Compensation for Electrode Detachment in Electrical Impedance Tomography with Wearable Textile Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Image Reconstruction
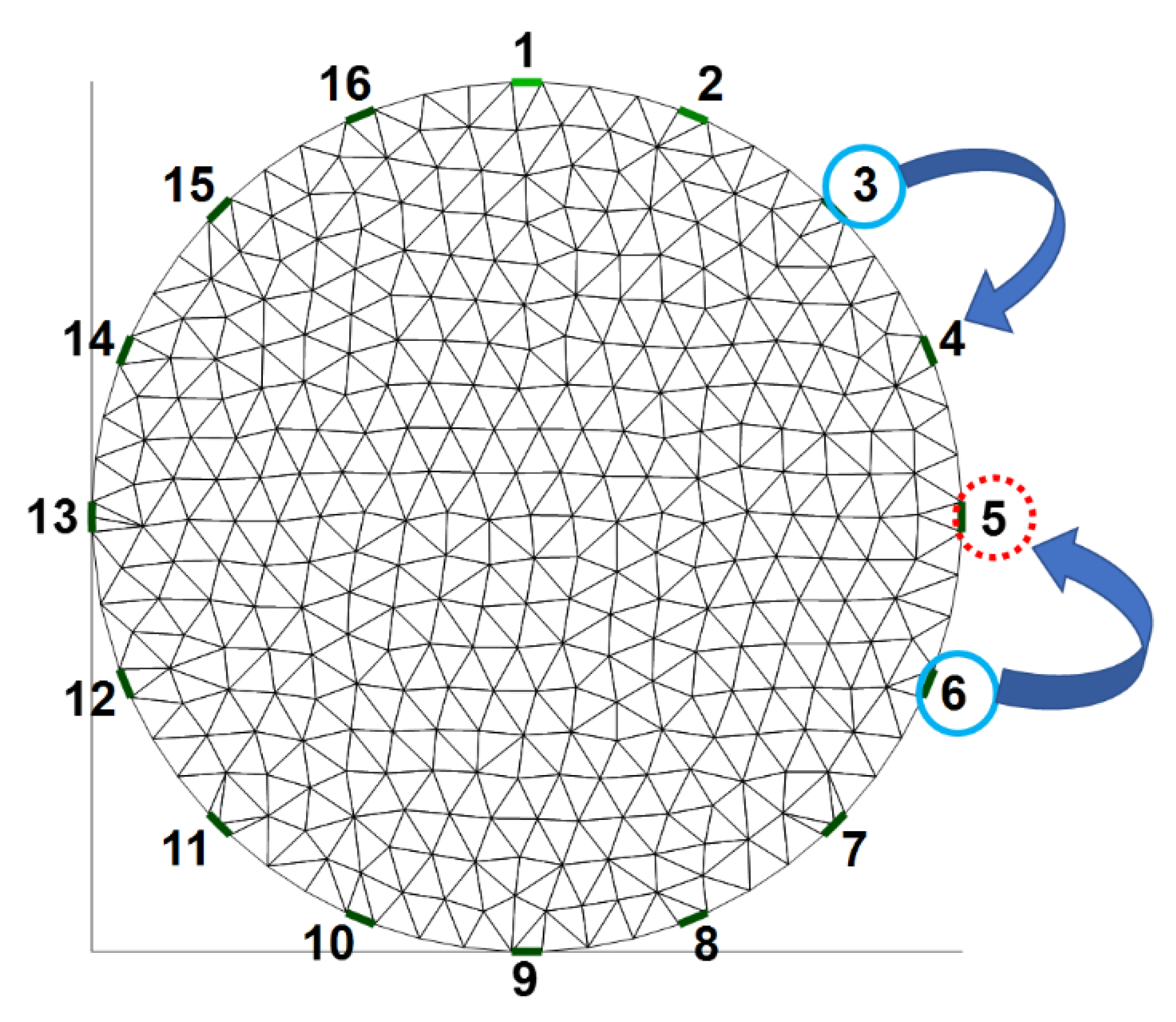
2.2. Detection of Faulty Electrodes
2.3. Algorithm for Compensating for the Invalid Data from Faulty Electrodes
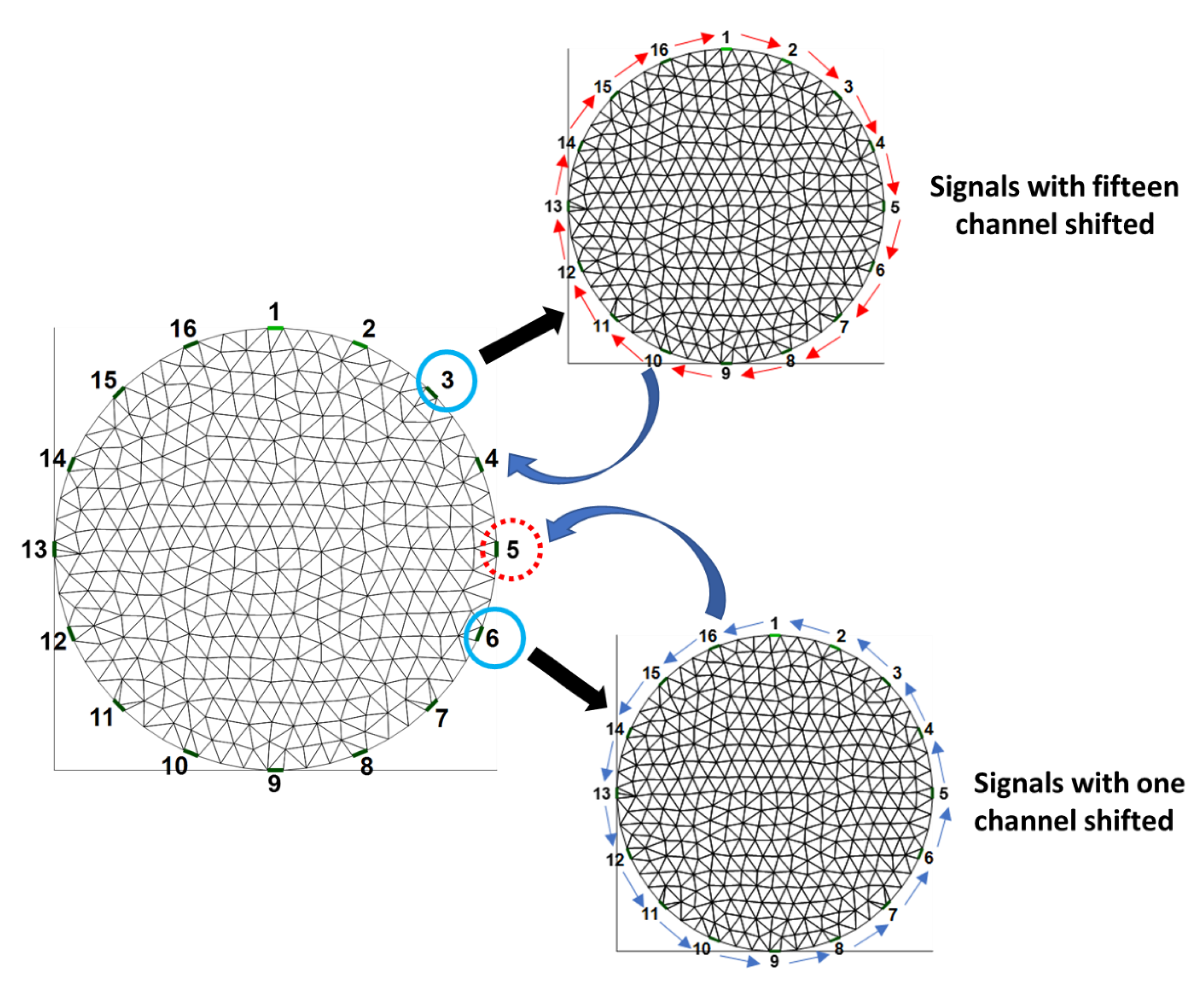
2.3.1. Voltage-Replace Method
2.3.2. Voltage-Shift Method
2.4. Portable EIT System
2.5. Simulation, Experimental, and In Vivo Lung Setups
2.6. In Vivo Lung Imaging with Wearable Textile Electrode Belt
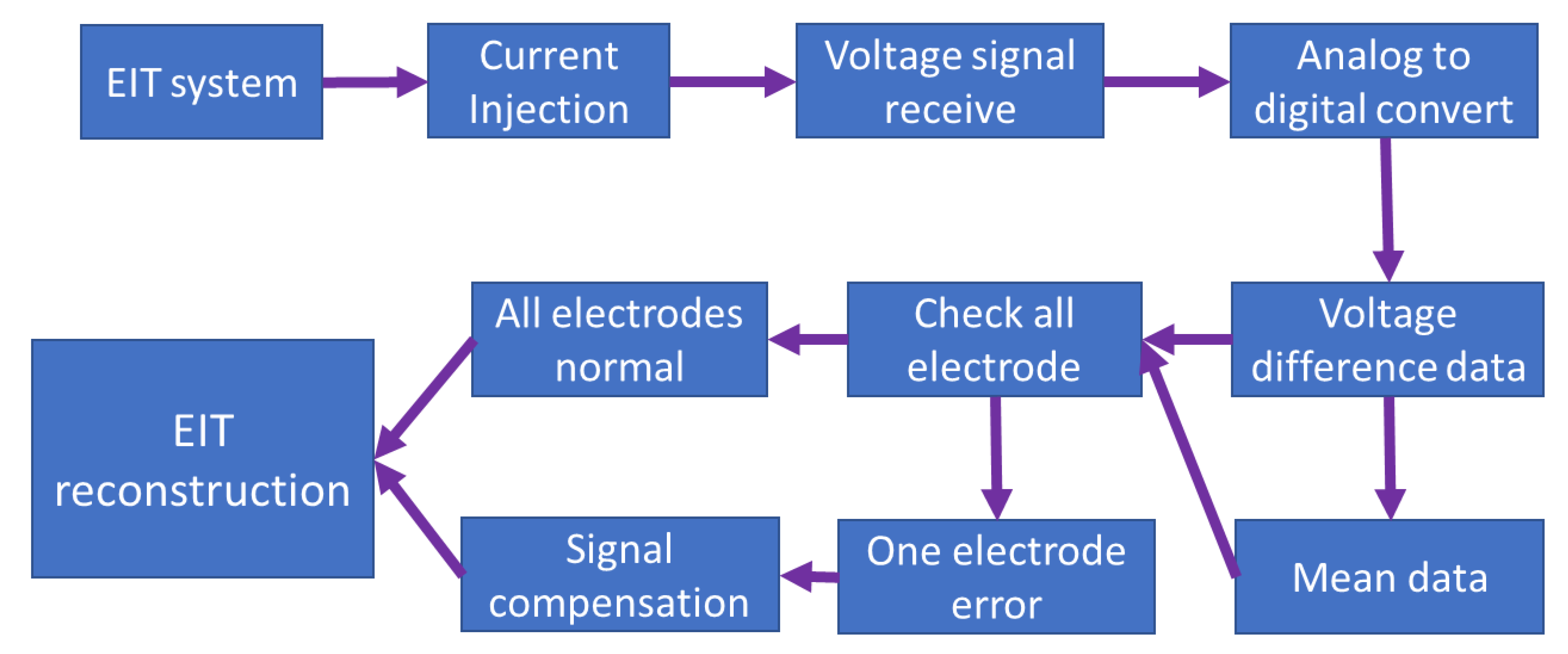
2.7. The EIT System with Compensation for Invalid Data
3. Results and Discussion
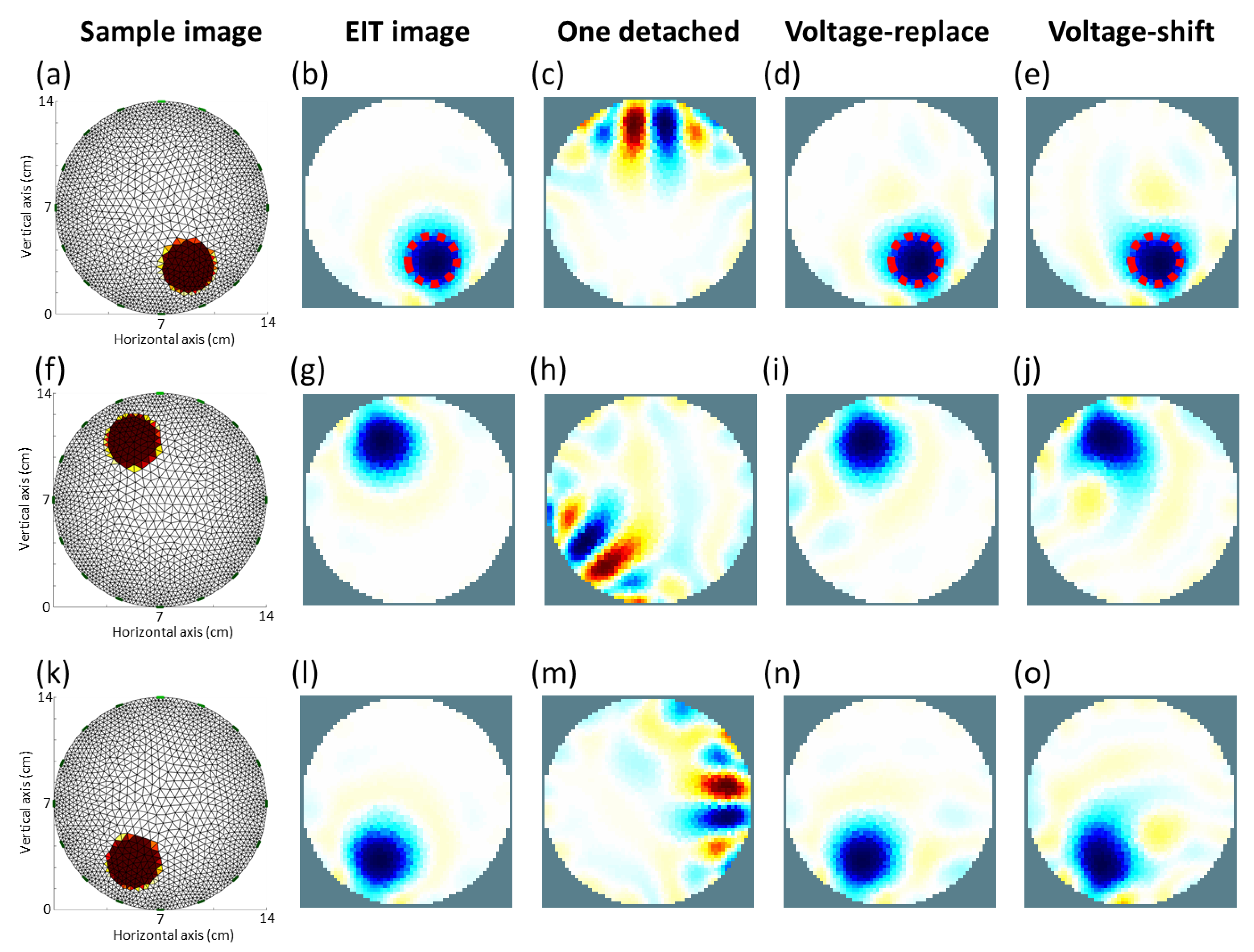
3.1. EIDORS Simulation
3.2. Experimental Results
3.3. Results of In Vivo Lung EIT Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Bardill, A.; de Gelidi, S.; Bayford, R.; Demosthenous, A. A High Frame Rate Wearable EIT System Using Active Electrode ASICs for Lung Respiration and Heart Rate Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 3810–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.H. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT): A review. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2003, 27, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putensen, C.; Hentze, B.; Muenster, S.; Muders, T. Electrical Impedance Tomography for Cardio-Pulmonary Monitoring. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasarow, L.; Vogt, B.; Zhao, Z.; Balke, L.; Weiler, N.; Frerichs, I. Regional lung function measures determined by electrical impedance tomography during repetitive ventilation manoeuvres in patients with COPD. Physiol. Meas. 2021, 42, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhong, N.; Li, Y. A narrative review of electrical impedance tomography in lung diseases with flow limitation and hyperinflation: Methodologies and applications. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatenkova, V.; Teschner, E.; Jedlicka, J. Evaluation of regional ventilation by electric impedance tomography during percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy in neurocritical care: A pilot study. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.H.; Barber, D.C.; Seagar, A.D. Clinical Physics and Physiological Measurement Applied potential tomography: Possible clinical applications. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. Physiol. Meas. 1985, 6, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.P.; Webster, J.G. An Impedance Camera for Spatially Specific Measurements of the Thorax. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1978, 25, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.C.; Brown, B.H.; Freeston, I.L. Imaging spatial distributions of resistivity using applied potential tomography. Electron. Lett. 1983, 19, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.H. Tissue Impedance Methods, Imaging with Non-Ionising Radiation; Jackson, D.F., Ed.; Surrey University Press: Guilford, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- McEwan, A.; Cusick, G.; Holder, D. A review of errors in multi-frequency EIT instrumentation. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, S197–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boverman, G.; Isaacson, D.; Newell, J.C.; Saulnier, G.J.; Kao, T.-J.; Amm, B.C.; Wang, X.; Davenport, D.M.; Chong, D.H.; Sahni, R.; et al. Efficient Simultaneous Reconstruction of Time-Varying Images and Electrode Contact Impedances in Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.A.; Ling, S.H. Review on Electrical Impedance Tomography: Artificial Intelligence Methods and its Applications. Algorithms 2019, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, E.J.; Hua, P.; Webster, J.G.; Tompkins, W.J. Measuring lung resistivity using electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 39, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Lee, J.; Yoo, H.J. Wearable lung-health monitoring system with electrical impedance tomography. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 1707–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, E.L.V.; Chaves, C.N.; Gomes, S.; Beraldo, M.A.; Volpe, M.S.; Tucci, M.R.; Schettino, I.A.L.; Bohm, S.H.; Carvalho, C.R.R.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Real-time detection of pneumothorax using electrical impedance tomography. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, T.; Bellani, G.; Salerno, D.; Mantegazza, F.; Pesenti, A. Regional Distribution of Air Trapping in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Goel, V. Design and development of Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) based System. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 74, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.; Teschner, E.; Leonhardt, S. Electrical Impedance Tomography: The Realisation of Regional Ventilation Monitoring, 2nd ed.; Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA: Lübeck, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.M.; Jung, T.-P.; Cauwenberghs, G. Dry-Contact and Noncontact Biopotential Electrodes: Methodological Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 3, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokus, M.A.; Jur, J.S. Fabric-Based Wearable Dry Electrodes for Body Surface Biopotential Recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, R.; De, D.R. Advances in textile technologies for unobtrusive monitoring of vital parameters and movements. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006; pp. 392–395. [Google Scholar]
- Poh, M.-Z.; Swenson, N.C.; Picard, R.W. A Wearable Sensor for Unobtrusive, Long-Term Assessment of Electrodermal Activity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, T.; Foster, R.; Hao, Y. Detecting Vital Signs with Wearable Wireless Sensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 10837–10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacelli, M.; Loriga, G.; Taccini, N.; Paradiso, R. Sensing Fabrics for Monitoring Physiological and Biomechanical Variables: E-textile solutions. In Proceedings of the 2006 3rd IEEE/EMBS International Summer School on Medical Devices and Biosensors, Cambridge, MA, USA, 4–6 September 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Scilingo, E.P.; Gemignani, A.; Paradiso, R.; Taccini, N.; Ghelarducci, B.; De Rossi, D. Performance Evaluation of Sensing Fabrics for Monitoring Physiological and Biomechanical Variables. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arquilla, K.; Webb, A.K.; Anderson, A.P. Textile Electrocardiogram (ECG) Electrodes for Wearable Health Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.J.; Milnes, P.; Waterworth, A.R.; Smallwood, R.; Brown, B.H. Mk3.5: A modular, multi-frequency successor to the Mk3a EIS/EIT system. Physiol. Meas. 2001, 22, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, G.K.; Gómez-Laberge, C.; Rettig, J.S.; Vargas, S.O.; Smallwood, C.D.; Prabhu, S.P.; Arnold, J.H. Mechanical ventilation guided by electrical impedance tomography in experimental acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Lee, J.; Bae, J.; Yoo, H.J. A 10.4 mW Electrical Impedance Tomography SoC for Portable Real-Time Lung Ventilation Monitoring System. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Bae, J.; Yoo, H.J. Wearable 3D lung ventilation monitoring system with multi frequency electrical impedance tomography. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Torino, Italy, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, J.X.; Bohm, S.H. Belt for Electro Impedance Measurement and Method Using such Belt. U.S. Patent No. 10,278,643, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pleyers, T.; Levionnois, O.; Siegenthaler, J.; Spadavecchia, C.; Raillard, M. Investigation of selected respiratory effects of (dex)medetomidine in healthy Beagles. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2020, 47, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, L.; Frerichs, I.; Miedema, M.; Kallio, M.; Papadouri, T.; Karaoli, C.; Becher, T.; Tingay, D.G.; Van Kaam, A.H.; Bayford, R.H.; et al. Clinical performance of a novel textile interface for neonatal chest electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 044004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-L.; Cheng, I.-C.; Huang, C.-H.; Liao, Y.-T.; Lin, W.-C.; Tsai, K.-J.; Chi, C.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Wu, C.-H.; Lin, I.-T.; et al. Dry Wearable Textile Electrodes for Portable Electrical Impedance Tomography. Sensors 2021, 21, 6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djajaputra, D.; Holder, D. Electrical Impedance Tomography: Methods, History and Applications. Med. Phys. 2005, 32, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayford, R.; Tizzard, A. Bioimpedance imaging: An overview of potential clinical applications. Analyst 2012, 137, 4635–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A. Accounting for erroneous electrode data in electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartinger, A.E.; Guardo, R.; Adler, A.; Gagnon, H.G. Real-Time Management of Faulty Electrodes in Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 56, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfaw, A.; Adler, A. Automatic detection of detached and erroneous electrodes in electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, S175–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, R. Virtual crack closure technique: History, approach, and applications. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2004, 57, 109–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsic, A. Regularisation Methods for Imaging from Electrical Measurements. Ph.D. Thesis, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tizzard, A.; Horesh, L.; Yerworth, R.J.; Holder, D.S.; Bayford, R.H. Generating accurate finite element meshes for the forward model of the human head in EIT. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, S251–S261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Lionheart, W.R.B. Uses and abuses of EIDORS: An extensible software base for EIT. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, S25–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöberl, J. NETGEN—An advancing front 2D/3D-mesh generator based on abstract rules. Comput. Vis. Sci. 1997, 1, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Arnold, J.H.; Bayford, R.; Borsic, A.; Brown, B.; Dixon, P.; Faes, T.J.C.; Frerichs, I.; Gagnon, H.; Gärber, Y.; et al. GREIT: A unified approach to 2D linear EIT reconstruction of lung images. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, S35–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Hashimoto, J.; Suzuki, T.; Nakahara, T.; Kubo, A.; Iwanaga, S.; Ogawa, S. Comparison of image reconstruction algo-rithms in myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2001, 15, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauhkonen, M.; Lionheart, W.R.; Heikkinen, L.M.; Vauhkonen, P.J.; Kaipio, J.P. A MATLAB package for the EIDORS project to reconstruct two-dimensional EIT images. Physiol. Meas. 2001, 22, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.; Nefti-Meziani, S.; Carbonaro, N.; Tognetti, A. A quantitative evaluation of drive pattern selection for optimizing EIT-based stretchable sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.-L.; Wu, G.-Z.; Chang, C.-C.; Li, M.-L. Acoustic-Field Beamforming for Low-Power Portable Ultrasound. Ultrason. Imaging 2021, 43, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.L.; Li, C.J.; Cheng, I.C.; Sun, P.Z.; Hsu, B.; Cheng, H.H.; Lin, Z.S.; Lin, C.W.; Li, M.L. Acoustic-Field Beam-forming-Based Generalized Coherence Factor for Handheld Ultrasound. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Duan, X. EIT Image Reconstruction Method Based on DnCNN. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Glasgow, UK, 17–20 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, S.; Schiffmann, H.; Frerichs, A.; Klockgether-Radke, A.; Frerichs, I. Body and head position effects on regional lung ventilation in infants: An electrical impedance tomography study. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






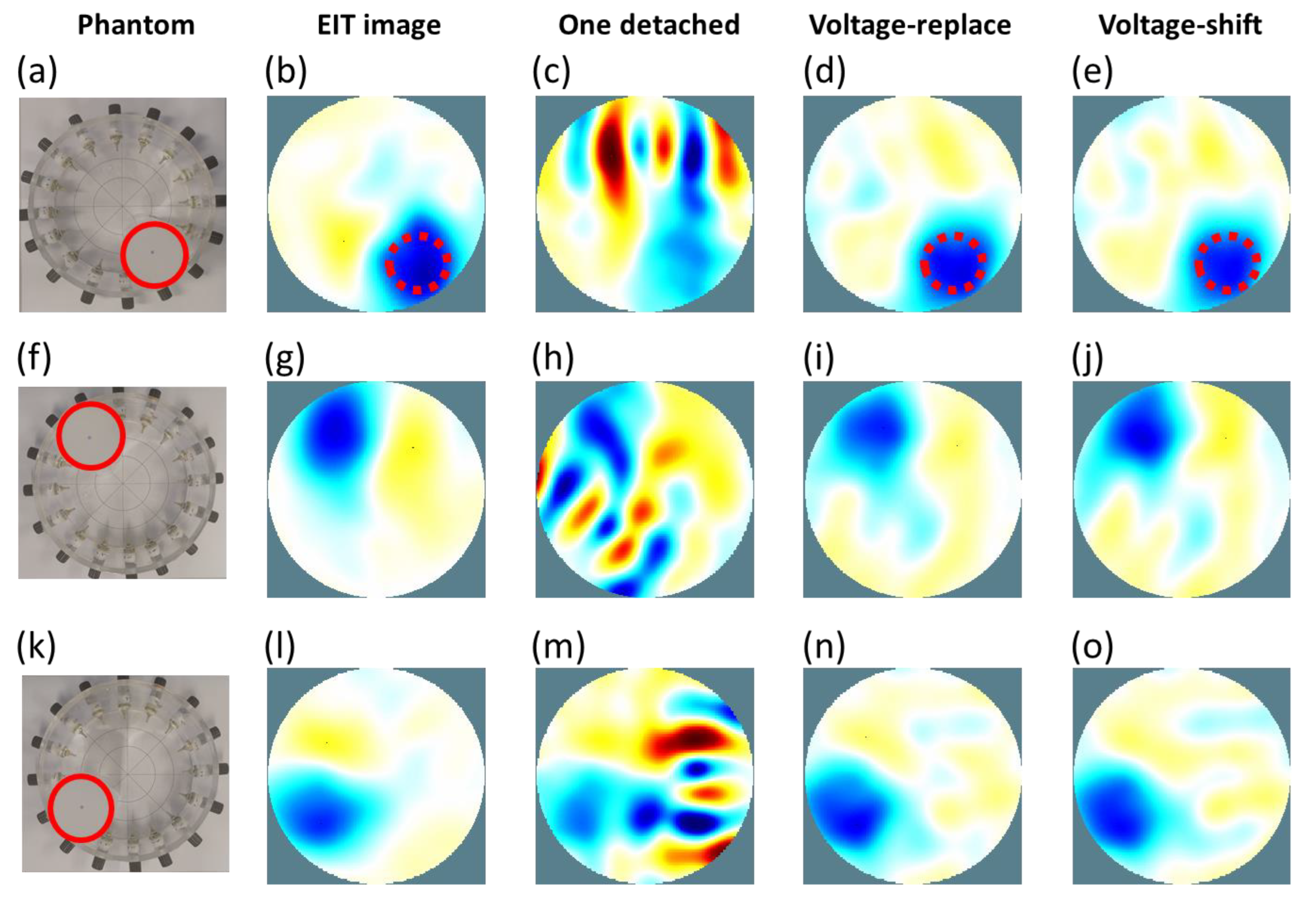
| Circular Inclusion Shown in Figure 10a | Circular Inclusion Shown in Figure 10f | Circular Inclusion Shown in Figure 10k | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIT Image | Voltage-Replace | Voltage-Shift | EIT Image | Voltage-Replace | Voltage-Shift | EIT Image | Voltage-Replace | Voltage-Shift | |
| SD (%) | 11.30 | 12.19 | 15.60 | 10.37 | 12.87 | 22.80 | 12.63 | 13.45 | 21.27 |
| PE (mm) | 0.30 | 1.00 | 2.30 | 0. 40 | 1.00 | 2.30 | 0. 50 | 1.20 | 1.50 |
| Circular Inclusion Shown in Figure 11a | Circular Inclusion Shown in Figure 11f | Circular Inclusion Shown in Figure 11k | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIT Image | Voltage-Replace | Voltage-Shift | EIT Image | Voltage-Replace | Voltage-Shift | EIT Image | Voltage-Replace | Voltage-Shift | |
| SD (%) | 18.77 | 20.20 | 19.13 | 20.08 | 20.75 | 21.18 | 21.28 | 22.33 | 22.71 |
| PE (mm) | 0.50 | 1.70 | 1.60 | 0.70 | 1.62 | 1.72 | 1.21 | 1.81 | 1.92 |
| Original EIT Image | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
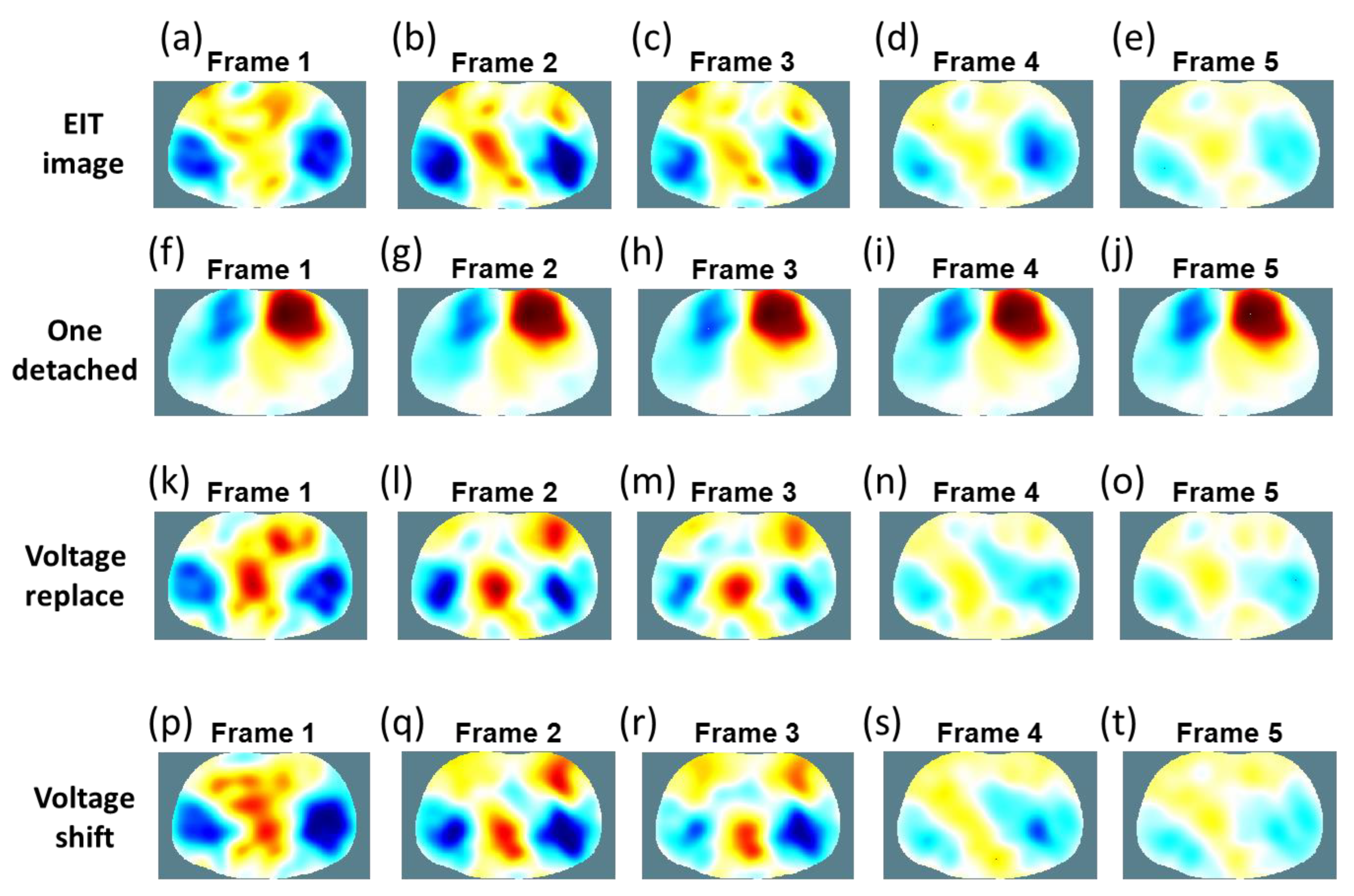
| SSIM | Frame 1 | Frame 2 | Frame 3 | Frame 4 | Frame 5 |
| One detached | 0.5213 | 0.5706 | 0.6225 | 0.6924 | 0.7158 |
| Voltage-replace method | 0.8847 | 0.8621 | 0.8958 | 0.9633 | 0.9873 |
| Voltage-shift Method | 0.9031 | 0.9041 | 0.9288 | 0.9703 | 0.9883 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.-L.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Hu, S.-Y.; Cheng, I.-C.; Huang, C.-H.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, C.-J.; Lin, C.-W. Compensation for Electrode Detachment in Electrical Impedance Tomography with Wearable Textile Electrodes. Sensors 2022, 22, 9575. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249575
Hu C-L, Lin Z-Y, Hu S-Y, Cheng I-C, Huang C-H, Li Y-H, Li C-J, Lin C-W. Compensation for Electrode Detachment in Electrical Impedance Tomography with Wearable Textile Electrodes. Sensors. 2022; 22(24):9575. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249575
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Chang-Lin, Zong-Yan Lin, Shu-Yun Hu, I-Cheng Cheng, Chih-Hsien Huang, Yu-Hao Li, Chien-Ju Li, and Chii-Wann Lin. 2022. "Compensation for Electrode Detachment in Electrical Impedance Tomography with Wearable Textile Electrodes" Sensors 22, no. 24: 9575. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249575
APA StyleHu, C.-L., Lin, Z.-Y., Hu, S.-Y., Cheng, I.-C., Huang, C.-H., Li, Y.-H., Li, C.-J., & Lin, C.-W. (2022). Compensation for Electrode Detachment in Electrical Impedance Tomography with Wearable Textile Electrodes. Sensors, 22(24), 9575. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249575






