Effective Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensor for Detection of Atrazine Residue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
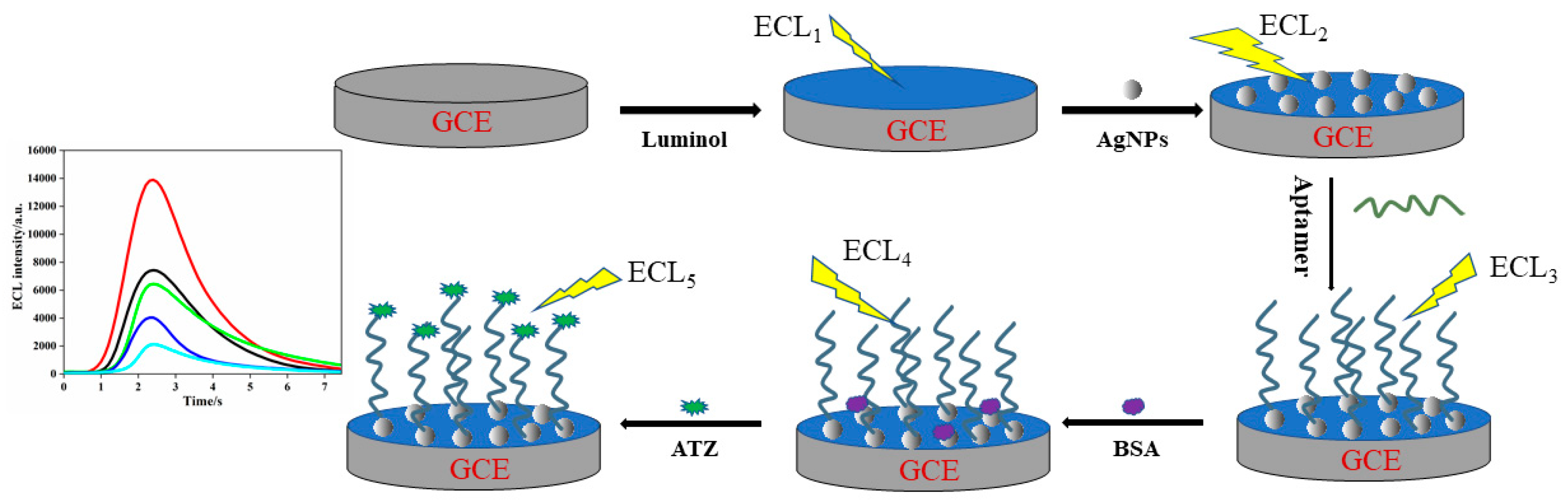
2.3. Fabrication of the ECL Aptasensor
2.4. Experimental Conditions
2.5. Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of AgNPs
3.2. Electrochemical and ECL Properties of the Fabricated Electrodes
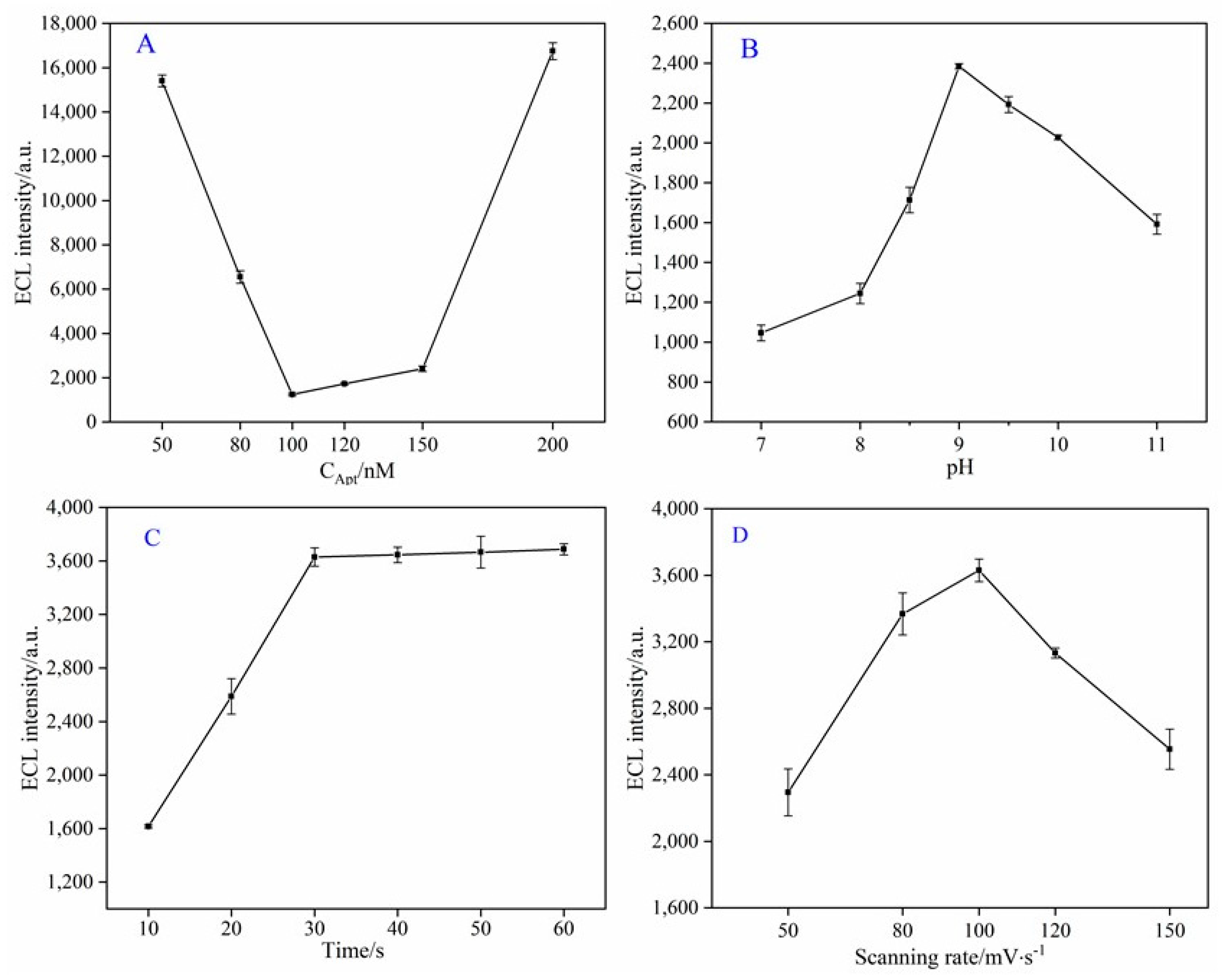
3.3. Optimization of Experiment Parameters
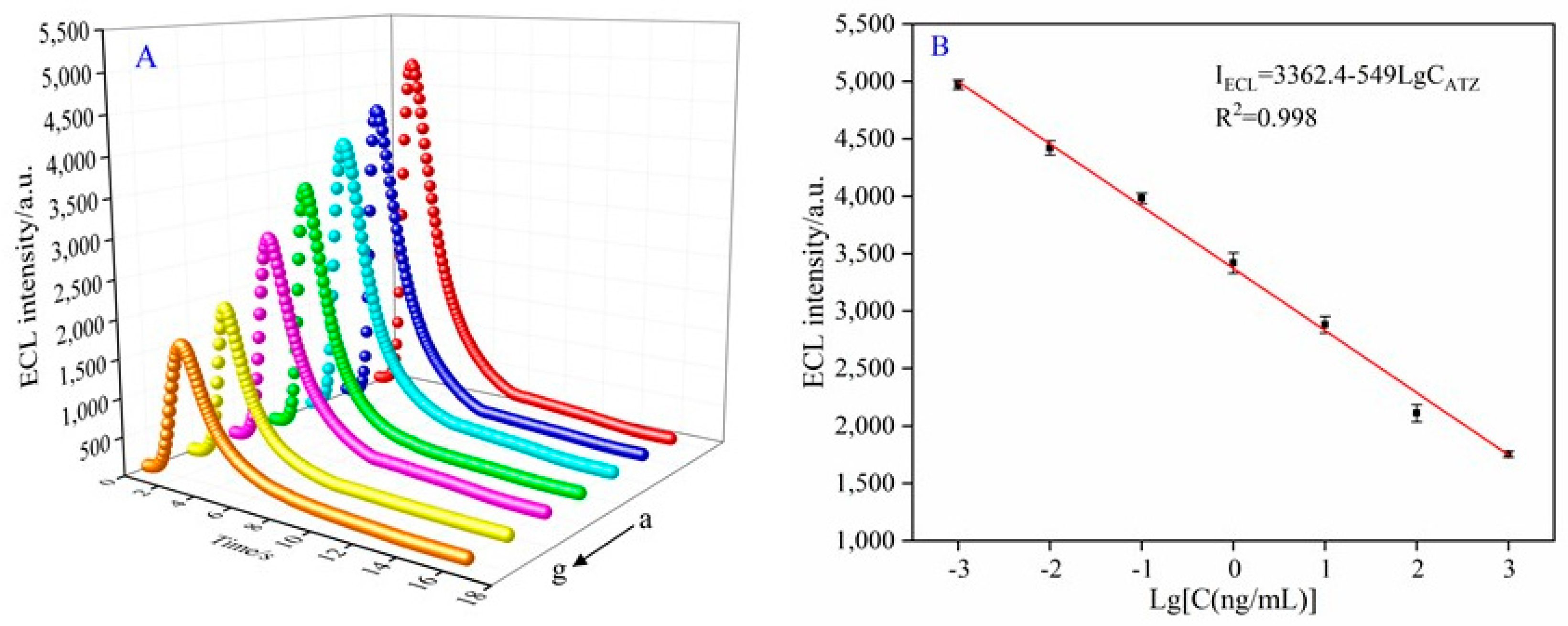
3.4. ECL Analytical Performance of the Aptasensor
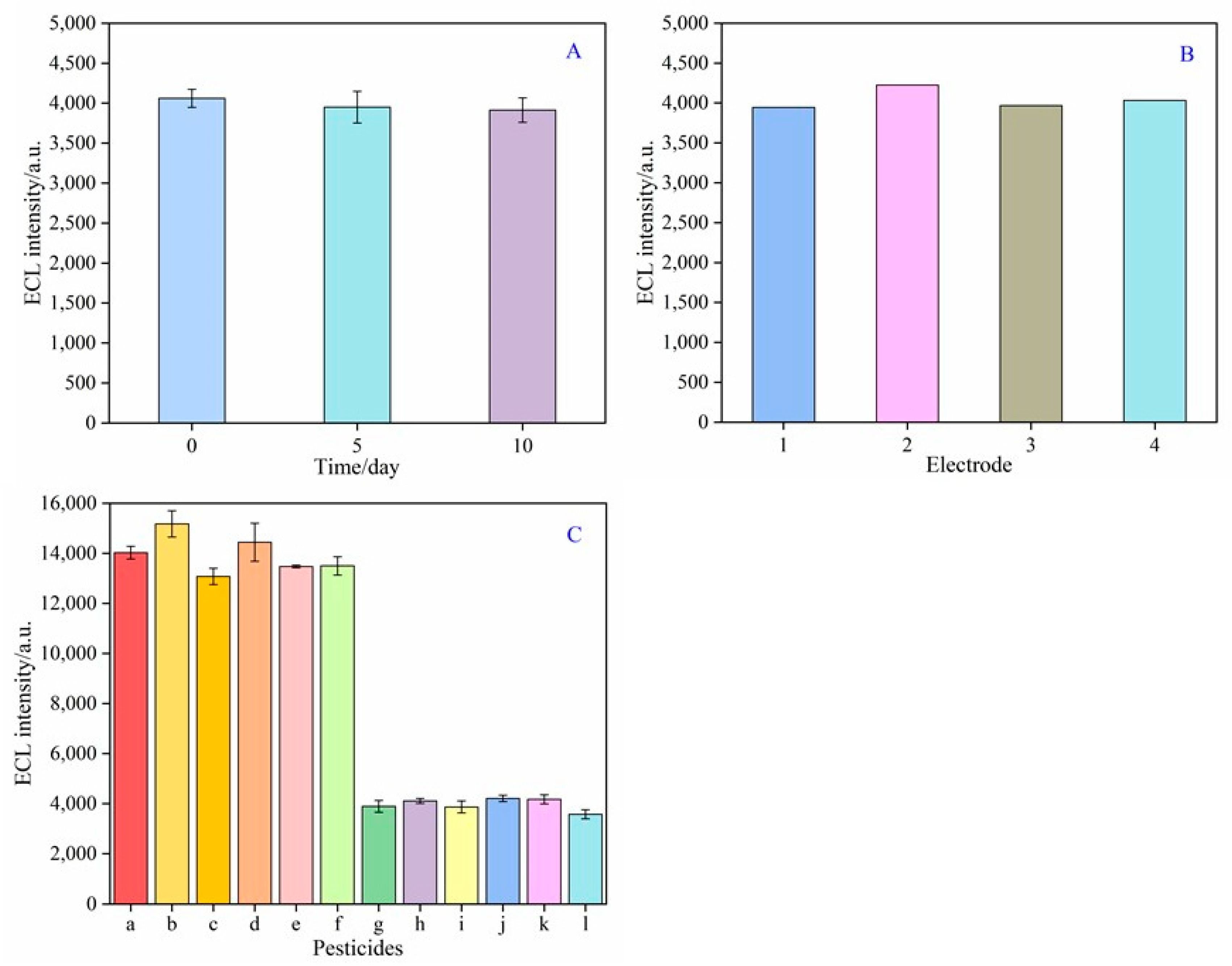
3.5. Stability, Reproducibility, and Specificity of the Aptasensor
3.6. Analysis of Actual Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Acronyms
| ATZ | atrazine |
| AgNPs | Ag nanoparticles |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CV | cyclic voltammetry |
| ECL | electrochemiluminescence |
| GCE | glass carbon electrode |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| GC-MS | gas chromatography-mass spectrometer |
| HPLC-MS | high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| LC | liquid chromatography |
| NH2-MIL-88(Fe) | Fe-based metal-organic framework |
| PBS | phosphate buffer saline |
| RSD | relative standard deviation |
References
- Bia, G.; Borgnino, L.; Ortiz, P.I.; Pfaffen, V. Multivariate optimization of square wave voltammetry using bismuth film electrode to determine atrazine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Yola, M.L.; Eren, T.; Atar, N. Selective QCM sensor based on ATZ imprinted polymer: Its application to wastewater sample. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 218, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Locoro, G.; Comero, S.; Contini, S.; Schwesig, D.; Werres, F.; Balsaa, P.; Gans, O.; Weiss, S.; Blaha, L. Pan-European survey on the occurrence of selected polar organic persistent pollutants in ground water. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4115–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonowski, N.D.; Schffer, A.; Burauel, P. Still present after all these years: Persistence plus potential toxicity raise questions about the use of atrazine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovaios, I.D.; Paraskeva, C.A.; Koutsoukos, P.G. Adsorption of ATZ azine from aqueous electrolyte solutions on humic acid and silica. J. Colloid. Interface. Sci. 2011, 356, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, D.; Gu, Z.; Yan, X. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes coated fibers for solid-phase microextraction of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in water and milk samples before gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1137, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berijani, S.; Assady, Y.; Anbia, M.; Hosseini, M.R.M. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with gas chromatography-flame photometric detection Very simple, rapid and sensitive method for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1123, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhamssa, N.; Justino, C.I.; Santos, P.S.; Cardoso, S.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Ksibi, M. Label-free disposable immunosensor for detection of atrazine. Talanta 2016, 146, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, G.M.; Jardim, I.S. Use of solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of triazine residues in water: Validation of the method. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 869, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezić, I.; Horvat, A.J.M.; Babić, S.; Macan, K.M. Determination of pesticides in honey by ultrasonic solvent extraction and thin-layer chromatography. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2005, 12, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.K.; Filipov, N.M. Determination of atrazine and its metabolites in mouse urine and plasma by LC–MS analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 351, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; He, G.; Wang, J.; Lü, C. Joint toxic effects of heavy metals and atrazine on invasive plant species Solidago Canadensis L. Chin. J. Geochem. 2011, 30, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, R.P.Z.; Marcilio, K.M.; Leme, F.M.; Tfouni, S.A.V. Analysis of pesticide residues in sugarcane juice using QuEChERS sample preparation and gas chromatography with electron capture detection. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Su, M.; Wu, X.; Sun, H. Rapid selective accelerated solvent extraction and simultaneous determination of herbicide atrazine and its metabolites in fruit by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4512–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Shen, S.; Yan, H.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X. Efficient enrichment and analysis of atrazine and its degradation products in Chinese Yam using accelerated solvent extraction and pipette tip solid-phase extraction followed by UPLC–DAD. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djozan, D.; Ebrahimi, B. Preparation of new solid phase micro extraction fiber on the basis of atrazine-molecular imprinted polymer: Application for GC and GC/MS screening of triazine herbicides in water, rice and onion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 616, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, E.O.; Çağlak, A.; Engin, G.O.; Bakirdere, S. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive solid phase extraction based on Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for the determination of 4-tertoctylphenol and atrazine by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Cheng, H. Rapid extraction and determination of atrazine and its degradation products from microporous mineral sorbents using microwave-assisted solvent extraction followed by ultra-HPLC-MS/MS. Mikrochim. Acta 2013, 180, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, D.; Jin, R.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Yan, X.; Su, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, F.; Sun, P.; Liu, X.; et al. Fluorescent hydrogel test kit coordination with smartphone: Robust performance for on-site dimethoate analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; He, J.; Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. Smart plant-wearable biosensor for in-situ pesticide analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 170, 112636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Gu, Y.; Han, C.; Yang, G.; Cao, Z.; Qu, L. Highly sensitive SERS substrates with multi-hot spots for on-site detection of pesticide residues. Food Chem. 2022, 381, 132208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhang, P. A label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles for direct detection of atrazine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, P.; Tripathy, S.; Vanjari, S.R.K.; Singh, V.; Singh, S.G. Electrospun tin (IV) oxide nanofiber based electrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive and selective detection of atrazine in water at trace levels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, C.; Yan, W.; Guo, Y.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Bi, Y. Design of a facile and label-free electrochemical aptasensor for detection of atrazine. Talanta 2019, 201, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Tan, W. The optical property of core-shell nanosensors and detection of atrazine based on localized surface plasmon resonance(LSPR) Sensing. Sensors 2014, 14, 13273–13284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Mao, L.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Shu, Z.; Hu, Y. SPR quantitative analysis of direct detection of atrazine traces on Au-nanoparticles: Nanoparticles size effect. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 218, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Çimen, D.; Derazshamshir, A.; Bereli, N.; Yılmaz, F.; Denizli, A. Development of surface plasmon resonance sensors based on molecularly imprinted nanofilms for sensitive and selective detection of pesticides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.Y.; Ruan, X.; Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Du, D.; Wie, B.J.V. Mesoporous Pd@Pt nanoparticle-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of atrazine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1116, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chen, W.; Ju, H. Sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of atrazine based on aggregation of silver nanoparticles modified carbon dots Sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of aggregation of silver nanoparticles modified carbon dots. Talanta 2019, 201, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; She, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Jin, F.; Shao, M.; et al. Competitive fluorescence assay for specific recognition of atrazine by Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer based on Fe3O4-chitosan. Carbohyd Polym. 2016, 137, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.; Bera, M.K.; Das, R.K. Rapid “turn-on” detection of atrazine using highly luminescent N-doped carbon quantum dot. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, R.; Basinger, N.T.; Iersel, M.W. Low-Cost Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging for Stress Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, D.J.; Porter, N.A.; Roddick, F.A. A fast screening method for the presence of atrazine and other triazines in water using flow injection with chemiluminescent detection. Talanta 2009, 78, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, C.R.; Boro, R.; Nangia, Y.; Gandhi, S.; Sharma, P.; Wangoo, N.; Rajesh, K.; Shekhawat, G.S. Immunoanalytical techniques for analyzing pesticides in the environment. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.M.; Crihfield, C.L.; Gattu, S.; Holland, L.A.; Sooter, L.J. In vitro selection of a single-stranded DNA molecular recognition element against atrazine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 14332–14347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Cao, Y.; Gou, X.; Zhu, J. Recent Progress in Electrochemiluminescence Sensing and Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolci, L.S.; Zanarini, S.; Ciana, L.D.; Paolucci, F.; Roda, A. Development of a new device for ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence microscopy imaging. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6234–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, R.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on Ru(bpy)32+ and Ag nanoparticles doped SBA-15 for detection of cancer antigen 15-3. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Chu, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for kanamycin detection based on silver nanoparticle-catalyzed chemiluminescent reaction between luminol and hydrogen peroxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, F.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, Y. Novel Au-tetrahedral aptamer nanostructure for the electrochemiluminescence detection of acetamiprid. J. Hazard. Mater 2021, 401, 123794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence and its biorelated applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2506–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Amplification strategies using electrochemiluminescence biosensors for the detection of DNA, bioactive molecules and cancer biomarkers. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 65, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J. Recent advances in electrochemiluminescence analysis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Tan, X.; Ou, X.; Chen, S.; Wei, S. An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for the detection of concanavalin A based on Au nanoparticles-thiosemicarbazide functionalized PtNi nanocubes as signal enhancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiong, C.; Yuan, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. A sensitive electro-chemiluminescence immunosensor based on luminophore capped Pd@Au core-shell nanoparticles as signal tracers and ferrocenyl compounds as signal enhancers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jie, G. An “on-off” electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on DNA nanotweezer probe coupled with tripod capture DNA for high sensitive detection of Pb2+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Bian, W.; Tian, D.; Xia, F.; Zhou, C. A novel electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based CdTe QDs@NH2-MIL-88(Fe) for signal amplification. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 354, 136644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yi, J.; Xia, F.; Zhou, C. Electrochemical luminescence sensor based on double suppression for highly sensitive detection of glyphosate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Li, J.; Kong, Q.; Zhai, H.; Xu, R.; Yang, F.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y. A novel electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on copper-gold bimetallic nanoparticles and its applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Gong, J. Bifunctional S, N-Codoped carbon dots-based novel electrochemiluminescent bioassay for ultrasensitive detection of atrazine using activated mesoporous biocarbon as enzyme nanocarriers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1073, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, M.; Sun, H.; Lu, H.; Zhao, G. Immobilization-free photoelectrochemical aptasensor for environmental pollutants: Design, fabrication and mechanism. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 140, 111352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Method | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Detection limit (ng/mL) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GC | 25–200 | 40 | [13] |
| HPLC | 10–5000 | 3 | [15] |
| GC-MS | 25–500 | 6.81 | [17] |
| HPLC-MS | 1–1000 | 89.6 | [18] |
| Electrochemical | 0.05–0.5 | 0.016 | [22] |
| SERS | 0.22–21.57 | 0.22 | [29] |
| Fluorescent | 50.04–3998.71 | 18.85 | [30] |
| Chemiluminescence | 2.15–2150 | 1.3 | [33] |
| ECL | 0.0001–0.01; 0.01–20 | 0.08 | [50] |
| Photoelectrochemical | 0.001–0.0065 | 2.59 × 10−6 | [51] |
| ECL | 0.001–1000 | 3.3 × 10−4 | This work |
| Sample | Spiked Concentration (ng/mL) | Detected Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Recovery Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 0.1 | 0.12 | 3.32 | 123.03 | |
| 1 | 0.89 | 2.15 | 95.50 | |
| 10 | 10.96 | 3.49 | 109.65 | |
| Soil | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 0.1 | 0.10 | 3.74 | 102.33 | |
| 1 | 1.05 | 3.07 | 104.71 | |
| 10 | 11.22 | 3.14 | 112.20 | |
| Cabbage | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 0.1 | 0.12 | 2.63 | 114.82 | |
| 1 | 1.17 | 0.69 | 117.48 | |
| 10 | 8.91 | 5.12 | 89.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Li, H.; Hu, M.; Bai, M.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X. Effective Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensor for Detection of Atrazine Residue. Sensors 2022, 22, 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093430
Huang X, Li H, Hu M, Bai M, Guo Y, Sun X. Effective Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensor for Detection of Atrazine Residue. Sensors. 2022; 22(9):3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093430
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xue, He Li, Mengjiao Hu, Mengyuan Bai, Yemin Guo, and Xia Sun. 2022. "Effective Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensor for Detection of Atrazine Residue" Sensors 22, no. 9: 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093430
APA StyleHuang, X., Li, H., Hu, M., Bai, M., Guo, Y., & Sun, X. (2022). Effective Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensor for Detection of Atrazine Residue. Sensors, 22(9), 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093430





