Case-Specific Focal Sensor Design for Cardiac Electrical Impedance Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Principle of EIT
2.2. Inverse Problem
3. Modeling
3.1. Anatomical Model
3.2. Boundary Element Simulation Model
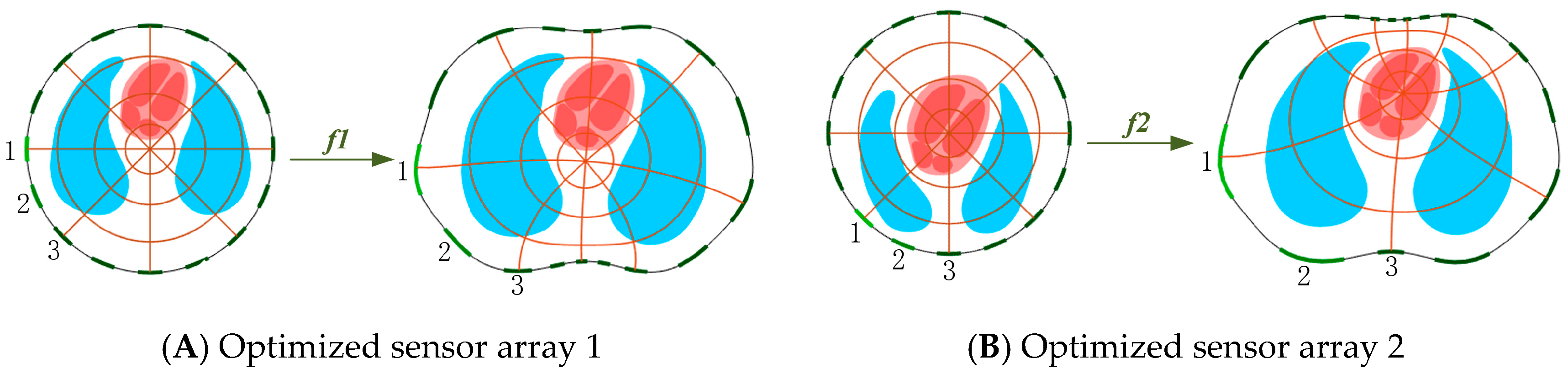
3.3. Sensor Optimization
4. Result Analysis
4.1. Sensitivity Calculation
4.2. Boundary Potential
4.3. Analysis of Reconstruction Results
4.4. Average Cardiac Impedance
5. Experimental Result
5.1. Measurement Voltage Analysis
5.2. Analysis of Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holder, D.S. Electrical Impedance Tomography: Methods, History and Applications; Medical Physics; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.F.; Takei, M. Application of Process Tomography to Multiphase Flow Measurement in Industrial and Biomedical Fields: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 8196–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, F.; Proenca, M.; Rapin, M.; Lemay, M.; Adler, A. Aortic blood pressure measured via EIT: Investigation of different measurement settings. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, S.H.; Murphy, E.K.; Callahan, J.M.; DeVries, J.T. Cardiac eigen imaging: A novel method to isolate cardiac activity in thoracic electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2020, 41, 095008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.; Mueller, J.L. Calderon’s Method with a Spatial Prior for 2-D EIT Imaging of Ventilation and Perfusion. Sensors 2021, 21, 5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frerichs, I.; Becher, T. Chest electrical impedance tomography measures in neonatology and paediatrics-a survey on clinical usefulness. Physiol. Meas. 2019, 40, 054001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, G.; Niewenhuys, J.; Just, A. Monitoring lung impedance changes during long-term ventilator-induced lung injury ventilation using electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2020, 41, 095011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romsauerova, A.; McEwan, A.; Horesh, L.; Yerworth, R.; Bayford, R.H.; Holder, D.S. Multi-frequency electrical impedance tomography (EIT) of the adult human head: Initial findings in brain tumours, arteriovenous malformations and chronic stroke, development of an analysis method and calibration. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 27, S147–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, G.; Song, J.L.; Dai, M.; Xu, C.H.; Dong, X.Z.; Fu, F. Ex-Vivo Characterization of Bioimpedance Spectroscopy of Normal, Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Rabbit Brain Tissue at Frequencies from 10 Hz to 1 MHz. Sensors 2014, 16, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Bagnaninchi, P.O.; Jia, J.B. Electrical impedance tomography for real-time and label-free cellular viability assays of 3D tumour spheroids. Analyst 2018, 143, 4189–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, M.X.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.C. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value of three-dimensional (3D) electrical impedance tomography imaging in patients with breast cancer. Gland Surg. 2021, 10, 2673–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Soleimani, M. Combining Multiple Boundary Shapes in Deformable EIT a Potential Use in Breast Imaging. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2020, 4, 5500604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Y.; Jiang, J.J.; Liu, Y.L. Electrical Impedance Tomography-guided PEEP Titration in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Abdominal Surgery. Medicine 2016, 95, e3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, W.J.; You, F.S.; Zhang, W. Image monitoring for an intraperitoneal bleeding model of pigs using electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Zlochiver, S.; Freimark, D.; Arad, M.; Adunsky, A.; Abboud, S. Parametric EIT for monitoring cardiac stroke volume. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Janse, A.; Marcus, J.T.; Bronzwaer, J.G.F.; Postmus, P.E.; Faes, T.J. Determination of stroke volume by means of electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2000, 21, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Zhang, Y.M.; Dong, X.Z. Preliminary results of real-time electrical impedance tomography imaging system on the isolated heart filling model. Heart J. 2003, 15, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Proenca, M.; Braun, F.; Rapin, M.; Sola, J.; Adler, A.; Grychtol, B.; Bohm, S.H.; Lemay, M.; Thiran, J.P. Influence of heart motion on cardiac output estimation by means of electrical impedance tomography: A case study. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, F.; Proena, M.; Wendler, A.; Sola, J.; Becher, T. Noninvasive measurement of stroke volume changes in critically ill patients by means of electrical impedance tomography. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2019, 34, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, S.J.; Dong, F. Focusing Sensor Design for Open Electrical Impedance Tomography Based on Shape Conformal Transformation. Sensors 2019, 19, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.J.; Soleimani, M.; Dong, F. Inclusion boundary reconstruction and sensitivity analysis in electrical impedance tomography. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2018, 26, 1037–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.Z.; Wu, H.L.; Yang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, Y. 3-D electrical impedance tomography forward problem with finite element method. IEEE Trans. Mangetics 2005, 41, 1832–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Tehrani, J.N.; McEwan, A.; Jin, C. L1 regularization method in electrical impedance tomography by using the L1-curve (Pareto frontier curve). Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauhkonen, M.; Vadasz, D.; Karjalainen, P.A.; Somersalo, E.; Kaipio, J.P. Tikhonov regularization and prior information in electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheney, M.; Isaacson, D.; Newell, J.C.; Simske, S.; Goble, J. NOSER: An algorithm for solving the inverse conductivity problem. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 1990, 2, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xu, Y.; Dong, F. A spatially adaptive total variation regularization method for electrical resistance tomography. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 125401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Lionheart, W.R.B. Uses and abuses of EIDORS: An extensible software base for EIT. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, S25–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.J.; Hauptmann, A. Deep D-bar: Real time Electrical Impedance Tomography Imaging with Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 37, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasgall, P.A.; Baumgartner, C.; Neufeld, E.; Lloyd, B.; Gosselin, M.C.; Kuster, N.; IT’IS Database for Thermal and Electromagnetic Parameters of Biological Tissues. Version 4.1. 2022. Available online: www.itis.swiss/database (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Driscoll, T.A.; Trefethen, L.N. Algorithm 843: Improvements to the Schwarz-Christoffel toolbox for MATLAB. Acm Trans. Math. Softw. 2005, 31, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstatter, B. Jacobian calculation for electrical impedance tomography based on the reciprocity principle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Arnold, J.H.; Bayford, R.; Borsic, A.; Brown, B.; Dixon, P.; Faes, T.J.C.; Frerichs, I.; Gagnon, H. GREIT: A unified approach to 2D linear EIT reconstruction of lung images. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, S35–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, S. Design of parallel electrical resistance tomography system for measuring multiphase flow. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Avg (×10−7) | Std (×10−7) | |
|---|---|---|
| Evenly | 4.18 | 2.05 |
| Focus1 | 4.76 | 2.63 |
| Focus2 | 5.10 | 3.42 |
| Phantoms | ev | foc1 | foc2 | ev | foc1 | foc2 | ev | foc1 | foc2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t2 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t3 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t4 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t5 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t6 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t7 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t8 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t9 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Phantoms | ev | foc1 | foc2 | ev | foc1 | foc2 | ev | foc1 | foc2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t2 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t3 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t4 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t5 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t6 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t7 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t8 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| t9 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ren, S.; Dong, F. Case-Specific Focal Sensor Design for Cardiac Electrical Impedance Tomography. Sensors 2022, 22, 8698. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228698
Zhang C, Wang Y, Ren S, Dong F. Case-Specific Focal Sensor Design for Cardiac Electrical Impedance Tomography. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8698. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228698
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chenke, Yu Wang, Shangjie Ren, and Feng Dong. 2022. "Case-Specific Focal Sensor Design for Cardiac Electrical Impedance Tomography" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8698. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228698
APA StyleZhang, C., Wang, Y., Ren, S., & Dong, F. (2022). Case-Specific Focal Sensor Design for Cardiac Electrical Impedance Tomography. Sensors, 22(22), 8698. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228698






