Sensing Trace-Level Metal Elements in Water Using Chirped Femtosecond Laser Pulses in the Filamentation Regime
Abstract
1. Introduction
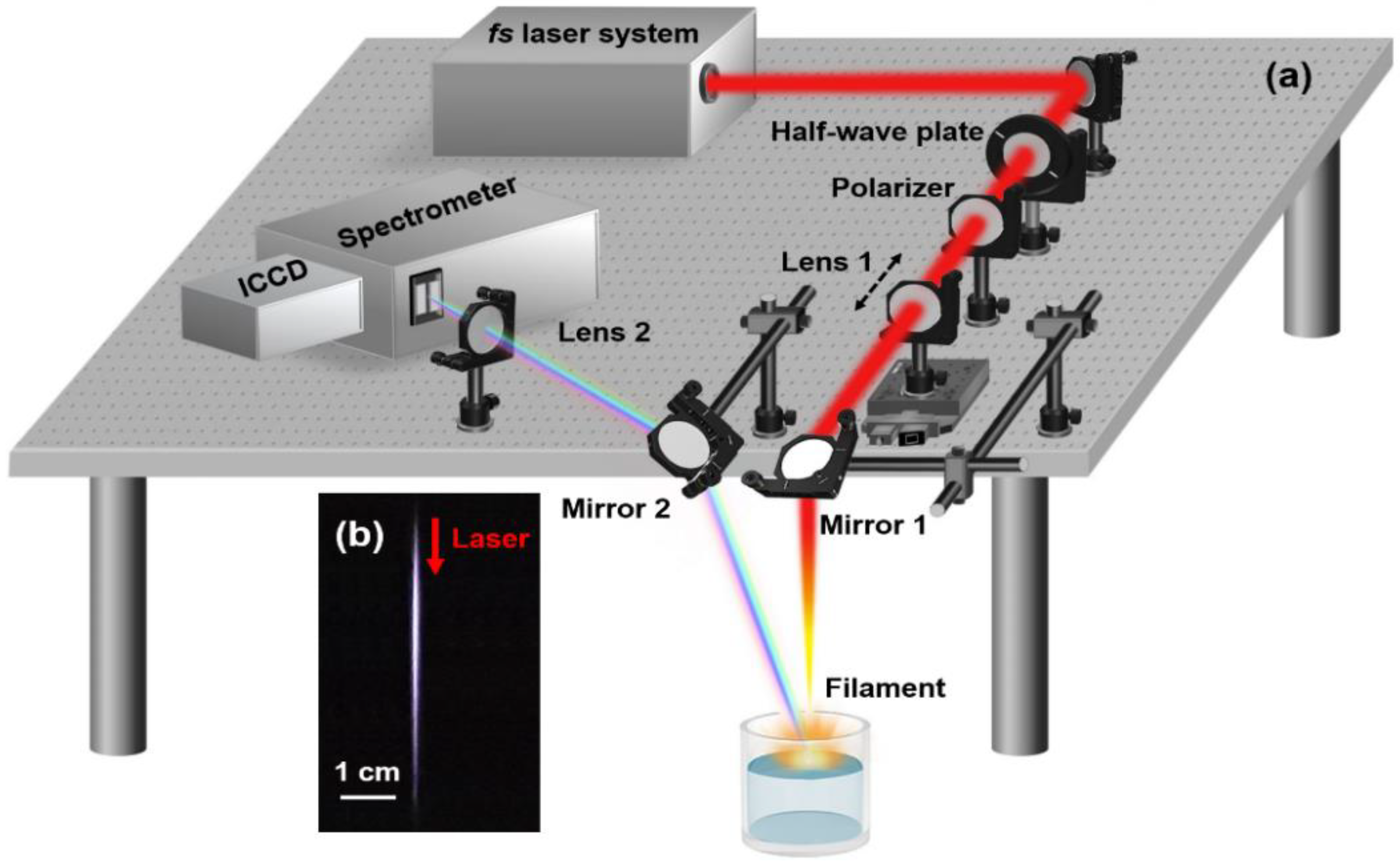
2. Experimental Setup
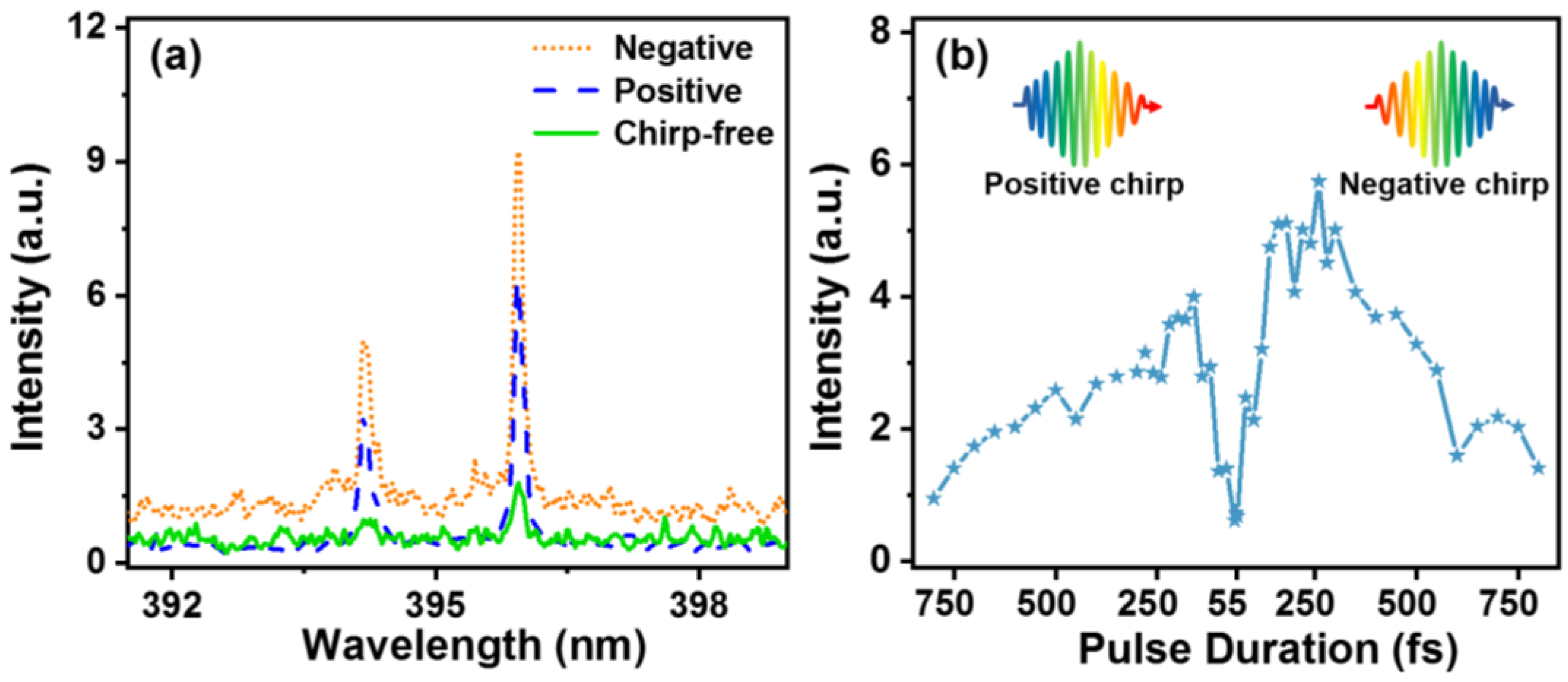
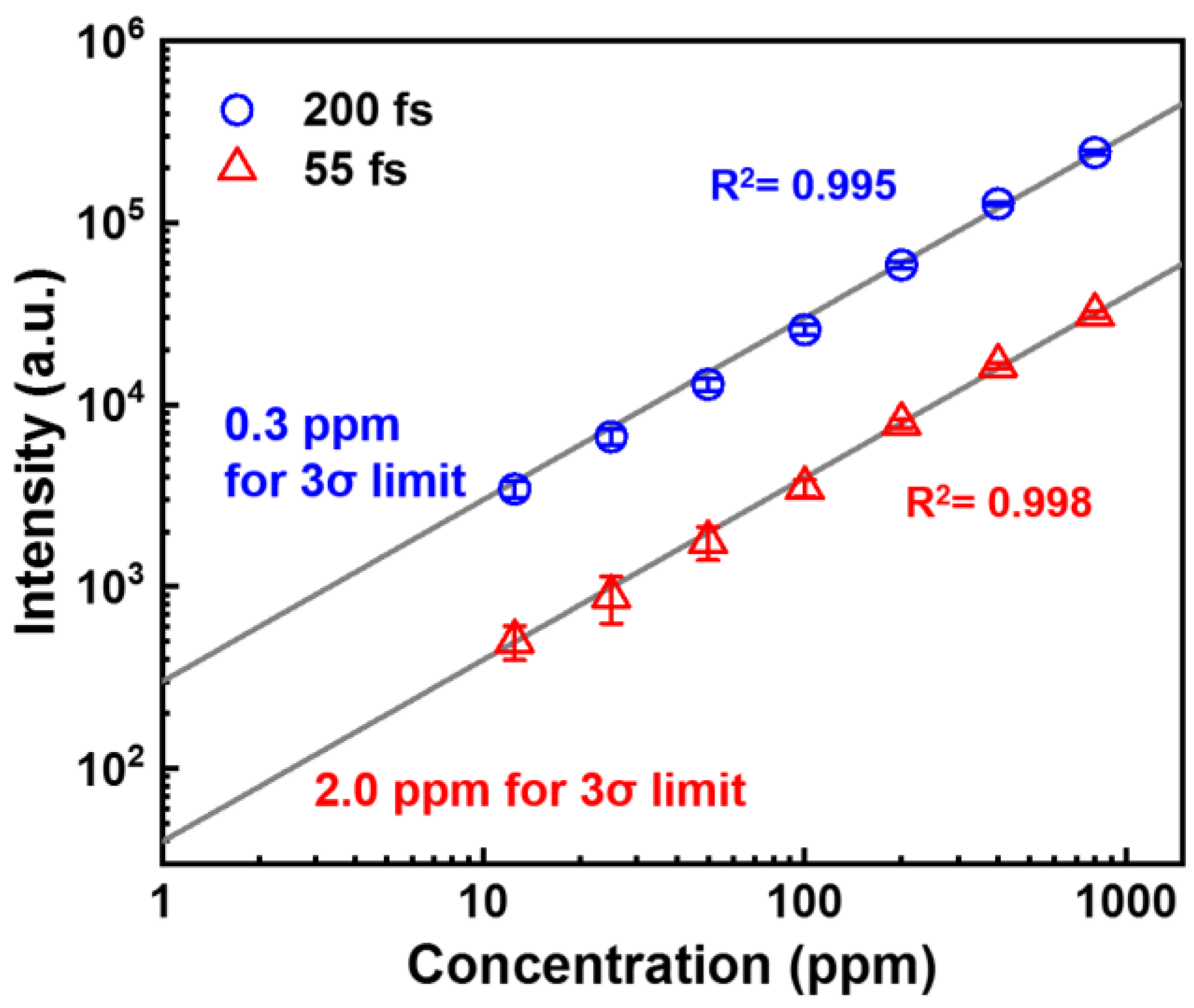
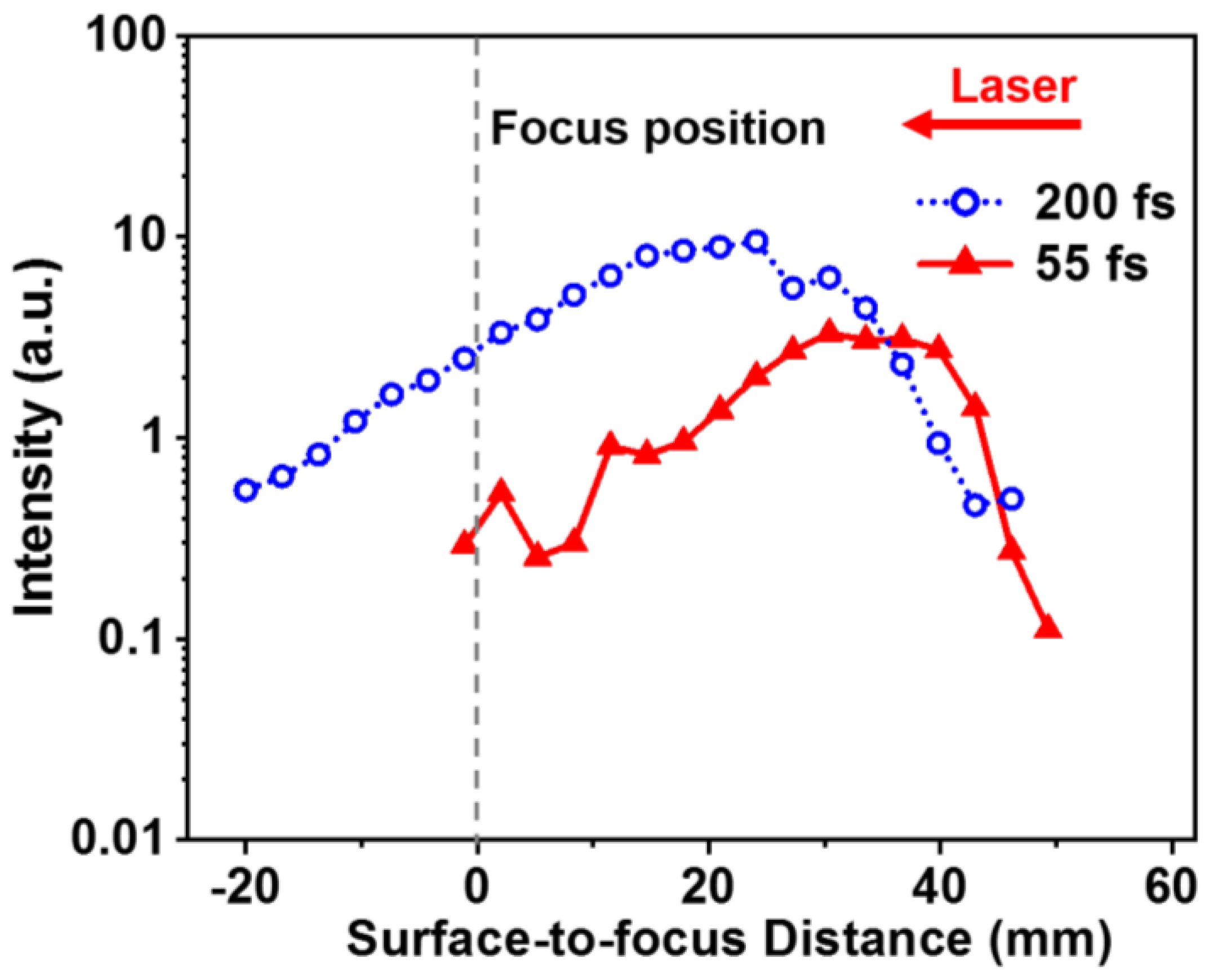
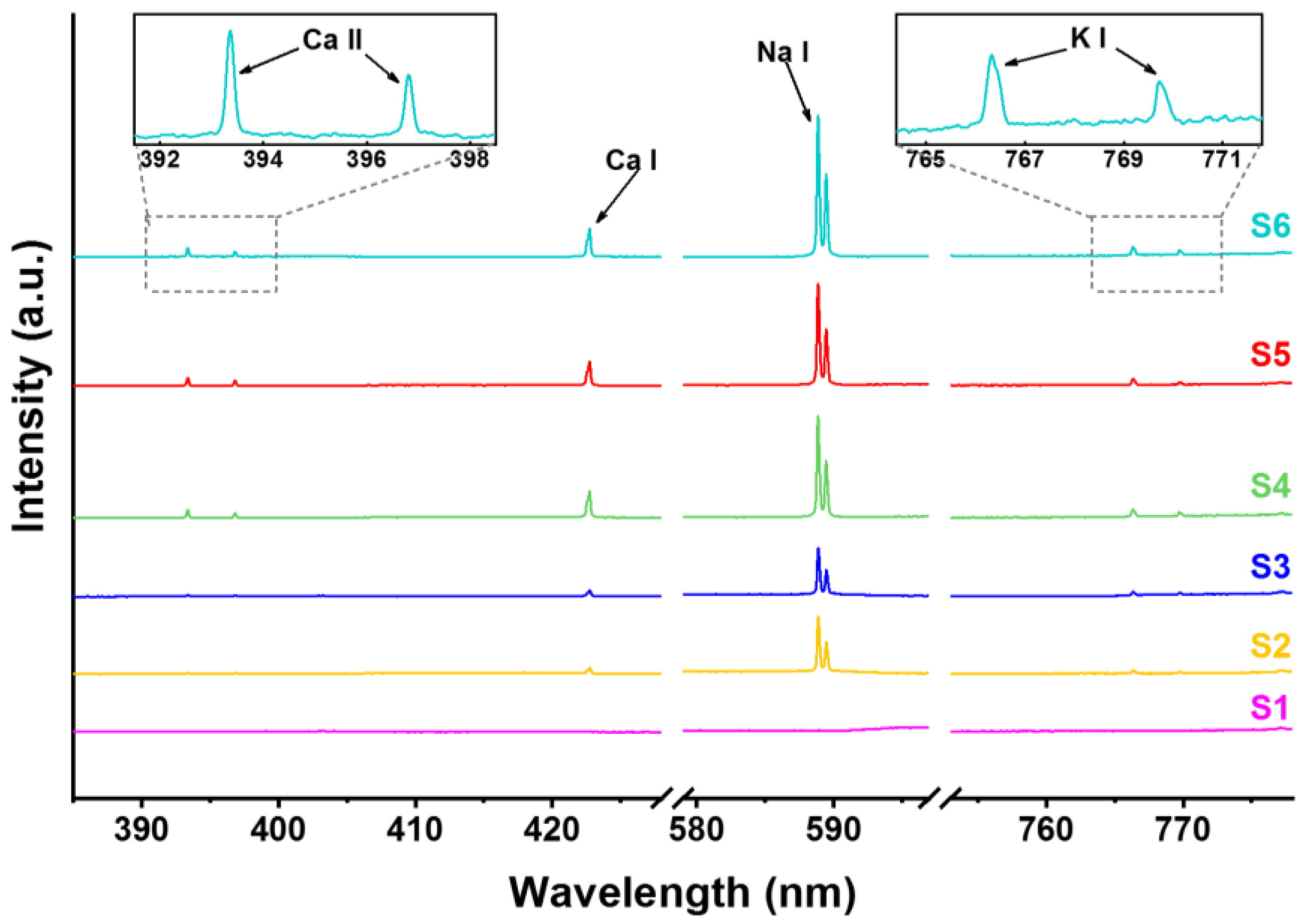
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciucci, A.; Corsi, M.; Palleschi, V.; Rastelli, S.; Salvetti, A.; Tognoni, E. New procedure for quantitative elemental analysis by laser-induced plasma spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 1999, 53, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Andrade, D.; Pereira-Filho, E.R.; Amarasiriwardena, D. Current trends in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: A tutorial review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2021, 56, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantzi, S.C.; Motto-Ros, V.; Trichard, F.; Markushin, Y.; Melikechi, N.; De Giacomo, A. Sample treatment and preparation for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2016, 115, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, V.; Jovićević, S. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy inside liquids: Processes and analytical aspects. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2014, 101, 288–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, C.; Cortez, J.; Silva, L.; Gonzaga, F.B. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 463–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, H.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Li, Z.; Ni, W. Quantitative carbon analysis in coal by combining data processing and spatial confinement in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2015, 111, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; Delgado, T.; Cabalín, L.; Laserna, J. At-line monitoring of continuous casting sequences of steel using discriminant function analysis and dual-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.V.; Hubinger, S.Z.; Neto, J.A.G.; Milori, D.M.B.P.; Ferreira, E.J.; Ferreira, E.C. Potential of Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for analyzing the quality of unroasted and ground coffee. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2017, 135, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Zhou, F.; Peng, J.; Sun, M. Fast classification of geographical origins of honey based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, J.; Tröger, J.; Li, Z.; Aldén, M. Laser-induced plasma in methane and dimethyl ether for flame ignition and combustion diagnostics. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2011, 103, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Yao, D.; Wang, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Xu, H. In situ determination of the equivalence ratio in a methane/air flow field by femtosecond filament excitation. Laser Phys. 2020, 30, 035402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J.; Novotný, K.; Martin, M.Z.; Hrdlička, A.; Malina, R.; Hartl, M.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. Trace elemental analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy—Biological applications. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2012, 67, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehse, S.; Salimnia, H.; Miziolek, A. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS): An overview of recent progress and future potential for biomedical applications. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2012, 36, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Bao, J.; Yang, H.; Sun, L. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy application in environmental monitoring of water quality: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8969–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, H. Application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) in environmental monitoring. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2021, 181, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arca, G.; Ciucci, A.; Palleschi, V.; Rastelli, S.; Tognoni, E. Trace element analysis in water by the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technique. Appl. Spectrosc. 1997, 51, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi, K.; George, S.D.; Kulkarni, S.D.; Chidangil, S.; Unnikrishnan, V. Elemental analysis of liquid samples by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS): Challenges and potential experimental strategies. Opt. Laser. Technol. 2022, 147, 107622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Oh, S.-W.; Han, S.-H. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) of heavy metal ions at the sub-parts per million level in water. Appl. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zang, H.; Xu, H.; Sun, H.B.; Baltuška, A.; Polynkin, P. Robust Remote Sensing of Trace-Level Heavy-Metal Contaminants in Water Using Laser Filaments. Glob. Chall. 2019, 3, 1800070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergé, L.; Skupin, S.; Nuter, R.; Kasparian, J.; Wolf, J.-P. Ultrashort filaments of light in weakly ionized, optically transparent media. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2007, 70, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couairon, A.; Mysyrowicz, A. Femtosecond filamentation in transparent media. Phys. Rep. 2007, 441, 47–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-L.; Cheng, W.; Petrarca, M.; Polynkin, P. Measurements of fluence profiles in femtosecond laser filaments in air. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4751–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, S.; Hosseini, S.; Liu, W.; Luo, Q.; Théberge, F.; Aközbek, N.; Becker, A.; Kandidov, V.; Kosareva, O.; Schröder, H. The propagation of powerful femtosecond laser pulses in opticalmedia: Physics, applications, and new challenges. Can. J. Phys. 2005, 83, 863–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Chin, S.L.; Sun, H.B. Femtosecond laser ionization and fragmentation of molecules for environmental sensing. Laser Photonics Rev. 2015, 9, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Cao, J.; Yamanouchi, K.; Xu, H. Air-laser-based standoff coherent Raman spectrometer. Ultrafast Sci. 2022, 2022, 9867028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, S.; Yao, D.; Fu, Y.; Zang, H.; Xu, H.; Polynkin, P. Stand-off fabrication of irregularly shaped, multi-functional hydrophobic and antireflective metal surfaces using femtosecond laser filaments in air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Fu, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, H.; Li, R. Robust and ultralow-energy-threshold ignition of a lean mixture by an ultrashort-pulsed laser in the filamentation regime. Light-Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cong, X.; Chen, J.; Cao, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zang, H.; Li, H.; Xu, H. The key role of the semiconductor property of water in femtosecond laser-induced plasma spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2022, 195, 106499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.; Varma, S.; Hillenius, S. Liquid water as a lone-pair amorphous semiconductor. J. Chem. Phys. 1976, 64, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louzon, E.; Henis, Z.; Pecker, S.; Ehrlich, Y.; Fisher, D.; Fraenkel, M.; Zigler, A. Reduction of damage threshold in dielectric materials induced by negatively chirped laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 241903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
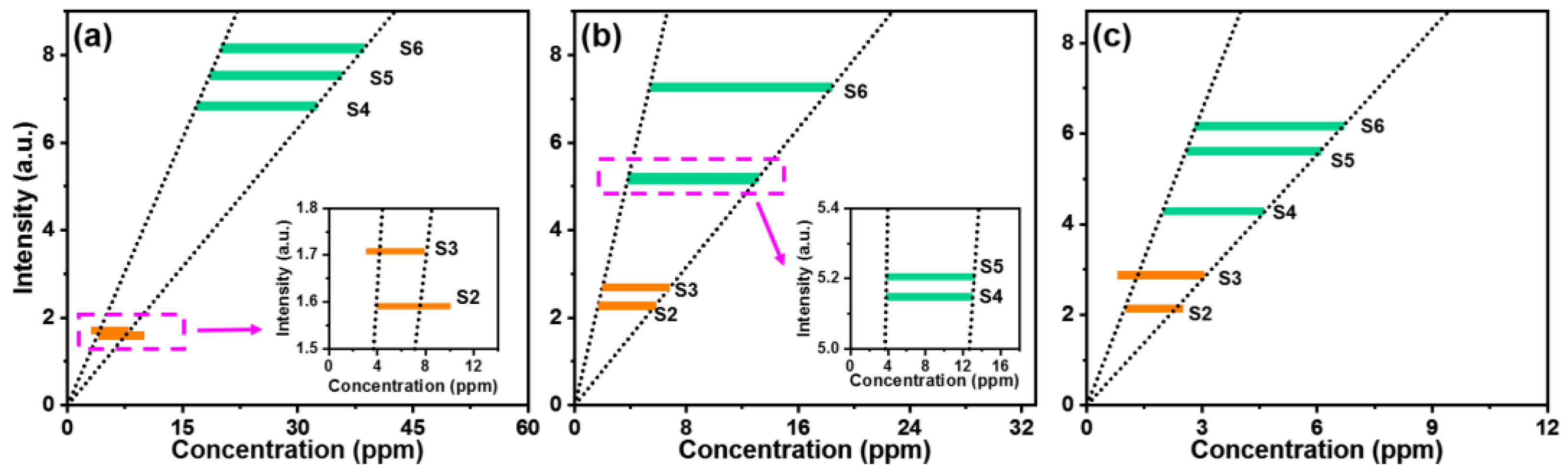
| Sample | Ca | Na | K |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrations given by the manufacturers | |||
| Nongfu Spring (S2) | 4.0~10.0 | 2.0~6.8 | 1.0~2.5 |
| Quanyangquan (S3) | 3.1~7.9 | 1.7~5.8 | 0.8~3.0 |
| Concentrations calculated by the FIBS technique | |||
| Tap water (S4) | 18.5~35.7 | 3.8~13.2 | 2.6~6.1 |
| Jingyuetan Park (S5) | 16.8~32.5 | 3.8~13.0 | 2.0~4.6 |
| Nanhu Park (S6) | 20.0~38.6 | 5.4~18.4 | 2.8~6.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Cong, X.; Chen, J.; Zang, H.; Li, H.; Xu, H. Sensing Trace-Level Metal Elements in Water Using Chirped Femtosecond Laser Pulses in the Filamentation Regime. Sensors 2022, 22, 8775. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228775
Chen S, Cong X, Chen J, Zang H, Li H, Xu H. Sensing Trace-Level Metal Elements in Water Using Chirped Femtosecond Laser Pulses in the Filamentation Regime. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8775. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228775
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shanming, Xun Cong, Junyan Chen, Hongwei Zang, Helong Li, and Huailiang Xu. 2022. "Sensing Trace-Level Metal Elements in Water Using Chirped Femtosecond Laser Pulses in the Filamentation Regime" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8775. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228775
APA StyleChen, S., Cong, X., Chen, J., Zang, H., Li, H., & Xu, H. (2022). Sensing Trace-Level Metal Elements in Water Using Chirped Femtosecond Laser Pulses in the Filamentation Regime. Sensors, 22(22), 8775. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228775







