Graphene Incorporated Electrospun Nanofiber for Electrochemical Sensing and Biomedical Applications: A Critical Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fabrication of GNM-Based Materials
2.1. GNM-Loaded NFs
2.2. Engineering Electrospun GNM Composites Using Pre-Processing Techniques
2.3. Direct Blending of GNMs in Electrospun Polymeric NFs
2.4. Uniform Distribution of GNMs Utilizing External Forces
2.5. In Situ Synthesis of GNMs into Polymeric Nanofiber Matrix
2.6. Dispersal of GNMs Using Electrospinning
2.7. Fabrication of GNM NF Composites Using Post-Processing Approaches
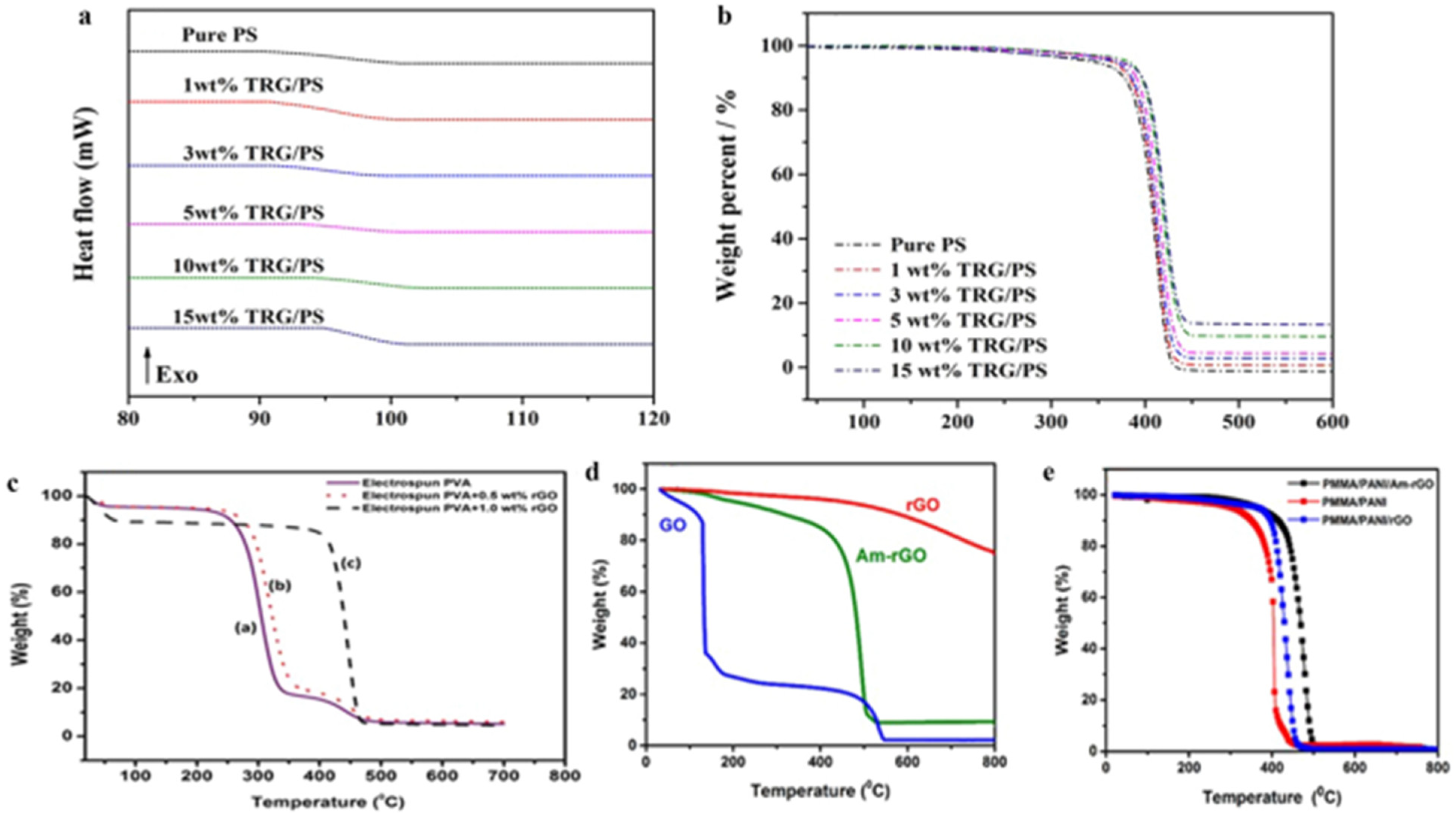
2.8. Characteristics of NF-Loaded GNMs
2.9. Electrospun GNM Nanocomposites as Electrochemical Biosensors
3. Biomedical Applications of Electrospun Graphene Oxide
3.1. Biomedical Prospects of GO
3.2. Electrospinning in Tissue Engineering
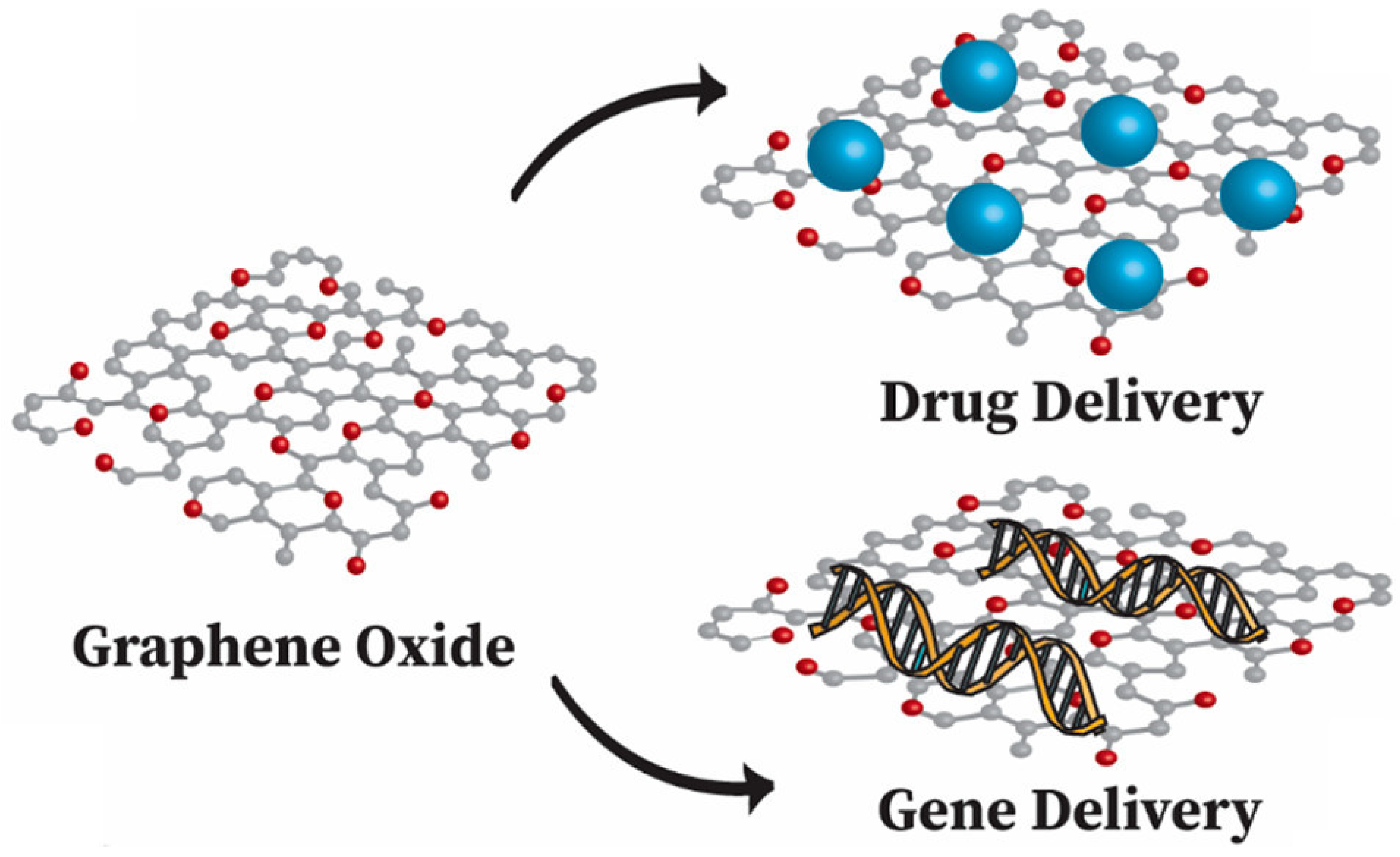
3.3. Drug and Gene Delivery
3.4. Cancer Therapy
3.5. Wound Healing
3.6. Biomaterials/Medical Equipment
4. Conclusions
Perspective and Future Outlook
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, C.K.; Pumera, M. Chemical reduction of graphene oxide: A synthetic chemistry viewpoint. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P.; Schwab, M.; Kim, K. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 2012, 490, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Ni, G.-X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Castro Neto, A.H.; Loh, K.P. Face-to-face transfer of wafer-scale graphene films. Nature 2014, 505, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Dubonos, S.V.; Firsov, A.A. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 2005, 438, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Jiang, D.; Schedin, F.; Booth, T.J.; Khotkevich, V.V.; Morozov, S.V.; Geim, A.K. Two-dimensional atomic crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10451–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolotin, K.; Sikes, K.; Jiang, Z.; Klima, M.; Fudenberg, G.; Hone, J.; Kim, P.; Stormer, H. Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene. Solid State Commun. 2008, 146, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Skachko, I.; Barker, A.; Andrei, E.Y. Approaching ballistic transport in suspended graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, C.R.; Young, A.F.; Meric, I.; Lee, C.; Wang, L.; Sorgenfrei, S.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Kim, P.; Shepard, K.L.; et al. Boron nitride substrates for high-quality graphene electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorov, A.S.; Gorbachev, R.V.; Morozov, S.V.; Britnell, L.; Jalil, R.; Ponomarenko, L.A.; Blake, P.; Novoselov, K.S.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; et al. Micrometer-Scale Ballistic Transport in Encapsulated Graphene at Room Temperature. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2396–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Superior Thermal Conductivity of Single-Layer Graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.; Zhu, Y.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-Based Ultracapacitors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.-W.; Stormer, H.L.; Kim, P. Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry’s phase in graphene. Nature 2005, 438, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nair, R.R.; Blake, P.; Grigorenko, A.N.; Novoselov, K.S.; Booth, T.J.; Stauber, T.; Peres, N.M.R.; Geim, A.K. Fine Structure Constant Defines Visual Transparency of Graphene. Science 2008, 320, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Lin, Y. Graphene Based Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors: A Review. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Rahighi, R. Toward Single-DNA Electrochemical Biosensing by Graphene Nanowalls. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2904–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, N.; Berry, V. Graphene-Based Single-Bacterium Resolution Biodevice and DNA Transistor: Interfacing Graphene Derivatives with Nanoscale and Microscale Biocomponents. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4469–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Peng, C.; Luo, W.; Lv, M.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. Graphene-Based Antibacterial Paper. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4317–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Escherichia coli bacteria reduce graphene oxide to bactericidal graphene in a self-limiting manner. Carbon 2012, 50, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Yong, Y.; Zhao, X.S. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial properties of silver-modified graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 21, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Photocatalytic Reduction of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets on TiO2 Thin Film for Photoinactivation of Bacteria in Solar Light Irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 20214–20220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Choobtashani, M.; Ghaderi, E. Protein Degradation and RNA Efflux of Viruses Photocatalyzed by Graphene–Tungsten Oxide Composite Under Visible Light Irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. 2012, 116, 9653–9659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Lee, S.-T.; Liu, Z. Graphene in Mice: Ultrahigh In Vivo Tumor Uptake and Efficient Photothermal Therapy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3318–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wan, J.; Zhang, S.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. The influence of surface chemistry and size of nanoscale graphene oxide on photothermal therapy of cancer using ultra-low laser power. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Aghayee, S.; Fereydooni, Y.; Talebi, A. The use of a glucose-reduced graphene oxide suspension for photothermal cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13773–13781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Tabakman, S.M.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Casalongue, H.S.; Vinh, D.; Dai, H. Ultrasmall Reduced Graphene Oxide with High Near-Infrared Absorbance for Photothermal Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6825–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Huang, D.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhong, H. Synergistic effect of chemo-photothermal therapy using PEGylated graphene oxide. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8555–8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Robinson, J.T.; Sun, X.; Dai, H. PEGylated Nanographene Oxide for Delivery of Water-Insoluble Cancer Drugs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10876–10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xia, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z. Functional Graphene Oxide as a Nanocarrier for Controlled Loading and Targeted Delivery of Mixed Anticancer Drugs. Small 2010, 6, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, C.; Yoo, J.; Lee, S.; Jo, A.; Jung, S.; Yoo, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Suh, M. The control of neural cell-to-cell interactions through non-contact electrical field stimulation using graphene electrodes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Dong, S. Graphene nanosheet: Synthesis, molecular engineering, thin film, hybrids, and energy and analytical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2644–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.; Sood, A.E.K.; Subrahmanyam, K.E.S.; Govindaraj, A. Graphene: The New Two-Dimensional Nanomaterial. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7752–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Bocchetta, P. Polymer/Graphene Nanocomposite Membranes: Status and Emerging Prospects. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.Y.; Laurent, S.; Chen, W.; Akhavan, O.; Imani, M.; Ashkarran, A.A.; Mahmoudi, M. Graphene: Promises, Facts, Opportunities, and Challenges in Nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3407–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.T.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Luo, K.Q.; Chen, P. Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: Properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 2015, 11, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene Quantum Dots Derived from Carbon Fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. ChemInform Abstract: Graphene-Based Photocatalysts for Solar-Fuel Generation. ChemInform 2015, 46, 11350–11366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, D.; Yan, J.; Lai, L.; Ni, Z.; Liu, L.; Shen, Z. Engineering the Electronic Structure of Graphene. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4055–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.T.; Shah, S.; Chhowalla, M.; Lee, K.B. Design, synthesis, and characterization of graphene-nanoparticle hybrid materials for bioapplications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2483–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.; Lee, E.; Lee, K.; Jang, J. A graphene quantum dots based fluorescent sensor for anthrax biomarker detection and its size dependence. J. Mater. Chem. 2015, 3, 4865–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Wu, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Feng, X. Porous Graphene Materials for Advanced Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion Devices. Adv. Mater. 2013, 26, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, D.; Zhang, F.; Liang, H.; Gao, P.; Cheng, C.; Feng, X. Two-Dimensional Carbon-Coated Graphene/Metal Oxide Hybrids for Enhanced Lithium Storage. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8349–8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, D.; Liang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, X.; Mai, Y.; Su, Y.; Feng, X. Metal-Nitrogen Doping of Mesoporous Carbon/Graphene Nanosheets by Self-Templating for Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 3002–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellinger, T.-P.; Thomas, A.; Yuan, J.; Antonietti, M. 25th Anniversary Article: “Cooking Carbon with Salt”: Carbon Materials and Carbonaceous Frameworks from Ionic Liquids and Poly(ionic liquid)s. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5838–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wu, S.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, H. Graphene-based electronic sensors. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chabot, V.; Higgins, D.; Yu, A.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. A review of graphene and graphene oxide sponge: Material synthesis and applications to energy and the environment. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1564–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.C.; Rodrigues, D.F. Carbon-based nanomaterials for removal of chemical and biological contaminants from water: A review of mechanisms and applications. Carbon 2015, 91, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Su, B.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, C. Graphene oxide interpenetrated polymeric composite hydrogels as highly effective adsorbents for water treatment. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 42346–42357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, F.; de Faria, A.F.; Elimelech, M. Environmental applications of graphene-based nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5861–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Feng, L.; Shi, X.; Liu, Z. Nano-graphene in biomedicine: Theranostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Wu, L.; Qu, X. New Horizons for Diagnostics and Therapeutic Applications of Graphene and Graphene Oxide. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.; Kim, S.; Chae, S.; Han, H.; Le, T.-H.; Yang, K.S.; Chang, M.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H. Combining SWNT and Graphene in Polymer Nanofibers: A Route to Unique Carbon Precursors for Electrochemical Capacitor Electrodes. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3077–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, E.; Moncada, M.; Gutiérrez, O.; Vargas, C.; Zapata, V. Characterization of polycaprolactone/rGO nanocomposite scaffolds obtained by electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 103, 109773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, B.S.; Stalin, T. Cerium oxide and peppermint oil loaded polyethylene oxide/graphene oxide electrospun nanofibrous mats as antibacterial wound dressings. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 21, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, D.; Kandasubramanian, B. Progress in the Development of Intrinsically Conducting Polymer Composites as Biosensors. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1800561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avossa, J.; Paolesse, R.; Di Natale, C.; Zampetti, E.; Bertoni, G.; De Cesare, F.; Scarascia-Mugnozza, G.; Macagnano, A. Electrospinning of Polystyrene/Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanofibers Doped with Porphyrin and Graphene for Chemiresistor Gas Sensors. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, A.; Jiang, X.; Hong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Zhu, D. Recent Developments Concerning the Dispersion Methods and Mechanisms of Graphene. Coatings 2018, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Ruan, K.; Kong, J.; Dong, M.; Zhang, J.; Gu, J.; Guo, Z. Reduced Graphene Oxide Heterostructured Silver Nanoparticles Significantly Enhanced Thermal Conductivities in Hot-Pressed Electrospun Polyimide Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25465–25473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, L.A.; Scagion, V.P.; Migliorini, F.L.; Mattoso, L.H.; Correa, D.S. Electrospinning-based (bio)sensors for food and agricultural applications: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Wei, G. Recent advances in the synthesis and applications of graphene–polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 6107–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.; Khalil, A.; Karim, S.; Osman, T.A.; Khattab, A. High performance of PAN/GO-ZnO composite nanofibers for photocatalytic degradation under visible irradiation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 96, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.Y.; Chen, N.; Peng, S.; Li, L.; Tian, L.; Thakor, N.; Ramakrishna, S. Polymer-based composites by electrospinning: Preparation & functionalization with nanocarbons. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 86, 40–84. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafov, S.D.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Seydibeyoğlu, M.Ö. Fabrication of conductive Lignin/PAN carbon nanofibers with enhanced graphene for the modified electrodes. Carbon 2019, 147, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzi, M.E.; Golestaneh, S.I.; Kamali, M.; Karimi, G. Thermal and electrical performance analysis of co-electrospun-electrosprayed PCM nanofiber composites in the presence of graphene and carbon fiber powder. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.K.; Singh, E.; Singh, P.; Meyyappan, M.; Singh Nalwa, H. A review on graphene-based nanocomposites for electrochemical and fluorescent biosensors. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8778–8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, C. Advanced electrospun nanomaterials for highly efficient electrocatalysis. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 3012–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, H.; Zhong, J.; Song, L.; Wu, J.; Su, W. Graphene field emitters: A review of fabrication, characterization and properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 220, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.; Jung, I.H.; An, J.H.; Yang, D.; Velamakanni, A.; Piner, R.; Colombo, L.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties of Large-Area Graphene Films. ECS Trans. 2009, 19, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J. Graphene−metal particle nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. 2008, 112, 19841–19845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Yoon, H.; Kwon, O.S. Graphene-based nanoelectronic biosensors. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 38, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.-E.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haar, S.; Ciesielski, A.; Clough, J.; Yang, H.; Mazzaro, R.; Richard, F.; Conti, S.; Merstorf, N.; Cecchini, M.; Morandi, V.; et al. A Supramolecular Strategy to Leverage the Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Graphene in the Presence of Surfactants: Unraveling the Role of the Length of Fatty Acids. Small 2015, 11, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Ahn, K.J.; Lee, Y.; Noh, S.; Yoon, H. Free-standing, multilayered graphene/polyaniline-glue/graphene nanostructures for flexible, solid-state electrochemical capacitor application. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1500117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bai, H.; Lu, G.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Flexible graphene films via the filtration of water-soluble noncovalent functionalized graphene sheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5856–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilescu, A.; Hayat, A.; Gáspár, S.; Marty, J.-L. Advantages of Carbon Nanomaterials in Electrochemical Aptasensors for Food Analysis. Electroanalysis 2017, 30, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumera, M. Graphene-based nanomaterials and their electrochemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4146–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, A.; Chua, C.K.; Bonanni, A.; Pumera, M. Electrochemistry of Graphene and Related Materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7150–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumera, M. Electrochemistry of graphene: New horizons for sensing and energy storage. Chem. Rec. 2009, 9, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pumera, M. Electrochemistry of graphene, graphene oxide and other graphenoids: Review. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 36, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.; Yuan, Z.; Benck, J.D.; Rajan, A.G.; Chu, X.S.; Wang, Q.H.; Strano, M.S. Current and future directions in electron transfer chemistry of graphene. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4530–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, D.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Wu, X.; Yang, B. CVD graphene as an electrochemical sensing platform for simultaneous detection of biomolecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Bukkitgar, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.; Reddy, K.R.; Shetti, N.P.; Reddy, C.V.; Sadhu, V.; Naveen, S.; Pratibha. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors Based on Graphene Functionalized with Metal Oxide Nanostructures for Healthcare Applications. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 5322–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Leng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Fu, L. Synthesis of graphene and related two-dimensional materials for bioelectronics devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprinkle, M.; Ruan, M.; Hu, Y.; Hankinson, J.H.; Rubio-Roy, M.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Berger, C.; De Heer, W.A. Scalable templated growth of graphene nanoribbons on SiC. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.E.; Han, T.H.; Hwang, J.W.; Jeon, S.; Choi, S.-Y.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, W.J.; Ruoff, R.S.; Kim, S.O. Versatile Carbon Hybrid Films Composed of Vertical Carbon Nanotubes Grown on Mechanically Compliant Graphene Films. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.; An, J.; Kim, S.; Nah, J.; Yang, D.; Piner, R.; Velamakanni, A.; Jung, I.; Tutuc, E.; et al. Large-Area Synthesis of High-Quality and Uniform Graphene Films on Copper Foils. Science 2009, 324, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C. Review of Chemical Vapor Deposition of Graphene and Related Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, I.; Wesolowski, M.; Jozwik, I.; Lukosius, M.; Lupina, G.; Dabrowski, P.; Baranowski, J.M.; Strupinski, W. Graphene growth on Ge(100)/Si(100) substrates by CVD method. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowski, J.; Lippert, G.; Avila, J.; Baringhaus, J.; Colambo, I.; Dedkov, Y.; Herziger, F.; Lupina, G.; Maultzsch, J.; Schaffus, T.; et al. Understanding the growth mechanism of graphene on Ge/Si(001) surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baraton, L.; He, Z.B.; Lee, C.S.; Cojocaru, C.S.; Châtelet, M.; Maurice, J.-L.; Lee, Y.H.; Pribat, D. On the mechanisms of precipitation of graphene on nickel thin films. Eur. Lett. 2011, 96, 46003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Losurdo, M.; Giangregorio, M.M.; Capezzuto, P.; Bruno, G. Graphene CVD growth on copper and nickel: Role of hydrogen in kinetics and structure. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 20836–20843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Niu, T.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, W. Elementary Process for CVD Graphene on Cu(110): Size-selective Carbon Clusters. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, T.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Chen, W. Growth Intermediates for CVD Graphene on Cu(111): Carbon Clusters and Defective Graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8409–8414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, D.; Ji, Q.; Gao, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Single and Polycrystalline Graphene on Rh(111) Following Different Growth Mechanisms. Small 2013, 9, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordatos, A.; Kelaidis, N.; Giamini, S.A.; Marquez-Velasco, J.; Xenogiannopoulou, E.; Tsipas, P.; Kordas, G.; Dimoulas, A. AB stacked few layer graphene growth by chemical vapor deposition on single crystal Rh(1 1 1) and electronic structure characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 369, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lohe, M.R.; Müllen, K.; Feng, X. New-Generation Graphene from Electrochemical Approaches: Production and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6213–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Peng, H.; Xia, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, K.; Yin, F.; Yuan, W. Highly Sensitive, Selective, and Flexible NO(2) Chemiresistors Based on Multilevel Structured Three-Dimensional Reduced Graphene Oxide Fiber Scaffold Modified with Aminoanthroquinone Moieties and Ag Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9309–9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cote, L.J.; Kim, F.; Yuan, W.; Shull, K.R.; Huang, J. Graphene Oxide Sheets at Interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8180–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Li, S.; Thomas, A.; Kotov, N.A.; Haag, R. Functional Graphene Nanomaterials Based Architectures: Biointeractions, Fabrications, and Emerging Biological Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 1826–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, M.; Bradley, S.J.; Nann, T. Graphene Quantum Dots. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhahebi, A.M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Saheed, M.S.M. Graphene impregnated electrospun nanofiber sensing materials: A comprehensive overview on bridging laboratory set-up to industry. Nano Converg. 2020, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Narita, A.; Müllen, K. Precision synthesis versus bulk-scale fabrication of graphenes. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 2, 0100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Guan, H.-Y.; Argueta, M.; Yue, Y. Free-standing nitrogen-doped graphene-carbon nanofiber composite mats: Electrospinning synthesis and application as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 3793–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleeton, C.; Keirouz, A.; Chen, X.; Radacsi, N. Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery and Biosensing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4183–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YDing, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Ezazi, N.Z.; Liu, D.; Santos, H.A. Electrospun Fibrous Architectures for Drug Delivery, Tissue Engineering and Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 29, 1802852. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, S.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, S.; Fang, H.; Song, Y.; Duan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, H. Nanofibers with diameter below one nanometer from electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4794–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.T. Nanofiber technology: Current status and emerging developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Aliheidari, N.; Aliahmad, N.; Agarwal, M.; Dalir, H. Electrospun Nanofibers for Label-Free Sensor Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydogdu, A.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. A novel electrospun hydroxypropyl methylcellulose/polyethylene oxide blend nanofibers: Morphology and physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathani, A.; Sharma, C.S. Electrospun Mesoporous Poly(Styrene-Block-Methyl- Methacrylate) Nanofibers as Biosensing Platform: Effect of Fibers Porosity on Sensitivity. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 2138–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, D.; Mikšíček, J.; Wacławek, S.; Torres-Mendieta, R.; Padil, V.V.; Černík, M. Production of electrospun nanofibers based on graphene oxide/gum Arabic. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 124, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Lu, X.; Wang, C. Electrospinning based all-nano composite materials: Recent achievements and perspectives. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.; Wei, G.; Su, Z. Electrospinning design of functional nanostructures for biosensor applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T. Graphene-based nano composites and their applications. A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavagione, H.J.; Gómez-Fatou, M.A.; Shuttleworth, P.S.; Ellis, G.J. New Perspectives on Graphene/Polymer Fibers and Fabrics for Smart Textiles: The Relevance of the Polymer/Graphene Interphase. Front. Mater. 2018, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Liu, A.; Shi, G. Supercapacitors Based on Flexible Graphene/Polyaniline Nanofiber Composite Films. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.A.; Choi, H.-J.; Shin, Y.R.; Chang, D.W.; Dai, L.; Baek, J.-B. Polyaniline-Grafted Reduced Graphene Oxide for Efficient Electrochemical Supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.; Samulski, E.T. Synthesis of Water Soluble Graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Bai, H.; Shi, G. High-performance supercapacitor electrodes based on graphene hydrogels modified with 2-aminoanthraquinone moieties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 11193–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q. Ultrasensitive analysis of kanamycin residue in milk by SERS-based aptasensor. Talanta 2019, 197, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahatiya, P.; Badhulika, S. One-step in situ synthesis of single aligned graphene–ZnO nanofiber for UV sensing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82481–82487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Ding, B.; Cui, S. Electrospinning in Situ Synthesis of Graphene-Doped Porous Copper Indium Disulfide/Carbon Composite Nanofibers for Highly Efficient Counter Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Electrochimica Acta 2016, 215, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-L.; Baji, A.; Tien, H.-W.; Yang, Y.-K.; Yang, S.-Y.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Liu, H.-Y.; Mai, Y.-W.; Wang, N.-H. Self-assembly of graphene onto electrospun polyamide 66 nanofibers as transparent conductive thin films. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 475603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, M.V.; Steinert, B.W.; Thomas, V.; Dean, D.R.; Abdalla, M.A.; Price, G.; Janowski, G.M. Morphology and mechanical properties of Nylon 6/MWNT nanofibers. Polymer 2007, 48, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasso-Ramos, L.; Ojeda-Hernández, A.; Guerrero-Bermea, C.; García-Gómez, N.; Manriquez, J.; Sepúlveda-Guzmán, S.; Cruz-Silva, R. Simultaneous intercalated assembly of mesostructured hybrid carbon nanofiber/reduced graphene oxide and its use in electrochemical sensing. Nanotechnology 2018, 30, 025601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-Q.; Wu, F.; Jin, L.; Wang, T.; Dong, W.; Zheng, J. Graphene Nanofibrous Foam Designed as an Efficient Oil Absorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 3000–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soikkeli, M.; Kurppa, K.; Kainlauri, M.; Arpiainen, S.; Paananen, A.; Gunnarsson, D.; Joensuu, J.J.; Laaksonen, P.; Prunnila, M.; Linder, M.B.; et al. Graphene Biosensor Programming with Genetically Engineered Fusion Protein Monolayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8257–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Wei, G.; Su, Z. One-Step Synthesis of Large-Scale Graphene Film Doped with Gold Nanoparticles at Liquid–Air Interface for Electrochemistry and Raman Detection Applications. Langmuir 2014, 30, 8980–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beachley, V.; Wen, X. Polymer nanofibrous structures: Fabrication, biofunctionalization, and cell interactions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 868–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, H.; Yong, T.; Chan, C.; Ramakrishna, S. Enhancement of neurite outgrowth using nano-structured scaffolds coupled with laminin. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3574–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, C.S.; Murali, G.; Reddy, A.S.; Park, S.; In, I. GO incorporated SnO2 nanotubes as fast response sensors for ethanol vapor in different atmospheres. J. Alloy Compd. 2020, 813, 152251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, G.; Wang, G.; Mishra, P.; Jia, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, P.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z. Preparation and electrochemical studies of electrospun phosphorus doped porous carbon nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6898–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motsoeneng, R.G.; Kortidis, I.; Ray, S.S.; Motaung, D.E. Designing SnO2 Nanostructure-Based Sensors with Tailored Selectivity toward Propanol and Ethanol Vapors. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 13696–13709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, S.; Lu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yao, Q. Electrospun fibers and their application in drug controlled release, biological dressings, tissue repair, and enzyme immobilization. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25712–25729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanjwal, M.A.; Lo, K.K.S.; Leung, W.W.-F. Graphene composite nanofibers as a high-performance photocatalyst for environmental remediation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjwal, M.A.; Leung, W.W.-F. Titanium based composite-graphene nanofibers as high-performance photocatalyst for formaldehyde gas purification. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 5617–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjwal, M.A.; Leung, W.W.-F. Electrospun Nanofibers of p-Type CuO/n-type TZB-Gr Heterojunctions with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 232, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, H.; Azadi, S.; Hatamie, S.; Zomorrod, M.S.; Ashtari, K.; Soleimani, M.; Hosseinzadeh, S. Fabrication of graphene-silver/polyurethane nanofibrous scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 2086–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Lin, H.L.; He, F.X.; Wang, L.; Wei, X.W.; Chang, I.-T.; Sancaktar, E. Processing and assessment of high-performance poly(butylene terephthalate) nanocomposites reinforced with microwave exfoliated graphite oxide nanosheets. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 1406–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, C.; Yu, W.; Zhou, C. Effect of thermally reduced graphite oxide (TrGO) on the polymerization kinetics of poly (butylene terephthalate)(pCBT)/TrGO nanocomposites prepared by in situ ring-opening polymerization of cyclic butylene terephthalate. Polymer 2013, 54, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Tang, G.; Zhang, H.-B.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Yavari, F.; Koratkar, N.; Lim, S.-H.; Lee, M.-W. In situ thermal reduction of graphene oxide for high electrical conductivity and low percolation threshold in polyamide 6 nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hou, L.; Peng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X. Fabrication and characterization of polyamide 6-functionalized graphene nanocomposite fiber. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 8052–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoonessi, M.; Shi, Y.; Scheiman, D.A.; Lebron-Colon, M.; Tigelaar, D.M.; Weiss, R.A.; Meador, M.A. Graphene Polyimide Nanocomposites; Thermal, Mechanical, and High-Temperature Shape Memory Effects. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7644–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, I.-H.; Chang, J.-C.; Huang, S.-L.; Tsai, M.-H. Enhanced thermal conductivity and dimensional stability of flexible polyimide nanocomposite film by addition of functionalized graphene oxide. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, M.; Pandele, A.M.; Crica, L.; Pilan, L. Improving the thermal and mechanical properties of polysulfone by incorporation of graphene oxide. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 59, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, R.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mousavi, S.A.; Rashidi, A.; Jafari, A.; Nazmara, S. Fabrication and characterization of a polysulfone-graphene oxide nanocomposite membrane for arsenate rejection from water. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoonessi, M.; Gaier, J.R. Highly Conductive Multifunctional Graphene Polycarbonate Nanocomposites. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 7211–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedler, G.; Antunes, M.; Realinho, V.; Velasco, J. Thermal stability of polycarbonate-graphene nanocomposite foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, M.; Sadeghianmaryan, A.; Rajabinejad, H.; Nasherolahkam, S.; Chen, X. Development of highly pH-sensitive hybrid membranes by simultaneous electrospinning of amphiphilic nanofibers reinforced with graphene oxide. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-I.; Hwang, B.-U.; Meeseepong, M.; Hanif, A.; Ramasundaram, S.; Trung, T.Q.; Lee, N.-E. Stretchable and transparent nanofiber-networked electrodes based on nanocomposites of polyurethane/reduced graphene oxide/silver nanoparticles with high dispersion and fused junctions. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3916–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, K.; Guo, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, M.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. Improved thermal conductivities in polystyrene nanocomposites by incorporating thermal reduced graphene oxide via electrospinning-hot press technique. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdali, H.; Ajji, A. Preparation of Electrospun Nanocomposite Nanofibers of Polyaniline/Poly(methyl methacrylate) with Amino-Functionalized Graphene. Polymers 2017, 9, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozutok, M.; Sadhu, V.; Sasmazel, H.T. Development of poly (vinyl alcohol)(PVA)/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) electrospun mats. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 4292–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavinatto, A.; Mercante, L.A.; Facure, M.H.M.; Pena, R.B.; Sanfelice, R.C.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. Ultrasensitive biosensor based on polyvinylpyrrolidone/chitosan/reduced graphene oxide electrospun nanofibers for 17α—Ethinylestradiol electrochemical detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, A.; Jia, X.; Ho, J.; Nezich, D.; Son, H.; Bulovic, V.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Kong, J. Large area, few-layer graphene films on arbitrary substrates by chemical vapor deposition. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Delgado, J.; Romo-Herrera, J.M.; Jia, X.; Cullen, D.A.; Muramatsu, H.; Kim, Y.A.; Hayashi, T.; Ren, Z.; Smith, D.J.; Okuno, Y.; et al. Bulk Production of a New Form of sp2 Carbon: Crystalline Graphene Nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Xu, X.; Park, J.-S.; Zheng, Y.; Balakrishnan, J.; Lei, T.; Kim, H.R.; Song, Y.I. Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernaez, M.; Zamarreño, C.; Melendi-Espina, S.; Bird, L.R.; Mayes, A.G.; Arregui, F.J. Optical Fibre Sensors Using Graphene-Based Materials: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Duan, Y. Application of Graphene-Based Materials for Detection of Nitrate and Nitrite in Water—A Review. Sensors 2019, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuriya, B.D.; Altintas, Z. Applications of Graphene Quantum Dots in Biomedical Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Debliquy, M.; Lahem, D.; Yan, Y.; Raskin, J.-P. A Review on Functionalized Graphene Sensors for Detection of Ammonia. Sensors 2021, 21, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revanappa, S.K.; Soni, I.; Siddalinganahalli, M.; Jayaprakash, G.K.; Flores-Moreno, R.; Nanjegowda, C.B. A Fukui Analysis of an Arginine-Modified Carbon Surface for the Electrochemical Sensing of Dopamine. Materials 2022, 15, 6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrati, H.; Mamoory, R.S.; Dabir, F.; Le, D.Q.S.; Bünger, C.E.; Perez, M.C.; Rodríguez, M.A. Effects of hydrothermal pressure on in situ synthesis of 3D graphene- hydroxyapatite nano structured powders. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Wu, H.-H.; Jeng, Y.-C.; Liang, W.-Z. Electrospun graphene nanosheet-filled poly (trimethylene terephthalate) composite fibers: Effects of the graphene nanosheet content on morphologies, electrical conductivity, crystallization behavior, and mechanical properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, F.; He, Y.; She, Y.; Hong, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, T.; I-Aty, A.A.E. A disposable electrochemical sensor based on electrospinning of molecularly imprinted nanohybrid films for highly sensitive determination of the organotin acaricide cyhexatin. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macagnano, A.; Zampetti, E.; Kny, E. Electrospinning for High Performance Sensors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PZhang, P.; Zhao, X.; Ji, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Wen, X.; Li, J.; Su, Z.; Wei, G. Electrospinning graphene quantum dots into a nanofibrous membrane for dual-purpose fluorescent and electrochemical biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. 2015, 3, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Deng, D.; Si, X.; Ding, Y.; He, H.; Luo, L.; Wang, Z. Electrospun graphene decorated MnCo2O4 composite nanofibers for glucose biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dhahebi, A.M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Saheed, M.S.M.; Mustapha, M. Electrospun cellulose acetate-doped 3D-graphene nanofibre for enhanced transduction of ochratoxin A determination. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2022, 45, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhoyan, K.A.; Contryman, A.W.; Silcox, J.; Stewart, D.A.; Eda, G.; Mattevi, C.; Miller, S.; Chhowalla, M. Atomic and electronic structure of graphene-oxide. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, G. Assembly of chemically modified graphene: Methods and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3311–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, S.H.; Gong, C.; Robertson, A.W.; Warner, J.H.; Grossman, J.C. Chemistry and Structure of Graphene Oxide via Direct Imaging. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7515–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and graphene oxide: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.C. Applications of Graphene and Graphene-Oxide Based Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Fang, Y. Biomedical Applications of Graphene; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 215–232. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi, M.; Rahmani, F.; Nouranian, S. Molecular simulation of pH-dependent diffusion, loading, and release of doxorubicin in graphene and graphene oxide drug delivery systems. J. Mater. Chem. 2016, 4, 7441–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, S.D.; Bhaskar, R.; Singh, H.; Yadav, I.; Gupta, M.K.; Mishra, N.C. Development of a nanocomposite scaffold of gelatin–alginate–graphene oxide for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Bahrami, S.H.; Ranjbar-Mohammadi, M.; Milan, P. Smart electrospun nanofibers containing PCL/gelatin/graphene oxide for application in nerve tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 103, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmoradi, S.; Golzar, H.; Hashemi, M.; Mansouri, V.; Omidi, M.; Yazdian, F.; Yadegari, A.; Tayebi, L. Optimizing the nanostructure of graphene oxide/silver/arginine for effective wound healing. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 475101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.R.U.; Augustine, R.; Zahid, A.A.; Ahmed, R.; Tariq, M.; Hasan, A. Reduced Graphene Oxide Incorporated GelMA Hydrogel Promotes Angiogenesis for Wound Healing Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9603–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, X.; Mi, H.-Y.; Peng, X.-F.; Turng, L.-S. Biocompatible, self-healing, highly stretchable polyacrylic acid/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogel sensors via mussel-inspired chemistry. Carbon 2018, 136, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, V.; Papi, M.; Conti, C.; Ciasca, G.; Maulucci, G.; De Spirito, M. The future development of bacteria fighting medical devices: The role of graphene oxide. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2016, 13, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiteru, O.; Sultan, T.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, Y.B.; Hong, R.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.; Suh, Y.J.; Ju, H.W.; Lee, O.J.; et al. A 3D Printable Electroconductive Biocomposite Bioink Based on Silk Fibroin-Conjugated Graphene Oxide. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 6873–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.M.; Paino, I.M.M.; Santos, F.A.; Scagion, V.P.; Correa, D.S.; Zucolotto, V. Fabrication of random and aligned electrospun nanofibers containing graphene oxide for skeletal muscle cells scaffold. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, S.; Nowroozi, N.; Nouralishahi, A.; Shayeh, J.S. Electrospun poly-caprolactone/graphene oxide/quercetin nanofibrous scaffold for wound dressing: Evaluation of biological and structural properties. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ali, S.F.; Dervishi, E.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Casciano, D.; Biris, A.S. Cytotoxicity Effects of Graphene and Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes in Neural Phaeochromocytoma-Derived PC12 Cells. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kim, J.-H. Synthesis, toxicity, biocompatibility, and biomedical applications of graphene and graphene-related materials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1927–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Wong, H.M.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Tjong, S.C. Novel Electrospun Polylactic Acid Nanocomposite Fiber Mats with Hybrid Graphene Oxide and Nanohydroxyapatite Reinforcements Having Enhanced Biocompatibility. Polymers 2016, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jun, I.; Han, H.-S.; Edwards, J.R.; Jeon, H. Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: Viewpoints on Architecture and Fabrication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Biomimetic porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 80, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.A.; Vig, K.; Baganizi, D.R.; Sahu, R.; Dixit, S.; Dennis, V.; Singh, S.R.; Pillai, S.R. Future Prospects for Scaffolding Methods and Biomaterials in Skin Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisson, K.; Zhang, C.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Fiber diameters control osteoblastic cell migration and differentiation in electrospun gelatin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part 2010, 94A, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Carlson, M.A.; Gombart, A.F.; Reilly, D.A.; Xie, J. Recent advances in electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, M. Electrospun multicomponent and multifunctional nanofibrous bone tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Miszuk, J.M.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Fong, H. Electrospun Polycaprolactone 3D Nanofibrous Scaffold with Interconnected and Hierarchically Structured Pores for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2015, 4, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmandi, M.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E.; Ghiaseddin, A.; Ganji, F. Skeletal muscle regeneration via engineered tissue culture over electrospun nanofibrous chitosan/PVA scaffold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part 2016, 104, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, Y.; Lekakou, C.; Labeed, F.; Tomlins, P. Smooth muscle tissue engineering in crosslinked electrospun gelatin scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part 2016, 104, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Yang, T.; Han, B. Electrospun fibrous silk fibroin/poly(L-lactic acid) scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 13, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.; Columbus, S.; Krishnan, L. Alteration of Electrospun Scaffold Properties by Silver Nanoparticle Incorporation: Evaluation for Blood Vessel Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part 2015, 21, S239–S240. [Google Scholar]
- Vatankhah, E.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Semnani, D.; Razavi, S.; Morshed, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun tecophilic/gelatin nanofibers with potential for small diameter blood vessel tissue engineering. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamadi, F.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S.; Nourani, M.R.; Derakhshan, M.A.; Goodarzi, V.; Nazockdast, M.S.; Farokhi, M.; Tajerian, R.; Majidi, R.F.; Ai, J. Electrospun nerve guide scaffold of poly(ε-caprolactone)/collagen/nanobioglass: An in vitro study in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part 2017, 105, 1960–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, B.K.; Kim, J.I.; Ko, S.W.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Electrodeless coating polypyrrole on chitosan grafted polyurethane with functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes electrospun scaffold for nerve tissue engineering. Carbon 2018, 136, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaina-Lorenzo, E.; Martínez-Ramos, C.; Monleón-Pradas, M.; Herrera-Kao, W.; Cauich-Rodríguez, J.V.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M. Electrospun polycaprolactone/chitosan scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering: Physicochemical characterization and Schwann cell biocompatibility. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 12, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidun, A.; Firoozabady, A.S.; Moharrami, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Haghighipour, N.; Bonakdar, S.; Faghihi, S. Graphene oxide incorporated polycaprolactone/chitosan/collagen electrospun scaffold: Enhanced osteogenic properties for bone tissue engineering. Artif. Organs 2019, 43, E264–E281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.J.; Pillai, S.C.; Hehir, S.; McAfee, M.; Breen, A. Biomedical Applications of Electrospun Graphene Oxide. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1278–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.O.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Shin, Y.C.; Huh, J.B.; Bae, J.-H.; Kang, S.H.; Hong, S.W.; Kim, B.; Yang, D.J.; et al. Graphene oxide-coated guided bone regeneration membranes with enhanced osteogenesis: Spectroscopic analysis and animal study. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2016, 51, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasadh, S.; Suresh, S.; Wong, R. Osteogenic Potential of Graphene in Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Materials 2018, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, A.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, D.; Zeng, D.; Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Jiang, X. Enhanced bone regeneration of the silk fibroin electrospun scaffolds through the modification of the graphene oxide functionalized by BMP-2 peptide. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.F.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, J.; Yao, Y.; Ahmad, Z.; Chang, M.W. A novel core-shell nanofiber drug delivery system intended for the synergistic treatment of melanoma. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, S.; Shafiei, S.S.; Asadi-Eydivand, M.; Ardeshir, M.; Solati-Hashjin, M. Graphene oxide-enriched poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun nanocomposite scaffold for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2017, 32, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Teyssier, C.; Balme, S.; Miele, P.; Kalkura, N.; Cavaillès, V.; Bechelany, M. Design of graphene oxide/gelatin electrospun nanocomposite fibers for tissue engineering applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 109150–109156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safikhani, M.M.; Zamanian, A.; Ghorbani, F. Synergistic effects of retinoic acid and graphene oxide on the physicochemical and in-vitro properties of electrospun polyurethane scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. e-Polymers 2017, 17, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, B.; Mondal, B.; Kumar, S.; Sarkar, S. Myoblast differentiation and protein expression in electrospun graphene oxide (GO)-poly (ε-caprolactone, PCL) composite meshes. Mater. Lett. 2016, 182, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Bai, H.; Zhu, J.; Niu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Bai, Y. Enhanced cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in electrospun PLGA/hydroxyapatite nanofibre scaffolds incorporated with graphene oxide. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, F.; Zamanian, A.; Aidun, A. Bioinspired polydopamine coating-assisted electrospun polyurethane-graphene oxide nanofibers for bone tissue engineering application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrella, A.; Tedeschi, G.; Giannoni, P.; Lagazzo, A.; Sbrana, F.; Barberis, F.; Quarto, R.; Puglisi, F.; Scaglione, S. “Green-reduced” graphene oxide induces in vitro an enhanced biomimetic mineralization of polycaprolactone electrospun meshes. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 93, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; He, J.; Sang, F.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Cui, S.; Ding, B. Enhanced bone formation in electrospun poly(l-lactic-co-glycolic acid)–tussah silk fibroin ultrafine nanofiber scaffolds incorporated with graphene oxide. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 62, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. Promoting tendon to bone integration using graphene oxide-doped electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibrous membrane. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalvuran, H.; Elçin, A.E.; Elçin, Y.M. Nanofibrous silk fibroin/reduced graphene oxide scaffolds for tissue engineering and cell culture applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananth, K.P.; Guo, B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Zhou, P.; Bai, J. Investigation of biphasic calcium phosphate (BCp)/polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVp)/graphene oxide (GO) composite for biomedical implants. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 24413–24423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, G.; Lin, S.; Tian, T.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, S.; Xue, C.; Ma, W.; Cai, X.; et al. Electrospun Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)/Graphene Oxide Scaffold: Enhanced Properties and Promoted in Vivo Bone Repair in Rats. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42589–42600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanoska-Dacikj, A.; Bogoeva-Gaceva, G.; Krumme, A.; Tarasova, E.; Scalera, C.; Stojkovski, V.; Gjorgoski, I.; Ristoski, T. Biodegradable polyurethane/graphene oxide scaffolds for soft tissue engineering: In vivo behavior assessment. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 69, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghianmaryan, A.; Karimi, Y.; Naghieh, S.; Sardroud, H.A.; Gorji, M.; Chen, X. Electrospinning of Scaffolds from the Polycaprolactone/Polyurethane Composite with Graphene Oxide for Skin Tissue Engineering. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 191, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Park, G.T.; Han, S.S. Electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/reduced graphene oxide nanofibrous scaffolds for skin tissue engineering, Colloids and surfaces. Biointerfaces 2020, 191, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampi, S.; Thekkuveettil, A.; Muthuvijayan, V.; Parameswaran, R. Accelerated outgrowth of neurites on graphene oxide-based hybrid electrospun fibro-porous polymeric substrates. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2160–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaz, A.; Li, X.; Gough, J.E.; Blaker, J.J. Graphene oxide and electroactive reduced graphene oxide-based composite fibrous scaffolds for engineering excitable nerve tissue. Mater. Sci. Eng. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 119, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depan, D.; Shah, J.; Misra, R. Controlled release of drug from folate-decorated and graphene mediated drug delivery system: Synthesis, loading efficiency, and drug release response. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 31, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulzadeh, M.; Namazi, H. Carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene oxide bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads as anticancer drug carrier agent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Liu, J.; He, W.; Li, Z.; Luan, Y.; Song, Y.; Garg, S. Folic acid-grafted bovine serum albumin decorated graphene oxide: An efficient drug carrier for targeted cancer therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabakaran, S.; Jeyaraj, M.; Nagaraj, A.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Rajan, M. Polymethyl methacrylate–ovalbumin @ graphene oxide drug carrier system for high anti-proliferative cancer drug delivery. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui-Hong, X.; Peng-Gang, R.; Jian, H.; Fang, R.; Lian-Zhen, R.; Zhen-Feng, S. Preparation and properties of graphene oxide-regenerated cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel with pH-sensitive behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wei, S.; Ge, X.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, F.; Shen, J. Combination of chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy using graphene oxide as drug delivery system. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Biol. 2014, 135, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Zhou, J.-H.; Jiang, H.-J.; Shen, J. Graphene Oxide Noncovalent Photosensitizer and Its Anticancer Activity In Vitro. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 12084–12091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Q.; Xing, D. A graphene oxide based smart drug delivery system for tumor mitochondria-targeting photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3530–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.-L.; Bao, H.-C.; Hou, X.-L.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.-G.; Gu, M. Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles as a Nonbleaching Optical Probe for Two-Photon Luminescence Imaging and Cell Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinbasak, I.; Jijie, R.; Barras, A.; Golba, B.; Sanyal, R.; Bouckaert, J.; Drider, D.; Bilyy, R.; Dumych, T.; Paryzhak, S. Reduced graphene-oxide-embedded polymeric nanofiber mats: An “on-demand” photothermally triggered antibiotic release platform. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41098–41106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Xu, G.; Kharaghani, D.; Nishino, M.; Song, K.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.S. Electrospun tri-layered zein/PVP-GO/zein nanofiber mats for providing biphasic drug release profiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, P.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zeng, S. Regulation of biphasic drug release behavior by graphene oxide in polyvinyl pyrrolidone/poly(ε-caprolactone) core/sheath nanofiber mats. Colloids Surf. Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, W.; Jiang, H.; Zimba, B.L.; Chen, L.; Wan, J.; Wu, Q. Preparation of poly (lactic acid)/graphene oxide nanofiber membranes with different structures by electrospinning for drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16619–16625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asadi, H.; Ghaee, A.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Mashak, A. Electrospun zein/graphene oxide nanosheet composite nanofibers with controlled drug release as antibacterial wound dressing. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 69, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, F.; Tamjid, E.; Behmanesh, M. Drug-eluting PCL/graphene oxide nanocomposite scaffolds for enhanced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 115, 111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Fu, J.; Ning, X.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Release of methylene blue from graphene oxide-coated electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds to modulate functions of neural progenitor cells. Acta Biomater. 2019, 88, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdoli, M.; Sadrjavadi, K.; Arkan, E.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Moradi, S.; Zangeneh, A.; Shahlaei, M.; Khaledian, S. Polyvinyl alcohol/Gum tragacanth/graphene oxide composite nanofiber for antibiotic delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, H.; Song, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Z. Graphene Oxide Incorporated PLGA Nanofibrous Scaffold for Solid Phase Gene Delivery into Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Guo, W.; Zheng, S.; Fu, C.; Ma, Y.; Pan, S.; Liu, Q.; Yang, X. Enhancement of neural stem cell survival, proliferation and differentiation by IGF-1 delivery in graphene oxide-incorporated PLGA electrospun nanofibrous mats. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8315–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ardeshirzadeh, B.; Anaraki, N.A.; Irani, M.; Rad, L.R.; Shamshiri, S. Controlled release of doxorubicin from electrospun PEO/chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite nanofibrous scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 48, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, S.; Moradkhani, M.; Beheshti, H.; Irani, M.; Aliabadi, M. Fabrication of chitosan/poly (lactic acid)/graphene oxide/TiO2 composite nanofibrous scaffolds for sustained delivery of doxorubicin and treatment of lung cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beri, P.; Matte, B.F.; Fattet, L.; Kim, D.; Yang, J.; Engler, A.J. Biomaterials to model and measure epithelial cancers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauro, N.; Scialabba, C.; Pitarresi, G.; Giammona, G. Enhanced adhesion and in situ photothermal ablation of cancer cells in surface-functionalized electrospun microfiber scaffold with graphene oxide. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Lin, Z.; Gan, D.; Cui, T.; Wan, M.; Yao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, H. Effect of Graphene Oxide Incorporation into Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Scaffolds on Breast Cancer Cell Culture. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Meng, Z. Melt electrospinning vs. solution electrospinning: A comparative study of drug-loaded poly (ε-caprolactone) fibres. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 74, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surucu, S.; Sasmazel, H.T. Development of core-shell coaxially electrospun composite PCL/chitosan scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, M.; Dadashpour, M.; Hejazi, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Behnam, B.; de la Guardia, M.; Shadjou, N.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Anti-bacterial activity of graphene oxide as a new weapon nanomaterial to combat multidrug-resistance bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 74, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majd, S.A.; Khorasgani, M.R.; Moshtaghian, S.J.; Talebi, A.; Khezri, M. Application of Chitosan/PVA Nano fiber as a potential wound dressing for streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Ikram, S. Chitosan based scaffolds and their applications in wound healing. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Ikram, S. Chitosan: Derivatives, Composites and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rieger, K.A.; Birch, N.P.; Schiffman, J.D. Designing electrospun nanofiber mats to promote wound healing—A review. J. Mater. Chem. 2013, 1, 4531–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poonguzhali, R.; Basha, S.K.; Kumari, V.S. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-PVP-nanocellulose composites for in-vitro wound dressing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Biodegradable core-shell electrospun nanofibers based on PLA and γ-PGA for wound healing. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 116, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golafshan, N.; Rezahasani, R.; Esfahani, M.T.; Kharaziha, M.; Khorasani, S. Nanohybrid hydrogels of laponite: PVA-Alginate as a potential wound healing material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K.; Kim, K. Study of antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide using Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, E.; Miyaji, H.; Kato, A.; Takita, H.; Iwanaga, T.; Momose, T.; Ogawa, K.; Murakami, S.; Sugaya, T.; Kawanami, M. Graphene oxide scaffold accelerates cellular proliferative response and alveolar bone healing of tooth extraction socket. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2265. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, K.H.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Zou, X.; Woo, H.-M. Ultrasonicated graphene oxide enhances bone and skin wound regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 94, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Gao, H.; Zhu, G.; Cao, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y. The preparation and characterization of polycaprolactone/graphene oxide biocomposite nanofiber scaffolds and their application for directing cell behaviors. Carbon 2015, 95, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kocbek, P.; Kristl, J. Critical attributes of nanofibers: Preparation, drug loading, and tissue regeneration. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Li, B. Biomimetic electrospun nanofibrous structures for tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, S.; Mohebbali, M.; Imani, R.; Mahmoodi, M.; Solouk, A. Electrospun Fibroin/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Mats: An Optimization for Potential Wound Dressing Applications. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-D.; Ma, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, H.-W. Improving antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of bioinspired electrospinning silk fibroin nanofibers modified by graphene oxide. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. High antibacterial performance of electrospinning silk fibroin/gelatin film modified with graphene oxide-sliver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, N.; Eslahi, N.; Mehdipour, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Akbari, M.; Samadikuchaksaraei, A.; Simchi, A. Temporary skin grafts based on hybrid graphene oxide-natural biopolymer nanofibers as effective wound healing substitutes: Pre-clinical and pathological studies in animal models. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. Electrospun chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide nanofibrous membrane with ciprofloxacin antibiotic drug for potential wound dressing application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senthil, R.; Berly, R.; Ram, T.B.; Gobi, N. Electrospun poly(vinyl) alcohol/collagen nanofibrous scaffold hybridized by graphene oxide for accelerated wound healing. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 41, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Du, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, H.; Deng, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Graphene oxide-modified electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous scaffolds with potential as skin wound dressings. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28826–28836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimba, B.L.; Wang, M.; Hao, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Xiong, G.; Wu, Q. Preparation of collagen/carboxylated graphene oxide nanofibrous membranes by electrospinning and their hemocompatibilities. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, E.; Eslami-Arshaghi, T.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Elahirad, E.; Jamalpoor, Z.; Hatamie, S.; Soleimani, M. The biomedical potential of cellulose acetate/polyurethane nanofibrous mats containing reduced graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites and curcumin: Antimicrobial performance and cutaneous wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, N.; Drago, S.E.; Cavallaro, G.; Giammona, G. Near-infrared, light-triggered, on-demand anti-inflammatories and antibiotics release by graphene oxide/elecrospun PCL patch for wound healing. C 2019, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Song, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. Enhanced antimicrobial activity and pH-responsive sustained release of chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide nanofibrous membrane loading with allicin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Wei, Y.; Zuo, M.; Li, R.; Ren, X.; Huang, T.-S. Antibacterial poly (ε-caprolactone) fibrous membranes filled with reduced graphene oxide-silver. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 603, 125186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghianmaryan, A.; Sardroud, H.A.; Allafasghari, S.; Yazdanpanah, Z.; Naghieh, S.; Gorji, M.; Chen, X. Electrospinning of polyurethane/graphene oxide for skin wound dressing and its in vitro characterization. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 35, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
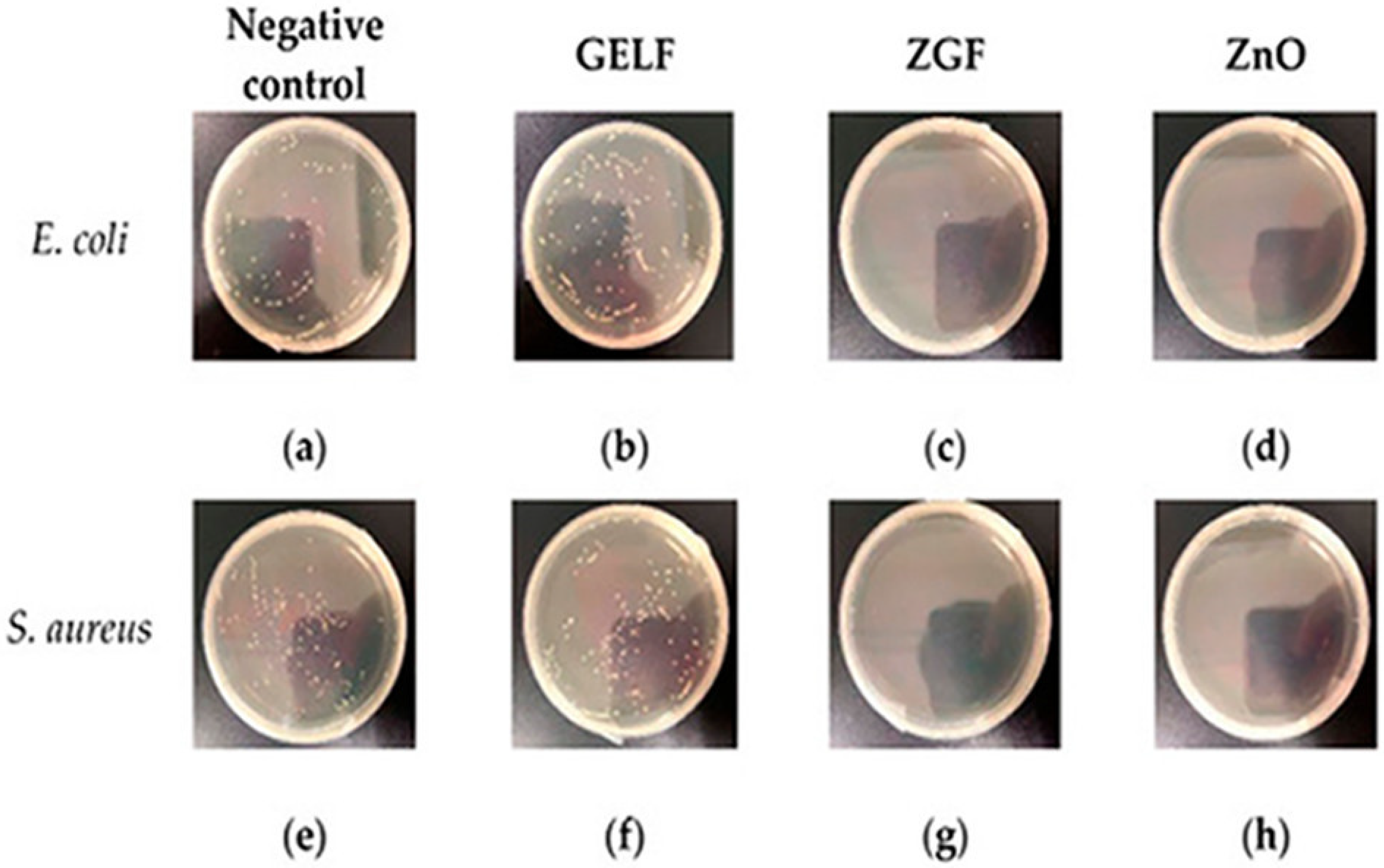
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, G. Preparation of electrospun gelatin mat with incorporated zinc oxide/graphene oxide and its antibacterial activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marín, J.A.T.; Londoño, S.R.; Delgado, J.; Porras, D.P.N.; Zapata, M.E.V.; Hernandez, J.H.M.; Valencia, C.H.; Tovar, C.D.G. Biocompatible and antimicrobial electrospun membranes based on nanocomposites of chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teo, A.J.; Mishra, A.; Park, I.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, W.-T.; Yoon, Y.-J. Polymeric biomaterials for medical implants and devices. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 454–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thampi, S.; Nandkumar, A.M.; Muthuvijayan, V.; Parameswaran, R. Differential adhesive and bioactive properties of the polymeric surface coated with graphene oxide thin film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4498–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Mi, H.-Y.; Salick, M.R.; Cordie, T.M.; Peng, X.-F.; Turng, L.-S. Electrospinning thermoplastic polyurethane/graphene oxide scaffolds for small diameter vascular graft applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 49, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Imani, R.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Bonakdar, S.; Solouk, A.; Fakhrzadeh, H. Studying the Potential Application of Electrospun Polyethylene Terephthalate/Graphene Oxide Nanofibers as Electroconductive Cardiac Patch. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1900187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, A.; Labbaf, S.; Karimzadeh, F.; Masaeli, E.; Esfahani, M.-H.N. Electroconductive Graphene-Containing Polymeric Patch: A Promising Platform for Future Cardiac Repair. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4214–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Yao, Q.; Yu, F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Sun, H.; Lin, J.; Fu, Y. Surface modified electrospun poly(lactic acid) fibrous scaffold with cellulose nanofibrils and Ag nanoparticles for ocular cell proliferation and antimicrobial application. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 111, 110767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, X. Electrospinning and emerging healthcare and medicine possibilities. APL Bioeng. 2020, 4, 030901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xiong, F.; Yao, B.; Du, Q.; Cao, J.; Qu, J.; Feng, W.; Yuan, H. Preparation and characterization of antibacterial dopamine-functionalized reduced graphene oxide/PLLA composite nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 18614–18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboamera, N.M.; Mohamed, A.; Salama, A.; Osman, T.; Khattab, A. Characterization and mechanical properties of electrospun cellulose acetate/graphene oxide composite nanofibers. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Rivera, L.M.; Hernández-Navarro, N.; Hoyos-Palacio, L.M.; de Coss, R.; Ornelas-Soto, N.E.; García-García, A. Doped graphene oxide functionalization strategy for synthesis of nanocomposite membranes: Electrospun coatings in biomedical field application. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.01820. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H.; Roh, J.; Park, C.Y.; Kim, M.W.; Shi, R.; Kailasa, S.K.; Park, T.J. Cu-nanoflower decorated gold nanoparticles-graphene oxide nanofiber as electrochemical biosensor for glucose detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 107, 110273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parandeh, S.; Kharaziha, M.; Karimzadeh, F. An eco-friendly triboelectric hybrid nanogenerators based on graphene oxide incorporated polycaprolactone fibers and cellulose paper. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, J.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Flexible electrically resistive-type strain sensors based on reduced graphene oxide-decorated electrospun polymer fibrous mats for human motion monitoring. Carbon 2018, 126, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Yu, S.-H. Nanoparticles meet electrospinning: Recent advances and future prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4423–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, N.; Sánchez-González, S.; Lázaro-Díez, M.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Urtiaga, A. Facile fabrication of poly (ε-caprolactone)/graphene oxide membranes for bioreactors in tissue engineering. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Peng, C.; Lv, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Protein Corona-Mediated Mitigation of Cytotoxicity of Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3693–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y. A comparative study of cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes, graphene oxide, and nanodiamond. Toxicol. Res. 2012, 1, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Su, X.; Liang, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, Q.; Shan, X.; Wan, J.; Hu, Z. Synthesis of polymer-functionalized nanoscale graphene oxide with different surface charge and its cellular uptake, biosafety and immune responses in Raw264.7 macrophages. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 90, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzynska, M.; Cendrowski, K.; Barylak, M.; Tkacz, M.; Piotrowska, K.; Kurzawski, M.; Mijowska, E.; Drozdzik, M. Comparative in vitro study of single and four layer graphene oxide nanoflakes—Cytotoxicity and cellular uptake. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 41, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Yang, S.-T.; Liu, J.-H.; Dong, E.; Wang, Y.; Cao, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. In vitro toxicity evaluation of graphene oxide on A549 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 200, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, A.; Panchakarla, L.S.; Chandran, P.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Rao, C.N.R.; Koyakutty, M. Differential nano-bio interactions and toxicity effects of pristine versus functionalized graphene. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2461–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, J.; Peng, C.; Hu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Distribution and biocompatibility studies of graphene oxide in mice after intravenous administration. Carbon 2011, 49, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.-H.; Lin, Y.-S.; Macosko, C.W.; Haynes, C.L. Cytotoxicity of Graphene Oxide and Graphene in Human Erythrocytes and Skin Fibroblasts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2607–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Yazdi, A.Z.; Han, X.X.; al Husaini, K.; Haime, J.; Waye, N.; Chen, P. Mechanistic insights into the cytotoxicity of graphene oxide derivatives in mammalian cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2247–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelin, M.; Fusco, L.; León, V.; Martín, C.; Criado, A.; Sosa, S.; Vázquez, E.; Tubaro, A.; Prato, M. Differential cytotoxic effects of graphene and graphene oxide on skin keratinocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liu, Z. Graphene in biomedicine: Opportunities and challenges. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Gu, Z.; Yan, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, A. Toxicological Evaluation of Graphene-Family Nanomaterials. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duch, M.C.; Budinger, G.R.S.; Liang, Y.T.; Soberanes, S.; Urich, D.; Chiarella, S.E.; Campochiaro, L.A.; Gonzalez, A.; Chandel, N.S.; Hersam, M.C.; et al. Minimizing Oxidation and Stable Nanoscale Dispersion Improves the Biocompatibility of Graphene in the Lung. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5201–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, C.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Liang, Q.; Meng, X. Effects of graphene oxide on the development of offspring mice in lactation period. Biomaterials 2015, 40, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Mansour, S.; Al-Wafi, R.; Menazea, A. Composition and design of nanofibrous scaffolds of Mg/Se- hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide @ ε-polycaprolactone for wound healing applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 7472–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandeh, S.; Kharaziha, M.; Karimzadeh, F.; Hosseinabadi, F. Triboelectric nanogenerators based on graphene oxide coated nanocomposite fibers for biomedical applications. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 385402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanjwal, M.A.; Ghaferi, A.A. Graphene Incorporated Electrospun Nanofiber for Electrochemical Sensing and Biomedical Applications: A Critical Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228661
Kanjwal MA, Ghaferi AA. Graphene Incorporated Electrospun Nanofiber for Electrochemical Sensing and Biomedical Applications: A Critical Review. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228661
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanjwal, Muzafar A., and Amal Al Ghaferi. 2022. "Graphene Incorporated Electrospun Nanofiber for Electrochemical Sensing and Biomedical Applications: A Critical Review" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228661
APA StyleKanjwal, M. A., & Ghaferi, A. A. (2022). Graphene Incorporated Electrospun Nanofiber for Electrochemical Sensing and Biomedical Applications: A Critical Review. Sensors, 22(22), 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228661




