CPMF-Net: Multi-Feature Network Based on Collaborative Patches for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- A multi-feature segmentation network is proposed for retinal vessel segmentation. The two-level sub-networks complete the pre-segmentation and main-segmentation tasks, respectively. The pre-extraction of basic information of blood vessels in pre-segmentation and the cooperation of multiple information features in main-segmentation provide a lot of effective information for blood vessel segmentation, which improves the segmentation accuracy of the network, especially in the face of difficult blood vessels.
- 2.
- A collaborative patch training strategy is designed to reduce the information loss in the patch-based method. On the basis of patches, the segmentation method combining one small patch with simple vessel structure and five large patches with global information not only effectively retains the advantages of patch-based method but also effectively reduces the information loss caused by patch extraction.
- 3.
- An adaptive coordinate attention module is designed to extract the direction information of blood vessels. This module provides the model with very helpful vessel orientation information for vessel structure segmentation and improves the vessel continuity in the model segmentation results.
- 4.
- A gated self-attention module suitable for retinal image segmentation task is designed. The self-attention module integrated into the main-segmentation network can alleviate the local dependence of convolution operation and help the network to obtain long-distance dependence.
2. Related Work
2.1. Network Structure for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
2.2. Training Method of the Model
3. Methods
3.1. Multi-Feature Segmentation Network
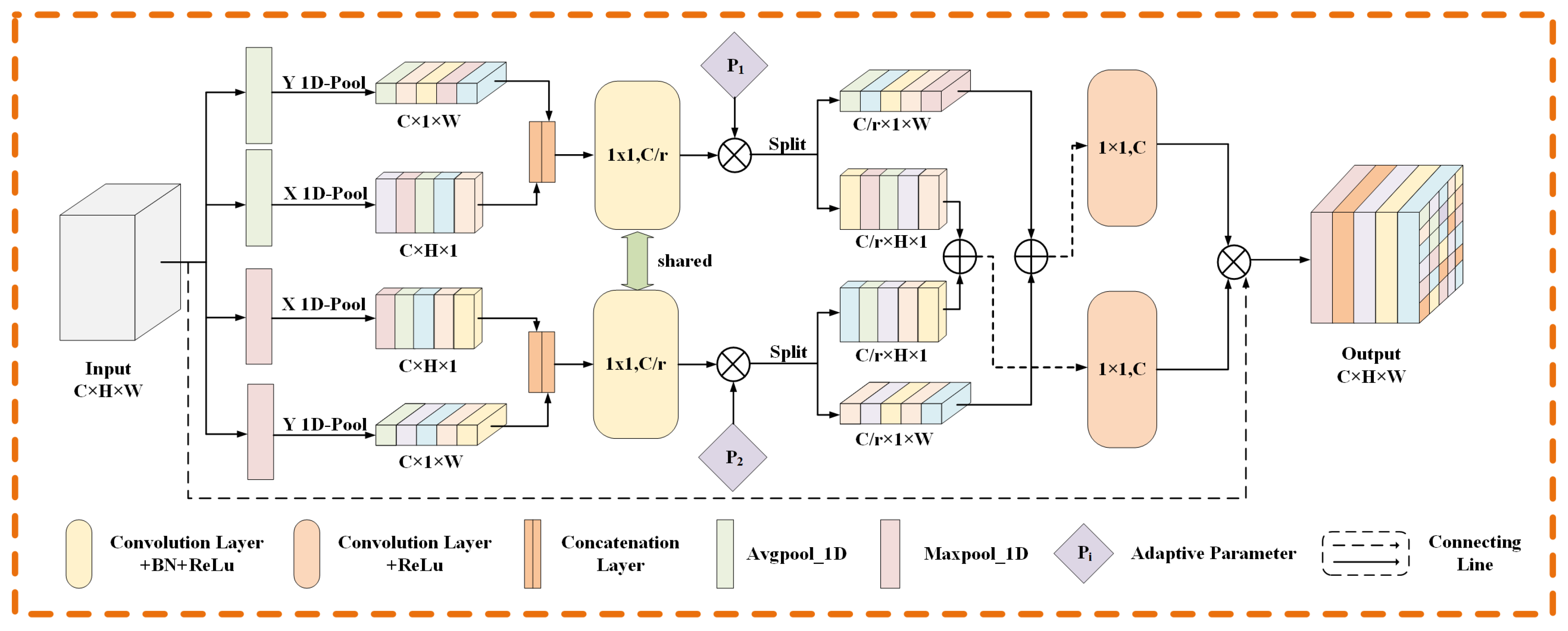
3.2. Adaptive Coordinate Attention Module
3.3. Gated Self-Attention Module
3.4. Collaborative Patch Training Strategy
3.4.1. Patch Collaborative Extraction
3.4.2. Associated Information Transmission
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
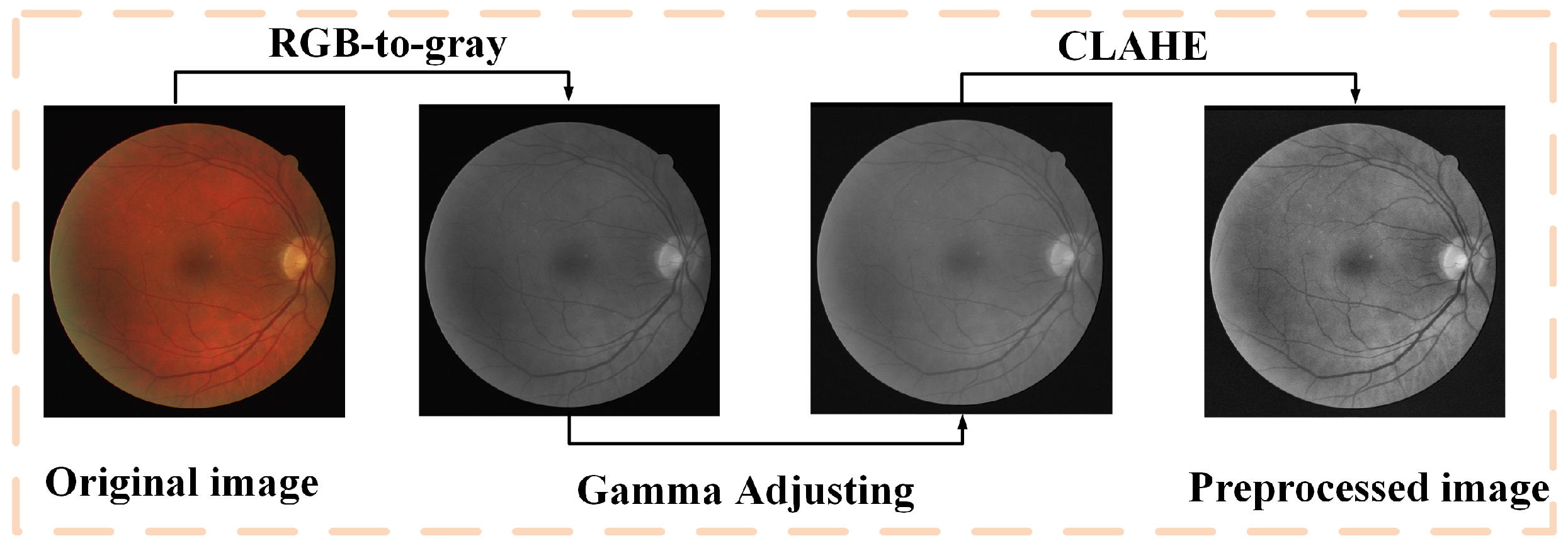
4.2. Pre-Processing
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Experimental Settings
5. Results
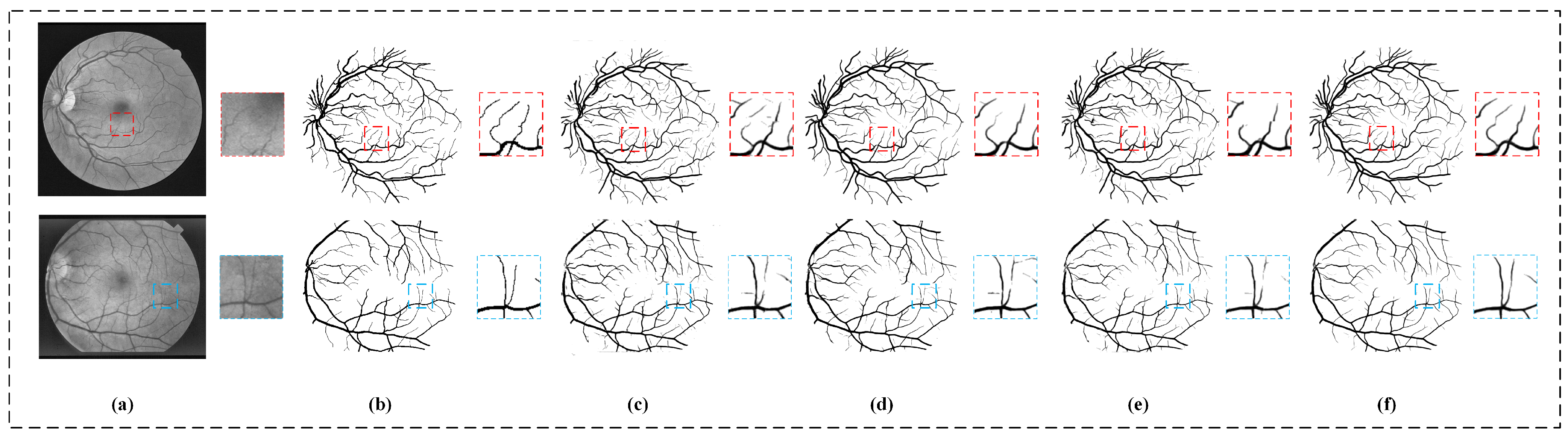
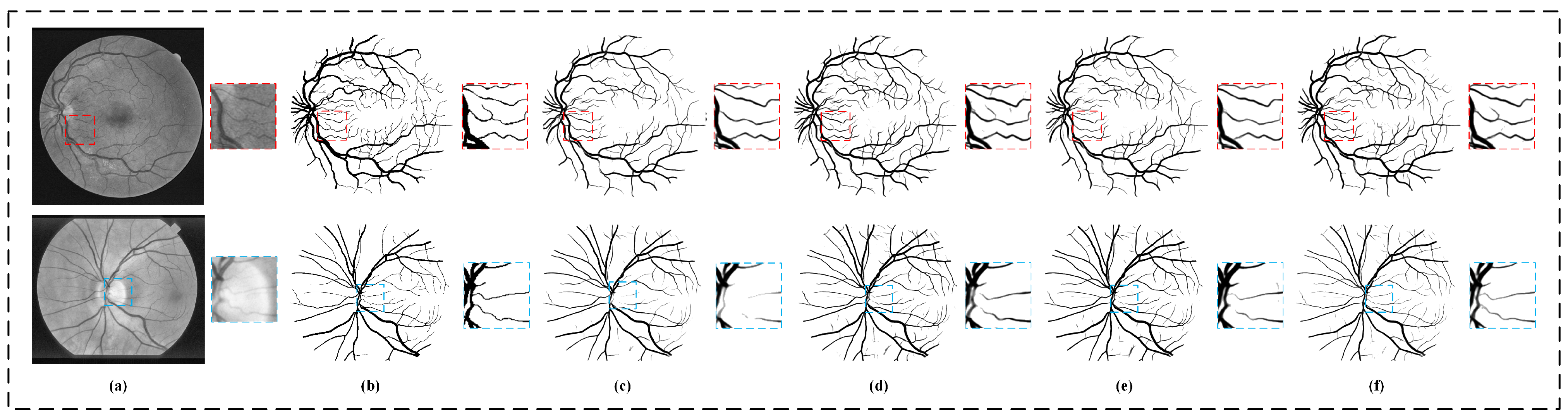
5.1. Experiment of Training Strategy
5.2. Experiment of Segmentation Model
5.2.1. Experiment of Adaptive Coordinate Attention Module
5.2.2. Experiment of Gated Self-Attention Module
5.2.3. Ablation Experiment
5.3. Comparison with the State-of-the-Art Methods
| Model | Year | DRIVE | STARE | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (%) | SE (%) | SP (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | F1 (%) | SE (%) | SP (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | ||
| U-Net [8] | 2015 | 81.36 | 77.92 | 98.12 | 95.61 | 97.66 | 83.27 | 82.95 | 98.15 | 96.60 | 98.76 |
| R2U-Net [24] | 2018 | 78.07 | 83.05 | 95.86 | 94.27 | 95.95 | 77.58 | 79.62 | 97.08 | 95.30 | 97.17 |
| CE-Net [25] | 2019 | 78.64 | 77.78 | 97.21 | 94.80 | 97.11 | 82.74 | 84.04 | 97.83 | 96.42 | 98.68 |
| Xu et al. [26] | 2020 | 82.52 | 79.53 | 98.07 | 95.57 | 98.04 | 83.08 | 83.78 | 97.41 | 95.90 | 98.17 |
| Zhou et al. [27] | 2020 | 80.35 | 74.73 | 98.35 | 95.35 | 97.13 | 81.32 | 77.76 | 98.32 | 96.05 | 97.40 |
| Li et al. [28] | 2021 | - | 79.21 | 98.10 | 95.68 | 98.06 | - | 83.52 | 98.23 | 96.78 | 98.75 |
| CSU-Net [29] | 2021 | 82.51 | 80.71 | 98.01 | 95.65 | 98.01 | 85.16 | 84.32 | 98.45 | 97.02 | 98.25 |
| Bridge-Net [30] | 2022 | 82.03 | 78.53 | 98.18 | 95.65 | 98.34 | 82.89 | 80.02 | 98.64 | 96.68 | 99.01 |
| Li et al. [31] | 2022 | 82.88 | 83.59 | 97.31 | 95.71 | 98.10 | 83.63 | 83.52 | 98.23 | 96.71 | 98.75 |
| CPMF-Net(ours) | 2022 | 82.94 | 83.54 | 97.53 | 95.78 | 98.19 | 85.66 | 86.81 | 98.20 | 97.03 | 99.16 |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cui, L.; Zhang, J. Molecular guidance cues in the development of visual pathway. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 909–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipli, K.; Hoque, M.E.; Lim, L.T.; Mahmood, M.H.; Sahari, S.K.; Sapawi, R.; Rajaee, N.; Joseph, A. A review on the extraction of quantitative retinal microvascular image feature. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2018, 2018, 4019538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.Y.L.; Zheng, Y.; Hsu, W.; Lee, M.L.; Lau, Q.P.; Mitchell, P.; Wang, J.J.; Klein, R.; Wong, T.Y. Retinal vascular tortuosity, blood pressure, and cardiovascular risk factors. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liang, J.; Cheng, T.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J. MTPA_Unet: Multi-scale transformer-position attention retinal vessel segmentation network joint transformer and CNN. Sensors 2022, 22, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. HT-Net: A hybrid transformer network for fundus vessel segmentation. Sensors 2022, 22, 6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yao, H.; Tao, S.; Liang, J. Gated skip-connection network with adaptive upsampling for retinal vessel segmentation. Sensors 2021, 21, 6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention MICCAI 2015—18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Xu, Y.; Lin, S.; Kee Wong, D.W.; Liu, J. DeepVessel: Retinal vessel segmentation via deep learning and conditional random field. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2016—19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; pp. 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, L. Multi-level deep supervised networks for retinal vessel segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Yi, Y. Channel attention residual U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP 2021, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–12 June 2021; pp. 1185–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Liskowski, P.; Krawiec, K. Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2016, 35, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W. Multiscale network followed network model for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2018—21st International Conference, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; pp. 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W. NFN+: A novel network followed network for retinal vessel segmentation. Neural Netw. 2020, 126, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2021, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2021, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Gu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Dai, J.; Wei, Y. Relation networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3588–3597. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Lin, S. Local relation networks for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3464–3473. [Google Scholar]
- Staal, J.; Abràmoff, M.D.; Niemeijer, M.; Viergever, M.A.; van Ginneken, B. Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2004, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, A.D.; Kouznetsova, V.; Goldbaum, M. Locating blood vessels in retinal images by piecewise threshold probing of a matched filter response. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2000, 19, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gegúndez-Arias, M.E.; Aquino, A.; Bravo, J.M.; Marín, D. A function for quality evaluation of retinal vessel segmentations. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2012, 31, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraz, M.M.; Remagnino, P.; Hoppe, A.; Uyyanonvara, B.; Rudnicka, A.R.; Owen, C.G.; Barman, S.A. Blood vessel segmentation methodologies in retinal images—A survey. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2012, 108, 407–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Feng, B.; Xie, L.; Liang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T. A cross-modality learning approach for vessel segmentation in retinal images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 35, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Yakopcic, C.; Hasan, M.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. J. Med. Imag. 2019, 6, 014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, J. Ce-Net: Context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ye, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Tanaka, S. Retinal vessel segmentation via a semantics and multi-Scale aggregation network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP 2020, Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 1085–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2020, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Yin, S. Lightweight attention convolutional neural network for retinal vessel image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2021, 17, 1958–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Qiu, S.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; He, H. CSU-Net: A context spatial U-Net for accurate blood vessel segmentation in fundus images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health. Inf. 2021, 25, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, M.; Chen, Z.; Hu, K.; Li, X.; Gao, X. Bridge-Net: Context-involved U-net with patch-based loss weight mapping for retinal blood vessel segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 195, 116526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, W.; Lei, B.; Kuang, X.; Zhang, T. Dual encoder-based dynamic-channel graph convolutional network with edge enhancement for retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2022, 41, 1975–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, K. Joint segment-level and pixel-wise losses for deep learning based retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Dataset | DRIVE | STARE |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Images | 40 | 20 |
| Original Size | 584 × 565 | 700 × 605 |
| Patch Size | 72 × 72 | 72 × 72 |
| Tran/Test Split | 20/20 | 16/4 |
| Model | DRIVE | STARE | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (%) | SE (%) | SP (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | F1 (%) | SE (%) | SP (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | |
| U-Net | 81.36 | 77.92 | 98.12 | 95.61 | 97.66 | 83.27 | 82.95 | 98.15 | 96.60 | 98.76 |
| CPU-Net | 82.55 | 82.77 | 97.54 | 95.70 | 98.07 | 84.67 | 86.21 | 98.02 | 96.81 | 98.94 |
| MF-Net | 82.10 | 82.19 | 97.50 | 95.59 | 97.84 | 83.64 | 80.77 | 98.60 | 96.78 | 98.84 |
| CPMF-Net | 82.94 | 83.45 | 97.53 | 95.78 | 98.19 | 85.66 | 86.81 | 98.20 | 97.03 | 99.16 |
| Model | Flops | Memory |
|---|---|---|
| MF-Net | 2.04 G | 38.43 M |
| CPMF-Net | 2.05 G | 41.25 M |
| WMF-Net | 141.51 G | 2651 M |
| Model | DRIVE | STARE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | F1 (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | |
| Basenet | 82.03 | 95.74 | 98.06 | 84.84 | 97.01 | 99.13 |
| SE | 82.49 | 95.60 | 98.11 | 84.95 | 96.72 | 99.12 |
| CA | 82.46 | 95.62 | 98.14 | 84.66 | 96.59 | 99.15 |
| ACA | 82.82 | 95.67 | 98.18 | 85.14 | 97.07 | 99.15 |
| Model | DRIVE | STARE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | F1 (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | |
| Basenet | 82.03 | 95.74 | 98.06 | 84.84 | 97.01 | 99.13 |
| SW | 81.54 | 95.73 | 98.11 | 84.86 | 96.97 | 99.07 |
| GSA | 82.04 | 95.75 | 98.15 | 85.27 | 97.15 | 99.14 |
| Model | DRIVE | STARE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | F1 (%) | ACC (%) | AUC (%) | |
| Basenet | 82.03 | 95.74 | 98.06 | 84.84 | 97.01 | 99.13 |
| Basenet + GSA | 82.04 | 95.75 | 98.15 | 85.27 | 97.15 | 99.14 |
| Basenet + ACA | 82.82 | 95.67 | 98.18 | 85.14 | 97.07 | 99.15 |
| Basenet + GSA + ACA | 82.94 | 95.78 | 98.19 | 85.66 | 97.03 | 99.16 |
| Test Set | Training Set | Model | SE | SP | ACC | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STARE | DRIVE | Fraz [22] | 72.42 | 97.92 | 94.56 | 96.97 |
| Li [23] | 72.73 | 98.10 | 94.86 | 96.77 | ||
| Yan [32] | 72.92 | 98.15 | 94.94 | 95.99 | ||
| CPMF-Net(ours) | 75.93 | 98.15 | 95.39 | 97.53 | ||
| DRIVE | STARE | Fraz [22] | 70.10 | 97.70 | 94.95 | 96.71 |
| Li [23] | 70.27 | 98.28 | 95.45 | 96.71 | ||
| Yan [32] | 72.11 | 98.40 | 95.69 | 97.08 | ||
| CPMF-Net(ours) | 80.24 | 98.12 | 96.04 | 98.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, W.; Deng, H.; Yin, S. CPMF-Net: Multi-Feature Network Based on Collaborative Patches for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Sensors 2022, 22, 9210. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239210
Tang W, Deng H, Yin S. CPMF-Net: Multi-Feature Network Based on Collaborative Patches for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Sensors. 2022; 22(23):9210. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239210
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Wentao, Hongmin Deng, and Shuangcai Yin. 2022. "CPMF-Net: Multi-Feature Network Based on Collaborative Patches for Retinal Vessel Segmentation" Sensors 22, no. 23: 9210. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239210
APA StyleTang, W., Deng, H., & Yin, S. (2022). CPMF-Net: Multi-Feature Network Based on Collaborative Patches for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Sensors, 22(23), 9210. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239210




