Applying Ternion Stream DCNN for Real-Time Vehicle Re-Identification and Tracking across Multiple Non-Overlapping Cameras
Abstract
1. Introduction
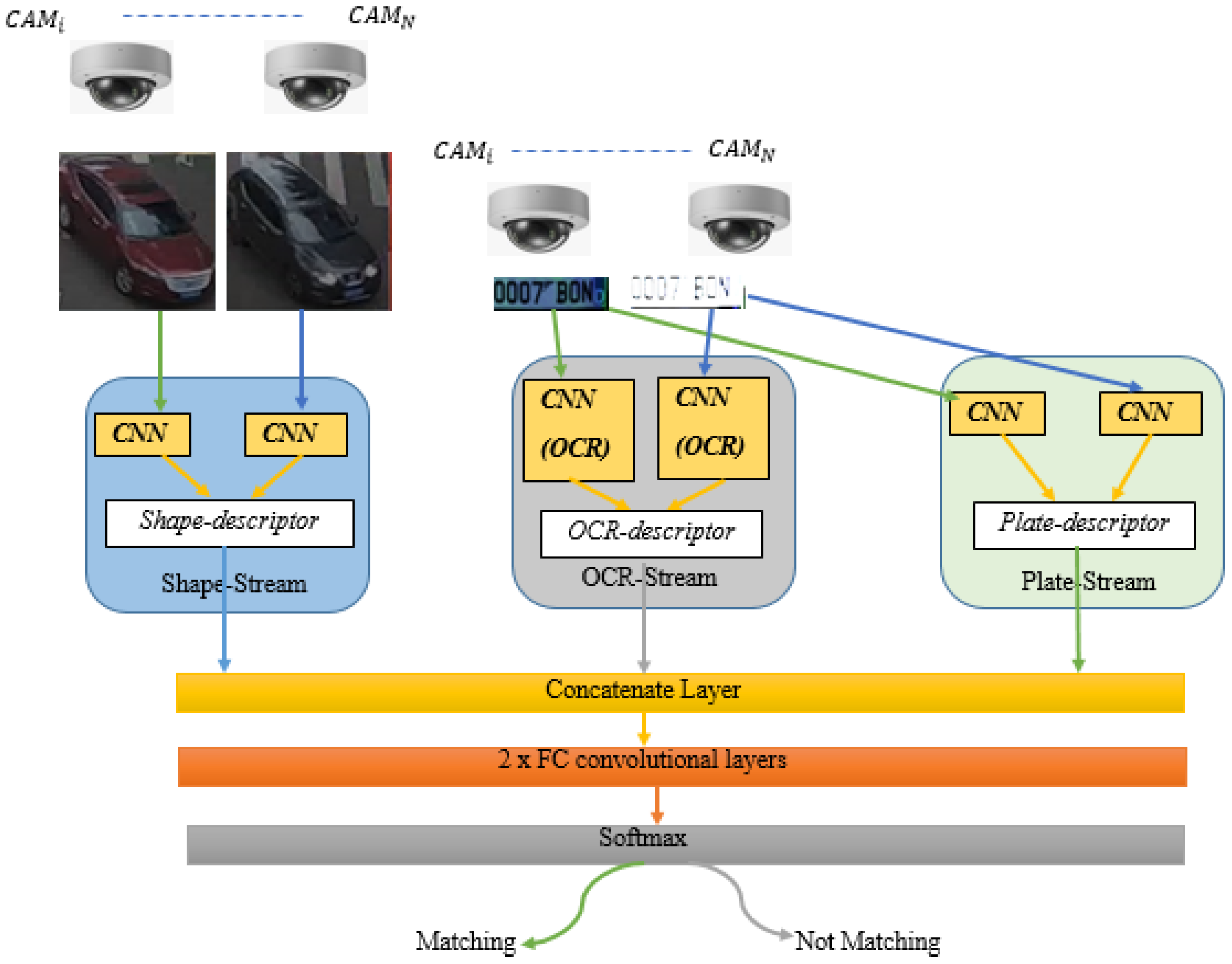
2. Proposed Ternion Stream DCNNs for Real-Time Vehicle Tracking (VT)
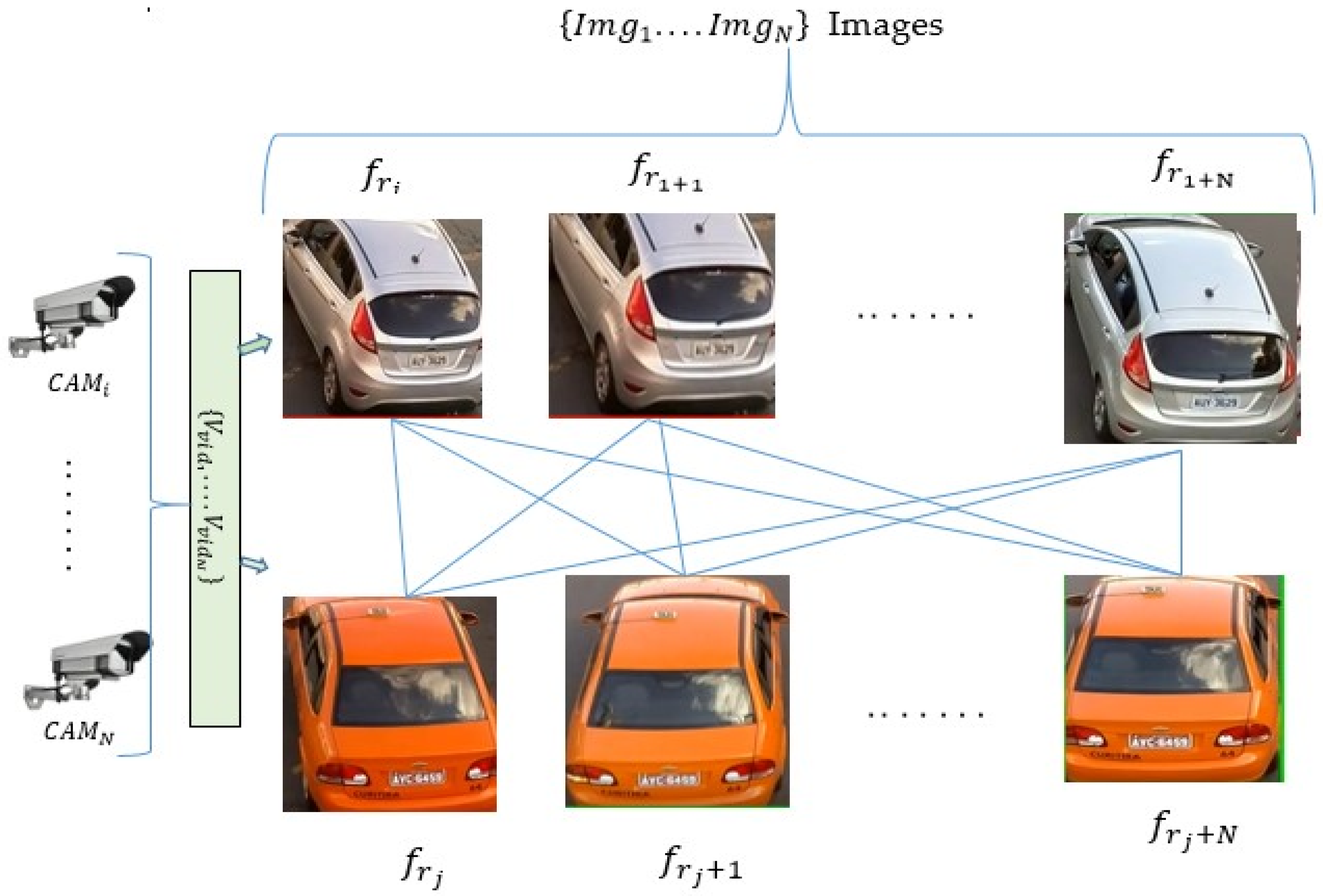
2.1. Data Collection and Preparation Process
2.2. Appearance Features’ Learning and Handling
2.3. License Plate-Based Vehicle Re-ID
3. Experiments Settings
Implementation Details
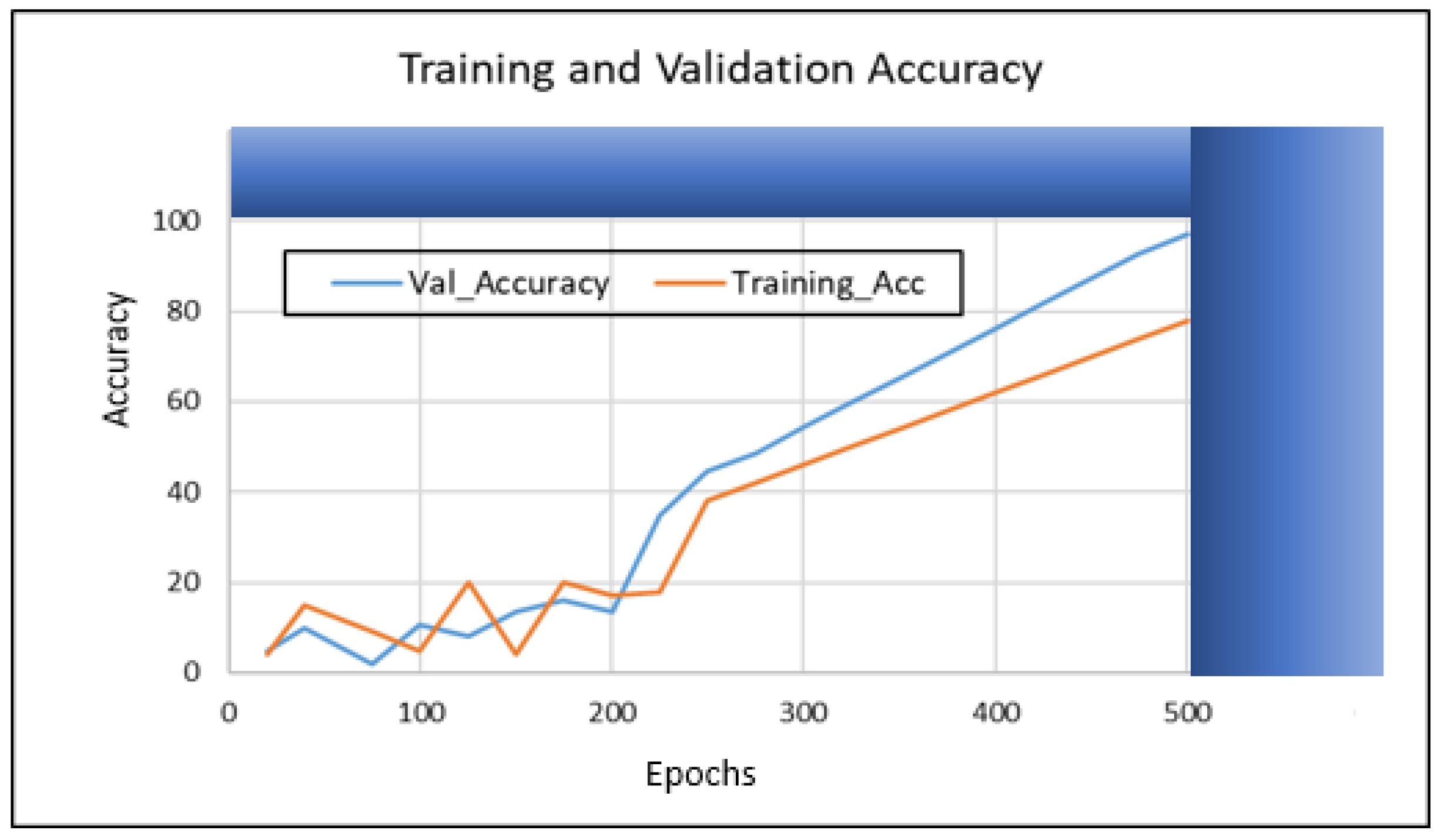
4. Results
5. Results Analysis
Performance Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheel, A.; Knill, C.; Reuter, S.; Dietmayer, K. Multi-sensor multi-object tracking of vehicles using high-resolution radars. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Gothenburg, Sweden, 19–22 June 2016; pp. 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A. Multi-Object Tracking and Identification over Sets. 2016. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.07960 (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; Luo, W.; An, W. The Application of Neural Network in Multiple Object Tracking. DEStech Trans. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2018, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin-Reyes, P.A.; Bergamini, L.; Lorenzo-Navarro, J.; Palazzi, A.; Calderara, S.; Cucchiara, R. Unsupervised vehicle re-identification using triplet networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Yun, B.; Kim, T.; Lee, J. Recognition of Vehicle License Plates Based on Image Processing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BrundhaElci, J.; Punith, R.; Gowda, S.C.; Shivaprasad, B.M.; Buvaneshwaran, S.V. Criminal Recognition and Tracking System. Int. Res. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 6, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Park, J.H.; Yoo, S.; Cui, Y.; Thomas, M.; Moeslinger, M. Using Machine Learning to Track Objects Across Cameras. In Using Machine Learning to Track Objects Across Cameras; Brookhaven National Lab.: Upton, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, K.; Yoon, S.; Ko, K.; Kim, C. Multi-target multi-camera vehicle tracking for city-scale traffic management. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4188–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wan, W.; Hwang, J.-N.; Muhammad, R.; Yang, M.; Han, K. Human tracking over camera networks: A review. Eurasip J. Adv. Signal Process. 2017, 1, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Ullah, I.; Wan, W.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Z. Real-Time vehicle make and model recognition with the residual squeezenet architecture. Sensors 2019, 19, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.; Emami, H.; Sangar, A.B. A new comparison framework to survey neural networks-based vehicle detection and classification approaches. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2021, 34, e4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X. Vehicle color recognition using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science (AICS 2019), Wuhan, China, 12–13 July 2019; pp. 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, U.; Saeed, M.; Rahim, R.U.; Khan, M.G.; Zulfiqar, A.; Bhatti, M.T. Development of ANPR Framework for Pakistani Vehicle Number Plates Using Object Detection and OCR. Complexity 2021, 2021, 5597337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantha Kumar, S.; Vykunth, P.; Jayanthi, D. Real-time smart vehicle surveillance system. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.12289. [Google Scholar]
- Nafzi, M.; Brauckmann, M.; Glasmachers, T. Vehicle Shape and Color Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.08612. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xue, Q.; Cui, T.; Li, Y.; Zeng, H. Cold start problem of vehicle model recognition under cross-scenario based on transfer learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 63, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Rozario, L.J.; Islam, E. Vision-based On-Road Nighttime Vehicle Detection and Tracking Using Taillight and Headlight Features. J. Comput. Commun. 2021, 9, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Huttunen, H. Vehicle Attribute Recognition by Appearance: Computer Vision Methods for Vehicle Type, Make and Model Classification. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2021, 93, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, S.; Aboutabit, N. Transfer Learning for classifying front and rear views of vehicles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1743, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhou, S.; Bi, X. Multi-Modal Vehicle Trajectory Prediction by Collaborative Learning of Lane Orientation, Vehicle Interaction, and Intention. Sensors 2022, 22, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yao, R.; Rezatofighi, S.H.; Reid, I.; Shi, Q. Multi-Object Model-Free Tracking with Joint Appearance and Motion Inference. In Proceedings of the DICTA 2017—2017 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 29 November–1 December 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.U.M.; Ullah, A.; Muhammad, K.; Haq, I.U.; Baik, S.W. Violence detection using spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional neural network. Sensors 2019, 19, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Cho, Y.; Kim, D.; Chang, M. Moving object detection from moving camera image sequences using an inertial measurement unit sensor. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetsier, C.; Fiosina, J.; Gremmel, J.N.; Müller, J.P.; Woisetschläger, D.M.; Sester, M. Detection of anomalous vehicle trajectories using federated learning. ISPRS Open J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 4, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramshahi, P.; Shenoy, V.; Pack, M.; Chellappa, R. Scalable and Real-time Multi-Camera Vehicle Detection, Re-Identification, and Tracking. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.07442. [Google Scholar]
- Subhalakhsmi, K.; Soundharam, V.S. Automatic License Plate Recognition System Based on Color Features and Vehicle Tracking. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 3483, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhuo, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Vehicle Color Recognition with Vehicle-Color Saliency Detection and Dual-Orientational Dimensionality Reduction of CNN Deep Features. Sens. Imaging 2017, 18, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, A.; Masood, S.Z.; Shu, G.; Ortiz, E.G. View Independent Vehicle Make, Model and Color Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.01721. [Google Scholar]
- Biglari, M.; Soleimani, A.; Hassanpour, H. Vehicle Make and Model Recognition using Auto Extracted Parts. In Proceedings of the Itscongress2017: The 2nd International ITS Congress 2017, Teheran, Iran, 7–8 February 2017; pp. 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Boonsim, N.; Prakoonwit, S. Car make and model recognition under limited lighting conditions at night. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2017, 20, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Han, L.; Li, L.; Pan, X. A vehicle re-identification framework based on the improved multi-branch feature fusion network. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Zhang, Y. Fine-grained vehicle type detection and recognition based on dense attention network. Neurocomputing 2020, 399, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolovaite, D.; Krisciunas, A.; Lagzdinyte-Budnike, I.; Budnikas, A.; Rentelis, D. Vehicle Make Detection Using the Transfer Learning Approach. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2022, 28, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NKhani, N.; Rezaeian, M. Three-stream Very Deep Neural Network for Video Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, IPRIA 2019, Teheran, Iran, 6–7 March 2019; pp. 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, T.A.M.; Jose, V.I.M. Three stream network model for lung cancer classification in the CT images. Open Comput. Sci. 2021, 11, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, I.O.; Laroca, R.; Menotti, D.; Fonseca, K.V.O.; Minetto, R. Vehicle-Rear: A New Dataset to Explore Feature Fusion for Vehicle Identification Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 101065–101077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakria; Cai, J.; Deng, J.; Aftab, M.U.; Khokhar, M.S.; Kumar, R. Efficient and deep vehicle re-identification using multi-level feature extraction. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Y. Hierarchical Scheme for Vehicle Make and Model Recognition. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2675, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Precision | Recall | F Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 97.20% | 95.09% | 96.10% | 98.70% |
| Precision | Recall | F Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 89.40% | 89.97% | 90.00% | 89.40% |
| Methods | Precision | Recall | F Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MatchNet [5] | 98.42% | 94.50% | 87.10% | 90.70% |
| LENETS [37] | 97.80% | 89.60% | 85.20% | 87.30% |
| MICRO [27] | 97.40% | 88.80% | 81.80% | 85.10% |
| VAMI [31] | 98.40% | 91.30% | 90.60% | 92.60% |
| TSDCNN (Ours) | 98.20% | 97.20% | 95.09% | 96.10% |
| Methods | Precision | Recall | F Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance+Color+Model [19] | 87.70% | 61.11% | 89.27% | 90.76% |
| FACT+Plate-SNN+STR [37] | 58.21% | 59.47% | 61.44% | 62.61% |
| Combining Network [27] | 77.40% | 60.19% | 60.54% | 60.60% |
| CNN-FT+CBL-8FT [38] | 78.55% | 62.62% | 61.83% | 60.83% |
| TSDCNN (Ours) | 89.40% | 90.30% | 89.97% | 90.00% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalake, L.; Wan, W.; Dong, Y. Applying Ternion Stream DCNN for Real-Time Vehicle Re-Identification and Tracking across Multiple Non-Overlapping Cameras. Sensors 2022, 22, 9274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239274
Kalake L, Wan W, Dong Y. Applying Ternion Stream DCNN for Real-Time Vehicle Re-Identification and Tracking across Multiple Non-Overlapping Cameras. Sensors. 2022; 22(23):9274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239274
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalake, Lesole, Wanggen Wan, and Yanqiu Dong. 2022. "Applying Ternion Stream DCNN for Real-Time Vehicle Re-Identification and Tracking across Multiple Non-Overlapping Cameras" Sensors 22, no. 23: 9274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239274
APA StyleKalake, L., Wan, W., & Dong, Y. (2022). Applying Ternion Stream DCNN for Real-Time Vehicle Re-Identification and Tracking across Multiple Non-Overlapping Cameras. Sensors, 22(23), 9274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239274





