Photo-Electro-Thermal Model and Fuzzy Adaptive PID Control for UV LEDs in Charge Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
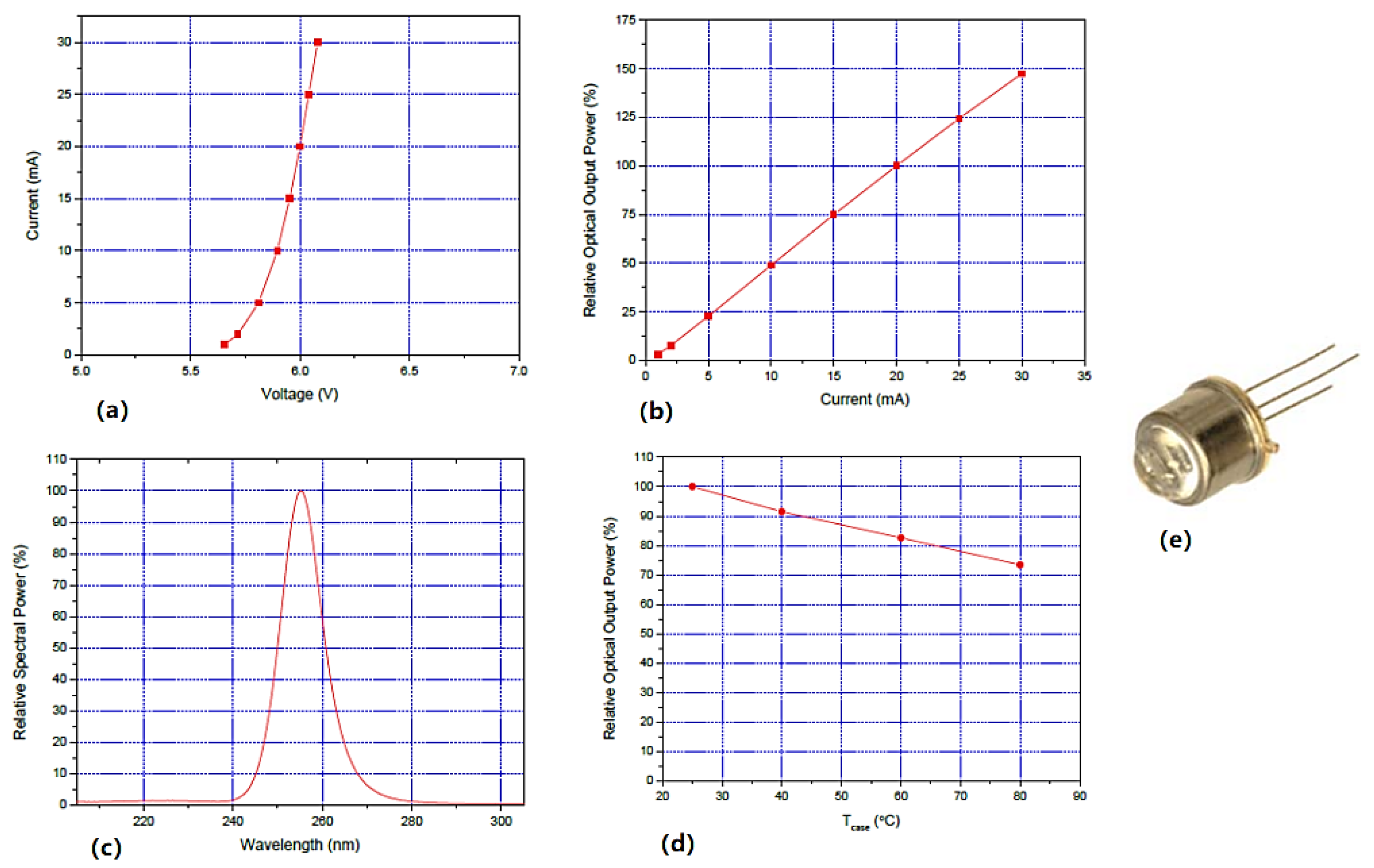
2. UV LEDs in Charge Management
3. Low-Power PET Model and Fuzzy Adaptive PID Controller Design
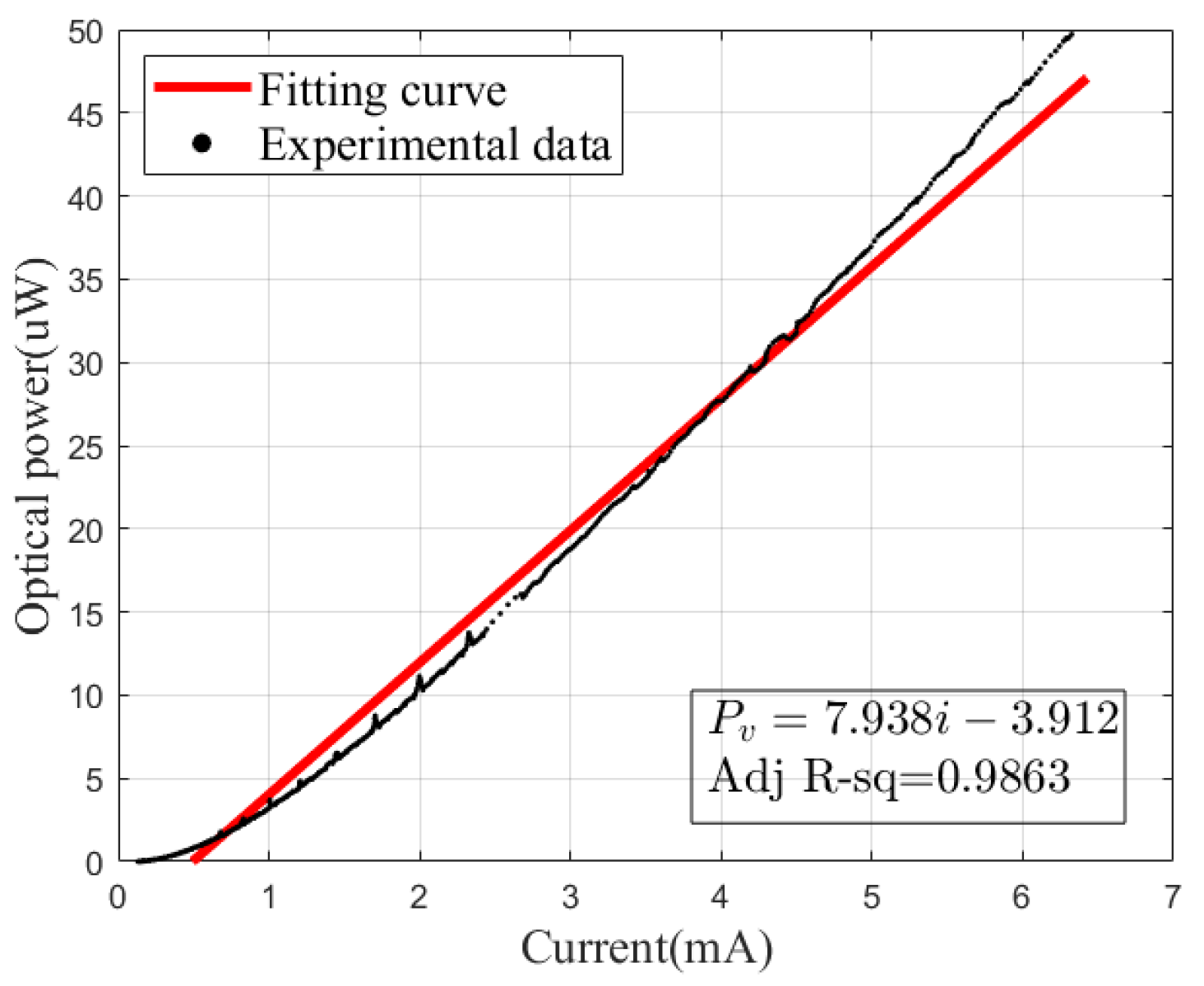
3.1. Low-Power PET Model of UV LEDs
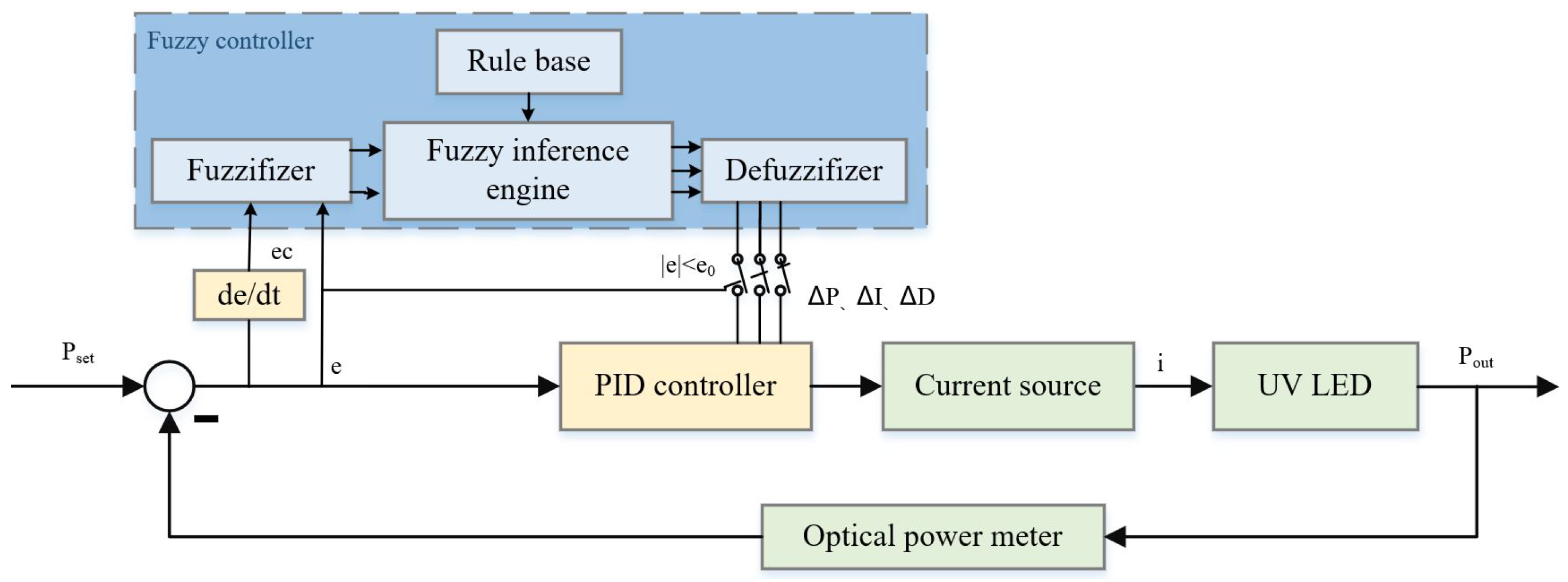
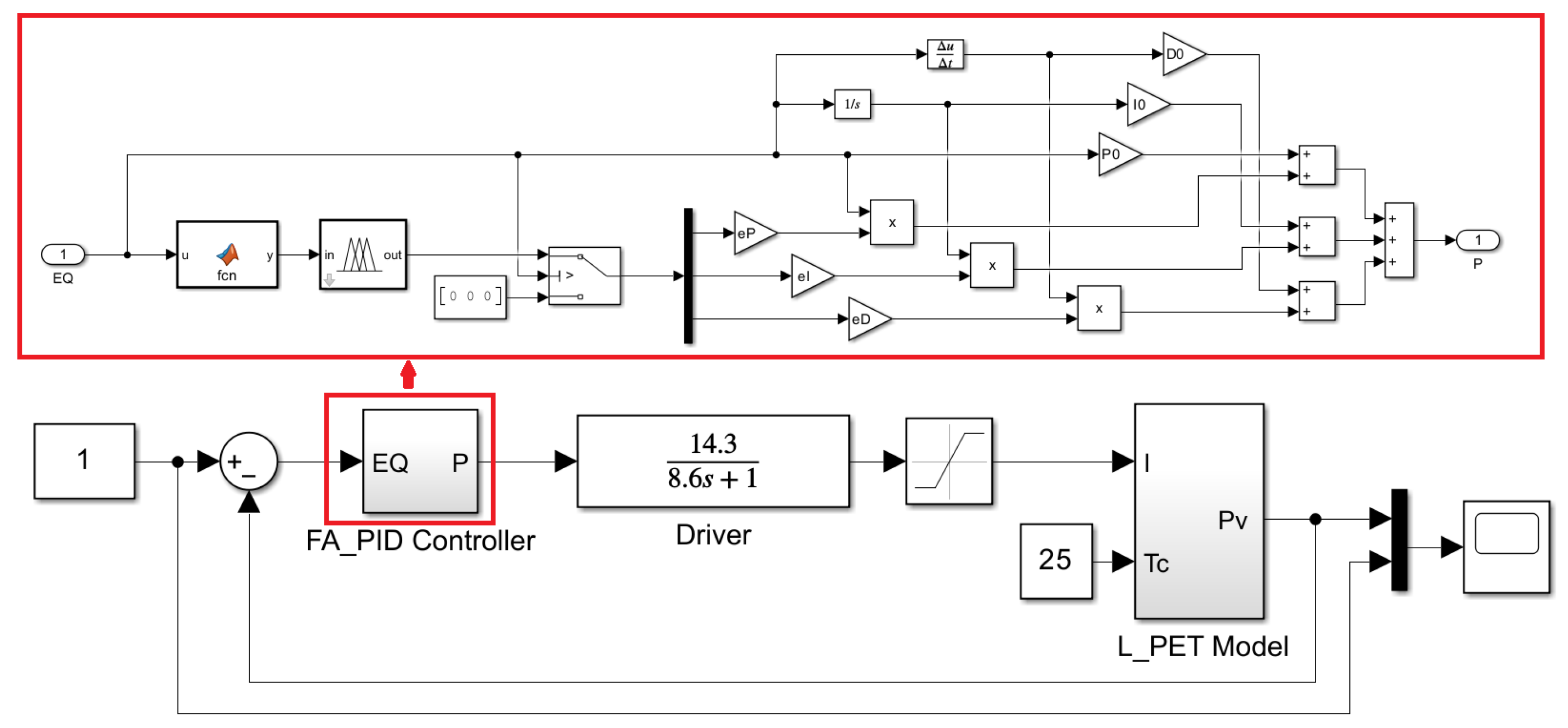
3.2. Design of Fuzzy Adaptive PID Controller
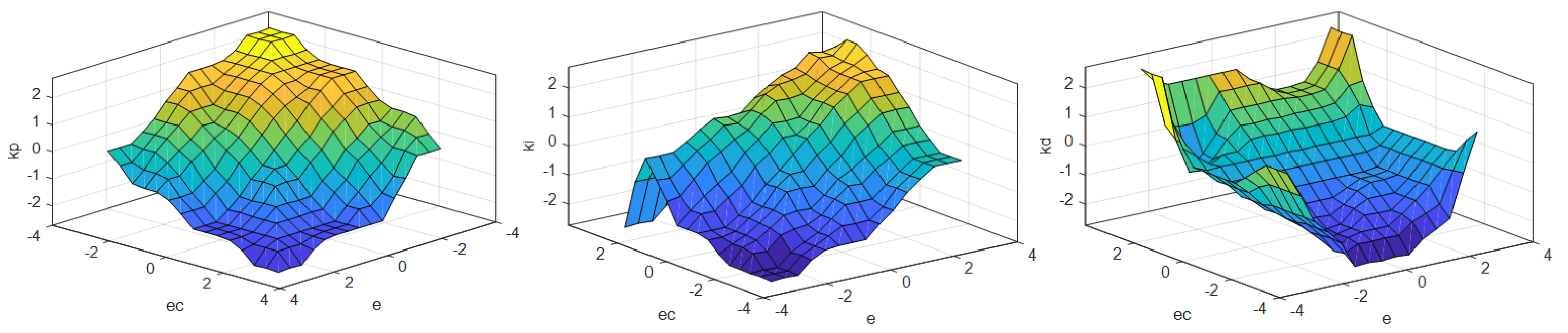
- When e is large, in order to eliminate the error as soon as possible and prevent the differential supersaturation that may be caused by the excessive moment of e, takes a large value, and and take a small value or zero.
- When e is small, in order to further eliminate the error and prevent the oscillation caused by excessive overshoot, should be reduced, should be small, and should be moderate to ensure the response speed of the system.
- When e is very small, in order to eliminate the static error and avoid oscillation near the set value, continues to decrease, remains unchanged or slightly larger, and can be slightly larger.
- The magnitude of indicates the rate of error changes. The larger the , the smaller the , the larger the , and vice versa.
- When e and have the same sign, the controlled variable deviates from the given value direction, and the control action should be strengthened to make the error change in the direction of reduction. Thus, a larger and a smaller should be taken, and should not be too large.
- When e and have different signs, the controlled variable changes in the direction close to the given value, so when e is large, take a smaller or zero to accelerate the dynamic process.
4. Results and Discussion
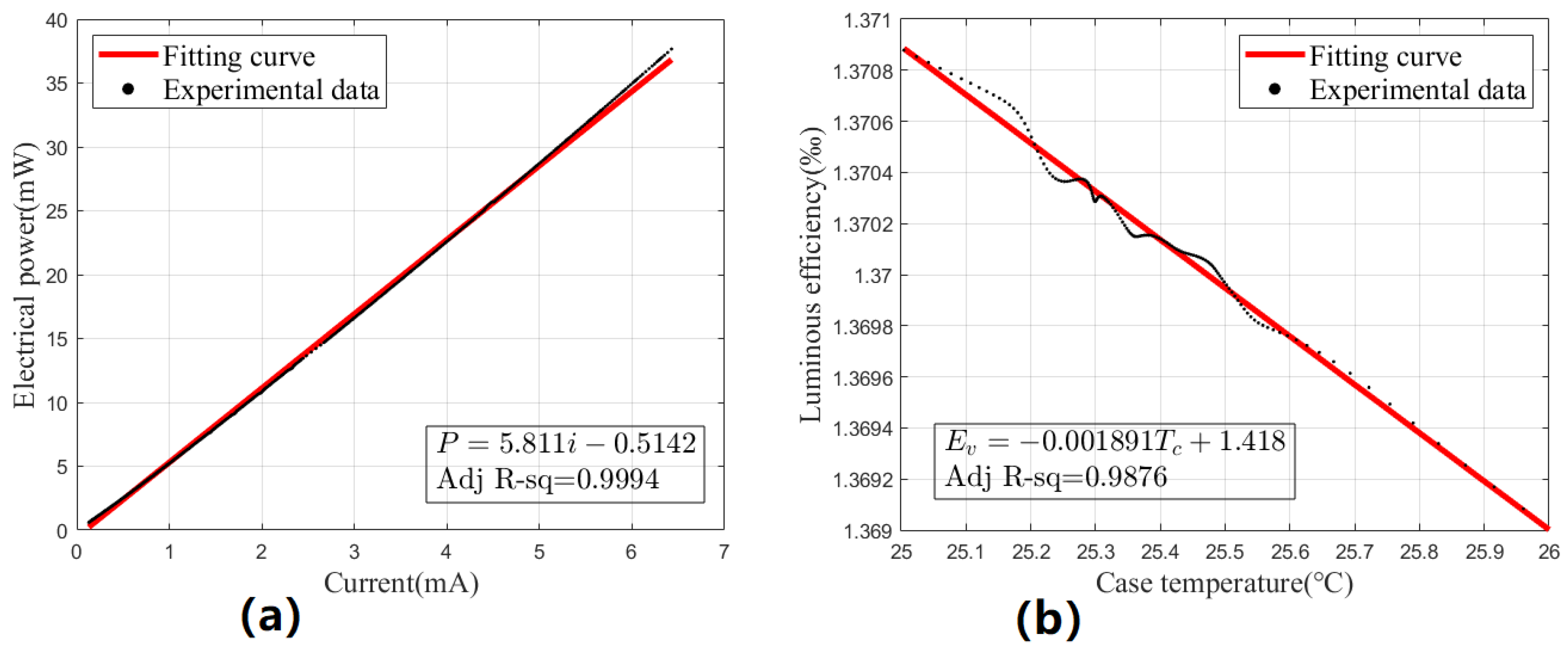
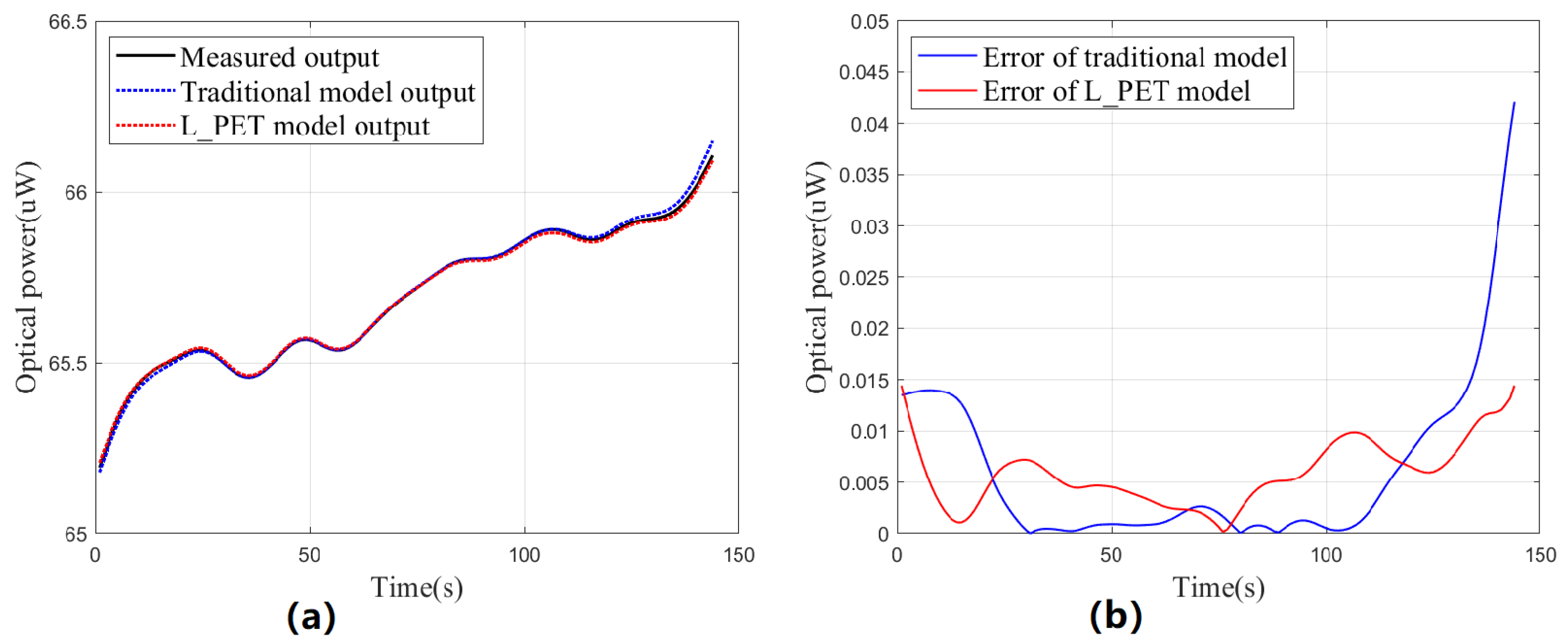
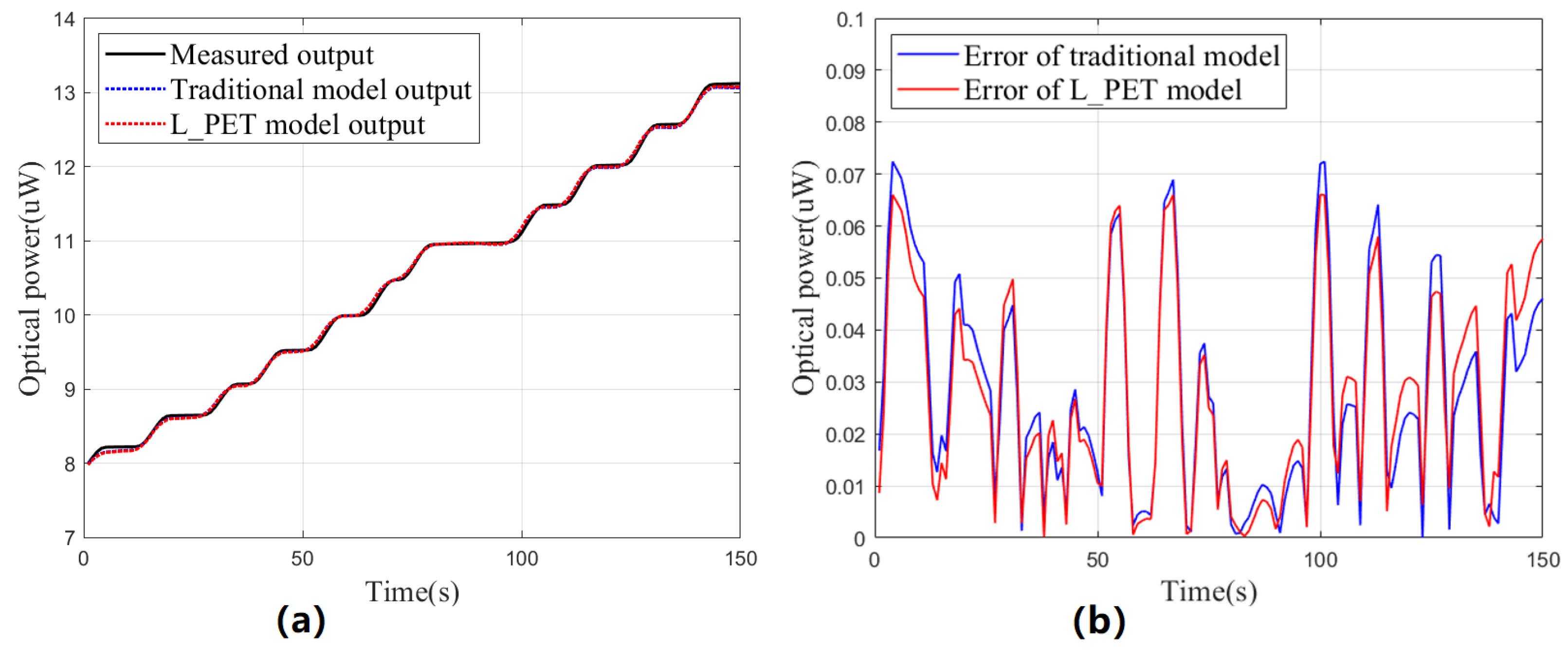
4.1. Modeling Low-Power PET Characteristics of UV LEDs
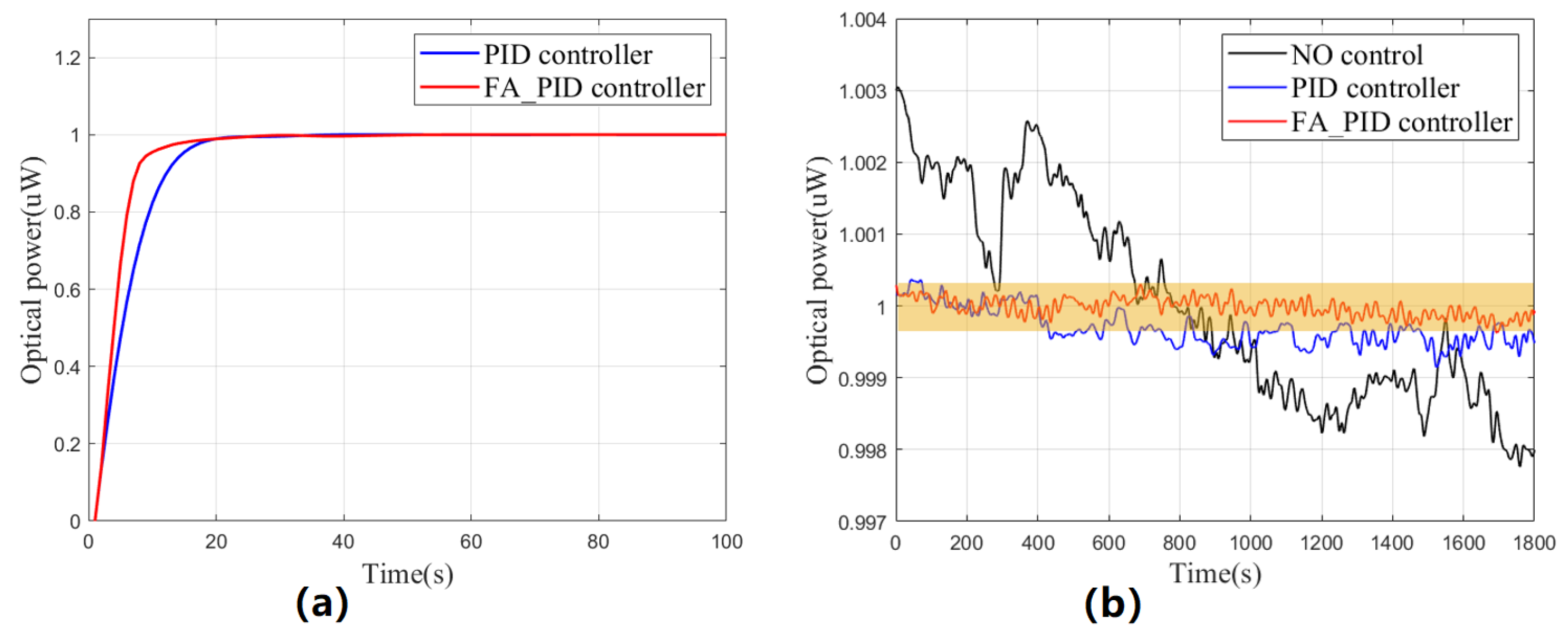
4.2. Results of the Optical Power Control System for UV LEDs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, W.; Jin, G. The Taiji program: A concise overview. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2021, 5, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimani, C.; Fabi, M.; Lobo, A.J.; Mateos, I.; Telloni, D. Role of GCR positive and negative particles in charging the LISA-PF test masses in 2015. J. Phys. Conf. 2015, 61, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimani, C.; Villani, M.; Fabi, M.; Cesarini, A.; Sabbatini, F. Bridging the gap between Monte Carlo simulations and measurements of the LISA Pathfinder test-mass charging for LISA. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 66, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Taiji Scientific Collaboration. China’s first step towards probing the expanding universe and the nature of gravity using a space borne gravitational wave antenna. Commun. Phys. 2021, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Armano, M.; Audley, H.; Baird, J.; Binetruy, P.; Born, M. Precision charge control for isolated free-falling test masses: LISA pathfinder results. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 6, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Saraf, S.; Lipa, J.; Yadav, D.; Buchman, S. Two approaches for the passive charge management of contactless test masses. Class. Quantum Gravity 2022, 19, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Luo, J. Continuous charge management scheme for TianQin. Class. Quantum Gravity 2023, 40, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunde, T.; Shelley, R.; Chilton, A.; Serra, P.; Ciani, G.; Mueller, G.; Conklin, J. 240 nm UV LEDs for LISA test mass charge control. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 61, 12–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letson, B.C.; Barke, S.; Kenyon, S.P.; Olatunde, T.; Mueller, G.; Wass, P.; Ren, F.; Pearton, S.J.; Conklin, J.W. High volume UV LED performance testing. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2022, 11, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollington, D.; Baird, J.T.; Sumner, T.J.; Wass, P.J. Characterising and testing deep UV LEDs for use in space applications. Class. Quantum Gravity 2015, 32, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollington, D.; Baird, J.T.; Sumner, T.J.; Wass, P.J. Lifetime testing UV LEDs for use in the LISA charge management system. Class. Quantum Gravity 2017, 34, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Yang, F.; Hong, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, Z. Coupling efficiency improvement of light source with a convex lens for space charge managements. Optik 2021, 248, 167999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.X.; Higuchi, S.; Goh, A.; Allard, B.; Byer, R. Spectral and Power Stability Tests of Deep UV LEDs for AC Charge Management. In Proceedings of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna: International Lisa Symposium, Greenbelt, MD, USA, 19–23 June 2006; pp. 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Bai, Y.; Hong, W.; Sumner, T.J.; Zhou, Z. A charge control method for space-mission inertial sensor using differential UV LED emission. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchauspé, H.; Olatunde, T.; Apple, S.; Parry, S.; Letson, B.; Turetta, N.; Mueller, G.; Wass, P.J.; Conklin, J.W. Numerical modeling and experimental demonstration of pulsed charge control for the space inertial sensor used in LISA. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 038–041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.C.; Hong, W.; Li, H.G.; Ma, D. Adaptive charge control for the space inertial sensor. Class. Quantum Gravity 2023, 40, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S.; Qin, Y.X. A General Photo-Electro-Thermal Theory for Light Emitting Diode (LED) Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Hui, S.Y.R. Dynamic Photoelectrothermal Theory for Light-Emitting Diode Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sheng, X.; Huang, X.; Lin, W. Study on the LED control strategy of constant luminous flux based on photoelectric model. In Proceedings of the China International Forum on Solid State Lighting, Beijing, China, 1–3 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Bian, H.; He, H.; Li, F. An Improved Differential Evolution Adaptive Fuzzy PID Control Method for Gravity Measurement Stable Platform. Sensors 2023, 23, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Y.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Lei, D.J.; Yao, M. An Adaptive Dimming System of High-Power LED Based on Fuzzy PID Control Algorithm for Machine Vision Lighting. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Electr Network, Chongqing, China, 12–14 June 2020; pp. 2198–2202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Gao, C.; Yin, X.; Jiang, N. The LED Lighting Control System of Railway Vehicle Design Based On The Fuzzy PID Algorithm. Control Eng. China 2014, 21, 882–890. [Google Scholar]
- Buchman, S.; Al Saud, T.S.M.; Alfauwaz, A.; Byer, R.I.; Klupar, P.; Lipa, J.; Lui, C.Y.; Saraf, S.; Wang, S.; Worden, P. Flight and ground demonstration of reproducibility and stability of photoelectric properties for passive charge management using LEDs. Class. Quantum Gravity 2023, 40, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, T.J.; Mueller, G.; Conklin, J.W.; Wass, P.J.; Hollington, D. Charge induced acceleration noise in the LISA gravitational reference sensor. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, T.; Bergner, P.; Hechenblaikner, G.; Brandt, N.; Fichter, W. Modeling and performance of contact-free discharge systems for space inertial sensors. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 1493–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, S.P.; Letson, B.; Clark, M.; Olatunde, T.; Ritten, L.; Schindler, J.; Wass, P.J.; Conklin, J.W.; Barke, S.; Mueller, G.; et al. A Charge Management System for Gravitational Reference Sensors – Design and Instrument Testing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Beijing, China, 6–13 March 2021; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.-X.; Allard, B.; Buchman, S.; Williams, S.; Byer, R.L. LED deep UV source for charge management of gravitational reference sensors. Class. Quantum Gravity 2006, 23, S141–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Lenka, T.R.; Talukdar, F.A.; Velpula, R.T.; Jain, B.; Nguyen, H.P.T. Performance Enhancement of AlInGaN Quantum Well based UV-LED. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th India Council International Conference (INDICON), Guwahati, India, 19–21 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Juárez, M.A.; Martínez, J.A.; Vázquez, G.; Sosa, J.M.; Martínez, P.R.; Villanueva, I.; Osorio, R. A model for electrical characteristics of high power UV LED. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Conference on Power Electronics (CIEP), Guanajuato, Mexico, 20–23 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.A.; LeBoeuf, S.F.; Stecher, T.E. Temperature-dependent electroluminescence of AlGaN-based UV LEDs. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2006, 27, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanlin, M.; Bulashevich, K. Critical aspects of deep-UV LED design and operation. In Proceedings of the 2022 19th China International Forum on Solid State Lighting & 2022 8th International Forum on Wide Bandgap Semiconductors (SSLCHINA: IFWS), Suzhou, China, 7–10 November 2023; 329–331. [Google Scholar]
- Apple, S.; Alvarez, A.D.; Kenyon, S.P.; Chilton, A.; Klein, D.; Bickerstaff, B.; Barke, S.; Clark, M.; Letson, B.; Olatunde, T.; et al. Design and performance characterization of a new LISA-like (laser interferometer space antenna-like) gravitational reference sensor and torsion pendulum testbed. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2023, 94, 05450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, K.; Dong, J. Optimization of a Fuzzy PID Controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electric and Electronics, Bursa, Turkey, 1–4 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, C.-T.; Sutarna, N.; Chiou, J.-S.; Wang, C.-J. An Optimal Fuzzy PID Controller Design Based on Conventional PID Control and Nonlinear Factors. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Lei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F. PID control of the mechanical legs based on fuzzy adaptive. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Shenyang, China, 8–12 June 2015; pp. 1965–1970. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Su, W.; Liu, Z. PID controllers: Design and tuning methods. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 9th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Hangzhou, China, 9–11 June 2014; pp. 808–813. [Google Scholar]



| E | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PB | ||
| EC | NB | PB | PB | PM | PM | PS | ZO | ZO |
| NM | PB | PB | PM | PS | PS | ZO | NS | |
| NS | PM | PM | PM | PS | ZO | NS | NS | |
| ZO | PM | PM | PS | ZO | NS | NM | NM | |
| PS | PS | PS | ZO | NS | NS | NM | NM | |
| PM | PS | ZO | NS | NM | NM | NM | NB | |
| PB | ZO | ZO | NM | NM | NM | NB | NB | |
| E | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PB | ||
| EC | NB | NB | NB | NM | NM | NS | ZO | ZO |
| NM | NB | NB | NM | NS | NS | ZO | ZO | |
| NS | NB | NM | NS | NS | ZO | PS | PS | |
| ZO | NM | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PM | |
| PS | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PS | PM | PB | |
| PM | ZO | ZO | PS | PS | PM | PB | PB | |
| PB | NB | NB | NM | NM | NS | ZO | ZO | |
| E | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PB | ||
| EC | NB | PS | NS | NB | NB | NB | NM | PS |
| NM | PS | NS | NB | NM | NM | NS | ZO | |
| NS | ZO | NS | NM | NM | NS | NS | ZO | |
| ZO | ZO | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ZO | |
| PS | ZO | ZO | ZO | ZO | ZO | ZO | ZO | |
| PM | PB | NS | PS | PS | PS | PS | PB | |
| PB | PB | PM | PM | PM | PS | PS | PB | |
| Model | Maximum (nW) | Mean (nW) | SD (nW) | IAE (uW) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steady-state test | Traditional | 42.1062 | 5.9819 | 8.1184 | 0.8614 |
| L_PET | 14.4455 | 5.8485 | 3.1558 | 0.8322 | |
| Dynamic test | Traditional | 72.4263 | 27.8624 | 20.0623 | 4.1794 |
| L_PET | 66.0562 | 27.7786 | 19.3699 | 4.1668 |
| Parameter | Meaning | Value |
|---|---|---|
| , , | Initial parameters of PID | 125.087, 0.035, 0.007 |
| , , | Output scaling factor | 1, 0.01, 10 |
| Switching threshold | 0.1 |
| Controller | Range (nW) | Mean (uW) | SD (nW) | IQR (nW) | IAE (uW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO control | 5.2870 | 1.0000 | 1.4080 | 2.5486 | 2.2284 |
| PID | 1.2234 | 0.9997 | 0.2528 | 0.3113 | 0.6391 |
| FA_PID | 0.6731 | 1.0000 | 0.1287 | 0.1987 | 0.1957 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Photo-Electro-Thermal Model and Fuzzy Adaptive PID Control for UV LEDs in Charge Management. Sensors 2023, 23, 5946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135946
Wang Y, Yu T, Wang Z, Liu Y. Photo-Electro-Thermal Model and Fuzzy Adaptive PID Control for UV LEDs in Charge Management. Sensors. 2023; 23(13):5946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135946
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuhua, Tao Yu, Zhi Wang, and Yang Liu. 2023. "Photo-Electro-Thermal Model and Fuzzy Adaptive PID Control for UV LEDs in Charge Management" Sensors 23, no. 13: 5946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135946
APA StyleWang, Y., Yu, T., Wang, Z., & Liu, Y. (2023). Photo-Electro-Thermal Model and Fuzzy Adaptive PID Control for UV LEDs in Charge Management. Sensors, 23(13), 5946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135946







