Differences between Systems Using Optical and Capacitive Sensors in Treadmill-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis of Level and Sloping Gait
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample
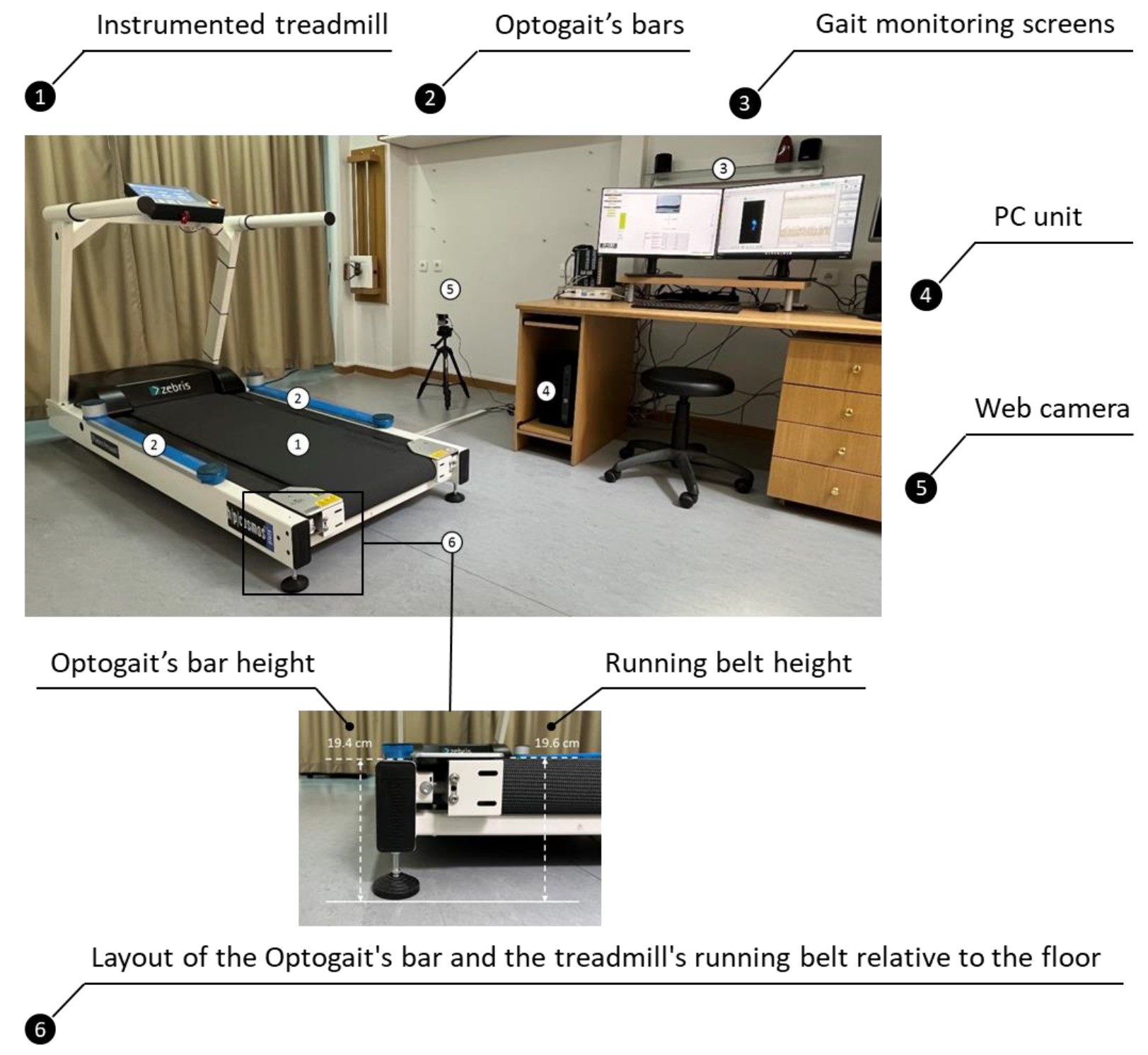
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Testing Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
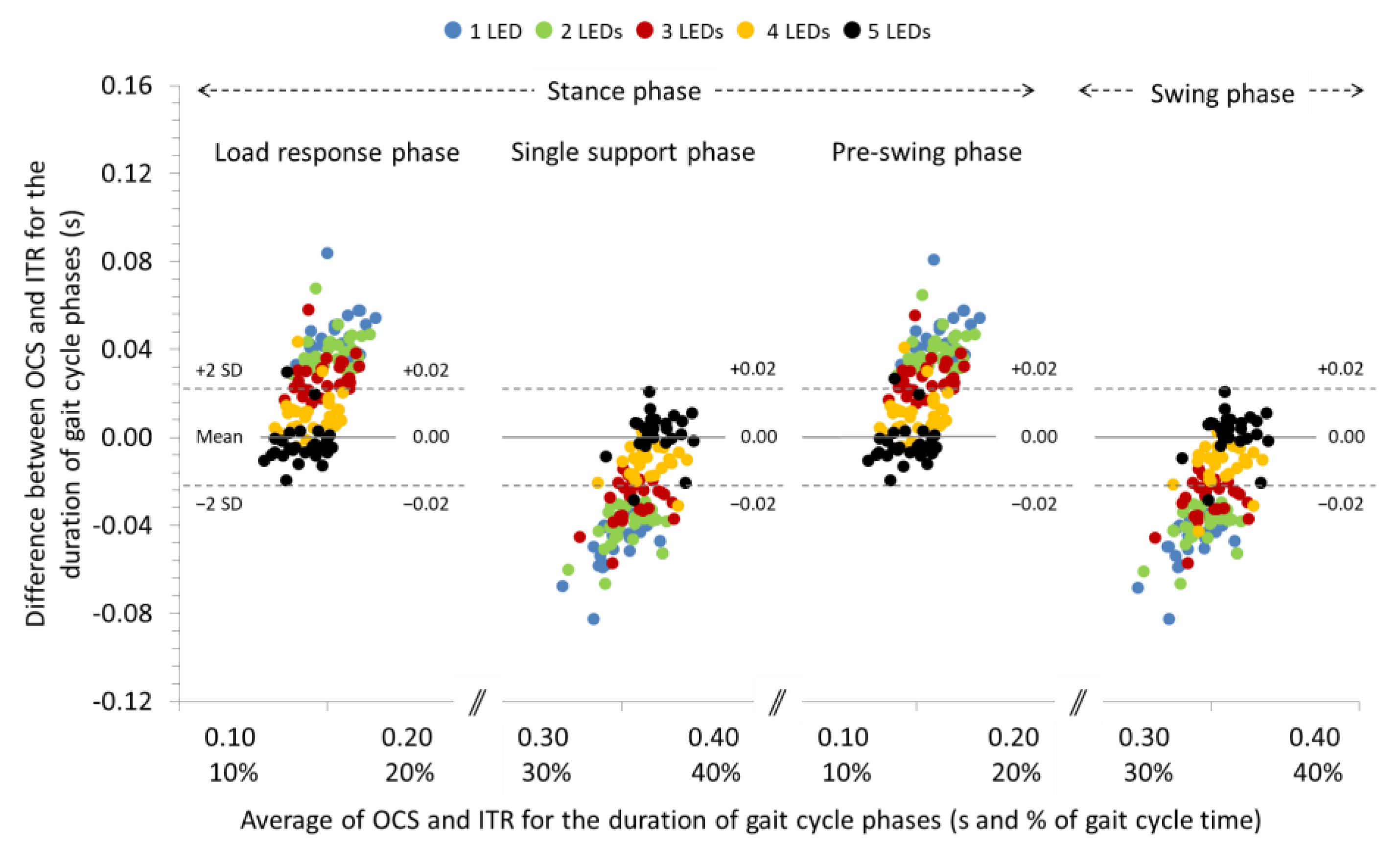
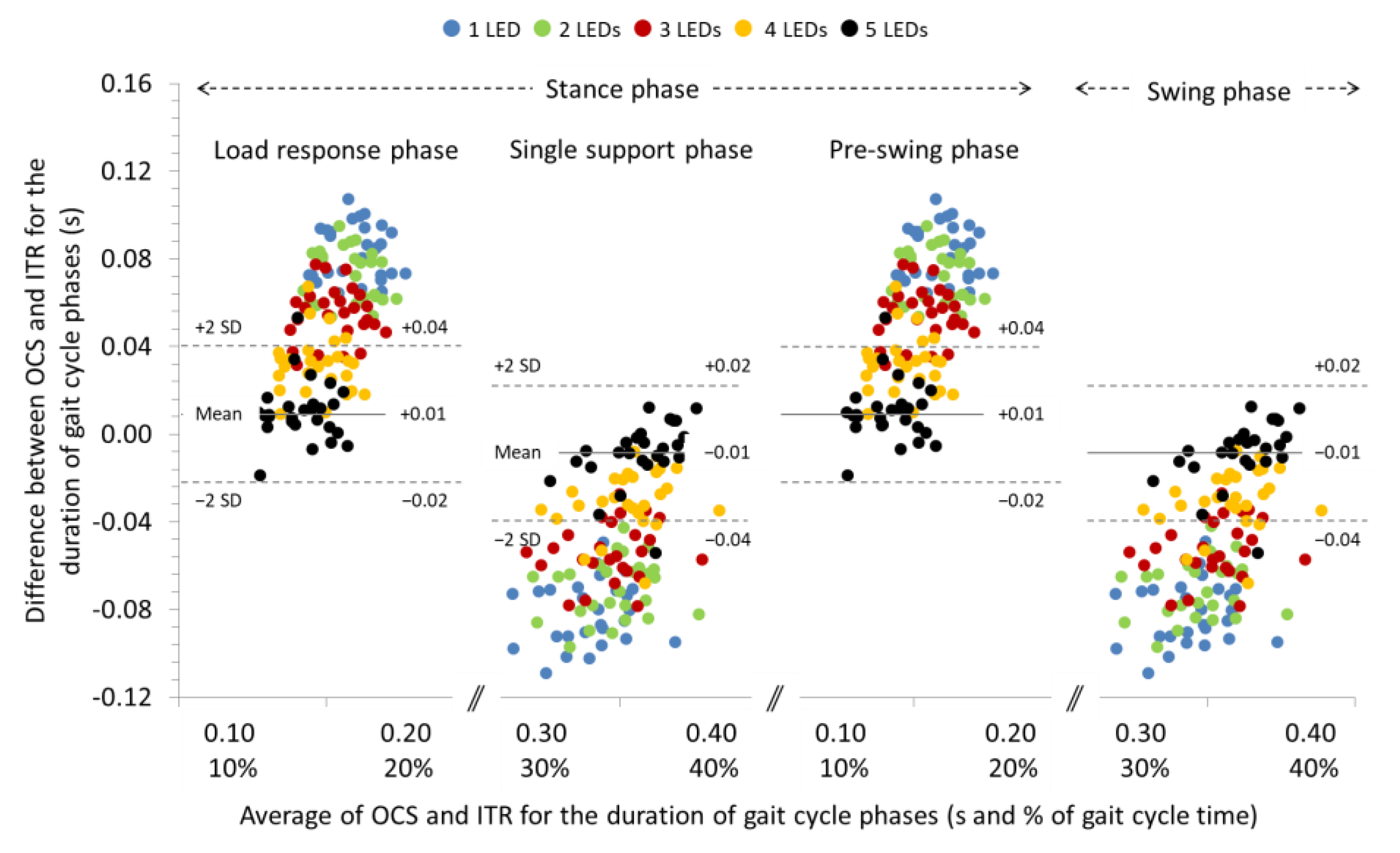
3.1. Agreement between OCS and ITR for the Spatiotemporal Parameters of Gait at 0% Slope
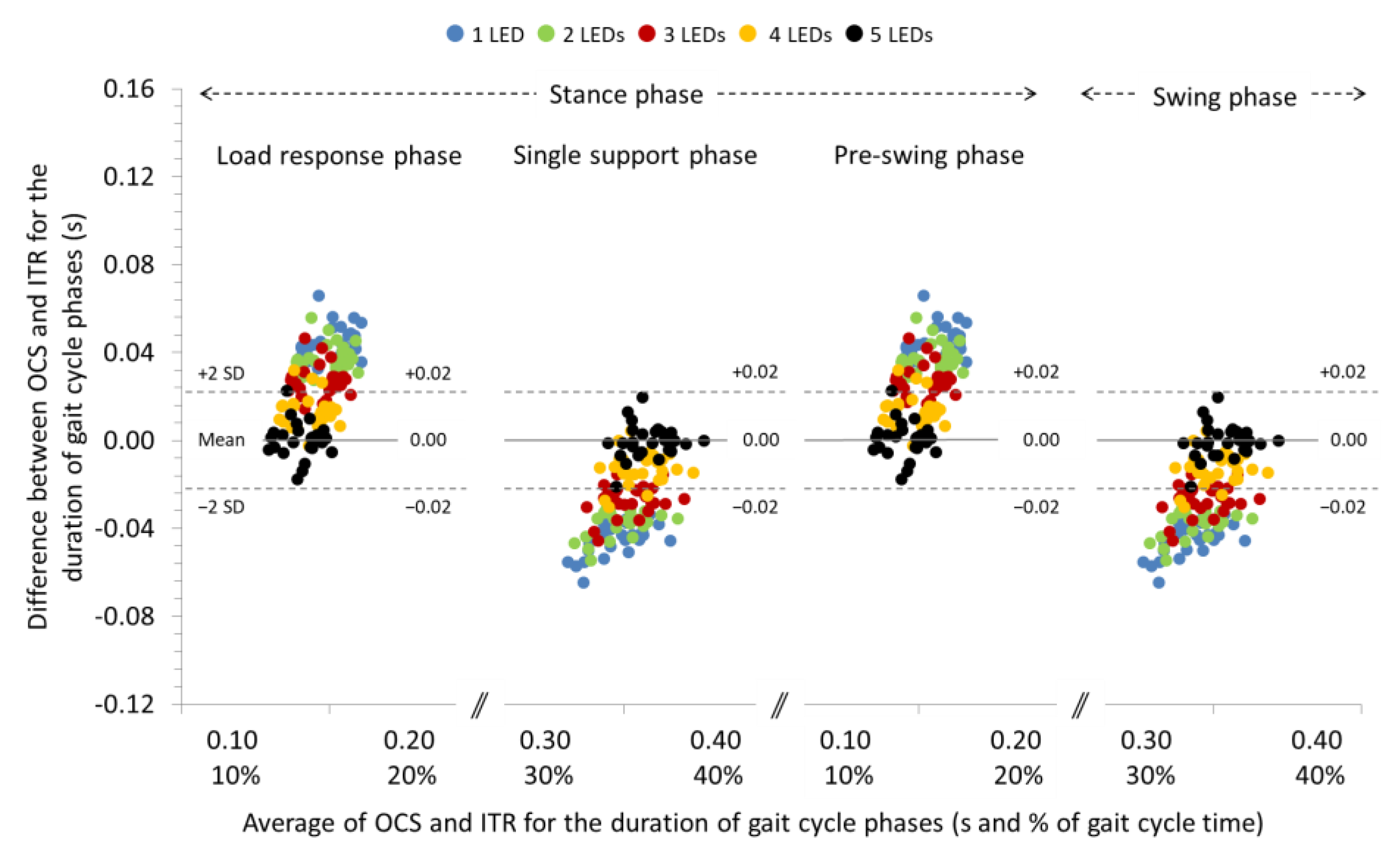
3.2. Agreement between OCS and ITR for the Spatiotemporal Parameters of Gait at −10% and −20% Slopes
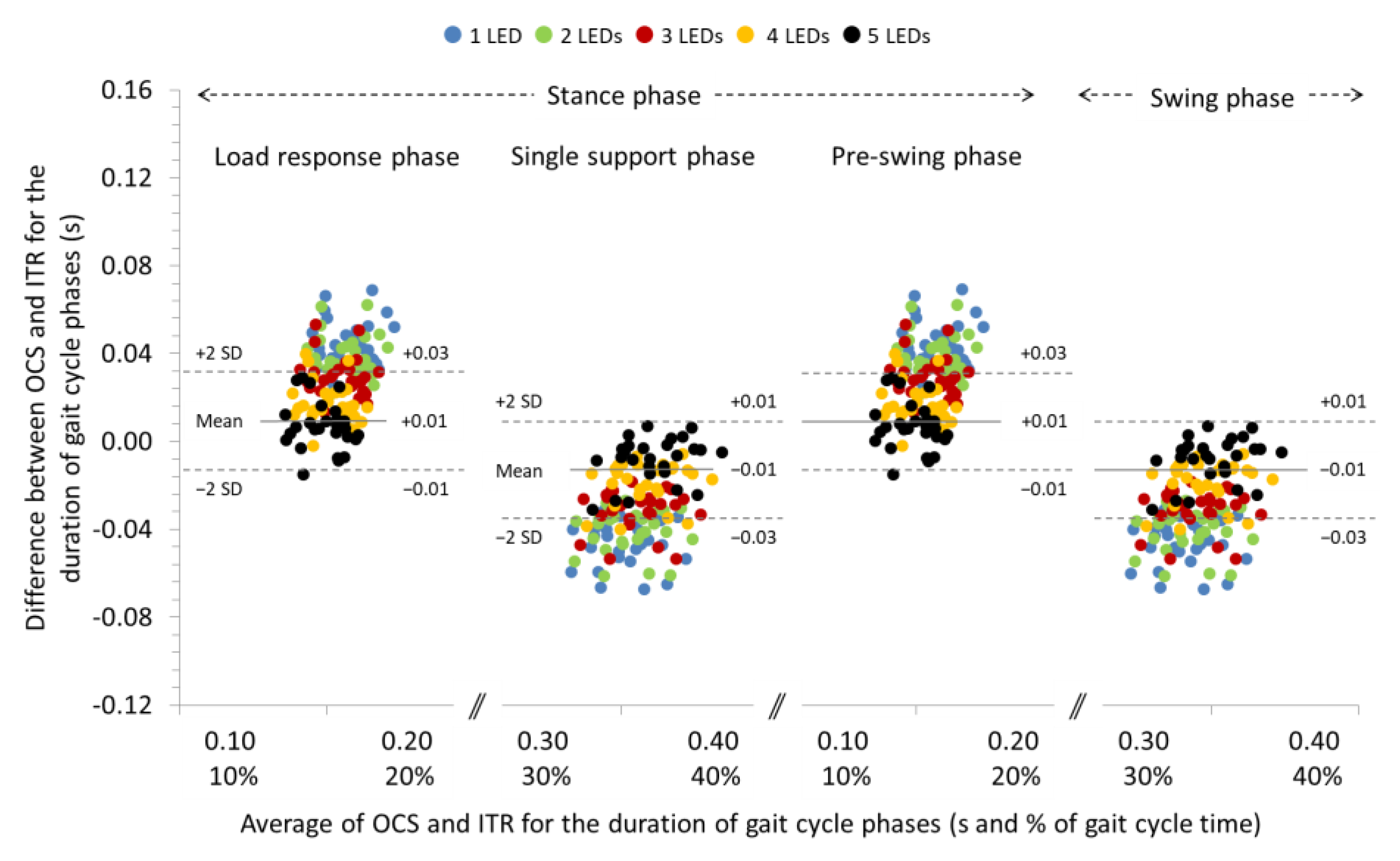
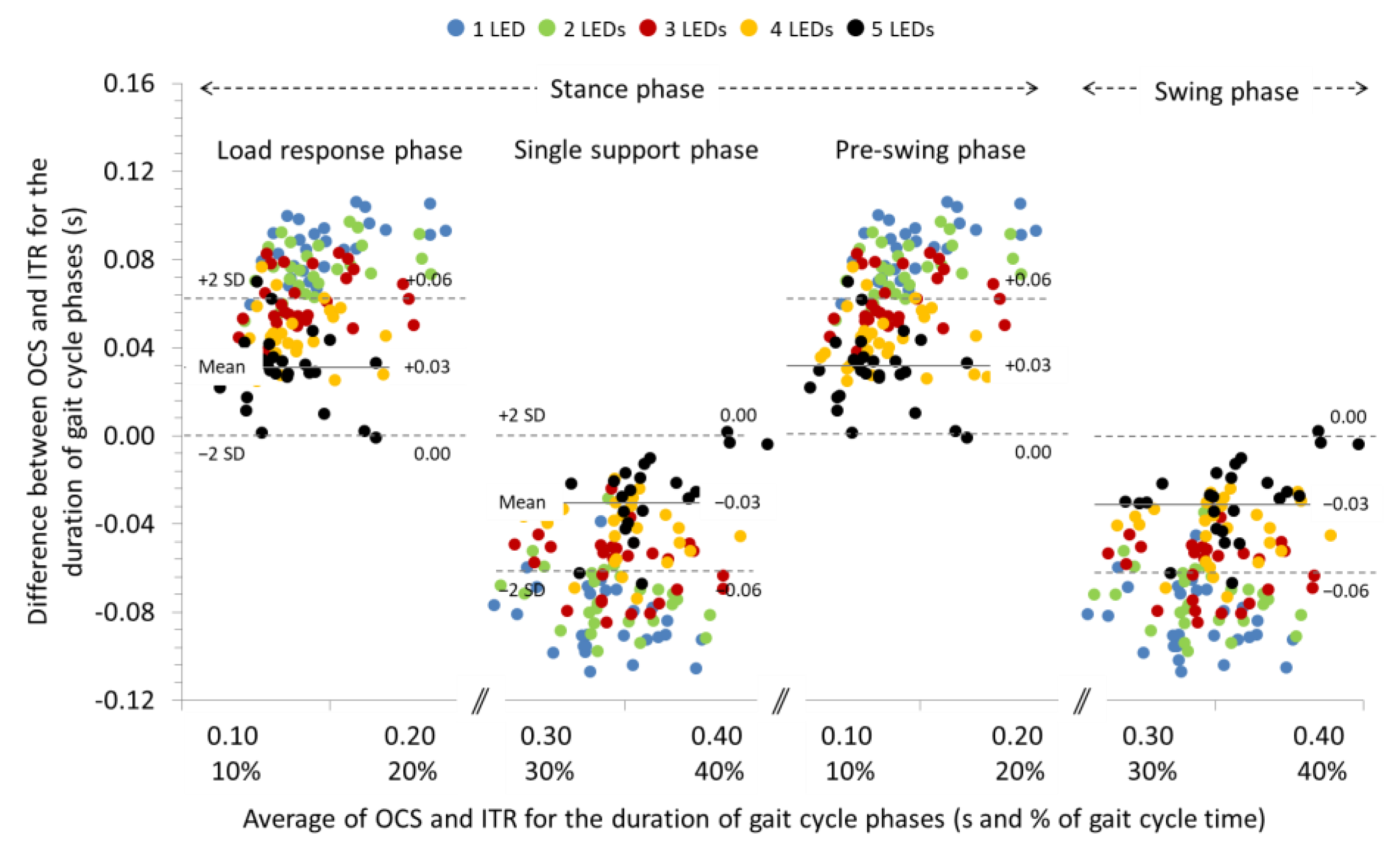
3.3. Agreement between OCS and ITR for the Spatiotemporal Parameters of Gait at +10% and +20% Slopes
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wren, T.A.L.; Tucker, C.A.; Rethlefsen, S.A.; Gorton III, G.E.; Õunpuu, S. Clinical efficacy of instrumented gait analysis: Systematic review 2020 update. Gait Posture 2020, 80, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajales-Lopez, J.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Casado-Hernández, I.; Benito-De Pedro, M.; Rodríguez-Sanz, D.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Antolín, M.S. The optogait motion analysis system for clinical assessment of 2D spatio-temporal gait parameters in young adults: A reliability and repeatability observational study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Bernal, A.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E. Reliability of the OptoGait portable photoelectric cell system for the quantification of spatial-temporal parameters of gait in young adults. Gait Posture 2016, 50, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, E.S.; Jung, B.; Park, S.W.; Ha, I.H. Association between pain and gait instability in patients with lumbar disc herniation. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymczak, M.; Krupa, P.; Oszkinis, G.; Majchrzycki, M. Gait pattern in patients with peripheral artery disease. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Lago, H.; Bello, O.; López-Alonso, V.; Sánchez, J.A.; Morenilla, L.; Fernández-Del-Olmo, M.Á. Gait pattern and cognitive performance during treadmill walking in Parkinson disease. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabi.l 2015, 94, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul Razak, A.H.; Zayegh, A.; Begg, R.K.; Wahab, Y. Foot plantar pressure measurement system: A review. Sensors 2012, 12, 9884–9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.L.; Hidler, J. Biomechanics of overground vs. treadmill walking in healthy individuals. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faude, O.; Donath, L.; Roth, R.; Fricker, L.; Zahner, L. Reliability of gait parameters during treadmill walking in community-dwelling healthy seniors. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüesch, C.; Overberg, J.A.; Schwameder, H.; Pagenstert, G.; Mündermann, A. Repeatability of spatiotemporal, plantar pressure and force parameters during treadmill walking and running. Gait Posture 2018, 62, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.F.; Urry, S.R.; Wearing, S.C. Reliability of spatiotemporal and kinetic gait parameters determined by a new instrumented treadmill system. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Item-Glatthorn, J.F.; Casartelli, N.C.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Reproducibility of gait parameters at different surface inclinations and speeds using an instrumented treadmill system. Gait Posture 2016, 44, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.W.; Kwon, O.S.; Seo, D.K.; Jung, S.W.; Lee, K.J.; Choi, S.; Lee, S.W. Changes of normal adult physiological states and gait parameters with treadmill inclined. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2012, 24, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milic, M.; Erceg, M.; Palermi, S.; Iuliano, E.; Borrelli, M.; Cè, E.; Esposito, F.; Padulo, J. Uphill walking at iso-efficiency speeds. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, P.; Clémençon, M.; Morel, B.; Quiniou, G.; Saboul, D.; Hautier, C.A. Comparison of level and graded treadmill tests to evaluate endurance mountain runners. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2016, 15, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Mo Lee, M.; Song, C.H.; Lee, K.J.; Jung, S.W.; Shin, D.C.; Shin, S.H. Concurrent Validity and Test-retest Reliability of the OPTOGait Photoelectric Cell System for the Assessment of Spatio-temporal Parameters of the Gait of Young Adults. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lienhard, K.; Schneider, D.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Validity of the Optogait photoelectric system for the assessment of spatiotemporal gait parameters. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, A.; Linyard-Tough, K.; Chockalingam, N. Agreement between the Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters of Healthy Adults from the OptoGait System and a Traditional Three-Dimensional Motion Capture System. J. Biomech. Eng. 2019, 141, 014501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Song, C.; Lee, K.; Shin, D.; Shin, S. Agreement between the spatio-temporal gait parameters from treadmill-based photoelectric cell and the instrumented treadmill system in healthy young adults and stroke patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weart, A.N.; Miller, E.M.; Freisinger, G.M.; Johnson, M.R.; Goss, D.L. Agreement Between the OptoGait and Instrumented Treadmill System for the Quantification of Spatiotemporal Treadmill Running Parameters. Front. Sport. Act. Living. 2020, 2, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearing, S.C.; Reed, L.F.; Urry, S.R. Agreement between temporal and spatial gait parameters from an instrumented walkway and treadmill system at matched walking speed. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strutzenberger, G.; Leutgeb, L.; Claußen, L.; Schwameder, H. Gait on slopes: Differences in temporo-spatial, kinematic and kinetic gait parameters between walking on a ramp and on a treadmill. Gait Posture 2021, 91, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Mu, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, S. Cities are going uphill: Slope gradient analysis of urban expanpLEASEsion and its driving factors in China. Sci. Total Environ 2021, 775, 145836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trailism. Available online: https://trailism.com/ (accessed on 2 January 2022).
- Bohannon, R.W.; Williams Andrews, A. Normal walking speed: A descriptive meta-analysis. Physiotherapy 2011, 97, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingel, T.J. Modeling slope as a contributor to route selection in mountainous areas. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 37, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobler, W. Three Presentations on Geographical Analysis and Modeling: Non- Isotropic Geographic Modeling; Speculations on the Geometry of Geography and Global Spatial Analysis. Tech. Rep. 1993, 93. Available online: https://escholarship.org/content/qt05r820mz/qt05r820mz.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- Meyer, C.; Killeen, T.; Easthope, C.S.; Curt, A.; Bolliger, M.; Linnebank, M.; Zörner, B.; Filli, L. Familiarization with treadmill walking: How much is enough? Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, A.; Tarantola, J.; Giordano, A.; Schieppati, M. Fatigue effects on body balance. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol./Electromyogr. Mot. Control. 1997, 105, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eston, R. Use of ratings of perceived exertion in sports. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2012, 7, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portney, L.G.; Watkins, M.P. Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2002, 47, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistics Notes: Measurement error. Br. Med. J. 1996, 313, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Analysis of continuous data from small samples. Br. Med. J. 2009, 338, a3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, B.; Tucker, C.B. Reliability of the Optojump next system for measuring temporal values in elite racewalking. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 3438–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tirosh, O.; Sparrow, W.A. Identifying heel contact and toe-off using forceplate thresholds with a range of digital-filter cutoff frequencies. J. Appl. Biomech. 2003, 19, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, A.; Aoi, W.; Takami, M.; Hirano, N.; Ogaya, Y.; Wada, S.; Higashi, A. Effect of downhill walking on next-day muscle damage and glucose metabolism in healthy young subjects. J. Physiol. Sci. 2019, 69, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Chaloupka, E.C.; Mastrangelo, M.A.; Hoffman, J.R. Physiological and biomechanical analysis of treadmill walking up various gradients in men and women. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 86, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strutzenberger, G.; Leutged, L.; Clauβen, L.; Schwameder, H. Gait on slopes Differences in temporo-spatial, kinematic. Gait Posture 2022, 91, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmelat, V.; Duncan, A.; Meltz, S. Effect of sampling frequency on fractal fluctuations during treadmill walking. PLoS One 2019, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarvestan, J.; Ataabadi, P.A.; Yazdanbakhsh, F.; Abbasi, S.; Abbasi, A.; Svoboda, Z. Lower limb joint angles and their variability during uphill walking. Gait Posture 2021, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Shin, G. Foot kinematics and leg muscle activation patterns are altered in those with limited ankle dorsiflexion range of motion during incline walking. Gait Posture 2022, 92, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, O.; Malhotra, K.; Buraimoh, O.; Cullen, N.; Welck, M.; Goldberg, A.; Singh, D. Gastrocnemius tightness: A population based observational study. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 25, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, P.; Ahn, J. A Pressure-Pad-Embedded Treadmill Yields Time-Dependent Errors in Estimating Ground Reaction Force during Walking. Sensors 2021, 21, 5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, J.R.; Kram, R. The effects of grade and speed on leg muscle activations during walking. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| Step length (cm) | The distance between the point of heel contact of one foot and the point of a successive heel contact of the contralateral foot |
| Stride length (cm) | The distance between the point of heel contact of one foot and the point of a successive heel contact of the same foot |
| Step time (s) | The time between the point of heel contact of one foot and the point of a successive heel contact of the contralateral foot |
| Stride time (s) | The time between the point of heel contact of one foot and the point of a successive heel contact of the same foot |
| Cadence (step/min) | The frequency of steps per unit time |
| Loading response phase (s) | The time between heel contact of one foot and just before toe off of the contralateral foot. |
| Single support phase (s) | The time during which the entire plantar aspect of the weight-bearing foot has contact with the ground. |
| Pre-swing phase (s) | The time between heel contact of the contralateral foot and just before toe off of the other foot. |
| Swing phase (s) | The period of time during which the foot has no contact with the ground. |
| Gait Parameter | Reliability | Minimum Sensors Used for Detection of the Contact Event | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0% Slope) | Indices | 1 LED | 2 LEDs | 3 LEDs | 4 LEDs | 5 LEDs |
| Step length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.45, 0.57) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.45, 0.58) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.45, 0.58) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.07 (−0.45, 0.59) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.08 (−0.44, 0.59) b |
| Stride length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.04 (−0.87, 0.95) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.04 (−0.87, 0.95) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.05 (−0.85, 0.95) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.86, 0.98) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.85, 0.98) |
| Step time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) |
| Stride time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.994 (0.987, 0.997) 0.00 (−0.01 0.01) | 0.994 (0.987, 0.997) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.994 (0.987, 0.997) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.994 (0.987, 0.997) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.994 (0.987, 0.997) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) |
| Cadence (steps/min) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.08 (−0.47, 0.62) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.08 (−0.47, 0.62) c | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.48, 0.62) c,d | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.48, 0.62) c,d | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.48, 0.62) c,d |
| Load response phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.871 (0.717, 0.941) 0.05 a (0.03, 0.07) | 0.921 (0.826, 0.964) 0.04 a (0.02, 0.06) e | 0.911 (0.805, 0.960) 0.03 a (0.01, 0.04) e | 0.888 (0.755, 0.949) 0.01 a (−0.01, 0.03) e | 0.880 (0.737, 0.945) 0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) e |
| Single support phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.878 (0.732, 0.944) −0.05 a (−0.07, −0.02) | 0.901 (0.784, 0.955) −0.04 a (−0.06, −0.02) e | 0.888 (0.754, 0.949) −0.03 a (−0.05, −0.01) e | 0.868 (0.709, 0.940) −0.01 a (−0.03, 0.01) e | 0.865 (0.703, 0.938) 0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) e |
| Pre-swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.882 (0.741, 0.946) 0.05 a (0.03, 0.07) | 0.928 (0.841, 0.967) 0.04 a (0.02, 0.05) e | 0.918 (0.820, 0.963) 0.03 a (0.01, 0.04) e | 0.895 (0.770, 0.952) 0.01 a (−0.01, 0.03) e | 0.888 (0.754, 0.949) 0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) e |
| Swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.885 (0.747, 0.947) −0.05 a (−0.07, −0.02) | 0.908 (0.798, 0.958) −0.04 a (−0.06, −0.02) e | 0.895 (0.769, 0.952) −0.03 a (−0.05, −0.01) e | 0.870 (0.715, 0.941) −0.01 a (−0.03, 0.01) e | 0.868 (0.710, 0.940) 0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) e |
| Gait Parameter | Reliability | Minimum Sensors Used for Detection of the Contact Event | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (−10% Slope) | Indices | 1 LED | 2 LEDs | 3 LEDs | 4 LEDs | 5 LEDs |
| Step length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.04 (−0.53, 0.60) | 0.997 (0.995, 0.999) 0.04 (−0.54, 0.62) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.04 (−0.52, 0.61) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.53, 0.65) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) 0.07 (−0.51, 0.65) b |
| Stride length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.21a (−0.62, 1.04) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.23 a (−0.61, 1.07) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.25 a (−0.62, 1.12) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.26 a (−0.62, 1.15) | 0.998 (0.997, 0.999) 0.26 a (−0.63, 1.16) |
| Step time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.996 (0.992, 0.998) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.998) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.997 (0.992, 0.998) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.996 (0.992, 0.998) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.998) 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) |
| Stride time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.00 (0.01, 0.01) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) |
| Cadence (steps/min) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.08 (−0.54, 0.70) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.08 (−0.54, 0.69) c | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.55, 0.69) c,d | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.55, 0.69) c,d,e | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.55, 0.68) c,d,e |
| Load response phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.921 (0.826, 0.964) 0.04 a (0.03, 0.06) | 0.938 (0.865, 0.972) 0.04 a (0.02, 0.05) f | 0.920 (0.824, 0.963) 0.03 a (0.01, 0.04) f | 0.903 (0.786, 0.956) 0.01 a (0.00, 0.03) f | 0.899 (0.779, 0.954) 0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) f |
| Single support phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.952 (0.895, 0.978) −0.04 a (−0.06, −0.03) | 0.964 (0.920, 0.983) −0.04 a (−0.05, −0.02) f | 0.952 (0.896, 0.978) −0.03 a (−0.04, −0.01) f | 0.944 (0.878, 0.975) −0.01 a (−0.03, 0.00) f | 0.940 (0.869, 0.973) 0.00 (−0.02, 0.01) f |
| Pre-swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.924 (0.834, 0.965) 0.04 a (0.03, 0.06) | 0.941 (0.870, 0.973) 0.04 a (0.02, 0.05) f | 0.923 (0.832, 0.965) 0.03 a (0.01, 0.04) f | 0.905 (0.792, 0.957) 0.01 a (0.00, 0.03) f | 0.899 (0.779, 0.954) 0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) f |
| Swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.952 (0.894, 0.978) −0.04 a (−0.06, −0.03) | 0.963 (0.919, 0.983) −0.04 a (−0.05, −0.02) f | 0.952 (0.895, 0.978) −0.03 a (−0.04, −0.01) f | 0.944 (0.877, 0.975) −0.01 a (−0.03, 0.00) f | 0.940 (0.868, 0.973) 0.00 (−0.02, 0.01) f |
| Gait Parameter | Reliability | Minimum Sensors Used for Detection of the Contact Event | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (−20% Slope) | Indices | 1 LED | 2 LEDs | 3 LEDs | 4 LEDs | 5 LEDs |
| Step length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.50, 0.63) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.52, 0.63) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.50, 0.62) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.999) 0.06 (−0.51, 0.64) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) 0.05 (−0.52, 0.62) |
| Stride length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.999) 0.15 (−1.03, 1.33) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.999) 0.15 (−1.03, 1.33) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.999) 0.15 (−1.03, 1.33) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.999) 0.15 (−1.02, 1.33) | 0.997 (0.993, 0.999) 0.15 (−1.03, 1.33) |
| Step time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.994 (0.987, 0.997) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.00) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.00) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.00) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.00) |
| Stride time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.979 (0.954, 0.990) 0.00 (−0.04, 0.03) | 0.979 (0.955, 0.991) 0.00 (−0.04, 0.03) | 0.979 (0.955, 0.991) 0.00 (−0.03, 0.03) | 0.980 (0.955, 0.991) 0.00 (−0.03, 0.03) | 0.980 (0.955, 0.991) 0.00 (−0.03, 0.03) |
| Cadence (steps/min) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.984 (0.966, 0.993) −0.47 (−3.82, 2.88) | 0.996 (0.991, 0.998) −0.27 (−2.08, 1.54) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) −0.23 (−1.69, 1.23) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) −0.14 (−1.20, 0.92) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) −0.13 (−1.13, 0.88) |
| Load response phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.896 (0.771, 0.952) 0.05 a (0.02, 0.07) | 0.908 (0.798, 0.958) 0.04 a (0.02, 0.06) b | 0.916 (0.816, 0.962) 0.03 a (0.01, 0.05) b | 0.893 (0.764, 0.951) 0.02 a (0.00, 0.04) b | 0.865 (0.704, 0.938) 0.01 a (−0.01, 0.03) b |
| Single support phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.983 (0.863, 0.972) −0.05 a (−0.07, −0.03) | 0.946 (0.881, 0.975) −0.04 a (−0.06, −0.02) b | 0.950 (0.891, 0.977) −0.03 a (−0.05, −0.01) b | 0.950 (0.890, 0.977) −0.02 a (−0.04, 0.00) b | 0.946 (0.882, 0.975) −0.01 a (−0.03, 0.01) b |
| Pre-swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.893 (0.765, 0.951) 0.05 a (0.02, 0.07) | 0.907 (0.797, 0.958) 0.04 a (0.02, 0.06) b | 0.915 (0.813, 0.961) 0.03 a (0.01, 0.05) b | 0.892 (0.763, 0.951) 0.02 a (0.00, 0.04) b | 0.864 (0.701, 0.938) 0.01 a (−0.01, 0.03) b |
| Swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.938 (0.865, 0.972) −0.05 a (−0.07, −0.03) | 0.946 (0.882, 0.976) −0.04 a (−0.06, −0.02) b | 0.951 (0.893, 0.978) −0.03 a (−0.05, −0.01) b | 0.950 (0.891, 0.977) −0.02 a (−0.04, 0.00) b | 0.947 (0.883, 0.976) −0.01 a (−0.03, 0.01) b |
| Gait Parameter | Reliability | Minimum Sensors Used for Detection of the Contact Event | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (+10% Slope) | Indices | 1 LED | 2 LEDs | 3 LEDs | 4 LEDs | 5 LEDs |
| Step length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) −0.21 a (−0.83, 0.41) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) −0.22 a (−0.85, 0.42) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) −0.22 a (−0.87, 0.43) | 0.998 (0.995, 0.999) −0.23 a (−0.89, 0.44) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) −0.26 a (−0.97, 0.46) |
| Stride length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) −0.41 b (−1.29, 0.46) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) −0.41 b (−1.33, 0.50) | 0.999 (0.998, 0.999) −0.43 b (−1.38, 0.51) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) −0.45 b (−1.45, 0.55) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) −0.46 b (−1.51, 0.58) |
| Step time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.987 (0.971, 0.994) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.02) | 0.987 (0.971, 0.994) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.02) | 0.987 (0.971, 0.994) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.02) | 0.987 (0.971, 0.994) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.02) | 0.987 (0.971, 0.994) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.02) |
| Stride time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.989 (0.977, 0.995) 0.00 (−0.03, 0.03) | 0.989 (0.977, 0.995) 0.00 (−0.03, 0.03) | 0.989 (0.977, 0.995) 0.00 (−0.03, 0.03) | 0.989 (0.977, 0.995) 0.00 (−0.03, 0.03) | 0.989 (0.977, 0.995) 0.00 (−0.03, 0.03) |
| Cadence (steps/min) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.999 (0.999, 1.000) 0.08 (−0.49, 0.64) | 0.999 (0.999, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.49, 0.64) d | 0.999 (0.999, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.49, 0.63) | 0.999 (0.999, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.49, 0.63) e | 0.999 (0.999, 1.000) 0.07 (−0.49, 0.63) |
| Load response phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.884 (0.747, 0.947) 0.08 c (0.06, 0.11) | 0.890 (0.759, 0.950) 0.07 c (0.05, 0.10) f | 0.891 (0.760, 0.950) 0.05 c (0.03, 0.08) f | 0.871 (0.717, 0.941) 0.03 c (0.01, 0.06) f | 0.867 (0.708, 0.939) 0.01 c (−0.02, 0.04) f |
| Single support phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.918 (0.819, 0.962) −0.08 c (−0.11, −0.05) | 0.932 (0.850, 0.969) −0.07 c (−0.10, −0.04) f | 0.934 (0.856, 0.970) −0.05 c (−0.08, −0.03) f | 0.931 (0.848, 0.969) −0.03 c (−0.06, 0.00) f | 0.932 (0.851, 0.969) −0.01 c (−0.04, 0.02) f |
| Pre-swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.882 (0.742, 0.946) 0.08 c (0.06, 0.11) | 0.889 (0.756, 0.949) 0.07 c (0.05, 0.10) f | 0.891 (0.761, 0.950) 0.05 c (0.03, 0.08) f | 0.870 (0.715, 0.941) 0.03 c (0.01, 0.06) f | 0.866 (0.706, 0.939) 0.01 c (−0.02, 0.04) f |
| Swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.920 (0.825, 0.964) −0.08 c (−0.11, −0.05) | 0.934 (0.855, 0.970) −0.07 c (−0.10, −0.04) f | 0.935 (0.858, 0.971) −0.05 c (−0.08, −0.03) f | 0.930 (0.847, 0.968) −0.03 c (−0.06, 0.00) f | 0.931 (0.849, 0.969) −0.01 c (−0.04, 0.02) f |
| Gait Parameter | Reliability | Minimum Sensors Used for Detection of the Contact Event | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (+20% Slope) | Indices | 1 LED | 2 LEDs | 3 LEDs | 4 LEDs | 5 LEDs |
| Step length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.24 a (−0.46, 0.93) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.25 a (−0.47, 0.96) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.24 a (−0.47, 0.95) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.24 a (−0.47, 0.96) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.23 a (−0.47, 0.93) |
| Stride length (cm) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.58 b (−0.83, 2.00) | 0.999 (0.996, 0.999) 0.59 b (−0.86, 2.04) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.58 b (−0.84, 2.00) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.59 b (−0.84, 2.03) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) 0.57 b (−0.78, 1.93) |
| Step time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.999 (0.999, 1.000) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.00) | 0.999 (0.999, 1.000) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.999 (0.999, 1.000) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) e | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.01) |
| Stride time (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.02) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.00 (−0.01, 0.02) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.00 c (−0.01, 0.02) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.00 c (−0.01, 0.02) | 0.999 (0.998, 1.000) 0.00 c (−0.01, 0.02) |
| Cadence (steps/min) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.996 (0.991, 0.998) −0.29 (−2.19, 1.60) | 0.997 (0.994, 0.999) −0.21 (−1.82, 1.41) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) −0.11 (−1.47, 1.25) | 0.998 (0.996, 0.999) −0.10 (−1.43, 1.24) | 0.999 (0.997, 0.999) −0.07 (−1.23, 1.09) |
| Load response phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.968 (0.929, 0.985) 0.09 d (0.06, 0.11) | 0.969 (0.933, 0.986) 0.08 d (0.05, 0.10) f | 0.961 (0.914, 0.982) 0.06 d (0.04, 0.09) f | 0.952 (0.894, 0.978) 0.04 d (0.02, 0.07) f | 0.918 (0.819, 0.962) 0.03 d (0.00, 0.06) f |
| Single support phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.950 (0.890, 0.977) −0.08 d (−0.12, −0.05) | 0.956 (0.904, 0.980) −0.07 d (−0.10, −0.04) f | 0.960 (0.911, 0.982) −0.06 d (−0.09, −0.03) f | 0.967 (0.927, 0.985) −0.04 d (−0.07, −0.01) f | 0.962 (0.917, 0.983) −0.03 d (−0.06, 0.00) f |
| Pre-swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.966 (0.925, 0.985) 0.09 d (0.06, 0.11) | 0.969 (0.931, 0.986) 0.08 d (0.05, 0.10) f | 0.960 (0.913, 0.982) 0.06 d (0.04, 0.09) f | 0.949 (0.888, 0.977) 0.04 d (0.02, 0.07) f | 0.915 (0.813, 0.961) 0.03 d (0.00, 0.06) f |
| Swing phase (s) | ICC (95% CI) SB (95% LoA) | 0.952 (0.895, 0.978) −0.08 d (−0.11, −0.05) | 0.959 (0.911, 0.982) −0.07 d (−0.10, −0.05) f | 0.962 (0.916, 0.983) −0.06 d (−0.09, −0.03) f | 0.967 (0.928, 0.985) −0.04 d (−0.07, −0.01) f | 0.961 (0.915, 0.982) −0.03 d (−0.06, 0.00) f |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandalidis, D.; Kafetzakis, I. Differences between Systems Using Optical and Capacitive Sensors in Treadmill-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis of Level and Sloping Gait. Sensors 2022, 22, 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072790
Mandalidis D, Kafetzakis I. Differences between Systems Using Optical and Capacitive Sensors in Treadmill-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis of Level and Sloping Gait. Sensors. 2022; 22(7):2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072790
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandalidis, Dimitris, and Ioannis Kafetzakis. 2022. "Differences between Systems Using Optical and Capacitive Sensors in Treadmill-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis of Level and Sloping Gait" Sensors 22, no. 7: 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072790
APA StyleMandalidis, D., & Kafetzakis, I. (2022). Differences between Systems Using Optical and Capacitive Sensors in Treadmill-Based Spatiotemporal Analysis of Level and Sloping Gait. Sensors, 22(7), 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22072790







