CNN–LSTM Neural Network for Identification of Pre-Cooked Pasta Products in Different Physical States Using Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel deep-learning model combined with IR spectroscopy is proposed for the identification of Italian pasta products.
- Compared with the CNN, LSTM, SVM, DT, plain Bayesian (NB), and K-nearest neighbor (KNN), our model achieves the highest performance.
- This paper analyzes the classification performance of deep learning in the thawed state outperforming the frozen state.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets and Sample Partition
2.2. Spectra Standardization and PCA
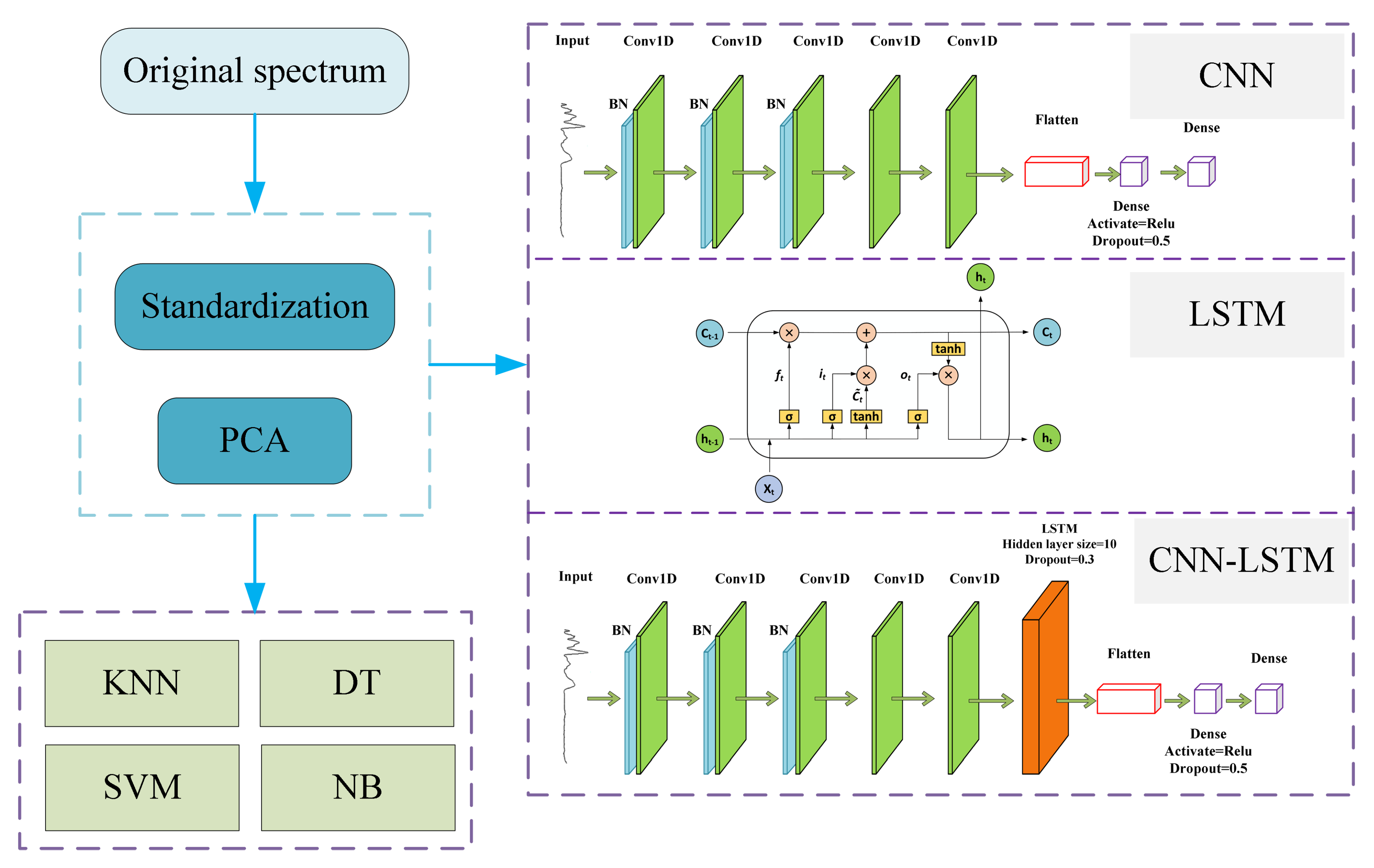
2.3. Hybrid 1D-CNN and LSTM Neural Network Model Development
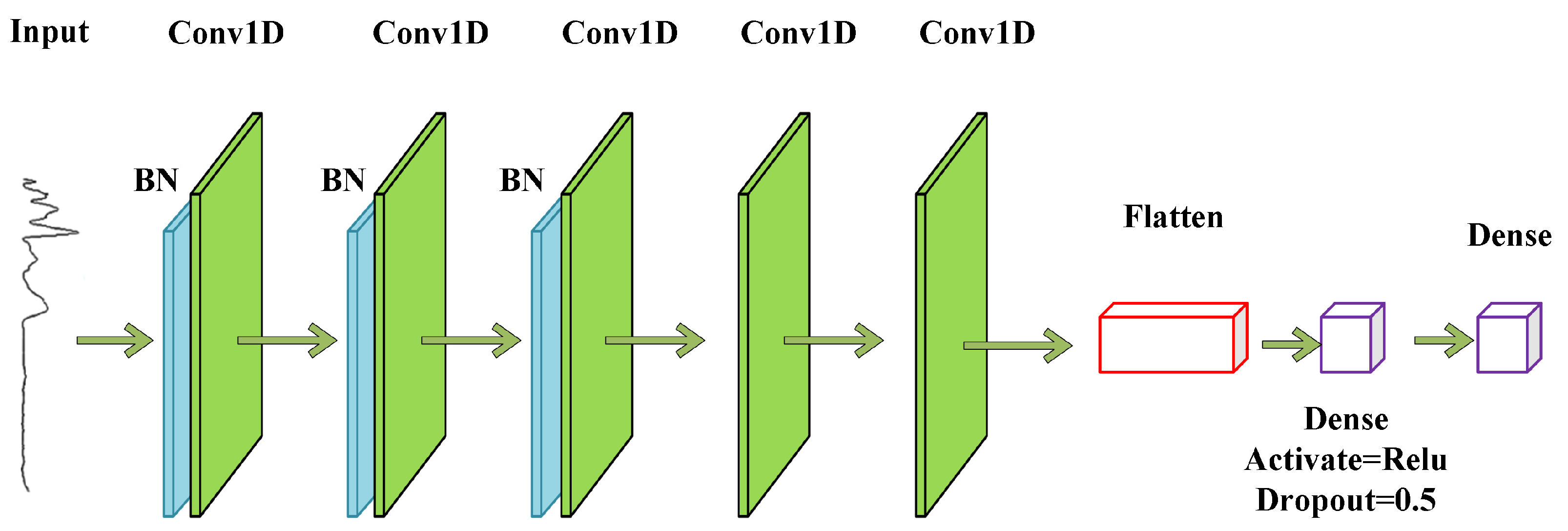
2.3.1. 1D-CNN
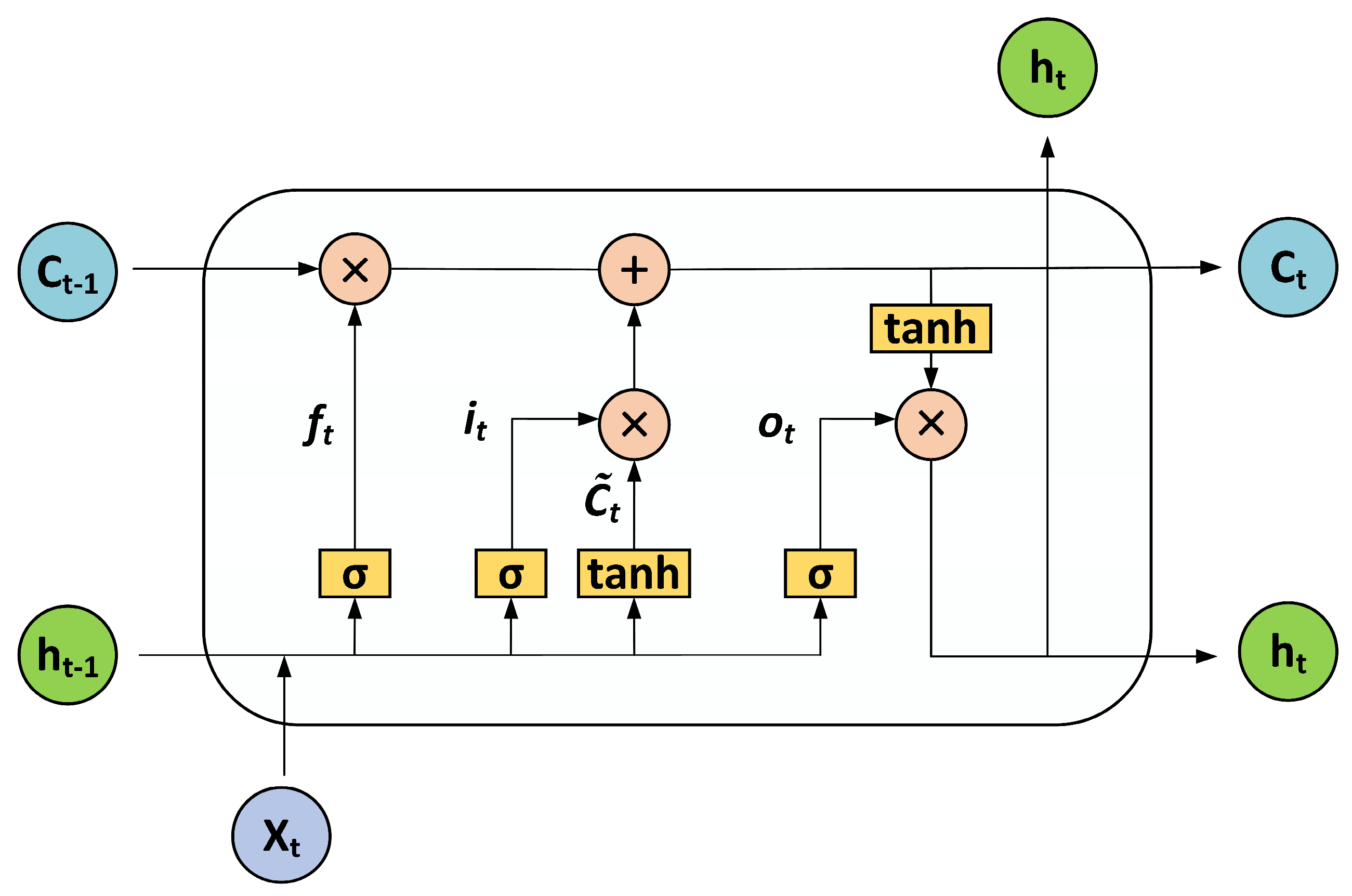
2.3.2. LSTM
2.4. Model Evaluation Indexes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Subsection
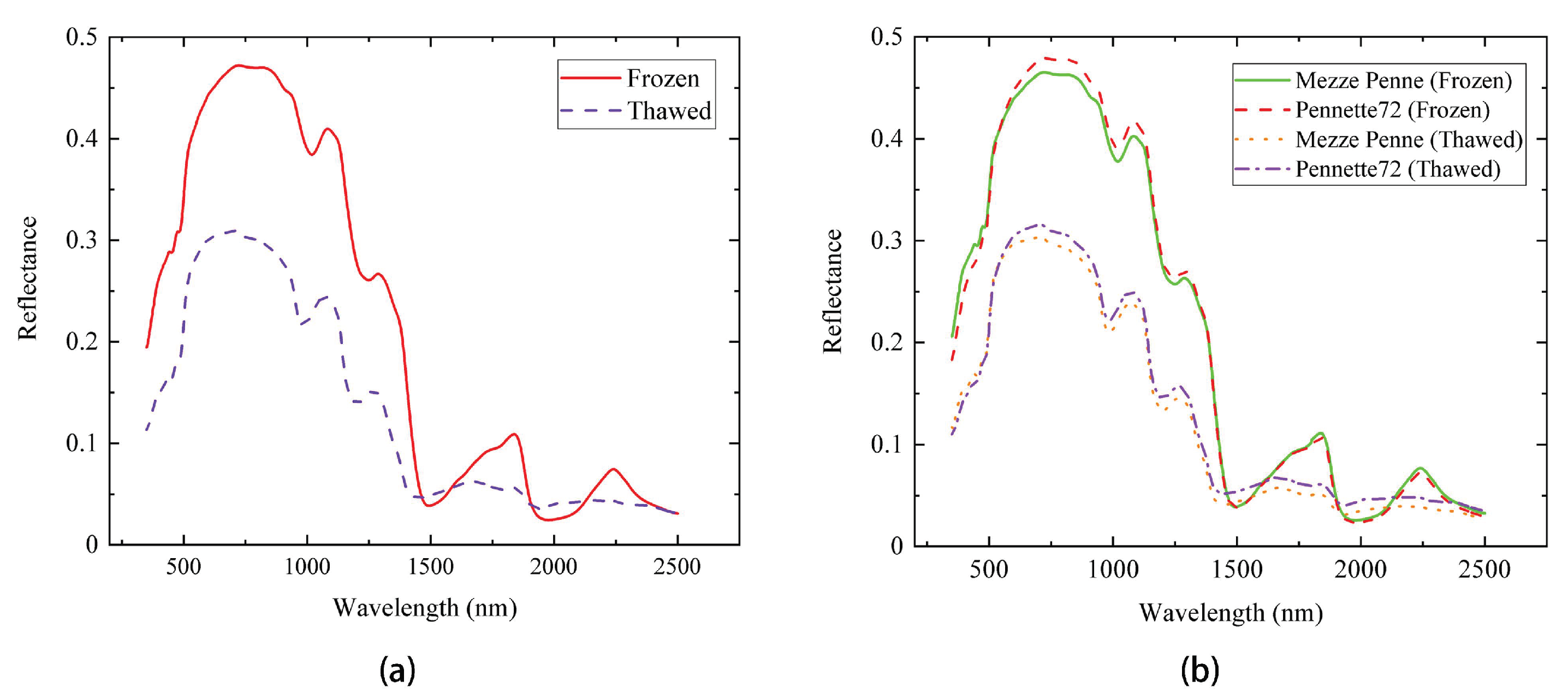
3.2. Spectral Analysis Result Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonifazi, G.; Capobianco, G.; Gasbarrone, R.; Serranti, S. Cold Chain Maintenance Evaluation of Pre-Cooked Pasta by Visible and Short Wave InfraRed Spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electrical, Communication, and Computer Engineering (ICECCE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–13 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://internationalpasta.org/news/pasta-world-consumption-boom-since-the-lockdown-started-1-consumer-out-of-4-ate-more-25-export-increase-in-6-months/#:~:text=16.10.2020- (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Jachimowicz, K.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A.; Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Bąkowski, M. Pasta as a Source of Minerals in the Diets of Poles; Effect of Culinary Processing of Pasta on the Content of Minerals. Foods 2021, 10, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melini, V.; Melini, F.; Acquistucci, R. Phenolic compounds and bioaccessibility thereof in functional pasta. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, F.S.; Brand-Miller, J.C.; Foster-Powell, K.; Buyken, A.E.; Goletzke, J. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values 2021: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardetto, S. Potential applications of near infrared spectroscopy for evaluating thermal treatments of fresh egg pasta. Food Control. 2005, 16, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, F.; Benning, R.; Bindrich, U.; Franke, K.; Heinz, V.; Delgado, A. Optical online measurement technique used for process control of the drying step during pasta production. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, M.; Bucci, R.; Materazzi, S.; Marini, F. Application of near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy coupled to chemometrics for dried egg-pasta characterization and egg content quantification. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Lu, R.; Chen, Y.; Fu, K.; Song, J.; Xie, L.; Zhai, R.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Xu, L. Nondestructive testing of pear based on Fourier near-infrared spectroscopy. Foods 2022, 11, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Hu, Z.; Wei, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Guan, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Fu, H. Accurate identification of the geographical origins of lily using near-infrared spectroscopy combined with carbon dot-tetramethoxyporphyrin nanocomposite and chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2022, 271, 120932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, A.C.; Dalmolin, R.S.D.; Grunwald, S.; ten Caten, A.; Pereira Filho, W. Two preprocessing techniques to reduce model covariables in soil property predictions by Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 172, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, W.; De-la-Torre, M.; Avila-George, H.; Torres-Jimenez, J.; Guivin, A.; Acevedo-Juárez, B. Amazonian cacao-clone nibs discrimination using NIR spectroscopy coupled to naïve Bayes classifier and a new waveband selection approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2022, 270, 120815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H. Classification of tea quality levels using near-infrared spectroscopy based on CLPSO-SVM. Foods 2022, 11, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Sohng, W.; Cha, K.; Chung, H. A weighted twin support vector machine as a potential discriminant analysis tool and evaluation of its performance for near-infrared spectroscopic discrimination of the geographical origins of diverse agricultural products. Talanta 2022, 237, 122973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Guo, M.; Pu, F.; Wang, H. Rapid identification of lamb freshness grades using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy (Vis-NIR). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 111, 104590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Mouazen, A. On-line vis-NIR spectroscopy prediction of soil organic carbon using machine learning. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wei, Y.; Duan, H.; Xi, L.; Wu, X. Discrimination of the geographical origin of Codonopsis pilosula using near infrared diffuse reflection spectroscopy coupled with random forests and k-nearest neighbor methods. Vib. Spectrosc. 2012, 62, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandak, J.; Niemz, P.; Hänsel, A.; Mai, J.; Sandak, A. Feasibility of portable NIR spectrometer for quality assurance in glue-laminated timber production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 308, 125026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Feng, J.; Yang, L.; Xing, J.; Pan, G.; Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, C.; Jiang, Y. Combination of NIR spectroscopy and algorithms for rapid differentiation between one-year and two-year stored rice. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2023, 291, 122343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Gao, Z.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Rapid detection of volatile compounds in apple wines using FT-NIR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, F.; Olivieri, A.C. An integrated approach to the simultaneous selection of variables, mathematical pre-processing and calibration samples in partial least-squares multivariate calibration. Talanta 2013, 115, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasi, S.; Minaei, S.; Jamshidi, B.; Fathi, D.; Khoshtaghaza, M.H. Rapid measurement of apple quality parameters using wavelet de-noising transform with Vis/NIR analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 252, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Wang, X. Hybrid 1D-CNN and attention-based Bi-GRU neural networks for predicting moisture content of sand gravel using NIR spectroscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravartula, S.S.N.; Moscetti, R.; Bedini, G.; Nardella, M.; Massantini, R. Use of convolutional neural network (CNN) combined with FT-NIR spectroscopy to predict food adulteration: A case study on coffee. Food Control. 2022, 135, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Chen, E.; Zheng, T.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X. Blended fabric with integrated neural network based on attention mechanism qualitative identification method of near infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2022, 276, 121214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, R.; Niu, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, H. Total synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with deep learning to rapidly identify the authenticity of sesame oil. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2021, 244, 118841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, R.; Zhangzhong, L. Deep neural networks for the classification of pure and impure strawberry purees. Sensors 2020, 20, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, B.; Si, R.; Chen, C.; Chen, F.; Gao, R.; Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Lv, X. Fast detection of cumin and fennel using NIR spectroscopy combined with deep learning algorithms. Optik 2021, 242, 167080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, F.; Du, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, B.; Zuo, E.; Xiao, M.; Lv, X. Raman spectroscopy and FTIR spectroscopy fusion technology combined with deep learning: A novel cancer prediction method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2023, 285, 121839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifazi, G.; Gasbarrone, R.; Capobianco, G.; Serranti, S. A dataset of visible–Short wave InfraRed reflectance spectra collected on pre-cooked pasta products. Data Brief 2021, 36, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/ (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Chen, T.; Ma, L.; Tang, Z.; Yu, L.X. Identification of coumarin-based food additives using terahertz spectroscopy combined with manifold learning and improved support vector machine. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Mao, L.; Kan, J. Application of terahertz spectroscopy and chemometrics for discrimination of transgenic camellia oil. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2019, 206, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mao, X.; Chen, L. Speech emotion recognition using deep 1D & 2D CNN LSTM networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2019, 47, 312–323. [Google Scholar]
- Alayba, A.M.; Palade, V.; England, M.; Iqbal, R. A combined CNN and LSTM model for Arabic sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction: Second IFIP TC 5, TC 8/WG 8.4, 8.9, TC 12/WG 12.9 International Cross-Domain Conference, CD-MAKE 2018, Hamburg, Germany, 27–30 August 2018; Proceedings 2. pp. 179–191. [Google Scholar]
- Borovkova, S.; Tsiamas, I. An ensemble of LSTM neural networks for high-frequency stock market classification. J. Forecast. 2019, 38, 600–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Qin, L. A CNN-BiLSTM-AM method for stock price prediction. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 4741–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-Y.; Cho, S.-B. Predicting residential energy consumption using CNN-LSTM neural networks. Energy 2019, 182, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Liao, J.; Yang, J.; Sun, W.; Nong, M.; Li, F. Multi-hour and multi-site air quality index forecasting in Beijing using CNN, LSTM, CNN-LSTM, and spatiotemporal clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 169, 114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lam, J.C.; Li, V.O.; Han, Y. Deep-AIR: A hybrid CNN-LSTM framework forFine-grained air pollution forecast. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.11957. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Singh, S.K.; Tavakkoli, M.; Amiri, N.; Yang, Y.; Karami, M.A.; Rai, R. CNN-LSTM deep learning architecture for computer vision-based modal frequency detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. Acm 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

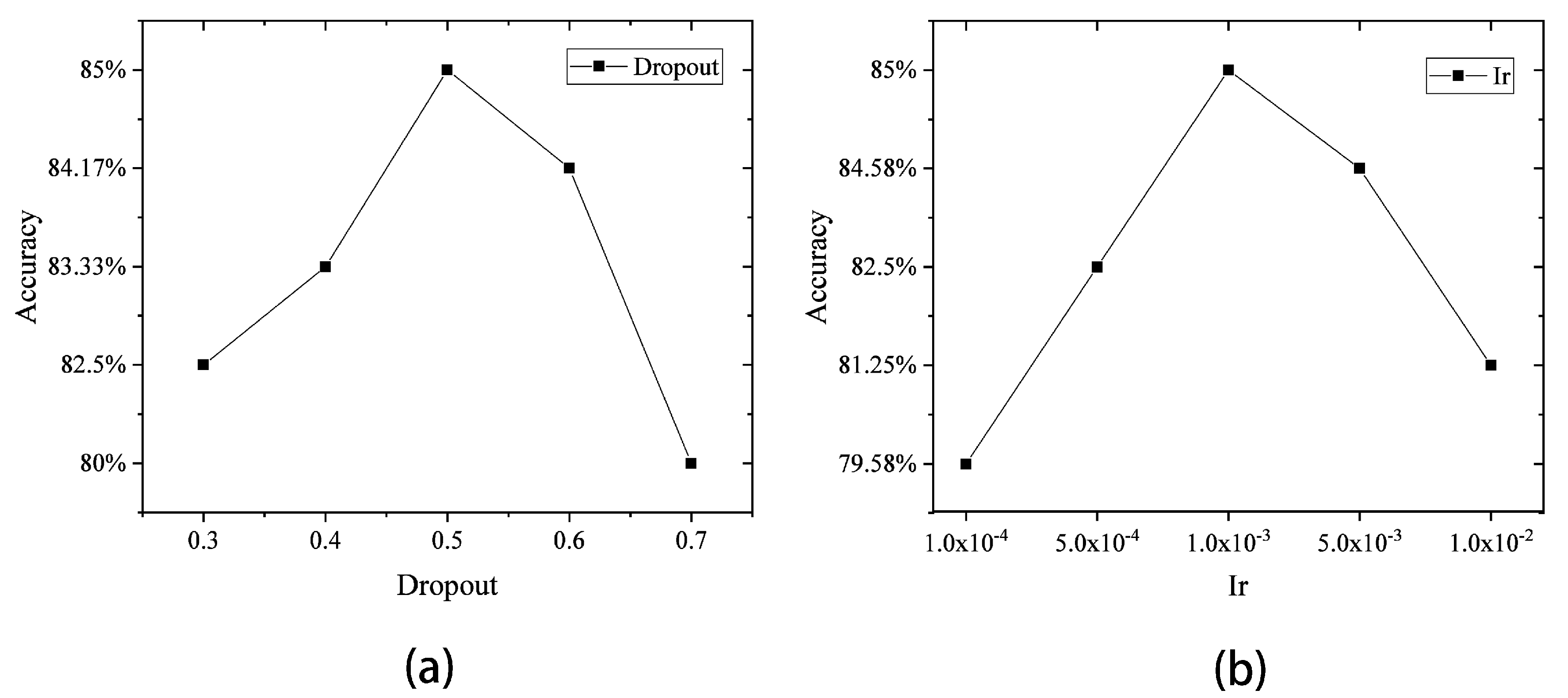
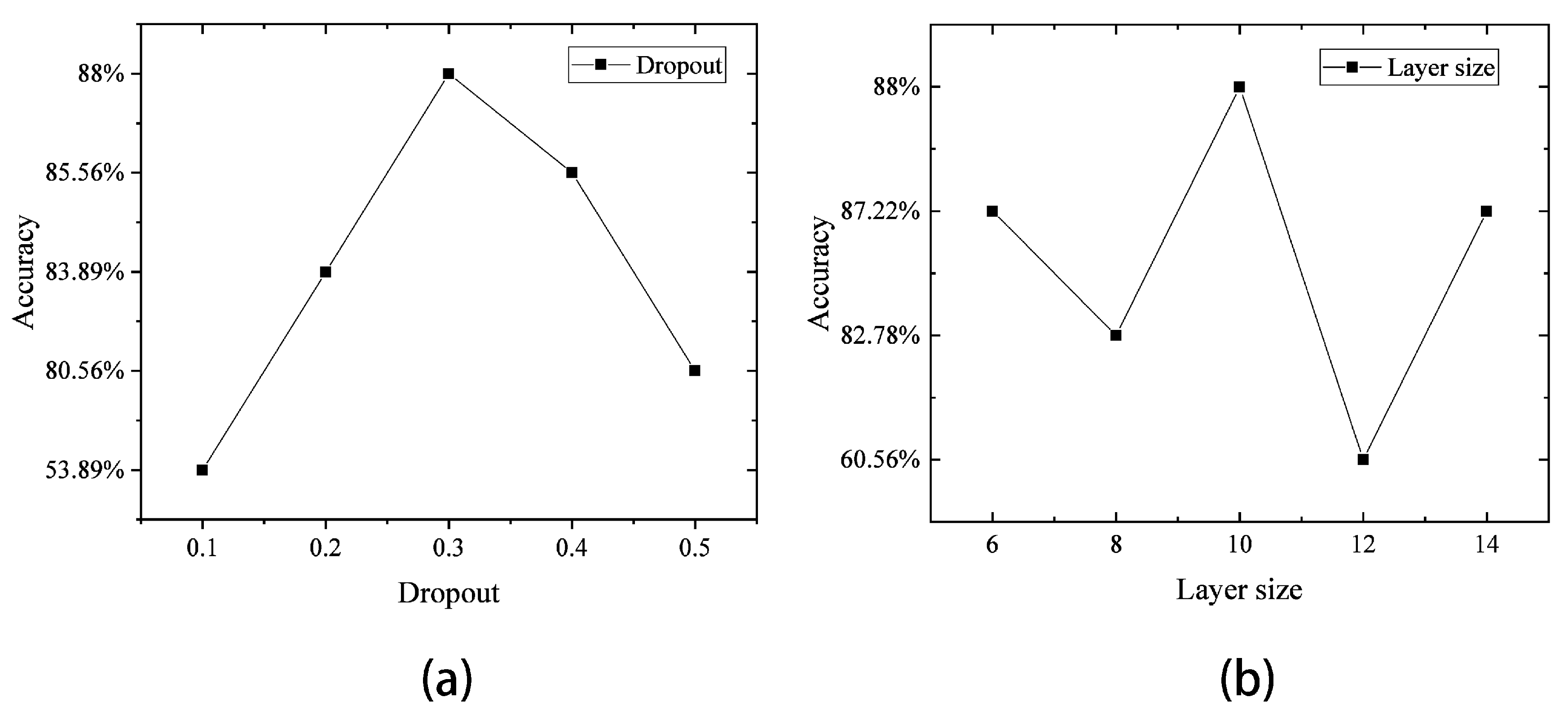
| Physical Condition | Training Samples | Testing Samples | Variables | Classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frozen pasta | 420 | 180 | 2151 | 2 |
| Thawed pasta | 420 | 180 | 2151 | 2 |
| Operator | Filters | Kernel Size | Strides |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conv1D | 64 | 11 | 4 |
| 64 | 5 | 1 | |
| 92 | 3 | 1 | |
| 92 | 3 | 1 | |
| 64 | 3 | 1 |
| Model | Physical Condition | Raw | Standardization | PCA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | Frozen | 72.67% | 80.44% | 72.67% |
| Thawed | 75.17% | 75.72% | 75.17% | |
| DT | Frozen | 76.39% | 85.17% | 86.39% |
| Thawed | 76.50% | 76.61% | 88.56% | |
| NB | Frozen | 52.94% | 94.39% | 94.5% |
| Thawed | 69.44% | 69.44% | 98.67% | |
| SVM | Frozen | 70.28% | 83.50% | 80.78% |
| Thawed | 74.44% | 81.22% | 77.78% | |
| Alexnet | Frozen | - | 99.17% | 95.56% |
| Thawed | - | 96.67% | 97.77% | |
| CNN | Frozen | 85.41% | 96.11% | 98.33% |
| Thawed | 80% | 97.78% | 100% | |
| Alexnet–LSTM | Frozen | - | 98.75% | 96.11% |
| Thawed | - | 97.22% | 98.82% | |
| CNN–LSTM | Frozen | 84.58% | 99.44% | 99.44% |
| Thawed | 80% | 99.44% | 100% |
| Data Processing | Model | Physical Condition | ACC | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardization | CNN | Frozen | 96.11% | 96.21% | 96.05% | 96.10% |
| Thawed | 97.78% | 97.94% | 97.70% | 97.77% | ||
| LSTM | Frozen | 88.33% | 88.33% | 88.38% | 88.33% | |
| Thawed | 92.78% | 93.27% | 92.97% | 92.77% | ||
| CNN–LSTM | Frozen | 99.44% | 99.43% | 99.46% | 99.44% | |
| Thawed | 99.44% | 99.47% | 99.43% | 99.44% | ||
| PCA | CNN | Frozen | 98.33% | 98.33% | 98.39% | 98.33% |
| Thawed | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | ||
| LSTM | Frozen | 96.11% | 96.10% | 96.13% | 96.11% | |
| Thawed | 91.06% | 91.42% | 91.27% | 91.59% | ||
| CNN–LSTM | Frozen | 99.44% | 99.47% | 99.43% | 99.44% | |
| Thawed | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Dong, Z. CNN–LSTM Neural Network for Identification of Pre-Cooked Pasta Products in Different Physical States Using Infrared Spectroscopy. Sensors 2023, 23, 4815. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104815
Sun P, Wang J, Dong Z. CNN–LSTM Neural Network for Identification of Pre-Cooked Pasta Products in Different Physical States Using Infrared Spectroscopy. Sensors. 2023; 23(10):4815. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104815
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Penghui, Jiajia Wang, and Zhilin Dong. 2023. "CNN–LSTM Neural Network for Identification of Pre-Cooked Pasta Products in Different Physical States Using Infrared Spectroscopy" Sensors 23, no. 10: 4815. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104815
APA StyleSun, P., Wang, J., & Dong, Z. (2023). CNN–LSTM Neural Network for Identification of Pre-Cooked Pasta Products in Different Physical States Using Infrared Spectroscopy. Sensors, 23(10), 4815. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104815





