Automated Breast Cancer Detection Models Based on Transfer Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Using various evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall (sensitivity), specificity, and F1-Score. Extensive comparative comparisons were performed to assess the effectiveness of the proposed systems;
- Mammograms show radiological indications that are readily detectable symptoms. As a result, deep learning-based methods can be used to automatically analyze mammograms, which significantly reduces analysis time;
- To fine-tune the weights of pre-trained networks on small datasets, as well as train the weights of networks on large datasets, a customized version of ResNet50 (MOD-RES) and a hybrid version of Nasnet and Mobile net were utilized;
- To improve the generalization effectiveness of the suggested method and prevent overfitting, a different training protocol assisted by different combinations of training policies (e.g., validation patience, and data augmentation) was used.
2. Related Works
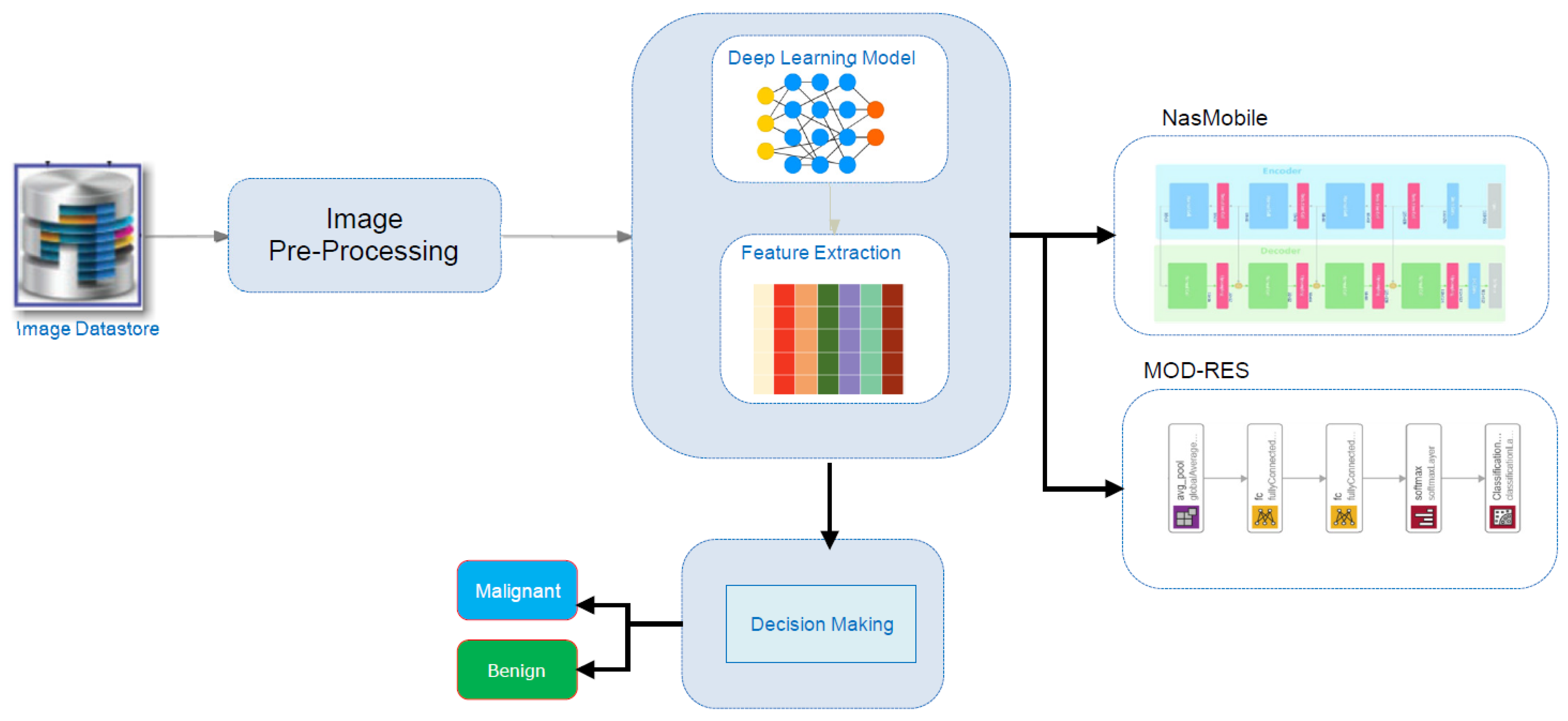
3. Proposed System
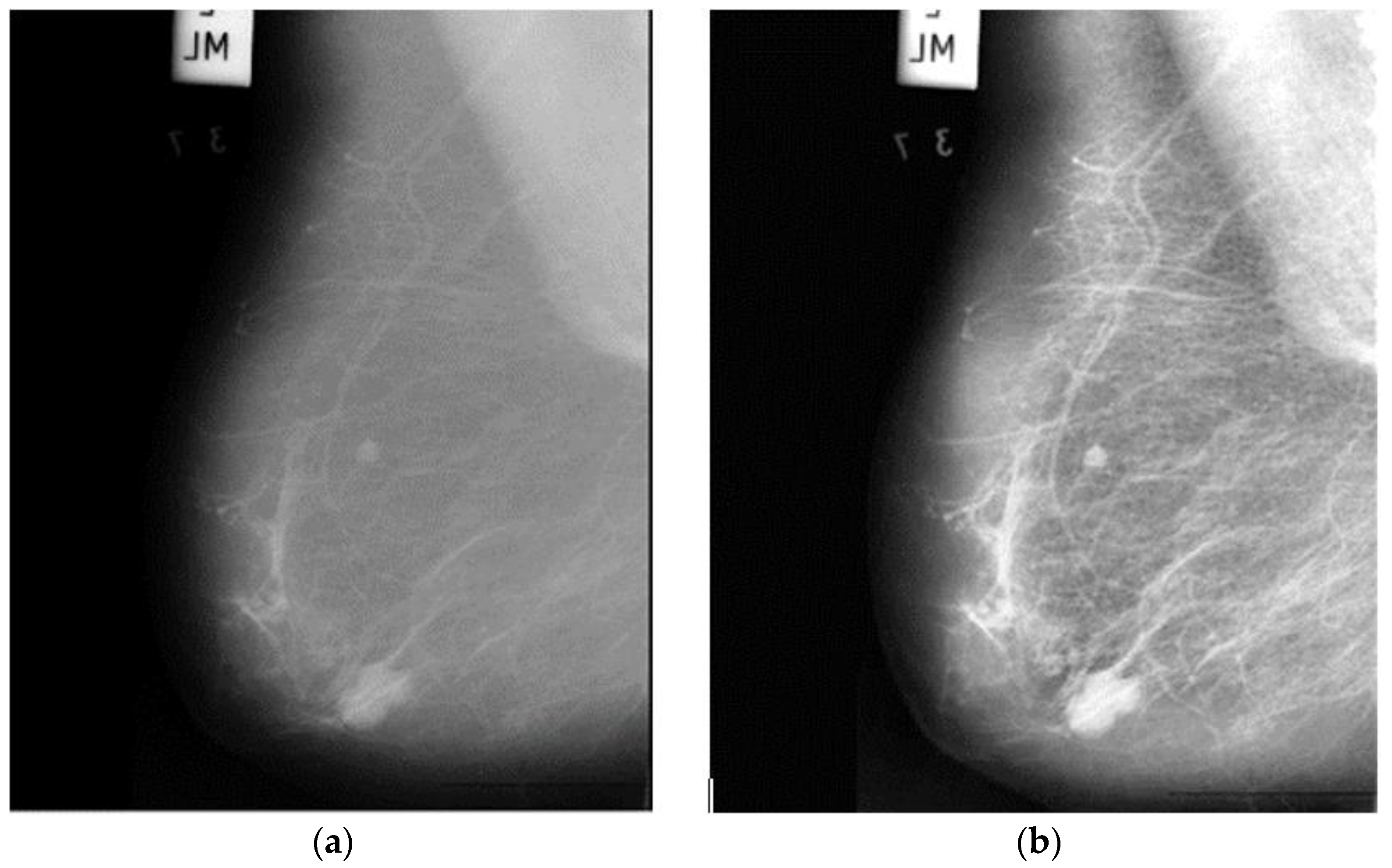
3.1. MIAS Datasets
3.2. Image Pre-Processing
3.3. Proposed Learning Methods
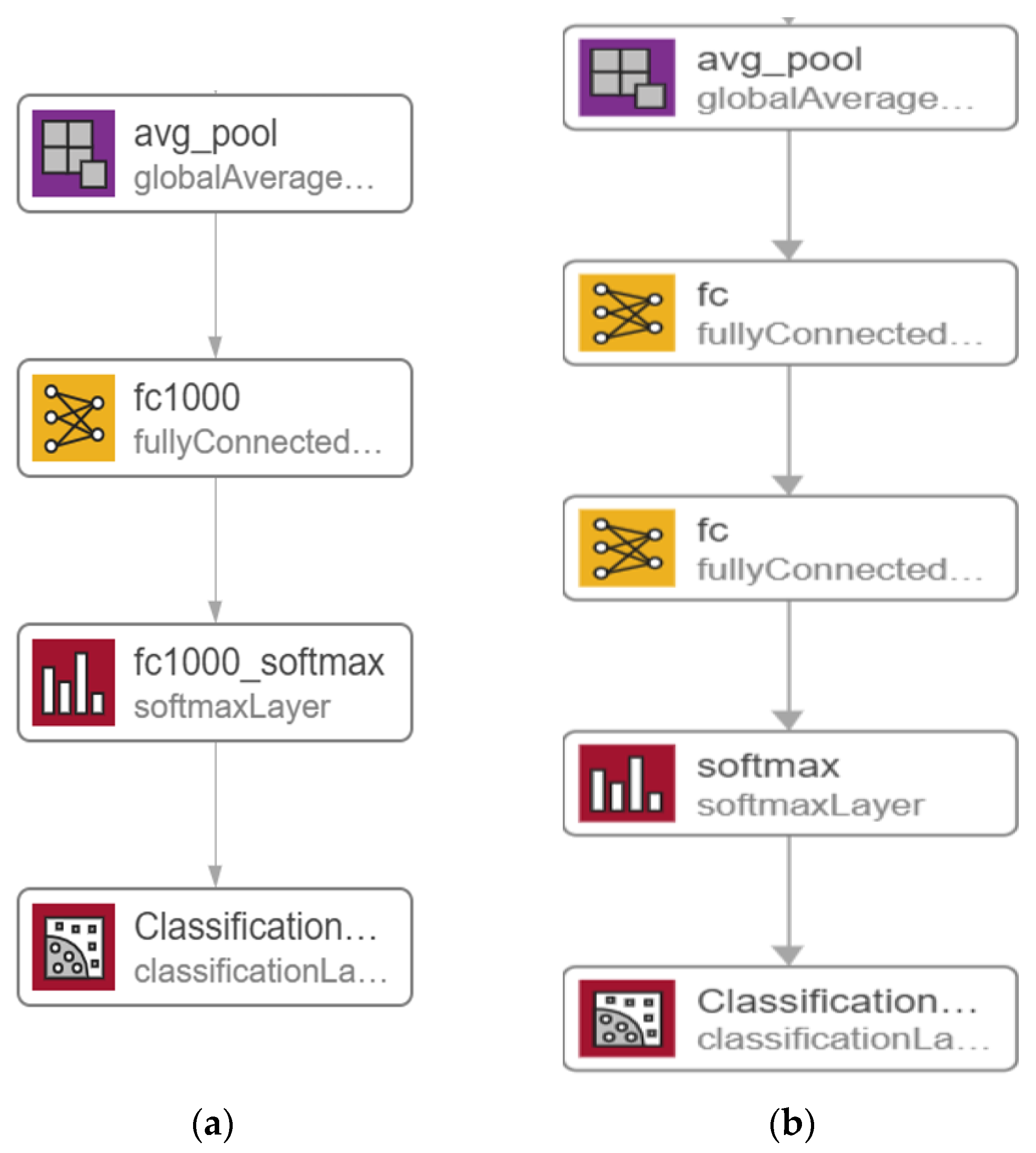
3.3.1. Nasnet-Mobile
3.3.2. MOD-RES
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Assessment Metrices
4.2. Results of the Proposed Systems
4.3. Comparison to State-of-the-Art Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macías-García, L.; Martínez-Ballesteros, M.; Luna-Romera, J.M.; García-Heredia, J.M.; García-Gutiérrez, J.; Riquelme-Santos, J.C. Autoencoded DNA methylation data to predict breast cancer recurrence: Machine learning models and gene-weight significance. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 110, 101976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, M.H.; Goyal, M.; Osman, F.; Martí, R.; Denton, E.; Juette, A.; Zwiggelaar, R. Breast ultrasound region of interest detection and lesion localisation. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 107, 101880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, W.; Selim, M.M.; Elshishtawy, T. An Approach for Breast Cancer Mass Detection in Mammograms. 2012. Available online: https://www.bu.edu.eg/portal/uploads/Engineering,%20Shoubra/Electrical%20Engineering/839/publications/Walaa%20Gouda%20Hassan%20Mohammed_An%20Approach%20for%20Breast%20Cancer%20Mass%20Detection%20in%20Mammograms.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Mehmood, M.; Ayub, E.; Ahmad, F.; Alruwaili, M.; Alrowaili, Z.A.; Alanazi, S.; Rizwan, M.H.M.; Naseem, S.; Alyas, T. Machine learning enabled early detection of breast cancer by structural analysis of mammograms. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 67, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.S.A.; Belhaouari, S.B.; Bouzerdoum, A.; Baali, H.; Alam, T.; Eldaraa, A.M. Breast Mass Tumor Classification using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Informatics, IoT, and Enabling Technologies (ICIoT), Doha, Qatar, 2–5 February 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; A Khan, S.; Luo, Y. Prediction of breast cancer distant recurrence using natural language processing and knowledge-guided convolutional neural network. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 110, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.P.; Bokde, N.; Sinha, S. Photoacoustic imaging for management of breast cancer: A literature review and future perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, N. SSEGEP: Small SEGment Emphasized Performance evaluation metric for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.03435. [Google Scholar]
- Falconi, L.G.; Perez, M.; Aguila, W.G.; Conci, A. Transfer learning and fine tuning in breast mammogram abnormalities classification on CBIS-DDSM database. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2020, 5, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkhaleefah, M.; Ma, S.-C.; Chang, Y.-L.; Huang, B.; Chittem, P.K.; Achhannagari, V.P. Double-shot transfer learning for breast cancer classification from X-ray images. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatfield, K.; Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Return of the devil in the details: Delving deep into convolutional nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.3531. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.-I. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, Z.; Gimenez, F.; Yi, D.; Rubin, D. Differential data augmentation techniques for medical imaging classification tasks. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. Arch. 2017, 2017, 979–984. [Google Scholar]
- Perre, A.C.; Alexandre, L.; Freire, L.C. Lesion classification in mammograms using convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2018, 7, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamparia, A.; Bharati, S.; Podder, P.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Phung, T.K.; Thanh, D.N.H. Diagnosis of breast cancer based on modern mammography using hybrid transfer learning. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 32, 747–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Singh, G.; Kaur, P. Intellectual detection and validation of automated mammogram breast cancer images by multi-class SVM using deep learning classification. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2019, 16, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, K.; Krishnan, S.; Thanki, R. Deep Learning Model for Classification of Breast Cancer, in Artificial Intelligence in Breast Cancer Early Detection and Diagnosis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, N.; Khan, A.; Lee, Y.S. Transfer learning based deep CNN for segmentation and detection of mitoses in breast cancer histopathological images. Microscopy 2019, 68, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Liu, H.; Yu, S.; Xie, Y. Breast mass lesion classification in mammograms by transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, Hong Kong, China, 6–8 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Bernard, S.; Heutte, L.; Sabourin, R. Improve the performance of transfer learning without fine-tuning using dissimilarity-based multi-view learning for breast cancer histology images. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference, ICIAR 2018, Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal, 27–29 June 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Charan, S.; Khan, M.J.; Khurshid, K. Breast cancer detection in mammograms using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), Wuhan, China, 7–8 February 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Suckling, J.P. The mammographic image analysis society digital mammogram database. Digil. Mammo 1994, 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; Berg, A.C.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxen, F.; Werner, P.; Handrich, S.; Othman, E.; Dinges, L.; Al-Hamadi, A. Face attribute detection with mobilenetv2 and nasnet-mobile. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis (ISPA), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 23–25 September 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.; Rattani, A.; Derakhshani, R. Comparison of deep learning models for biometric-based mobile user authentication. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 22–25 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, S.S.; Dubey, S.R.; Pulabaigari, V.; Mukherjee, S. Impact of fully connected layers on performance of convolutional neural networks for image classification. Neurocomputing 2020, 378, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renard, F.; Guedria, S.; De Palma, N.; Vuillerme, N. Variability and reproducibility in deep learning for medical image segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldin, S.N.; Hamdy, J.K.; Adnan, G.T.; Hossam, M.; Elmasry, N.; Mohammed, A. Deep Learning Approach for Breast Cancer Diagnosis from Microscopy Biopsy Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Mobile, Intelligent, and Ubiquitous Computing Conference (MIUCC), Cairo, Egypt, 26–27 May 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Siddeeq, S.; Li, J.; Ali Bhatti, H.M.; Manzoor, A.; Malhi, U.S. Deep Learning RN-BCNN Model for Breast Cancer BI-RADS Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 The 4th International Conference on Image and Graphics Processing, Sanya, China, 1–3 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salvi, S.; Kadam, A. Breast Cancer Detection Using Deep learning and IoT Technologies. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1831, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Tseng, T.-L.B.; Zhang, J.; Qian, W. Enhancing deep convolutional neural network scheme for breast cancer diagnosis with unlabeled data. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2017, 57, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, K.; Banik, D.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Nasipuri, M. Patch-based system for classification of breast histology images using deep learning. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 71, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazi, S.A.; Kamruzzaman, M.M.; Sarker, N.I.; Alruwaili, M.; Alhwaiti, Y.; Alshammari, N.; Siddiqi, M.H. Boosting breast cancer detection using convolutional neural network. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5528622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Matthews, T.P.; Shah, M.; Mombourquette, B.; Tsue, T.; Long, A.; Almohsen, R.; Pedemonte, S.; Su, J. Adaptation of a deep learning malignancy model from full-field digital mammography to digital breast tomosynthesis. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2020: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Houston, TX, USA, 15–20 February 2020; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mendel, K.; Li, H.; Sheth, D.; Giger, M. Transfer learning from convolutional neural networks for computer-aided diagnosis: A comparison of digital breast tomosynthesis and full-field digital mammography. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, A.; Teuwen, J.; Vreemann, S.; Bouwman, R.W.; E Van Engen, R.; Karssemeijer, N.; Mann, R.; Gubern-Merida, A.; Sechopoulos, I. New reconstruction algorithm for digital breast tomosynthesis: Better image quality for humans and computers. Acta Radiol. 2018, 59, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousefi, M.; Krzyżak, A.; Suen, C.Y. Mass detection in digital breast tomosynthesis data using convolutional neural networks and multiple instance learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 96, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
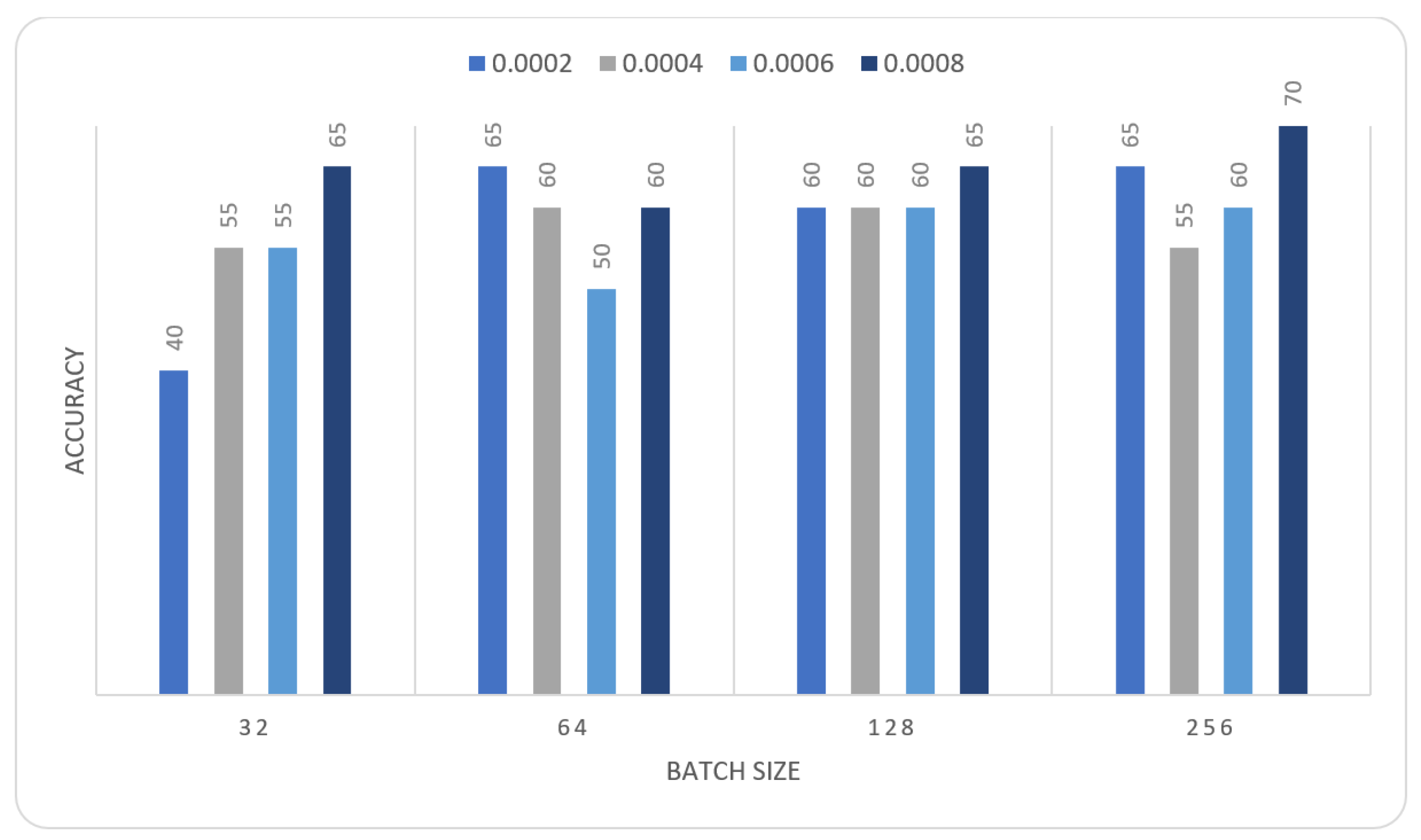
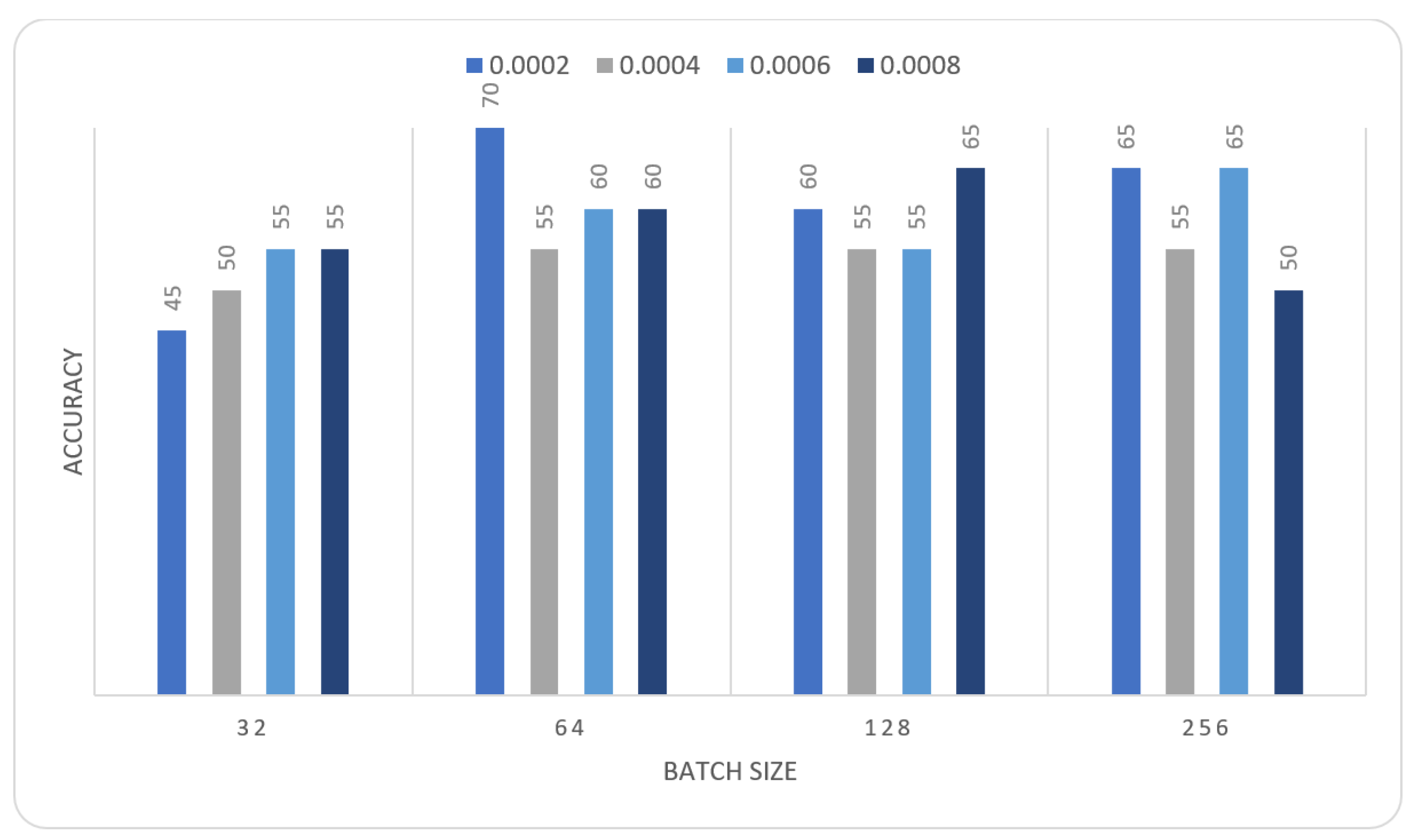


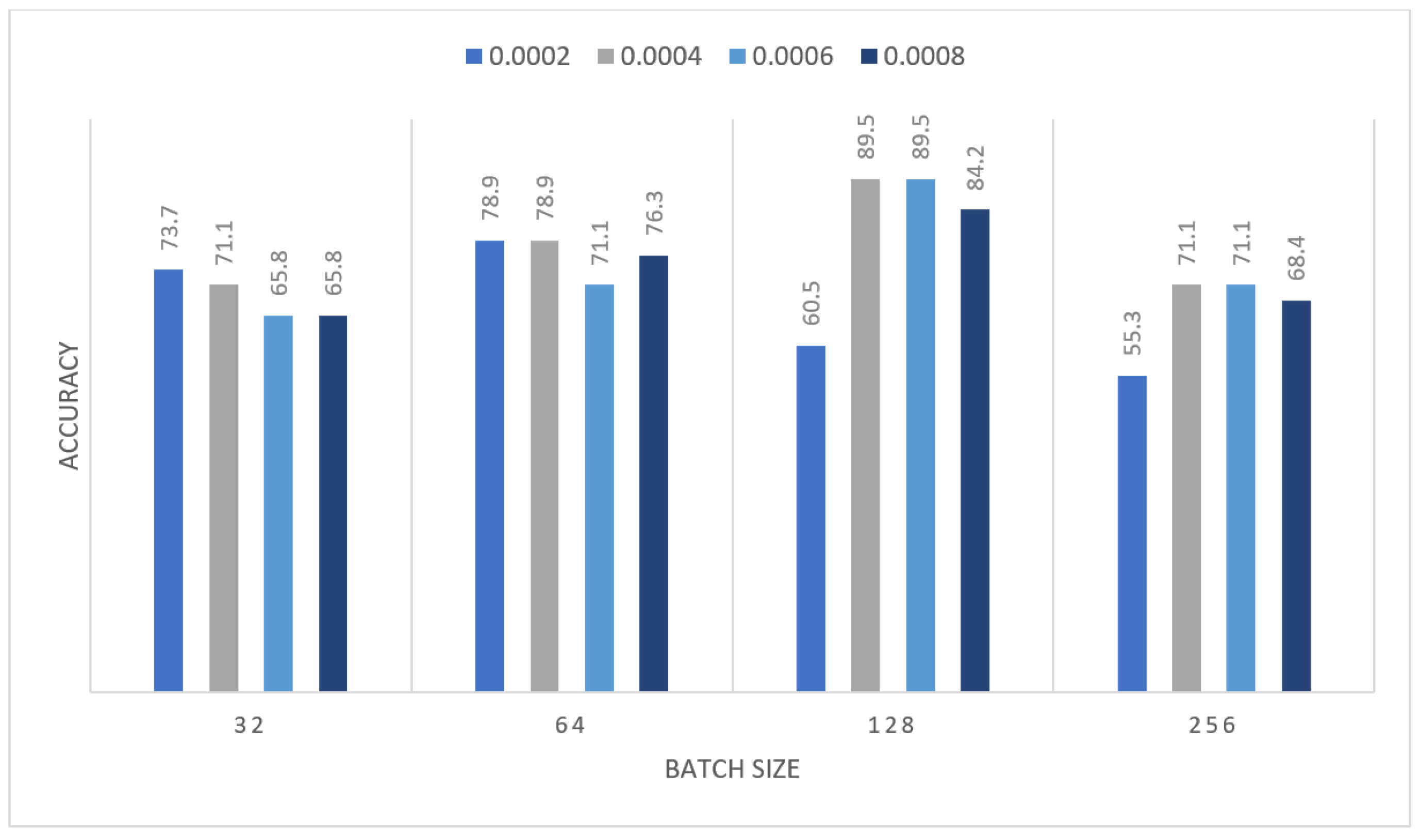
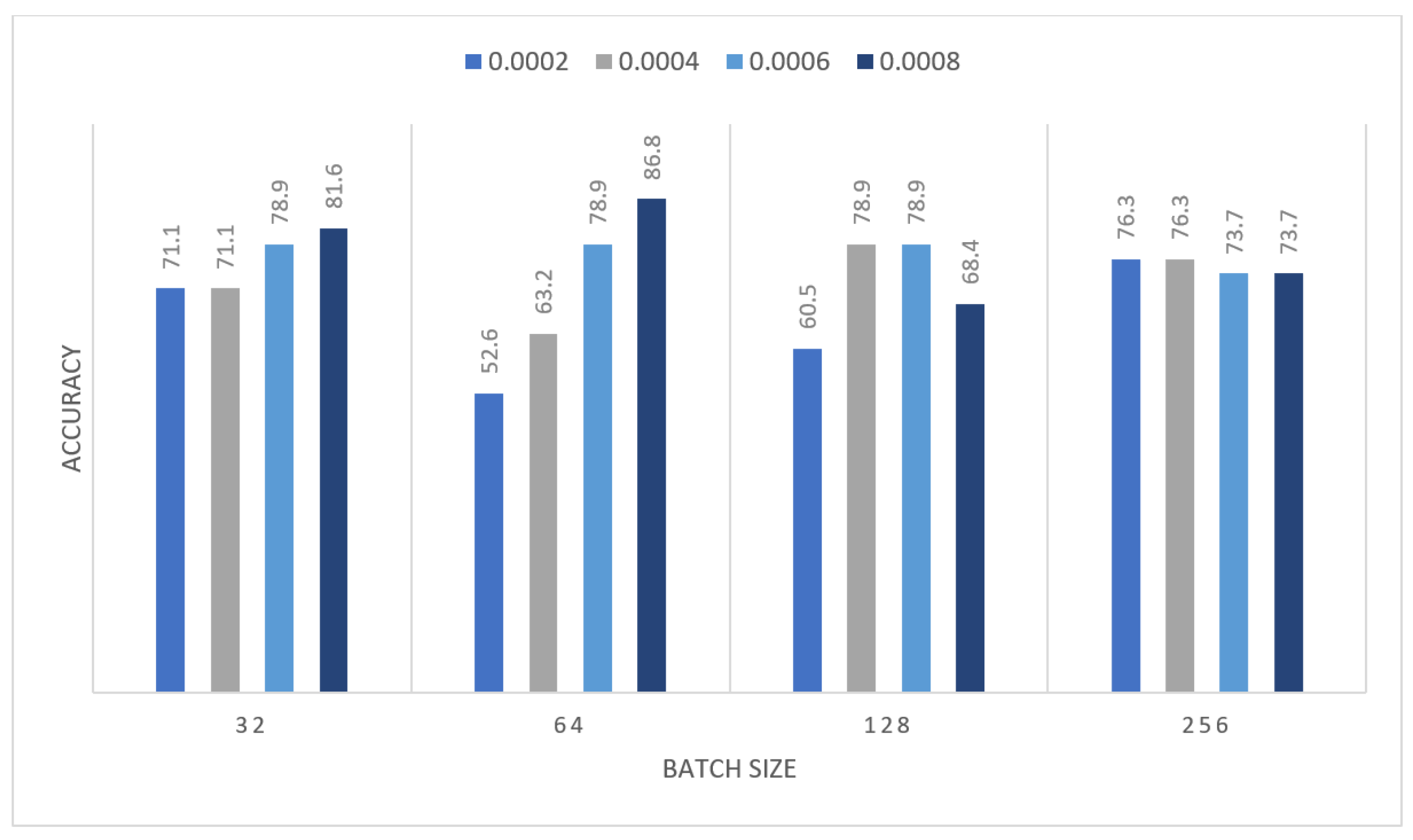

| Learning Rate | Ensemble Using Several Runs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Size = 32 | Batch Size = 64 | Batch Size = 128 | Batch Size = 265 | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 0.0002 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.45 | 0.65 |
| 0.0004 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.5 |
| 0.0006 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| 0.0008 | 0.55 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.65 | 0.6 | 0.65 | 0.7 |
| Learning Rate | Ensemble Using Several Runs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Size = 32 | Batch Size = 64 | Batch Size = 128 | Batch Size = 265 | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 0.0002 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.65 |
| 0.0004 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| 0.0006 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.65 | 0.5 |
| 0.0008 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.45 |
| Learning Rate | Ensemble Using Several Runs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Size = 32 | Batch Size = 64 | Batch Size = 128 | Batch Size = 265 | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 0.0002 | 0.35 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.5 |
| 0.0004 | 0.4 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| 0.0006 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55 |
| 0.0008 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.5 |
| Learning Rate | Ensemble Using Several Runs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Size = 32 | Batch Size = 64 | Batch Size = 128 | Batch Size = 265 | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 0.0002 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.45 | 0.4 |
| 0.0004 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| 0.0006 | 0.4 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.45 |
| 0.0008 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Learning Rate | Ensemble Using Several Runs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Size = 32 | Batch Size = 64 | Batch Size = 128 | Batch Size = 265 | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 0.0002 | 0.737 | 0.711 | 0.658 | 0.658 | 0.553 | 0.605 | 0.526 | 0.711 |
| 0.0004 | 0.5 | 0.789 | 0.658 | 0.711 | 0.763 | 0.737 | 0.632 | 0.763 |
| 0.0006 | 0.395 | 0.605 | 0.895 | 0.842 | 0.816 | 0.711 | 0.658 | 0.658 |
| 0.0008 | 0.553 | 0.526 | 0.711 | 0.684 | 0.526 | 0.789 | 0.579 | 0.763 |
| Learning Rate | Ensemble Using Several Runs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Size = 32 | Batch Size = 64 | Batch Size = 128 | Batch Size = 265 | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 0.0002 | 0.632 | 0.711 | 0.684 | 0.789 | 0.816 | 0.737 | 0.526 | 0.5 |
| 0.0004 | 0.5 | 0.526 | 0.632 | 0.789 | 0.868 | 0.737 | 0.711 | 0.5 |
| 0.0006 | 0.605 | 0.526 | 0.789 | 0.658 | 0.684 | 0.737 | 0.579 | 0.474 |
| 0.0008 | 0.658 | 0.763 | 0.605 | 0.737 | 0.658 | 0.632 | 0.579 | 0.526 |
| Quantitative Measures | MOD-RES Model (Oversampling) | MOD-RES Model | Nasnet-Mobile Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Accuracy | 89.5 | 70 | 70 |
| Precision | 89.5 | 64.3 | 83.3 |
| Recall | 89.5 | 90 | 50 |
| F1-score | 89.5 | 75 | 62.5 |
| Recent Work | Technique | Dataset | Number of Images | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Methodology | MOD-RES | MIAS |
| 89.5% |
| Charan et al. [23] | CNN | MIAS |
| 65% |
| Z. Hussain et al. [15] | VGG-16 | DDSM |
| 88% |
| L. Falconi et al. [9] | VGG | CBIS-DDSM |
| 84.4% |
| S. Eldin et al. [31] | DenseNet-169 | BACH |
| 82% |
| S. Eldin et al. [31] | ResNet50 | BACH |
| 85% |
| S. Eldin et al. [31] | ResNet101 | BACH |
| 88% |
| S. Siddeeq et al. [32] | ResNet | INbreast |
| 85.9% |
| K. Shaikh [19] | CNN | MIAS, DDSM, and BancoWeb LAPIMO |
| 87.5% |
| S. Salvi and A. Kadam, [33] | CNN | Private Dataset |
| 87.84% |
| W. Sun et al. [34] | CNN with Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) algorithm | full-field digital mammography (FFDM) | 3158 region of interests (ROI) | 82.43% |
| Roy et al. [35] | CNN | ICIAR 2018 |
| 87.4% |
| S. Alanazi et al. [36] | CNN | Kaggle 162 H and E |
| 87% |
| S. Singh et al. [37] | Histogram matching (HM) and DL fine-tuning | FFDM |
| 84.7% |
| K. Mendel et al. [38] | CNN and SVM | FFDM |
| 89% |
| A. Rodriguez-Ruiz et al. [39] | CNN | Private Dataset |
| 88% |
| M. Yousefi et al. [40] | CCN | Research Laboratory at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) |
| 87% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alruwaili, M.; Gouda, W. Automated Breast Cancer Detection Models Based on Transfer Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030876
Alruwaili M, Gouda W. Automated Breast Cancer Detection Models Based on Transfer Learning. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):876. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030876
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlruwaili, Madallah, and Walaa Gouda. 2022. "Automated Breast Cancer Detection Models Based on Transfer Learning" Sensors 22, no. 3: 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030876
APA StyleAlruwaili, M., & Gouda, W. (2022). Automated Breast Cancer Detection Models Based on Transfer Learning. Sensors, 22(3), 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030876






