Treatment Strategy Research on a Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor with Broken Rotor Bar Faults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
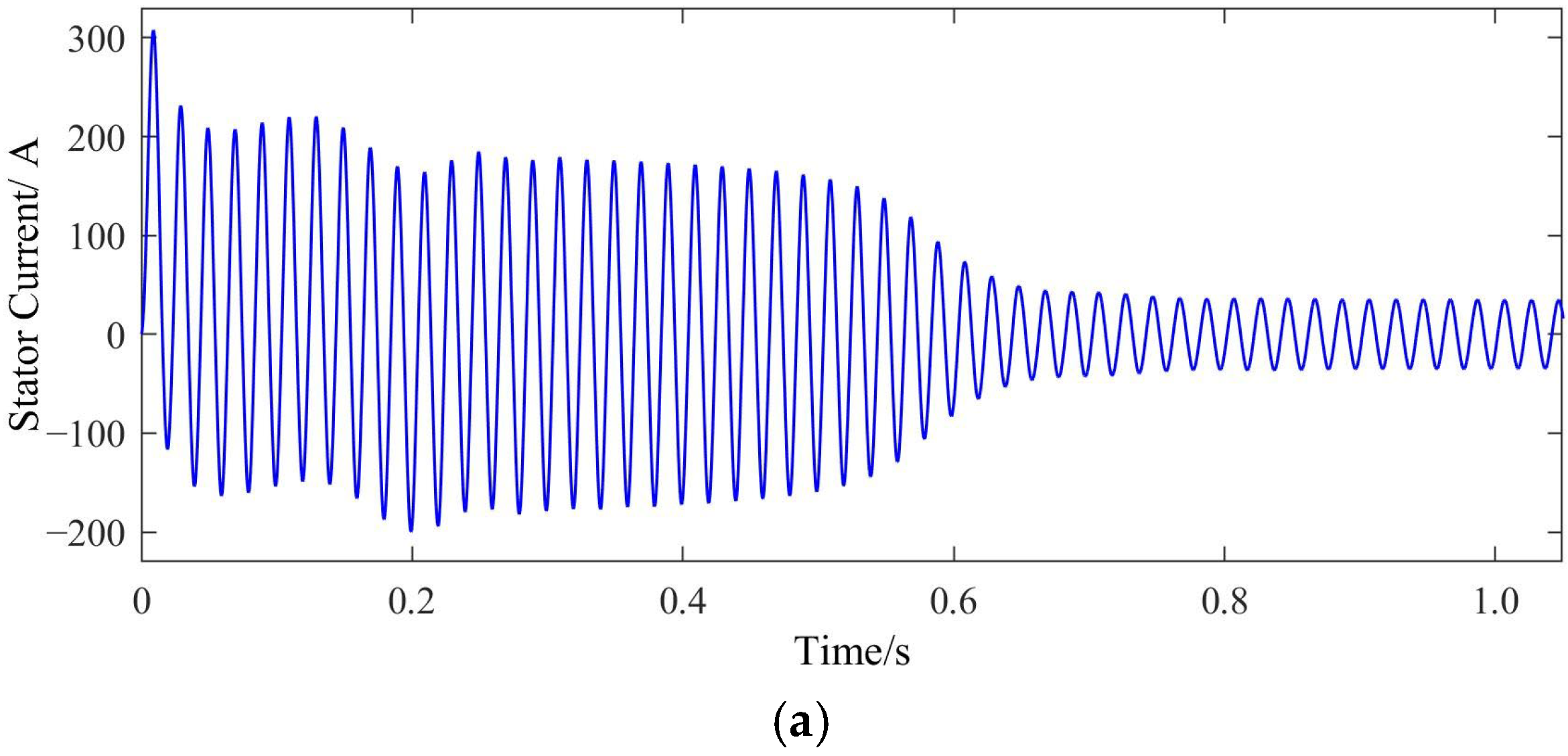
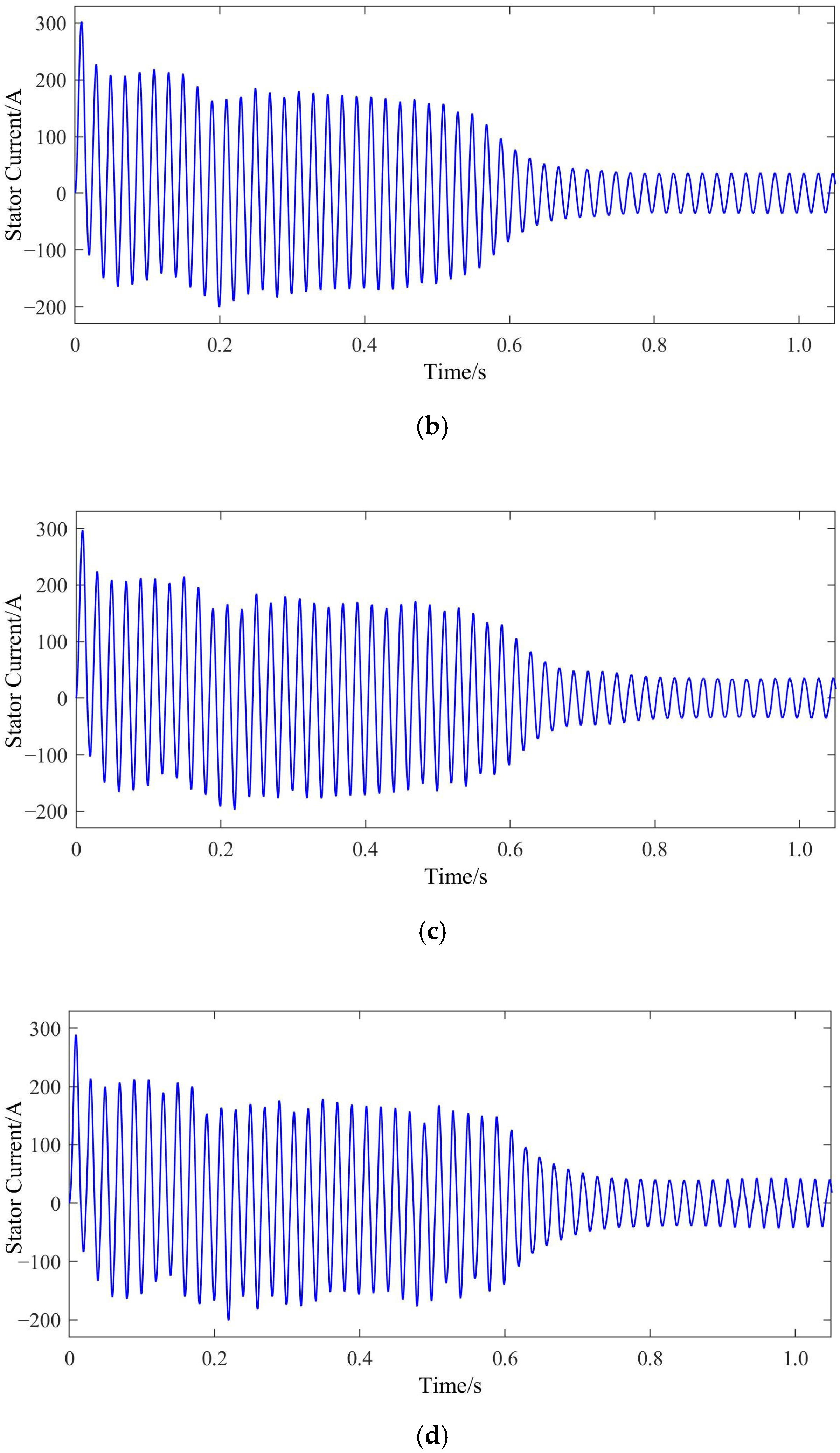
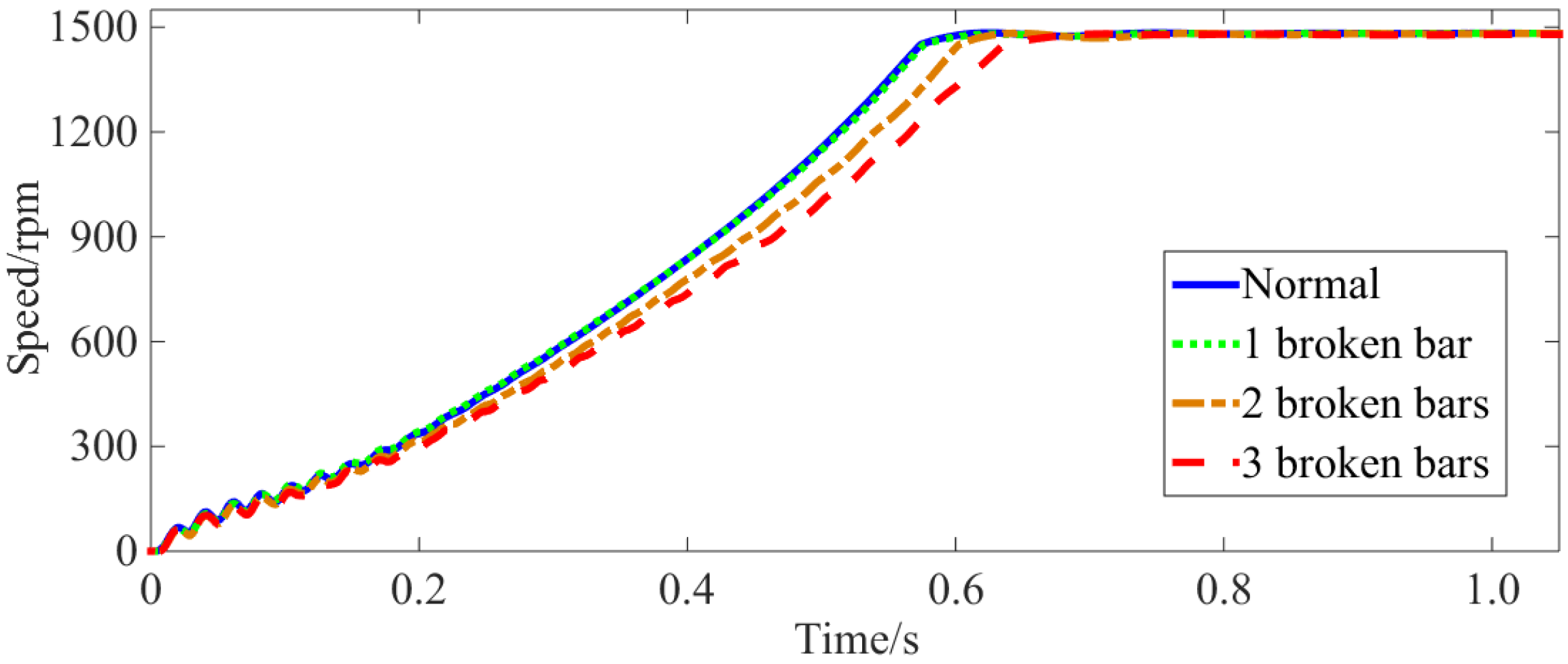
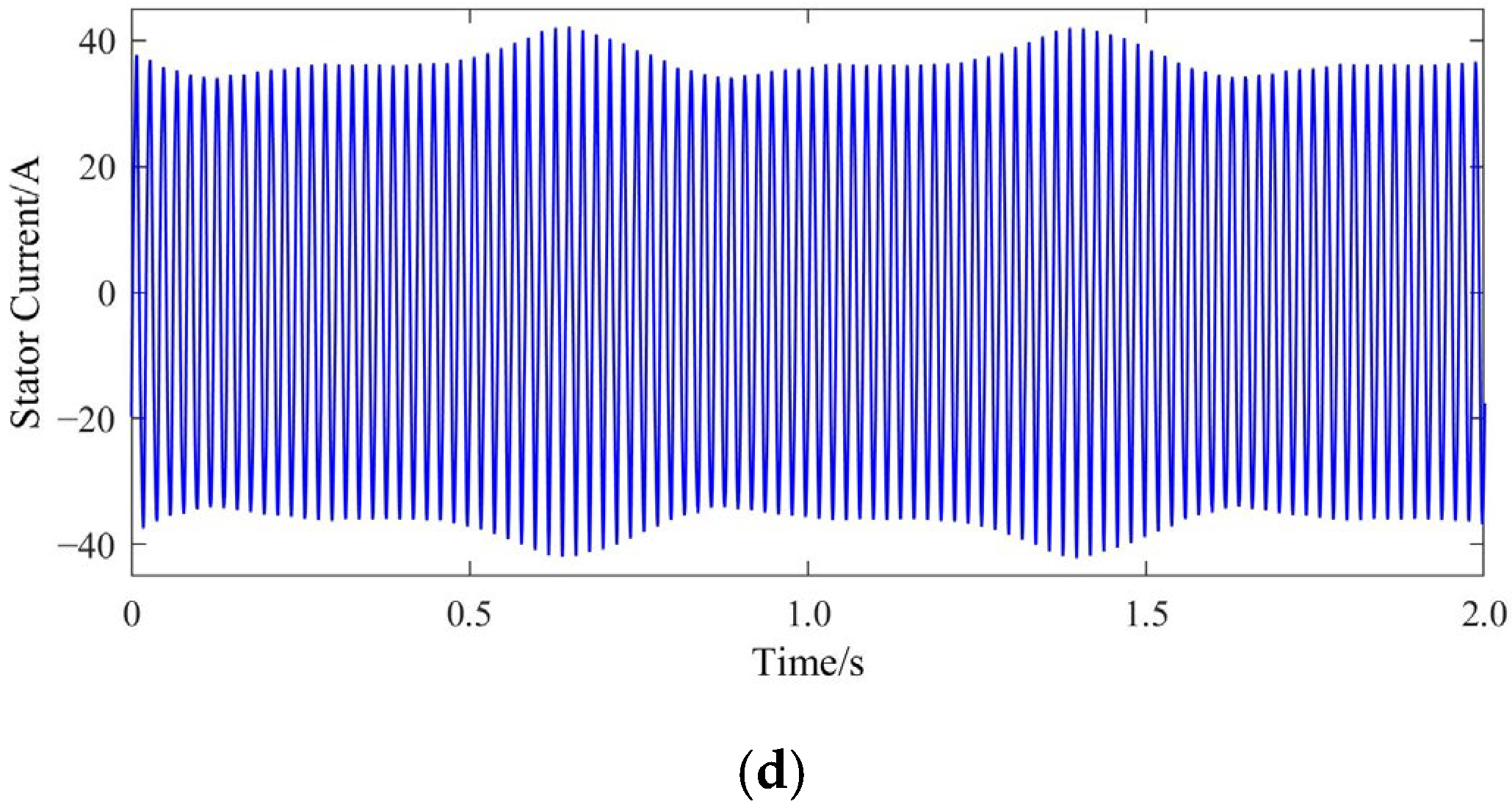
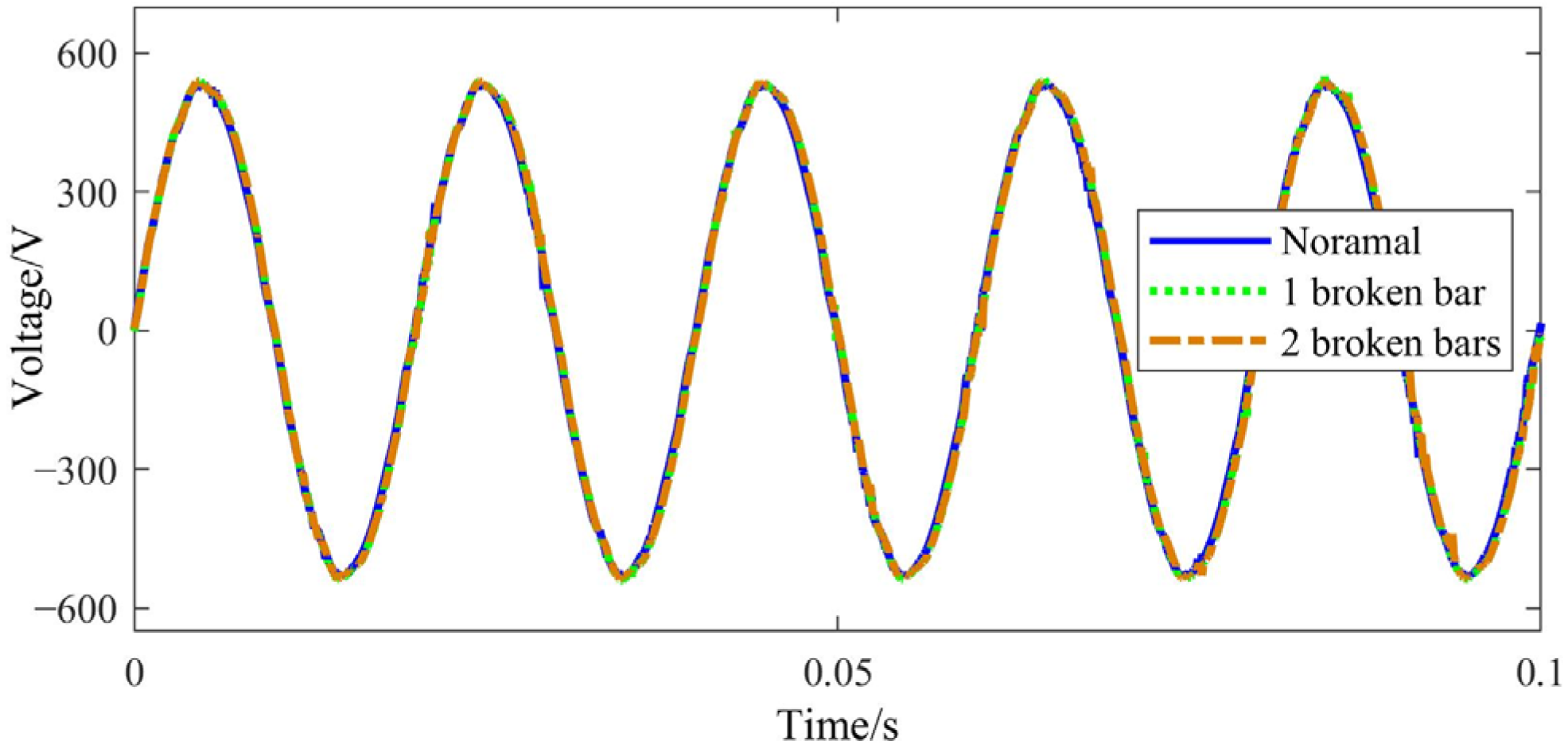
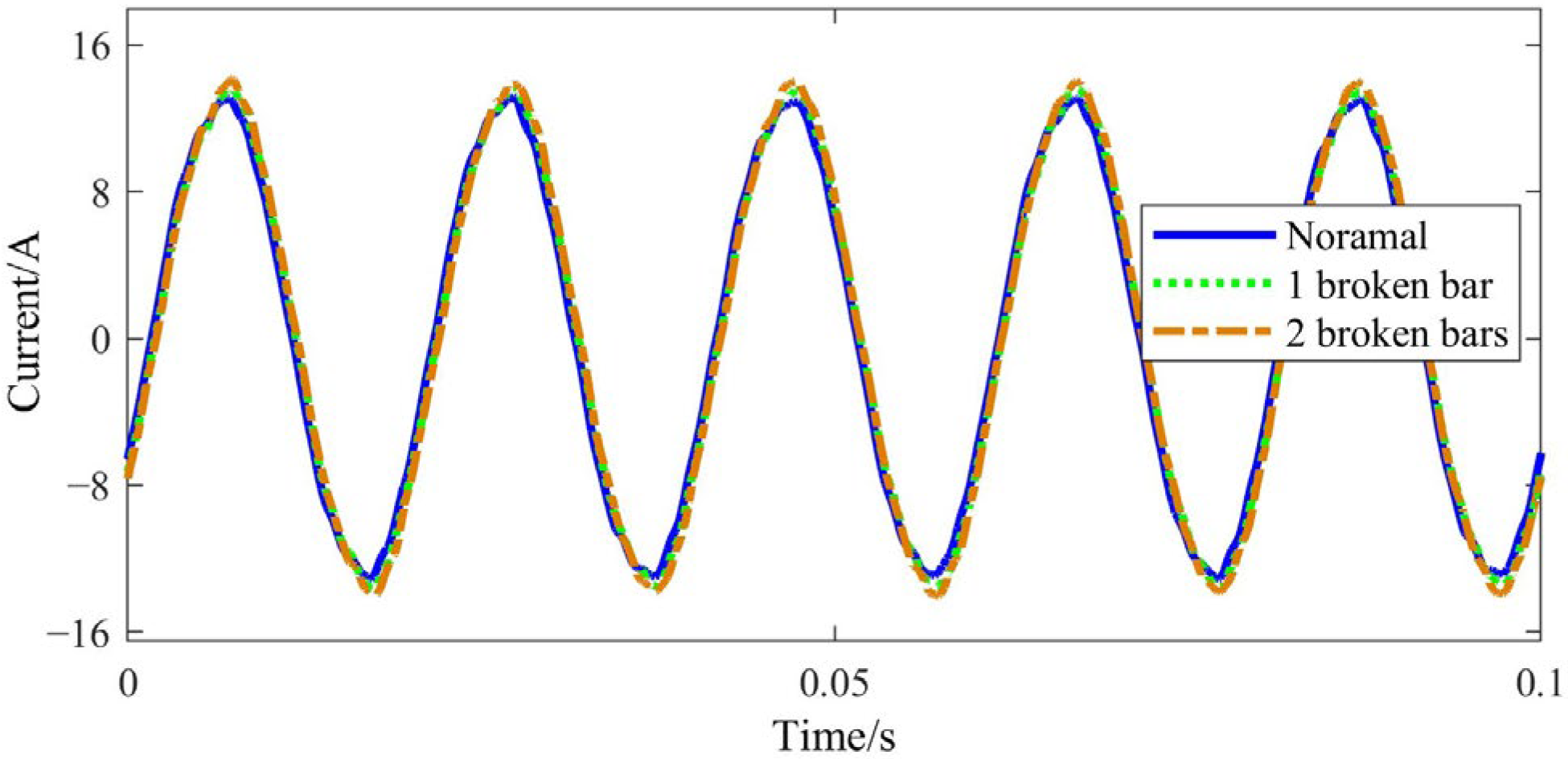
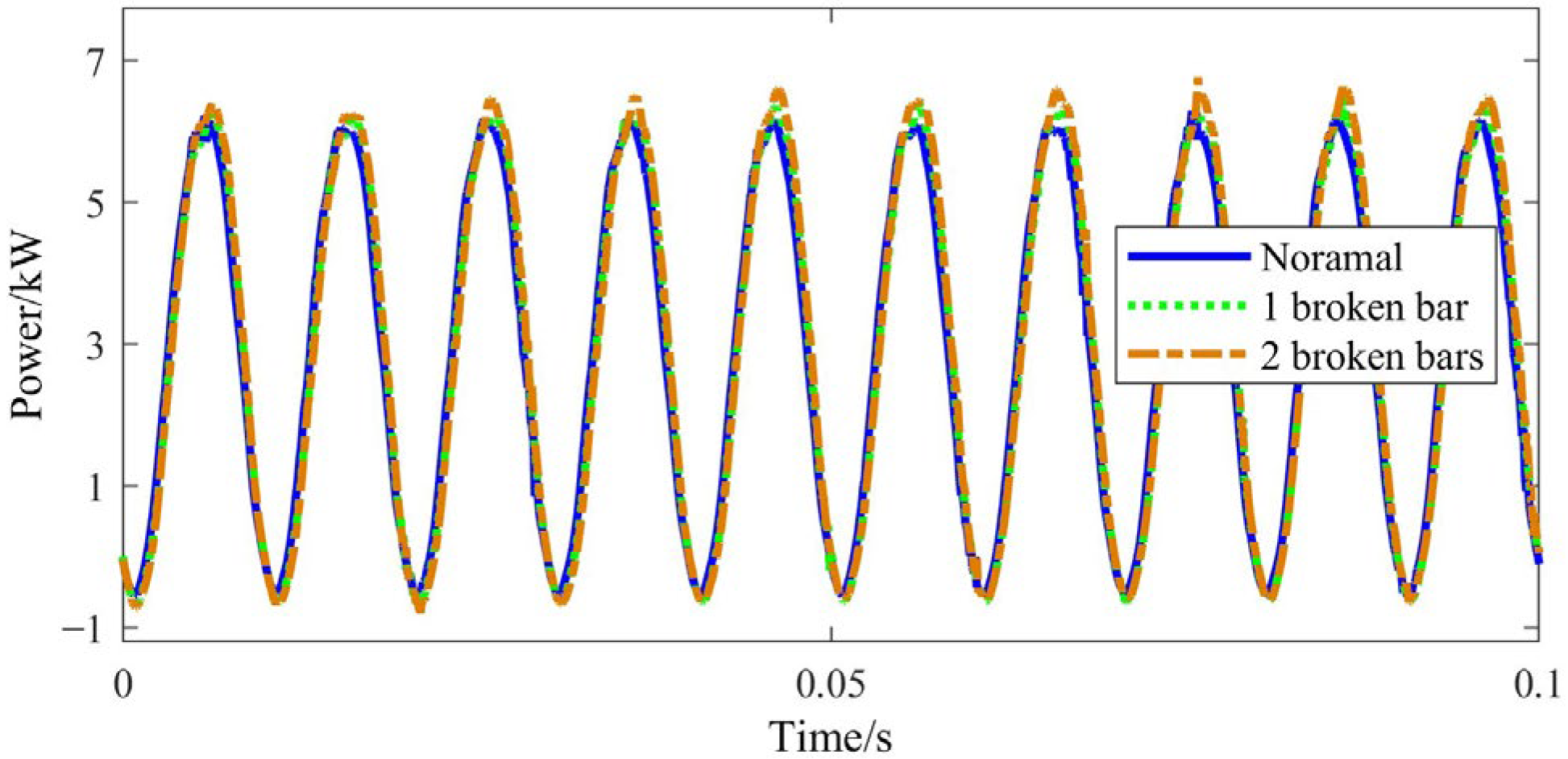
2. Influence BRB Faults on Starting and Operating Characteristics
3. Loss and Efficiency Calculation
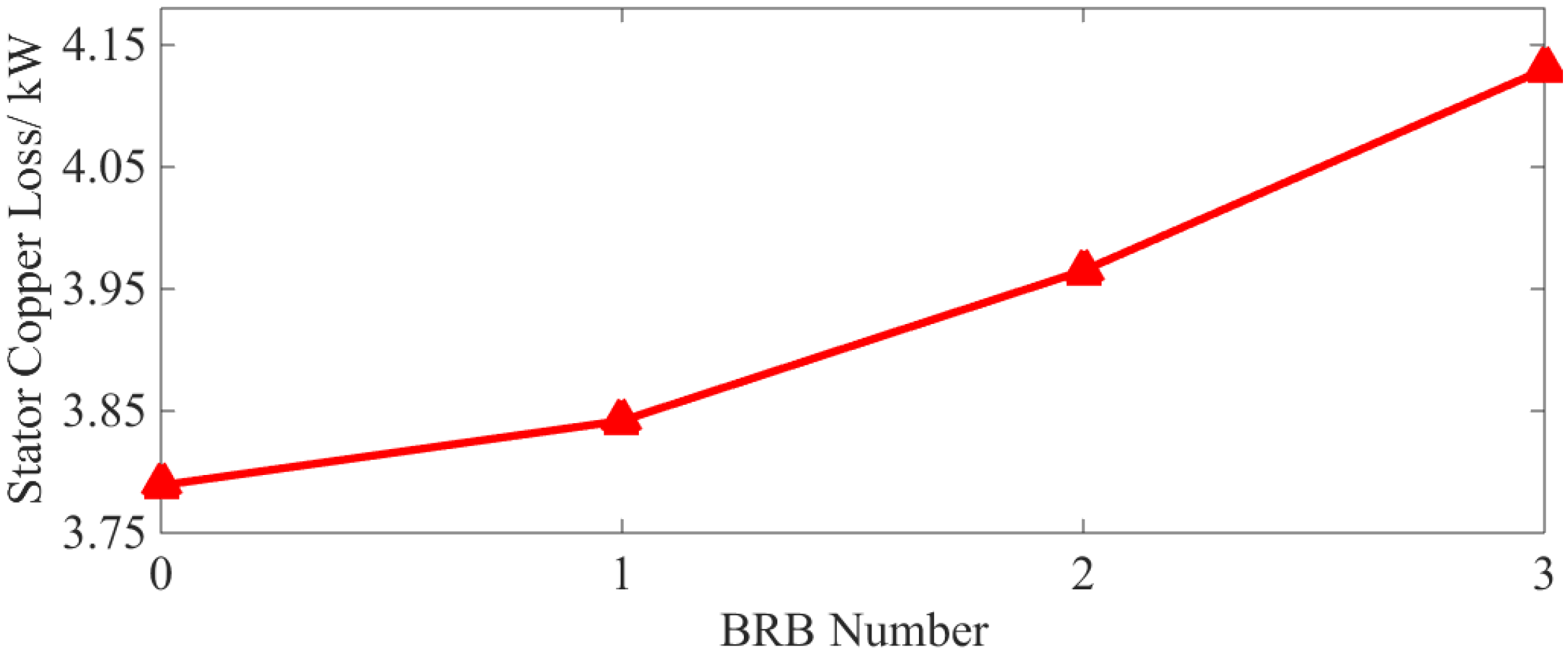
3.1. Stator Copper Loss
3.2. Rotor Copper Loss
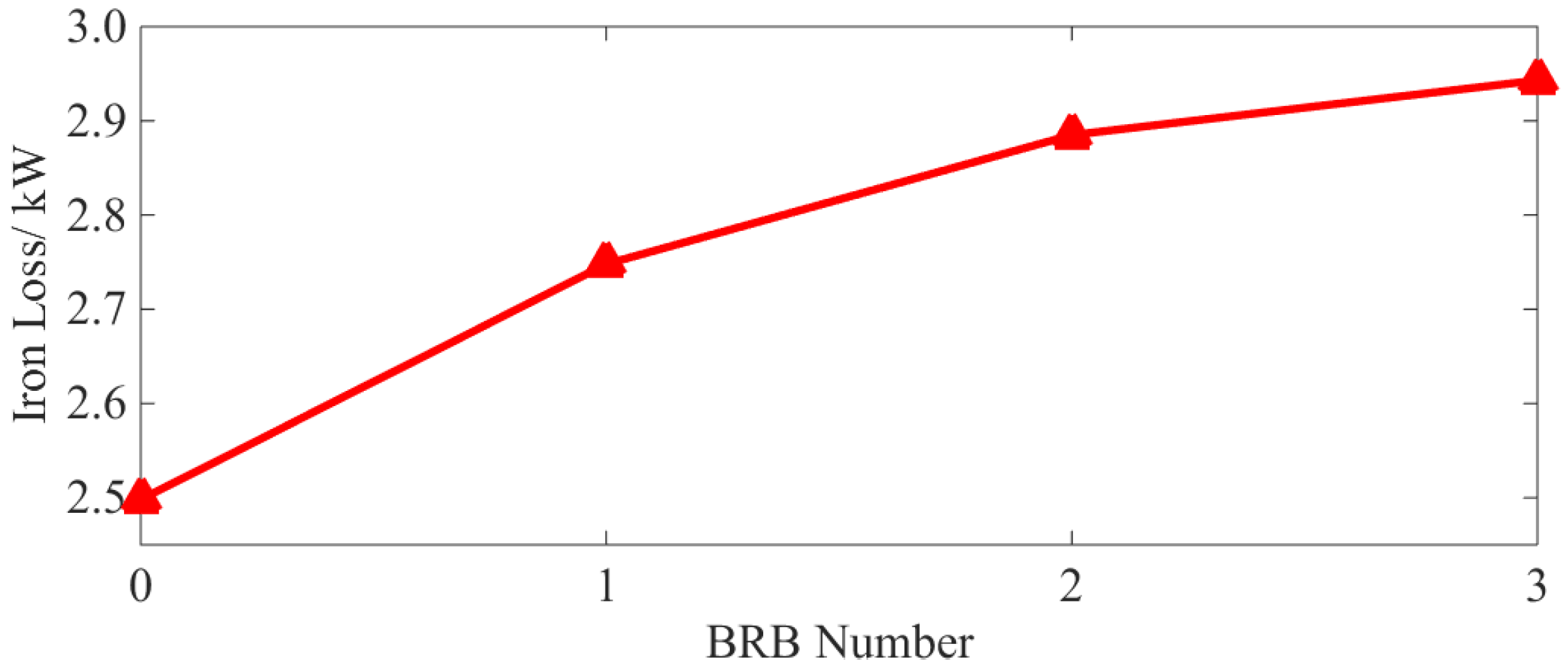
3.3. Iron Loss
3.4. Mechanical Loss and Additional Losses
3.5. Total Loss and Efficiency
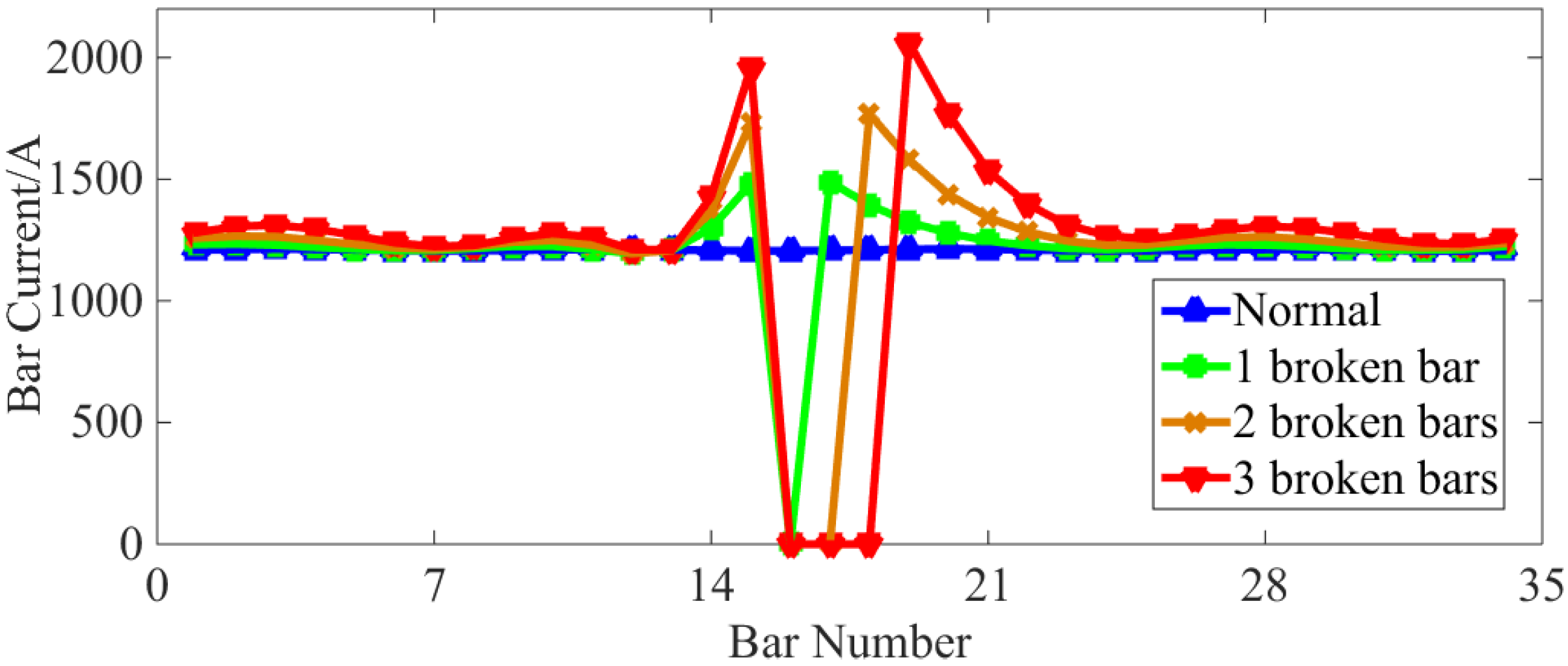
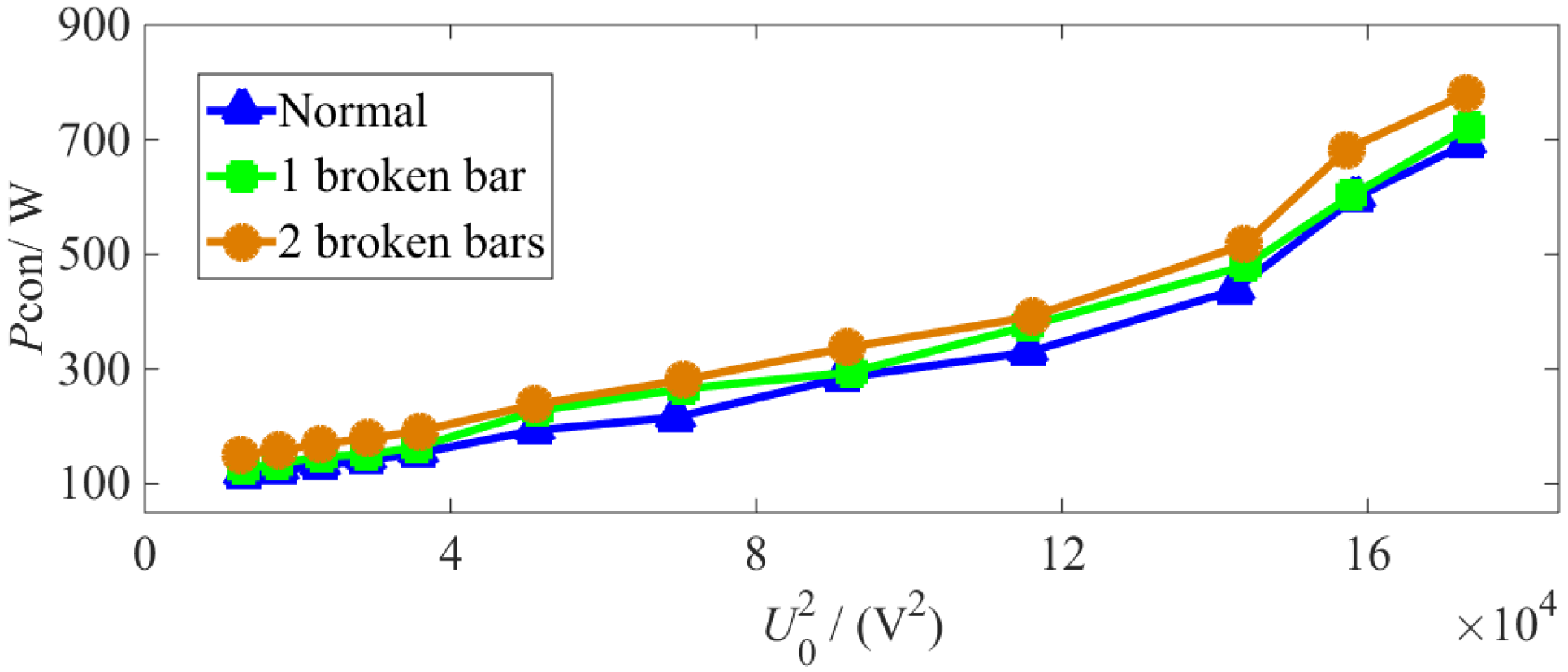
4. Experimental Verification
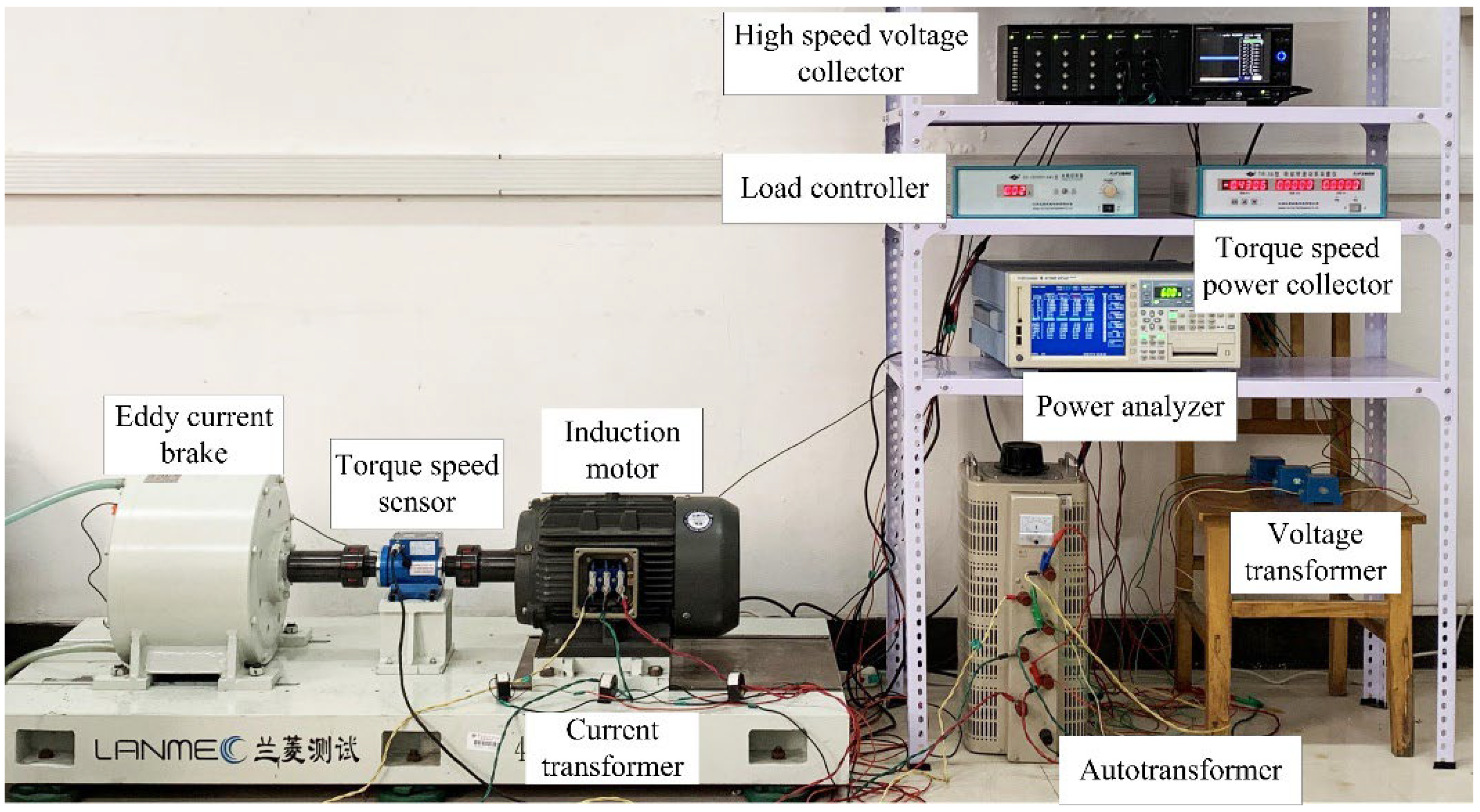
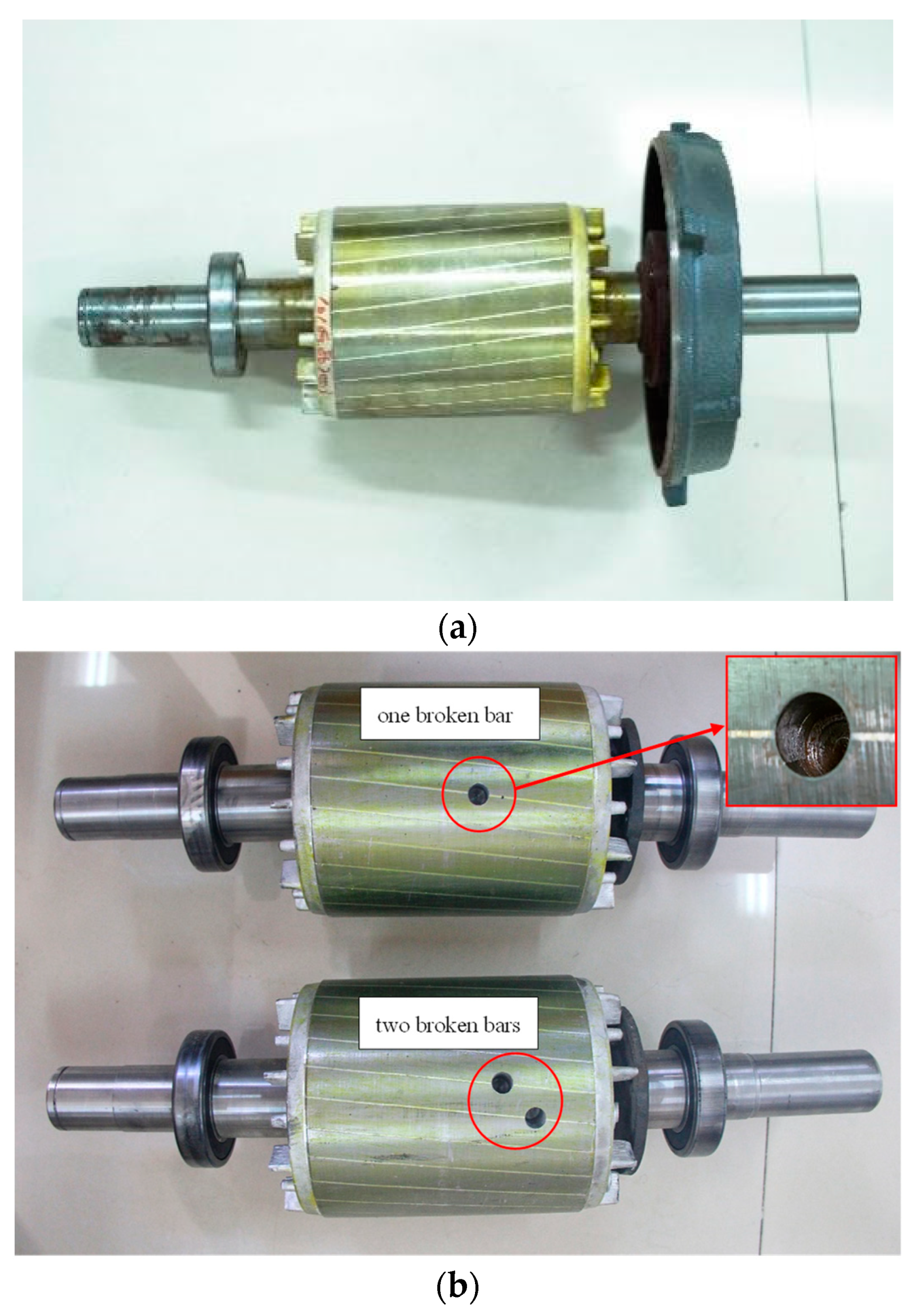
4.1. Experimental Platform
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Strategies to Deal with BRB Fault
- (1)
- The design and service life of the stator, rotor and entire squirrel-cage IM machine are all 15 years.
- (2)
- The rotor has broken bars at the beginning of N-th year during the use of the motor.
- (1)
- Assuming only the rotor is replaced, the new rotor will operate together with the original stator for (16 − N) years.
- (2)
- After 15 years of combined operation, both the stator and rotor are scrapped.
- (1)
- Assuming only the rotor is replaced, it will run together with the original stator for (16 − N) years.
- (2)
- After the motor reaches its service life of 15 years, the rotor still has a service life of (N − 1) years. The rotor is disassembled and combined with a new stator, and it will continue to exert its value. Then the rotor may be replaced later when its service life expires.
- (3)
- Based on this assumption (2), the economic cost of replacing the rotor can be considered using an annual depreciation cost of A = Mr/15.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P.; Du, Y.; Habetler, T.G.; Lu, B. A survey of condition monitoring and protection methods for medium voltage IMs. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2011, 47, 34–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.Q.; Sun, L. Concurrent discrimination of rotor fault and load oscillation in IMs. Proc. CSEE 2016, 36, 6518–6527. [Google Scholar]
- Mirafzal, B.; Demerdash, N.A.O. Induction machine broken-bar fault diagnosis using the rotor magnetic field space-vector orientation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2004, 40, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Hu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.Q. Simulating and experiment studying on rotor winding fault of IM. Proc. CSEE 2003, 23, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hanafy, H.H.; Abdo, T.M.; Adly, A.A. Using 2D finite element analysis in the calculation of current and force distributions for IMs with broken bars. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. Electromagnetic force calculation and structural static analysis on the rotor of squirrel-cage IMs before and after the broken bars fault. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 30, 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y. 3D temperature field analysis of the IMs with broken bar fault. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 66, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, F. Study on 3D thermal field and thermal stress field of the IM rotor. Electr. Mach. Control 2010, 14, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Casimir, R.; Bouteleux, E.; Yahoui, H.; Clerc, G.; Henao, H.; Delmotte, C.; Capolino, G.-A.; Rostaing, G.; Rognon, J.-P.; Foulon, E.; et al. Comparison of modelling methods and of diagnostic of asynchronous motor in case of defects. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Power Electronics Congress, Celaya, Mexico, 17–22 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Shan, X.T.; Guo, J.P.; WANG, Z. The relationship study between field changes and faulty condition in squirrel-cage IM with broken bars fault. Proc. CSEE 2017, 37, 4222–4231. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.K.; Chatterjee, T.K. Empirical relation for broken bar determination in SCIM. Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 37, 242–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouachtouk, I.; El Hani, S.; Guedira, S.; Dahi, K.; Mediouni, H. Broken rotor bar fault detection based on stator current envelopes analysis in squirrel cage induction machine. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 21–24 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ojaghi, M.; Sabouri, M.; Faiz, J. Performance analysis of squirrel-cage induction motors under broken rotor bar and stator inter-turn fault conditions using analytical modeling. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8203705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmida, M.A.; Braham, A. An on-line condition monitoring system for incipient fault detection in double-cage IM. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. Detection based on ESPRIT and Duffing system for broken rotor bar fault in cage induction motors. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2020, 40, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Li, T. Fault diagnosis method of asynchronous motors using fusion correlation spectrum. Electr. Mach. Control 2021, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Benbouzid, M.E.H.; Kliman, G.B. What stator current processing based technique to use for IM rotor faults diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.Z.; Li, X.M.; Fang, R.M. Diagnosing rotor winding fault in asynchronous motors by using residual voltages after AC dump. Proc. CSEE 2004, 24, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Drif, M.; Marques Cardoso, A.J. Discriminating the simultaneous occurrence of three-phase IM rotor faults and mechanical load oscillations by the instantaneous active and reactive power media signature analyses. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, L. Rotor fault diagnosis of squirrel cage asynchronous motor based on instantaneous reactive power in α-β coordinates. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 30, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.M.; Povinelli, R.J.; Demerdash, N.A.O. Rotor bar fault monitoring method based on analysis of air-gap torques of IMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 2274–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, F.; Huang, J. Rotor fault detection for IMs based on complex analytical wavelet transform of electromagnetic torque. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2005, 20, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Etien, E.; Doget, T.; Rambault, L.; Cauet, S.; Sakout, A.; Moreau, S. Transient Detection of Rotor Asymmetries in Squirrel-Cage Induction Motors Using a Model-Based Tacholess Order Tracking. Sensors 2022, 22, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Badri, M.; Pillay, P.; Angers, P. Induction machine rapid performance test. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 55, 4685–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binesti, D.; Ducreux, J.P. Core losses and efficiency of electrical motors using new magnetic Materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1996, 32, 4887–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bazzi, A.M. A general analytical three-phase induction machine core loss model in the arbitrary reference frame. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 53, 4210–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, C.S.; Kinyua, J.M.; Khan, M.A.; Barendse, P.S. Analysis of a nonintrusive efficiency estimation technique for induction machines compared to the IEEE 112B and IEC 34-2-1 Standards. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 51, 4541–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshhava, M.A.; Zarchi, H.A.; Markadeh, G.A. Arab Markadeh. Iron Loss Modeling in Dual Stator Winding Induction Machines with Unequal Pole Pairs and Squirrel Cage Rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2931–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Mi, C.C.; Gao, D.W. Modeling of eddy-current loss of electrical machines and transformers operated by pulse width-modulated inverters. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, K.; Cao, W.; Clare, J.; Wheeler, P. Predicting inverter-induced harmonic loss by improved harmonic injection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 2619–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, Z.; Ranta, M.; Hinkkanen, M.; Luomi, J. Loss-minimizing flux level control of induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odhano, S.A.; Bojoi, R.; Boglietti, A.; Roşu, Ş.G.; Griva, G. Griva. Maximum efficiency per torque direct flux vector control of induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 15, 4415–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Bindal, R. Direct Torque Control of Induction Machine: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electronics and Renewable Systems (ICEARS), Tuticorin, India, 16–18 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Carbonieri, M.; Di Leonardo, L.; Bianchi, N.; Tursini, M.; Villani, M.A.; Popescu, M. Cage Losses in Induction Motors Considering Harmonics: A New Finite Element Procedure and Comparison with the Time-Domain Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plathottam, S.J.; Salehfar, H. Transient Energy Efficiency Analysis of Field Oriented Induction Machines. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20545–20556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.R.; Quispe, E.C.; De Armas, M.A.; Viego, P.R. Estimation of induction motor efficiency in-situ under unbalanced voltages using genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Vilamoura, Portugal, 6–9 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Badri, M.; Pillay, P.; Angers, P. A Novel Technique for In Situ Efficiency Estimation of Three-Phase IM Operating with Unbalanced Voltages. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabaci, H.; Bilgin, O. Efficiency Analysis of Submersible Induction Motor with Broken Rotor Bar; Kim, H., Ao, S.I., Amouzegar, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 3 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, M.; Panagiotou, P.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Gyftakis, K.N. Efficiency assessment of induction motors operating under different fault conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8072–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wenjin, D. Theory and Practice of Motor Design; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, O.E.; Amer, M.; Abdelsalam, A.K.; Williams, B.W. IM broken rotor bar fault detection techniques based on fault signature analysis—A review. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; An, Q. Online diagnosis of broken rotor bar fault of squirrel-cage IM using a magnetic field measuring coil. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2020, 15, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.S.; Liu, X.F.; Luo, Y.L.; Cui, X.S. Losses characteristics of cage IMs under voltage deviation conditions. Electr. Mach. Control 2010, 14, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Haisen, Z.; Xiaofang, L.; Jia, H.; Yingli, L. The influence of wye and delta connection on IM losses taking slot opening and skew effect into account. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bertotti, G. General properties of power losses in soft ferromagnetic materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1988, 24, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaobo, S.; Dawei, M.; Xiaoni, Y. Influence of impeller’s torque ripple on motor loss and efficiency of contra-rotating axial-flow fan. Electr. Mach. Control 2018, 22, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- GB-T 1032-2012; Three Phase Asynchronous Motor Test Method. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China (AQSIQ); Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2012.
- 112-2017; IEEE Standard Test Procedure for Polyphase IMS and Generators. IEEE Standard: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017.













| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power/kW | 200 | Number of stator slots | 48 |
| Rated voltage/kV | 6 | Number of rotor slots | 34 |
| Power frequency/Hz | 50 | Rated slip | 0.012 |
| Rated power factor | 0.85 | Core length/mm | 320 |
| Rated efficiency/% | 94.2 | Air gap length/mm | 1.4 |
| Number of poles | 4 | Silicon steel grade | DW470-50 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power/kW | 7.5 | Power frequency/Hz | 50 |
| Rated voltage/V | 380 | Rated power factor | 0.85 |
| Rated current/A | 15.4 | Rated efficiency/% | 87.0 |
| Rated speed/rpm | 1450 | Winding connection | Δ |
| Working Condition | Torque/(N·m) | Speed/rpm | Power/kW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | −49.446 | 1450.1 | 7.509 |
| One broken bar | −49.464 | 1448.0 | 7.500 |
| Two broken bars | −49.451 | 1444.5 | 7.480 |
| Parameter | Normal | One Broken Bar | Two Broken Bars |
|---|---|---|---|
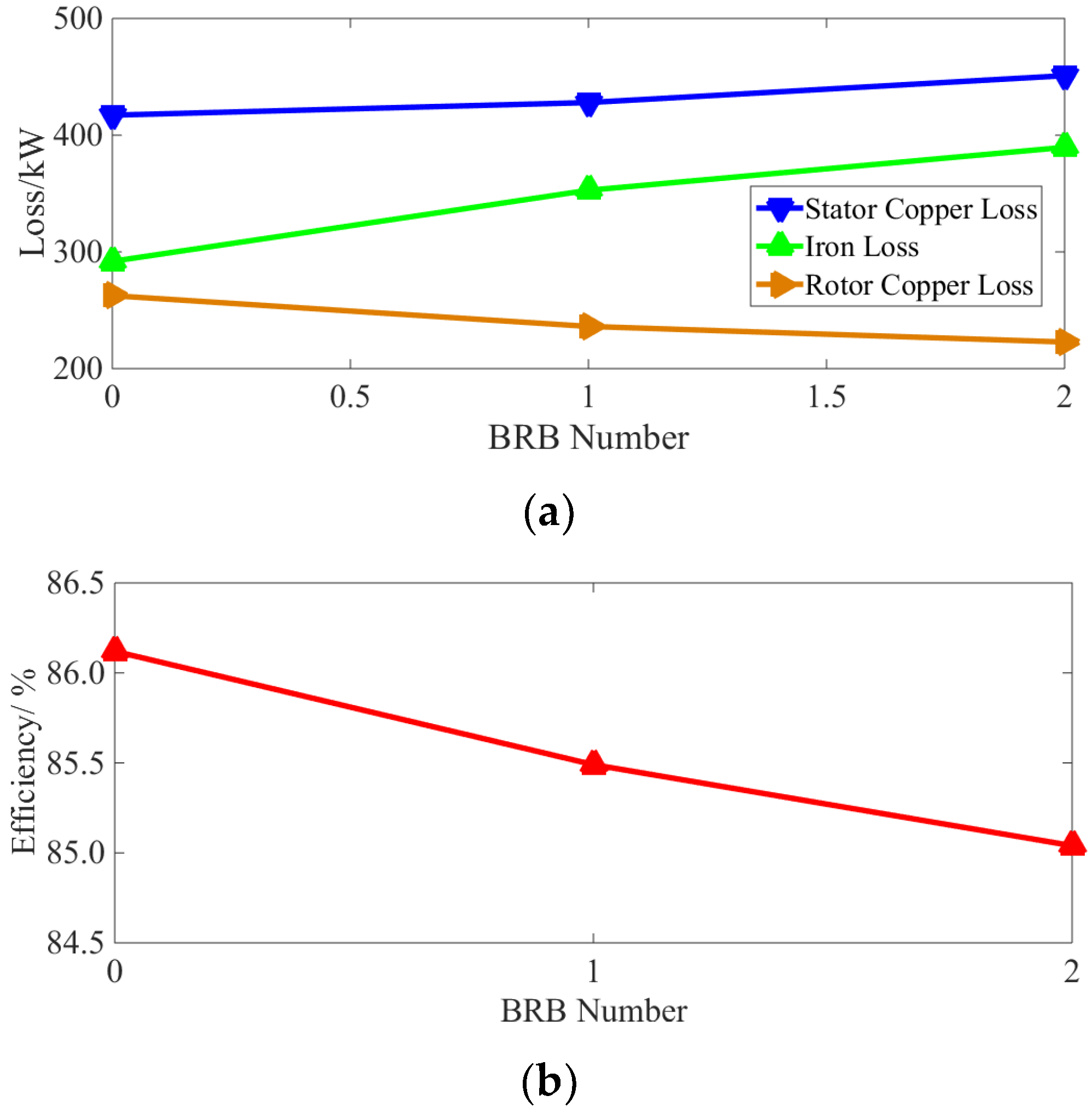
| Stator copper loss/W | 417.14 | 427.93 | 450.95 |
| Iron loss/W | 291.91 | 352.81 | 389.57 |
| Rotor copper loss/W | 262.51 | 236.16 | 222.78 |
| Mechanical loss/W | 87.37 | 94.02 | 115.31 |
| Additional loss/W | 150.92 | 162.33 | 169.77 |
| Total loss/W | 1209.85 | 1273.25 | 1348.38 |
| Efficiency/% | 86.12 | 85.49 | 84.75 |
| Parameter | Normal | One Broken Bar | Two Broken Bars | Three Broken Bars |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency/% | 93.52 | 93.22 | 93.01 | 92.77 |
| Input power/kW | 212.94 | 213.57 | 213.96 | 214.39 |
| Cost/k$ | 116.27 | 116.61 | 116.82 | 117.06 |
| Loss cost/k$ | 0.00 | 0.34 | 0.55 | 0.85 |
| Working Conditions | Strategy 1 | Strategy 2 | Strategy 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| One broken bar | ✗ | 14 | ✓ |
| Two broken bars | 1–3 | ✗ | ✓ |
| Three broken bars | 1–3 | ✗ | ✓ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Sun, S.; An, Q.; Lie, X. Treatment Strategy Research on a Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor with Broken Rotor Bar Faults. Sensors 2022, 22, 4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124345
Wu Y, Sun S, An Q, Lie X. Treatment Strategy Research on a Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor with Broken Rotor Bar Faults. Sensors. 2022; 22(12):4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124345
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yucai, Shuqiong Sun, Qingfei An, and Xu Lie. 2022. "Treatment Strategy Research on a Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor with Broken Rotor Bar Faults" Sensors 22, no. 12: 4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124345
APA StyleWu, Y., Sun, S., An, Q., & Lie, X. (2022). Treatment Strategy Research on a Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor with Broken Rotor Bar Faults. Sensors, 22(12), 4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124345






