Characterising Penetrometer Tip Contact during Concrete Condition Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
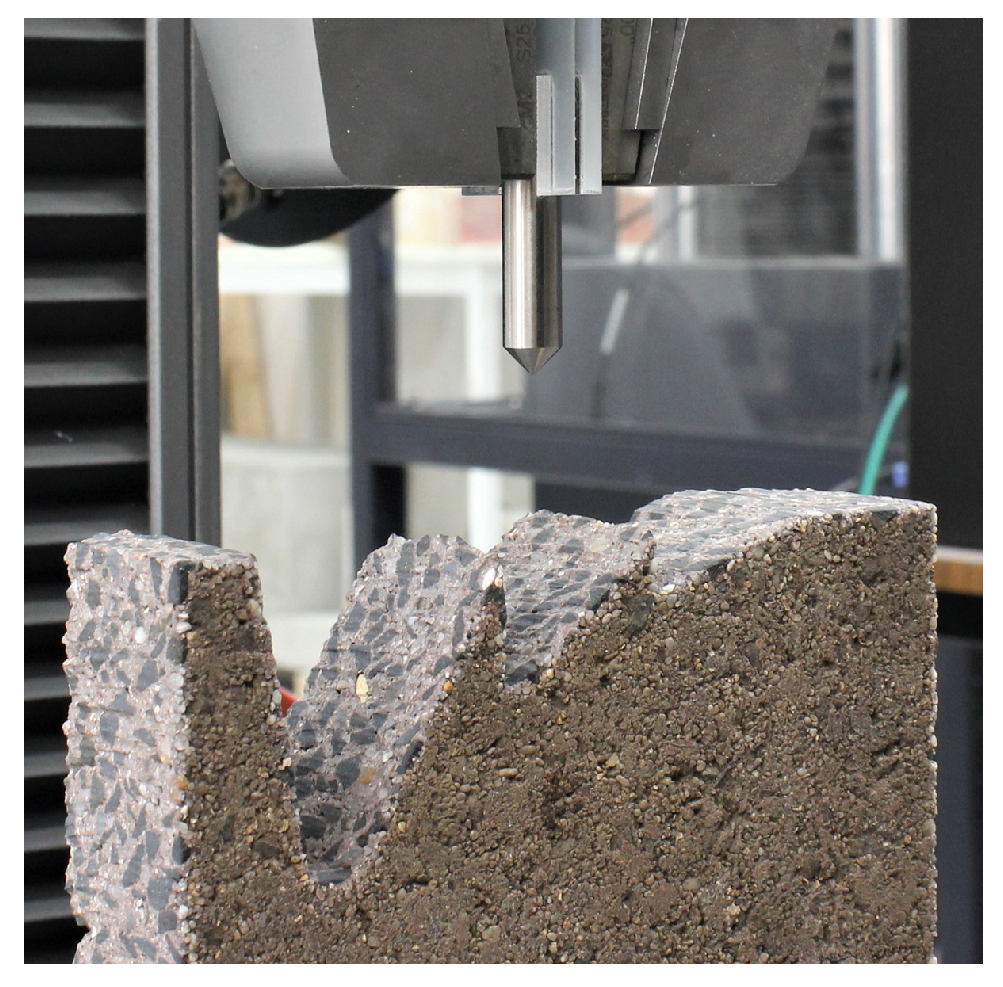
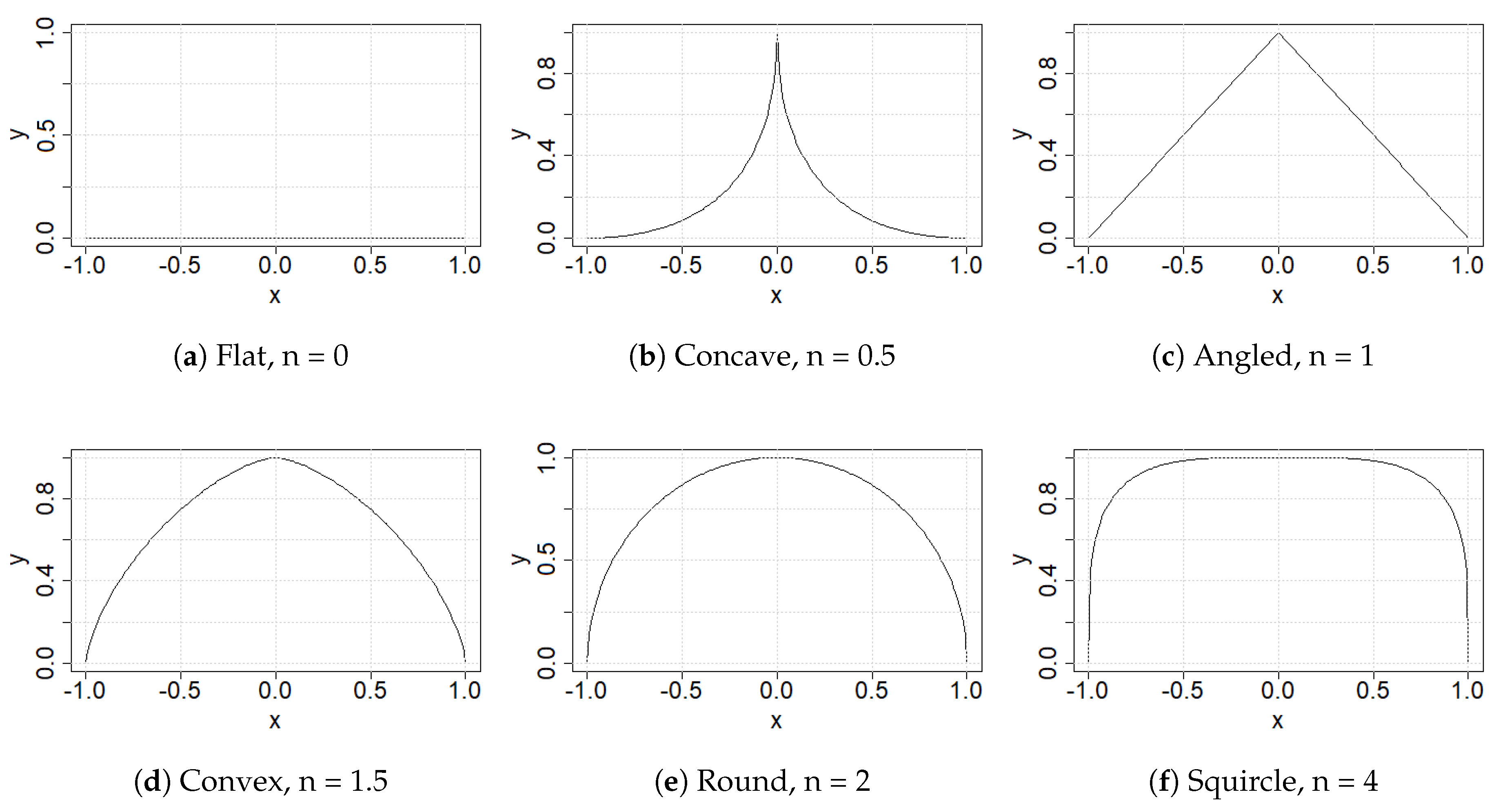
2. Design
3. Experiments
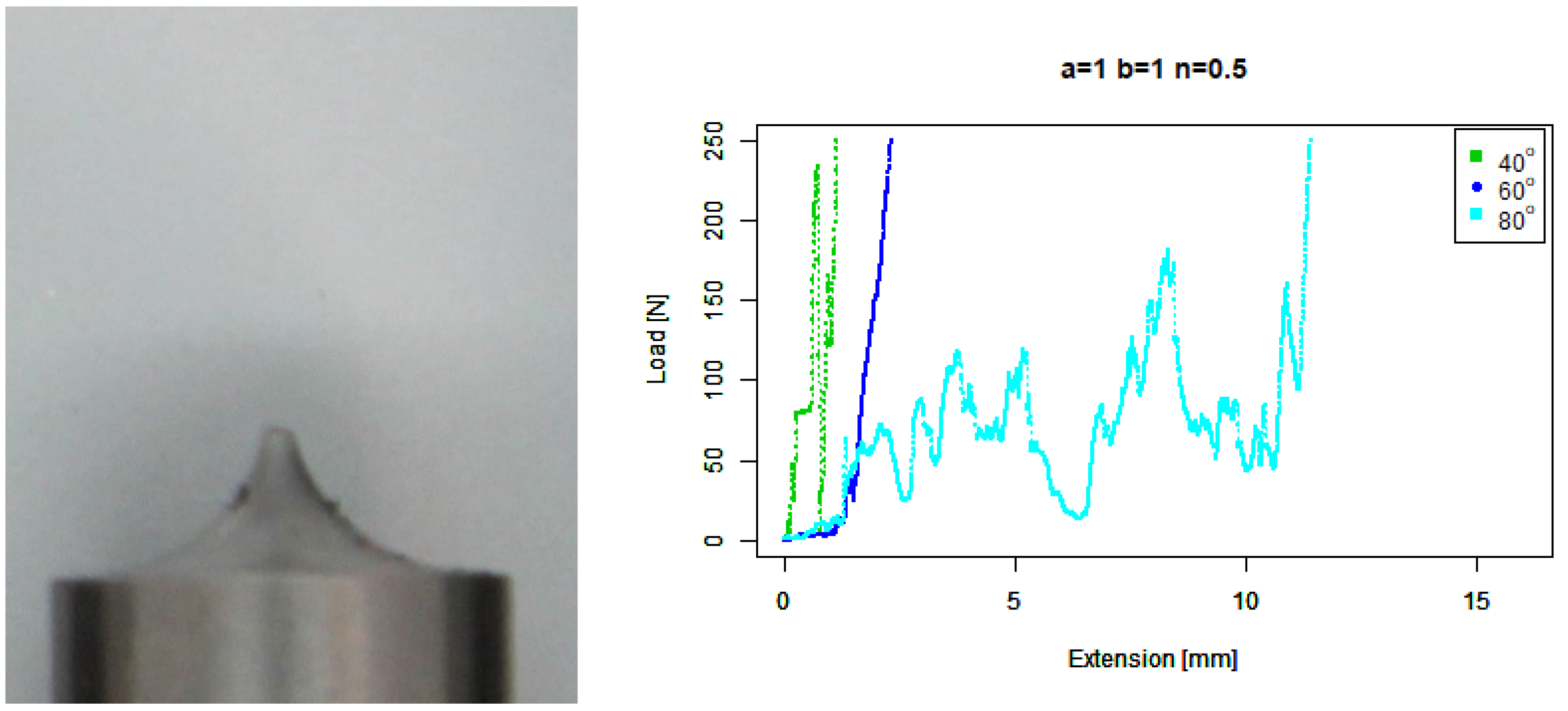
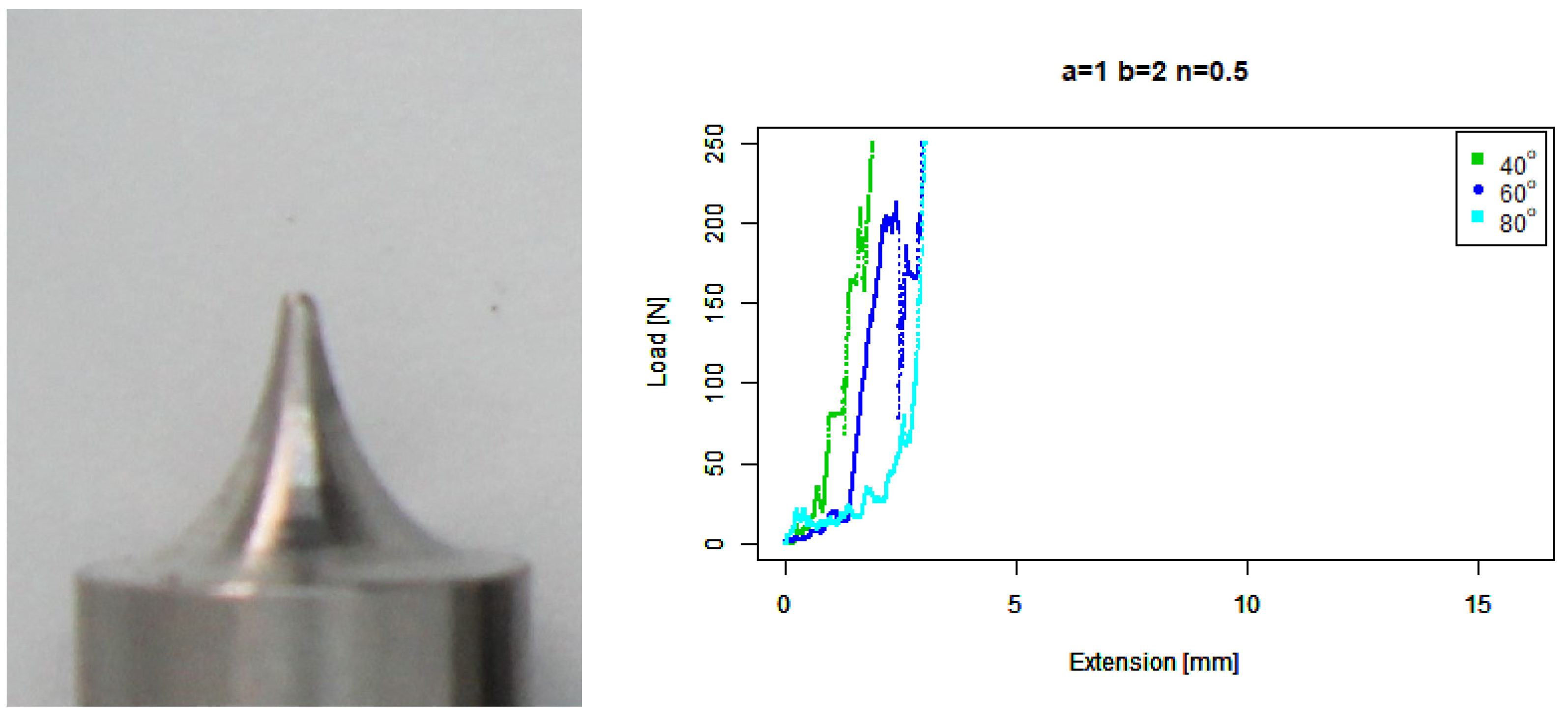
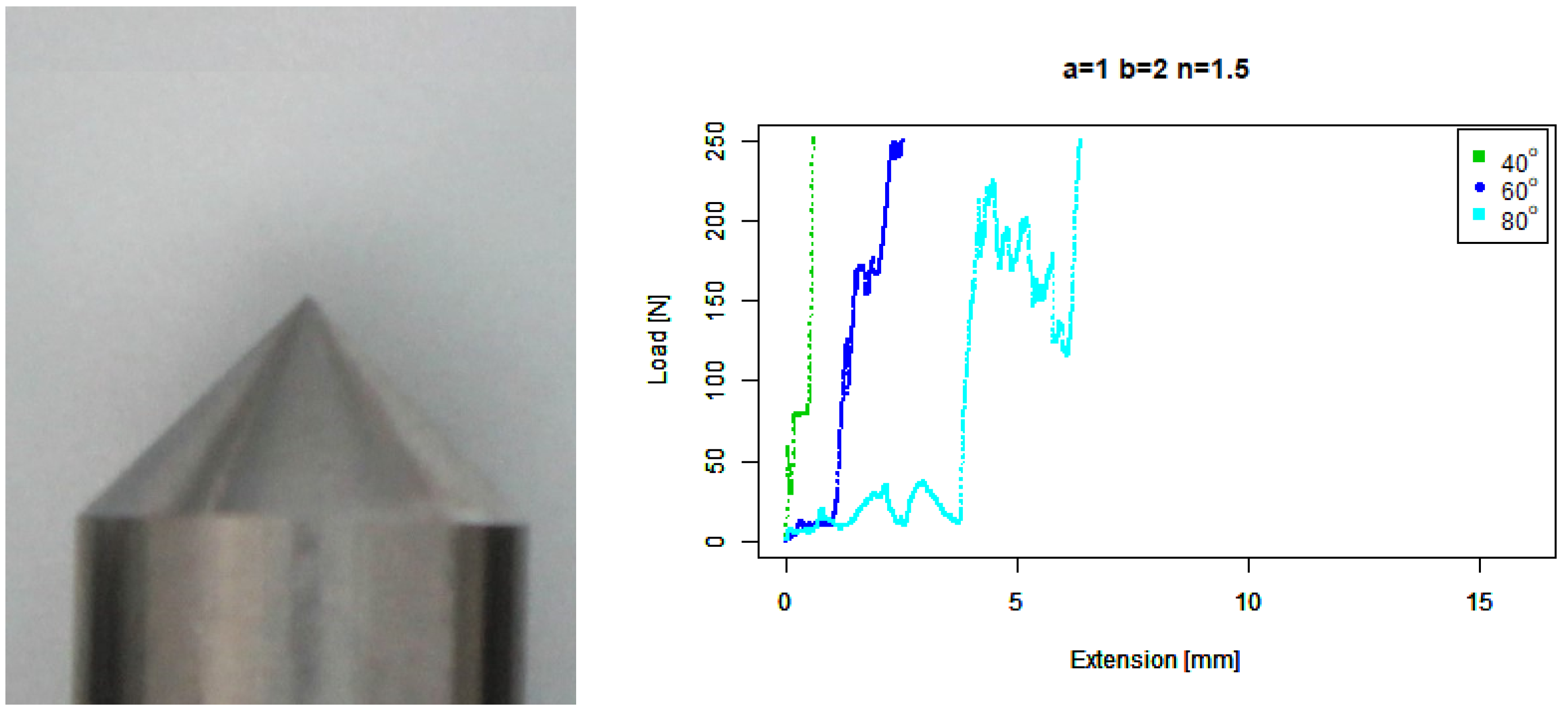
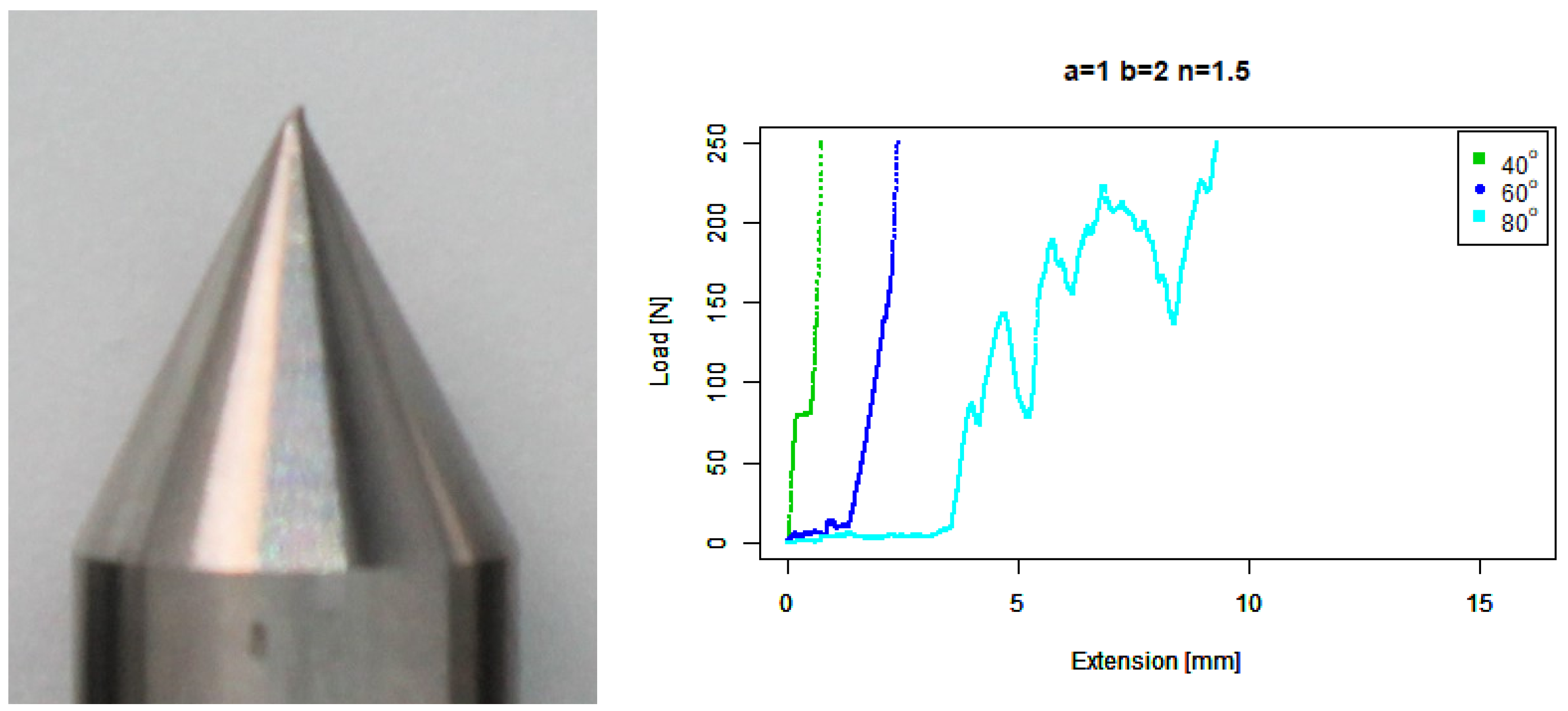
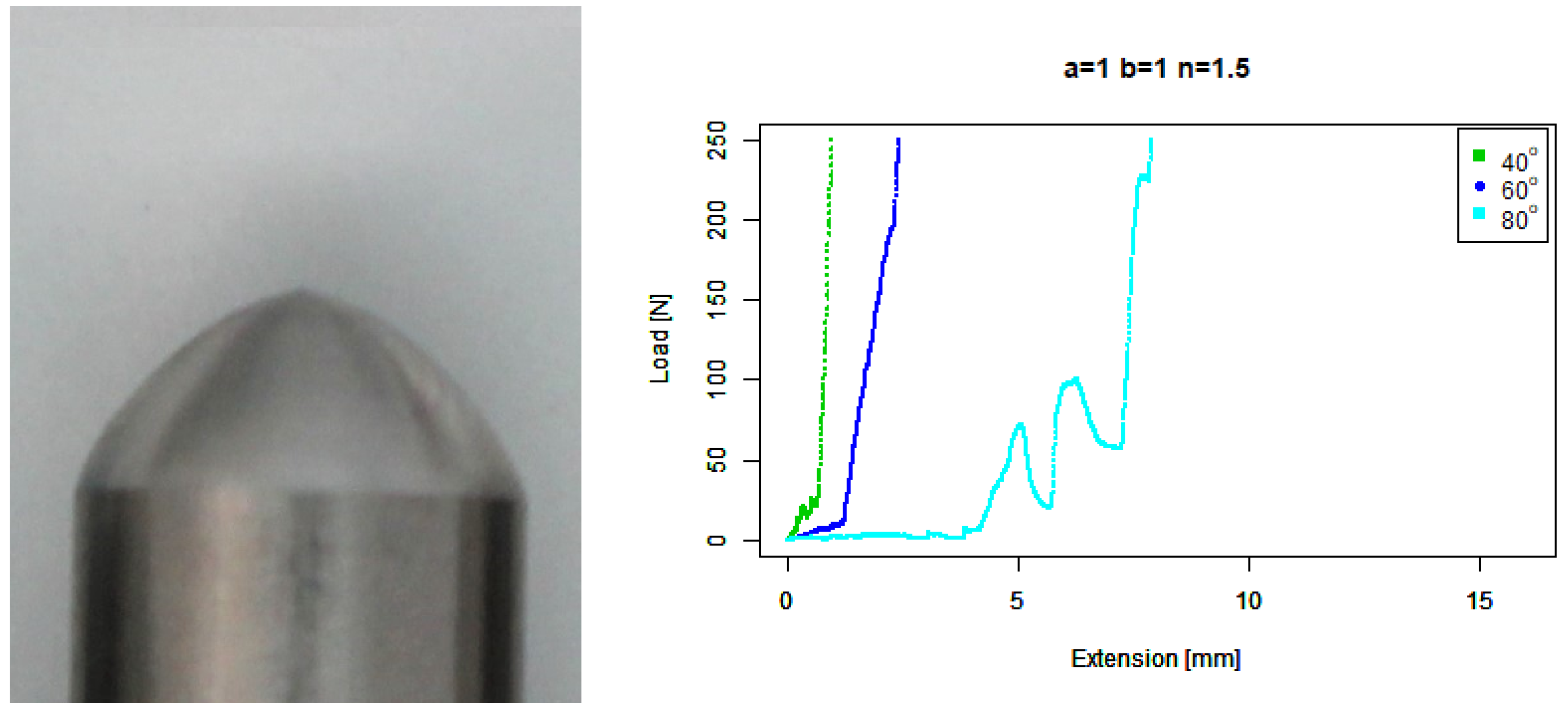
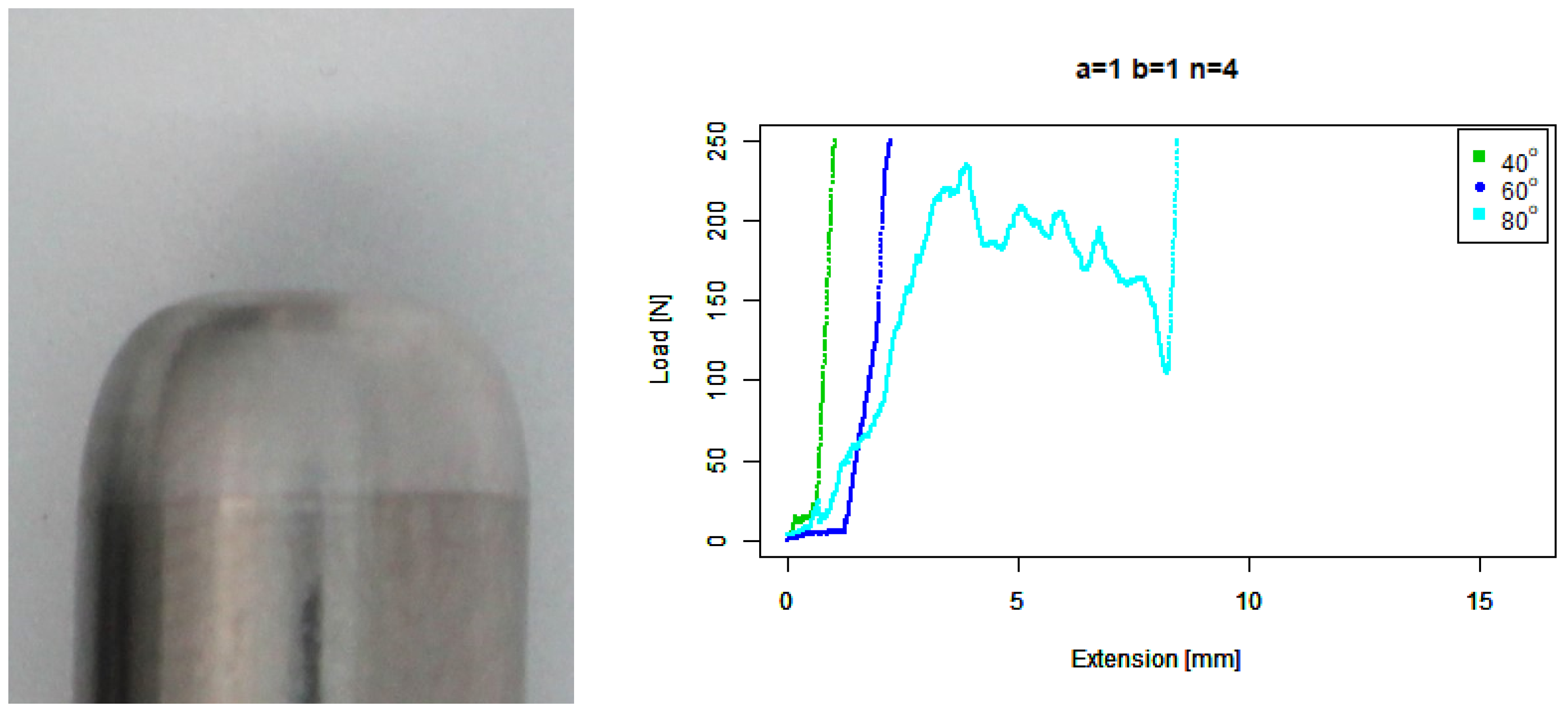
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brongers, M.; Virmani, P.; Payer, J. Drinking Water and Sewer Systems in Corrosion Costs and Preventative Strategies in the United States; United States Department of Transportation Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tscheikner-Gratl, F.; Caradot, N.; Cherqui, F.; Leitão, J.P.; Ahmadi, M.; Langeveld, J.G.; Le Gat, Y.; Scholten, L.; Roghani, B.; Rodríguez, J.P.; et al. Sewer asset management–state of the art and research needs. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvakumar, A.; Tuccillo, M.E.; Martel, K.D.; Matthews, J.C.; Feeney, C. Demonstration and evaluation of state-of-the-art wastewater collection systems condition assessment technologies. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2014, 5, 04013018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollertsen, J.; Nielsen, A.H.; Jensen, H.S.; Wium-Andersen, T.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T. Corrosion of concrete sewers—The kinetics of hydrogen sulfide oxidation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2008, 394, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C. The corrosion of concrete: 2. The function of Thiobacillus Concretivorus (nov. spec.) in the corrosion of concrete exposed to atmospheres containing hydrogen sulphide. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 1945, 23, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islander, R.L.; Devinny, J.S.; Mansfeld, F.; Postyn, A.; Shih, H. Microbial ecology of crown corrosion in sewers. J. Environ. Eng. 1991, 117, 751–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney, R.; Esfandi, E.; Surapaneni, S. Control concrete sewer corrosion via the crown spray process. Water Environ. Res. 1996, 68, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Feeney, C. Condition Assessment of Wastewater Collection Systems. In Proceedings of the EPA Science Forum, Washington, DC, USA, 20–22 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Kleiner, Y. State of the art review of inspection technologies for condition assessment of water pipes. Measurement 2013, 46, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, P.; Ross, R.; Martchenko, A.; Devlin, J. Dou-edge evaluation algorithm for automatic thin crack detection in pipelines. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications (ICSIPA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–21 October 2015; pp. 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen, J.; Clemens, F.; Korving, H.; Cherqui, F.; Le Gauffre, P.; Ertl, T.; Plihal, H.; Müller, K.; Snaterse, C. The consistency of visual sewer inspection data. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2013, 9, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanić, N.; De Haan, C.; Tirion, M.; Langeveld, J.; Clemens, F. Comparison of core sampling and visual inspection for assessment of concrete sewer pipe condition. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 2458–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanić, N.; Langeveld, J.; Salet, T.; Clemens, F. Relating the structural strength of concrete sewer pipes and material properties retrieved from core samples. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 13, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giovanangeli, N.; Piyathilaka, L.; Kodagoda, S.; Thiyagarajan, K.; Barclay, S.; Vitanage, D. Design and development of drill-resistance sensor technology for accurately measuring microbiologically corroded concrete depths. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Banff, AB, Canada, 21–24 May 2019; Volume 36, pp. 735–742. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, R.; Baji, A.; Barnett, D. Inner Profile Measurement for Pipes Using Penetration Testing. Sensors 2019, 19, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross, R.; Stumpf, A.; Barnett, D.; Hall, R. Condition assessment for concrete sewer pipes using displacement probes: A robotic design case study. Robotics 2021, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarsch, K. Cone penetration testing—A historic perspective. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 13–14 May 2014; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Perumpral, J. Cone penetrometer applications—A review. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 0939–0944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountas, S.; Paraforos, D.; Cavalaris, C.; Karamoutis, C.; Gemtos, T.A.; Abu-Khalaf, N.; Tagarakis, A. A five-point penetrometer with GPS for measuring soil compaction variability. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 96, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Pidakala, P.; Billing, D.; Burdon, J. Kiwifruit firmness: Measurement by penetrometer and non-destructive devices. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 120, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJong, J.; Yafrate, N.; DeGroot, D.; Low, H.E.; Randolph, M. Recommended practice for full-flow penetrometer testing and analysis. Geotech. Test. J. 2010, 33, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Watts, C.; Ren, T.; Whalley, W. The effects of compaction and soil drying on penetrometer resistance. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 125, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Ren, T.; Bengough, A.; Auneau, L.; Watts, C.; Whalley, W. Predicting penetrometer resistance from the compression characteristic of soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hossain, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H. Behaviour of ball penetrometer in uniform single-and double-layer clays. Géotechnique 2013, 63, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Georgieva, K.; Kasireddy, V.; Akinci, B.; Fieguth, P. A review on computer vision based defect detection and condition assessment of concrete and asphalt civil infrastructure. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garda, A.; Castillo, F.; Binet, G.; Litrico, X.; Gil, A. Needs and potential of unmanned vehicles in sewers. Houille Blanche 2016, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baah, K.; Dubey, B.; Harvey, R.; McBean, E. A risk-based approach to sanitary sewer pipe asset management. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, M. The superellipse: A curve that lies between the ellipse and the rectangle. Sci. Am. 1965, 213, 222–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.C.; Wang, M. Automated detection of sewer pipe defects in closed-circuit television images using deep learning techniques. Autom. Constr. 2018, 95, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hall, R.; Stumpf, A.; Baji, A.; Ross, R.; Barnett, D. Characterising Penetrometer Tip Contact during Concrete Condition Assessment. Sensors 2022, 22, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030737
Hall R, Stumpf A, Baji A, Ross R, Barnett D. Characterising Penetrometer Tip Contact during Concrete Condition Assessment. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030737
Chicago/Turabian StyleHall, Richard, Alex Stumpf, Avinash Baji, Robert Ross, and Dean Barnett. 2022. "Characterising Penetrometer Tip Contact during Concrete Condition Assessment" Sensors 22, no. 3: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030737
APA StyleHall, R., Stumpf, A., Baji, A., Ross, R., & Barnett, D. (2022). Characterising Penetrometer Tip Contact during Concrete Condition Assessment. Sensors, 22(3), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030737







