Development of Real-Time Landmark-Based Emotion Recognition CNN for Masked Faces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a new GNN structure with landmark features as the input and output;
- FER with more detailed input landmark modalities is applied by adopting an FER model by media-pipe face mesh algorithm;
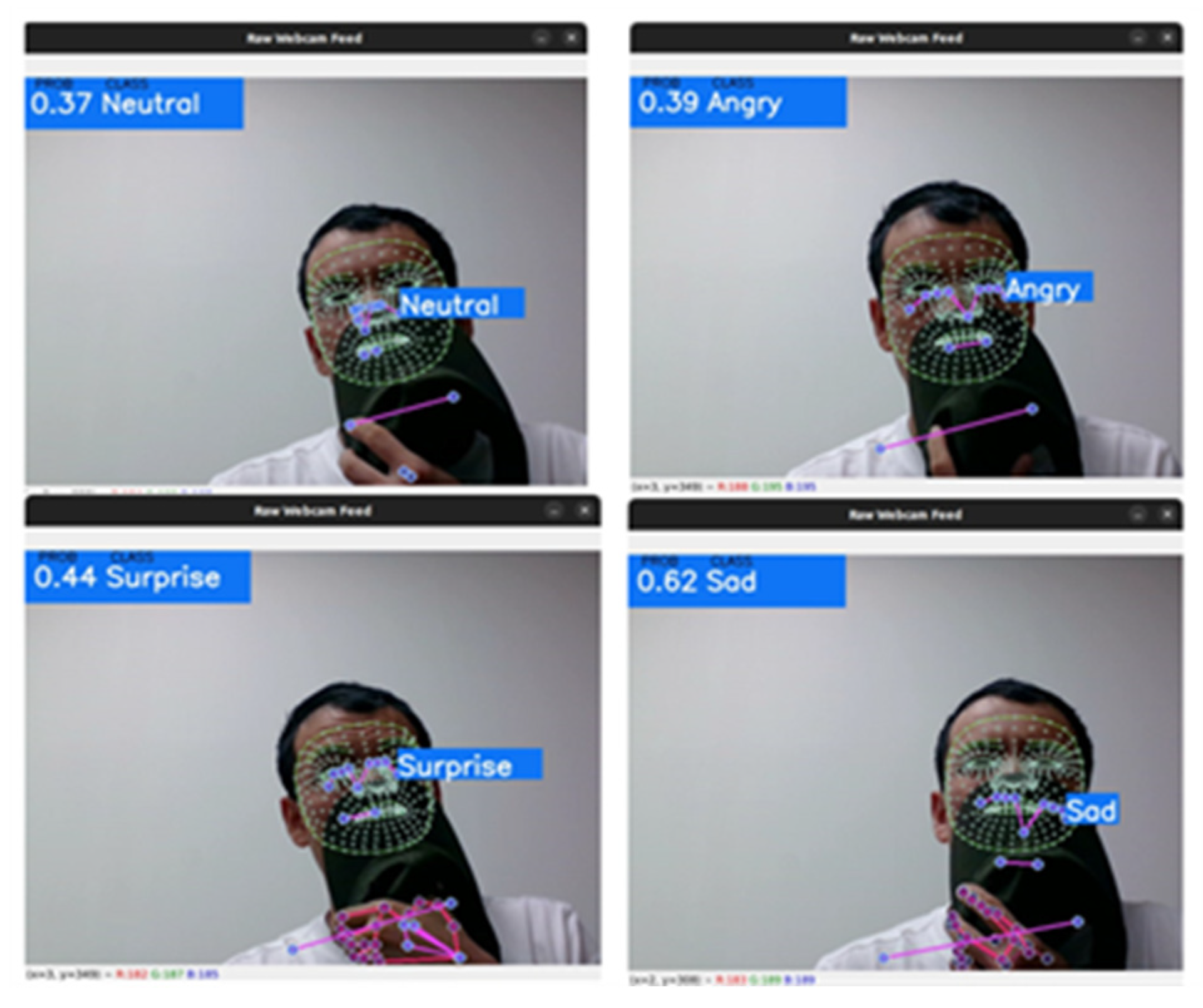
- Notably, this study proposes a two-fold contribution during expression recognition. That is, after the implementation of the face mesh algorithm on a masked face, the model detects facial expressions on either masked or non-masked faces.
2. Related Works
2.1. Face Landmark Detection
2.2. Classification of Facial Expressions
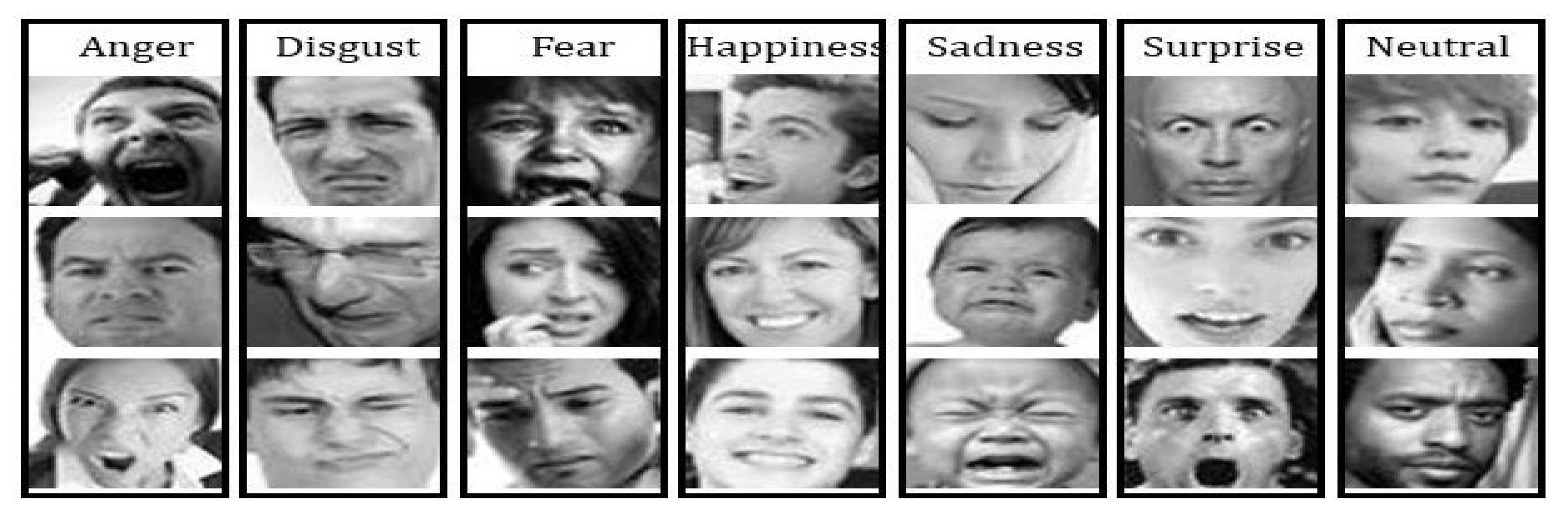
 | Happiness is a smiling expression that shows someone’s feeling of contentment or liking of something. A happy expression is classified as an upward movement of the cheek muscles and the sides or edges of the lips to form a smiling shape [7]. |
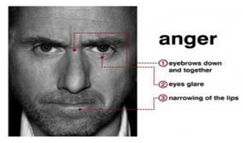 | Anger is an expression of aggression. The characteristics of anger are a merging downward leaning of the inner eyebrows. The eyes become close to the eyebrows, the lips join, and the sides of the cheek lean downward [7]. |
 | Disgust is an expression that shows a state of dissatisfaction with something or someone. An expression of disgust is classified when a person’s nose bridge between the eyebrows is wrinkled, and the lower lip goes down, showing the teeth [7]. |
 | Sadness is an expression that represents disappointment or a feeling of missing something. Sadness is classified based on a lost focus of eyes, joined lips with the corners of the lips moving slightly downward, and a relatively wide distance between the eyes and eyebrows [7]. |
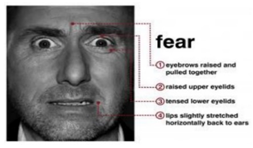 | Fear is an expression that shows someone’s scarcity or fear of someone or something. The expression of fear is seen when eyebrows slightly go up, eyelids tighten, and lips are open horizontally along the side of the cheek [7]. |
 | Contempt is an expression that shows no other expressions on the face, remaining neutral. Its characteristics are classified as a slight rise of one side of the lip corner [7]. |
 | Surprise is an expression showing one’s excitement for a certain act. Its characteristics include a shocked face representation, raised eyebrows, open eyes, and an open mouth on the vertical side [7]. |
2.3. Face Emotion Detection
2.4. Landmark-Based Emotion Recognition
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Haar–Cascade Classifier
3.2. Media-Pipe Model
3.3. Landmark Detection
3.4. Gaussian Processes
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Pre-Processing the Model
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
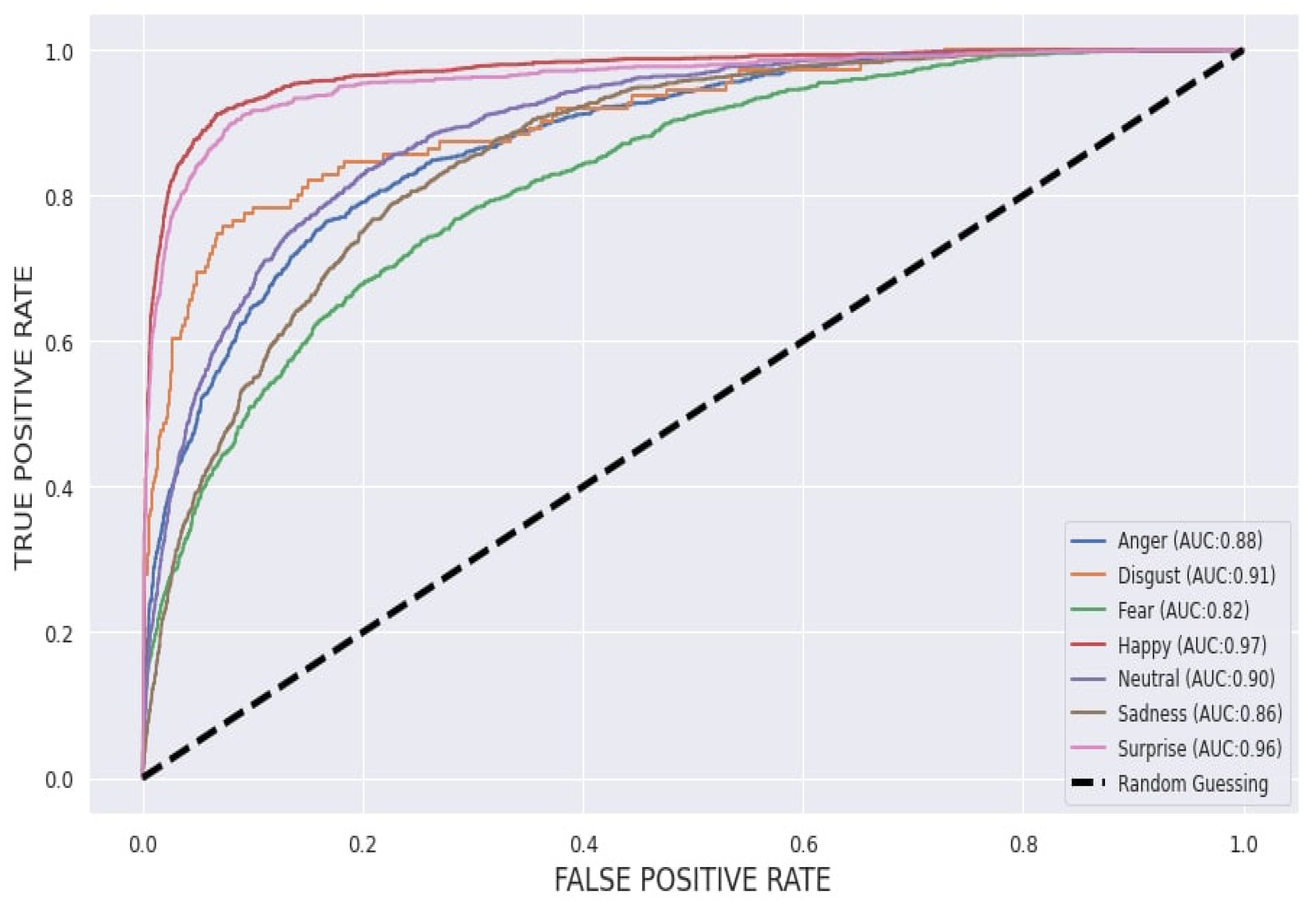
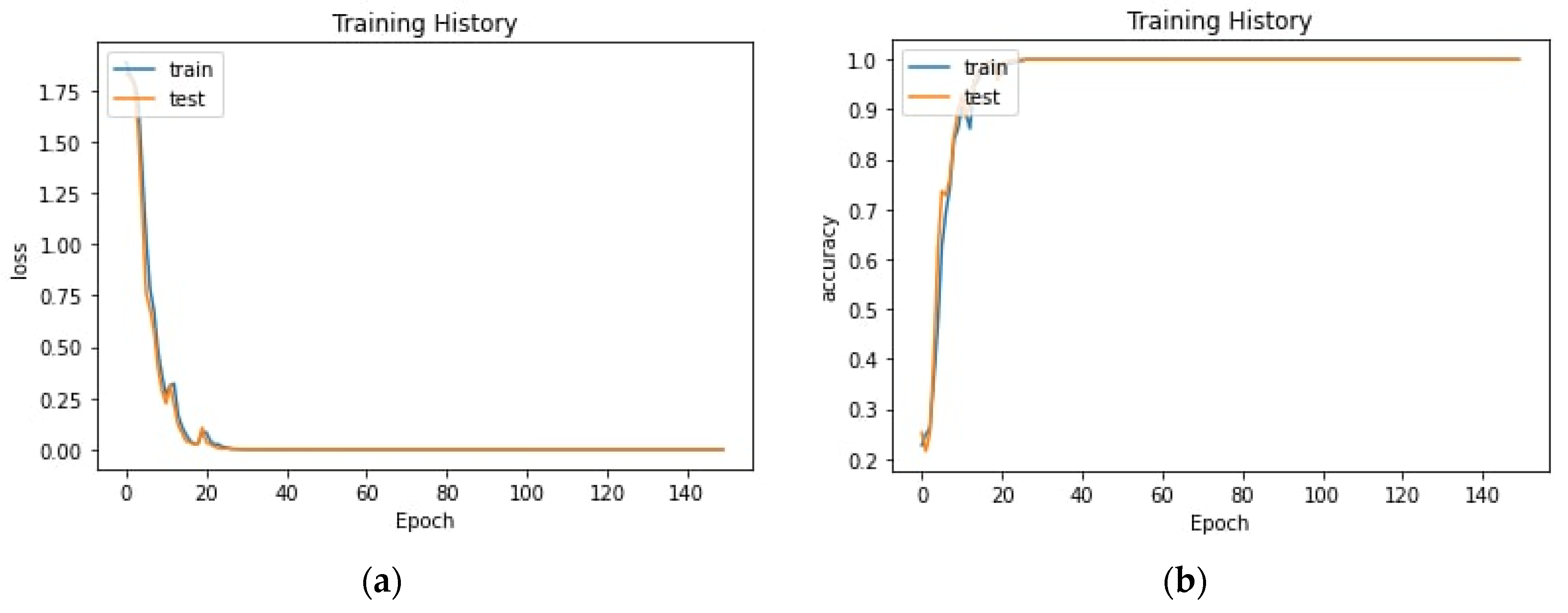
4.4. Proposed Model Performance
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Y.-I.; Kanade, T.; Cohn, J. Recognizing action units for facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, N.; Liang, R.; Shi, W. A lightweight convolutional neural network for real-time facial expression detection. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 5573–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarol, S.K.A.; Jaward, M.H.; Kälviäinen, H.; Parkkinen, J.; Parthiban, R. Joint facial expression recognition and intensity estimation based on weighted votes of image sequences. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 92, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chang, O.; Tang, X.-L.; Xue, C.; Wei, C. Facial Expression Recognition Method Based on Sparse Batch Normalization CNN. In Proceedings of the 2018 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Wuhan, China, 25–27 July 2018; pp. 9608–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Konar, A.; Chakraborty, U.K.; Chatterjee, A. Emotion Recognition From Facial Expressions and Its Control Using Fuzzy Logic. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.-Part A Syst. Humans 2009, 39, 726–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zheng, W.; Cui, Z.; Tang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zong, Y. Multi-cue fusion for emotion recognition in the wild. Neurocomputing 2018, 309, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Constants across cultures in the face and emotion. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1971, 17, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheon, Y.; Kim, D. Natural facial expression recognition using differential-AAM and manifold learning. Pattern Recognit. 2009, 42, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Pantic, M.; Roisman, G.I.; Huang, T.S. A Survey of Affect Recognition Methods: Audio, Visual, and Spontaneous Expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Ohyama, W.; Wakabayashi, T.; Kimura, F. Detection of eyes by circular Hough transform and histogram of gradient. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), Tsukuba Science City, Japan, 11–15 November 2012; pp. 1795–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Riopka, T.; Boult, T. The eyes have it. In Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGMM Workshop on Biometrics Methods and Applications (WBMA ‘03), Berkley, CA, USA, 8 November 2003; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristinacce, D.; Cootes, T.; Scott, I. A Multi-Stage Approach to Facial Feature Detection. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2004, Kingston, UK, 7–9 September 2004; Andreas, H., Sarah, B., Tim, E., Eds.; BMVA Press: Worcestershire, UK, 2004; pp. 30.1–30.10. [Google Scholar]
- Beumer, G.M.; Bazen, A.M.; Veldhuis, R.N.J. On the accuracy of EERs in face recognition and the importance of reliable registration. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE Benelux Signal Processing Symposium (SPS-2005), Antwerp, Belgium, 19–20 April 2005; pp. 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Umirzakova, S.; Abdusalomov, A.; Whangbo, T.K. Fully Automatic Stroke Symptom Detection Method Based on Facial Features and Moving Hand Differences. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Symposium on Multimedia and Communication Technology (ISMAC), Quezon City, Philippines, 19–21 August 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, A.; Bennamoun, M.; Owens, R. An Efficient Multimodal 2D-3D Hybrid Approach to Automatic Face Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 1927–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakadiaris, I.A.; Passalis, G.; Toderici, G.; Murtuza, M.N.; Lu, Y.; Karampatziakis, N.; Theoharis, T. Three-Dimensional Face Recognition in the Presence of Facial Expressions: An Annotated Deformable Model Approach. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Baltrušaitis, T.; Zadeh, A.; Morency, Lo.; Medioni, G. Holistically Constrained Local Model: Going Beyond Frontal Poses for Facial Landmark Detection. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), York, UK, 19–22 September 2016; Wilson, R.C., Hancock, E.R., Smith, W.A.P., Eds.; BMVA Press: Worcestershire, UK, 2016; pp. 95.1–95.12. [Google Scholar]
- Cootes, T.F.; Edwards, G.J.; Taylor, C.J. Active appearance models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cootes, T.F.; Taylor, C.J.; Cooper, D.H.; Graham, J. Active Shape Models-Their Training and Application. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1995, 61, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, A.J.; Eadeh, F.R.; Peak, S.A.; Scherer, L.D.; Schott, J.P.; Slochower, J.M. Toward a greater understanding of the emotional dynamics of the mortality salience manipulation: Revisiting the “affect-free” claim of terror management research. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2014, 106, 655–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Tao, Y.; Martinez, A.M. Compound facial expressions of emotion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1454–E1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donato, G.; Bartlett, M.; Hager, J.; Ekman, P.; Sejnowski, T. Classifying facial actions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1999, 21, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Álvarez, V.M.; Sánchez, C.N.; Gutiérrez, S.; Domínguez-Soberanes, J.; Velázquez, R. Facial Emotion Recognition: A Comparison of Different Landmark-Based Classifiers. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Research in Intelligent and Computing in Engineering (RICE), San Salvador, El Salvador, 22–24 August 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Mattar, M.; Berg, T.; Learned-Miller, E. Labeled Faces in the Wild: A Database for Studying Face Recognition in Unconstrained Environments. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Faces in ‘Real Life’ Images: Detection, Alignment, and Recognition, Marseille, France, 17–20 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jaber, A.K.; Abdel-Qader, I. Hybrid Histograms of Oriented Gradients-compressive sensing framework feature extraction for face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Electro Information Technology (EIT), Grand Forks, ND, USA, 19–21 May 2016; pp. 0442–0447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, Q.T.; Lee, S.; Song, B.C. Facial Landmark-Based Emotion Recognition via Directed Graph Neural Network. Electronics 2020, 9, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoeun, R.; Chophuk, P.; Chinnasarn, K. Emotion Recognition for Partial Faces Using a Feature Vector Technique. Sensors 2022, 22, 4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Cavallaro, A. 3-D Face Detection, Landmark Localization, and Registration Using a Point Distribution Model. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2009, 11, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- HShah, M.; Dinesh, A.; Sharmila, T.S. Analysis of Facial Landmark Features to determine the best subset for finding Face Orientation. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Data Science (ICCIDS), Gurugram, India, 6–7 September 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L. Multiple Attention Network for Facial Expression Recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 7383–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, S.; Sharma, G.; Dhall, A. Expression Empowered ResiDen Network for Facial Action Unit Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H. An Expression Recognition Method based on Improved Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications (ICAICA), Dalian, China, 27–29 June 2022; pp. 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeshina, S.O.; Ibrahim, H.; Teoh, S.S.; Hoo, S.C. Custom face classification model for classroom using Haar-like and LBP features with their performance comparisons. Electronics 2021, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ai, X. Face detection in color images using adaboost algorithm based on skin color information. In Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (WKDD 2008), Adelaide, SA, Australia, 23–24 January 2008; pp. 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, C.P.; Oren, M.; Poggio, T. A general framework for object detection. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision, Bombay, India, 7 January 1998; pp. 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- Kartynnik, Y.; Ablavatski, A.; Grishchenko, I.; Grundmann, M. Real-time Facial Surface Geometry from Monocular Video on Mobile GPUs. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.06724v1. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://google.github.io/mediapipe/solutions/face_mesh.html (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Bazarevsky, V.; Kartynnik, Y.; Vakunov, A.; Raveendran, K.; Grundmann, M. BlazeFace: Sub-millisecond Neural Face Detection on Mobile GPUs. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning Series; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, G. Delaunay Mesh Construction and Simplification with Feature Preserving Based on Minimal Volume Destruction. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaunay, B. Sur la sphere vide. Izv. Akad. Nauk. SSSR Otd. Mat. I Estestv. Nauk. 1934, 7, 793–800. [Google Scholar]
- Golzadeh, H.; Faria, D.R.; Manso, L.J.; Ekárt, A.; Buckingham, C.D. Emotion Recognition using Spatiotemporal Features from Facial Expression Landmarks. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS), Funchal, Portugal, 25–27 September 2018; pp. 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, R.; Shahabi, C.; Liu, Y. Diffusion Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network: Data-Driven Traffic Forecasting. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.01926v3. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.01926 (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Farkhod, A.; Abdusalomov, A.; Makhmudov, F.; Cho, Y.I. LDA-Based Topic Modeling Sentiment Analysis Using Topic/Document/Sentence (TDS) Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusalomov, A.; Whangbo, T.K. An improvement for the foreground recognition method using shadow removal technique for indoor environments. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolut. Inf. Process. 2017, 15, 1750039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusalomov, A.; Whangbo, T.K. Detection and Removal of Moving Object Shadows Using Geometry and Color Information for Indoor Video Streams. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kutlimuratov, A.; Abdusalomov, A.; Whangbo, T.K. Evolving Hierarchical and Tag Information via the Deeply Enhanced Weighted Non-Negative Matrix Factorization of Rating Predictions. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusalomov, A.B.; Safarov, F.; Rakhimov, M.; Turaev, B.; Whangbo, T.K. Improved Feature Parameter Extraction from Speech Signals Using Machine Learning Algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlimuratov, A.; Abdusalomov, A.B.; Oteniyazov, R.; Mirzakhalilov, S.; Whangbo, T.K. Modeling and Applying Implicit Dormant Features for Recommendation via Clustering and Deep Factorization. Sensors 2022, 22, 8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Xia, Y.; Yan, Q.; Xun, L. Facial Expression Recognition with Faster R-CNN. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 107, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Hu, H. Facial expression recognition with FRR-CNN. Electron. Lett. 2017, 53, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jolfaei, A.; Alazab, M. A Face Emotion Recognition Method Using Convolutional Neural Network and Image Edge Computing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 159081–159089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamadiyev, A.; Khujayarov, I.; Djuraev, O.; Cho, J. Automatic Speech Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning Approaches for Uzbek Language. Sensors 2022, 22, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wafa, R.; Khan, M.Q.; Malik, F.; Abdusalomov, A.B.; Cho, Y.I.; Odarchenko, R. The Impact of Agile Methodology on Project Success, with a Moderating Role of Person’s Job Fit in the IT Industry of Pakistan. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusalomov, A.; Mukhiddinov, M.; Djuraev, O.; Khamdamov, U.; Whangbo, T.K. Automatic salient object extraction based on locally adaptive thresholding to generate tactile graphics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Tarimer, I.; Alwageed, H.S.; Karadağ, B.C.; Fayaz, M.; Abdusalomov, A.B.; Cho, Y.-I. Effect of Feature Selection on the Accuracy of Music Popularity Classification Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Electronics 2022, 11, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodirov, J.; Abdusalomov, A.B.; Whangbo, T.K. Attention 3D U-Net with Multiple Skip Connections for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Images. Sensors 2022, 22, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhongir, N.; Abdusalomov, A.; Whangbo, T.K. 3D Volume Reconstruction from MRI Slices based on VTK. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Korea, 19–21 October 2021; pp. 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayvaz, U.; Gürüler, H.; Khan, F.; Ahmed, N.; Whangbo, T.; Abdusalomov, A. Automatic Speaker Recognition Using Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients Through Machine Learning. CMC-Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 71, 5511–5521. [Google Scholar]
- Makhmudov, F.; Mukhiddinov, M.; Abdusalomov, A.; Avazov, K.; Khamdamov, U.; Cho, Y.I. Improvement of the end-to-end scene text recognition method for “text-to-speech” conversion. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolut. Inf. Process. 2020, 18, 2050052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusalomov, A.; Baratov, N.; Kutlimuratov, A.; Whangbo, T.K. An Improvement of the Fire Detection and Classification Method Using YOLOv3 for Surveillance Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhiddinov, M.; Abdusalomov, A.B.; Cho, J. Automatic Fire Detection and Notification System Based on Improved YOLOv4 for the Blind and Visually Impaired. Sensors 2022, 22, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdusalomov, A.B.; Mukhiddinov, M.; Kutlimuratov, A.; Whangbo, T.K. Improved Real-Time Fire Warning System Based on Advanced Technologies for Visually Impaired People. Sensors 2022, 22, 7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
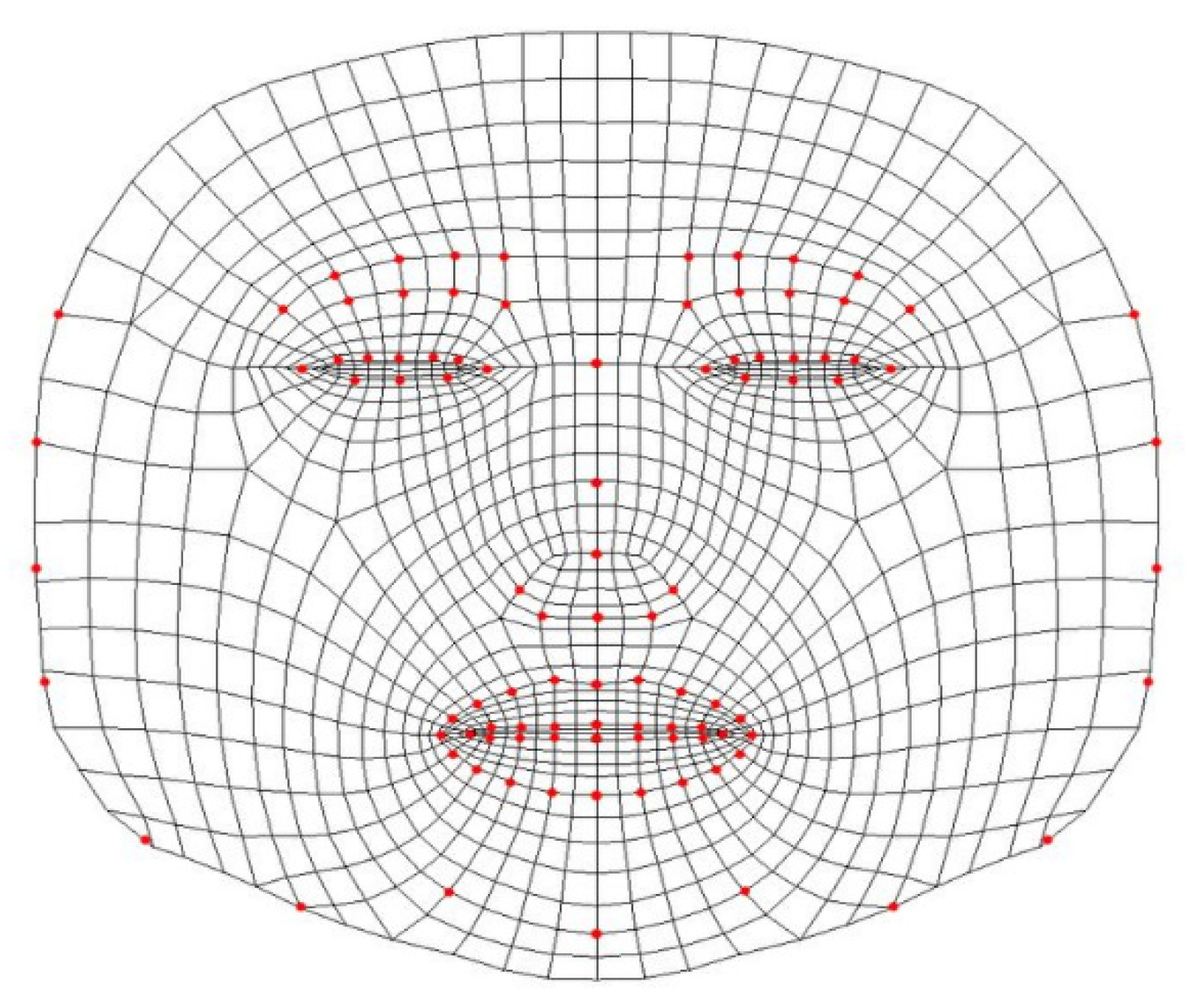






| Methods |
Input Feature Parts (Upper: Eyes, Eyebrows Lower: Nose, Mouth) | Landmark Application Area | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| RTFER [30] | Upper + Lower | Face landmarks | Mainly focus to Lower |
| ResiDen [31] | Upper + Lower | Face landmarks | Mainly focus to Lower |
| DenseNet [32] | Upper + Lower | Face landmarks | Mainly focus to Lower |
| Proposed method | Upper | Face landmarks | Mainly focus to Upper |
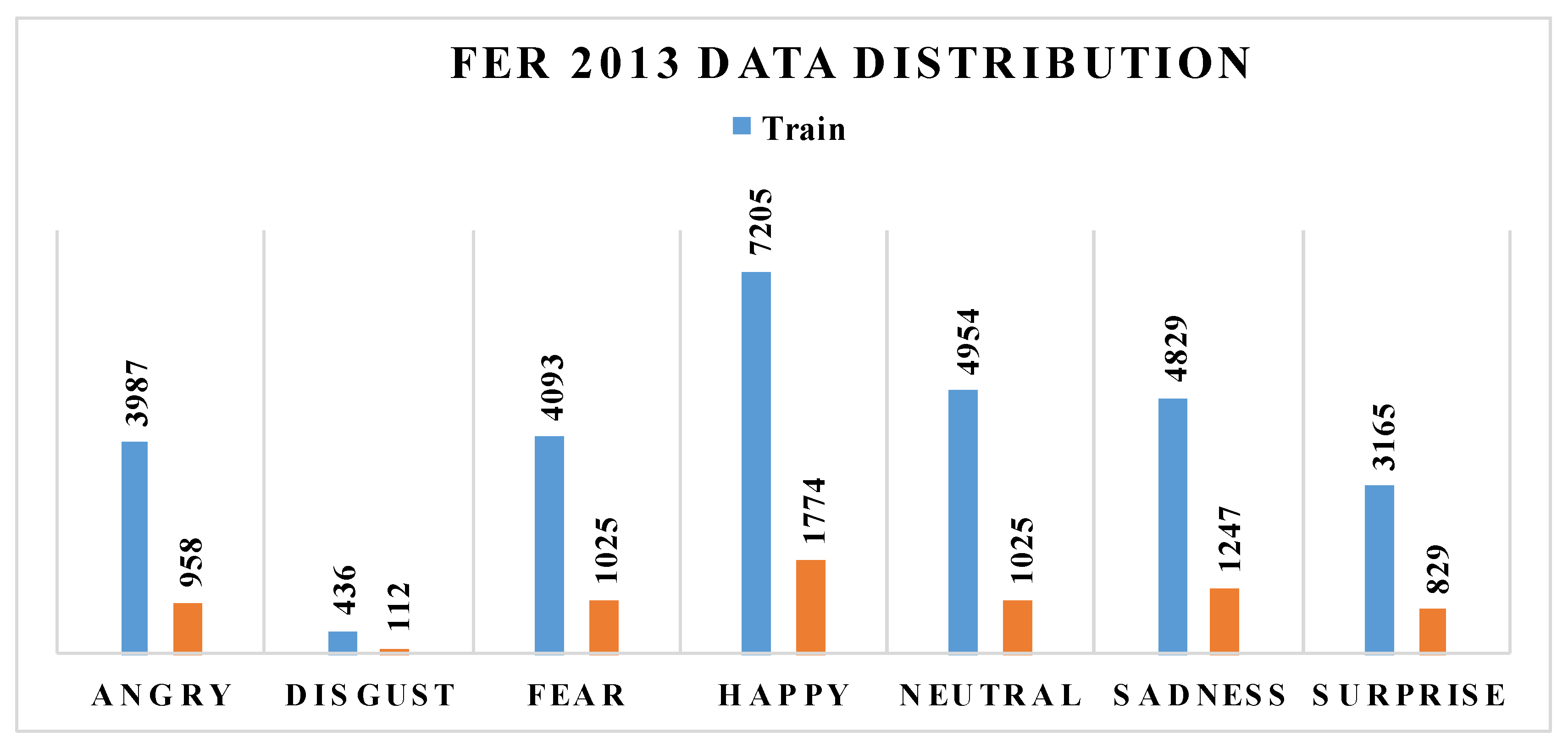
| Angry | Happy | Sad | Neutral | Fear | Disgust | Surprise | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 3987 | 7205 | 4829 | 4954 | 4093 | 436 | 3165 |
| Test | 958 | 1774 | 1247 | 1233 | 1025 | 112 | 829 |
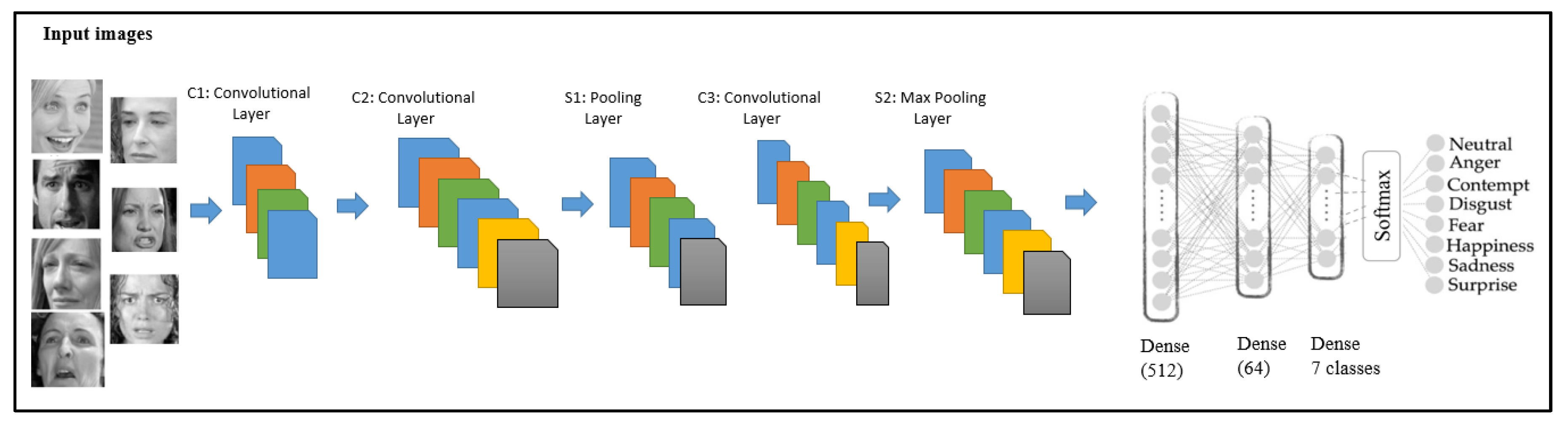
| Layer (Type) | Output Shape | Parameter Numbers | Activation |
|---|---|---|---|
| conv2d (Conv2D) | (None, 48, 48, 32) | 320 | ReLU |
| conv2d_1 (Conv2D) | (None, 48, 48, 32) | 9248 | ReLU |
| max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) | (None, 24, 24, 32) | 0 | ReLU |
| conv2d_2 (Conv2D) | (None, 24, 24, 64) | 18,496 | ReLU |
| conv2d_3 (Conv2D) | (None, 24, 24, 64) | 36,928 | ReLU |
| max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling 2D) | (None, 12, 12, 64) | 0 | ReLU |
| conv2d_4 (Conv2D) | (None, 12, 12, 128) | 73,856 | ReLU |
| conv2d_5 (Conv2D) | (None, 12, 12, 128) | 147,584 | ReLU |
| max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling 2D) | (None, 6, 6, 128) | 0 | ReLU |
| flatten (Flatten) | (None, 4608) | 0 | None |
| dense (Dense) | (None, 512) | 2,359,808 | ReLU |
| dense_1 (Dense) | (None, 64) | 32,832 | ReLU |
| dense_2 (Dense) | (None, 7) | 455 | Softmax |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Support | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anger | 0.53 | 0.60 | 0.56 | 957 |
| Disgust | 0.69 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 111 |
| Fear | 0.50 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 1024 |
| Happy | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 1773 |
| Neutral | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 1232 |
| Sad | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 1246 |
| Surprise | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 828 |
| Accuracy | 0.65 | 7171 | ||
| Macro avg | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.59 | 7171 |
| Weighted avg | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 7171 |
| Method | Recognition Rate (%) | Proposed Method with Four Different Classifiers (%) | Classification Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| R-CNN algorithm [50] | 79.34 | Linear regression | 99.04% |
| FRR-CNN algorithm [51] | 70.63 | Random forest | 99.8% |
| CNN-Edge detection method [52] | 88.86 | Gradient boosting | 99.42% |
| Our proposed method | 91.2 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farkhod, A.; Abdusalomov, A.B.; Mukhiddinov, M.; Cho, Y.-I. Development of Real-Time Landmark-Based Emotion Recognition CNN for Masked Faces. Sensors 2022, 22, 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228704
Farkhod A, Abdusalomov AB, Mukhiddinov M, Cho Y-I. Development of Real-Time Landmark-Based Emotion Recognition CNN for Masked Faces. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228704
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarkhod, Akhmedov, Akmalbek Bobomirzaevich Abdusalomov, Mukhriddin Mukhiddinov, and Young-Im Cho. 2022. "Development of Real-Time Landmark-Based Emotion Recognition CNN for Masked Faces" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228704
APA StyleFarkhod, A., Abdusalomov, A. B., Mukhiddinov, M., & Cho, Y.-I. (2022). Development of Real-Time Landmark-Based Emotion Recognition CNN for Masked Faces. Sensors, 22(22), 8704. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228704









