Analysis Method of Bending Effect on Transmission Characteristics of Ultra-Low-Profile Rectangular Microstrip Antenna
Abstract
:1. Introduction
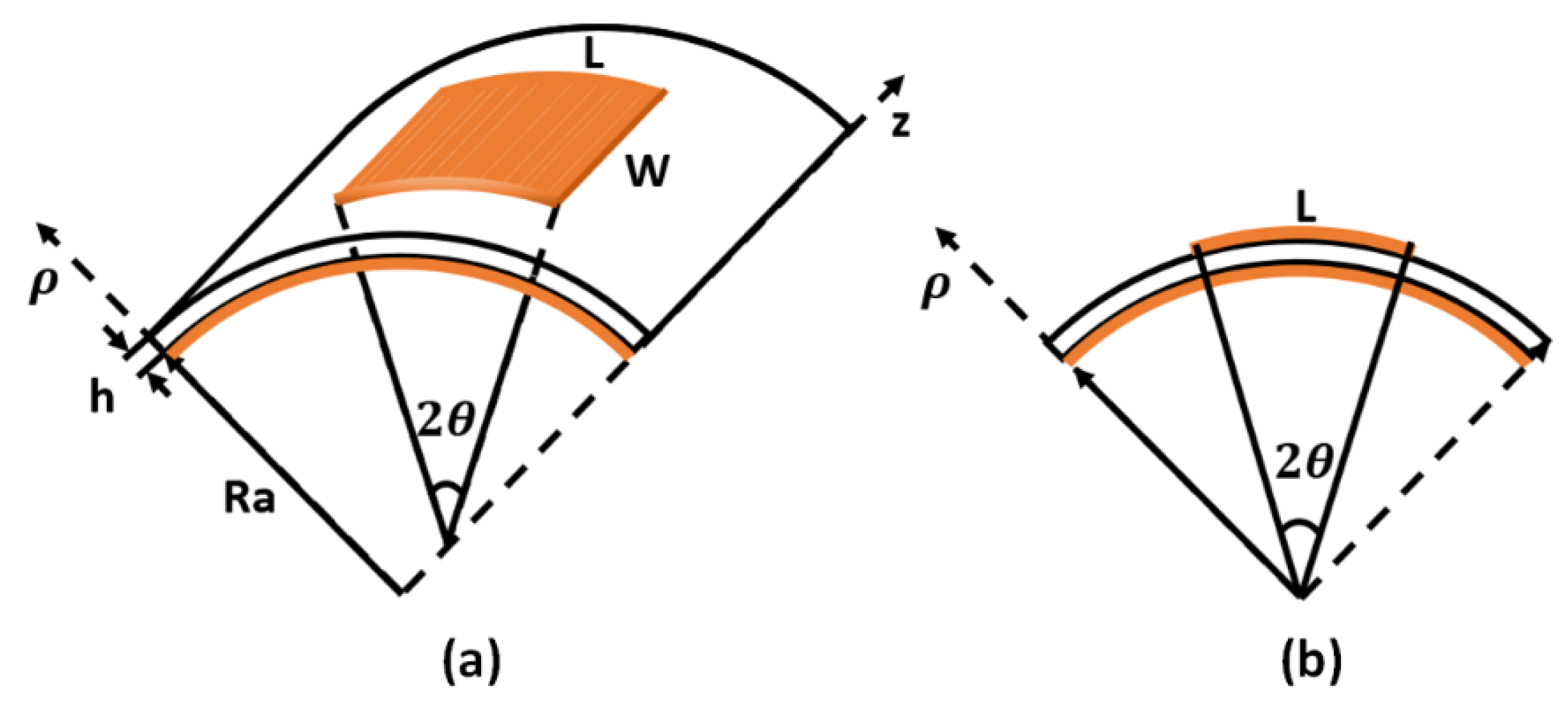
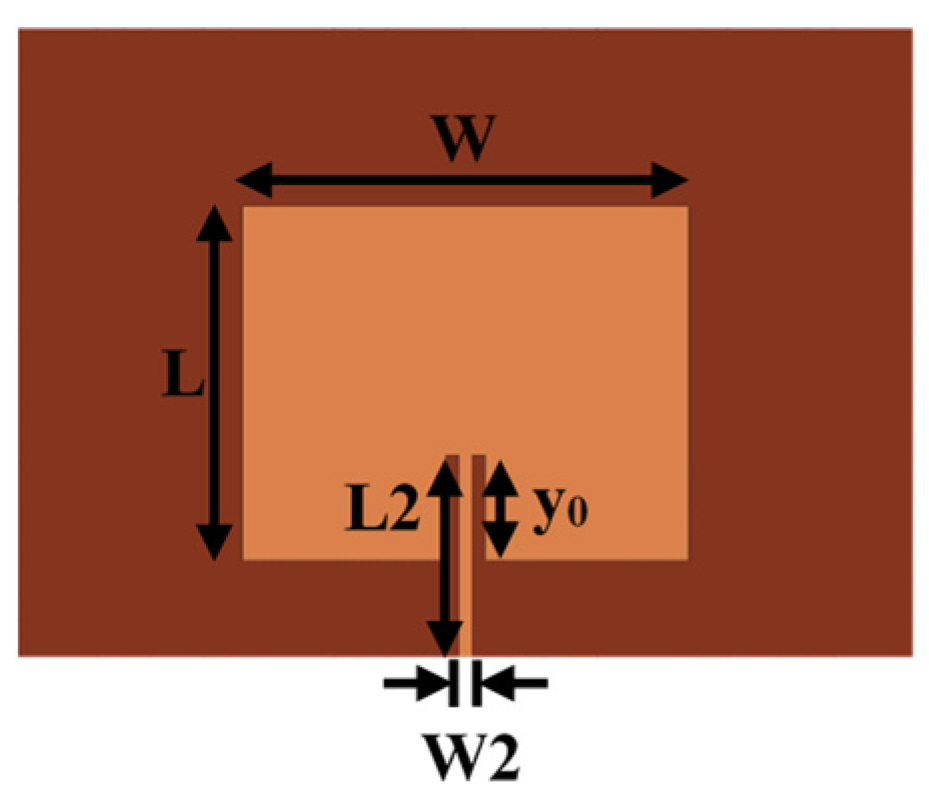
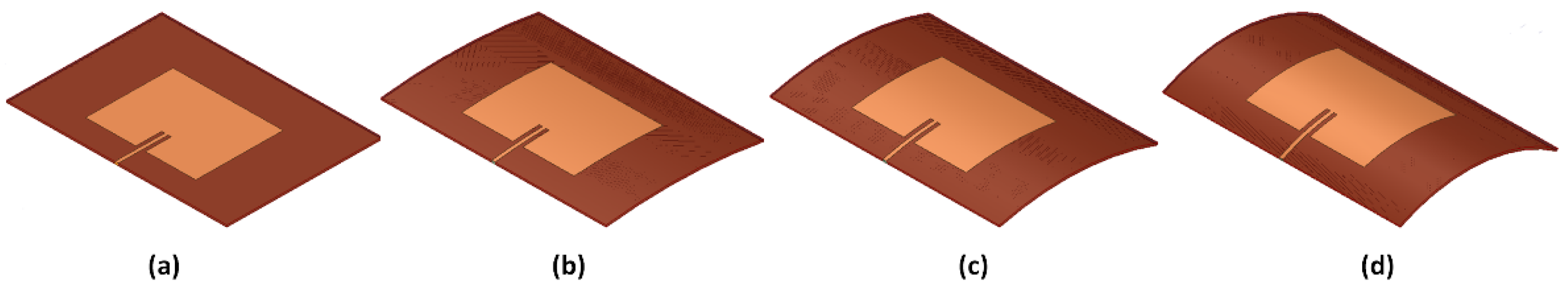
2. Patch Antenna Bending Model
2.1. Effective Dielectric Constant Frequency Prediction Model
2.2. Numerical Results and Comparison
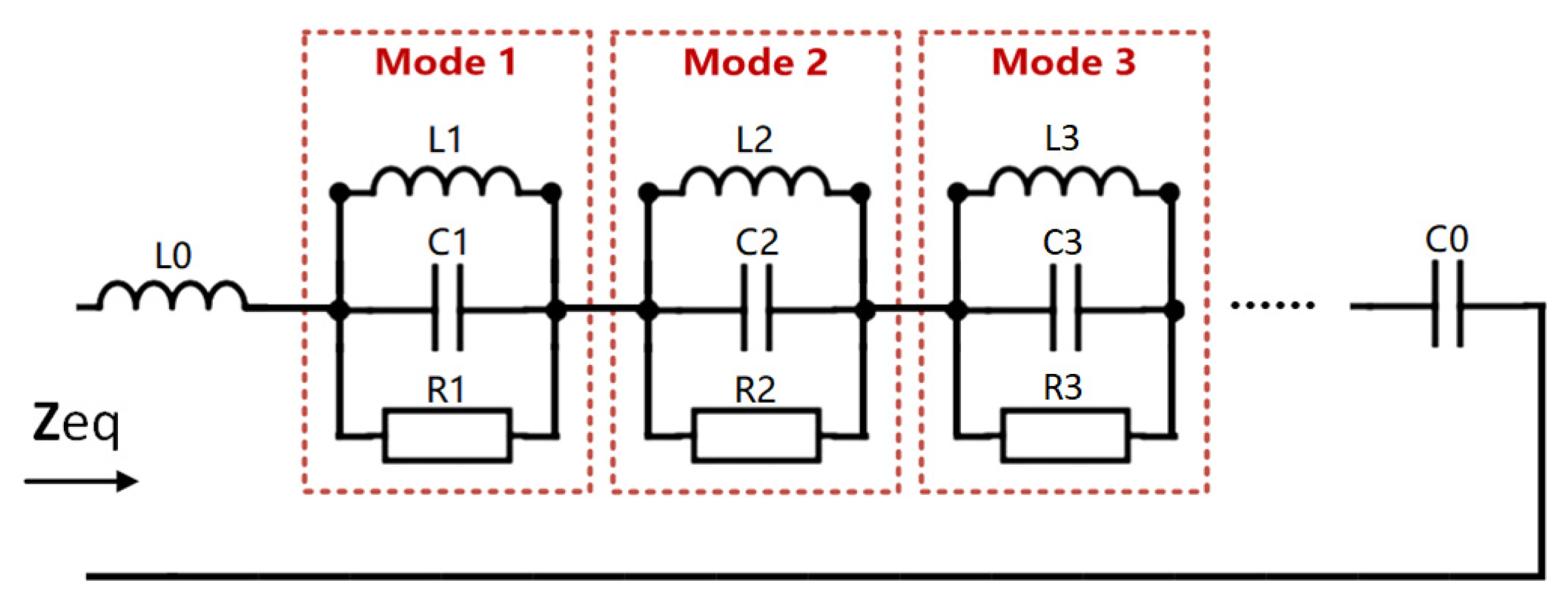
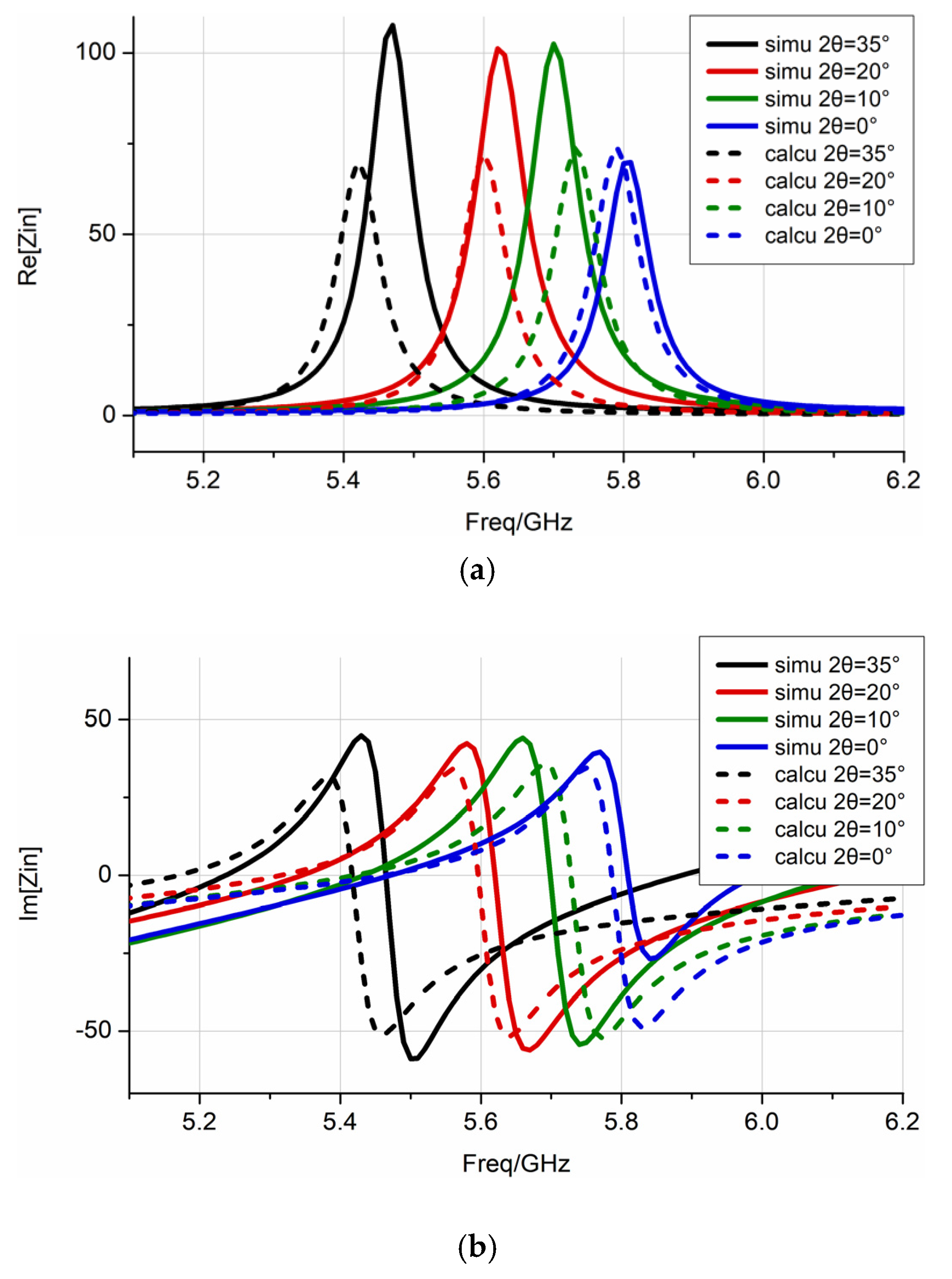
3. Equivalent Circuit Model
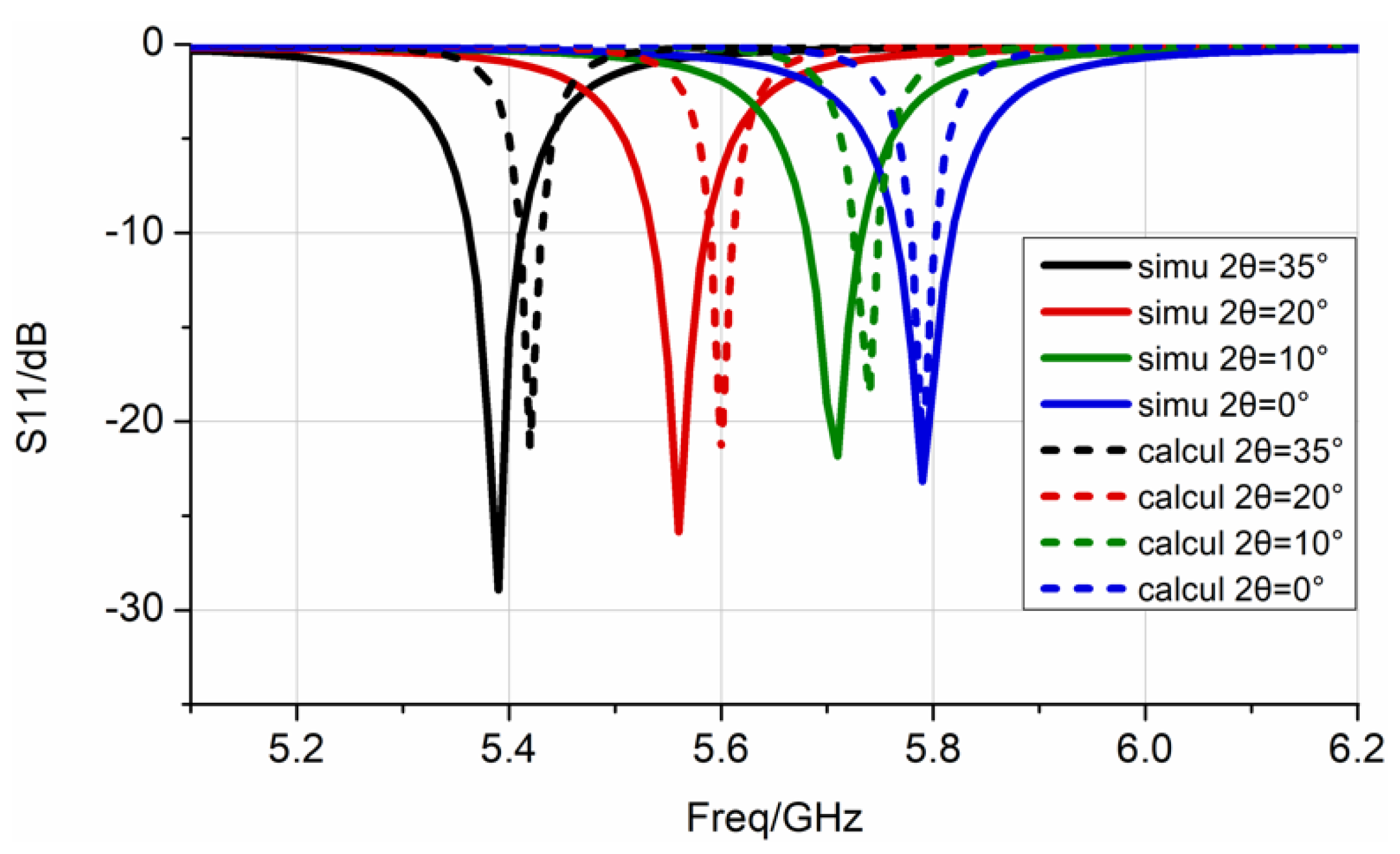
4. Experiment and Comparison
- (1)
- At the resonance frequency, the maximum difference between the experimental and the simulation frequency was 1.11%, whereas it was only 0.55% between the experimental and theoretical calculations. This slight difference may be due to the deviation of the dielectric constant of the polyimide material from the calibration, or the size error of the patch during processing.
- (2)
- For the amplitude at the resonant frequency point, the theoretical calculations were very close to the experimental data. The amplitude deviation of the simulation may be due to the position of the port and the feeding point, which affects the simulation result of the impedance. The S-parameter of the tested antenna exhibited a slight depression at high frequencies, which is caused by the excitation of higher resonance modes. The results show that the analysis method in this paper can reflect the bending effect of the patch antenna transmission.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mumtaz, S.; Bo, A.; Al-Dulaimi, A.; Tsang, K.F. Guest Editorial 5G and Beyond Mobile Technologies and Applications for Industrial IoT (IIoT). IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 2588–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Dipto, N.A.; Rafin, A.R.; Mojumder, S.; Shahrin, M. Design of Wearable Antenna System on Different Materials & Their Performance Analysis at the off and on Body Environment in Terms of Impedance Matching and Radiation Characteristics. Am. Acad. Sch. Res. J. 2013, 5, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar Singh, V.; Kumar Bhoi, A.; Marques, G.; Garcia-Zapirain, B.; de la Torre Díez, I. Wireless Body Area Networks: UWB Wearable Textile Antenna for Telemedicine and Mobile Health Systems. Micromachines 2020, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleel, H.R.; Al-Rizzo, H.M.; Rucker, D.G.; Mohan, S. A Compact Polyimide-Based UWB Antenna for Flexible Electronics. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, A.; Ahnood, A.; Cole, M.T.; Lee, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Hiralal, P.; Bonaccorso, F.; Hasan, T.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Dyadyusha, A.; et al. Flexible Electronics: The Next Ubiquitous Platform. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 1486–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, R.; Martelli, F.; Rosini, R.; Buratti, C.; Verdone, R. A Survey on Wireless Body Area Networks: Technologies and Design Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1635–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Maity, S.; Chaudhuri, S.R.B.; Mitra, M. A Compact Dual-Band Dual-Polarized Omnidirectional Antenna for On-Body Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 5044–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, I.K.; Jung, C.W. A Flexible and Transparent Antenna on a Polyamide Substrate for Laptop Computers. Microw. Opt. Techn. Let. 2015, 57, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.J.; Wang, H.; Chang, Y.M.; Bo, Y.M. A flexible UWB inverted-F antenna for wearable application. Microw. Opt. Techn. Let. 2017, 59, 2514–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, H. An UWB Antenna Array for Flexible IoT Wireless Systems. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2018, 162, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.L.; Qin, L.; Chen, Q.Y.; Yang, W.W.; Qu, H.W. Flexible UWB antenna fabricated on polyimide substrate by surface modification and in situ self-metallization technique. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 206, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krowne, C.M. Cylindrical-Rectangular Microstrip Antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1983, 31, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LUK, K.-M. Analysis of the cylindrical-rectangular patch antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1989, 37, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Alexopoulos, N.G.; Nakatani, A. Cylindrical Substrate Microstrip Line Characterization. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1987, 35, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.N.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. A Systematic Investigation of Rectangular Patch Antenna Bending Effects for Wearable Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, D. Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 202–227. [Google Scholar]
- Elrashidi, A. A New Analytical Performance Model for Cylindrical Microstrip Printed Antenna. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bridgeport, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ansarizadeh, M.; Ghorbani, A.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A. An approach to equivalent circuit modeling of rectangular microstrip antennas. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2008, 8, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 820–825. [Google Scholar]



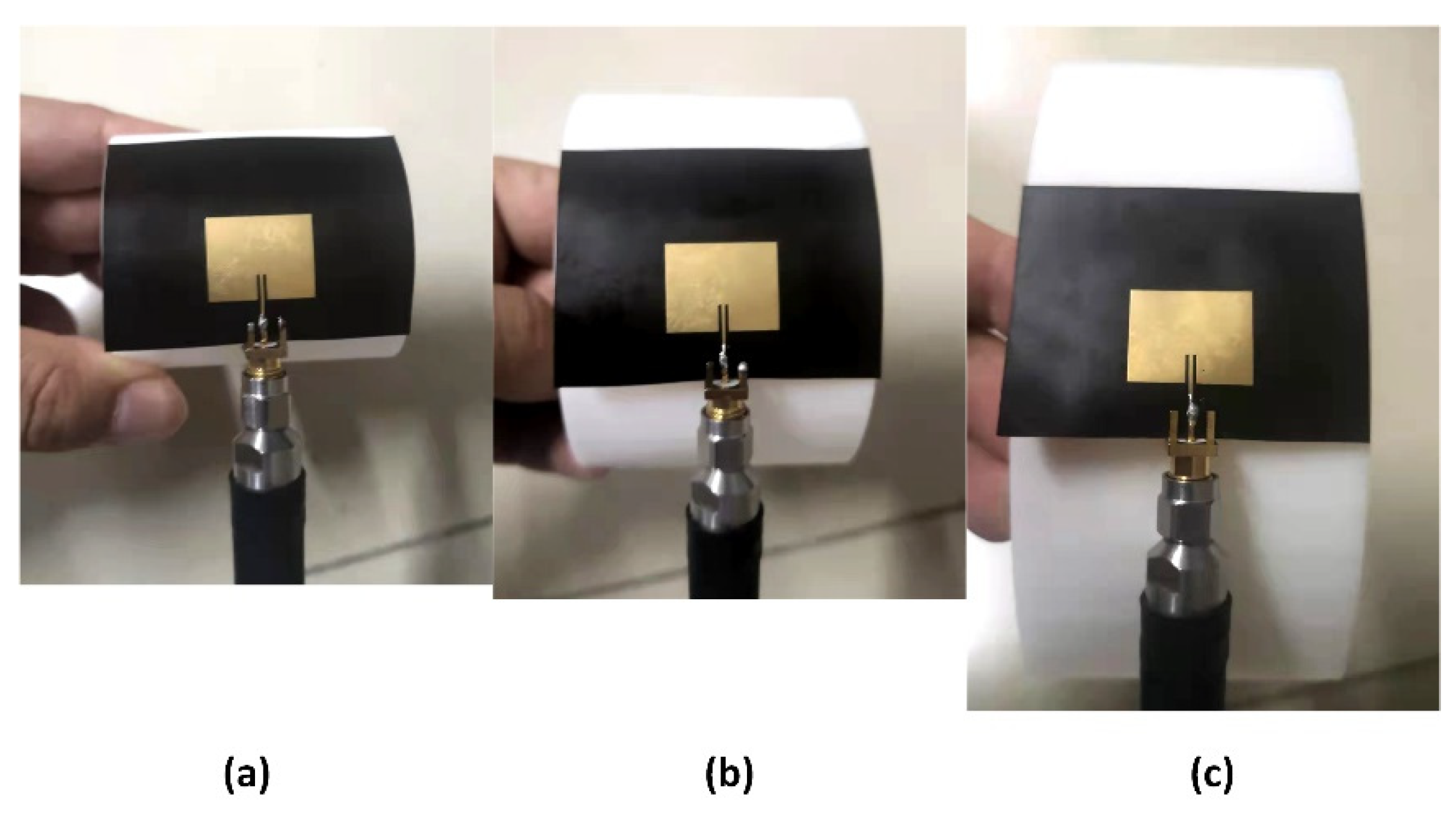

| Circuit Parameters | E-Plane Bending Angles | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | 5° | 10° | 15° | 20° | 25° | 30° | 35° | |
| 3.68 | 3.73 | 3.75 | 3.88 | 3.93 | 4.04 | 4.09 | 4.2 | |
| 394.42 | 391.84 | 391.11 | 384.04 | 381.86 | 379.11 | 374.28 | 369.18 | |
| 24.93 | 25.27 | 25.4 | 26.28 | 26.65 | 27.35 | 27.7 | 28.45 | |
| 5.79 | 5.75 | 5.73 | 5.64 | 5.6 | 5.53 | 5.49 | 5.42 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Sun, P.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, P. Analysis Method of Bending Effect on Transmission Characteristics of Ultra-Low-Profile Rectangular Microstrip Antenna. Sensors 2022, 22, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020602
Zhang J, Huang J, Sun P, Meng F, Zhang J, Zhao P. Analysis Method of Bending Effect on Transmission Characteristics of Ultra-Low-Profile Rectangular Microstrip Antenna. Sensors. 2022; 22(2):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020602
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiaying, Jin Huang, Peng Sun, Fanbo Meng, Jie Zhang, and Pengbing Zhao. 2022. "Analysis Method of Bending Effect on Transmission Characteristics of Ultra-Low-Profile Rectangular Microstrip Antenna" Sensors 22, no. 2: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020602
APA StyleZhang, J., Huang, J., Sun, P., Meng, F., Zhang, J., & Zhao, P. (2022). Analysis Method of Bending Effect on Transmission Characteristics of Ultra-Low-Profile Rectangular Microstrip Antenna. Sensors, 22(2), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020602





