Edge–Fog–Cloud Computing Hierarchy for Improving Performance and Security of NB-IoT-Based Health Monitoring Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The high delay because most NB-IoT frameworks do not incorporate delay-tolerant methodologies [19,20,21,22]. Additionally, the transmission time is affected by the large data size generated by the large number of terminals or by the healthcare applications, e.g., high-definition images [9,20], particularly because the NB-IoT depends on the UDP protocol for sending small-sized data in real time [20]. While a large data size is important for high throughput, caring about the delay is more important because healthcare is a critical domain.
- Proposing a hierarchical architecture consisting of edge, fog, and cloud computing for improving the performance of remote health monitoring.
- Utilizing the NB-IoT as the main communication medium between edge devices and other computing layers because the NB-IoT can cover a large number of devices in wide areas with minimum power consumption.
- Reducing the NB-IoT transmission delay by classifying and prioritizing data for minimizing congestion at base stations.
- Using efficient and accurate machine learning algorithms to support medical data analyses at each computing layer and to reduce the computation time.
- Investigating different IoT authentication protocols for securing the transmission over the NB-IoT and determining the most efficient one.
2. Related Work
2.1. Fog-Computing-Based Healthcare Monitoring
2.2. Edge-Computing-Based Healthcare Monitoring
| Objectives | Fog Computing Systems | Edge Computing Systems | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing transmission delay | examples | [12,13,14,29] | [9,26,30,31] |
| Limitations |
| ||
| Improving security | examples | [15,33,34,35] | [17,28,36,37] |
| limitations |
| ||
| Reducing power consumption | examples | [10,16,38,39] | [11,40,41,42] |
| limitations |
| ||
2.3. The NB-IoT in Healthcare
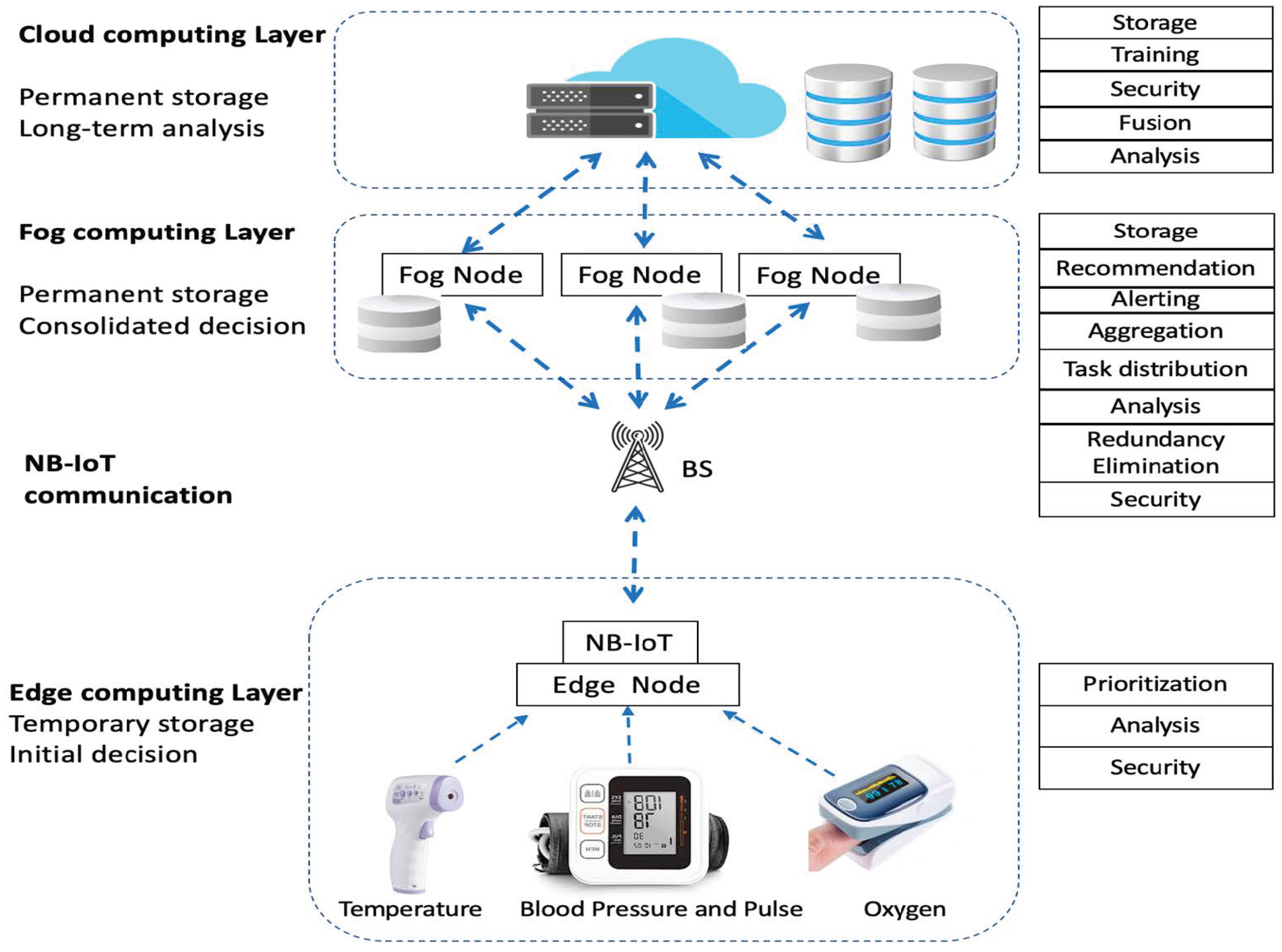
3. The Proposed Architecture
3.1. Architecture Components
3.1.1. The Edge Computing Layer
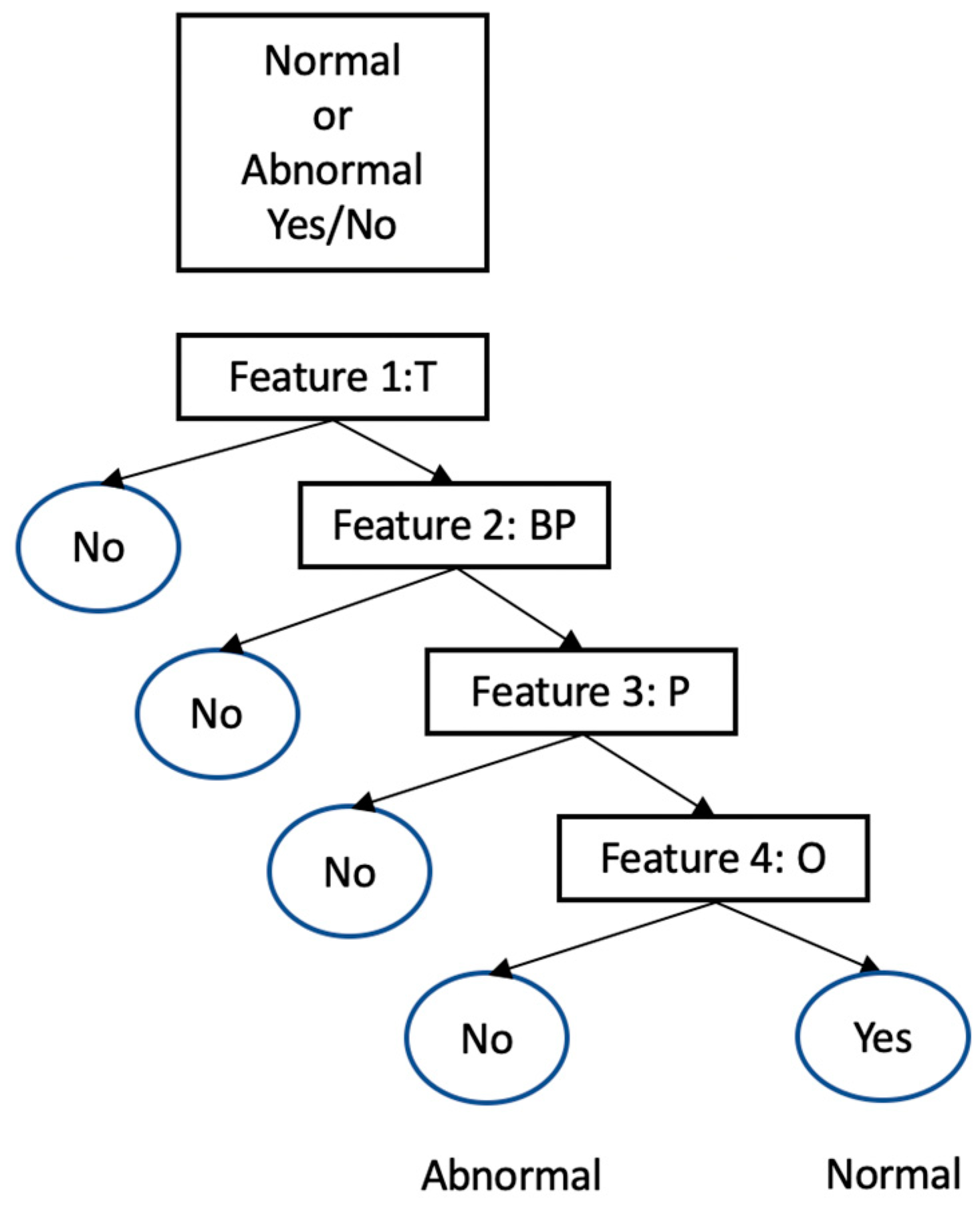
- Medical data classification
- Medical data prioritization
3.1.2. The Fog Computing Layer
3.1.3. The Cloud Computing Layer
3.2. The NB-IoT Communication
3.3. Authentication Protocols
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Experiment Setup
- -
- No edge No fog
- -
- No edge
- -
- No fog
- -
- The proposed architecture
4.2. Results and Analysis
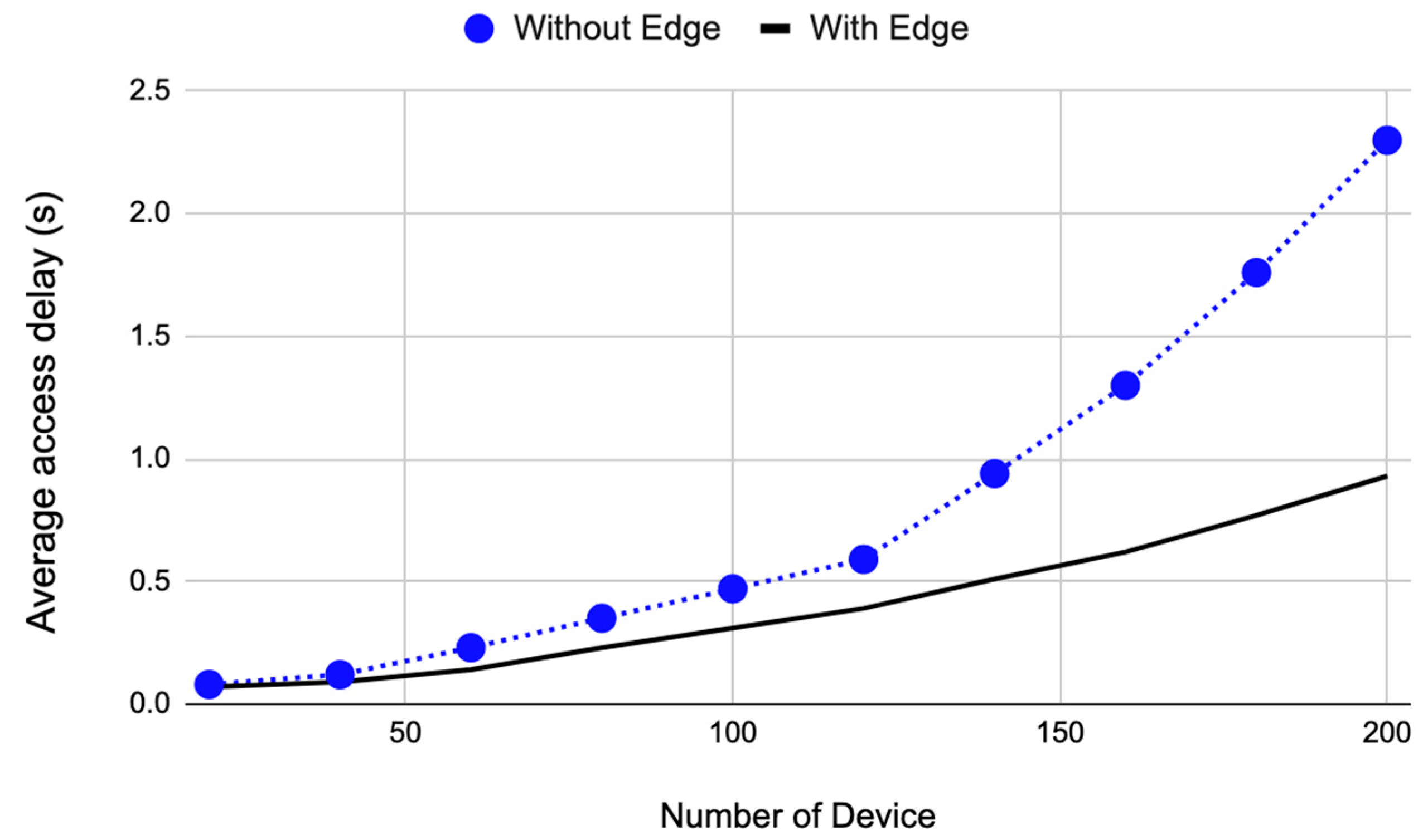
4.2.1. Average NB-IoT Delay Results (TR)
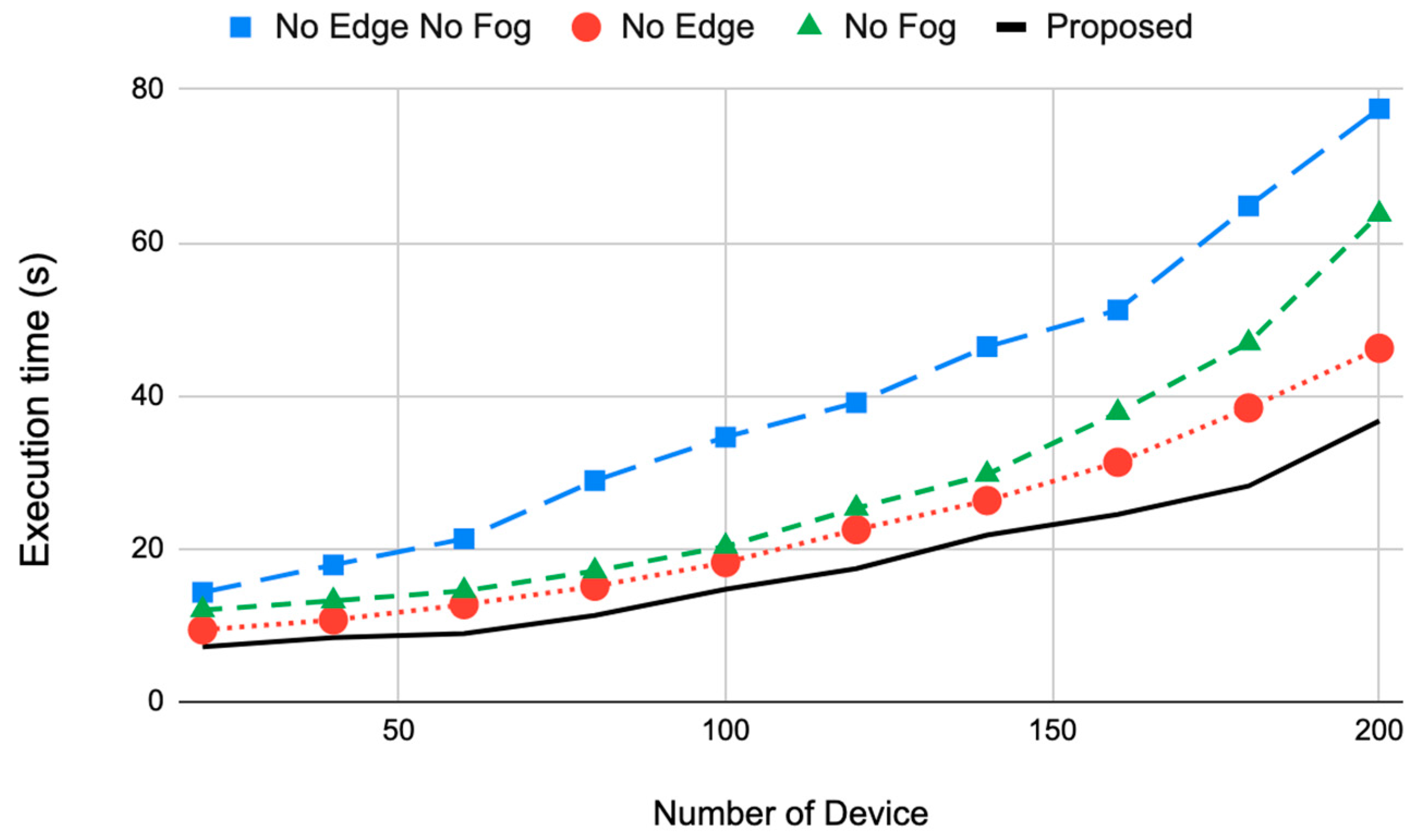
4.2.2. Execution Time Results (TC)
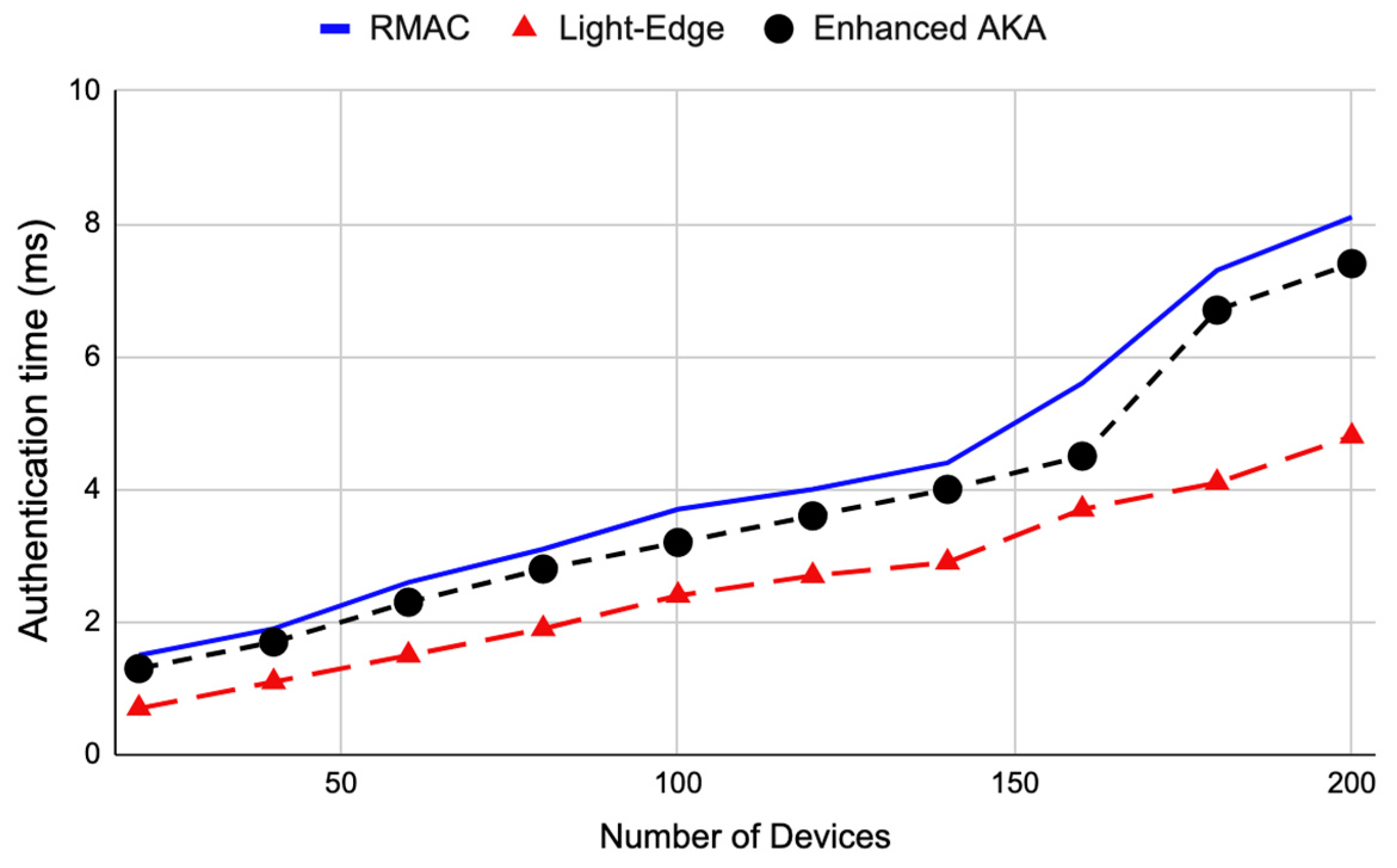
4.2.3. Authentication Time Results (TA)
4.2.4. Summary of Computational Complexity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadhu, P.K.; Yanambaka, P.; Abdelgawad, A. Internet of Things: Security and Solutions Survey. Sensors 2022, 22, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayyolalam, V.; Aloqaily, M.; Ozkasap, O.; Guizani, M. Edge-Assisted Solutions for IoT-Based Connected Healthcare Systems: A Literature Review. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 9419–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-kahtani, M.S.; Khan, F.; Taekeun, W. Application of Internet of Things and Sensors in Healthcare. Sensors 2022, 22, 5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Wen, B.; Xun, Y.; Liu, J. Connecting Intelligent Things in Smart Hospitals Using NB-IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berliandhy, I.E.; Rizal, A.; Hadiyoso, S.; Febyarto, R. A multiuser vital sign monitoring system using ZigBee wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Control, Electronics, Renewable Energy and Communications (ICCEREC), Bandung, Indonesia, 13–15 September 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Banuleasa, S.; Munteanu, R.; Rusu, A.; Tont, G. IoT system for monitoring vital signs of elderly population. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference and Exposition on Electrical and Power Engineering (EPE), lasi, Romania, 20–22 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Aledhari, M.; Razzak, R.; Qolomany, B.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Saeed, F. Biomedical IoT: Enabling Technologies, Architectural Elements, Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 31306–31339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shurafa, M.A.; Lee, I. Research on the Smart Medical System Based on NB-IoT Technology. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 7801365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Dong, P.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Guo, L.; Hu, B.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, T.; Kwok, R.Y.K. Mobile Edge Computing Enabled 5G Health Monitoring for Internet of Medical Things: A Decentralized Game Theoretic Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.; Bakhsh, S.T.; Abulkhair, M.; Alassafi, M.O. An energy-efficient fog-to-cloud Internet of Medical Things architecture. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2019, 15, 155014771985197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Min, G.; Chen, S. Mobile Edge Aided Data Dissemination for Wireless Healthcare Systems. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2019, 6, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalofi, H.; Abouelmehdi, K.; Beni-Hssane, A. Fog Computing in the Age of Big Healthcare Data: Powering the Medical Internet of Things. In Advances on Smart and Soft Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.; Zeng, D.; Guo, S.; Barnawi, A.; Xiang, Y. Cost Efficient Resource Management in Fog Computing Supported Medical Cyber-Physical System. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2017, 5, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Sood, S.K. Fog Assisted-IoT Enabled Patient Health Monitoring in Smart Homes. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, G.P.; Tripathi, R. An ensemble learning and fog-cloud architecture-driven cyber-attack detection framework for IoMT networks. Comput. Commun. 2021, 166, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzi, G.; Pozzebon, A. Combining LoRaWAN and NB-IoT for Edge-to-Cloud Low Power Connectivity Leveraging on Fog Computing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yao, X.; Yang, T.; Ning, H. Cooperative Privacy Preservation for Wearable Devices in Hybrid Computing-Based Smart Health. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, A.; Bianchi, V.; Ricci, A.; Munari, I.D. NB-IoT and Wi-Fi Technologies: An Integrated Approach to Enhance Portability of Smart Sensors. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 74589–74599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.; Alam, M.M.; Moullec, Y.L.; Kuusik, A. NarrowBand-IoT Performance Analysis for Healthcare Applications. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 130, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, S.K.; Anand, S. Narrowband IoT for healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information Communication and Embedded Systems (ICICES), Chennai, India, 23–24 February 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Agiwal, M.; Maheshwari, M.K.; Jin, H. Power Efficient Random Access for Massive NB-IoT Connectivity. Sensors 2019, 19, 4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, B.; Fan, W.; Tian, X.; Huang, S.; Yu, C.; Liu, Y. An Enhanced Random Access Algorithm Based onthe Clustering-Reuse Preamble Allocation in NB-IoT System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 183847–183859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Guizani, N.; Du, X. Efficient and Traceable Patient Health Data Search System for Hospital Management in Smart Cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 6425–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraghmi, E.-Y.; Wu, M.-C.; Yuan, S.-M. A Multilayer Data Processing and Aggregating Fog-Based Framework for Latency-Sensitive IoT Services. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, K.; Sharma, B.; Singh, R. Implementation analysis of IoT-based offloading frameworks on cloud/edge computing for sensor generated big data. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 3641–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Niu, Y.; Ahmed, M.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Han, Z. Mobility-Aware Fog Computing in Dynamic Environments: Understandings and Implementation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38867–38879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, P.; Aloi, G.; Gravina, R.; Caliciuri, G.; Fortino, G.; Liotta, A. An Edge-Based Architecture to Support Efficient Applications for Healthcare Industry 4.0. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Blockchain and SGX-Enabled Edge-Computing-Empowered Secure IoMT Data Analysis. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 15785–15795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif-Ur-Rahman, M.; Afsana, F.; Mahmud, M.; Kaiser, M.S.; Ahmed, M.R.; Kaiwartya, O.; James-Taylor, A. Toward a Heterogeneous Mist, Fog, and Cloud-Based Framework for the Internet of Healthcare Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 4049–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.A.; Mohamed, A.; Chiasserini, C.F.; Tlili, M.; Erbad, A. Edge Computing for Smart Health: Context-Aware Approaches, Opportunities, and Challenges. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, G.; Baldanzi, S.; Seidita, F.; Proietti, C.; Carlini, F.; Peviani, S.; Antonini, G.; Vianello, A.; Siciliano, G.; Musumeci, O.; et al. A mobile app for patients with Pompe disease and its possible clinical applications. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2018, 28, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellaji, C.; Sreehitha, G.; Lakshmi Devi, B. Efficient health care systems using intelligent things using NB-IoT. Mater. Today Proc. 2020; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Du, M.; Huang, J.; Jin, T. Groupchain: Towards a Scalable Public Blockchain in Fog Computing of IoT Services Computing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2020, 13, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deokar, S.; Mangla, M.; Akhare, R. A secure fog computing architecture for continuous health monitoring. In Fog Computing for Healthcare 4.0 Environments; Tanwar, S., Ed.; Signals and Communication Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 269–290. ISBN 978-3-030-46196-6. [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi, C.; Nawal, M.; Mishra, P.K. Security concerns of fog computing in field of healthcare using blockchain: A review. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Communication information and Computing Technology (ICCICT), Mumbai, India, 25–27 June 2021; IEEE: Mumbai, India, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Lin, J. A Privacy-Preserving Optimization of Neighborhood-Based Recommendation for Medical-Aided Diagnosis and Treatment. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 10830–10842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, Q.; Yin, X.; Abbasi, M.; Khosravi, M.R.; Qi, L. Intelligent Offloading for Collaborative Smart City Services in Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 7919–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merelli, I.; Morganti, L.; Corni, E.; Pellegrino, C.; Cesini, D.; Roverelli, L.; Zereik, G.; D’Agostino, D. Low-power portable devices for metagenomics analysis: Fog computing makes bioinformatics ready for the Internet of Things. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 88, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Lu, R.; Lai, C.; Luan, T.H. Towards power consumption-delay tradeoff by workload allocation in cloud-fog computing. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), London, UK, 8–12 June 2015; IEEE: London, UK, 2015; pp. 3909–3914. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Ning, Z.; Ngai, E.C.-H.; Zhou, L.; Wei, J.; Cheng, J.; Hu, B. Energy-Latency Tradeoff for Energy-Aware Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 2633–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-T.; Lin, Z.Y. A Survey on edge computing in bioinformatics and health informatics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Seoul, Korea, 16–19 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 2203–2208. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino, D.; Morganti, L.; Corni, E.; Cesini, D.; Merelli, I. Combining Edge and Cloud computing for low-power, cost-effective metagenomics analysis. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 90, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Tian, G. Optimization of Communication Network Fault Identification Based on NB-IoT. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 80, 103531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muteba, K.; Djouani, K.; Olwal, T. 5G NB-IoT: Design, Considerations, Solutions and Challenges; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.N.; Khalid, J.; Qureshi, H.K. Performance analysis of contention-based random access procedure in clustered LTE networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 Seventh International Conference on Next Generation Mobile Apps, Services and Technologies, Prague, Czech Republic, 25–27 September 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Alobaidy, H.A.H.; Singh, M.J.; Nordin, R.; Abdullah, N.F.; Wei, C.G.; Soon, M.L.S. Real-World Evaluation of Power Consumption and Performance of NB-IoT in Malaysia. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 11614–11632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.T.; Pham, H.Y.; Nguyen, D.S.L.; Iwata, Y.; Do, T.T.; Ishibashi, K.; Sun, G. Machine learning based classification model for screening of infected patients using vital signs. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 24, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, F.; Milito, R.; Zhu, J.; Addepalli, S. Fog computing and its role in the internet of things. In Proceedings of the First Edition of the MCC Workshop on Mobile Cloud Computing—MCC ’12, Helsinki, Finland, 17 August 2012; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, X.-Q.; Huh, E.-N. Towards task scheduling in a cloud-fog computing system. In Proceedings of the 2016 18th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Kanazawa, Japan, 5–7 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, A.; Pinjari, H.; Hong, W.-H.; Seo, H.C.; Rho, S. Fog Computing-Based IoT for Health Monitoring System. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 1386470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ka, A.K. RMAC—A Lightweight Authentication Protocol for Highly Constrained IoT Devices. Int. J. Cryptogr. Inf. Secur. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidinejad, A.; Ghobaei-Arani, M.; Souri, A.; Shojafar, M.; Kumari, S. Light-Edge: A Lightweight Authentication Protocol for IoT Devices in an Edge-Cloud Environment. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2022, 11, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Jabbar, S.; Ahmed, S.H.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Speeding Up the Internet of Things: LEAIoT: A Lightweight Encryption Algorithm Toward Low-Latency Communication for the Internet of Things. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2018, 7, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Wu, M.-E.; Kumari, S. Enhanced Authentication Protocol for the Internet of Things Environment. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 8543894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, K.; Sharma, B.; Singh, R. Comparative Analysis of Simulators for IoT Applications in Fog/Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Data Communication Systems (ICSCDS), Erode, India, 7–9 April 2022; IEEE: Erode, India, 2022; pp. 983–988. [Google Scholar]
- Buyya, R.; Ranjan, R.; Calheiros, R.N. Modeling and simulation of scalable cloud computing environments and the CloudSim toolkit: Challenges and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation, Leipzig, Germany, 21–24 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, R.; Buyya, R. Modelling and simulation of fog and edge computing environments using iFogSim toolkit. In Fog and Edge Computing: Principles and Paradigms; Wiley Series on Parallel and Distributed Computing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-119-52498-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.-Y.; Yang, S.-R. Simulating NB-IoT Random Access: Using ns-3 as an Example. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1RO6PNewPiJe7ZAkEgtAKxc5VUhM--pPT/view (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Mehrgardt, P.; Khushi, M.; Poon, S.; Withana, A. Pulse Transit Time PPG Dataset. PhysioNet 2022, 10, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraghmi, E.; Daraghmi, Y.; Daraghma, R.; Fouchal, H.; Ayaida, M. A Blockchain framework for Enhancing NB-IoT security and authentication: Health monitoring system as a case. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Science Technology and Management—ICSTM, Athens, Grecee, 24–25 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Daraghmi, E.-Y.; Daraghmi, Y.-A.; Yuan, S.-M. MedChain: A Design of Blockchain-Based System for Medical Records Access and Permissions Management. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 164595–164613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraghmi, E.-Y.; Abu Helou, M.; Daraghmi, Y.-A. A Blockchain-Based Editorial Management System. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 9927640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraghmi, E.Y.; Daraghmi, Y.A.; Yuan, S.M. UniChain: A Design of Blockchain-Based System for Electronic Academic Records Access and Permissions Management. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, A.; Waqas, M.; Abbas, G.; Muhammad, F.; Abbas, Z.H.; Vimal, S.; Bilal, M. LAKE-BSG: Lightweight authenticated key exchange scheme for blockchain-enabled smart grids. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of data centers | 1 |
| Number of hosts | 1 |
| Number of data center brokers | 1 |
| Number of Virtual machines VM | 4 |
| Number of processing elements PE | 1 |
| MIPS of PEs | 4000 |
| MIPS of each VM | 400 |
| VM RAM | 2048 MB |
| Data center scheduling | Space-shared |
| VM scheduling | Space-shared |
| Bandwidth | 1000 |
| Number of cloudlets | 10 |
| Cloudlets scheduling | Space-shared |
| CPU, RAM, BW | Full utilization |
| Parameter | Value | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Number of nodes | 6 | 1 |
| Speed MIPS | 3000 | 1000 |
| RAM | 16 | 8 |
| Uplink (MBPS) | 50 | 20 |
| Downlink (MBPS) | 100 | 50 |
| Busy power | 110 | 85 |
| Idle power | 90 | 78 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Preamble duration | 5.6 ms |
| Backoff Indicator | 0 ms |
| SIB2-NB periodicity | 64 ms |
| maxNumPreambleAttempCE-r13 | 3 |
| Nnpdcch-StartSF-CSS-RA | v2 |
| Npdcch-NumRepetitions-RA | r2 |
| PDCCH periodicity | 4 ms |
| RaResponseWindowSize | CE level 0 = 2 pp CE level 1 = 3 pp CE level 2 =4 pp |
| numRepetitionPerPreambleAttemp | CE level 0 = 2 CE level 1 = 8 CE level 2 = 32 |
| nprach-Periodicity-r13 | CE level 0 = 40 ms CE level 1 = 160 ms CE level 2 = 640 ms |
| Nprach-Start-r13 | CE level 0 = 8 ms CE level 1 = 32 ms CE level 2 = 256 ms |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daraghmi, Y.-A.; Daraghmi, E.Y.; Daraghma, R.; Fouchal, H.; Ayaida, M. Edge–Fog–Cloud Computing Hierarchy for Improving Performance and Security of NB-IoT-Based Health Monitoring Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 8646. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228646
Daraghmi Y-A, Daraghmi EY, Daraghma R, Fouchal H, Ayaida M. Edge–Fog–Cloud Computing Hierarchy for Improving Performance and Security of NB-IoT-Based Health Monitoring Systems. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8646. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228646
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaraghmi, Yousef-Awwad, Eman Yaser Daraghmi, Raed Daraghma, Hacène Fouchal, and Marwane Ayaida. 2022. "Edge–Fog–Cloud Computing Hierarchy for Improving Performance and Security of NB-IoT-Based Health Monitoring Systems" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8646. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228646
APA StyleDaraghmi, Y.-A., Daraghmi, E. Y., Daraghma, R., Fouchal, H., & Ayaida, M. (2022). Edge–Fog–Cloud Computing Hierarchy for Improving Performance and Security of NB-IoT-Based Health Monitoring Systems. Sensors, 22(22), 8646. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228646









