A Hybrid Intelligent Simulation System for Building IoT Networks: Performance Comparison of Different Router Replacement Methods for WMNs Considering Stadium Distribution of IoT Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We implement a hybrid intelligent system that is based on three intelligent algorithms: PSO, SA, and DGA.
- We present a comparison study for three different router replacement methods.
- We consider the Stadium distribution of IoT devices in order to find good solutions for similar real-life environment scenarios.
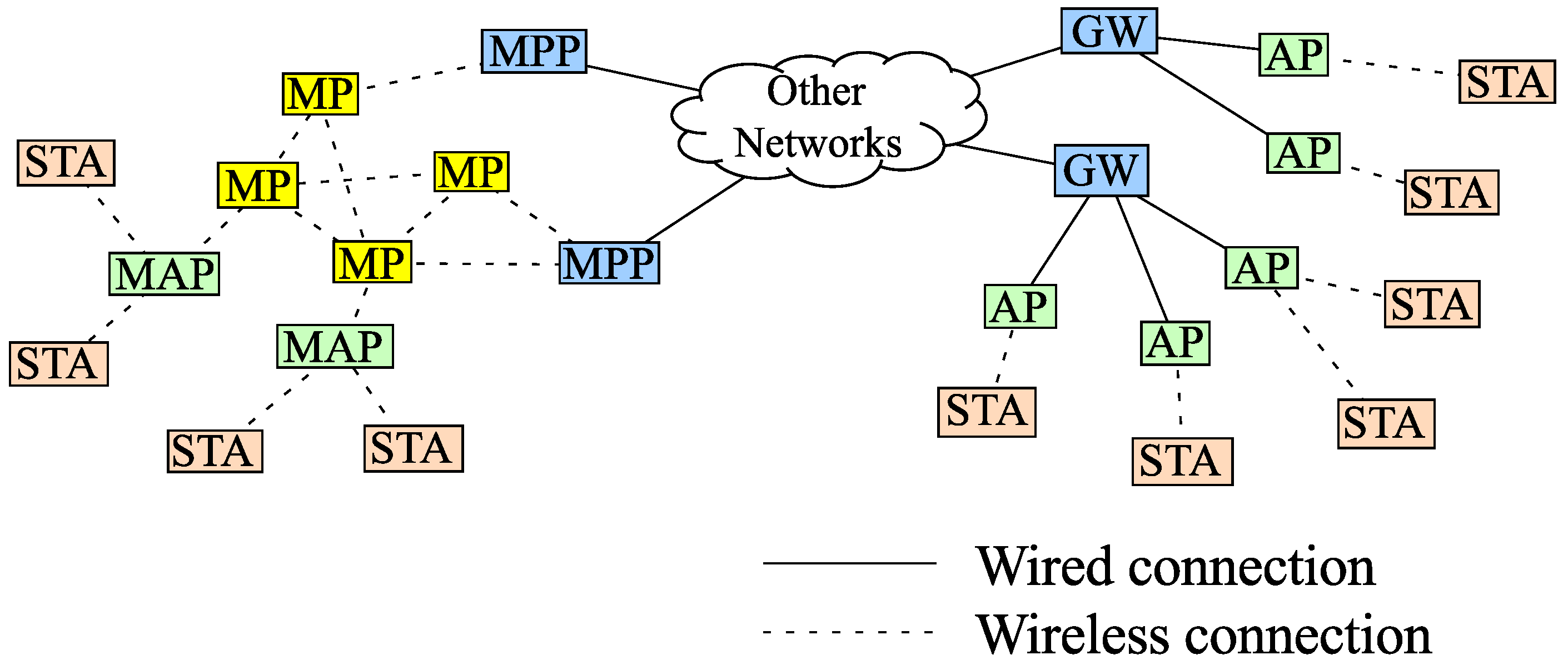
2. Related Work
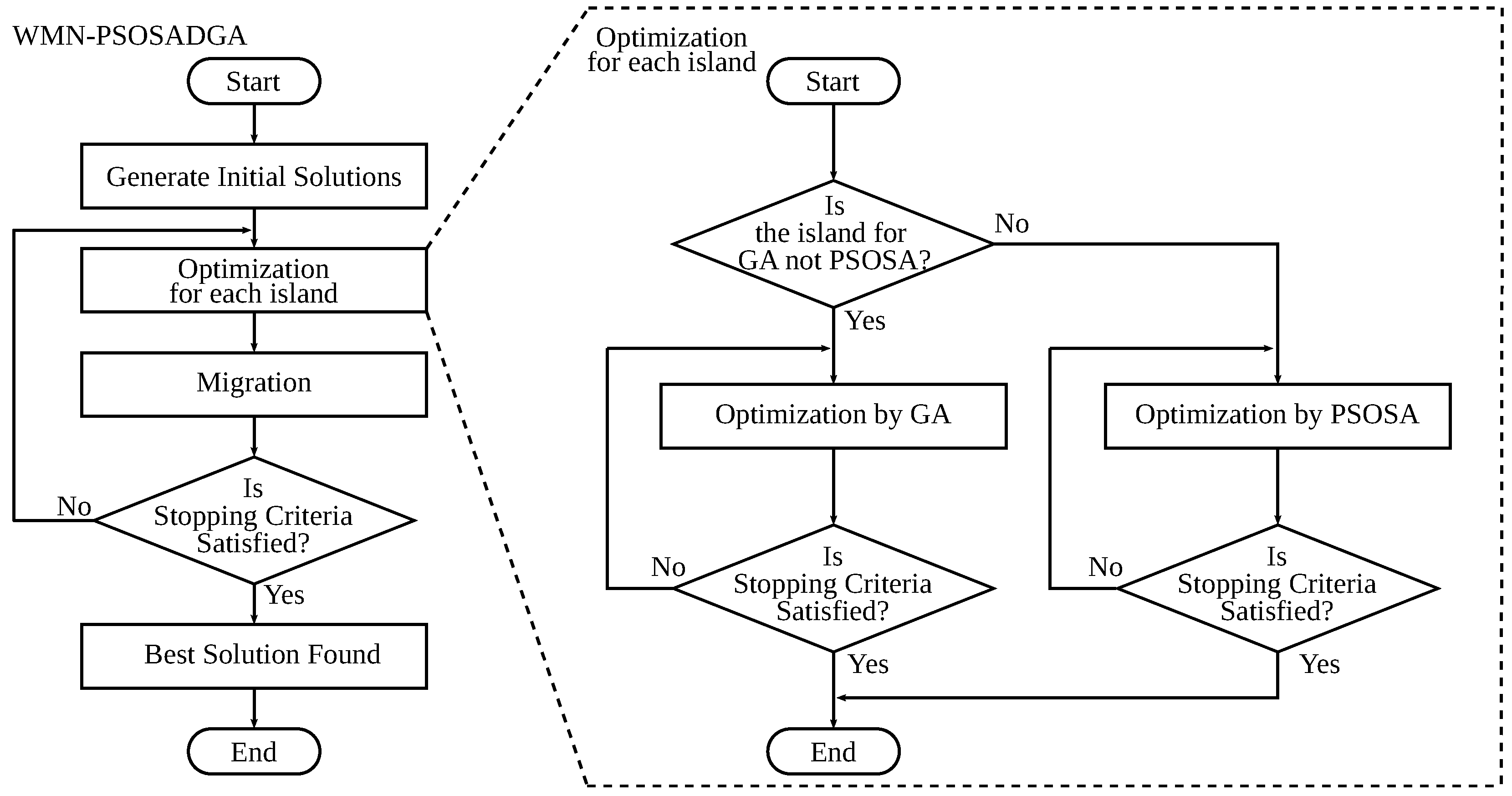
3. Proposed and Implemented Simulation System
3.1. PSO and SA
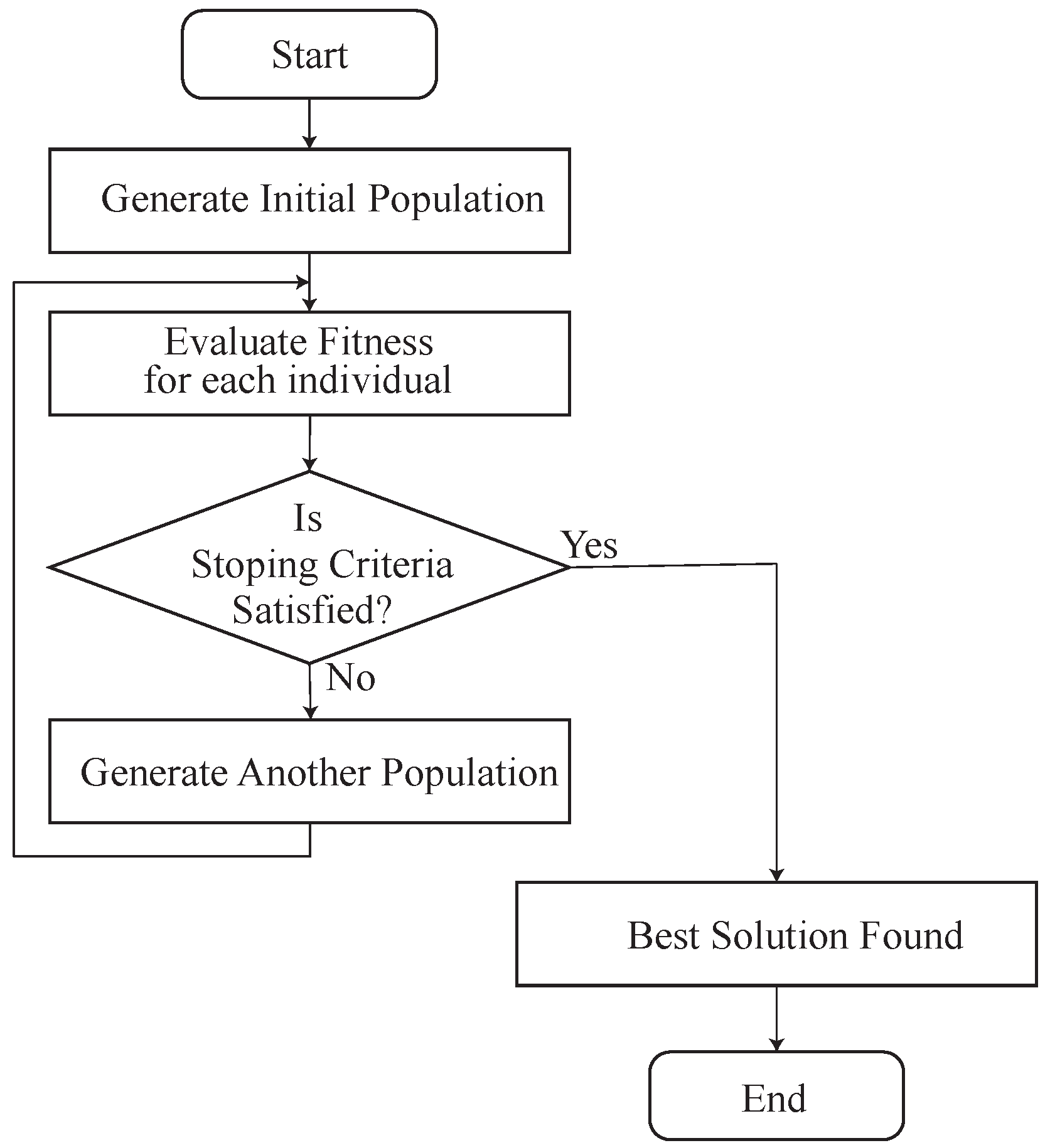
3.2. DGA
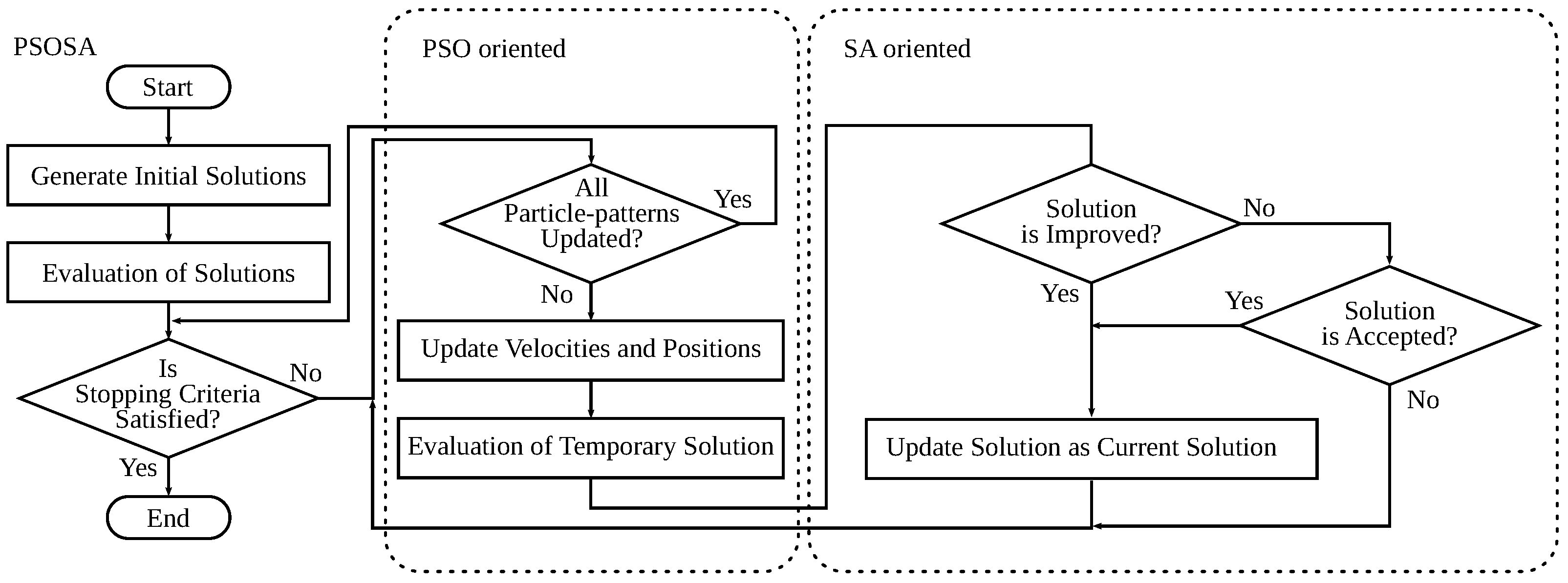
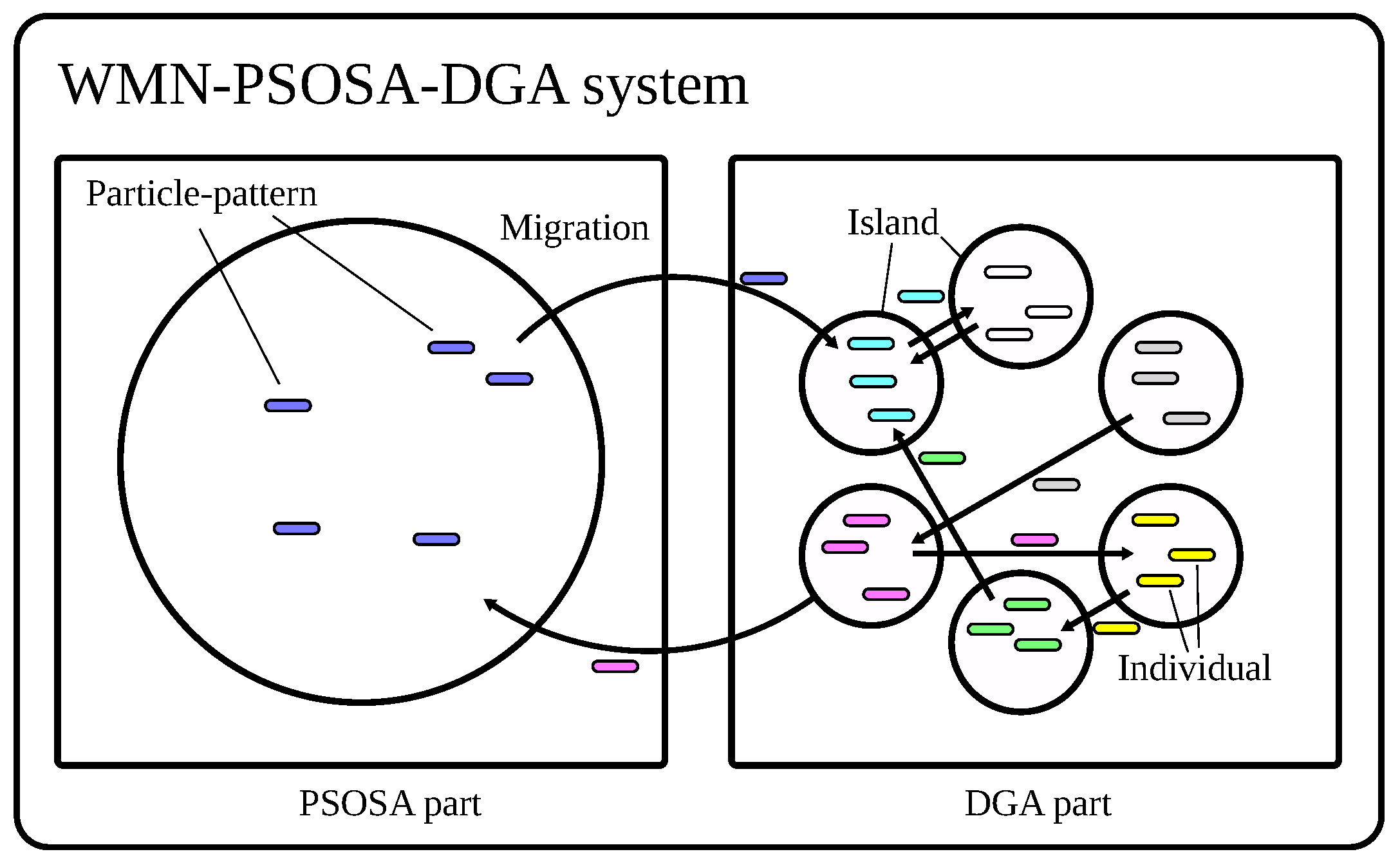
3.3. WMN-PSOSA-DGA
3.3.1. Fitness Function
3.3.2. PSOSA Implementation
3.3.3. DGA Implementation
3.3.4. Migration
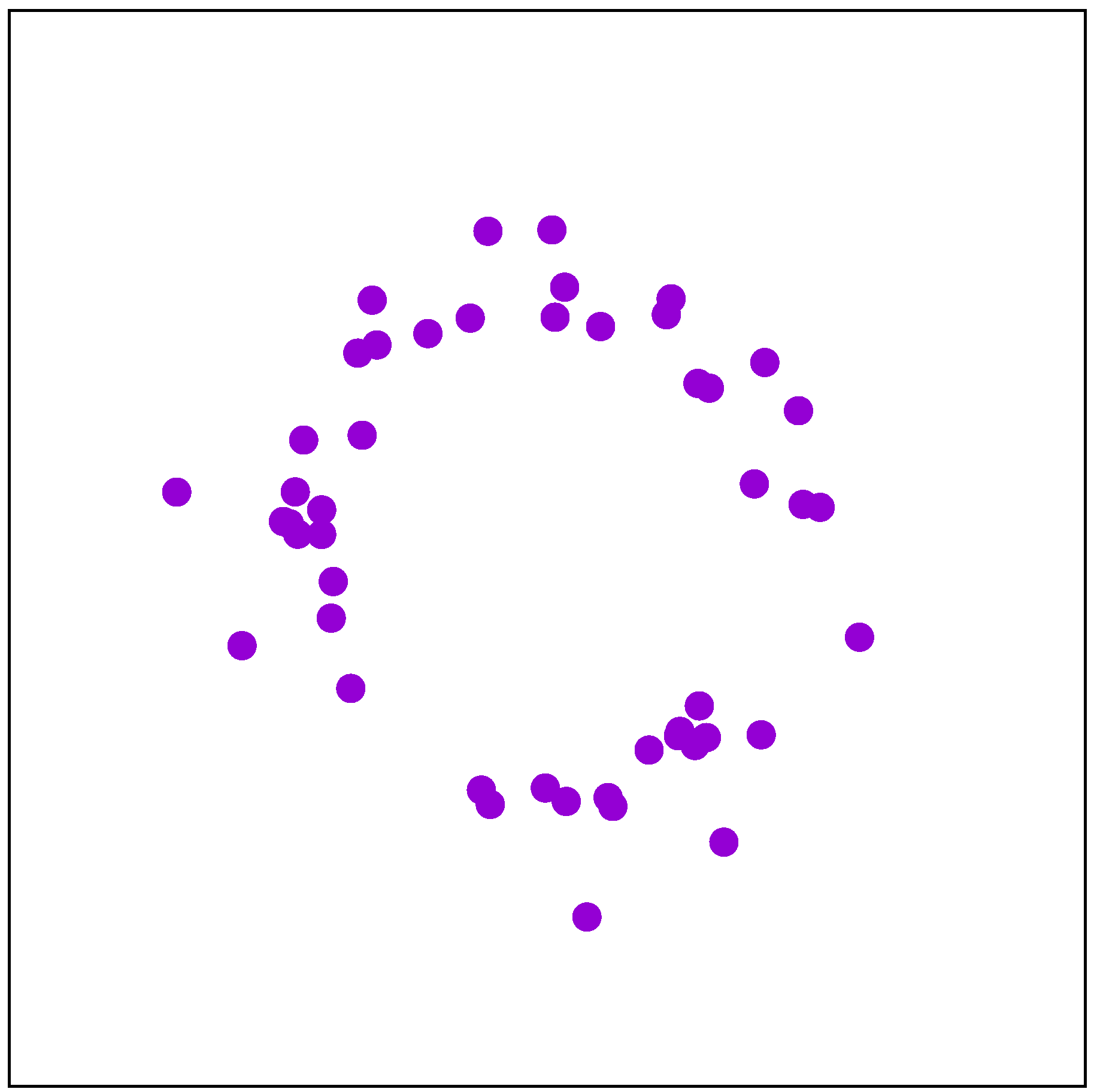
3.4. Distribution of IoT Devices
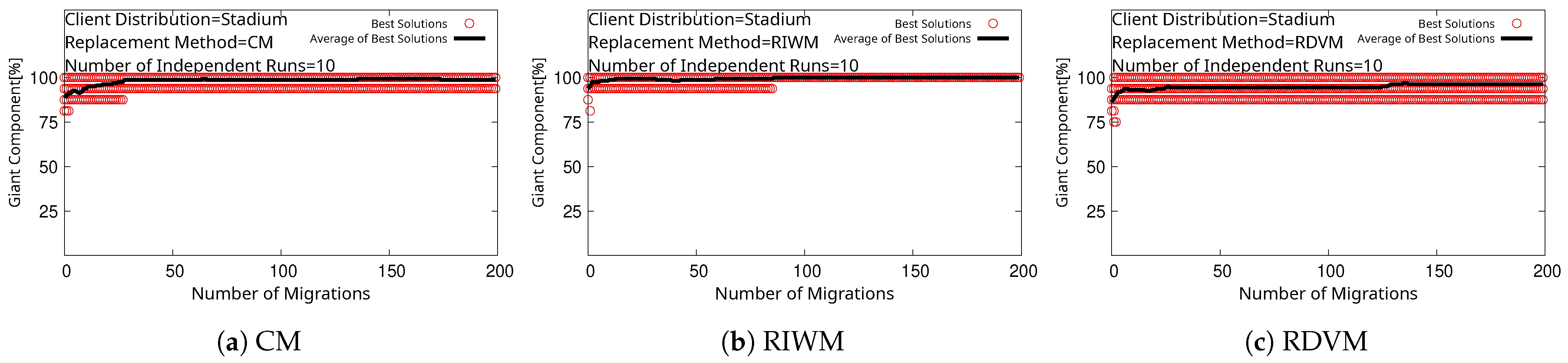
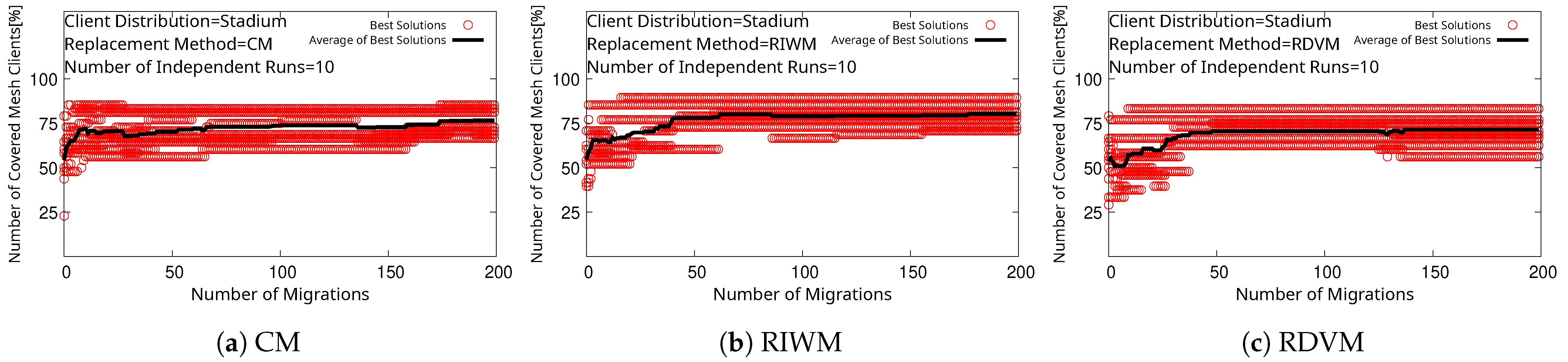
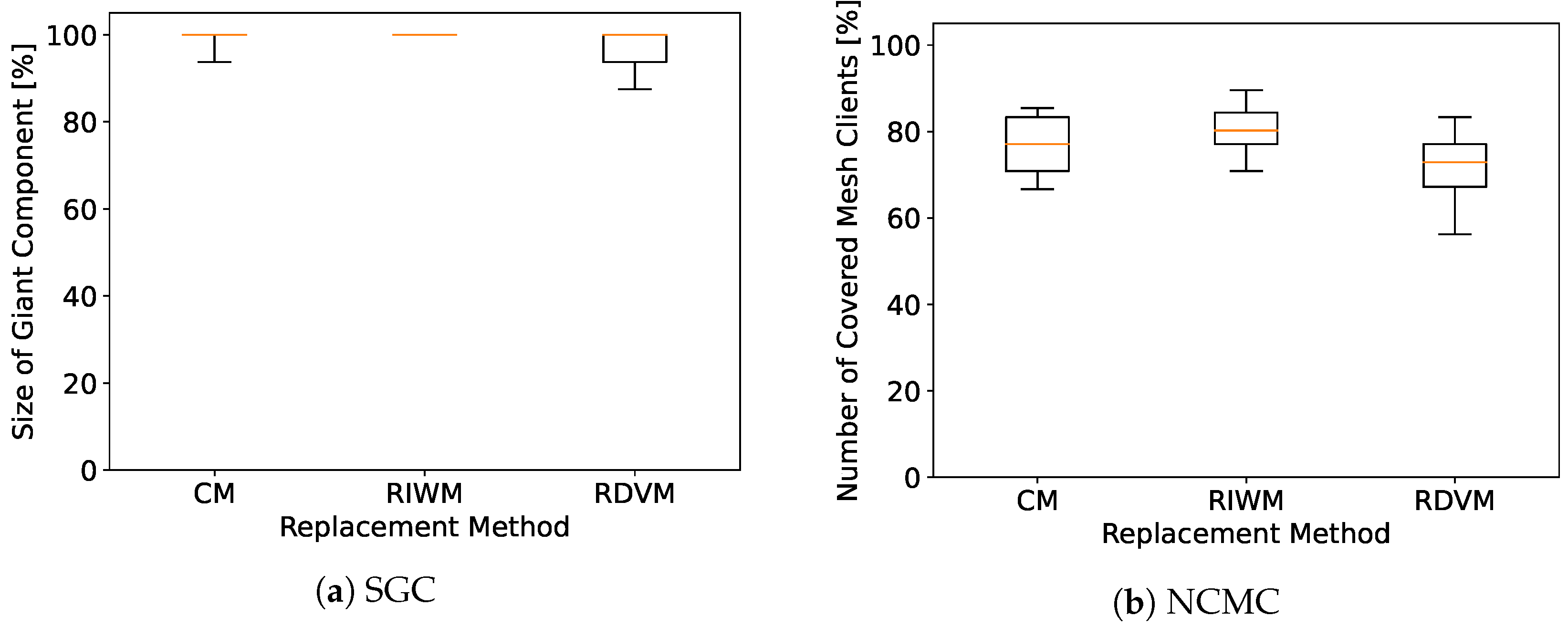
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinha, R.S.; Wei, Y.; Hwang, S.H. A Survey on LPWA Technology: LoRa and NB-IoT. ICT Express 2017, 3, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y.H. Scheduling Channel Access Based on Target Wake Time Mechanism in 802.11ax WLANs. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 20, 1529–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afaqui, M.S.; Garcia-Villegas, E.; Lopez-Aguilera, E. IEEE802.11ax: Challenges and Requirements for Future High Efficiency WiFi. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 24, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellalta, B. IEEE802.11ax: High-efficiency WLANs. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 23, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.; Song, M.; Chang, S.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, Y.T. A Signaling Emergency Alert System Multiplexed with T-DMB Channel for Emergency Alert Service. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2015, 61, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Chang, S. A consumer transceiver for long-range IoT communications in emergency environments. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2016, 62, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Ogiela, L.; Enokido, T.; Takizawa, M. An Information Flow Control Model in a Topic-Based Publish/Subscribe System. J. High Speed Netw. 2018, 24, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, J.D.; Knightly, E.W. The IEEE802.11s Extended Service Set Mesh Networking Standard. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2008, 46, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiertz, G.R.; Denteneer, D.; Max, S.; Taori, R.; Cardona, J.; Berlemann, L.; Walke, B. IEEE802.11s: The WLAN Mesh Standard. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2010, 17, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Barolli, L.; Okamoto, S. WMN-PSOSA: An Intelligent Hybrid Simulation System for WMNs and Its Performance Evaluations. Int. J. Web Grid Serv. 2019, 15, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barolli, A.; Sakamoto, S.; Oda, T.; Spaho, E.; Barolli, L.; Xhafa, F. Performance Evaluation of WMN-GA System for Different Settings of Population Size and Number of Generations. Hum.-Centric Comput. Inf. Sci. 2014, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barolli, A.; Bylykbashi, K.; Qafzezi, E.; Sakamoto, S.; Barolli, L. A comparison study of Weibull, normal and Boulevard distributions for wireless mesh networks considering different router replacement methods by a hybrid intelligent simulation system. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Al-Dubai, A.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Min, G. A New Efficient Cross-layer Relay Node Selection Model for Wireless Community Mesh Networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 61, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Subramanyam, M.; Prasad, K. QoS Based Mobility Management for Wireless Mesh Networks. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2018, 77, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Z.; Chen, Z. A High Reliability and Low Latency Routing Algorithm in Cognitive Wireless Mesh Networks. Int. J. Commun. Netw. Distrib. Syst. 2017, 18, 58–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasipuri, A.; Zhuang, J.; Das, S.R. A Multichannel CSMA MAC Protocol for Multihop Wireless Networks. In Proceedings of the WCNC. 1999 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (Cat. No. 99TH8466), New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 September 1999; Volume 3, pp. 1402–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Chen, Y.; Lin, W.S.; Liu, K.R. Indirect Reciprocity Security Game for Large-scale Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Luo, J.; He, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Cai, L. Cooperative Channel Allocation and Scheduling in Multi-interface Wireless Mesh Networks. Peer-to-peer Netw. Appl. 2019, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Zhou, K.; Xiong, N. A Cluster-based Dual-adaptive Topology Control Approach in Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2016, 16, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.P.; Gupta, H.; Das, S.R.; Cao, J. Minimum Interference Channel Assignment in Multiradio Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2008, 7, 1459–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, W.; Shi, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Resource Allocation for Hybrid RF/FSO Multi-Channel Multi-Radio Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 9358–9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.T.; Kao, C.Y.; Hsu, C.C. Applying the Genetic Approach to Simulated Annealing in Solving Some NP-hard Problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 1752–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, V.; Kamalakannan, R.; Sudhakarapandian, R.; Sivakumar, P. Heuristic and Meta-heuristic Algorithms for Solving Medium and Large Scale Sized Cellular Manufacturing System NP-hard Problems: A Comprehensive Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaldi, E.; Capone, A.; Cesana, M.; Filippini, I.; Malucelli, F. Optimization Models and Methods for Planning Wireless Mesh Networks. Comput. Netw. 2008, 52, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Sarram, M.A.; Derhami, V.; Sarvestani, H.M. Novel Placement Mesh Router Approach for Wireless Mesh Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Networks (ICWN), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 18–21 July 2011; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fendji, J.L.K.E.; Thron, C. A Simulated Annealing Based Centre of Mass (SAC) Approach for Mesh Routers Placement in Rural Areas. Int. J. Oper. Res. Inf. Syst. 2020, 11, 37–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Chen, T.H.; Jhong, S.Y. Wireless Mesh Router Placement with Constraints of Gateway Positions and QoS. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Heterogeneous Networking for Quality, Reliability, Security and Robustness (QSHINE), Taipei, Taiwan, 19–20 August 2015; pp. 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, N.A.; Aliouat, Z.; Naouri, A.; Hassak, S.A. Accelerated PSO Algorithm Applied to Clients Coverage and Routers Connectivity in Wireless Mesh Networks. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Tseng, P.T.; Wu, T.Y.; Deng, D.J. Social-aware Dynamic Router Node Placement in Wireless Mesh Networks. Wirel. Netw. 2016, 22, 1235–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, M.; Reed, B. The Size of the Giant Component of a Random Graph with a Given Degree Sequence. Comb. Probab. Comput. 1998, 7, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Van Laarhoven, P.J.; Aarts, E.H. Simulated Annealing. In Simulated Annealing: Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; pp. 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lambora, A.; Gupta, K.; Chopra, K. Genetic algorithm-A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing (COMITCon-2019), Faridabad, India, 14–16 February 2019; pp. 380–384. [Google Scholar]
- Clerc, M.; Kennedy, J. The Particle Swarm-Explosion, Stability, and Convergence in a Multidimensional Complex Space. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Connect. 2004, 2, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, S.; Oda, T.; Ikeda, M.; Barolli, L.; Xhafa, F. Implementation of a New Replacement Method in WMN-PSO Simulation System and Its Performance Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA-2016), Crans-Montana, Switzerland, 23–25 March 2016; pp. 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshelman, L.J.; Schaffer, J.D. Real-coded Genetic Algorithms and Interval-schemata. In Foundations of Genetic Algorithms; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 2, pp. 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, I. Real-coded Genetic Algorithm for Function Optimization Using Unimodal Normal Distribution Crossover. In Proceedings of the 7th ICGA, East Lansing, MI, USA, 19–23 July 1997; pp. 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kita, H.; Ono, I.; Kobayashi, S. Multi-parental Extension of the Unimodal Normal Distribution Crossover for Real-coded Genetic Algorithms. Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control. Eng. 2000, 36, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsutsui, S.; Yamamura, M.; Higuchi, T. Multi-parent Recombination with Simplex Crossover in Real Coded Genetic Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 July 1999; Volume 1, pp. 657–664. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, T.; Tsutsui, S.; Yamamura, M. Theoretical Analysis of Simplex Crossover for Real-Coded Genetic Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Parallel Problem Solving from Nature PPSN VI; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Alba, E.; Troya, J.M. A Survey of Parallel Distributed Genetic Algorithms. Complexity 1999, 4, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Oda, T.; Bravo, A.; Barolli, L.; Ikeda, M.; Xhafa, F. WMN-SA System for Node Placement in WMNs: Evaluation for Different Realistic Distributions of Mesh Clients. In Proceedings of the IEEE 28th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, Victoria, BC, Canada, 13–16 May 2014; pp. 282–288. [Google Scholar]
| Paper | Optimized Parameters | Approachd |
|---|---|---|
| [24] | Network connectivity, client coverage, and channel assignment | MILP and Relaxation-based Algorithm |
| [25] | Network connectivity and client coverage | GA |
| [26] | Network cost and client coverage | SA |
| [27] | Network connectivity and client coverage | PSO |
| [28] | Network connectivity and client coverage | PSO |
| [29] | Network connectivity and client coverage | PSO |
| [29] | Network connectivity and client coverage | PSO |
| This paper | Network connectivity and client coverage | PSO, SA, DGA |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Area size | |
| Number of mesh routers | 16 |
| Number of IoT Devices | 48 |
| IoT device distribution | Stadium |
| Radius of a mesh router | 2.0–3.5 |
| Number of GA islands | 16 |
| Number of particle patterns | 32 |
| Number of migrations | 200 |
| Evolution steps | 32 |
| Selection method | Roulette wheel |
| Crossover method | SPX |
| Mutation method | Boundary |
| Crossover rate | 0.8 |
| Mutation rate | 0.2 |
| SA starting value | 10.0 |
| SA ending value | 0.01 |
| Total number of iterations | 6400 |
| Router replacement method | CM, RIWM, RDVM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barolli, A.; Sakamoto, S.; Bylykbashi, K.; Barolli, L. A Hybrid Intelligent Simulation System for Building IoT Networks: Performance Comparison of Different Router Replacement Methods for WMNs Considering Stadium Distribution of IoT Devices. Sensors 2022, 22, 7727. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207727
Barolli A, Sakamoto S, Bylykbashi K, Barolli L. A Hybrid Intelligent Simulation System for Building IoT Networks: Performance Comparison of Different Router Replacement Methods for WMNs Considering Stadium Distribution of IoT Devices. Sensors. 2022; 22(20):7727. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207727
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarolli, Admir, Shinji Sakamoto, Kevin Bylykbashi, and Leonard Barolli. 2022. "A Hybrid Intelligent Simulation System for Building IoT Networks: Performance Comparison of Different Router Replacement Methods for WMNs Considering Stadium Distribution of IoT Devices" Sensors 22, no. 20: 7727. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207727
APA StyleBarolli, A., Sakamoto, S., Bylykbashi, K., & Barolli, L. (2022). A Hybrid Intelligent Simulation System for Building IoT Networks: Performance Comparison of Different Router Replacement Methods for WMNs Considering Stadium Distribution of IoT Devices. Sensors, 22(20), 7727. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207727


_Park.png)




