Study of Ionization Charge Density-Induced Gain Suppression in LGADs
Abstract
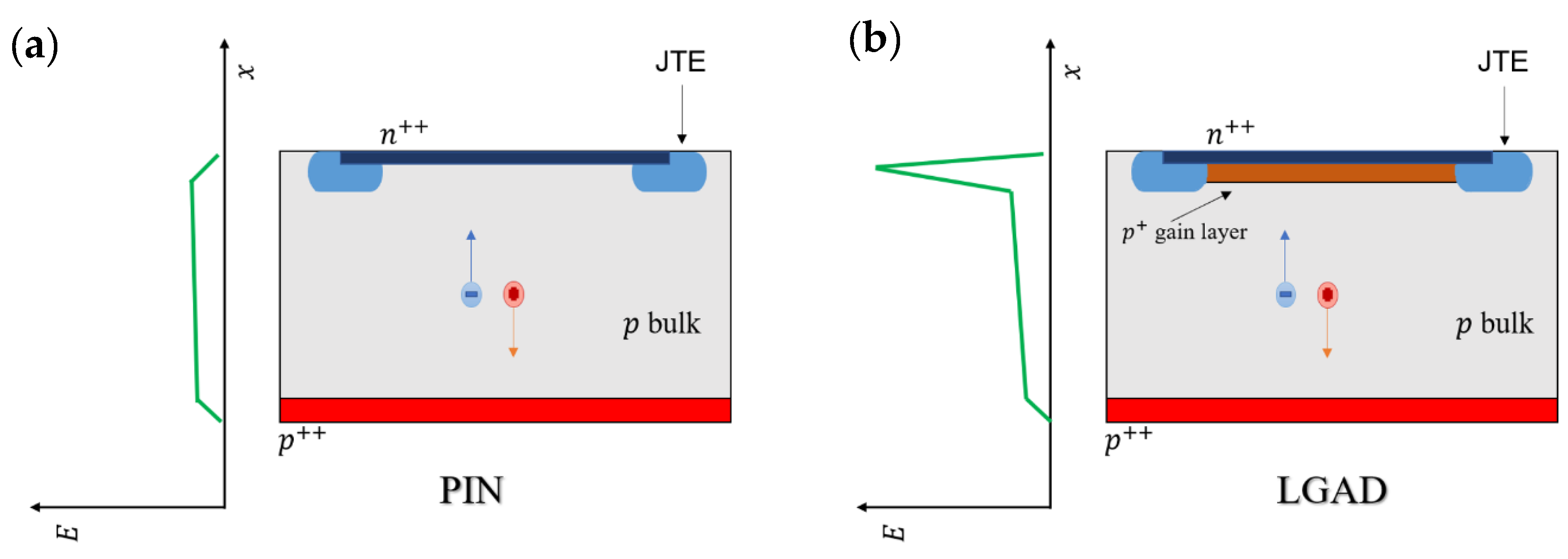
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
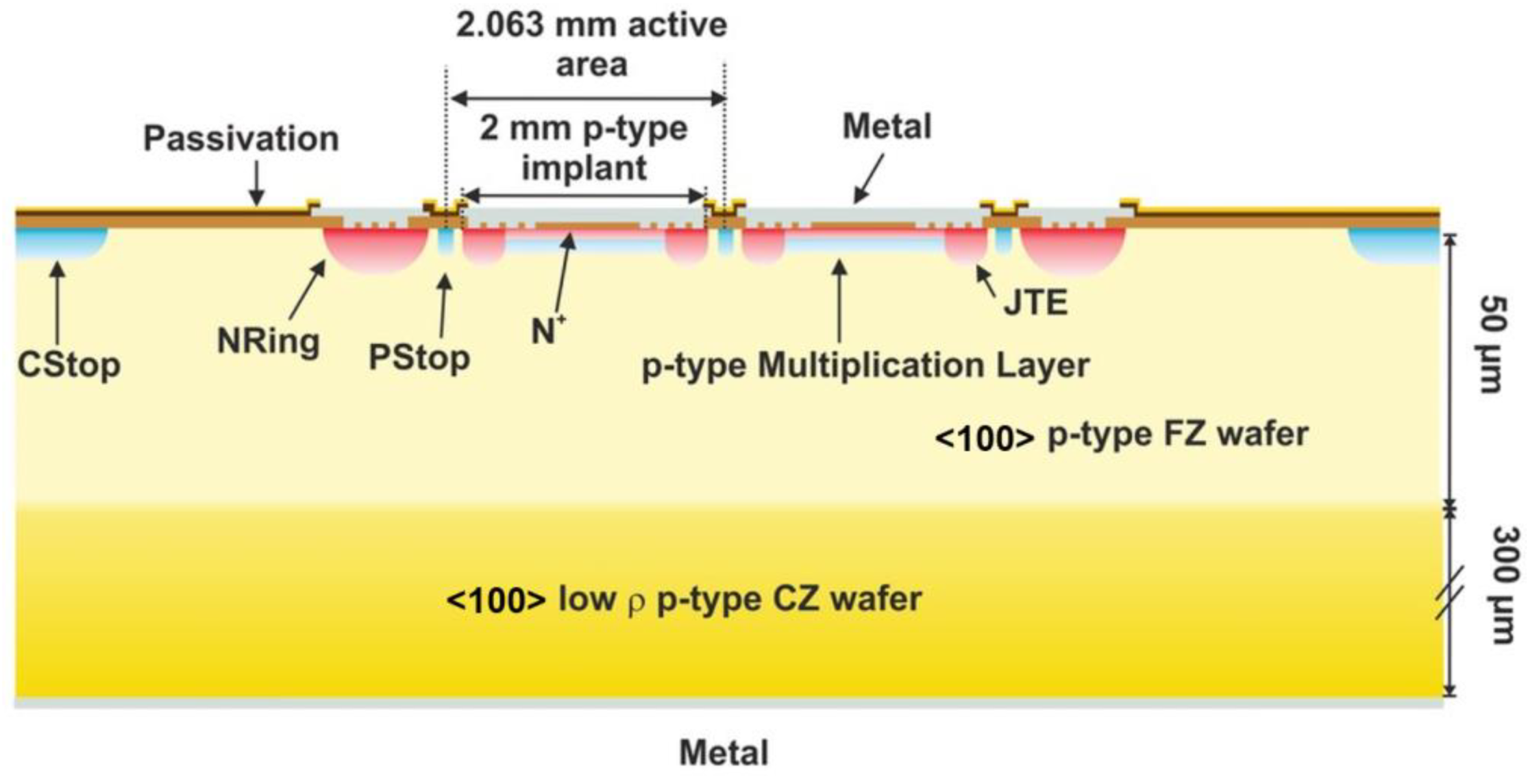
2.1. LGADs
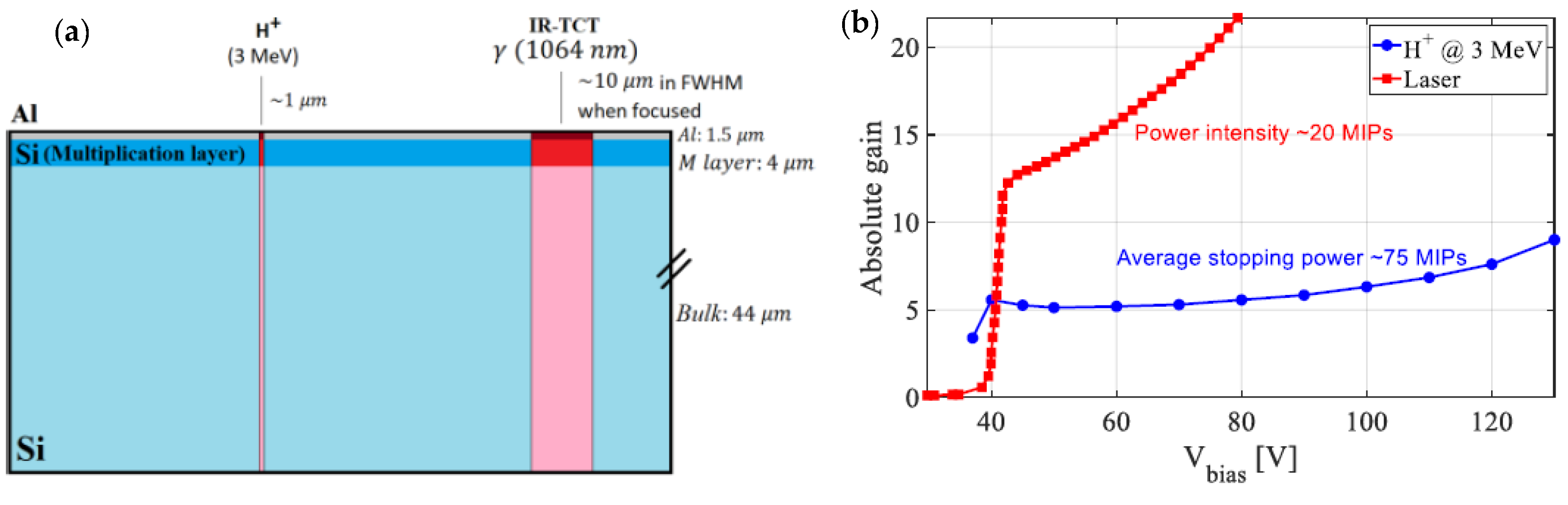
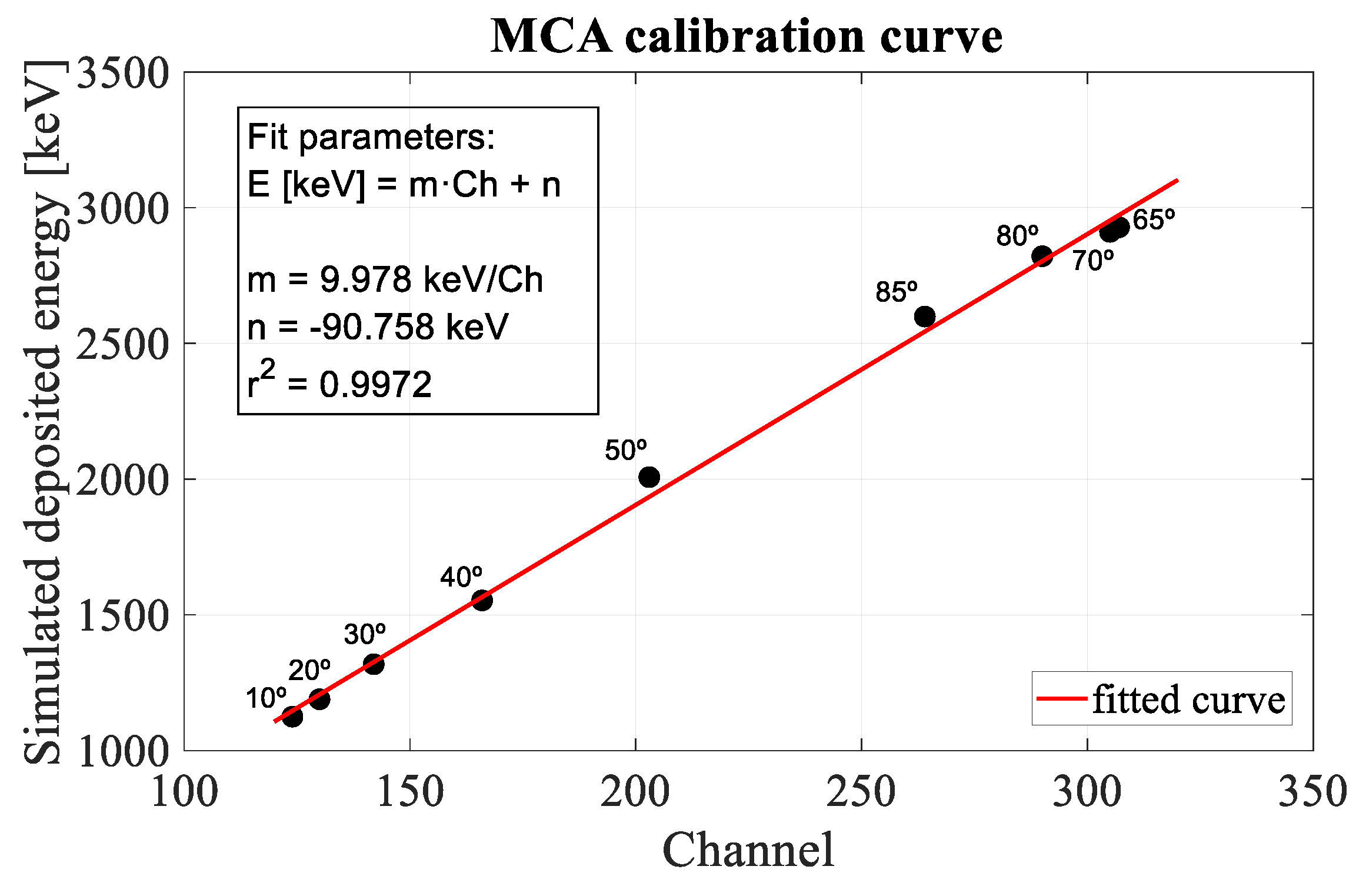
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
3. Results and Discussion
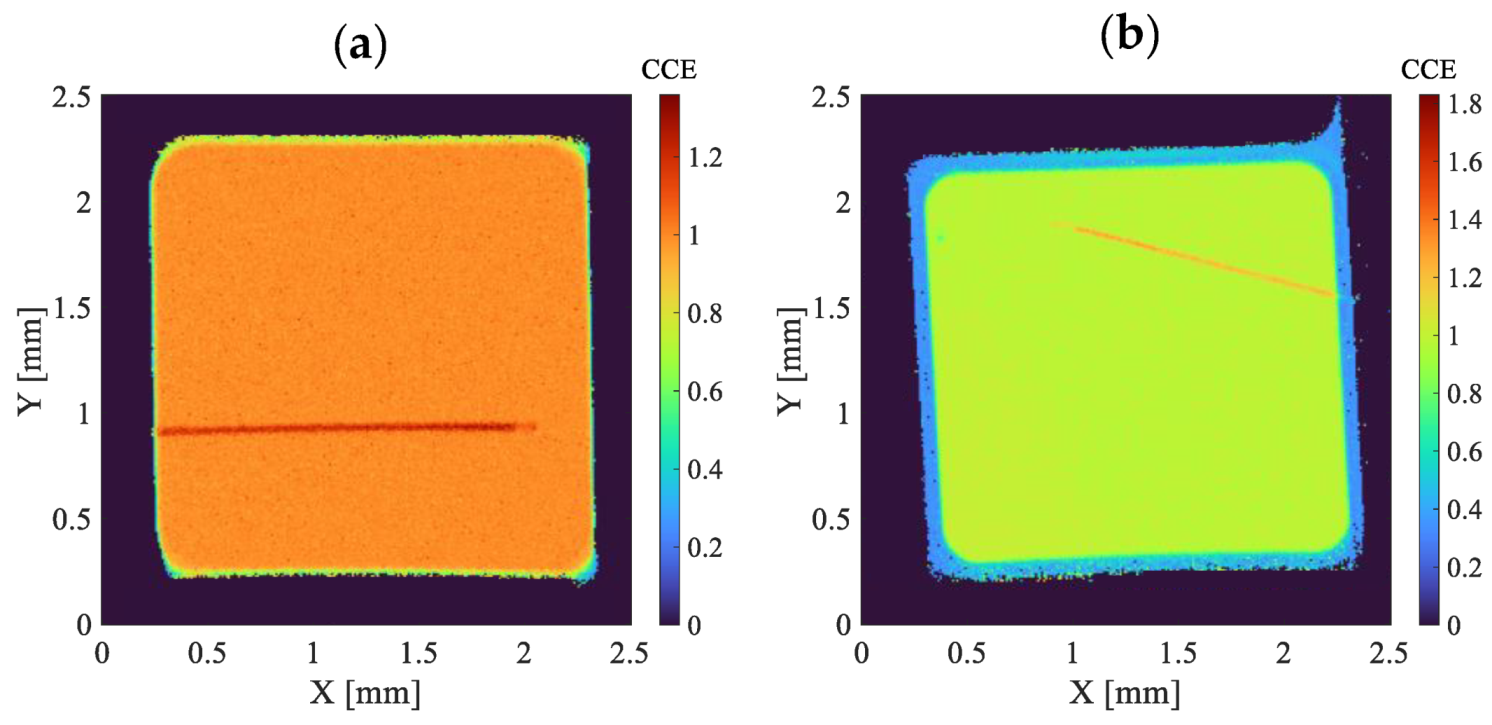
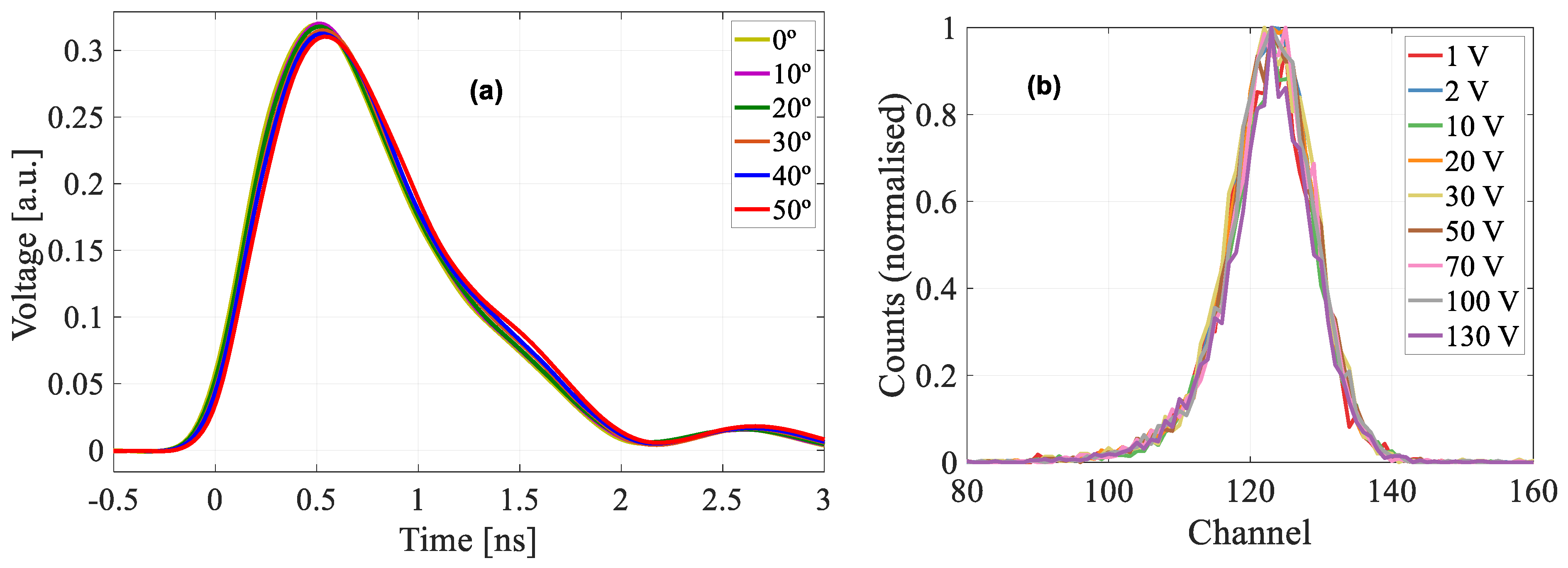
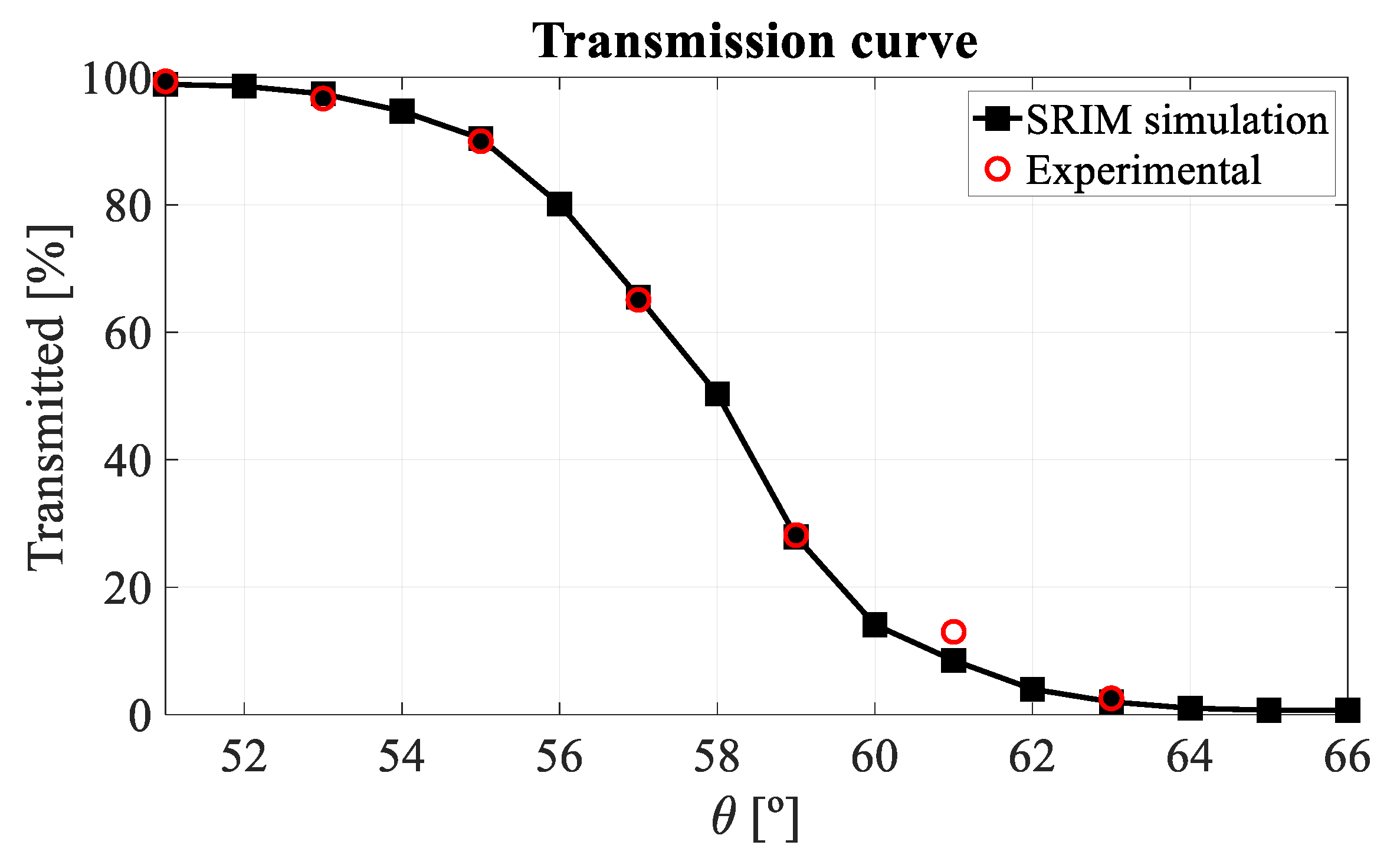
3.1. Detector Homogeneity and Structure
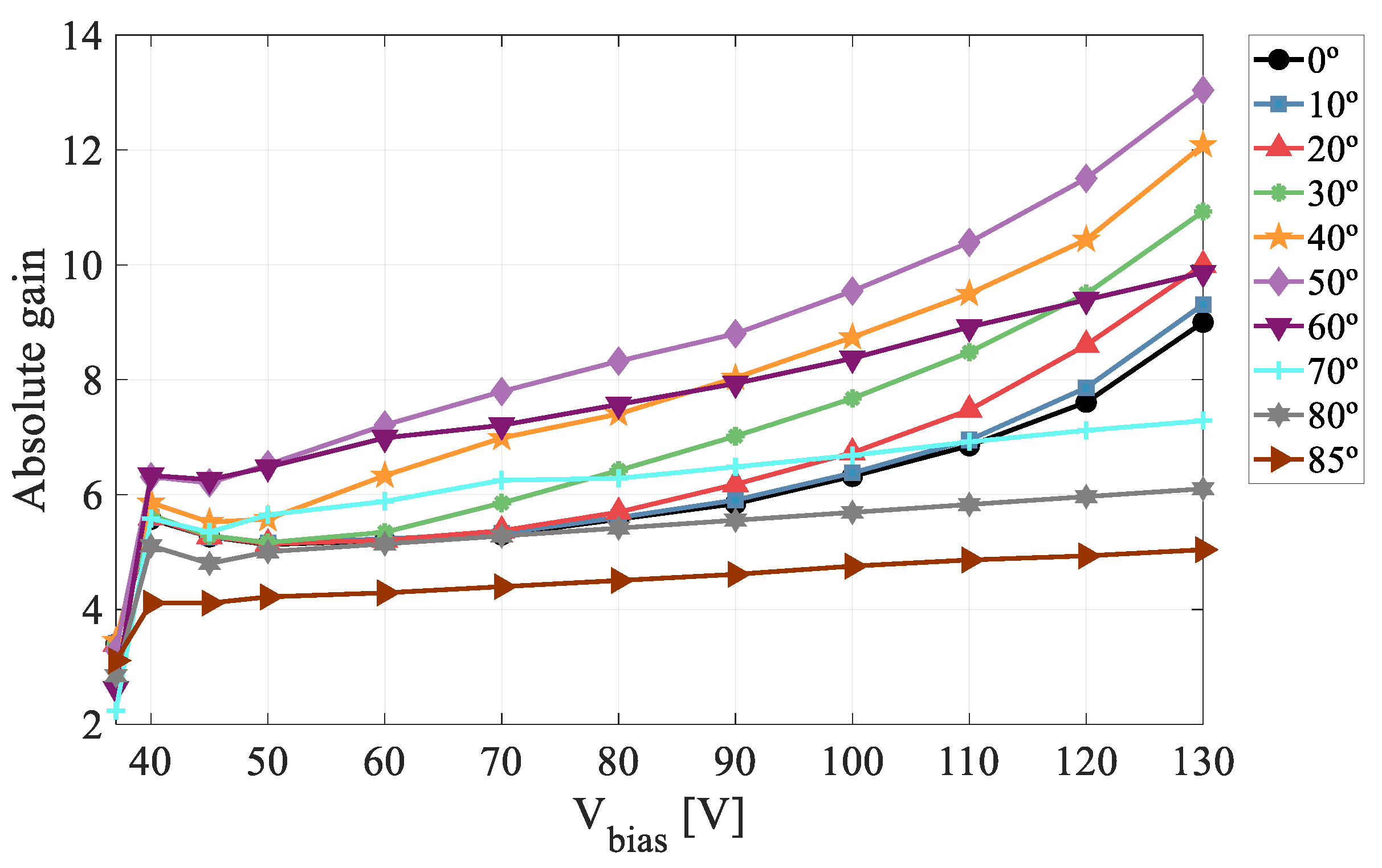
3.2. Absolute Gain Curves in the Microplasma-Free Regime
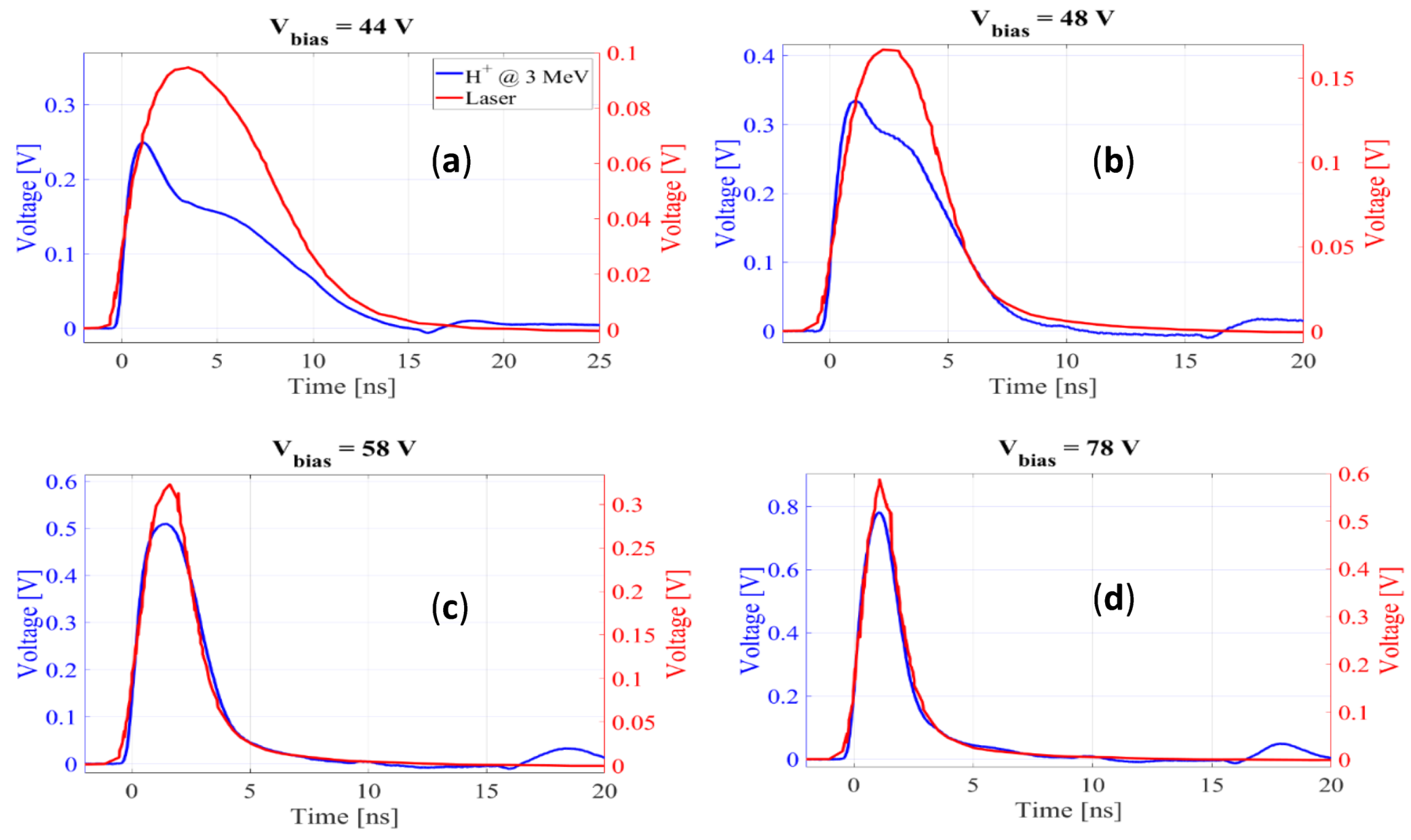
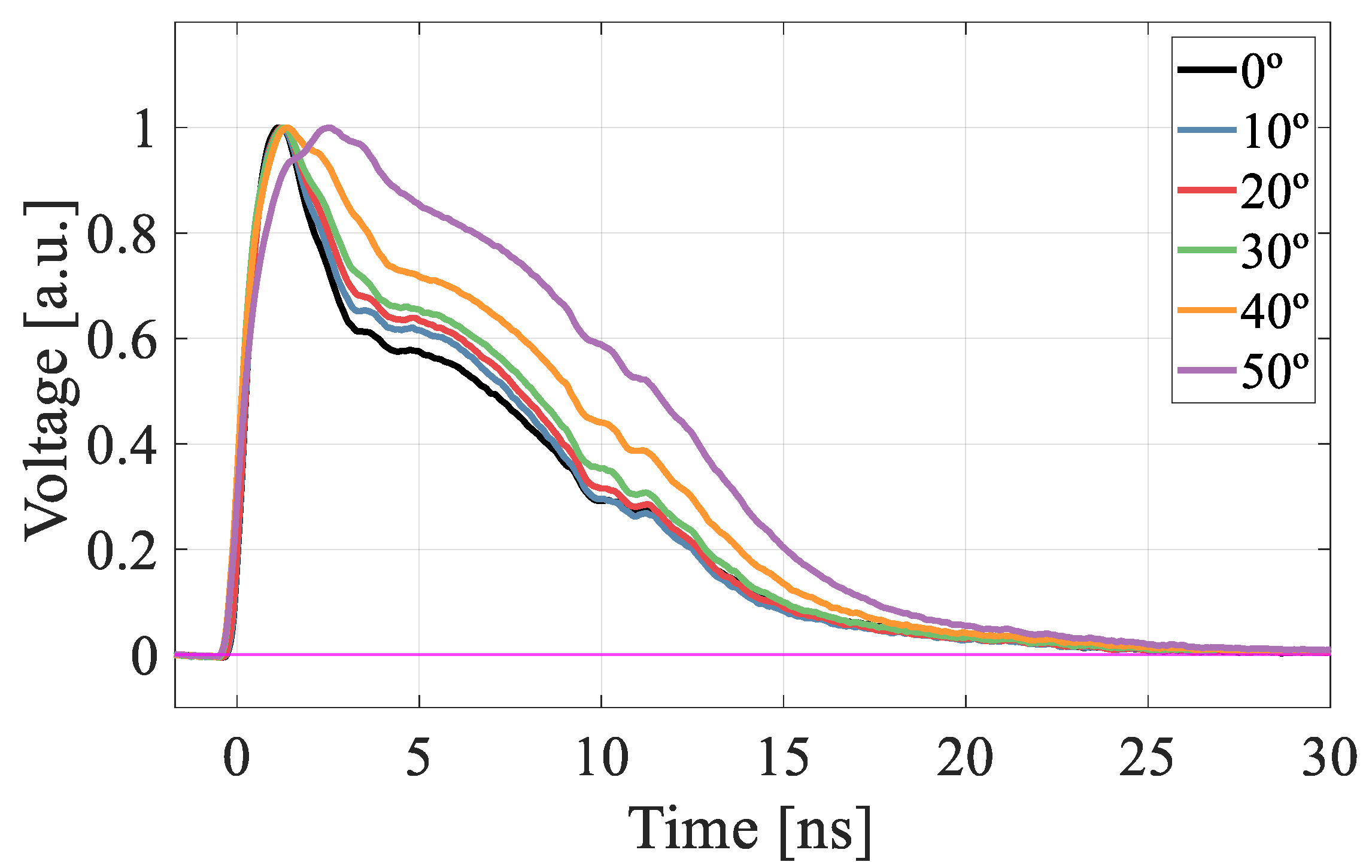
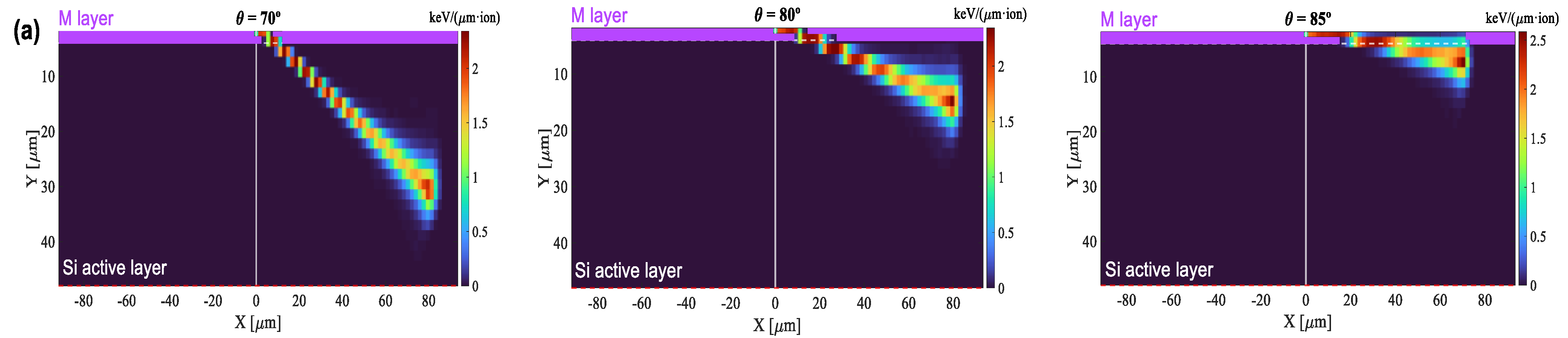
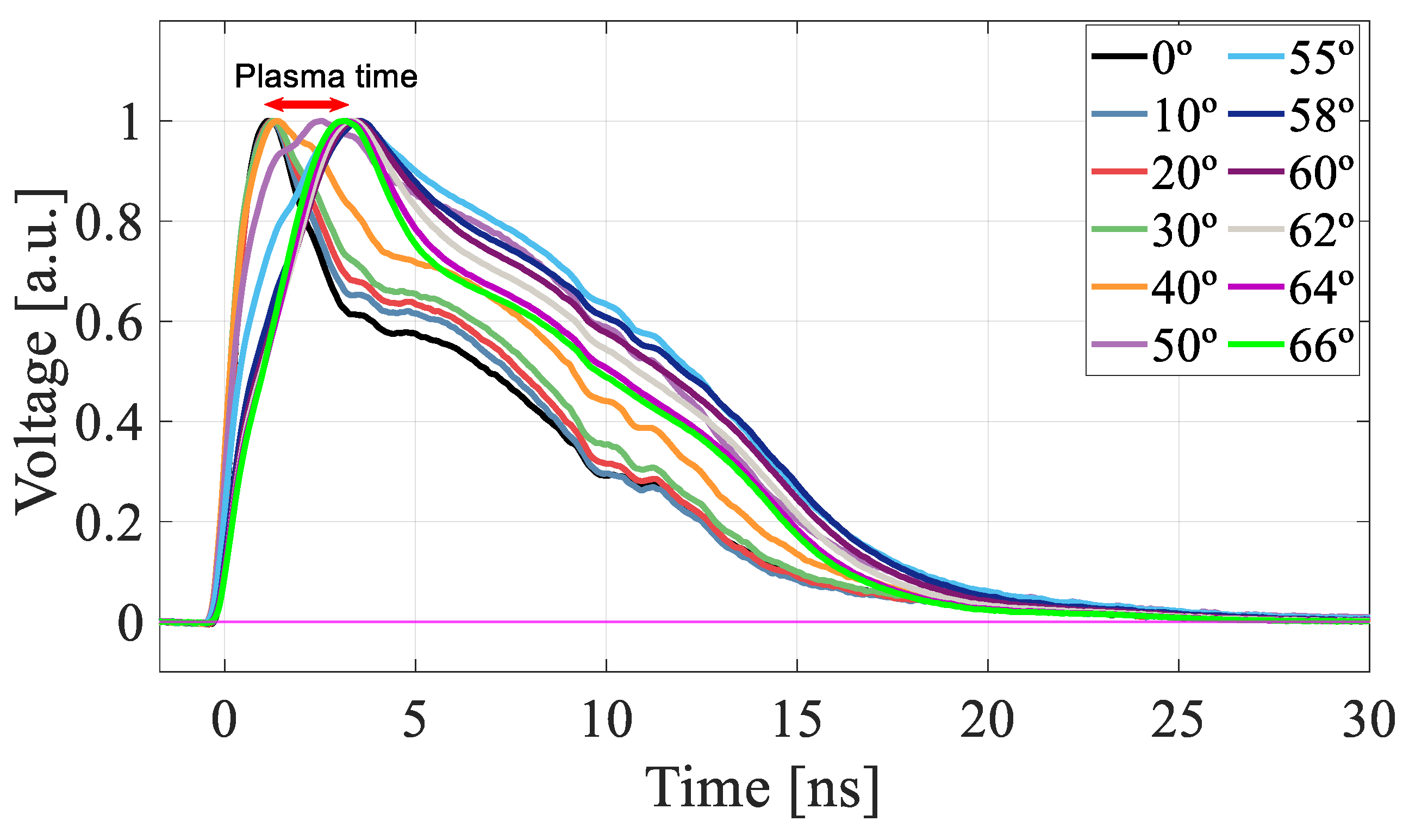
3.3. Absolute Gain Curves in the Microplasma Regime
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronym | Definition |
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter |
| APD | Avalanche Photo Diode |
| ATLAS | A Toroidal Large hadron collider ApparatuS |
| CCE | Charge Collection Efficiency |
| CERN | Conseil Européen pour la Recherche Nucléaire |
| CMS | Compact Muon Solenoid |
| CNA | Centro Nacional de Aceleradores |
| CNM | Centro Nacional de Microelectrónica |
| CSIC | Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas |
| EP-DT | Experimental Physics—Detector Technologies |
| HGTD | High Granularity Time Detector |
| IBIC | Ion Beam Induced Current |
| IFCA | Instituto de Física de Cantabria |
| IMB | Instituto de Microelectrónica de Barcelona |
| IR | InfraRed |
| LGAD | Low Gain Avalanche Detector |
| LHC | Large Hadron Collider |
| MCA | MultiChannel Analyzer |
| MIP | Minimum Ionizing Particle |
| MTD | Minimum ionizing particle Timing Detector |
| PIN | p-type—Intrinsic—n-type |
| PP&I | Particle Physics and Instrumentation |
| SMA | SubMiniature version A |
| SSD | Solid State Detector |
| TCT | Transient Current Technique |
| TPA | Two Photon Absorption |
| TRIBIC | Time-Resolved Ion Beam Induced Current |
| US | Universidad de Sevilla |
| λ | Linear ionization density |
References
- Pellegrini, G.; Fernández-Martínez, P.; Baselga, M.; Fleta, C.; Flores, D.; Greco, V.; Hidalgo, S.; Mandić, I.; Kramberger, G.; Quirion, D.; et al. Technology developments and first measurements of low gain avalanche detectors (LGAD) for high energy physics applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 2014, 765, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RD50’s Webpage. Available online: https://rd50.web.cern.ch/ (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Aberle, O.; Alonso, B.; Brüning, O.; Fessia, P.; Rossi, L.; Tavian, L.; Zerlauth, M.; Adorisio, C.; Adraktas, A.; Ady, M.; et al. High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider (HL-LHC) Technical Design Report V. 0.1; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Proposal for a MIP Timing Detector in the CMS Experiment Phase 2 Upgrade; Technical Report CERN-LHCC-2017-027. LHCC-P-009; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, December 2017; Available online: https://cds.cern.ch/record/2296612 (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Technical Proposal: A High-Granularity Timing Detector for the ATLAS Phase-II Upgrade; Technical Report CERN-LHCC-2018-023. LHCC-P-012; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, June 2018; Available online: https://cds.cern.ch/record/2623663CERN-ACC-2018-005 (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- RD50 Prolongation Request: May 2018. Available online: https://cds.cern.ch/record/2320882/files/LHCC-SR-007.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Currás, E. Low Gain Avalanche Detectors for 4-dimensional Tracking Applications in Severe Radiation Environments. In Proceedings of the 29th International Workshop on Vertex Detectors (VERTEX2020), Shonan, Japan, 4–9 October 2020; p. 010015. [Google Scholar]
- Sadrozinski, H.F.; Seiden, A.; Cartiglia, N. 4D tracking with ultra-fast silicon detectors. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2017, 81, 026101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, M.; Arcidiacono, R.; Barozzi, M.; Boscardin, M.; Cartiglia, N.; Dalla Betta, G.F.; Galloway, Z.; Mandurrino, M.; Mazza, S.; Paternoster, G.; et al. Radiation resistant LGAD design. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 2019, 919, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L.; Brown, W.L.; Donovan, P.F.; Mackintosh, I.M. Silicon p-n junction radiation detectors. IRE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1960, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, J.S.; Onoda, S.; Hirao, T.; Edmonds, L. Quenching of impact ionization in heavy-ion induced electronhole pair plasma tracks in wide bandwidth avalanche photodetectors. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 084501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currás, E.; Fernández, M.; Moll, M. Gain suppression mechanism observed in Low Gain Avalanche Detectors. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.10022. [Google Scholar]
- Maes, W.; De Meyer, K.; Van Overstraeten, R. Impact ionization in silicon: A review and update. Solid-State Electron. 1990, 33, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carulla, M.; Doblas, A.; Flores, D.; Galloway, Z.; Hidalgo, S.; Kramberger, G.; Luce, Z.; Mandic, I.; Mazza, S.; Merlos, A.; et al. 50 µm thin Low Gain Avalanche Detectors (LGAD) for timing applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 2019, 924, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Camacho, J.; López, J.G.; Guerrero, C.; Gutiérrez, J.L.; García-Tenorio, R.; Santos-Arévalo, F.J.; Chamizo, E.; Ferrer, F.J.; Jiménez-Ramos, M.C.; Balcerzyk, M.; et al. Research facilities and highlights at the Centro Nacional de Aceleradores (CNA). Eur. J. Plus 2021, 136, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grime, G.W.; Dawson, M.; Marsh, M.A.; McArthur, I.C.; Watt, F. Oxford Scanning Proton Microprobe Facility. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 1991, 54, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SRIM2013. Available online: http://www.srim.org/ (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Williams, R.N.; Lawson, E.M. The plasma effect in silicon semiconductor radiation detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1974, 120, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartiglia, N.; Arcidiacono, R.; Baselga, M.; Bellan, R.; Boscardin, M.; Cenna, F.; Spencer, N. Design optimization of ultra-fast silicon detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2015, 796, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tove, P.A.; Seibt, W. Plasma effects in semiconductor detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 1999, 30, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouskeftaras, A.; Chanal, M.; Chambonneau, M.; Clady, R.; Utéza, O.; Grojo, D. Direct measurement of ambipolar diffusion in bulk silicon by ultrafast infrared imaging of laser-induced microplasmas. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 041107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakhostin, M. Signal Processing for Radiation Detectors; John Willey & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Ramos, M.C.; García López, J.; García Osuna, A.; Vila, I.; Currás, E.; Jaramillo, R.; Hidalgo, S.; Pellegrini, G. Study of Ionization Charge Density-Induced Gain Suppression in LGADs. Sensors 2022, 22, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031080
Jiménez-Ramos MC, García López J, García Osuna A, Vila I, Currás E, Jaramillo R, Hidalgo S, Pellegrini G. Study of Ionization Charge Density-Induced Gain Suppression in LGADs. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031080
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Ramos, M. Carmen, Javier García López, Adrián García Osuna, Iván Vila, Esteban Currás, Richard Jaramillo, Salvador Hidalgo, and Giulio Pellegrini. 2022. "Study of Ionization Charge Density-Induced Gain Suppression in LGADs" Sensors 22, no. 3: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031080
APA StyleJiménez-Ramos, M. C., García López, J., García Osuna, A., Vila, I., Currás, E., Jaramillo, R., Hidalgo, S., & Pellegrini, G. (2022). Study of Ionization Charge Density-Induced Gain Suppression in LGADs. Sensors, 22(3), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031080





