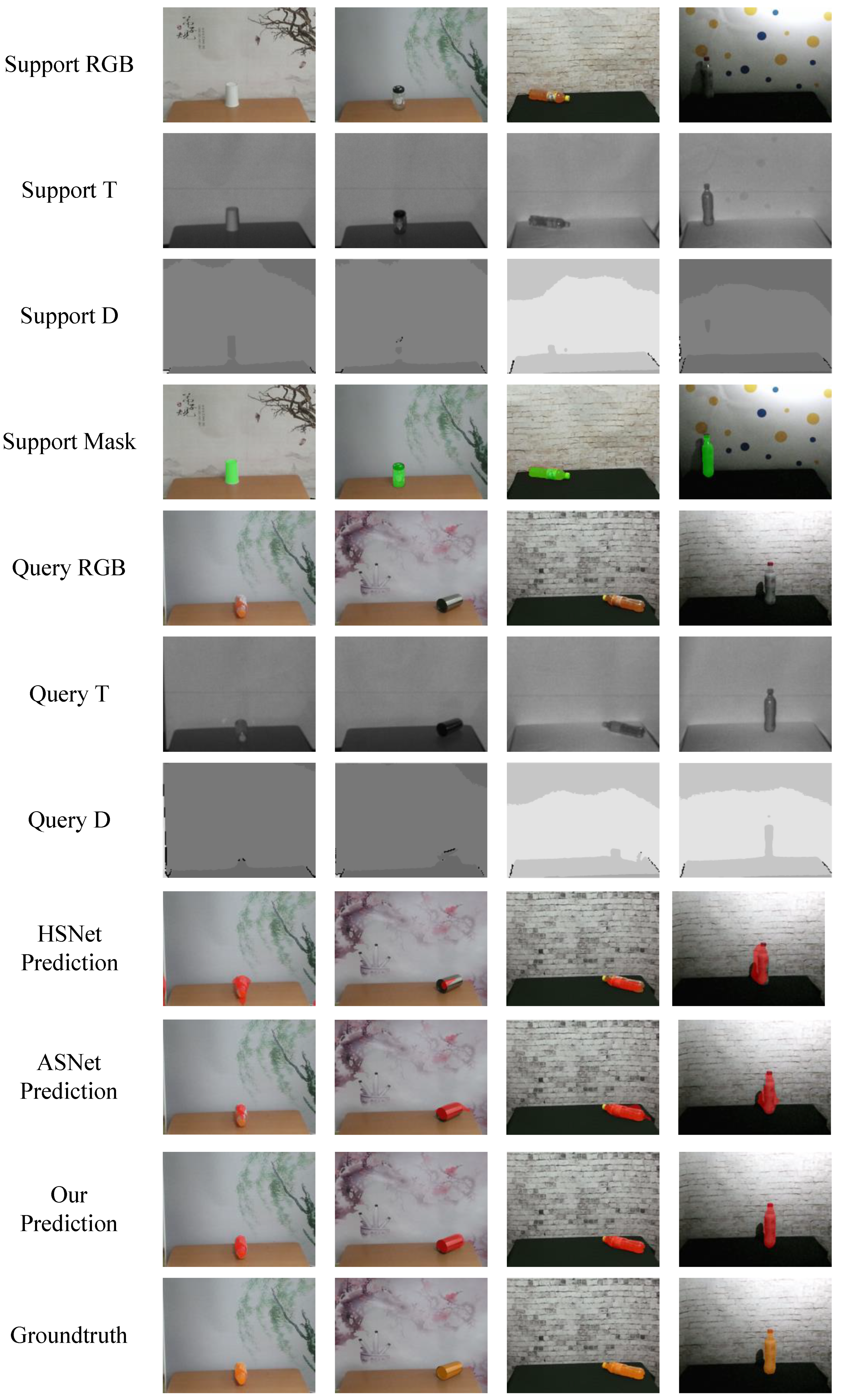
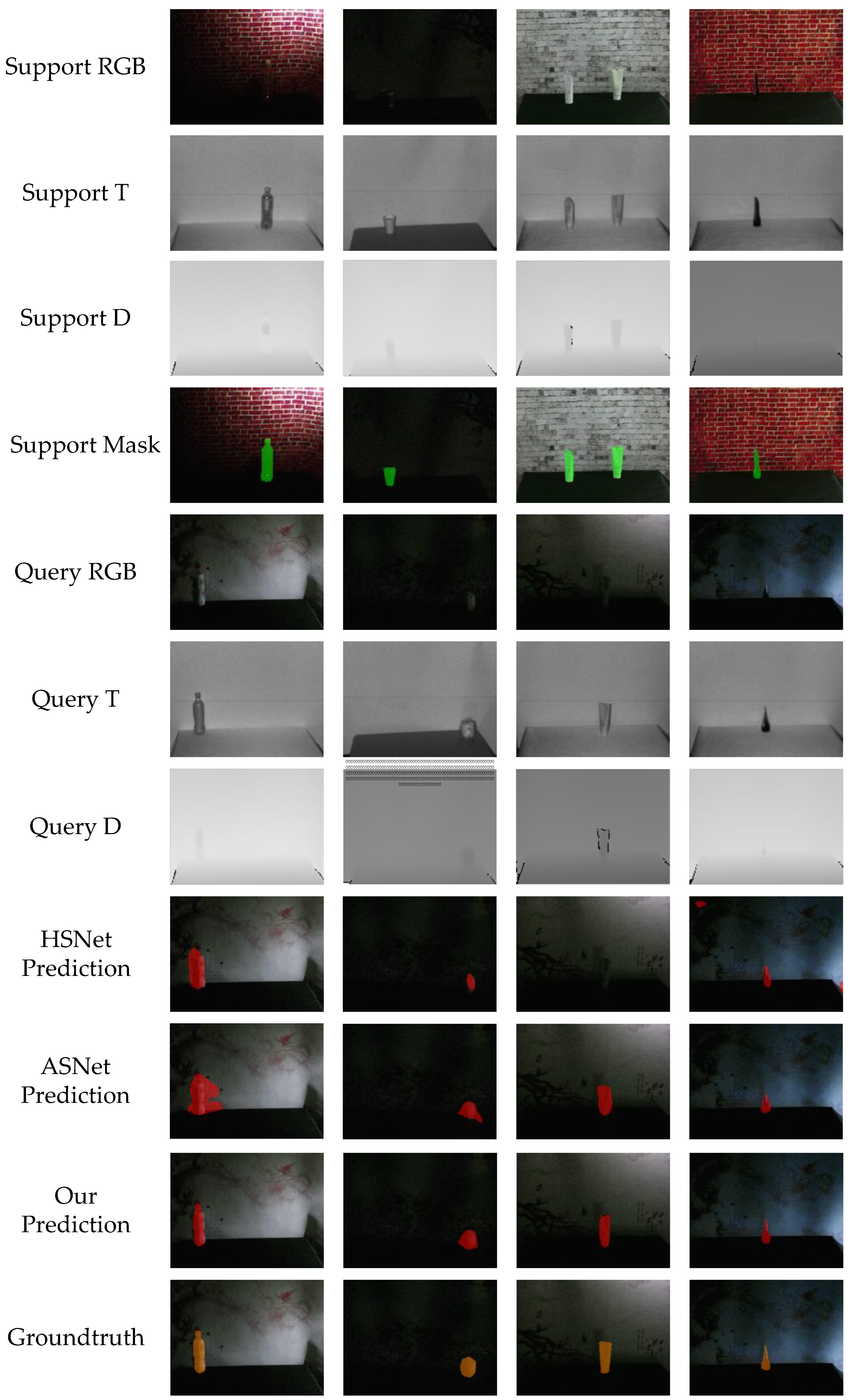
5.5. Visualization Results
5.6. Challenging Scenes
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kong, Y.; Wang, H.; Kong, L.; Liu, Y.; Yao, C.; Yin, B. Absolute and Relative Depth-Induced Network for RGB-D Salient Object Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Han, D.; Wang, X.; Yi, P.; Yan, L.; Li, X. Multi-sensor medical-image fusion technique based on embedding bilateral filter in least squares and salient detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, M.; Jin, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L. Multiscale Cascaded Attention Network for Saliency Detection Based on ResNet. Sensors 2022, 22, 9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Jian, M.; Shaheed, K.; Hussain, S.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Muhammad, K. AWANet: Attentive-Aware Wide-Kernels Asymmetrical Network with Blended Contour Information for Salient Object Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Shangguan, C.; Huang, S. RGBD Salient Object Detection, Based on Specific Object Imaging. Sensors 2022, 22, 8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, L.; Fan, J. YOLOv5s-Fog: An Improved Model Based on YOLOv5s for Object Detection in Foggy Weather Scenarios. Sensors 2023, 23, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Yan, Z.; Ye, S. STC-YOLO: Small Object Detection Network for Traffic Signs in Complex Environments. Sensors 2023, 23, 5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, M.; Liao, J.; Xie, Q. A Light-Weight Network for Small Insulator and Defect Detection Using UAV Imaging Based on Improved YOLOv5. Sensors 2023, 23, 5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, B. A Multi-Step Fusion Network for Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution Aerial Images. Sensors 2023, 23, 5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Cui, J.; Cui, W.; Yuan, Y.; Ren, X. Fast Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images Using a Network That Integrates Global and Local Information. Sensors 2023, 23, 5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Song, K.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Dong, H.; Yan, Y. Visible and thermal images fusion architecture for few-shot semantic segmentation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 80, 103306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xue, Z.; Wang, L. A novel framework for semantic segmentation with generative adversarial network. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 58, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Yung, N.H. Hybrid graphical model for semantic image segmentation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2015, 28, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, S.K.; Ng, T.C.; Yu, C. Unsupervised fuzzy model-based image segmentation. Signal Process. 2020, 171, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Yan, Y.; Meng, Q. RGB-T image analysis technology and application: A survey. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, S.K.; Yuen, K.; Yu, C. Fuzzy bit-plane-dependence image segmentation. Signal Process. 2019, 154, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhu, F.; Liu, L.; Shao, L.; Li, X. Generalized zero-shot learning with multiple graph adaptive generative networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 2903–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Qin, J.; Shao, L. Region graph embedding network for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 562–580. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.S.; Liu, L.; Jin, X.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Yao, Y.; Shao, L. Attentive region embedding network for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9384–9393. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Song, K.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, P. Deep metric learning-based for multi-target few-shot pavement distress Classification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xie, G.S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shen, F.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, J. Semantically meaningful class prototype learning for one-shot image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Song, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, X. Triplet-graph reasoning network for few-shot metal generic surface defect segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, S.H.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. Collaborative sparse representation leaning model for RGBD action recognition. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2017, 48, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q. RETRACTED: An iterative propagation based co-saliency framework for RGBD images. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 59, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Guan, D.; Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Qiao, Y. Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multispectral feature learning using deep neural networks. Inf. Fusion 2019, 46, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, Y. Learning discriminative update adaptive spatial-temporal regularized correlation filter for RGB-T tracking. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2020, 72, 102881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; He, B.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Scene flow estimation by depth map upsampling and layer assignment for camera-LiDAR system. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 64, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sidibé, D.; Morel, O.; Meriaudeau, F. Incorporating depth information into few-shot semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 3582–3588. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y. BMDENet: Bi-directional Modality Difference Elimination Network for Few-shot RGB-T Semantic Segmentation. In IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, A.; Bansal, S.; Liu, Z.; Essa, I.; Boots, B. One-shot learning for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.03410. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Wang, J.; Bao, Y.; Huang, L.; Yan, Y. A Novel Visible-Depth-Thermal Image Dataset of Salient Object Detection for Robotic Visual Perception. In IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, D.; Alonso, J.B.; Travieso, C.M.; Ferrer, M.A. Automatic scene calibration for detecting and tracking people using a single camera. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, S.S.; Rodrigues, N.; Zhou, A.; Miller, I.D.; Kumar, V.; Taylor, C.J. Pst900: Rgb-thermal calibration, dataset and segmentation network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 9441–9447. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Papanastasiou, G. Unsupervised image registration towards enhancing performance and explainability in cardiac and brain image analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jin, X.; Cao, H. SMRD: A Local Feature Descriptor for Multi-modal Image Registration. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Munich, Germany, 5–8 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Min, J.; Kang, D.; Cho, M. Hypercorrelation squeeze for few-shot segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 6941–6952. [Google Scholar]
- Balwant, M.K. A Review on Convolutional Neural Networks for Brain Tumor Segmentation: Methods, Datasets, Libraries, and Future Directions. IRBM 2022, 43, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.; Chong, K.T. Brainseg-net: Brain tumor mr image segmentation via enhanced encoder–decoder network. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Asis-Cruz, J.D.; Feng, X.; Wu, Y.; Kapse, K.; Largent, A.; Quistorff, J.; Lopez, C.; Wu, D.; Qing, K.; et al. Automated 3D fetal brain segmentation using an optimized deep learning approach. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 43, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Ryu, J.; Nizami, I.F.; Chong, K.T. RAAGR2-Net: A brain tumor segmentation network using parallel processing of multiple spatial frames. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, C. MR brain segmentation based on DE-ResUnet combining texture features and background knowledge. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 75, 103541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, A.; Ding, Z.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. Electrical thermal image semantic segmentation: Large-scale dataset and baseline. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswari, B.; Reeja, S.R. Thermal infrared image semantic segmentation for night-time driving scenes based on deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ding, Z.; Shi, T.; Tang, J. EdgeFormer: Edge-assisted transformer for thermal images semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering, Big Data, and Computer Technology (EIBDCT), Xishuangbanna, China, 6–8 January 2023; pp. 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y. CEKD: Cross-Modal Edge-Privileged Knowledge Distillation for Semantic Scene Understanding Using Only Thermal Images. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.K.; Saraswat, M. A novel fuzzy clustering based method for image segmentation in RGB-D images. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 111, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, N.; Han, J. ABMDRNet: Adaptive-weighted bi-directional modality difference reduction network for RGB-T semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2633–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Q.; Watanabe, K.; Karasawa, T.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5108–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Vertens, J.; Zürn, J.; Burgard, W. Heatnet: Bridging the day-night domain gap in semantic segmentation with thermal images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 8461–8468. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Gu, X.; Gu, X. MMNet: Multi-modal multi-stage network for RGB-T image semantic segmentation. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 5817–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Tao, D.; See, S.; Wang, G. Learning common and specific features for RGB-D semantic segmentation with deconvolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 664–679. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Zheng, L.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Z. Rednet: Residual encoder-decoder network for indoor rgb-d semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.01054. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Allibert, G.; Stolz, C.; Ma, C.; Demonceaux, C. Depth-adapted CNNs for RGB-D semantic segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.03939. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, G.; Liu, F.; Yao, R.; Shen, C. Canet: Class-agnostic segmentation networks with iterative refinement and attentive few-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5217–5226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, G.; Liu, F.; Guo, J.; Wu, Q.; Yao, R. Pyramid graph networks with connection attentions for region-based one-shot semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9587–9595. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Shu, M.; Yang, Z.; Li, R.; Jia, J. Prior guided feature enrichment network for few-shot segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 1050–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Jampani, V.; Sevilla-Lara, L.; Sun, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Adaptive prototype learning and allocation for few-shot segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8334–8343. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Cho, M. Integrative few-shot learning for classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 9979–9990. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Long, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C. Graph wavenet for deep spatial-temporal graph modeling. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.00121. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. NeurIPS 2019, 32, 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]

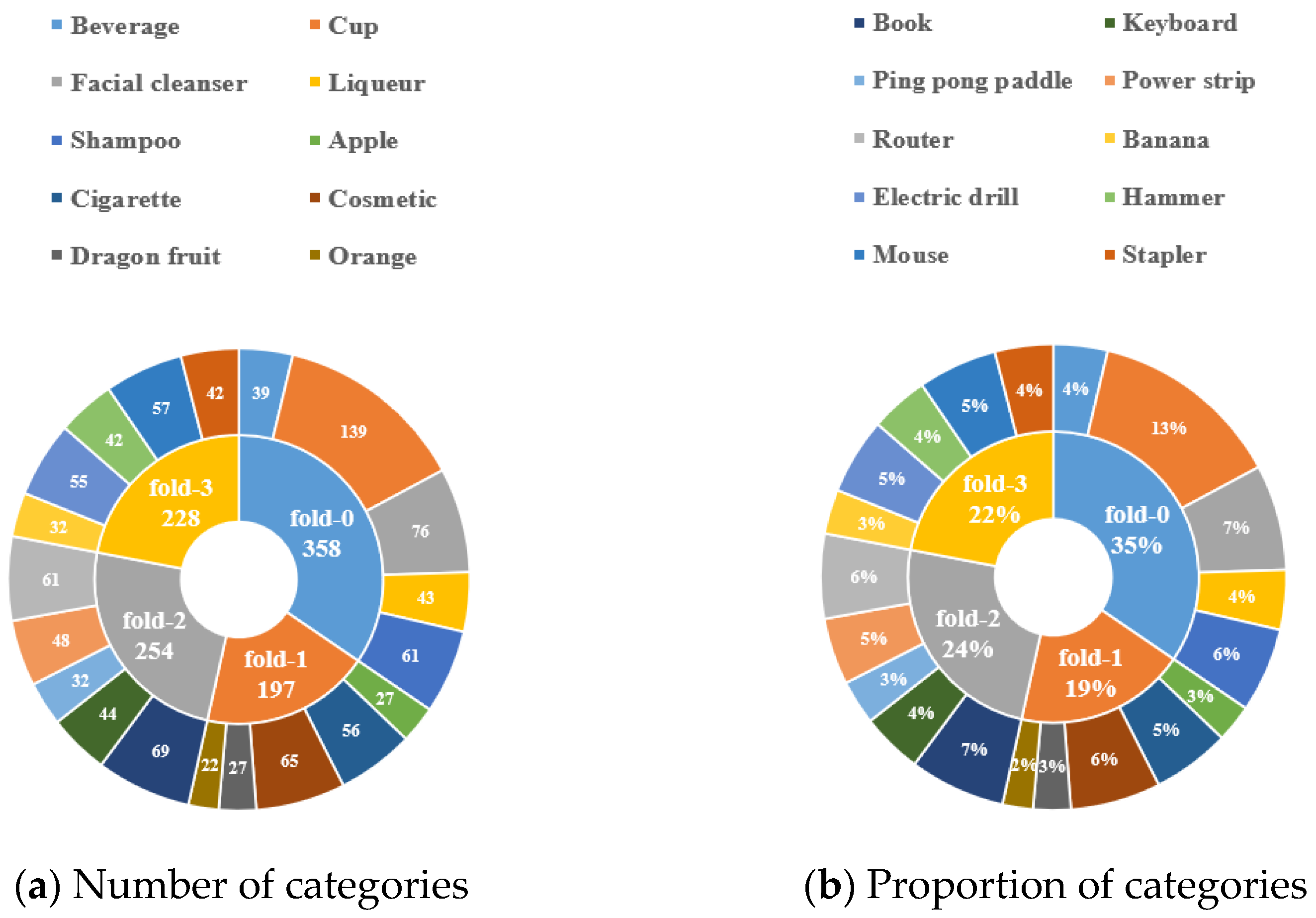

| Fold | Test Classes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold-0 | Beverage | Cup | Facial cleanser | Liqueur | Shampoo |
| Fold-1 | Apple | Cigarette | Cosmetic | Dragon fruit | Orange |
| Fold-2 | Book | Keyboard | Ping pong paddle | Power strip | Router |
| Fold-3 | Banana | Electric drill | Hammer | Mouse | Stapler |
| Method | 1-Way 1-Shot | 1-Way 5-Shot | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | mIoU | FB-IoU | 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | mIoU | FB-IoU | |
| CANet | 55.0 | 55.9 | 30.4 | 49.6 | 47.7 | 72.6 | 58.7 | 59.2 | 41.0 | 49.8 | 52.2 | 74.6 |
| PGNet | 54.2 | 56.4 | 33.6 | 45.2 | 47.4 | 71.8 | 59.7 | 59.7 | 34.4 | 48.5 | 50.5 | 73.7 |
| PFENet | 46.2 | 45.3 | 31.8 | 29.4 | 38.2 | 67.7 | 56.5 | 56.2 | 43.7 | 30.7 | 46.8 | 72.2 |
| ASGNet | 40.2 | 36.2 | 29.7 | 36.0 | 35.5 | 66.5 | 55.4 | 51.3 | 43.8 | 40.7 | 47.8 | 72.3 |
| V-TFSS | 55.6 | 53.5 | 31.0 | 29.4 | 42.4 | 72.6 | 60.6 | 57.3 | 45.2 | 48.5 | 52.9 | 75.2 |
| HSNet | 46.1 | 45.9 | 43.3 | 39.7 | 43.8 | 71.1 | 62.0 | 59.2 | 48.6 | 45.0 | 53.7 | 75.6 |
| ASNet | 62.9 | 57.4 | 41.0 | 41.9 | 50.8 | 73.8 | 68.5 | 64.2 | 48.9 | 48.5 | 57.5 | 76.1 |
| Ours | 68.9 | 58.2 | 49.8 | 41.3 | 54.6 | 75.8 | 74.9 | 62.2 | 58.9 | 47.2 | 60.8 | 78.9 |
| Method | Data | mIoU | FBIoU | Parameter (M) | Time (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single modality | RGB | 49.2 | 73.2 | 31 M | 25 FPS |
| Depth | 30.5 | 50.8 | 31 M | 25 FPS | |
| Thermal | 37.6 | 55.2 | 31 M | 25 FPS | |
| Two modalities | RGB-T | 51.2 | 74.5 | 42 M | 17 FPS |
| RGB-D | 52.2 | 75.1 | 42 M | 17 FPS | |
| Three modalities | RGB-D-T | 54.6 | 75.8 | 46 M | 14 FPS |
| Baseline | SE | SA | CA | 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | mIoU | FB-IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 46.1 | 45.9 | 43.3 | 39.7 | 43.8 | 71.1 | |||
| √ | √ | 61.7 | 55.9 | 49.3 | 40.3 | 51.8 | 74.3 | ||
| √ | √ | 54.3 | 49.7 | 48.5 | 39.6 | 48.0 | 72.3 | ||
| √ | √ | 57.3 | 50.7 | 48.8 | 39.9 | 49.2 | 73.3 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 54.0 | 56.7 | 49.0 | 41.8 | 50.4 | 73.3 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 65.5 | 57.0 | 50.0 | 37.7 | 52.4 | 74.9 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 64.0 | 56.3 | 52.1 | 37.5 | 52.5 | 74.9 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 68.9 | 58.2 | 49.8 | 41.3 | 54.6 | 75.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, K.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, Y. Self-Enhanced Mixed Attention Network for Three-Modal Images Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation. Sensors 2023, 23, 6612. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23146612
Song K, Zhang Y, Bao Y, Zhao Y, Yan Y. Self-Enhanced Mixed Attention Network for Three-Modal Images Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation. Sensors. 2023; 23(14):6612. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23146612
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Kechen, Yiming Zhang, Yanqi Bao, Ying Zhao, and Yunhui Yan. 2023. "Self-Enhanced Mixed Attention Network for Three-Modal Images Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation" Sensors 23, no. 14: 6612. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23146612
APA StyleSong, K., Zhang, Y., Bao, Y., Zhao, Y., & Yan, Y. (2023). Self-Enhanced Mixed Attention Network for Three-Modal Images Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation. Sensors, 23(14), 6612. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23146612







