Influence of Multimodal Emotional Stimulations on Brain Activity: An Electroencephalographic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.1.1. Participant Information
2.1.2. Emotional Stimulus
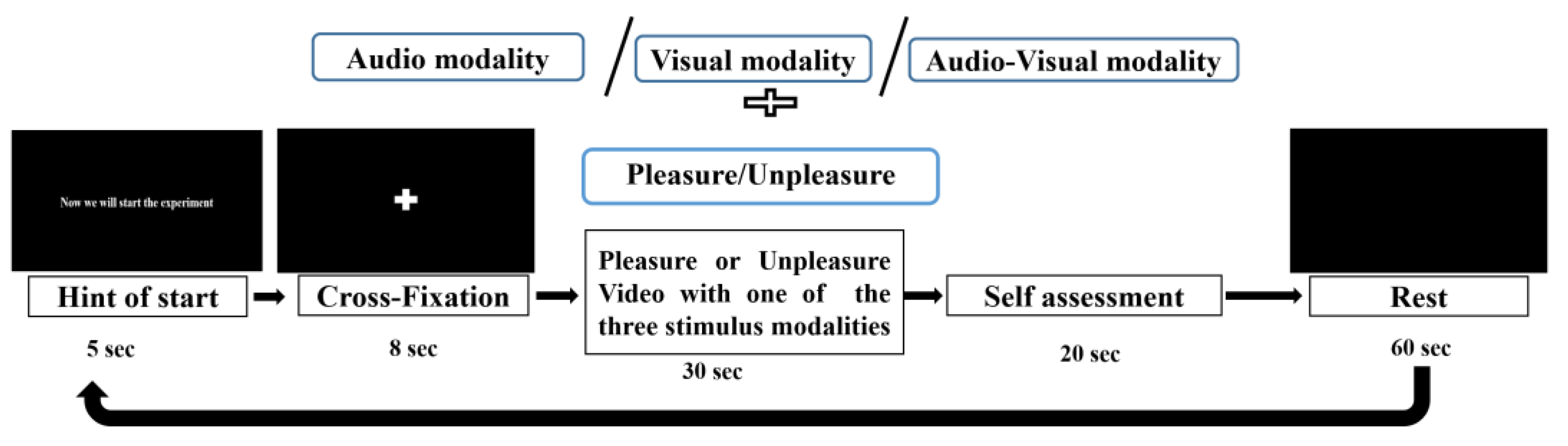
2.1.3. Experimental Protocol
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.1. EEG Data Acquisition
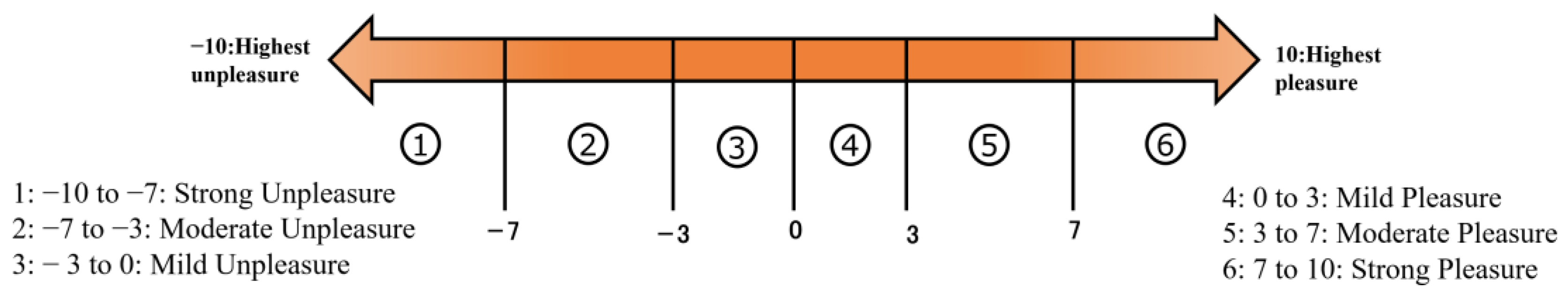
2.2.2. Self-Assessment Data
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. EEG Data Preprocessing
2.3.2. Power Spectral Density (PSD) Analysis of EEG
EEG Spectral Analysis
EEG Functional Brain Mapping
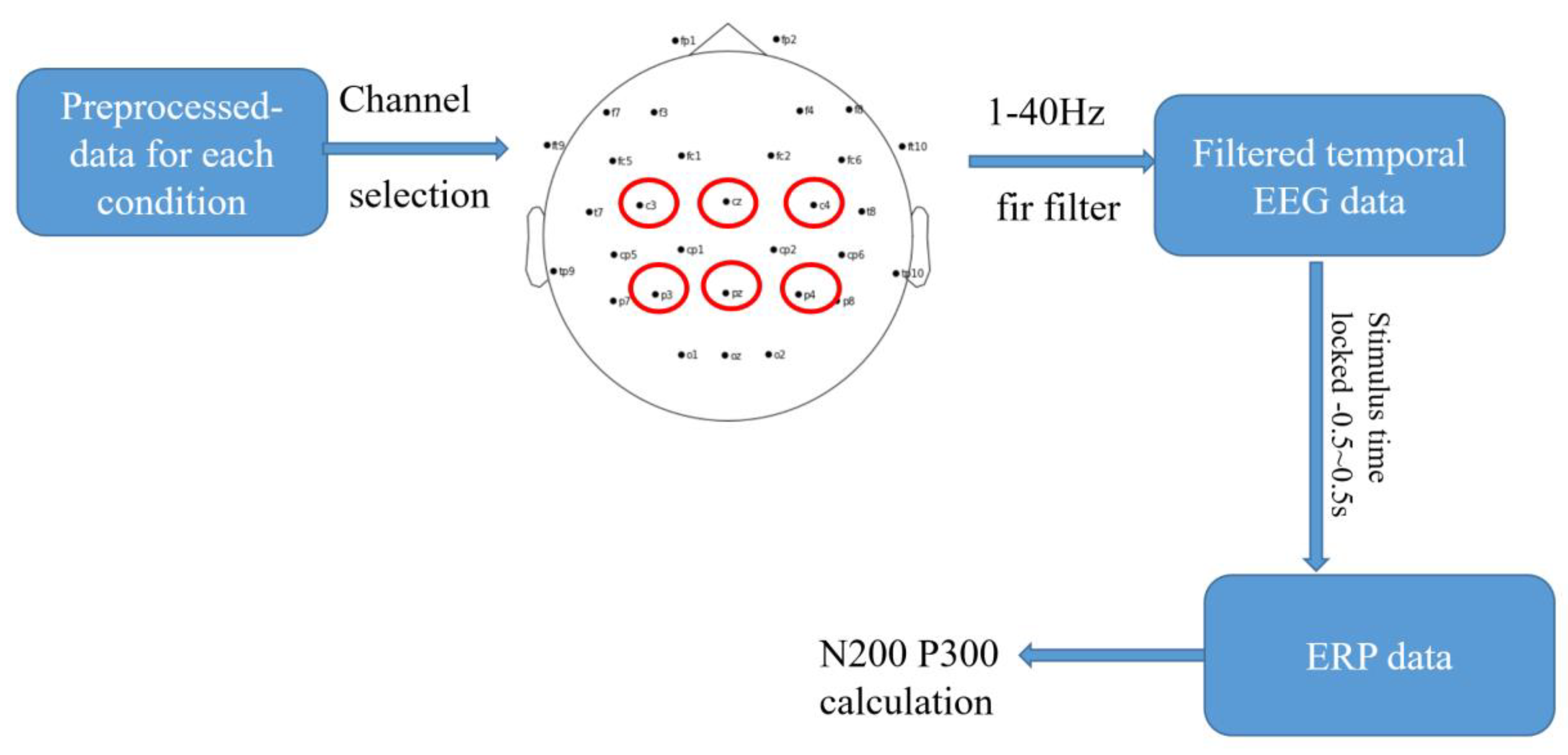
2.3.3. Event-Related Potential Analysis for Temporal EEG
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Self-Assessment
3.2. Comparison of PSD between Resting EEG and Multimodal Stimulation EEG
3.3. Emotion-Related PSD Analysis
3.4. Stimulus-Modality-Related PSD Analysis
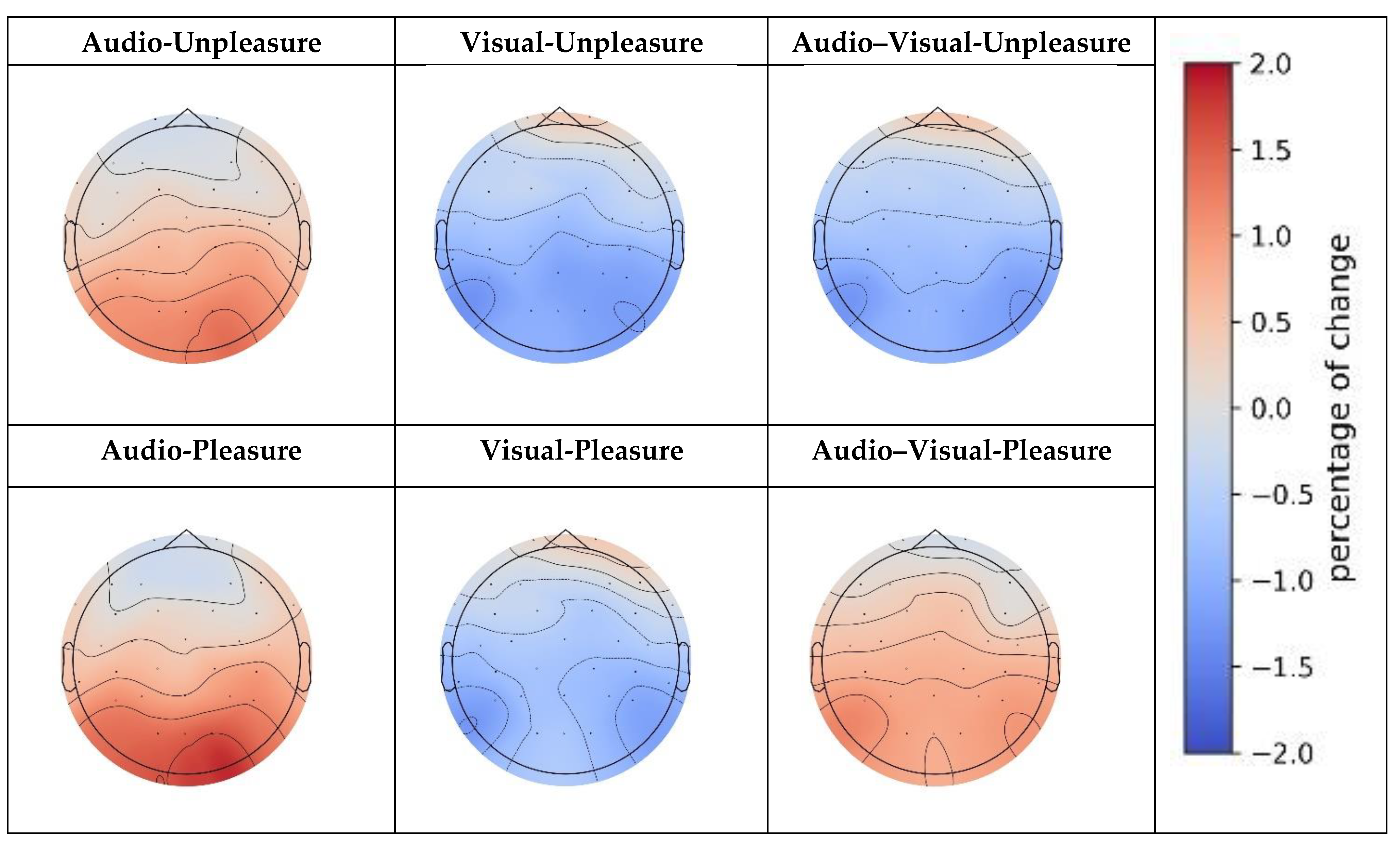
3.5. Temporal ERP Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berthold-Losleben, M.; Habel, U.; Brehlss, A.K.; Freiherr, J.; Losleben, K.; Schneider, F.; Amunts, K.; Kohn, N. Implicit affective rivalry: A behavioral and fMRI study combining olfactory and auditory stimulation. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiblanco Jimenez, I.A.; Gomez Acevedo, J.S.; Olivetti, E.C.; Marcolin, F.; Ulrich, L.; Moos, S.; Vezzetti, E. User Engagement Comparison between Advergames and Traditional Advertising Using EEG: Does the User’s Engagement Influence Purchase Intention? Electronics 2023, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzani, A.; Ravaioli, S.; Trieste, L.; Faraguna, U.; Turchetti, G. Is EEG Suitable for Marketing Research? A Systematic Review. Front Neurosci. 2020, 14, 594566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Xie, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Liao, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, X. A review of emotion recognition using physiological signals. Sensors 2018, 18, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Pan, J. Advances in multimodal emotion recognition based on brain–computer interfaces. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.P.; Torres, E.A.; Hernández-Álvarez, M.; Yoo, S.G. EEG-based brain-computer interfaces are an active area of research for emotion recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugappan, M.; Juhari MR, B.M.; Nagarajan, R.; Yaacob, S. An Investigation on visual and audiovisual stimulus based emotion recognition using EEG. Int. J. Med. Eng. Inform. 2009, 1, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Shi, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, S. Exploiting EEG signals and audiovisual feature fusion for video emotion recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59844–59861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Bailey, K.; Xiao, X. Midfrontal theta and posterior parietal alpha band oscillations support conflict resolution in a masked affective priming task. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Han, S.; Gelfand, M.J. The role of Gamma Interbrain Synchrony in social coordination when humans face territorial threats. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2017, 12, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelenz, P.; Klasen, M.; Reese, B.; Regenbogen, C.; Wolf, D.; Kato, Y.; Mathiak, K. Multisensory integration of dynamic emotional faces and voices: Method for simultaneous EEG-fMRI measurements. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Cao, D. The effectiveness of emotion cognitive reappraisal as measured by self-reported response and its link to EEG Alpha Asymmetry. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 400, 113042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Misrani, A.; Su, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, J.; Tang, B.; et al. Pelvic pain alters functional connectivity between anterior cingulate cortex and hippocampus in both humans and a rat model. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 642349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkusare, S.; Nguyen, V.T.; Moran, R.; van der Meer, J.; Ren, Y.; Koussis, N.; Dionisio, S.; Breakspear, M.; Guo, C. Intracranial-EEG evidence for medial temporal pole driving amygdala activity induced by multi-modal emotional stimuli. Cortex 2020, 130, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahirwal, M.K.; Kose, M.R. Audio-visual stimulation based emotion classification by correlated EEG channels. Health Technol. 2020, 10, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balconi, M.; Vanutelli, M.E. Vocal and visual stimulation, congruence and lateralization affect brain oscillations in interspecies emotional positive and negative interactions. Soc. Neurosci. 2016, 11, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balconi, M.; Carrera, A. Cross-modal integration of emotional face and voice in congruous and incongruous pairs: The P2 ERP effect. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2011, 23, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallotto, S.; Sack, A.T.; Schuhmann, T.; de Graaf, T.A. Oscillatory correlates of visual consciousness. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, M.; Poliakoff, E.; El-Deredy, W.; Klepousniotou, E.; Lloyd, D.M. Pre-stimulus alpha oscillations over somatosensory cortex predict tactile misperceptions. Neuropsychologia 2017, 96, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasen, M.; Kreifelts, B.; Chen, Y.-H.; Seubert, J.; Mathiak, K. Neural processing of emotion in multimodal settings. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugos, J.A.; Bidelman, G.M.; Moreno, S.; Shen, D.; Lu, J.; Alain, C. Music and visual art training increase auditory-evoked theta oscillations in older adults. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, U.; Wendt, M.; Pacharra, M. Enhancing allocation of visual attention with emotional cues presented in two sensory modalities. Behav. Brain Funct. 2022, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, B.; Dobri, S.; Jamali, S.; Bartel, L. Entrainment of somatosensory beta and gamma oscillations accompany improvement in tactile acuity after periodic and aperiodic repetitive sensory stimulation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2022, 177, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aricò, P.; Magosso, E.; De Crescenzio, F.; Ricci, G.; Piastra, S.; Ursino, M. EEG Alpha Power Is Modulated by Attentional Changes during Cognitive Tasks and Virtual Reality Immersion. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 7051079. [Google Scholar]
- Cantero, J.L.; Atienza, M.; Salas, R.M.; Dominguez-Marin, E. Effects of Prolonged Waking-Auditory Stimulation on Electroencephalogram Synchronization and Cortical Coherence during Subsequent Slow-Wave Sleep. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 4702–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, T.; Esslen, M.; Jäncke, L. From emotion perception to emotion experience: Emotions evoked by pictures and classical music. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2006, 60, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jääskeläinen, I.P.; Sams, M.; Glerean, E.; Ahveninen, J. Movies and narratives are useful naturalistic stimuli for neuroimaging studies. NeuroImage 2021, 224, 117445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulders, D.; De Bodt, C.; Lejeune, N.; Courtin, A.; Liberati, G.; Verleysen, M.; Mouraux, A. Dynamics of the perception and EEG signals triggered by tonic warm and cool stimulation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugappan, M.; Murugappan, S. Human emotion recognition through short time Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 9th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–10 March 2013; pp. 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Dmochowski, J.; Sajda, P.; Dias, J.; Parra, L. Correlated components of ongoing EEG point to emotionally laden attention—A possible marker of engagement? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhou, R. A New Standardized Emotional Film Database for Asian Culture. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betella, A.; Verschure, P.F.M.J. The Affective Slider: A Digital Self-Assessment Scale for the Measurement of Human Emotions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open-source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stancin, I.; Cifrek, M.; Jovic, A. A Review of EEG Signal Features and Their Application in Driver Drowsiness Detection Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Sarkar, A.K.; Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Hossain, M.B.; Quinn, J.M.W.; Moni, M.A. Recog-nition of human emotions using EEG Signals: A Review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Shu, L.; Liang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X. Design and Evaluation of Affective Virtual Reality System Based on Multimodal Physiological Signals and Self-Assessment Manikin. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2020, 4, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, G.G. Motivation, emotion, and their inhibitory control mirrored in brain oscillations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensen, A.; Marshall, W.; Tononi, G. EEG Differentiation Analysis and Stimulus Set Meaningfulness. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, E.H.F.; Corballis, P.M.; Hillyard, S.A.; Marzi, C.A.; Seth, A.; Lamme, V.A.F.; Volz, L.; Fabri, M.; Schechter, E.; Bayne, T.; et al. Split-Brain: What We Know Now and Why This is Important for Understanding Consciousness. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2020, 30, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Shou, G.; Yuan, H.; Urbano, D.; Cha, Y.-H. Lasting Modulation Effects of rTMS on Neural Activity and Connectivity as Revealed by Resting-State EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Z.Y.; Saidatul, A.; Ibrahim, Z. Power Spectral Density Analysis for Human EEG- based Biometric Identification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Approach in Smart Systems Design and Applications (ICASSDA), Kuching, Malaysia, 15–17 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gramfort, A.; Luessi, M.; Larson, E.; Engemann, D.A.; Strohmeier, D.; Brodbeck, C.; Parkkonen, L.; Hämäläinen, M.S. MNE software for processing MEG and EEG data. Neuroimage 2014, 86, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.H.; Azzam, P.N. Characterization of N200 and P300: Selected Studies of the Event-Related Potential. Int. J. Med Sci. 2005, 2, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, A.; Fazel-Rezai, R. Application of P300 Event-Related Potential in Brain-Computer Interface. Event-Relat. Potentials Evoked Potentials 2017, 1, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, T.; Hammer, E.; Kübler, A. ERPs contributing to classification in the “P300” BCI. In Proceedings of the 5th International BCI Conference, Graz, Austria, 22–24 September 2011; pp. 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, S.S.; Dirim, S.Y.; Yildirim, E. Emotion primitives estimation from EEG signals using Hilbert Huang transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI 2012), Hong Kong, China, 5–7 January 2012; pp. 623–626. [Google Scholar]
- Marín-Morales, J.; Higuera-Trujillo, J.L.; Greco, A.; Guixeres, J.; Llinares, C.; Gentili, C.; Scilingo, E.P.; Alcañiz, M.; Valenza, G. Real vs. immersive-virtual emotional ex-pe-rience: Analysis of psycho-physiological patterns in a free exploration of an art museum. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, H.-J.; Irtel, H. Emotional response to color across media. Color Res. Appl. 2010, 35, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagopoulos, J.; Xu, J.; Rasmussen, I.; Vik, A.; Malhi, G.S.; Eliassen, C.F.; Arntsen, I.E.; Sæther, J.G.; Hollup, S.; Holen, A.; et al. Increased Theta and Alpha EEG Activity During Nondirective Meditation. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2009, 15, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, P.A.; Pietrelli, M.; Zanon, M.; Làdavas, E.; Bertini, C. Alpha oscillations reveal implicit visual processing of motion in hemianopia. Cortex 2020, 122, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhar, L.I.; Babiker, A.; Rizki, E.E.; Lu, C.K.; Abdul Rahman, M. Emotion self-regulation in neurotic students: A pilot mind-ful-ness-based intervention to assess its effectiveness through brain signals and behavioral data. Sensors 2022, 22, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Burg, E.; Toet, A.; Brouwer, A.-M.; Van Erp, J.B.F. Serial Dependence of Emotion Within and Between Stimulus Sensory Modalities. Multisens. Res. 2021, 35, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddy, C.R. Corporate Psychopaths, Bullying, Conflict and Unfair Supervision in the Workplace. Corp. Psychopaths 2011, 100, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, A.; Adolphs, R. Emotion Perception from Face, Voice, and Touch: Comparisons and Convergence. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2017, 21, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.; Rognoni, E.; Galati, D. EEG phase synchronization during emotional response to positive and negative film stimuli. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 406, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplin, T.A.; Rosa, M.; Lui, L.L. Auditory and Visual Motion Processing and Integration in the Primate Cerebral Cortex. Front. Neural Circuits 2018, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnée, M.J.C.M.; de Gelder, B.; van Engeland, H. Atypical processing of fearful face–voice pairs in pervasive developmental disorder: An ERP study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, A.; Hopkinson, P.J.; Hermens, D.; Rowe, D.L.; Sumich, A.L.; Clark, C.R.; Drinkenburg, W.; Abdi, N.; Penrose, R.; McFarlane, A.; et al. Fronto-temporal alterations within the first 200 ms during an attentional task distinguish major depression, non-clinical participants with depressed mood and healthy controls: A potential biomarker? Hum. Brain Mapp. 2008, 30, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, Q.; Gao, N.; Yang, J.; Bai, O. Happy emotion cognition of bimodal audiovisual stimuli optimizes the performance of the P300 speller. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, N.; Vuilleumier, P. Effects of emotional and non-emotional cues on visual search in neglect patients: Evidence for dis-tinct sources of attentional guidance. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Audio-Unpleasure | Visual-Unpleasure | Audio-Visual-Unpleasure | Audio-Pleasure | Visual-Pleasure | Audio-Visual-Pleasure | Resting State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 trails | 200 trails | 200 trails | 200 trails | 200 trails | 200 trails | 20 trails |
| Audio Pleasure | Visual Pleasure | Audio-Visual Pleasure | Audio Unpleasure | Visual Unpleasure | Audio-Visual Unpleasure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub01 | 7.8 | 8.2 | 7.4 | −5.3 | −4.6 | −8.3 |
| Sub02 | 5.2 | 7.4 | 6.5 | −6.7 | −8.3 | −6.1 |
| Sub03 | 6.4 | 5.5 | 7.9 | −5.0 | −6.2 | −7.9 |
| Sub04 | 7.5 | 4.2 | 7.8 | −8.0 | −4.3 | −6.8 |
| Sub05 | 6.0 | 5.2 | 7.1 | −5.4 | −5.2 | −7.5 |
| Sub06 | 5.6 | 8.0 | 8.5 | −7.0 | −3.8 | −6.4 |
| Sub07 | 6.5 | 7.1 | 3.8 | −6.6 | −4.1 | −6.7 |
| Sub08 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 6.1 | −7.9 | −6.7 | −8.5 |
| Sub09 | 7.9 | 7.7 | 7.7 | −8.5 | −5.6 | −6.9 |
| Sub10 | 3.4 | 5.3 | 8.2 | −5.9 | −6.3 | −5.1 |
| Sub11 | 7.2 | 8.3 | 7.8 | −4.4 | −3.6 | −7.9 |
| Sub12 | 7.2 | 7.4 | 7.5 | −2.7 | −7.3 | −6.3 |
| Sub13 | 4.8 | 6.0 | 6.0 | −8.3 | −7.2 | −7.0 |
| Sub14 | 7.6 | 3.9 | 8.2 | −6.2 | −3.3 | −6.1 |
| Sub15 | 6.9 | 4.7 | 6.6 | −4.8 | −8.6 | −7.1 |
| Sub16 | 6.9 | 7.7 | 7.0 | −4.6 | −8.1 | −6.3 |
| Sub17 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 8.0 | −6.6 | −7.0 | −7.8 |
| Sub18 | 6.6 | 5.2 | 7.4 | −6.2 | −5.2 | −7.9 |
| Sub19 | 8.3 | 7.4 | 8.0 | −8.4 | −6.3 | −7.5 |
| Sub20 | 8.2 | 3.4 | 7.0 | −4.8 | −6.4 | −5.8 |
| Average | 6.50 ± 2.40 | 6.17 ± 2.51 | 7.23 ± 1.91 | −6.17 ± 2.35 | −5.90 ± 2.30 | −7.00 ± 2.02 |
| Stimulus Types | Band | Change in Percentage (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal | Temporal | Central | Parietal | Occipital | ||
| Audio Unpleasure | Delta | |||||
| Theta | ||||||
| Alpha | 2.177 * (0.0745) | |||||
| Visual Unpleasure | Delta | |||||
| Theta | ||||||
| Alpha | −1.814 ** (0.0434) | −2.449 ** (0.039) | −2.845 ** (0.020) | |||
| Audio-visual Unpleasure | Delta | |||||
| Theta | ||||||
| Alpha | −1.514 ** (0.0418) | −1.867 ** (0.0412) | −2.176 ** (0.0218) | |||
| Audio Pleasure | Delta | |||||
| Theta | ||||||
| Alpha | 1.465 * (0.0818) | 2.696 ** (0.0374) | ||||
| Visual Pleasure | Delta | |||||
| Theta | ||||||
| Alpha | −1.347 * (0.0506) | −1.759 ** (0.0470) | −1.876 ** (0.0382) | |||
| Audio-visual Pleasure | Delta | |||||
| Theta | ||||||
| Alpha | 0.359 ** (0.0236) | 0.727 * (0.0740) | 0.473 ** (0.0127) | 0.070 ** (0.0113) | ||
| Stimulus Types | Band | Change in Percentage (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal | Temporal | Central | Parietal | Occipital | ||
|
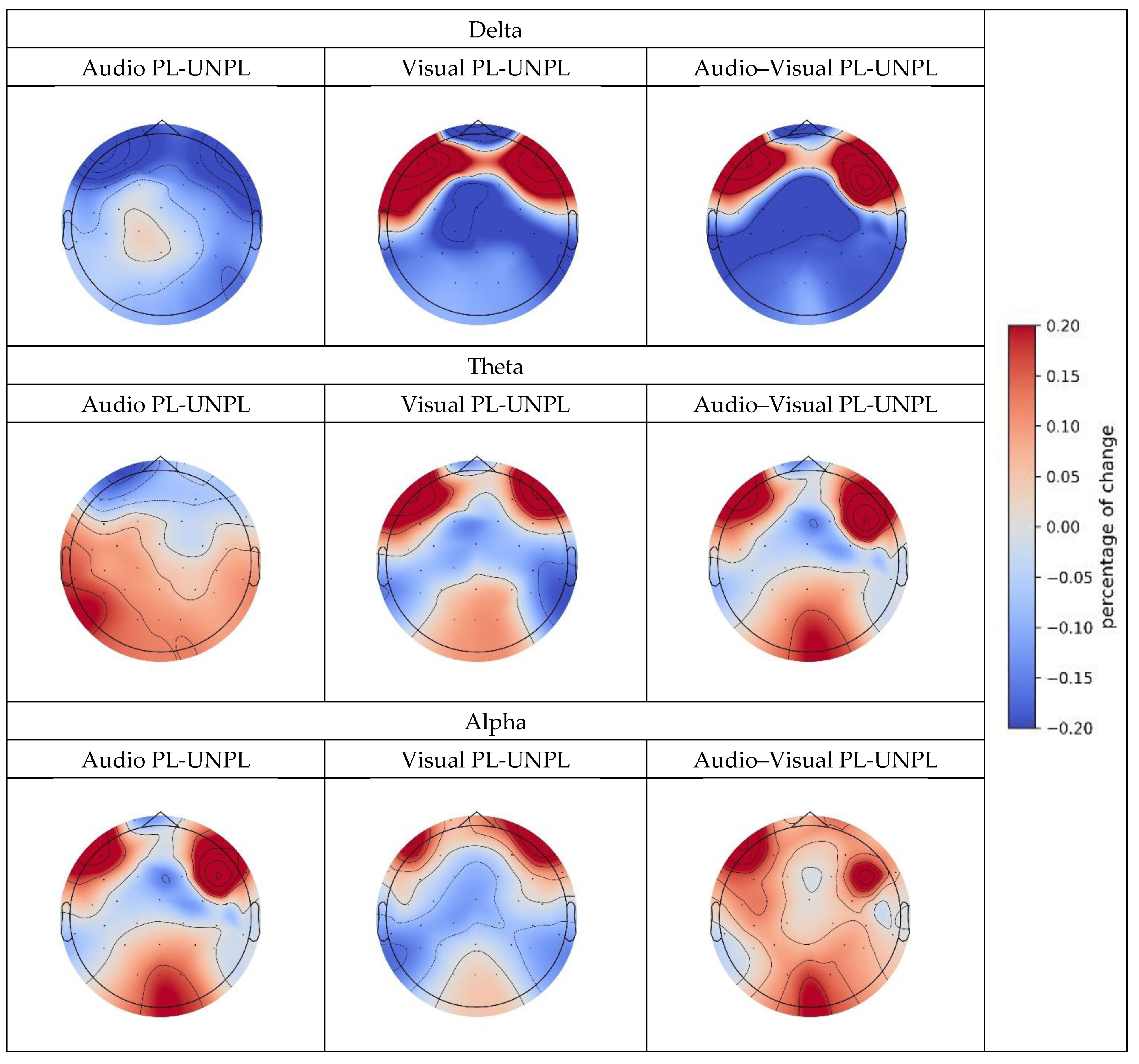
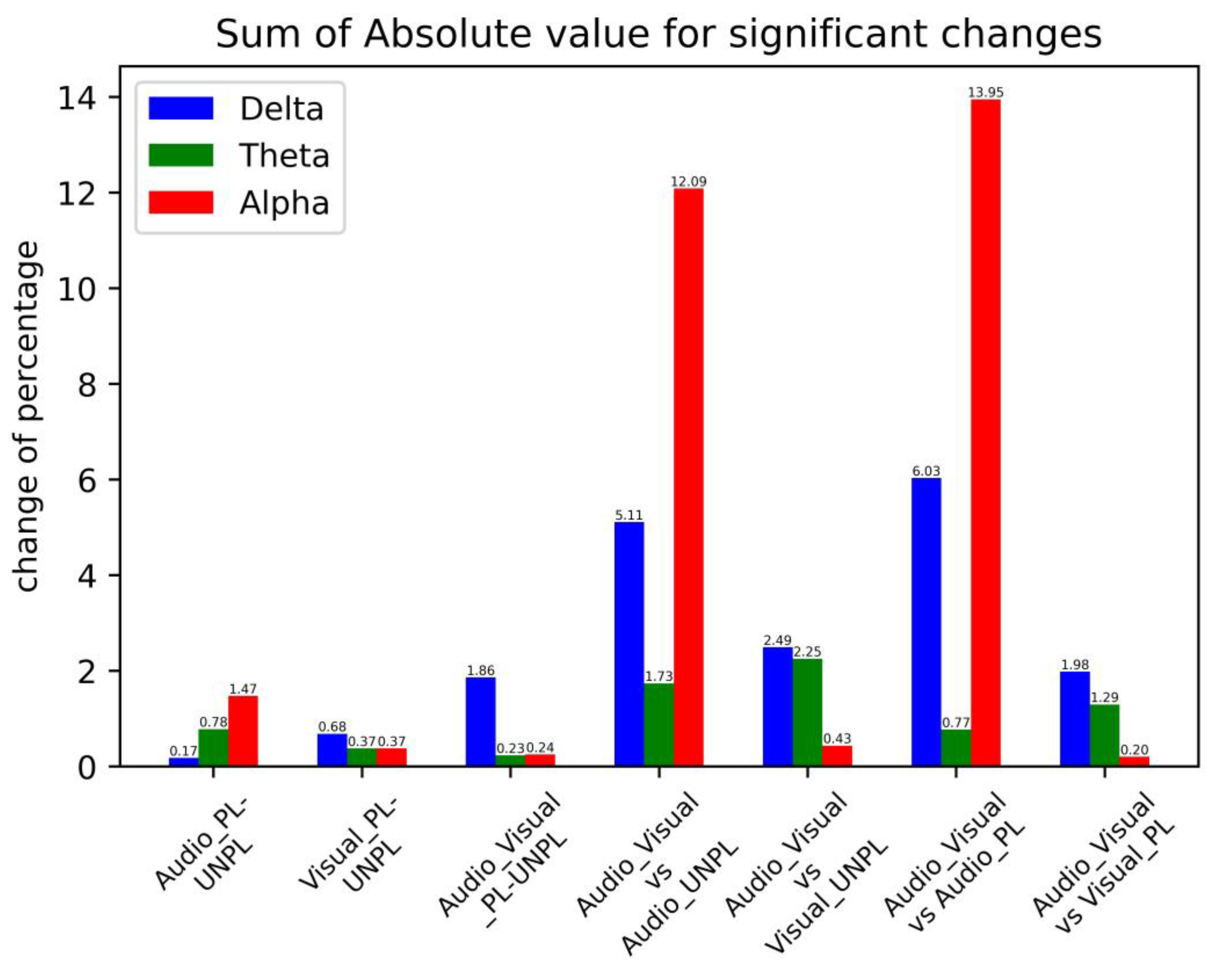
Audio PL-UNPL | Delta | −0.171 ** (0.0221) | ||||
| Theta | 0.148 * (0.098) | 0.174 ** (0.046) | 0.221 ** (0.026) | −0.234 ** (0.0477) | ||
| Alpha | 0.411 *** (0.008) | 0.362 ** (0.024) | 0.699 *** (0.0016) | |||
|
Visual PL-UNPL | Delta | −0.415 ** (0.011) | −0.253 * (0.0796) | |||
| Theta | 0.134 * (0.0956) | 0.238 ** (0.0596) | ||||
| Alpha | 0.269 ** (0.0378) | 0.104 ** (0.0240) | ||||
|
Audio-visual PL-UNPL | Delta | −0.4942 ** (0.0449) | −0.443 *** (0.0032) | −0.4889 *** (0.027) | −0.432 ** (0.011) | |
| Theta | 0.123 ** (0.0132) | 0.104 ** (0.0163) | ||||
| Alpha | 0.0492 ** (0.0331) | 0.031 *** (0.0014) | 0.034 ** (0.041) | 0.130 *** (0.0018) | ||
| Stimulus Types | Band | Change in Percentage (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal | Temporal | Central | Parietal | Occipital | ||
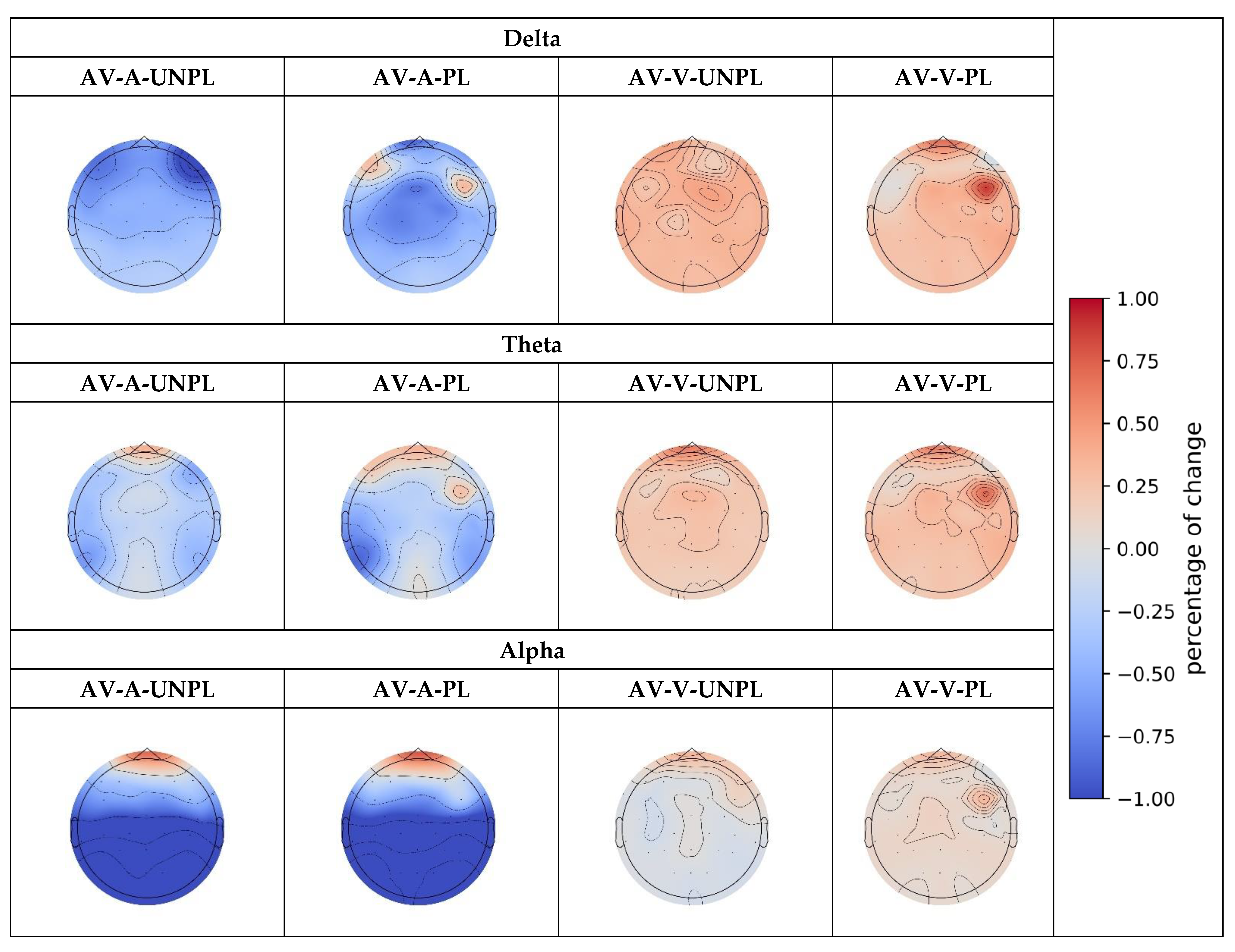
| AV-A UNPL | Delta | −1.205 *** (0.010) | −1.055 *** (0.009) | −1.022 *** (0.002) | −1.014 *** (0.002) | −0.813 *** (0.008) |
| Theta | 0.607 * (0.063) | 0.369 ** (0.040) | 0.758 *** (0.003) | |||
| Alpha | 0.309 * (0.095) | −2.752 *** (0.0001) | −1.821 *** (0.0001) | −3.382 ** (0.0001) | −4.441 *** (0.0002) | |
| AV-V UNPL | Delta | 0.693 *** (0.001) | 0.633 *** (0.003) | 0.559 *** (0.008) | 0.605 *** (0.004) | |
| Theta | 0.838 *** (0.0007) | 0.369 *** (0.0007) | 0.380 *** (0.0026) | 0.362 *** (0.002) | 0.300 ** (0.0027) | |
| Alpha | 0.234 ** (0.020) | −0.141 ** (0.030) | −0.141 * (0.075) | −0.182 ** (0.045) | −0.198 ** (0.040) | |
| AV-A PL | Delta | −1.528 ** (0.020) | −0.721 * (0.082) | −1.309 *** (0.004) | −1.381 *** (0.003) | −1.088 ** (0.011) |
| Theta | 0.123 ** (0.0132) | 0.768 ** (0.030) | ||||
| Alpha | −3.1379 *** (0.0001) | −1.942 *** (0.0004) | −3.811 ** (0.0002) | −5.060 *** (0.0001) | ||
| AV-V PL | Delta | 0.525 * (0.095) | 0.408 * (0.054) | 0.306 * (0.095) | 0.335 * (0.080) | 0.405 ** (0.043) |
| Theta | 0.359 *** (0.0017) | 0.306 ** (0.014) | 0.311 *** (0.004) | 0.313 *** (0.005) | ||
| Alpha | 0.197 * (0.077) | |||||
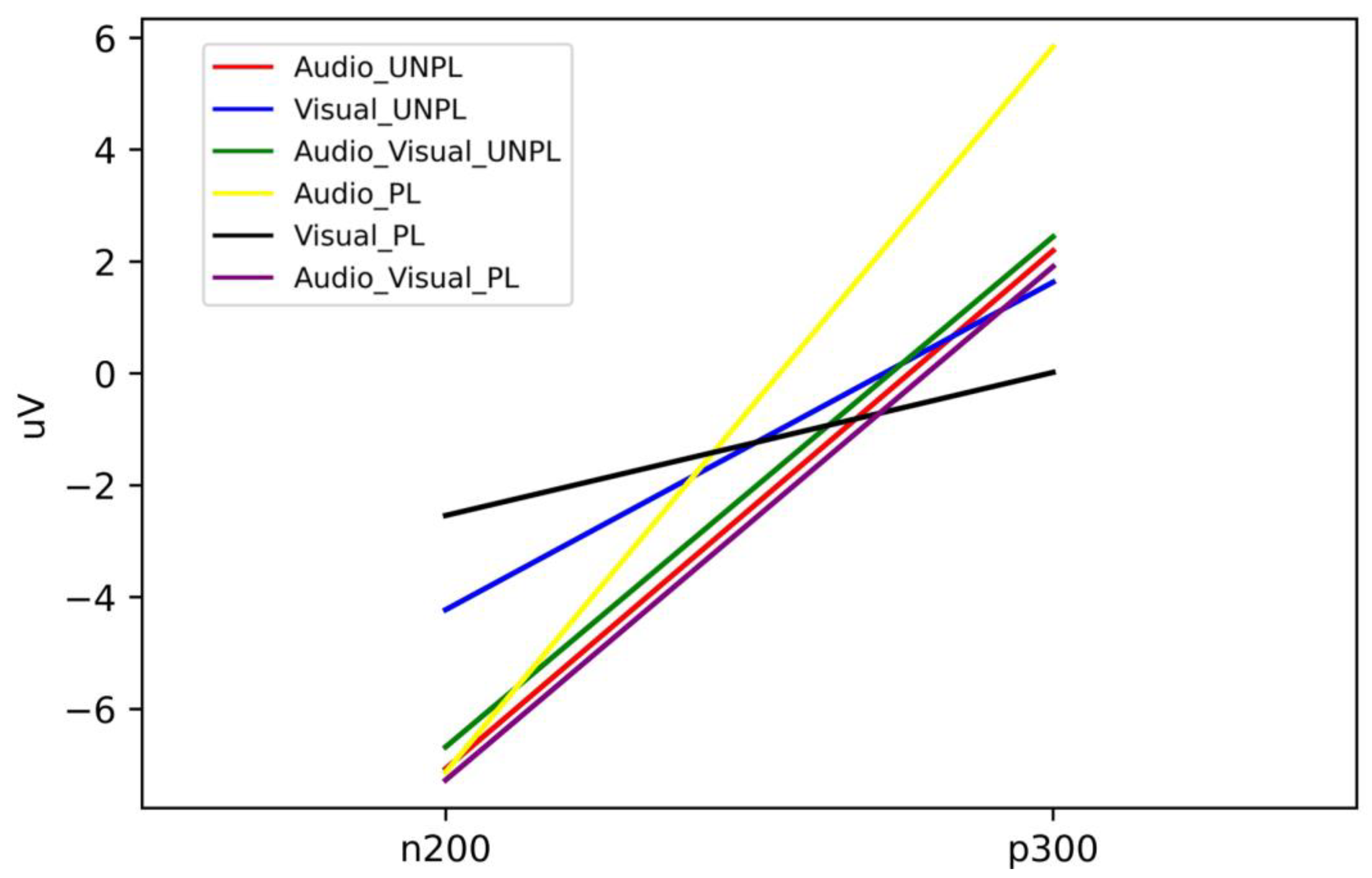
| N200 (μV) | P300 (μV) | |
|---|---|---|
| Audio_UNPL | −7.07 | 2.19 |
| Visual_UNPL | −4.23 | 1.63 |
| Audio-Visual_UNPL | −6.68 | 2.44 |
| Audio_PL | −7.13 | 5.84 |
| Visual_PL | −2.54 | 0.02 |
| Audio-Visual_PL | −7.27 | 1.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, C.; Uchitomi, H.; Miyake, Y. Influence of Multimodal Emotional Stimulations on Brain Activity: An Electroencephalographic Study. Sensors 2023, 23, 4801. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104801
Gao C, Uchitomi H, Miyake Y. Influence of Multimodal Emotional Stimulations on Brain Activity: An Electroencephalographic Study. Sensors. 2023; 23(10):4801. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104801
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Chenguang, Hirotaka Uchitomi, and Yoshihiro Miyake. 2023. "Influence of Multimodal Emotional Stimulations on Brain Activity: An Electroencephalographic Study" Sensors 23, no. 10: 4801. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104801
APA StyleGao, C., Uchitomi, H., & Miyake, Y. (2023). Influence of Multimodal Emotional Stimulations on Brain Activity: An Electroencephalographic Study. Sensors, 23(10), 4801. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104801






