Three Dimensional Shape Reconstruction via Polarization Imaging and Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Our method enhances the reconstruction of object textures by extracting more comprehensive information, mitigating the loss of texture information during the process.
- By reducing the number of parameters and increasing the network’s depth, our method enhances the model’s expressive and generalization abilities and reduces computational cost.
2. Related Work
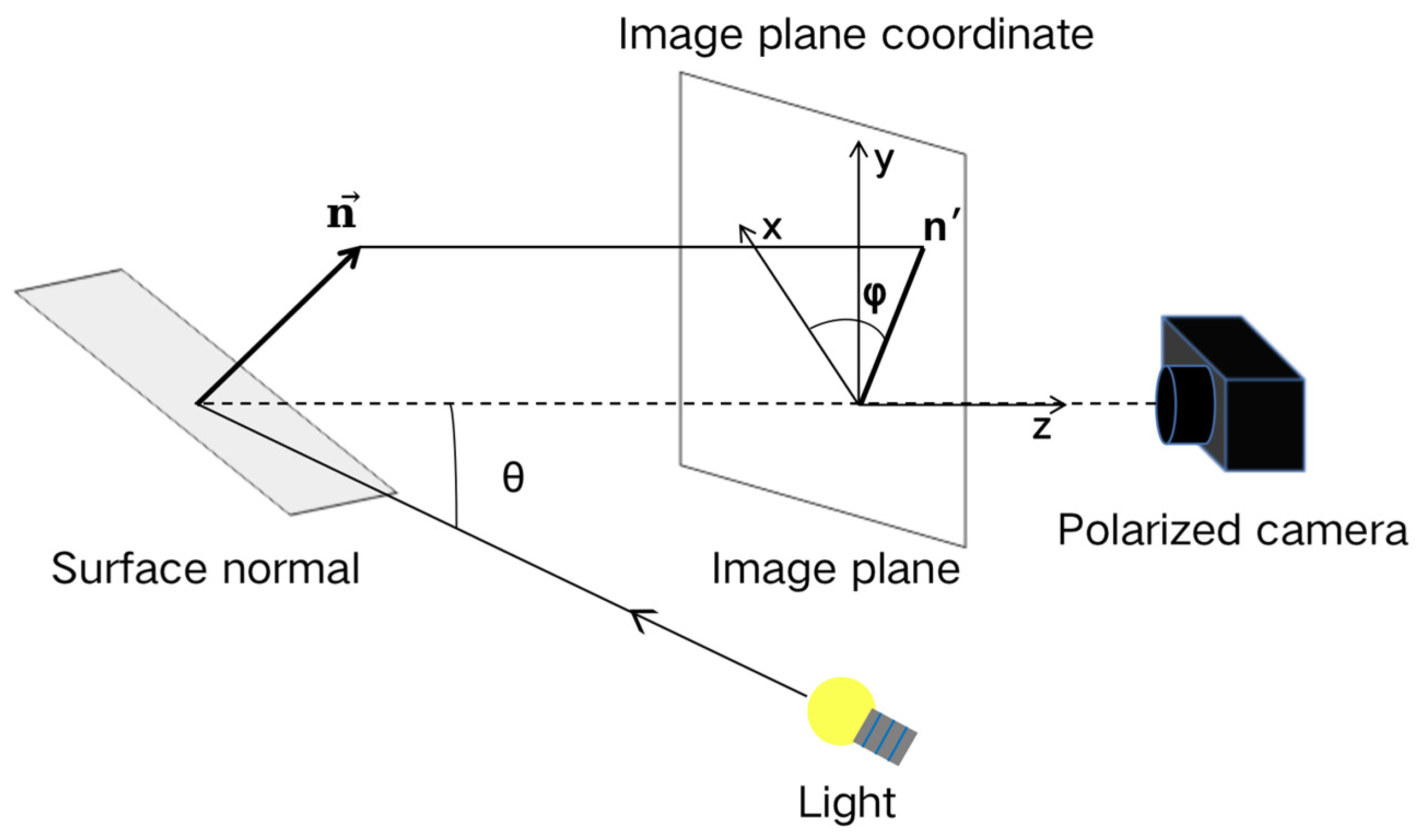
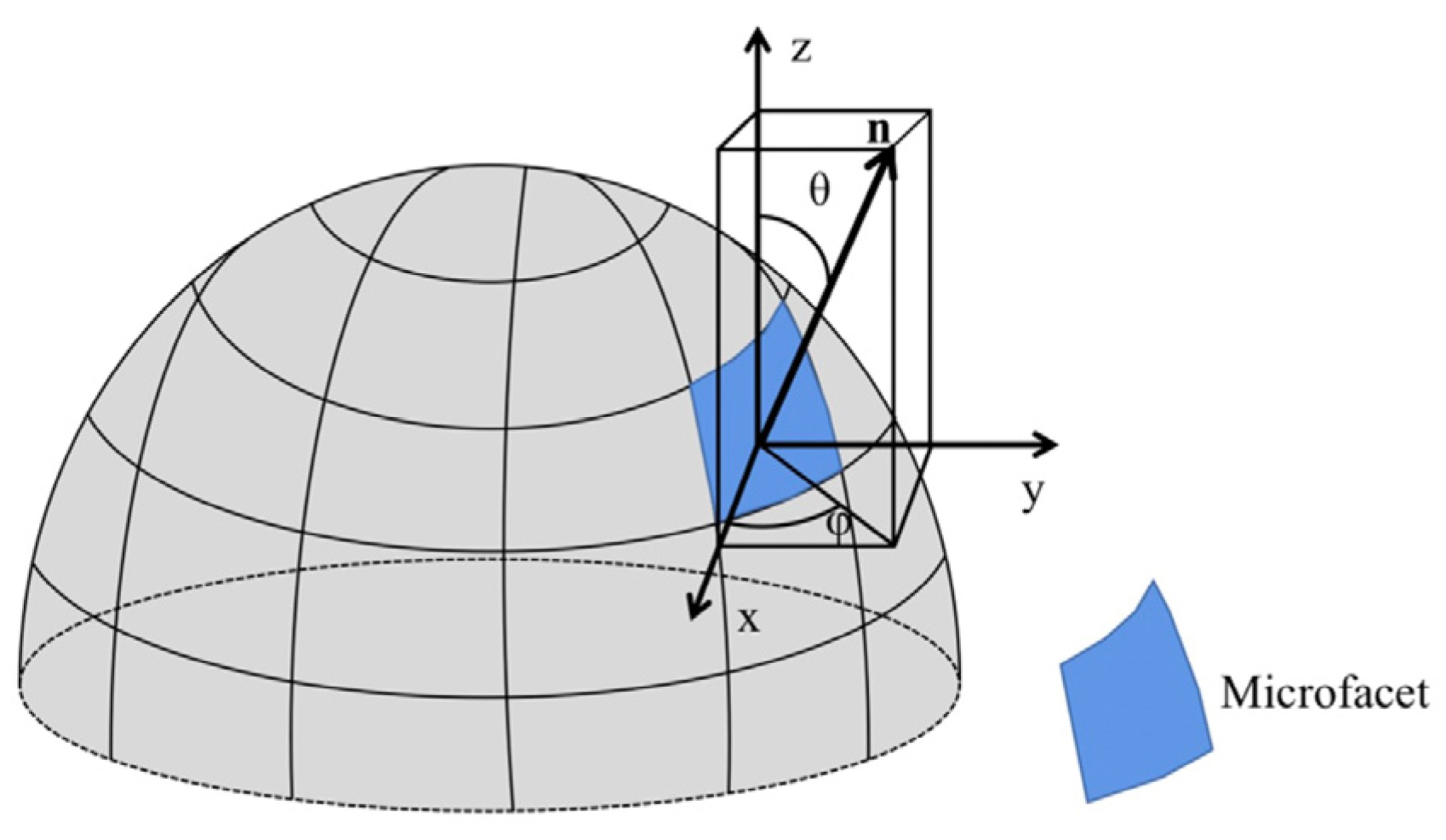
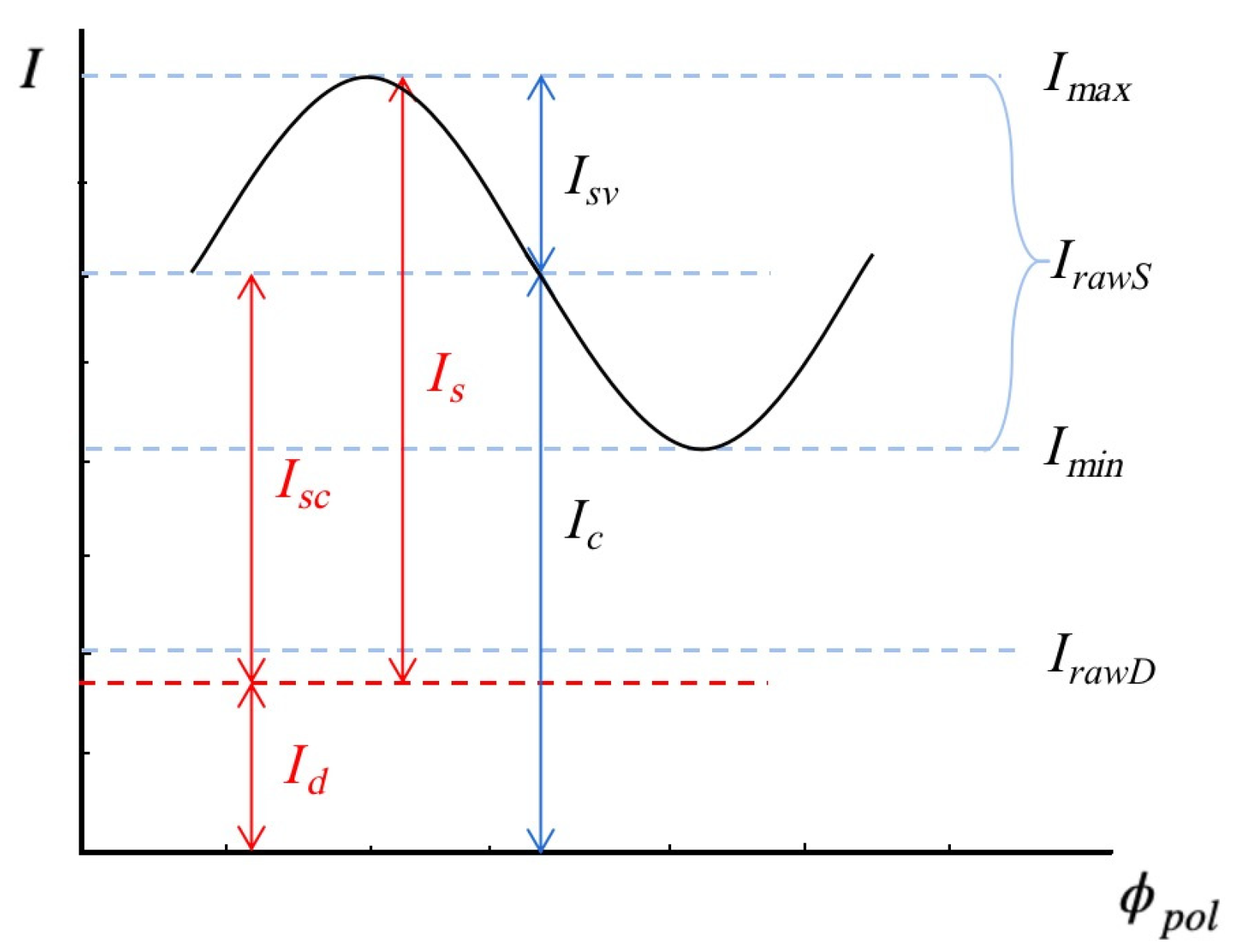
2.1. Shape from Polarization Principle
2.2. Network Input
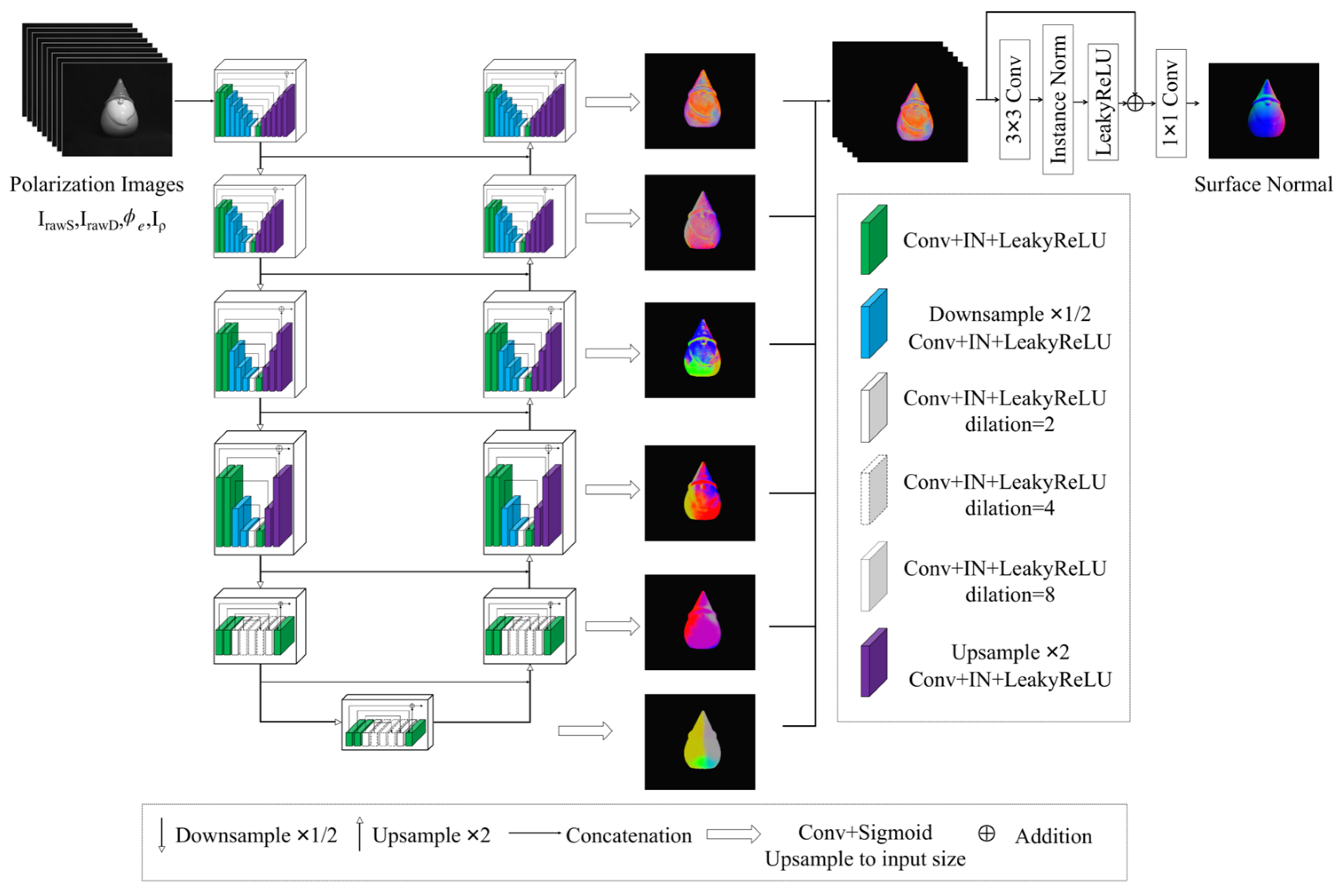
2.3. Network Structure
2.4. Loss Function
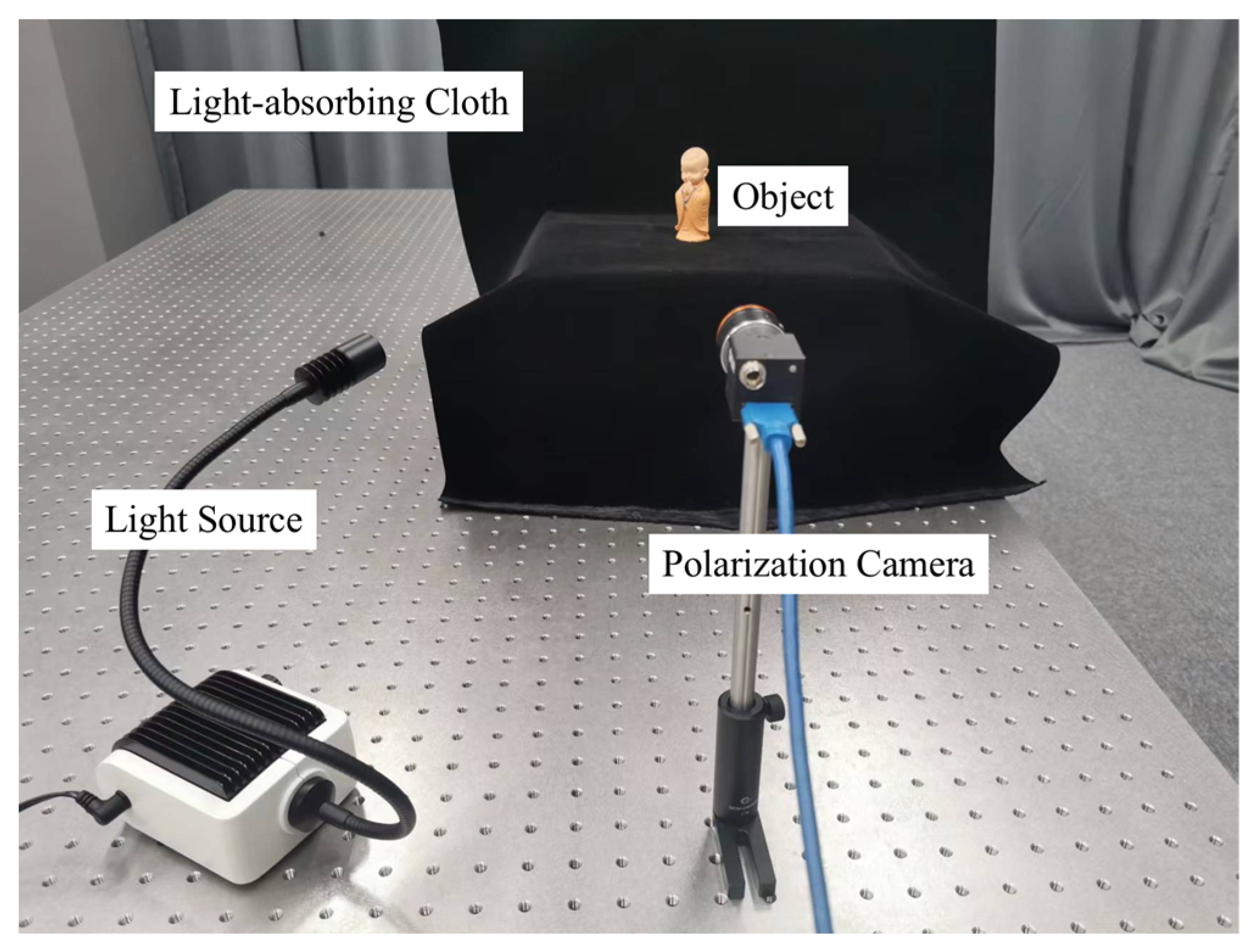
2.5. Experimental Device
3. Data and Implementation Details
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Training
3.3. Inference
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Network Input
4.2. Ablation Experiments
4.3. SfP-U2Net
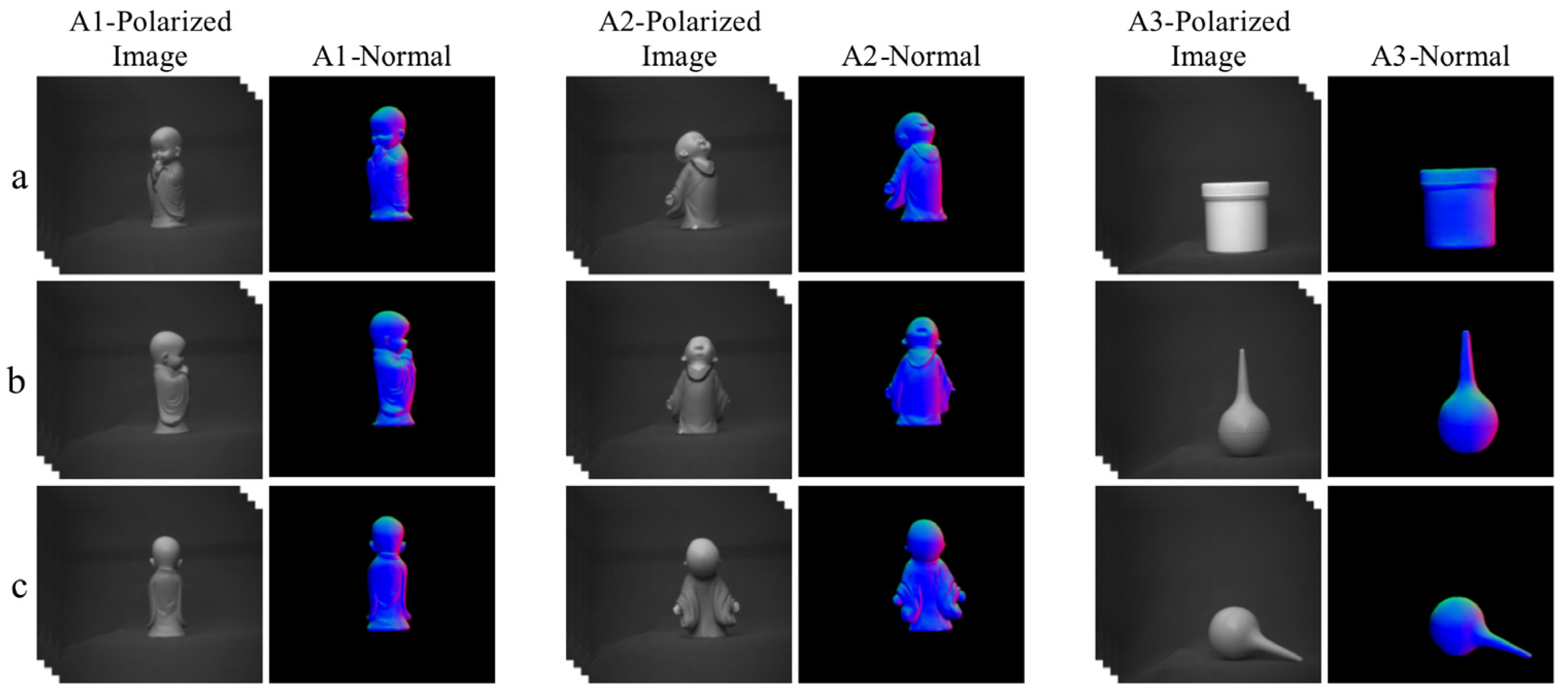
4.4. Experimental Results of the Actual Shooting
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, W.; Weng, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction for Photon Counting Imaging Using a Planar Catadioptric Method. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics/Pacific Rim, Singapore, 31 July 2017; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA; p. s2172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Kong, L.; Zhao, J.; Huang, H. Design of Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Robot Path Planning Based on Kinect System. In Proceedings of the 2017 29th Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC), Chongqing, China, 28–30 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 3829–3834. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Pan, W.; Shi, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, W. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction Method Based on Target Recognition for Binocular Humanoid Robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing (PIC), 23–25 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Popa, D.; Akhmediev, N. Revealing the transition dynamics from Q switching to mode locking in a soliton laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 093901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Lu, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J.; Shan, G. Functional porous MOF-derived CuO octahedra for harmonic soliton molecule pulses generation. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 2440–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yi, C.; Kong, S.G.; Pan, Q.; Cheng, Y. Multi-band polarization imaging. In Multi-Band Polarization Imaging and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 47–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ragheb, H.; Hancock, E.R. A probabilistic framework for specular shape-from-shading. Pattern Recognit. 2003, 36, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, D.; Shigetomi, T.; Baba, M.; Furukawa, R.; Hiura, S.; Asada, N. Surface normal estimation of black specular objects from multiview polarization images. Opt. Eng. 2016, 56, 041303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.A.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Tozza, S. Linear Depth Estimation from an Uncalibrated, Monocular Polarisation Image. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.H.; El-Melegy, M.T.; Farag, A.A. Direct Method for Shape Recovery from Polarization and Shading. In Proceedings of the 2012 19th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 September–3 October 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1769–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Kadambi, A.; Taamazyan, V.; Shi, B.; Raskar, R. Polarized 3d: Synthesis of polarization and depth cues for enhanced 3d sensing. In SIGGRAPH 2015: Studio; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kadambi, A.; Taamazyan, V.; Shi, B.; Raskar, R. Depth sensing using geometrically constrained polarization normals. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2017, 125, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Gu, J.; Shi, B.; Tan, P.; Kautz, J. Polarimetric Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1558–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Larsson, V.; Pollefeys, M. Polarimetric Relative Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 2671–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Koshikawa, K. A polarimetric approach to shape understanding of glossy objects. Adv. Robot. 1979, 2, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, F.; Shao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X. Joint 3d Face Reconstruction and Dense Alignment with Position Map Regression Network. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 534–551. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, L.; Liu, X. On learning 3d face morphable model from in-the-wild images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Cheng, S.; Huyan, K.; Hou, M.; Liu, R.; Luo, Z. Dual neural networks coupling data regression with explicit priors for monocular 3D face reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Zuo, X.; Qian, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, C.; Gong, M.; Cheng, L. 3D Human Shape Reconstruction from a Polarization Image. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Part XIV 16; 2020. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 351–368. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Zuo, X.; Wang, S.; Qian, Y.; Guo, C.; Cheng, L. Human pose and shape estimation from single polarization images. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Y.; Gilbert, A.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Yan, L.; Shi, B.; Kadambi, A. Deep Shape from Polarization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 554–571. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, Y.; Ono, T.; Sun, L.; Hirasawa, Y.; Murayama, J. Accurate Polarimetric BRDF for Real Polarization Scene Rendering. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 220–236. [Google Scholar]
- Deschaintre, V.; Lin, Y.; Ghosh, A. Deep Polarization Imaging for 3D Shape and SVBRDF Acquisition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15567–15576. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Qi, C.; Xie, J.; Fan, N.; Koltun, V.; Chen, Q. Shape from Polarization for Complex Scenes in the Wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12632–12641. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical image computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Wheeler, M.D.; Ikeuchi, K. Object Shape and Reflectance Modeling from Observation. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 3–8 August 1997; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Brewster, D. IX. On the laws which regulate the polarisation of light by reflexion from transparent bodies. By David Brewster, LL. DFRS Edin. and FSA Edin. In a letter addressed to Right Hon. Sir Joseph Banks, Bart. KBPR S. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1815, 105, 125–159. [Google Scholar]
- Winthrop, J.T.; Worthington, C.R. Theory of Fresnel images. I. Plane periodic objects in monochromatic light. JOSA 1965, 55, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, F. Polarization guided specular reflection separation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7280–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lin, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Huang, F. Rapid Detection of Camouflaged Artificial Target Based on Polarization Imaging and Deep Learning. IEEE Photonics J. 2021, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Dehghan, M.; Zaiane, O.R.; Jagersand, M. U2-Net: Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 106, 107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.A.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Tozza, S. Height-from-polarisation with unknown lighting or albedo. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 2875–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, D.; Tan, R.T.; Hara, K.; Ikeuchi, K. Polarization-Based Inverse Rendering from a Single View. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision, IEEE International Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–16 October 2003; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; p. 982. [Google Scholar]





| Polarization Images | Estimated Normal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input 1 [19] | √ | √ | |||||
| Input 2 | √ | √ | |||||
| Input 3 | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Input 4 [22] | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Input 5 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Input 6 (Ours) | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Network | Input | Mean Angular Error ↓ | Parameters (M) | Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SfP-UNet | 1 | Input 1 | 21.76° | 49.59 | 0.545 |
| 2 | Input 2 | 20.15° | 49.59 | 0.545 | |
| 3 | Input 3 | 19.88° | 49.59 | 0.550 | |
| Network | Input | Mean Angular Error ↓ | Parameters (M) | Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SfP-UNet | 1 | Input 1 | 21.76° | 49.59 | 0.545 |
| 2 | Input 2 | 20.15° | 49.59 | 0.545 | |
| 3 | Input 3 | 19.88° | 49.59 | 0.550 | |
| SfP-U2Net | 4 | Input 2 | 18.55° | 44.02 | 0.545 |
| 5 | Input 3 | 18.52° | 44.02 | 0.550 | |
| 6 | Input 4 | 18.46° | 44.01 | 0.180 | |
| 7 | Input 5 | 18.45° | 44.01 | 0.180 | |
| 8 | Input 6 (Ours) | 17.60° | 44.02 | 0.207 | |
| Method | Mean Angular Error ↓ |
|---|---|
| Miyazaki [35] | 50.97 |
| Mahmoud [10] | 58.43 |
| Smith [34] | 51.84 |
| DeepSfP [21] | 21.76 |
| SPW [24] | 21.75 |
| Ours | 17.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, F. Three Dimensional Shape Reconstruction via Polarization Imaging and Deep Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104592
Wu X, Li P, Zhang X, Chen J, Huang F. Three Dimensional Shape Reconstruction via Polarization Imaging and Deep Learning. Sensors. 2023; 23(10):4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104592
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xianyu, Penghao Li, Xin Zhang, Jiangtao Chen, and Feng Huang. 2023. "Three Dimensional Shape Reconstruction via Polarization Imaging and Deep Learning" Sensors 23, no. 10: 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104592
APA StyleWu, X., Li, P., Zhang, X., Chen, J., & Huang, F. (2023). Three Dimensional Shape Reconstruction via Polarization Imaging and Deep Learning. Sensors, 23(10), 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104592






