MT-GCNN: Multi-Task Learning with Gated Convolution for Multiple Transmitters Localization in Urban Scenarios
Abstract
1. Introduction
- In the proposed MT-GCNN, the multi-label classification and the bias regression are combined to predict the coarse results and correct biases. A joint loss function is also designed to train the two tasks simultaneously.
- Considering the challenges of NLOS propagation and limited layouts of sensors, an improved gated convolution module is applied for feature extraction in MT-GCNN. The gated mechanism [26] and convolutional module are combined to fuse the multi-dimensional features of sparse sensing data in complex environments.
- With the aid of the simulation software Winprop, the proposed localization scheme is validated based on the urban NLOS propagation datasets. Moreover, this paper analyzes the localization performance of different factors, including the number of transmitters, the number of sensors, the impact of measurement noise, and the complexity of models.
2. Problem Formulation
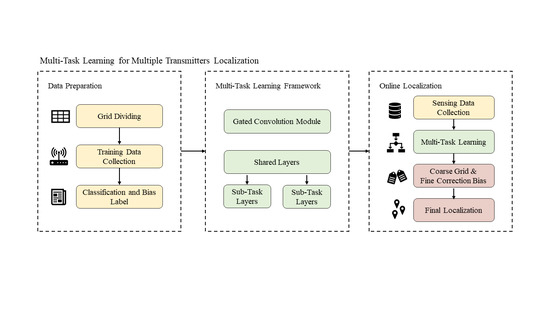
3. MT-GCNN Model for Multiple Transmitters Localization
3.1. The Design of MT-GCNN
3.2. Joint Loss Function
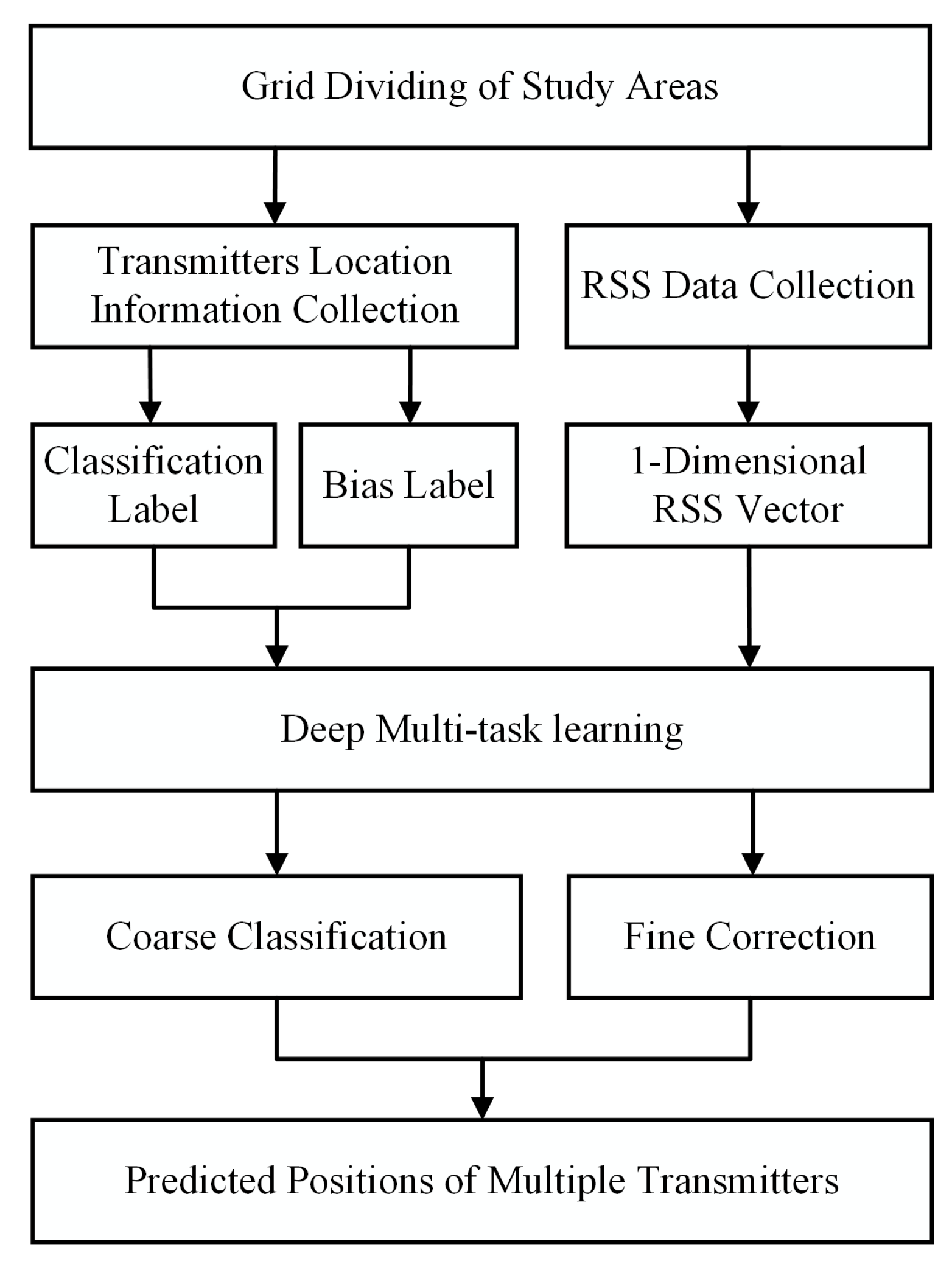
3.3. Training and Localization
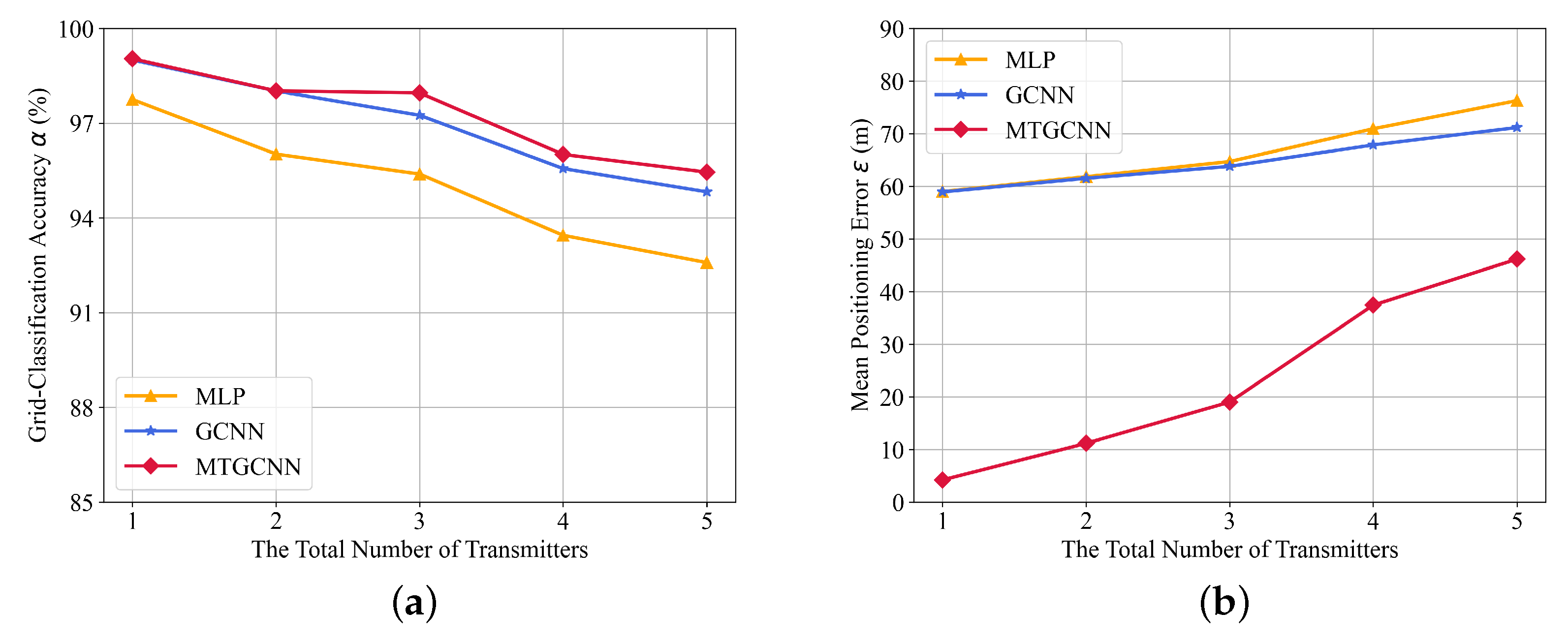
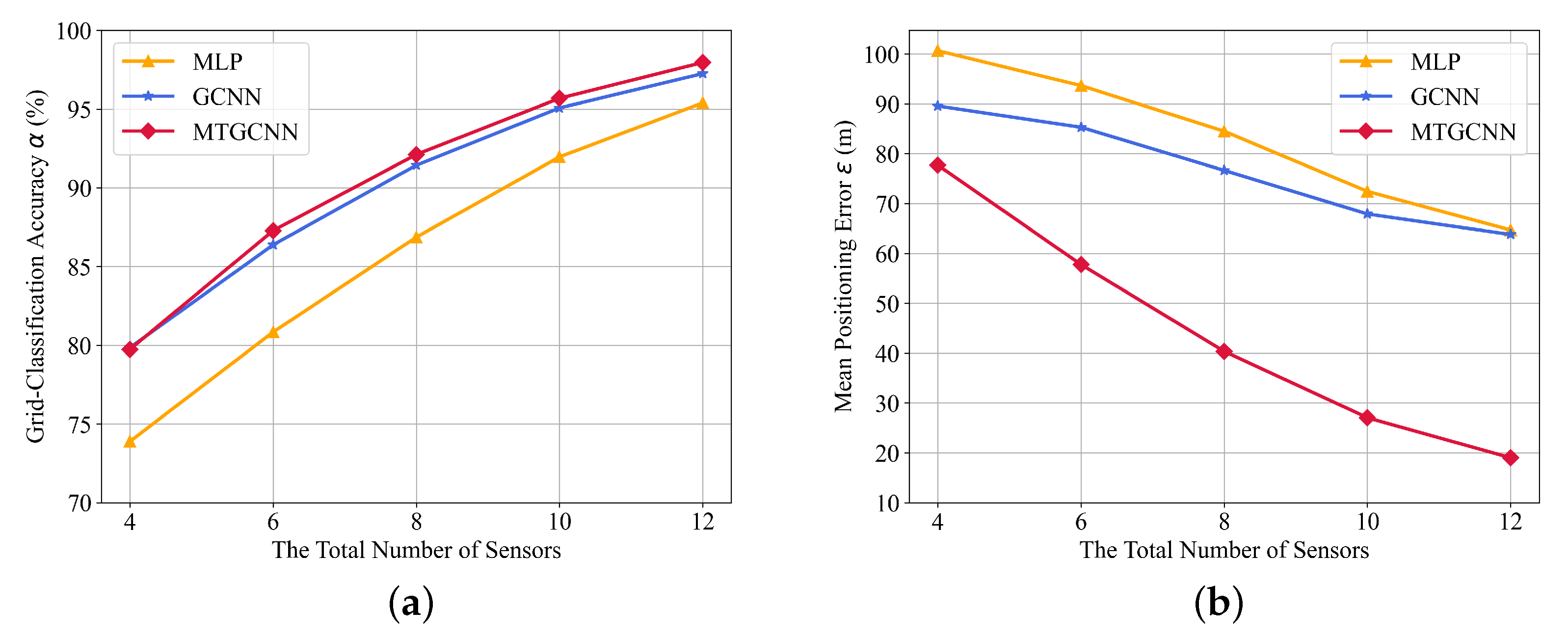
4. Numerical Evaluation
4.1. Simulation Setup
4.2. Performance Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOA | Angle of Arrival |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CS | Compressive Sensing |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| DPM | Dominant Path Model |
| FLOPs | Floating Point Operations |
| GCNN | Gated Convolutional Neural Network |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| LOS | Line of Sight |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| MT-GCNN | Multi-Task Gated Convolutional Neural Network |
| MTL | Multi-Task Learning |
| NLOS | Non Line of Sight |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| RSS | Received Signal Strength |
| TDOA | Time Difference of Arrival |
| TOA | Time of Arrival |
| WSN | Wireless Sensor Network |
References
- Liu, D.; Lee, M.C.; Pun, C.M.; Liu, H. Analysis of Wireless Localization in Nonline-of-Sight Conditions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Ansari, N. Improved Robust TOA-Based Localization via NLOS Balancing Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 6177–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, L. Three Passive TDOA-AOA Receivers-Based Flying-UAV Positioning in Extreme Environments. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 9589–9595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shu, F.; Shi, B.; Cheng, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, J. Enhanced RSS-Based UAV Localization Via Trajectory and Multi-Base Stations. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 1881–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.A.R.; Amiri, R.; Behnia, F. Data Association for Multi-Target Elliptic Localization in Distributed MIMO Radars. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2904–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, T.; Chung, W. Multi-Target Localization Based on Unidentified Multiple RSS/AOA Measurements in Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Xie, W.; Xu, K.; Guo, M. Localization of Multiple RF Sources via Priori Knowledge-Aided Bayesian Compressive Sensing in UAV-Based WSN. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 3848–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z. Grid Evolution: Joint Dictionary Learning and Sparse Bayesian Recovery for Multiple Off-Grid Targets Localization. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 2068–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y. Robust Cooperative Indoor Localization Based on Reliability Evaluation. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6836–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Xie, W.; Sheng, J. Multi-Emitter Localization via Concurrent Variational Bayesian Inference in UAV-Based WSN. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2255–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Fang, D. Multiple Target Counting and Localization Using Variational Bayesian EM Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2017, 65, 2985–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiao, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Yue, C. Passive localization of multiple sources using joint RSS and AOA measurements in spectrum sharing system. China Commun. 2021, 18, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.X.; Lu, A.N.; You, M.Y.; Huang, K.; Jiang, B. Wireless Localization Based on Deep Learning: State of Art and Challenges. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5214920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.; Bin Mahmood, A.K.; Yahya, N.; Saboor, A.; Abbas, M.Z.; Khan, Z.; Rimsan, M. State-of-the-Art Review on the Acoustic Emission Source Localization Techniques. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 101246–101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Q.; Ha, C. Machine learning in indoor visible light positioning systems: A review. Neurocomputing 2022, 491, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potortì, F.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Quezada-Gaibor, D.; Jiménez, A.R.; Seco, F.; Pérez-Navarro, A.; Ortiz, M.; Zhu, N.; Renaudin, V.; Ichikari, R.; et al. Off-line evaluation of indoor positioning systems in different scenarios: The experiences from IPIN 2020 competition. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 5011–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potorti, F.; Park, S.; Crivello, A.; Palumbo, F.; Girolami, M.; Barsocchi, P.; Lee, S.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Ruiz, A.R.J.; Pérez-Navarro, A.; et al. The IPIN 2019 indoor localisation competition—Description and results. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 206674–206718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, H.; Torki, M.; Youssef, M. CellinDeep: Robust and Accurate Cellular-Based Indoor Localization via Deep Learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, Q.D.; De, P. A survey of fingerprint-based outdoor localization. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2015, 18, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Mao, S.; Pandey, S. CSI-based fingerprinting for indoor localization: A deep learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 66, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubow, A.; Bayhan, S.; Gawłowicz, P.; Dressler, F. DeepTxFinder: Multiple Transmitter Localization by Deep Learning in Crowdsourced Spectrum Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2020 29th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–6 August 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, Z. Heatmap-Based Multiple Co-Channel Transmitter Localization with Fully Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society (ACES-China) Symposium, Virtual, 1–5 August 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Ghaderibaneh, M.; Sahu, P.; Gupta, H. DeepMTL Pro: Deep Learning Based Multiple Transmitter Localization and Power Estimation. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2022, 82, 101582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chang, J.; Lee, S. Deep learning-based method for multiple sound source localization with high resolution and accuracy. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 161, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, L. Deep Learning-Based Localization with Urban Electromagnetic and Geographic Information. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauphin, Y.N.; Fan, A.; Auli, M.; Grangier, D. Language Modeling with Gated Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; Precup, D., Teh, Y., Eds.; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 70. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R. Multitask learning. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Dolan, J.M.; Yang, M. DLT-Net: Joint Detection of Drivable Areas, Lane Lines, and Traffic Objects. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 4670–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Tao, X.; Zhang, P. ConFi: Convolutional Neural Networks Based Indoor Wi-Fi Localization Using Channel State Information. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18066–18074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adege, A.B.; Lin, H.P.; Tarekegn, G.B.; Jeng, S.S. Applying Deep Neural Network (DNN) for Robust Indoor Localization in Multi-Building Environment. Appl. Sci.-Basel 2018, 8, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Song, Y.; Chen, D.; He, S.; Yu, Y.; Yan, T.; Hancke, G.P.; Lau, R.W. Deformable Object Tracking With Gated Fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 3766–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. Gated Residual Networks With Dilated Convolutions for Monaural Speech Enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. 2019, 27, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santurkar, S.; Tsipras, D.; Ilyas, A.; Madry, A. How does batch normalization help optimization? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Y. Circle Loss: A Unified Perspective of Pair Similarity Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6397–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, R.; Wolfle, G.; Jakobus, U. Wave propagation and radio network planning software WinProp added to the electromagnetic solver package FEKO. In Proceedings of the Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium-Italy, Firenze, Italy, 26–30 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Woelfle, G.; Wahl, R.; Wertz, P.; Wildbolz, P.; Landstorfer, F. Dominant Path Prediction Model for Urban Scenarios. In Proceedings of the IST Mobile & Wireless Communications Summit, Dresden, Germany, 19–23 June 2005. [Google Scholar]


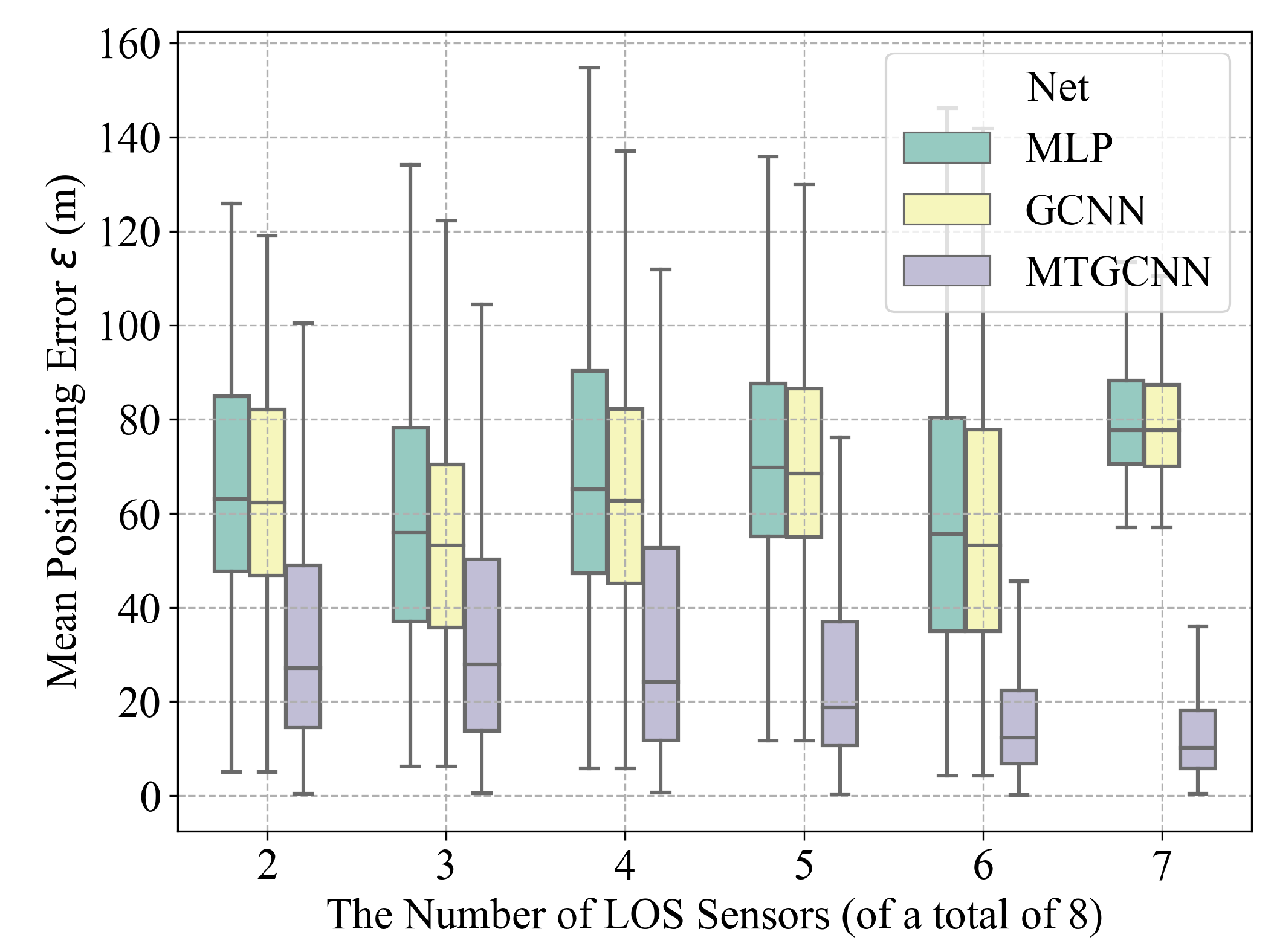
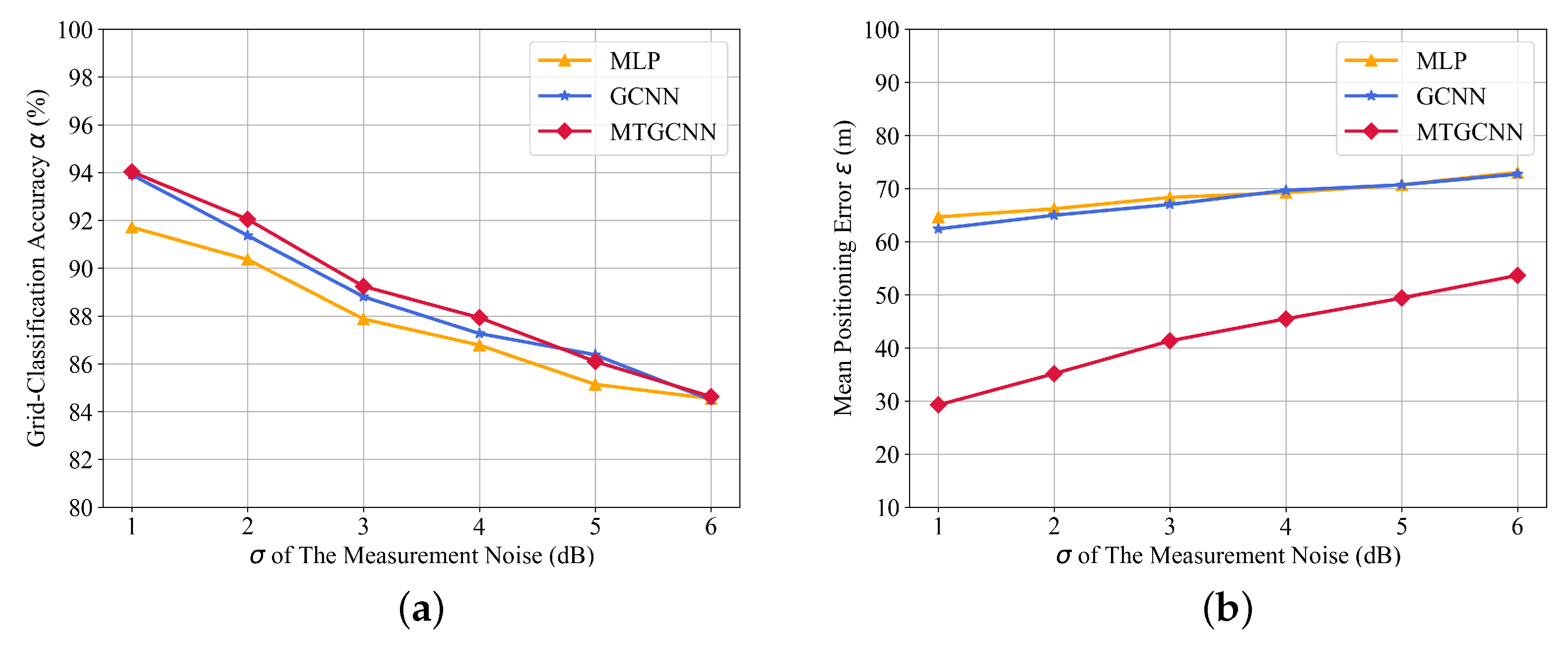
| Algorithms | Grid-Classification Accuracy (%) | Mean Positioning Error (m) |
|---|---|---|
| MT-GCNN | 98.25 | 5.73 |
| GCNN | 96.54 | 59.35 |
| CellinDeep | 93.00 | 59.95 |
| MLP | 93.21 | 62.75 |
| Algorithms | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Testing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MT-GCNN | 9.3447 | ||
| GCNN | 8.8990 | ||
| MLP | 2.1693 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, B.; Yu, L.; Cheng, K. MT-GCNN: Multi-Task Learning with Gated Convolution for Multiple Transmitters Localization in Urban Scenarios. Sensors 2022, 22, 8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228674
Wang W, Zhu L, Huang Z, Li B, Yu L, Cheng K. MT-GCNN: Multi-Task Learning with Gated Convolution for Multiple Transmitters Localization in Urban Scenarios. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228674
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenyu, Lei Zhu, Zhen Huang, Baozhu Li, Lu Yu, and Kaixin Cheng. 2022. "MT-GCNN: Multi-Task Learning with Gated Convolution for Multiple Transmitters Localization in Urban Scenarios" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228674
APA StyleWang, W., Zhu, L., Huang, Z., Li, B., Yu, L., & Cheng, K. (2022). MT-GCNN: Multi-Task Learning with Gated Convolution for Multiple Transmitters Localization in Urban Scenarios. Sensors, 22(22), 8674. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228674